Influence of Coarse Aggregate Type on the Mechanical Strengths and Durability of Cement Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Samples Preparation and Measurement
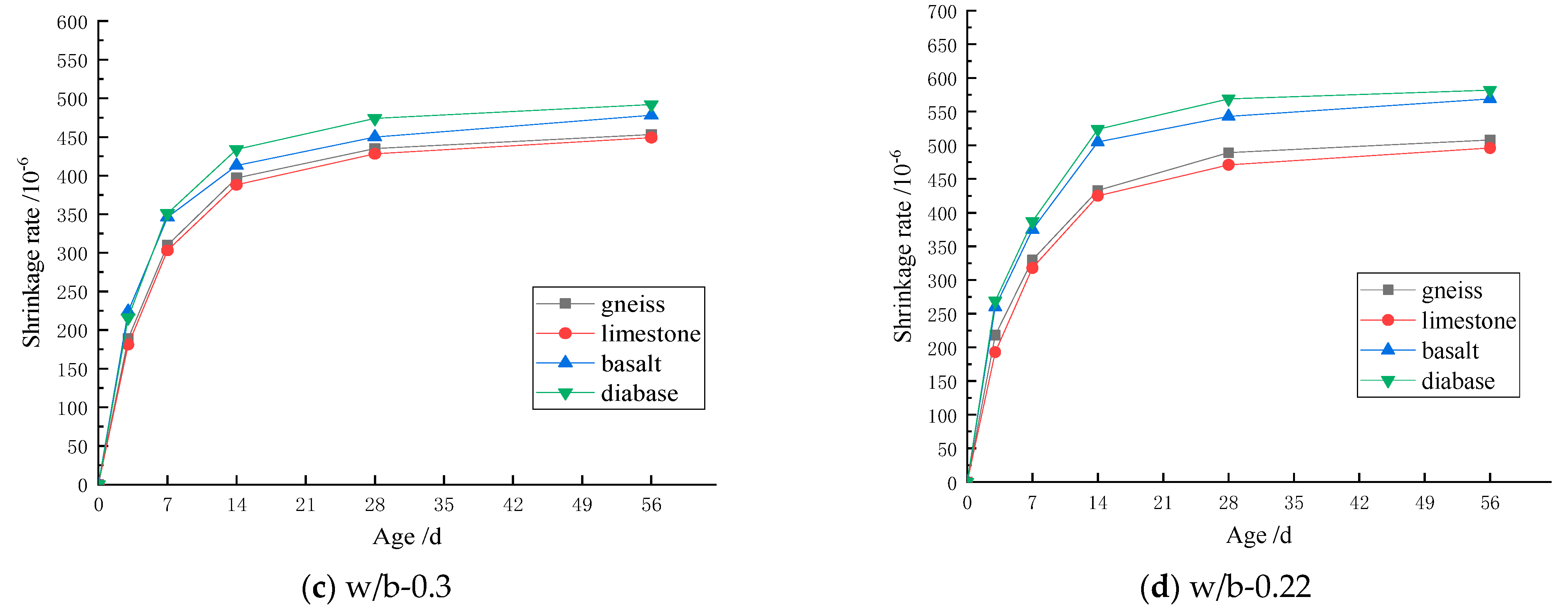
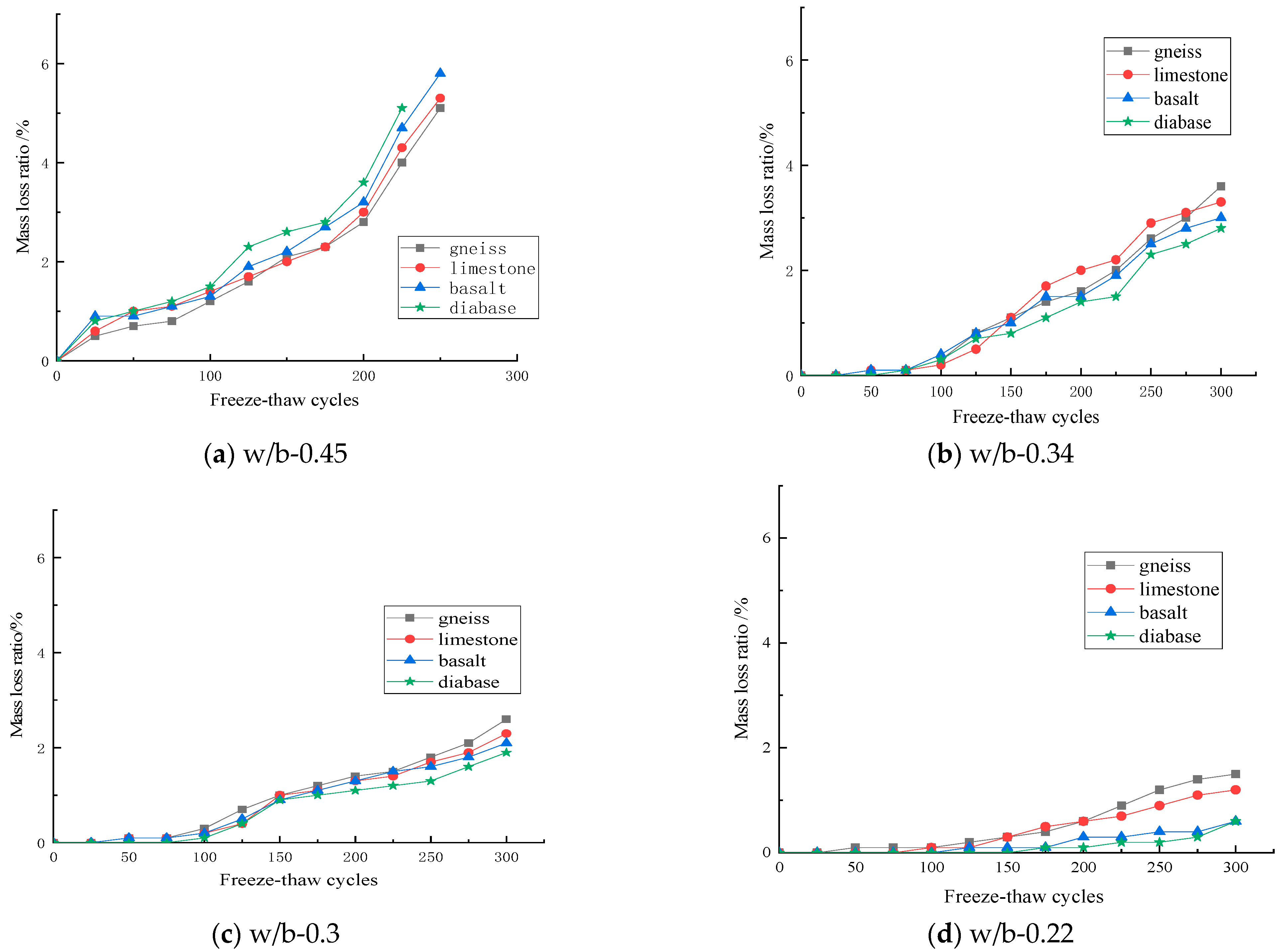
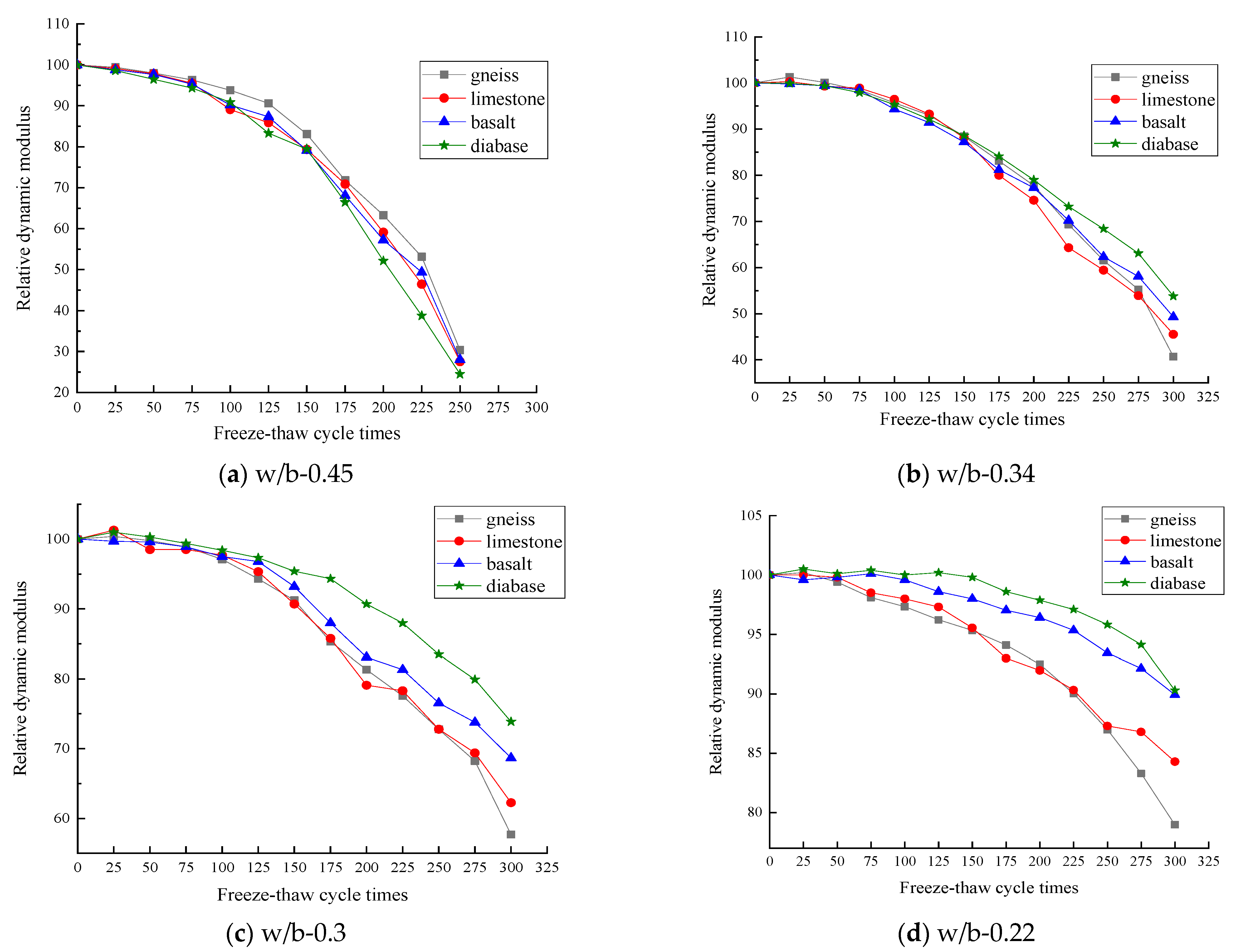
3. Results and Discussion
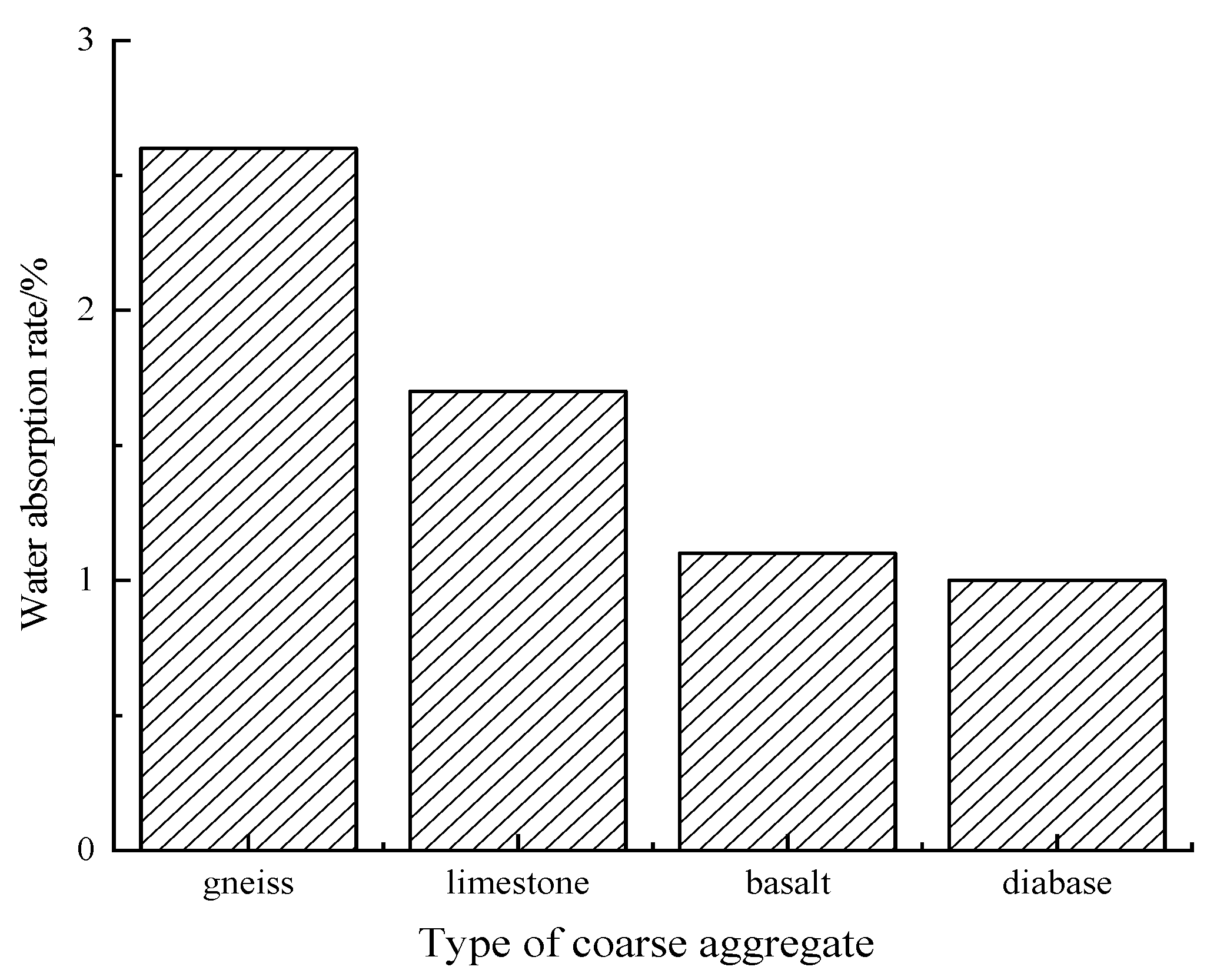
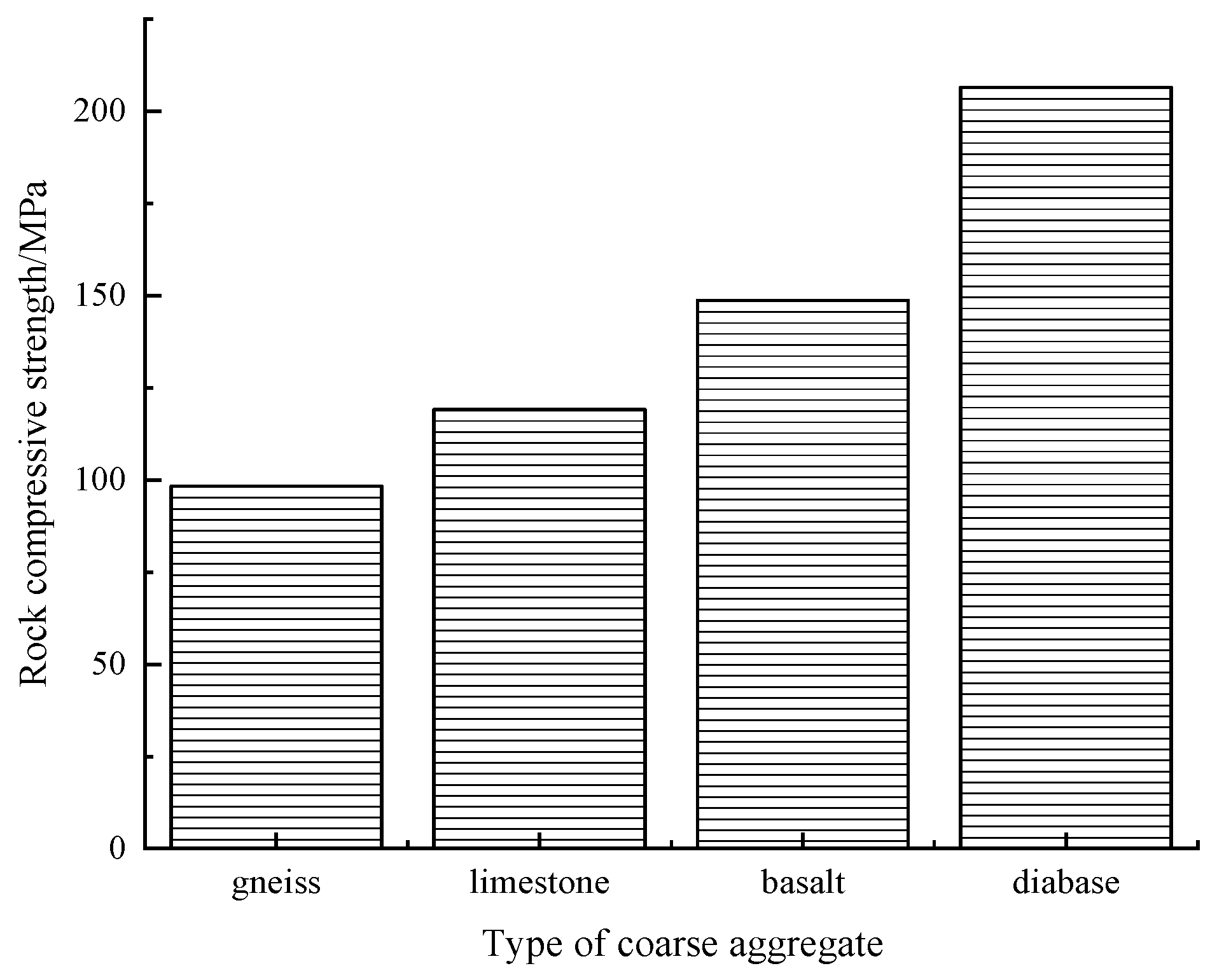
3.1. Properties of Coarse Aggregate
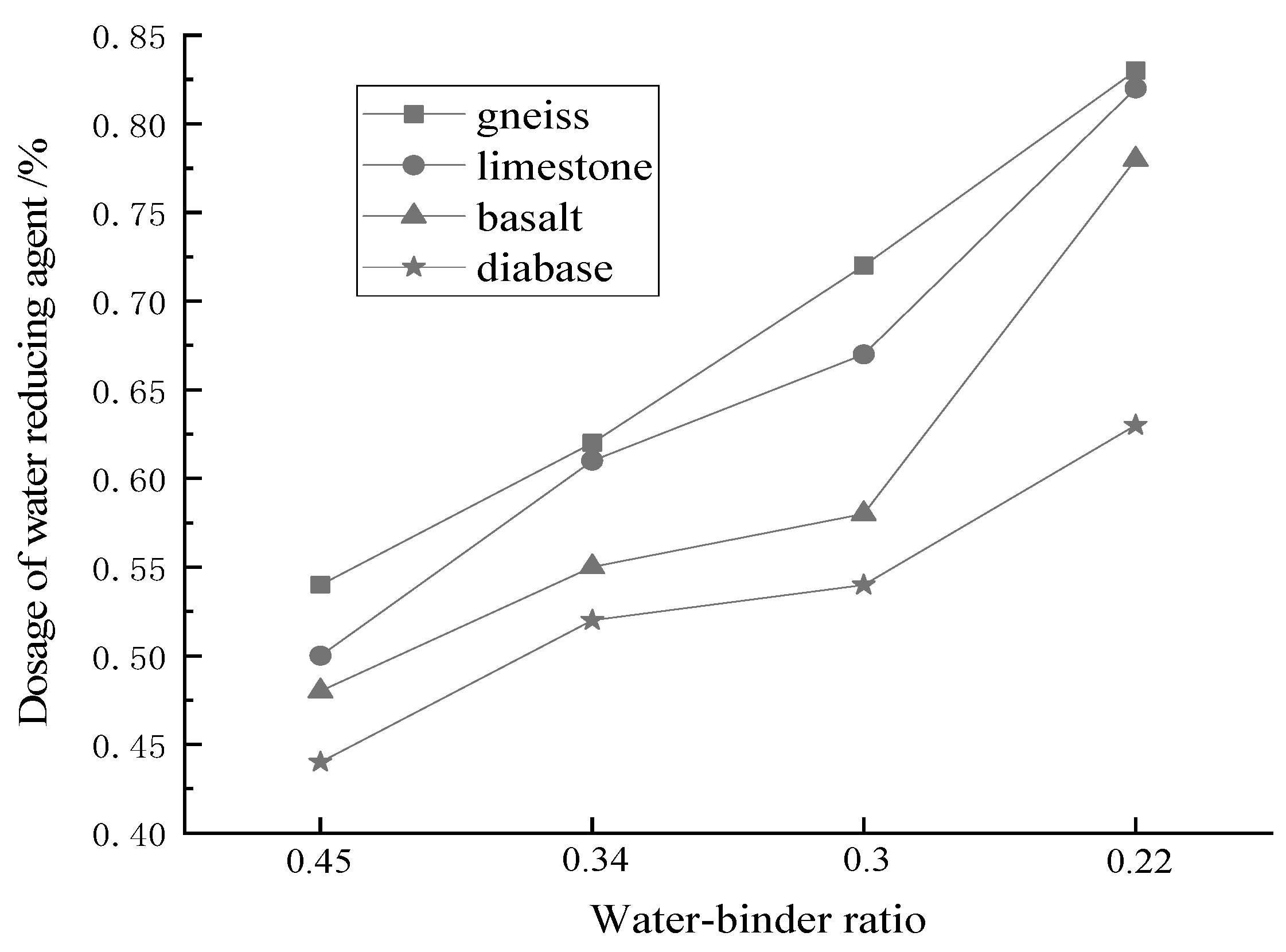
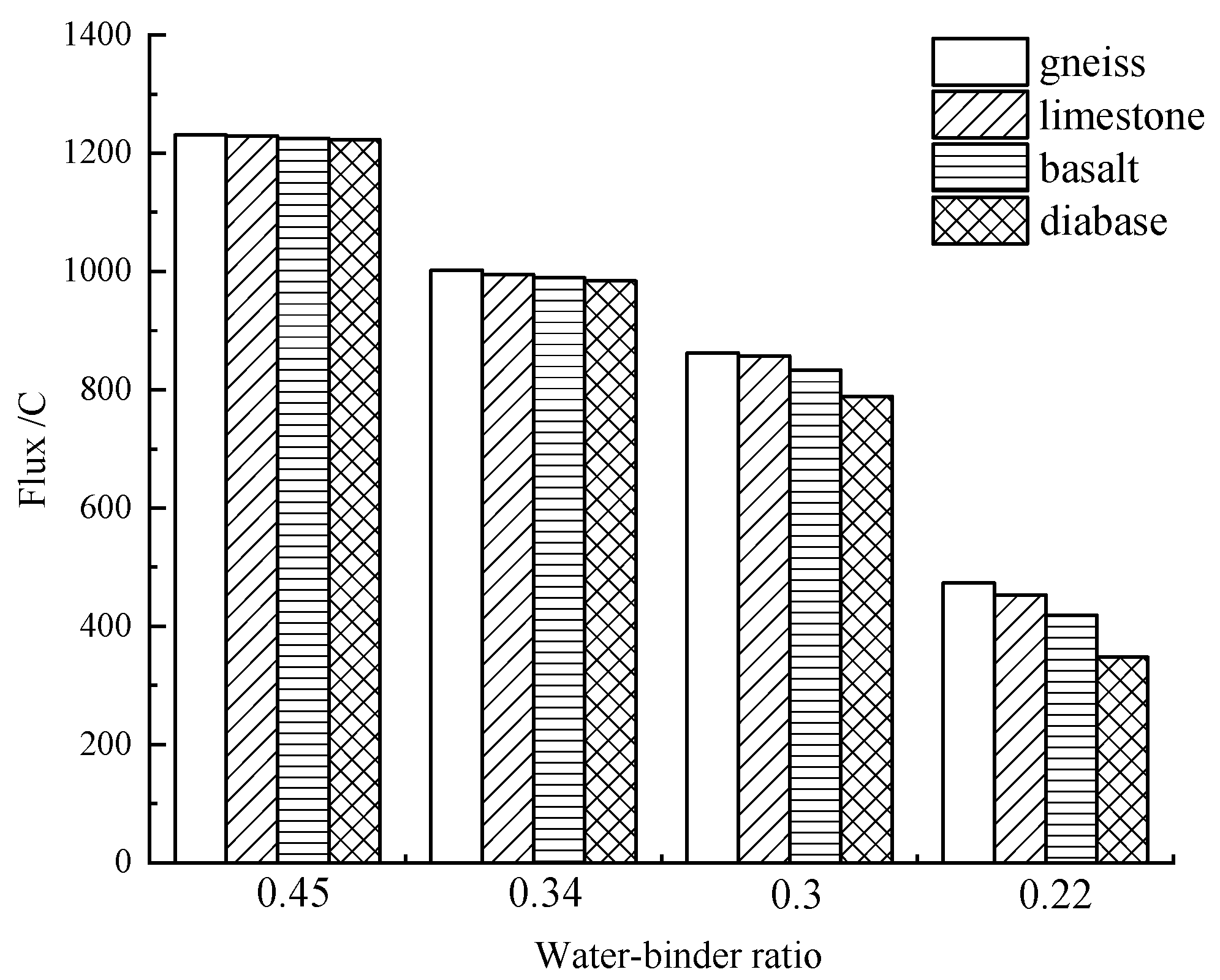
3.2. The Rheological Properties of Fresh Paste
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mo, Z.; Gao, X.; Su, A. Mechanical performances and microstructures of metakaolin contained UHPC matrix under steam curing conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Yao, B.; Huang, H.; Gao, X. Influence of sisal fibers on the mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Tsujino, M.; Noguchi, T.; Kitagaki, R. Expansion/contraction behavior and cracking control effect of expansive concrete in building structure. Proc. Jpn. Concr. Inst. 2012, 34, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, S.; Cise, U. Influence