Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Scandia Alumina Stabilized Zirconia Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formation of Thin Films
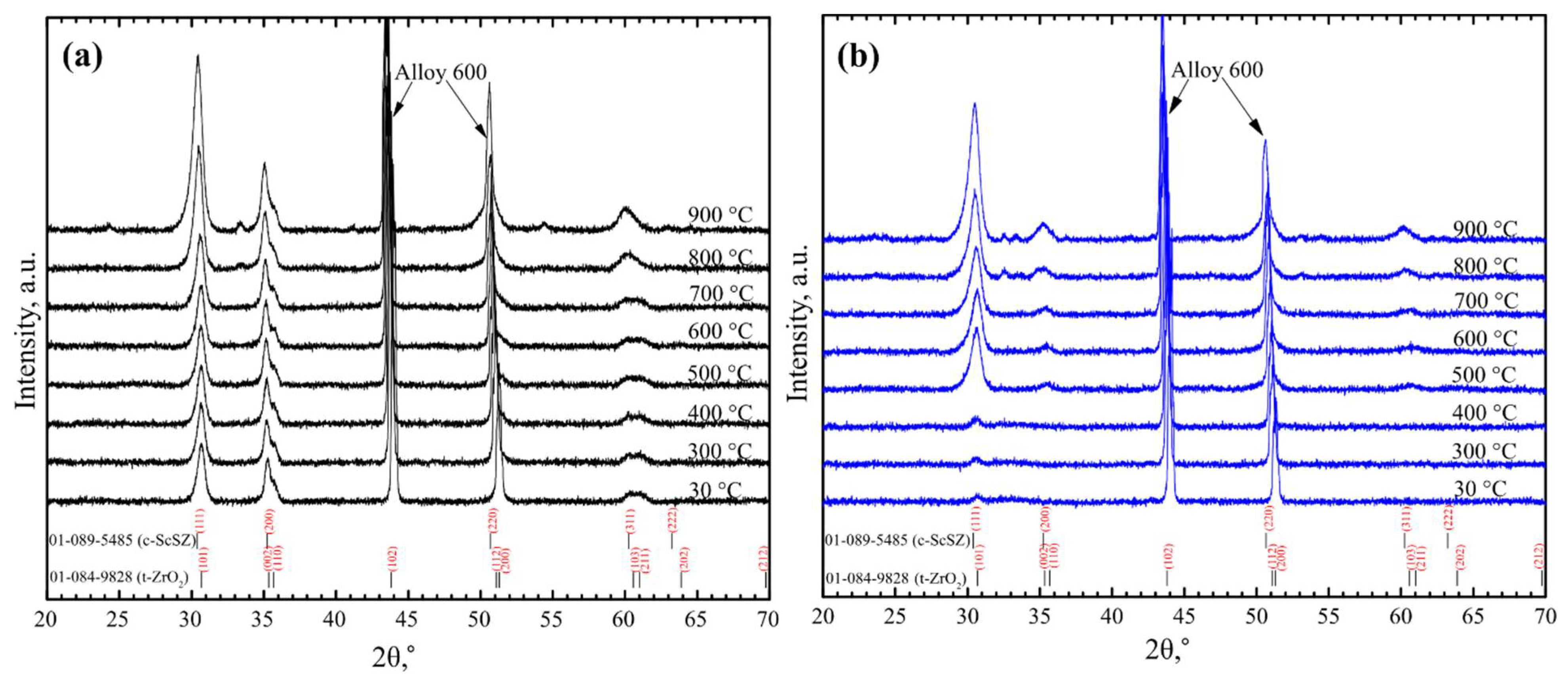
2.2. X-ray Diffraction
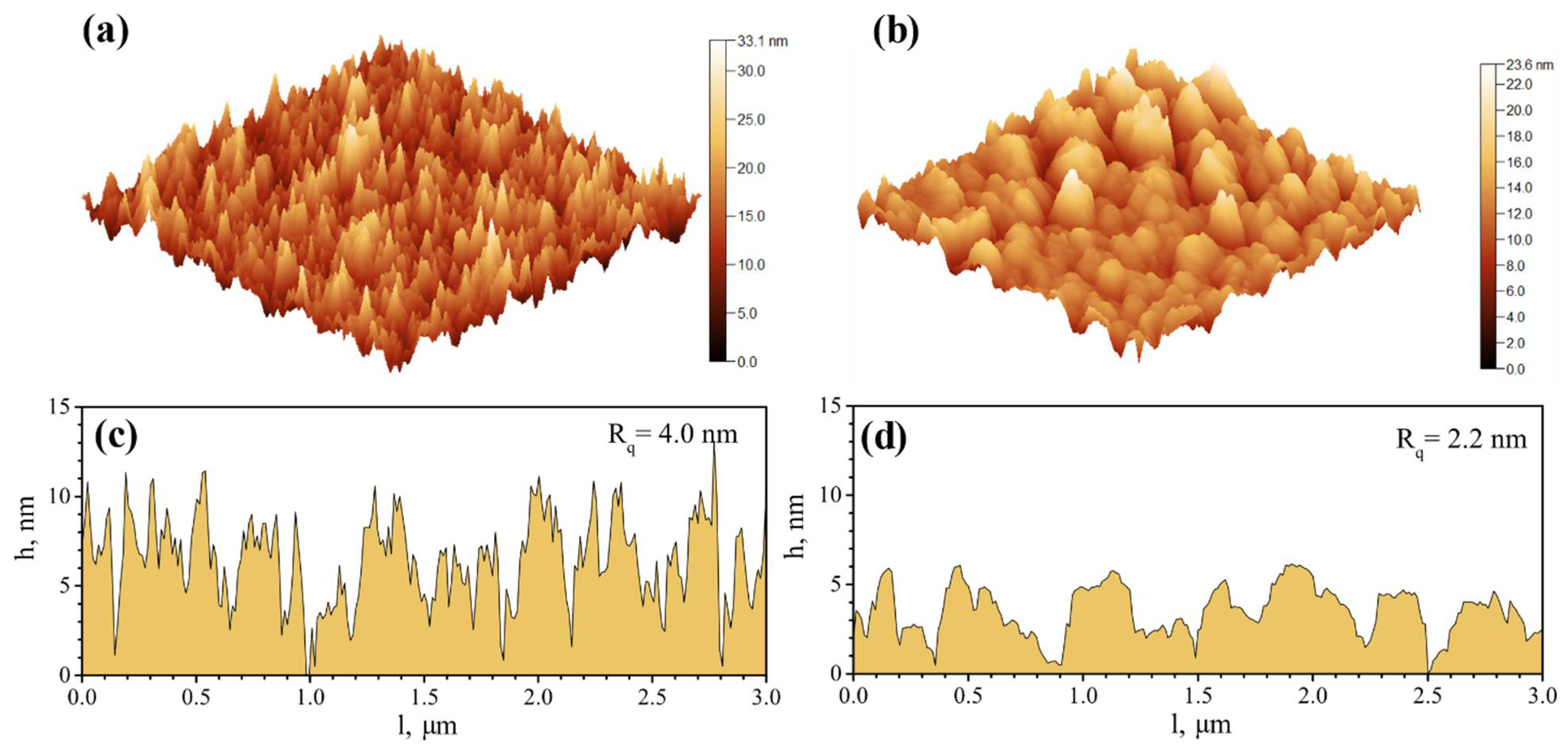
2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy
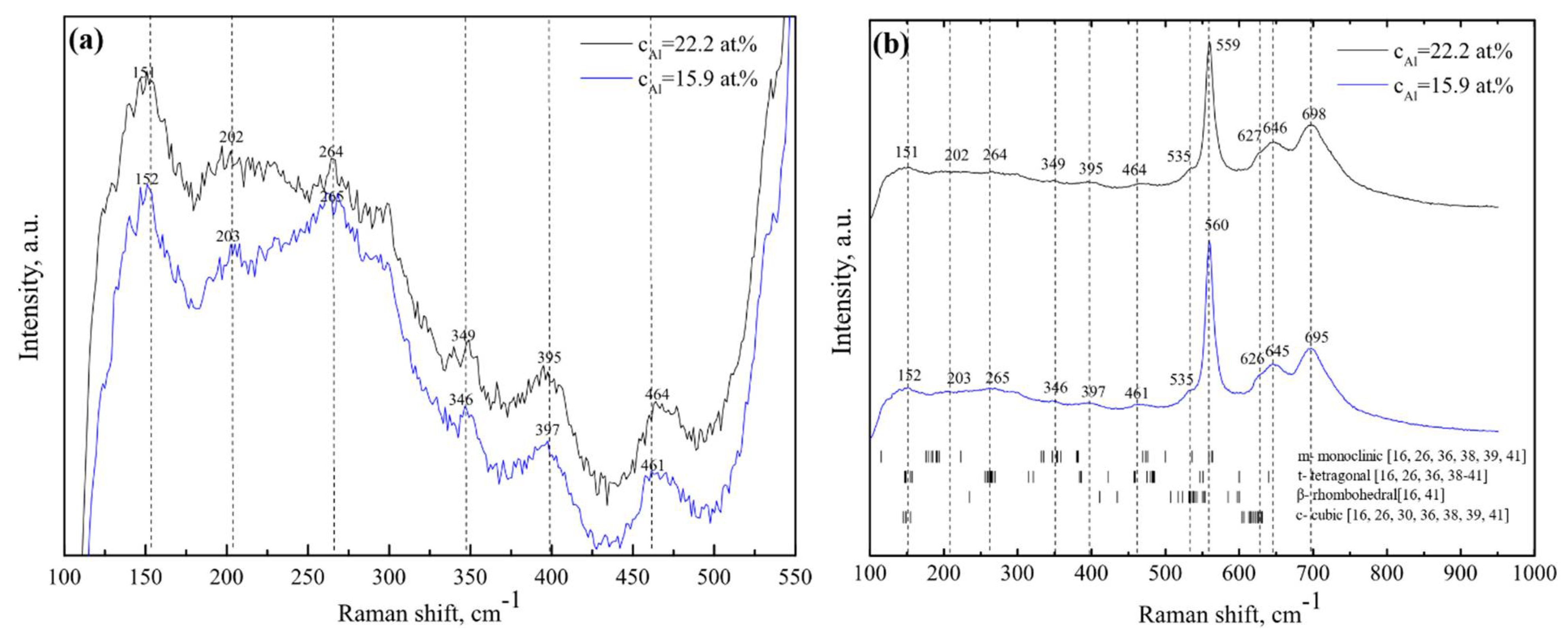
2.4. Raman Spectroscopy
2.5. Determination of Chemical Composition
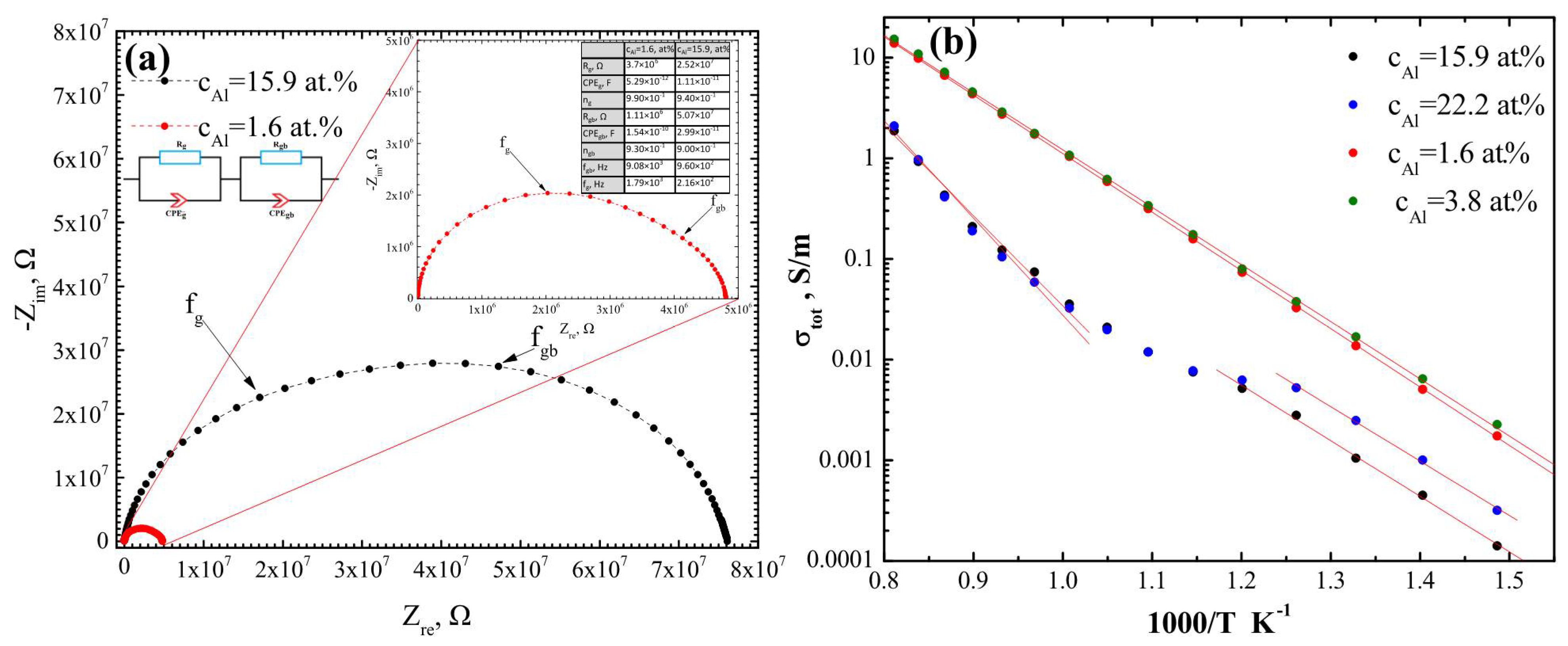
2.6. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogicevic, A.; Wolverton, C.; Crosbie, G.M.; Stechel, E.B. Defect ordering in aliovalently doped cubic zirconia from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 014106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.N.; Wang, L.G.; Huang, X.W.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, H. Influence of codoping on the conductivity of Sc-doped zirconia by first-principles calculations and experiments. Mater. Des. 2018, 160, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachi, Y.; Sakai, H.; Yamamoto, O.; Takeda, Y.; Imanishai, N. Electrical conductivity of the ZrO2-Ln2O3 (Ln = lanthanides) system. Solid State Ion. 1999, 121, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.P.; Dunlap, B.I.; Fleischer, A.S. Effects of dopant clustering in cubic zirconia stabilized by yttria and scandia from molecular dynamics. Solid State Ion. 2013, 253, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilner, J.A.; Druce, J.; Ishihara, T. Electrolytes. In High-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells for the 21st Century: Fundamentals, Design and Applications, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 85–132. ISBN 9780124104532. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Yangping, L. Review of solid oxide fuel cell materials: Cathode, anode, and electrolyte. Energy Transit. 2020, 4, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarat, S.; Sammes, N.; Smirnova, A. Bismuth oxide doped scandia-stabilized zirconia electrolyte for the intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sour. 2006, 160, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, L. A review of zirconia-based solid electrolytes. Ionics 2016, 22, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.X.; Wang, J.X.; He, C.R.; Wang, W.G. Effect of alumina on the properties of ceria and scandia co-doped zirconia for electrolyte-supported SOFC. