Evaluation of Streptococcus mutans Adhesion to Stainless Steel Surfaces Modified Using Different Topographies Following a Biomimetic Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates
2.2. Master Model
2.3. Sol-Gel Synthesis
2.4. Soft Lithography
2.5. Surface Characterization
2.6. Bacterial Adhesion Test
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Surface Characterization of Natural Leaves
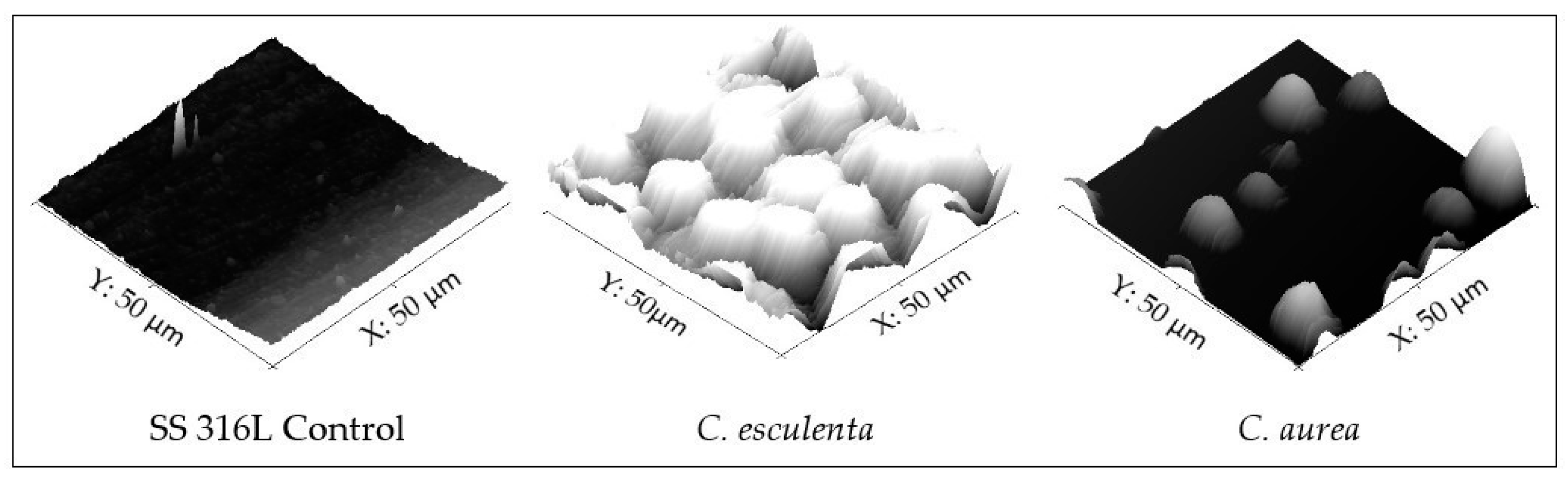
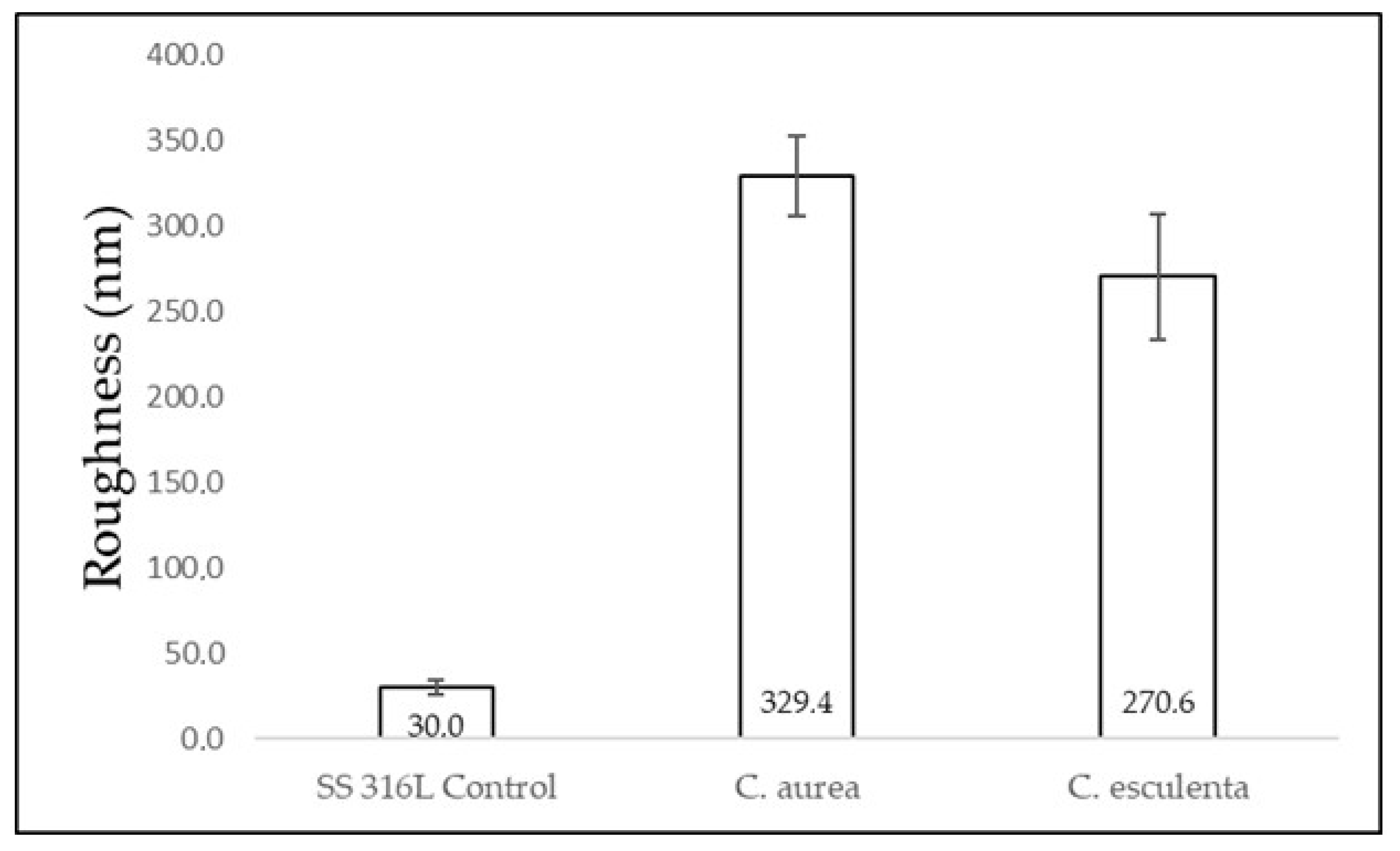
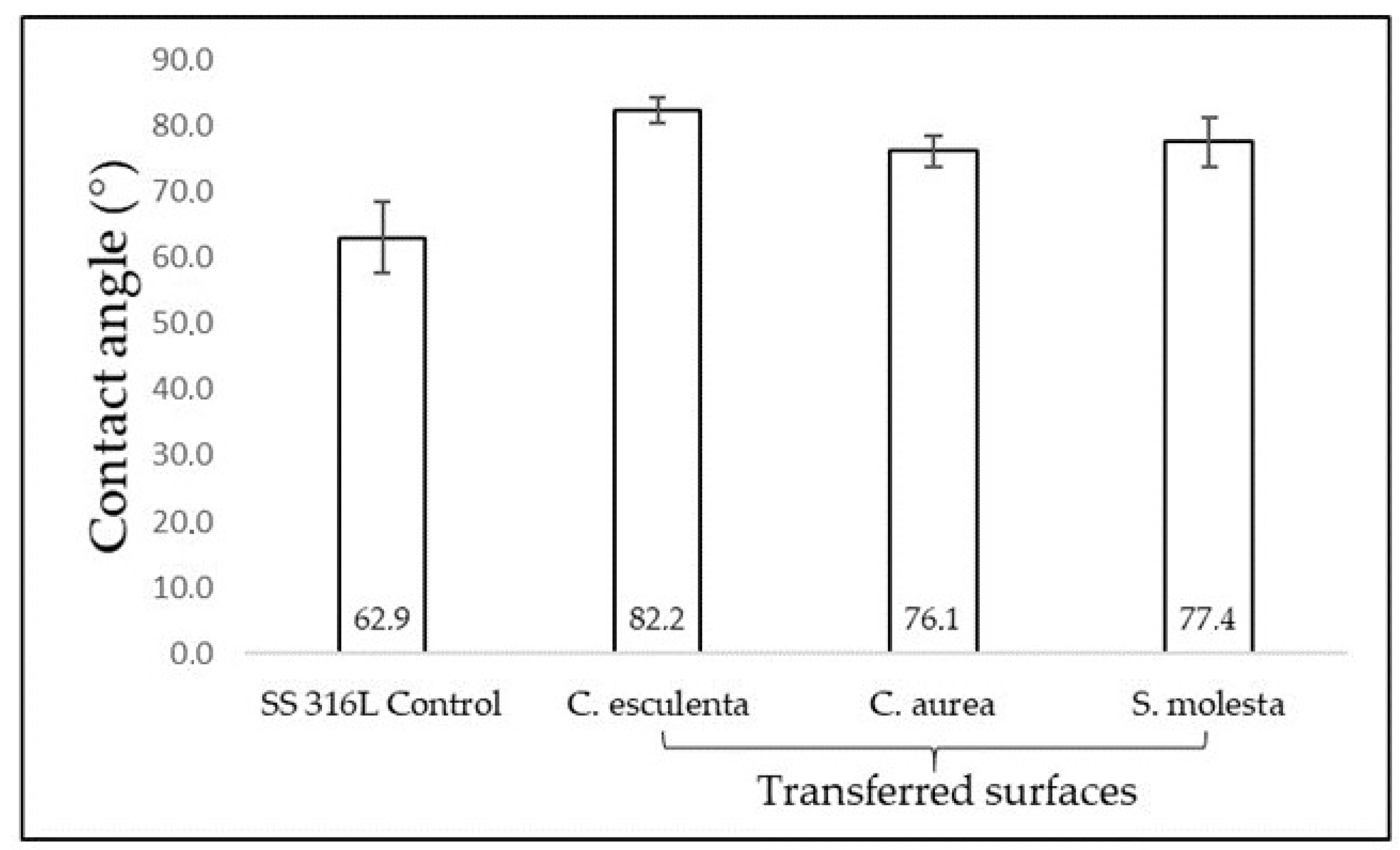
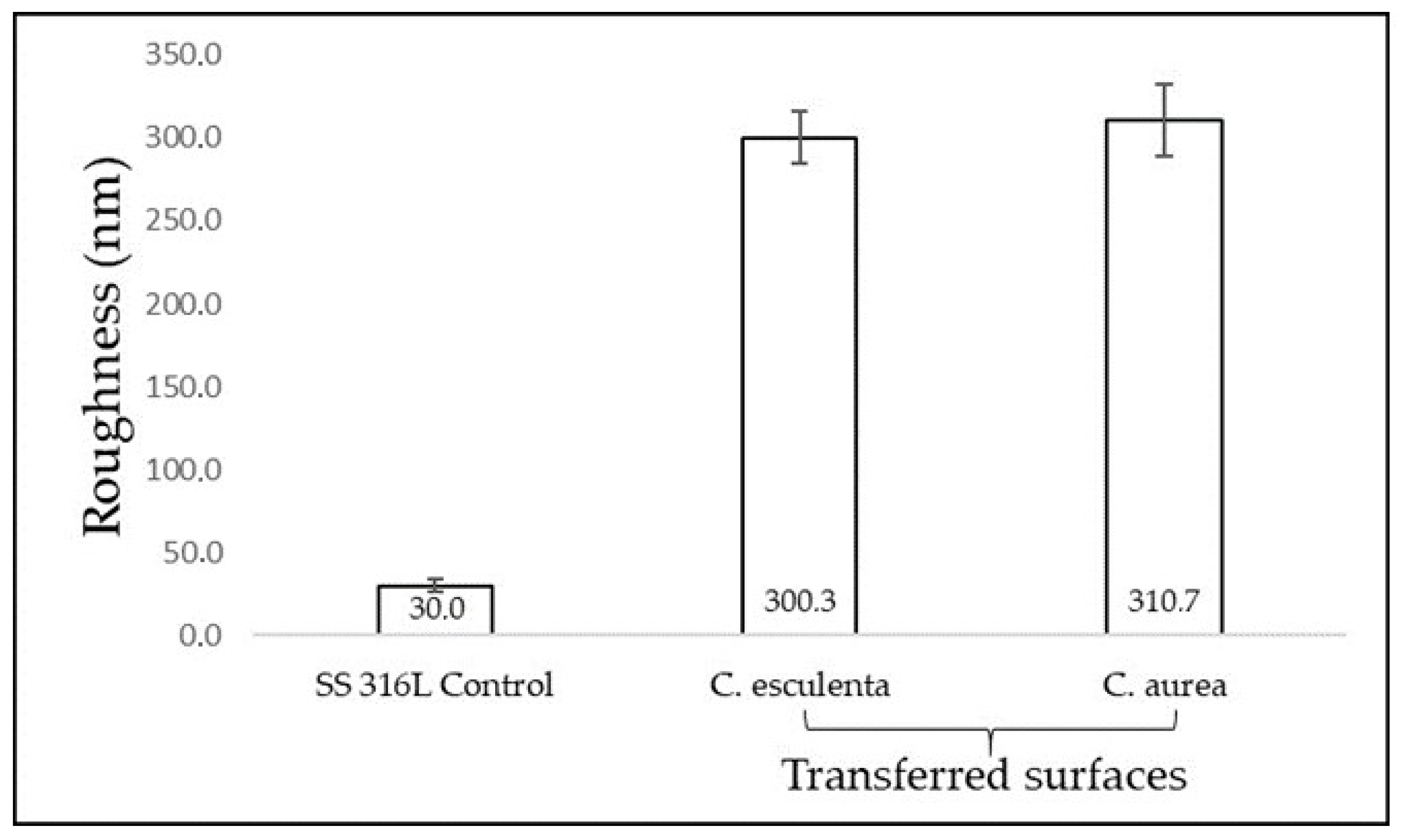
3.2. Surface Characterization of Modified and Control Surfaces
3.3. Evaluation of S. mutans Adhesion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robert, M.; Ezzell, J. Regulatory Affairs for Biomaterials and Medical Devices, 1st ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, N.R.; Gohil, P.P. A review on biomaterials: Scope, applications & human anatomy significance. IJETAE 2012, 2, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D. Orthodontic adhesive resins. In Orthodontic Material: Scientific and Clinical Aspects, 1st ed.; Thieme Medical Publ Inc.: Stuttgart, Germany, 2001; pp. 202–217. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.T.; Choo, S.U.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, K.N. A stainless steel bracket for orthodontic application. Eur. J. Orthod. 2005, 27, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, L.; Garmas, E. Mini implantes, una opción para el anclaje en ortodoncia. Gac. Médica Espirituana 2010, 12, 1–9. Available online: http://revgmespirituana.sld.cu (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Uribe, G.; Aristiz, J.F. Metales y Alambres De Ortodoncia. In Ortodoncia Teoría y Clínica, 1st ed.; Marcolud: Bogota, Colombia, 2004; pp. 226–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ábalos, C. Adhesión bacteriana a biomateriales. Av. Odontoestomatol. 2005, 21, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Barthlott, W. Superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic plant surfaces: An inspiration for biomimetic materials. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1487–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.; Romoser, A.; Banerjee, N.; Zebda, R.; Sayes, C.M. The relationship between pH and zeta potential of ~30 nm metal oxide nanoparticle suspensions relevant to in vitro toxicological evaluations. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiremitçi-Gümü, M. Microbial adhesion to ionogenic PHEMA, PU and PP implants. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, G.A.; Teixeira, A.I.; Nealey, P.F.; Murphy, C.J. Effects of substratum topography on cell behavior. Biomim. Mater. Des. 2002, 33, 91–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Levänen, E. Superhydrophobic surfaces for the reduction of bacterial adhesion. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12003–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, N.B.; Zero, D.T.; Marsh, P.D.; Ekstrand, K.; Weintraub, J.A.; Ramos-Gomez, F.; Tagami, J.; Twetman, S.; Tsakos, G.; Ismail, A. Dental caries. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moulis, E.; Chabadel, O.; Goldsmith, M.C.; Canal, P. Prevención de caries y ortodoncia. EMC-Pediatría 2008, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, P.D. Are dental diseases examples of ecological catastrophes? Microbiology 2003, 149, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, R.P.; Teles, F.R.F. Antimicrobial agents used in the control of periodontal biofilms: Effective adjuncts to mechanical plaque control? Braz. Oral Res. 2009, 23, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradshaw, D.J. To the control of oral biofilms. Adv. Dent. Res. 1997, 11, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Nistico, L.; Sambanthamoorthy, K.; Dice, B.; Nguyen, D.; Mershon, W.J.; Johnson, C.; Hu, F.Z.; Stoodley, P.; Ehrlich, G.D.; et al. Characterization of biofilm matrix, degradation by DNase treatment and evidence of capsule downregulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darouiche, R.O.; Mansouri, M.D.; Gawande, P.V.; Madhyastha, S. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm efficacy of triclosan and DispersinB® combination. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Bayer, I.S.; Biris, A.S.; Wang, T.; Dervishi, E.; Faupel, F. Advances in top-down and bottom-up surface nanofabrication: Techniques, applications & future prospects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 170, 2–27. [Google Scholar]