of supplementary cementitious materials on the performance and environmental impacts of reactive magnesia cement concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, M.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Tan, H.; Strnadel, B. New treatment technology: The use of wet-milling concrete slurry waste to substitute cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, D.; Green, M.; Noumowe, A. Residual strength of concrete containing recycled materials after exposure to fire: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.; Soomro, M.; Evangelista, A. A review of recycled aggregate in concrete applications (2000-2017). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, B.; Yu, H.; Ma, H.; Tan, Y.; Mi, R.; Dou, X. Experimental investigation of whole stress-strain curves of coral concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Z.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, C. Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete under uniaxial loading. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridou, C.; Angelopoulos, G.N.; Coutelieris, F.A. Mechanical and durability performance of concrete produced with recycled aggregates from Greek construction and demolition waste plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 1, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, C.Q.; Dhir, R.K.; Ghataora, G.S. Elastic modulus of concrete made with recycled aggregates Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Struct. Build. 2016, 169, 314–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huda, S.B.; Alam, M. Mechanical and freeze–thaw durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete made with recycled coarse aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jensen, O.; Yu, Q. Mechanism of rate dependent behaviour of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete containing coarse aggregates under flexural loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Fu, J.Y.; Pi, Y.L.; Tuan, C.Y.; Liu, A.R. Influence of demolished concrete blocks on mechanical properties of recycled blend concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno, M.; Isidoro, R.; Catarino, J. Mechanical performance evaluation of concrete