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9575–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badwal, S.P.S.; Ciacchi, F.T.; Milosevic, D. Scandia-zirconia electrolytes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell operation. Solid State Ion. 2000, 136–137, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, J.; Miao, H.; Guo, C.; Wang, W.G. Investigation of the crystal structure and ionic conductivity in the ternary system (Yb2O3)x-(Sc2O3)(0.11–x)-(ZrO2)0.89 (x = 0–0.11). J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 549, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhu, Q. Phase transformation and low temperature sintering of manganese oxide and scandia co-doped zirconia. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T. Structural phase transition and ionic conductivity in 0.88ZrO2(0.12–x)Sc2O3xAl2O3. Solid State Ion. 1995, 78, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, R.; Yoshimura, F.; Yamaki, J.; Ishii, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Endou, K. Ionic conductivity and morphology in Sc2O3 and Al2O3 doped ZrO2 films prepared by the sol-gel method. Solid State Ion. 1997, 104, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haering, C.; Roosen, A.; Schichl, H.; Schnöller, M. Degradation of the electrical conductivity in stabilised zirconia system Part II: Scandia-stabilised zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriubas, M.; Kainbayev, N.; Virbukas, D.; Bočkutė, K.; Rutkūnienė, Ž.; Laukaitis, G. Structure and conductivity studies of scandia and alumina doped zirconia thin films. Coatings 2019, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kainbayev, N.; Sriubas, M.; Bockute, K.; Virbukas, D.; Laukaitis, G. E-beam deposition of scandia-stabilized zirconia (ScSZ) thin films Co-doped with Al. Coatings 2020, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feighery, A.J.; Irvine, J.T.S. Effect of alumina additions upon electrical properties of 8 mol.% yttria-stabilized zirconia. Solid State Ion. 1999, 121, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizea, A.; Chirlesan, D.; Petot, C.; Petot-Ervas, G. The influence of alumina on the microstructure and grain boundary conductivity of yttria-doped zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2002, 146, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Mori, T.; Li, J.