Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Laser Cladding Fe-Based Alloy Coating on 27SiMn Steel Surface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Preparation of the Cladding Layer
2.3. Method
3. Results and Discussion
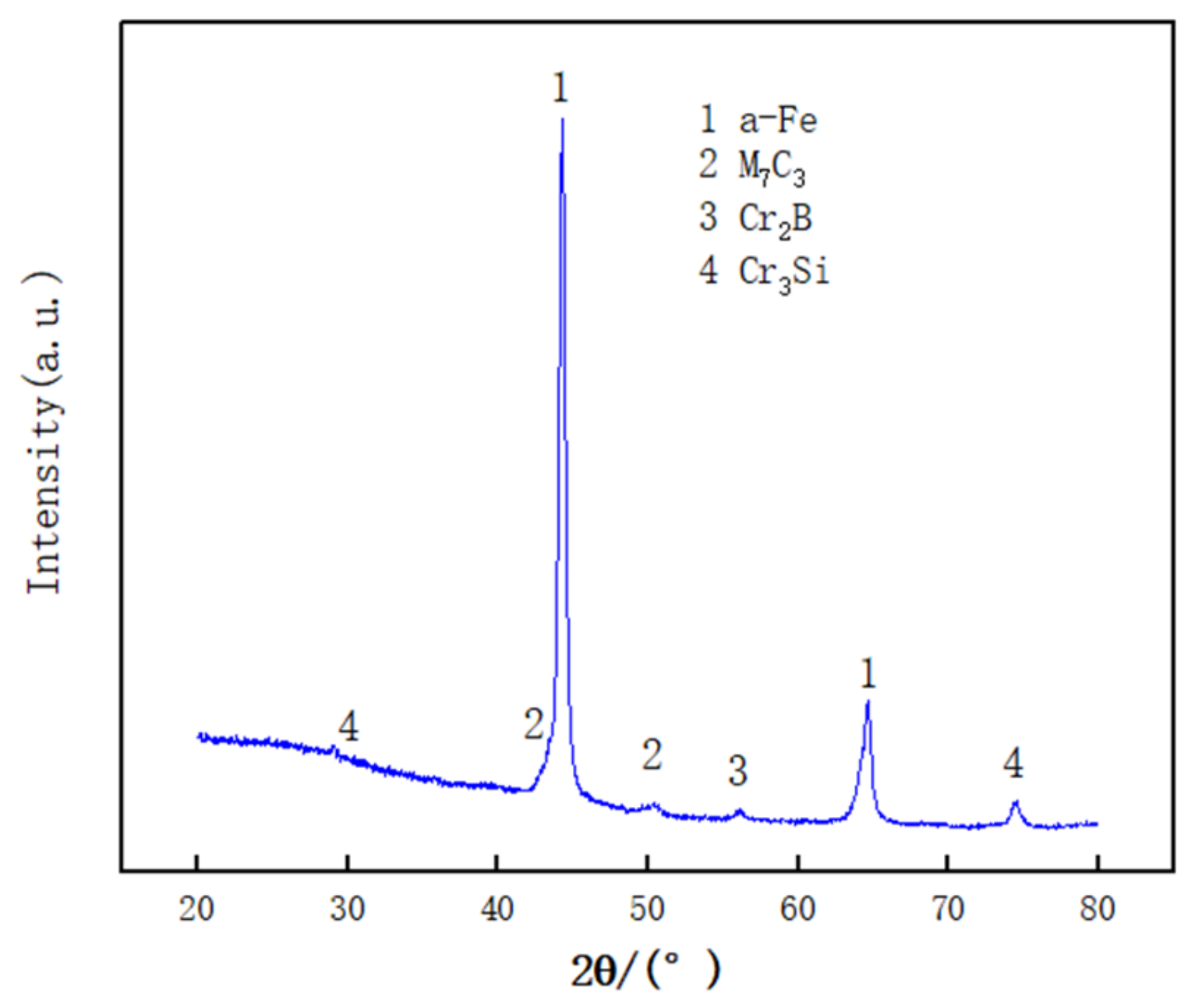
3.1. Phase Analysis
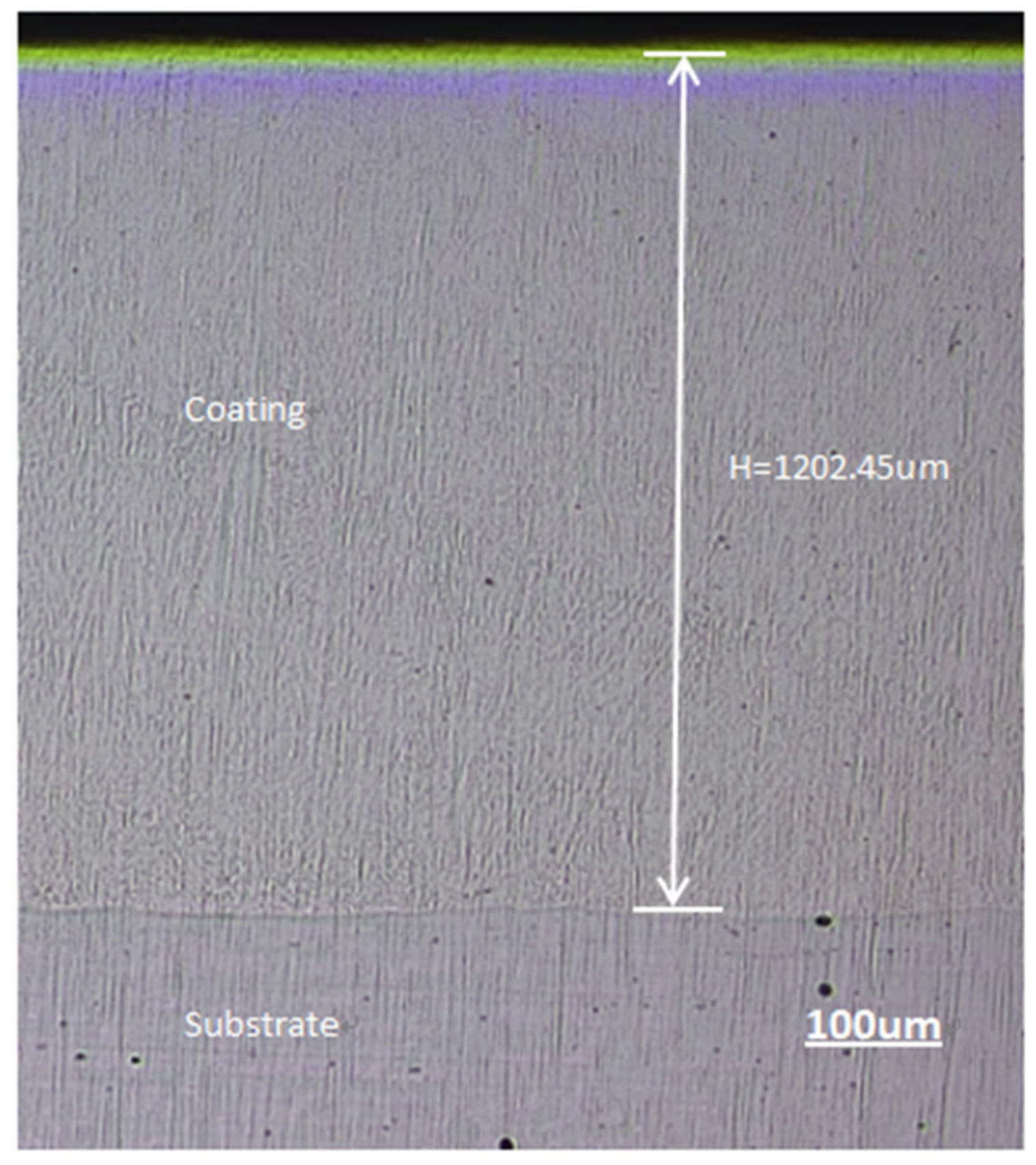
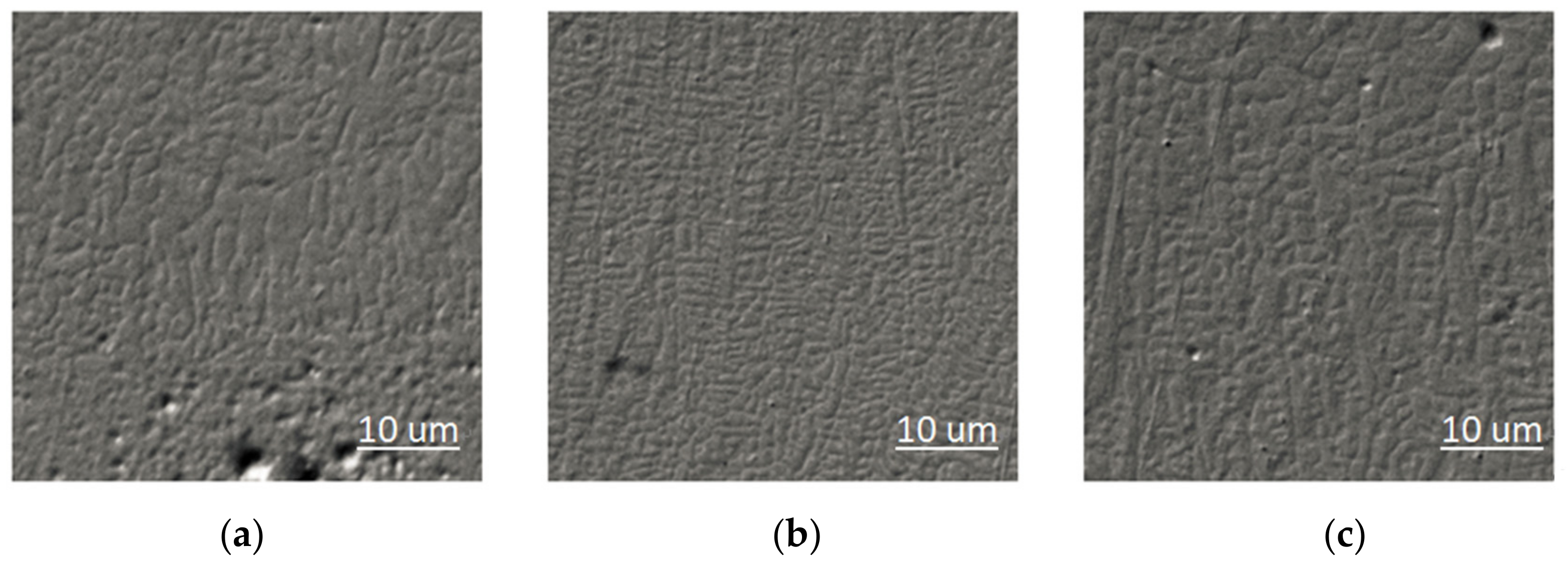
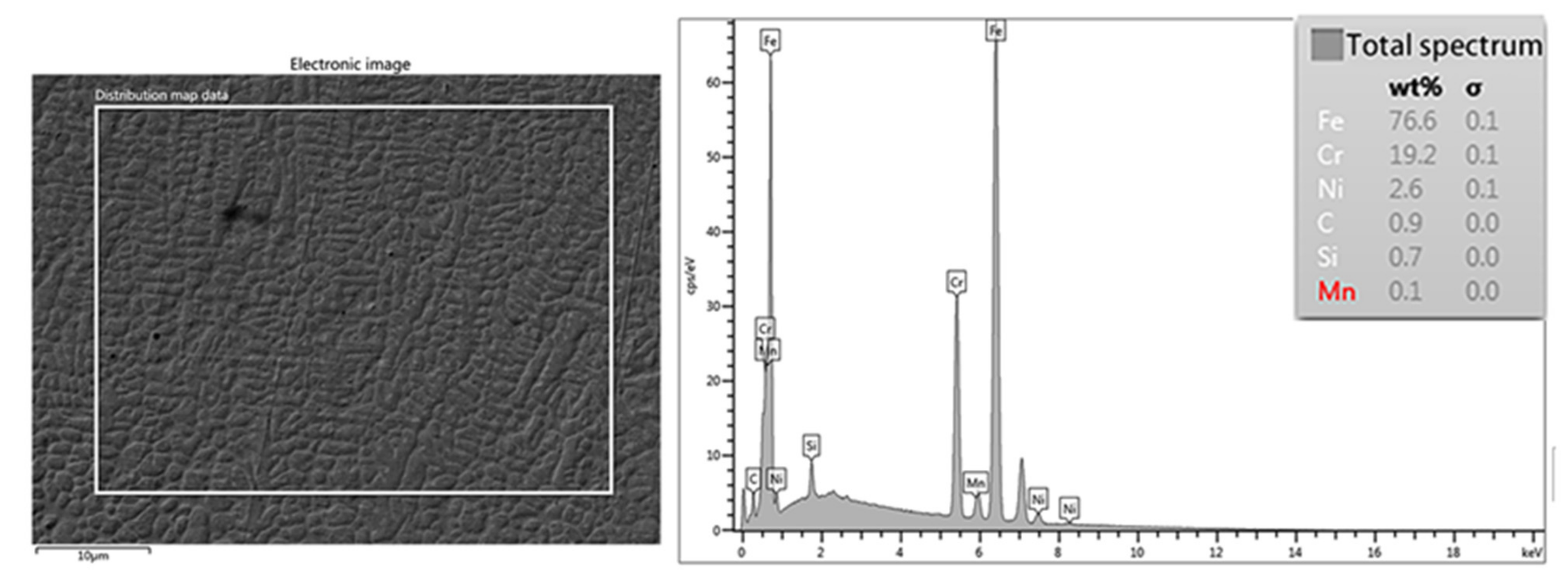
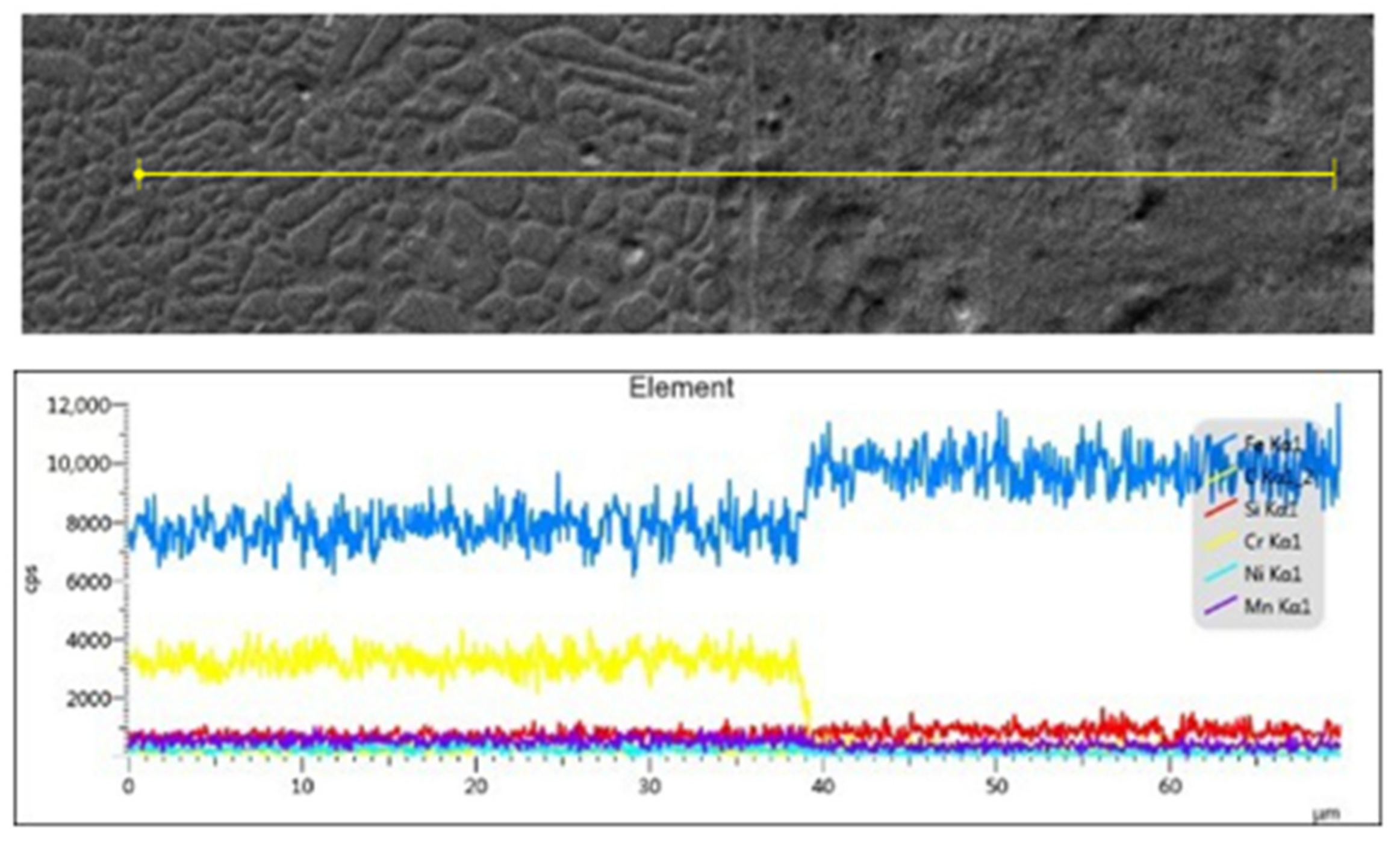
3.2. Microstructure Morphology of the Coating
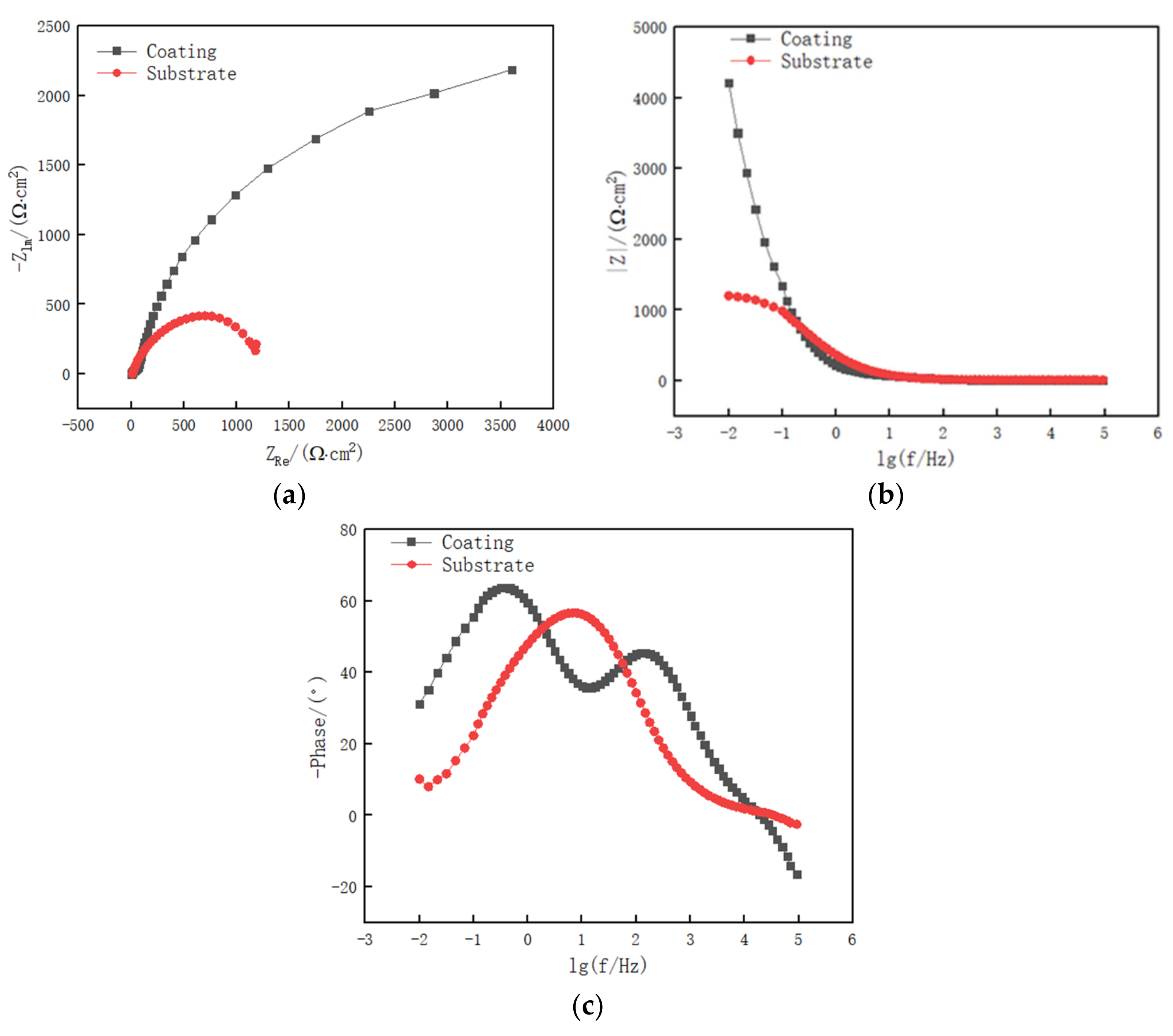
3.3. Electrochemical Corrosion Performance
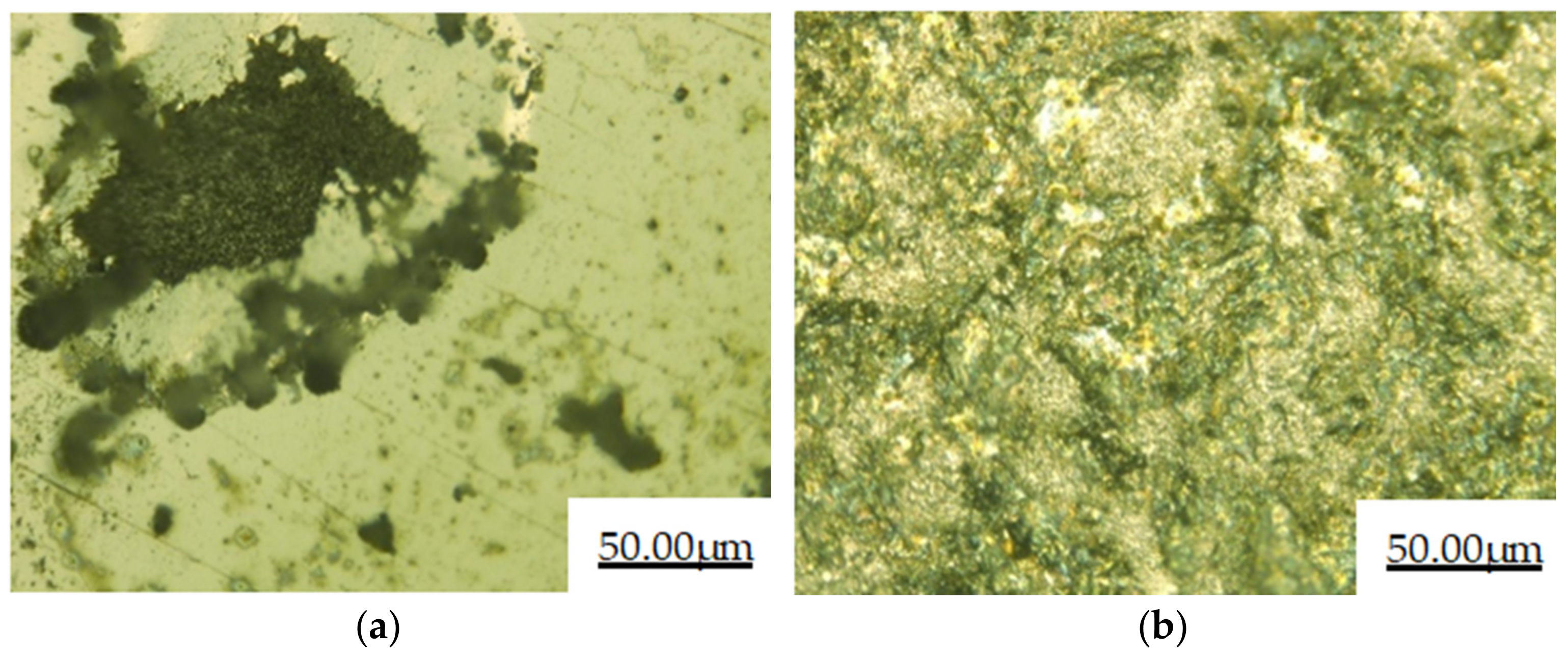
3.4. Salt Spray Corrosion Performance
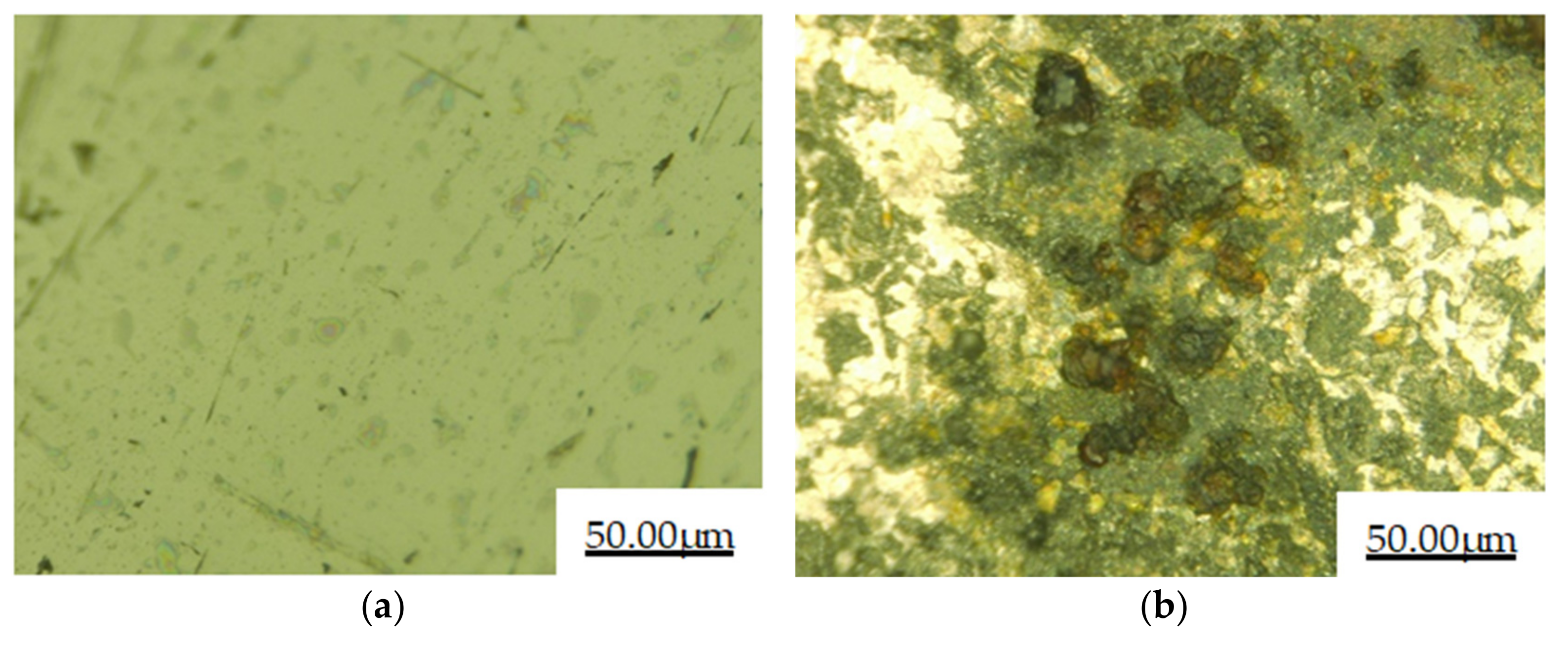
3.5. Immersion Corrosion Performance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Fe-based alloy cladding layer is mainly composed of a-Fe solid solution, M7C3, M2B, and Cr3Si. Planar crystals, cellular crystals, dendrites, and equiaxed dendrites are formed in the cladding layer.
- (2)
- The electrochemical corrosion performance test of the cladding layer and 27SiMn substrate shows that the corrosion potential of the cladding layer is larger, and the capacitive arc radius is larger than that of the substrate. This