- Arango, S.; Peláez-Vargas, A.; García, C. Coating and surface treatments on orthodontic metallic materials. Coatings 2012, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G. Soft lithography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1998, 28, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Ostuni, E.; Jiang, X.; Ingber, D.E. Soft lithography in biology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 3, 335–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bixler, G.D.; Theiss, A.; Bhushan, B.; Lee, S.C. Anti-fouling properties of microstructured surfaces bio-inspired by rice leaves and butterfly wings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 419, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Rangel, E. Biomimética: De la naturaleza a la creación humana. Ciencias 2010, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadra, C.M.; Khanh Truong, V.; Pham, V.T.H.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Seniutinas, G.; Wang, J.Y.; Juodkazis, S.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Antibacterial titanium nano-patterned arrays inspired by dragonfly wings. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochbaum, A.; Aizenberg, J. bacteria pattern spontaneously on periodic nanostructure arrays. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3717–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M.; Hoffman, M.G.; Sogo, M.J.; Parker, A.E.; O’Toole, G.A.; Brennan, A.B.; Reddy, S.T. Micro-patterned surfaces reduce bacterial colonization and biofilm formation in vitro: Potential for enhancing endotracheal tube designs. Clin. Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, K.K.; Schumacher, J.F.; Sampson, E.M.; Burne, R.A.; Antonelli, P.J.; Brennan, A.B. Impact of engineered surface microtopography on biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus. Biointerphases 2007, 2, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arango-Santander, S.; Gonzalez, C.; Aguilar, A.; Cano, A.; Castro, S.; Sanchez-Garzon, J.; Franco, J. Assessment of streptococcus mutans adhesion to the surface of biomimetically-modified orthodontic archwires. Coatings 2020, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arango-Santander, S.; Freitas, S.; Pelaez-Vargas, A.; Garcia, C. Silica sol-gel patterned surfaces based on dip-pen nanolithography and microstamping: A comparison in resolution and throughput. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 720, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcas, I.; Fernández, R.; Gómez-Rodríguez, J.M.; Colchero, J.