-G.; Ikegami, T.; Komatsu, M.; Haneda, H. Improvement of grain-boundary conductivity of 8 mol.% yttria-stabilized zirconia by precursor scavenging of siliceous phase. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Chen, C.; Varanasi, C.; Fellner, J.P. Electrical properties of heterogeneously doped yttria stabilized zirconia. J. Power Sources 2005, 140, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jaiswal, A.; Sanbui, M.; Omar, S. Oxygen-ion conduction in scandia-stabilized zirconia-ceria solid electrolyte (xSc2O3-1CeO2-(99−x)ZrO2, 5 ≤ x ≤ 11). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Abu Hassan, S.H.; Shaari, N.; Yahaya, A.Z.; Boon Kar, Y. A review on recent status and challenges of yttria stabilized zirconia modification to lowering the temperature of solid oxide fuel cells operation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 631–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaei, M.; Mozammel, M. Yttria-stabilized zirconia thin film electrolyte deposited by EB-PVD on porous anode support for SOFC applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 3035–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukaitis, G.; Virbukas, D. The structural and electrical properties of GDC10 thin films formed by e-beam technique. Solid State Ion. 2013, 247–248, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Asari, E.; Kitajima, M. Infrared and raman spectroscopic studies of ZrO2 polymorphs doped with Y2O3 or CeO2. J. Solid State Chem. 1994, 110, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russian Journal of Non-Ferrous Metals. Home. Available online: https://www.springer.com/journal/11981 (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Singh, R.K.; Singh, P. Electrical conductivity of barium substituted LSGM electrolyte materials for IT-SOFC. Solid State Ion. 2014, 262, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Sharma, S.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Hamilton, J. Probing the thermal deoxygenation of graphene oxide using high-resolution in situ X-ray-based spectroscopies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17009–17019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milanov, A.P.; Xu, K.; Cwik, S.; Parala, H.; De Los Arcos, T.; Becker, H.W.; Rogalla, D.; Cross, R.; Paul, S.; Devi, A. Sc2O3, Er2O3, and Y2O3 thin films by MOCVD from volatile guanidinate class of rare-earth precursors. Dalt. Trans. 