indicates that the cladding layer has better corrosion resistance than 27SiMn. The surface of the cladding layer undergoes pitting and local corrosion after electrochemical corrosion, and the surface of the substrate undergoes surface corrosion after electrochemical corrosion.
- (3)
- The cladding layer and 27SiMn matrix were corroded by salt spray for 48 h. It can be observed that the surface of the substrate is corroded seriously, while the surface of the cladding layer sample is still smooth and has almost no change in morphology. After immersion corrosion of the cladding layer and 27SiMn substrate in the mine water simulated by the corrosive solution for 120 h, the weight loss of the cladding layer during immersion corrosion is 0.0305 g·cm−2, less than that of the substrate. The cladding layer is more resistant to corrosion than the 27SiMn substrate in salt spray corrosion and immersion corrosion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, H.F.; Xue, K.N.; Xu, X.; Luo, K.Y.; Xing, F.; Yao, J.H.; Lu, J.Z. Effects of laser shock peening on microstructural evolution and wear property of laser hybrid remanufac-tured Ni25/Fe104 coating on H13 tool steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 291, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, R.; Razavi, R.S.; Bakhshi, S.R.; Erfanmanesh, M.; Bani, A.A. Optimization and characterization of laser cladding of NiCr and NiCr–TiC composite coatings on AISI 420 stainless steel. Ceram. Int. 2020, 47, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farotade, G.A.; Adesina, O.S.; Foluso Ogunbiyi, O.; Tobi Adesina, O.; Kazeem, R.A.; Adeniran, A.A. Microstructural characterization and surface properties of laser clad Ni-ZrB2 coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 38, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Li, K.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C. The effect of laser power on the structure and properties of laser cladding iron-based alloys on the sur-face of 27SiMn steel. Heat Treat. Met. 2018, 43, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Su, L.; Dong, C.; Du, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L. Performance of 27SiMn laser cladding iron-based alloy coating on hydraulic support column. China Surface Eng. 2013, 26, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, M. Failure analysis and preventive measures of hydraulic support column corrosion. Hebei Coal 2002, 5, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Ye, Z.; Yang, W.; Xu, B.; Zu, W.; Nie, H.; Tian, G. The structure and salt spray corrosion resistance of laser cladding layers of nickel-based and iron-based al-loys containing tungsten carbide. Plat. Finish. 2019, 38, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, X. Materials Science Research and Testing Methods, 2nd ed.; Southeast University Press: Nanjing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Lin, Z. Engineering Materials Science; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; He, D.; Du, K.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wu, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z. Study on the struc-ture and electrochemical corrosion behavior of FeCrNiMo laser cladding layer. Surface Technol. 2020, 49, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Sandvik, B.P.J.; Martikainen, H.O.; Lindroos, V.K. The crystallography and microstructure of lath martensite formed in type 301 stainless steel. Scr. Metall. 1984, 18, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Mallick, P.; Chattopadhyay, P.P. Effect of reversion of strain induced martensite on microstructure and mechanical properties in austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Wang, J. Crystal Growth and Control during Metal Solidification; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, S. The latest new engineering material production, new technology application and new product development and industry technical standards and practical encyclopedia. In Nine, Materials and Material Processing and Forming Theory Volume; Xueyuan Audio-Visual Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A.; Jurči, P. Laser cladding process of Fe/WC metal matrix composite coatings on low carbon steel using Yb: YAG disk laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 136, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, H.F.; Luo, K.Y.; Yao, J.H.; Xu, L.Z.; Lu, J.Z.; Lu, Y.F. Mechanical properties and electrochemical corrosion resistance of multilayer laser cladded Fe-based composite coatings on 4Cr5MoSiV1 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 284, 116736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, C. Corrosion Behavior of a Ni–Cr–Mo Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser Cladding in a Simulated Sulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion Environment. Coatings 