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; Baro, A.M. WSXM: A software for scanning probe microscopy and a tool for nanotechnology. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango-Santander, S.; Pelaez-Vargas, A.; Freitas, S.; García, C. Surface modification by combination of dip-pen nanolithography and soft lithography for reduction of bacterial adhesion. J. Nanotech. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naghili, H.; Tajik, H.; Mardani, K.; Razavi Rouhani, S.M.; Ehsani, A.; Zare, P. Validation of drop plate technique for bacterial enumeration by parametric and nonparametric tests. Vet. Res. Forum 2013, 4, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Choi, S.O. Superhydrophobicity. Waterproof and water repellent textiles and clothing. In The Textile Institute Book Series; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 267–297. [Google Scholar]
- Falde, E.; Yohe, S.; Colson, Y.; Grinstaff, M. Superhydrophobic materials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaggessar, A.; Shahali, H.; Mathew, A.; Yarlagadda, P. Bio-mimicking nano and micro-structured surface fabrication for antibacterial properties in medical implants. J. Nanobiotech. 2017, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burton, Z.; Bhushan, B. Surface characterization and adhesion and friction properties of hydrophobic leaf surfaces. Ultramicroscopy 2006, 106, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, H.; Cho, I.; Yoon, E. The role of bio-inspired hierarchical structures in wetting. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2015, 10, 026009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B. Biomimetics: Lessons from nature-An overview. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 1445–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, O.; Nylander, T.; Rosmaninho, R.; Rizzo, G.; Yiantsios, S.; Andritsos, N.; Karabelas, A.; Müller-Steinhagen, H.; Melo, L.; Boulangé-Petermann, L.; et al. Modified stainless steel surfaces targeted to reduce fouling—Surface characterization. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinalipour, S.M.; Ershad-langroudi, A.; Hayati, A.N.; Nabizade-Haghighi, A.M. Characterization of sol-gel coated 316L stainless steel for biomedical applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 67, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Pi, P.; Cai, Z.Q.; Wen, X.