2012, 41, 13936–13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, J.S.; Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lee, T.; Ng, A.K.; Detsi, E. Hierarchical bulk nanoporous aluminum for on-site generation of hydrogen by hydrolysis in pure water and combustion of solid fuels. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11194–11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, J.; Nguyen, C.P.T.; Lee, C.; Balaji, N.; Chatterjee, S.; Jang, K.; Kim, H.; Yi, J. Improved data retention of InSnZnO nonvolatile memory by H2O2 treated Al2O3 tunneling layer: A cost-effective method. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morant, C.; Sanz, J.M.; Galán, L.; Soriano, L.; Rueda, F. An XPS study of the interaction of oxygen with zirconium. Surf. Sci. 1989, 218, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young Choi, J.; Sig Kim, S.; Yeol Lee, S. Effect of hafnium addition on Zn-Sn-O thin film transistors fabricated by solution process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 022109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.X.; Liu, A.; Meng, Y.; Shan, F.K.; Shin, B.C.; Lee, W.J.; Cho, C.R. Annealing dependence of solution-processed ultra-thin ZrOx films for gate dielectric applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, H.P.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, K.; Park, S.Y.; Hong, J.; Kim, H.; Yoon, K.J.; Son, J.W.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.H. Synthesis, sintering and conductivity behavior of ceria-doped scandia-stabilized zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2014, 263, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, W. Synthesis and characterization of monoclinic ZrO2 nanorods by a novel and simple precursor thermal decomposition approach. Solid State Commun. 2003, 127, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.R.; Adar, F. Measurement of the crystallographically transformed zone produced by fracture in ceramics containing tetragonal zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1982, 65, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basahel, S.N.; Ali, T.T.; Mokhtar, M.; Narasimharao, K. Influence of crystal structure of nanosized ZrO2 on photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gazzoli, D.; Mattei, G.; Valigi, M. Raman and X-ray investigations of the incorporation of Ca2+ and Cd2+ in the ZrO2 structure. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Mizutani, Y.; Kawai, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamamoto, O. Aging and Raman scattering study of scandia and yttria doped zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2000, 132, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jaiswal, A.; Sanbui, M.; Omar, S. Scandia stabilized zirconia-ceria solid electrolyte (xSc1CeSZ, 5 <x <11) for IT-SOFCs: Structure and conductivity studies. Scr. Mater. 2016, 121, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Synthesis and characterization of high ionic conductivity ScSZ core/shell nanocomposites. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apriany, K.; Permadani, I.; Syarif, D.G.; Soepriyanto, S.; Rahmawati, F. Electrical conductivity of zirconia and yttrium-doped zirconia from indonesian local zircon as prospective material for fuel cells. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Solo, Indonesia, 8–9 September 2015; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 107, p. 012023. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, W.; Koshikawa, T.; Yamaji, A.; Adachi, T. Degradation mechanism of scandia-stabilised zirconia electrolytes: Discussion based on annealing effects on mechanical strength, ionic conductivity, and Raman spectrum. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Rosas, M.; Camacho-López, M.A.; Ruiz-Trejo, E. Structure, conductivity and luminescence of 8 mol.% scandia-doped zirconia prepared by sol-gel. Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhu, Q. Low temperature processing of dense nanocrystalline scandia-doped zirconia (ScSZ) ceramics. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 2791–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borik, M.A.; Bredikhin, S.I.; Bublik, V.T.; Kulebyakin, A.V.; Kuritsyna, I.E.; Lomonova, E.E.; Milovich, P.O.; Myzina, V.A.; Osiko, V.V.; Ryabochkina, P.A.; et al. Structure and conductivity of yttria and scandia-doped zirconia crystals grown by skull melting. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 5536–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkov, A.; Stanulis, A.; Sakaliuniene, J.; Butkute, S.; Abakeviciene, B.; Salkus, T.; Tautkus, S.; Orliukas, A.F.; Tamulevicius, S.; Kareiva, A. On the synthesis of yttria-stabilized zirconia: A comparative study. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 76, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamer, C.; Opitz, A.K.; Rupp, G.M.; Fleig, J. Revisiting the temperature dependent ionic conductivity of yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ). J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, F790–F803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Sakuragi, S.; Iwama, Y.; Sonoyama, N.; Ikeda, S.; Hirano, A.; Imanishi, N.; Takeda, Y.; Yamamoto, O. Crystal structure and oxygen ion conductivity of Ga3+ Co-doped scandia-stabilized zirconia. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoyama, N.; Martin, S.G.; Amador, U.; Imanishi, N.; Ikeda, M.; Erfu, N.; Tanimura, H.; Hirano, A.; Takeda, Y.; Yamamoto, O. Crystal structure and electrical properties of magnesia Co-doped scandia stabilized zirconia. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1397–F1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, M.; Bi, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, C. Structure and impedance of ZrO2 doped with Sc2O3 and CeO2. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2579–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyamina, G.; Ilela, A.; Khasanov, O.; Petyukevich, M.; Vaitulevich, E. Synthesis of Al2O3-ZrO2 powders from differently concentrated suspensions with a spray drying technique. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Tomsk, Russia, 26–29 April 2016; American Institute of Physics Inc.: College Park, MD, USA, 2016; Volume 1772, p. 20011. [Google Scholar]
- Barna, P.B.; Adamik, M. Fundamental structure forming phenomena of polycrystalline films and the structure zone models. Thin Solid Films 1998, 317, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haering, C.; Roosen, A.; Schichl, H. Degradation of the electrical conductivity in stabilised zirconia systems Part I: Yttria-stabilised zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya Lakshmi, V.; Bauri, R.; Gandhi, A.S.; Paul, S. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline ScSZ electrolyte for SOFCs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 14936–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, Y.L.; Chen, P.J.; Huang, S.H.; Shiu, T.J.; Tsai, T.Y.; Chow, Y.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Weng, S.C.; Chang, S.L.; Wang, G.; et al. Local structures surrounding Zr in nanostructurally stabilized cubic zirconia: Structural origin of phase stability. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 113535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabris, S.; Paxton, A.T.; Finnis, M.W. A stabilization mechanism of zirconia based on oxygen vacancies only. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 5171–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thangadurai, P.; Sabarinathan, V.; Bose, A.C.; Ramasamy, S. Conductivity behaviour of a cubic/tetragonal phase stabilized nanocrystalline La2O3—ZrO2. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2004, 65, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Virkar, A.V.; Liu, F. Defect configuration and phase stability of cubic versus tetragonal yttria-stabilized zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2012, 215, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| vd, nm/s | cO, at.% | cAl, at.% | cAl3+, at.% | cSc, at.% | cZr, at.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 53.3 | 15.9 | 11.8 | 3.4 | 27.4 |
| 0.4 | 50.2 | 22.2 | 20.1 | 3.4 | 24.2 |
| 1.2 | 55.6 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 7.4 | 35.4 |
| 1.6 | 54.1 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 7.7 | 34.4 |
| Powder | 52.0 | 12.6 | - | 3.9 | 32.5 |
| ScAlSZ Phase | cAl = 1.6 at.% | cAl = 3.8 at.% | cAl = 15.9 at.% | cAl = 22.2 at.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monoclinic | 22% | 18% | 18% | 31% |
| Tetragonal | 42% | 40% | 82% | 69% |
| Cubic | 36% | 42% | 0% | 0% |
| cAl, at.% | Temperature Range | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range 1 | Range 2 | |||
| σ, S/m | Ea, eV | σ, S/m | Ea, eV | |
| 1.6 | 0.033 | 1.16 | 2.74 | 1.16 |
| 3.8 | 0.038 | 1.14 | 2.89 | 1.14 |
| 15.9 | 0.0028 | 1.10 | 0.123 | 1.79 |
| 22.2 | 0.0025 | 1.08 | 0.105 | 1.93 |
| Compound | Phase | σtot, S/m | σ3.8 at.%, S/m | Tm, °C | Formation Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 | tetragonal | 3 | 1.8 | 750 | caustic fusion method | [44] |
| Doped ZrO2 | ||||||
| Sc0.7Zr0.93O2 | tetragonal + cubic | 25 | 19.2 | 1000 | solid-state reaction | [45] |
| Sc0.08Zr0.92O2 | cubic | 25.8 | 15.2 | 950 | sol–gel | [46] |
| Sc0.09Zr0.91O2 | cubic + tetragonal + rhombohedral | 31 | 19.2 | 1000 | solid-state reaction | [45] |
| Sc0.10Zr0.90O2 | cubic | 6 | 1.8 | 750 | solid-state reaction | [15] |
| Sc0.11Zr0.89O2 | rhombohedral | 9.3 | 2.9 | 800 | co-precipitation combined with supercritical ethanol drying route | [47] |