2020, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A.; Piasecki, A.; Jurči, P. Influence of Laser Cladding Parameters on Microstructure, Microhardness, Chemical Composition, Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Fe–B Composite Coatings Reinforced with B4C and Si Particles. Coatings 2020, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L. Research on Seawater Corrosion and Wear Behavior of 316L_2205 Stainless Steel. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yao, C.; Yao, L.; Fan, C. Corrosion properties of laser cladded CrCoNi medium entropy alloy coating. Surface Coat. Technol. 2020, 397, 126004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y. Guardian of Material Science and Metal Equipment; Shandong Education Press: Jinan, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zuo, Y. Corrosion Resistance and Corrosion Data of Materials; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Chen, H.; Ma, F.; Xie, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z. Corrosion behavior of low alloy steel in high salinity mine water environment. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2016, 36, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, K.A.; Kilcullen, M.B. Corrosion-resistant low-alloy steels: A review with particular reference to atmospheric condi-tions in the United Kingdom. Br. Corros. J. 1970, 5, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.J.; Sheu, H.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Lee, H.B. The study of mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of the Fe-based amor-phous alloy coatings using high velocity oxygen fuel spraying. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 867, 159132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Typical corrosion morphology of metals. Equip. Environ. Eng. 2006, 4, 31–37. [Google Scholar]


| C | Si | Mn | V | Ni | Cu | S | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.24–0.32 | 1.10–1.40 | 1.10–1.40 | 0.07–0.12 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.04 | Bal |
| C | Cr | Si | Ni | B | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 19.7 | 1.06 | 2.69 | 1.00 | 0.47 | Bal |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Power/W | 2700 |
| Powder feeding rate/(rad·min−1) | 2.8 |
| Cladding rate/(m·min−1) | 9 |
| Defocus/mm | 15 |
| Overlap rate (%) | 80 |
| Electrode Reaction | Mn = Mn2+ + 2e | Cr = Cr3+ + 3e | Fe = Fe2+ + 2e | Ni = Ni2+ + 2e | Mo = Mo3+ + 3e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard reduction potential Φ0 | −1.18 | −0.74 | −0.440 | −0.250 | −0.2 (about) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, C.; Bai, Q.; Yan, X.; Chen, Z.; Han, B.; Liu, Y. Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Laser Cladding Fe-Based Alloy Coating on 27SiMn Steel Surface. Coatings 2021, 11, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050552
Ouyang C, Bai Q, Yan X, Chen Z, Han B, Liu Y. Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Laser Cladding Fe-Based Alloy Coating on 27SiMn Steel Surface. Coatings. 2021; 11(5):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050552
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Changyao, Qiaofeng Bai, Xianguo Yan, Zhi Chen, Binhui Han, and Yan Liu. 2021. "Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Laser Cladding Fe-Based Alloy Coating on 27SiMn Steel Surface" Coatings 11, no. 5: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050552
APA StyleOuyang, C., Bai, Q., Yan, X., Chen, Z., Han, B., & Liu, Y. (2021). Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Laser Cladding Fe-Based Alloy Coating on 27SiMn Steel Surface. Coatings, 11(5), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050552