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Z. Facile preparation of super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic silica film on stainless steel mesh via sol-gel process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4095–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haßler-Grohne, W.; Hüser, D.; Klaus-Peter, J.; Frase, C.; Bosse, H. Current limitations of SEM and AFM metrology for the characterization of 3D nanostructures. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, T.; Dong, A.; Cao, D.; Li, H.; Xue, Y.; Lv, P.; Duan, H. Superrepellency of underwater hierarchical structures on salvinia leaf. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-la-Pinta, I.; Cobos, M.; Ibarretxe, J.; Montoya, E.; Eraso, E.; Guraya, T.; Quindós, G. Effect of biomaterials hydrophobicity and roughness on biofilm development. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspor, P.; Bohinc, K.; Dražić, G.; Fink, R.; Oder, M.; Jevšnik, M.; Nipič, D. Available surface dictates microbial adhesion capacity. Inter. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 50, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Bohinc, K.; Dražić, G.; Abram, A.; Jevšnik, M.; Jeršek, B.; Nipič, D.; Kurinčič, M.; Raspor, P. Metal surface characteristics dictate bacterial adhesion capacity. Inter. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 68, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.; Schilardi, P.; Salvarezza, R.; Fernández Lorenzo de Mele, M. Nano/microscale order affects the early stages of biofilm formation on metal surfaces. Langmuir 2007, 23, 11206–11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, C.; Schilardi, P.; dos Santos Claro, P.C.; Salvarezza, R.C.; Fernandez Lorenzo de Mele, M. Submicron trenches reduce the Pseudomonas fluorescens colonization rate on solid surfaces. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.C.; Siedlecki, C.A. Submicron-textured biomaterial surface reduces staphylococcal bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, J.; Fukunaga, A.; Satou, N.; Shintani, H.; Okuda, K. Streptococcal adherence on various restorative materials. J. Dent. Res. 1988, 67, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadillo-Rodríguez, V.; Guerra-García-Mora, A.; Perera-Costa, D.; Gónzalez-Martín, M.; Fernández-Calderón, M. Bacterial response to spatially organized microtopographic surface patterns with nanometer scale roughness. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 169, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, G.; Webster, T.J. Reduced bacterial growth and increased osteoblast proliferation on titanium with a nanophase TiO2 surface treatment. Inter. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carman, M.; Estes, T.; Feinberg, A.; Schumacher, J.; Wilkerson, W.; Wilson, L.; Callow, M.; Callow, J.; Brennan, A. Engineered antifouling microtopographies-Correlating wettability with cell attachment. Biofouling 2006, 22, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.; Chung, K.; McDaniel, C.; Darouiche, R.; Landman, J.; Brennan, A. Micropatterned surfaces for reducing the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infection: An in vitro study on the effect of sharklet micropatterned surfaces to inhibit bacterial colonization and migration of uropathogenic escherichia coli. J. Endourol. 2011, 25, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arango-Santander, S.; Serna, L.; Sanchez-Garzon, J.; Franco, J. Evaluation of Streptococcus mutans Adhesion to Stainless Steel Surfaces Modified Using Different Topographies Following a Biomimetic Approach. Coatings 2021, 11, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070829
Arango-Santander S, Serna L, Sanchez-Garzon J, Franco J. Evaluation of Streptococcus mutans Adhesion to Stainless Steel Surfaces Modified Using Different Topographies Following a Biomimetic Approach. Coatings. 2021; 11(7):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070829
Chicago/Turabian StyleArango-Santander, Santiago, Lina Serna, Juliana Sanchez-Garzon, and John Franco. 2021. "Evaluation of Streptococcus mutans Adhesion to Stainless Steel Surfaces Modified Using Different Topographies Following a Biomimetic Approach" Coatings 11, no. 7: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070829
APA StyleArango-Santander, S., Serna, L., Sanchez-Garzon, J., & Franco, J. (2021). Evaluation of Streptococcus mutans Adhesion to Stainless Steel Surfaces Modified Using Different Topographies Following a Biomimetic Approach. Coatings, 11(7), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11070829