| Y0.7Zr0.93O2 | tetragonal + cubic | 5.5 | 10.9 | 900 | skull melting | [48] |
| Y0.08Zr0.92O2 | monoclinic +cubic | 1 | 1.1 | 700 | sol–gel | [49] |
| Y0.09Zr0.91O2 | monoclinic +cubic | 1.5 | 2.9 | 800 | [8] | |
| Y0.10Zr0.90O2 | cubic | 6.2 | 10.9 | 900 | skull melting | [48] |
| Y0.11Zr0.89O2 | cubic | 6.5 | 16.2 | 950 | crystalline sample oxide-mixing method | [50] |
| Co-doped ZrO2 | ||||||
| Al0.01Sc0.10Zr0.89O2 | cubic | 9.2 | 2.9 | 800 | conventional tape-casting method | [9] |
| Al0.001Sc0.12Zr0.88O2 | rhombohedral | 10 | 4.6 | 850 | solid-state reaction | [13] |
| Al0.005Sc0.12Zr0.88O2 | cubic | 12 | 4.6 | 850 | solid-state reaction | [13] |
| Ga0.01Sc0.10Zr0.89O2 | cubic | 13 | 10.9 | 900 | Sol-gel | [51] |
| Ga0.07Sc0.04Zr0.89O2 | monoclinic + tetragonal | 1.6 | 10.9 | 900 | Sol-gel | [51] |
| Yb0.01Sc0.10Zr0.89O2 | cubic | 31 | 19.2 | 1000 | solid-state reaction | [45] |
| Yb0.02Sc0.10Zr0.88O2 | cubic | 24 | 19.2 | 1000 | solid-state reaction | [45] |
| Ce0.01Sc0.10Zr0.89O2 | cubic | 7.9 | 10.9 | 900 | self combustion synthesis | [36] |
| Mg0.03Sc0.08Zr0.89O2 | cubic | 10 | 10.9 | 900 | Sol-gel | [52] |
| ScAlSZ Phase | cAl = 15.9 at.% | cAl = 22.2 at.% |
|---|---|---|
| Monoclinic | 16% | 15% |
| Tetragonal + Rhombohedral | 61% | 61% |
| Cubic | 23% | 24% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sriubas, M.; Virbukas, D.; Kainbayev, N.; Bockute, K.; Laukaitis, G. Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Scandia Alumina Stabilized Zirconia Thin Films. Coatings 2021, 11, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070800
Sriubas M, Virbukas D, Kainbayev N, Bockute K, Laukaitis G. Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Scandia Alumina Stabilized Zirconia Thin Films. Coatings. 2021; 11(7):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070800
Chicago/Turabian StyleSriubas, Mantas, Darius Virbukas, Nursultan Kainbayev, Kristina Bockute, and Giedrius Laukaitis. 2021. "Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Scandia Alumina Stabilized Zirconia Thin Films" Coatings 11, no. 7: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070800
APA StyleSriubas, M., Virbukas, D., Kainbayev, N., Bockute, K., & Laukaitis, G. (2021). Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Scandia Alumina Stabilized Zirconia Thin Films. Coatings, 11(7), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070800