made with recycled ceramic coarse aggregates from industrial brick waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, R.; Ramamurthy, K. Study of compressive strength characteristics of coral aggregate concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 1996, 48, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C. The greening of the concrete industry. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qudoos, A.; Kim, H.; Ryou, J.-S. Influence of the surface roughness of crushed natural aggregates on the microhardness of the interfacial transition zone of concrete with mineral admixtures and polymer latex. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshr, H.; Almusallam, A.; Maslehuddin, M. Effect of coarse aggregate quality on the mechanical properties of high-strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2003, 17, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesniak, M.; Rougelot, T.; Burlion, N.; Shao, J. Compressive strength of cement-based composites: Roles of aggregate diameter and water saturation degree. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwirzen, A.; Penttala, V. Aggregate–cement paste transition zone properties affecting the salt–frost damage of high-performance concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisschop, J.; Van Mier, J. Effect of aggregates on drying shrinkage microcracking in cement-based composites. Mater. Struct. 2002, 35, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangert, F.; Grasberger, S.; Kuhl, D.; Meschke, G. Environmentally induced deterioration of concrete: Physical motivation and numerical modelling. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2003, 70, 891–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, N. Effect of shrinkage and load-induced cracking on water permeability of concrete. ACI Mater. J. 1999, 96, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Lagier, F.; Jourdain, X.; De Sa, C.; Benboudjema, F.; Colliat, J. Numerical strategies for prediction of drying cracks in heterogenous materials: Comparison upon experimental results. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashin, Z.; Monteiro, P. An inverse method to determine the elastic properties of the interphase between the aggregate and the cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebble and Crushed Stone for Construction; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine: Beijing, China, 2011; GB/T 14685-2011.
- Standard for Test Method of Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete; Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002; GB/T 50081-2002.
- Standard for Test Method of Long-term Performance and Durability of Ordinary Concrete; Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009; GB/T 50082-2009.
- Cho, J.; Joshi, M.; Sun, C. Effect of inclusion size on mechanical properties of polymeric composites with micro and nano particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.; Brito, D.; Pontes, J.; Evangelista, L. Mechanical performance of concrete made with aggregates from construction and demolition waste recycling plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miled, K.; Limam, O.; Sab, K. A probabilistic mechanical model for prediction of aggregates’ size distribution effect on concrete compressive strength. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2012, 391, 3366–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elices, M.; Rocco, C. Effect of aggregate size on fracture and mechanical properties of a simple concrete. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2008, 75, 3839–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtdas, I.; Burlion, N.; Skoczylas, F. Experimental characterisation of the drying effect on uniaxial mechanical behaviour of mortar. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassl, P.; Wong, H.; Buenfeld, N. Influence of aggregate size and volume fraction on shrinkage induced micro-cracking of concrete and mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, J. Eects of salt freeze–thaw cycles and cyclic loading on the piezoresistive properties of carbon nanofibers mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, F. Influence of NaCl freeze thaw cycles and cyclic loading on the mechanical performance and permeability of sulphoaluminate cement reactive powder concrete. Coatings 2020, 10, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.Q.; Shen, X.H.; Xia, J.; Mao, L.X.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.F. A numerical study on chloride diffusion in freeze–thaw affected concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 179, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Liu, J. Coupling effect of salt freeze–thaw cycles and cyclic loading on performance degradation of carbon nanofiber mortar. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fu, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Experimental studies on the chloride ionpermeability of concrete considering the effect of freeze–thaw damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.F.; Jiang, K.; Zhu, X.; Xu, L. An alternating experimental study on the combined effect of freeze–thaw and chloride penetration in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, L.; Yao, Y.; Li, K. Characterizing blended cement pastes under cyclic freeze–thaw actions by electrical resistivity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jalali, S.; Aguiar, J.B. Self-monitoring of freeze–thaw damage using triphasic electric conductive concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Types | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | SO3 | K2O | MgO | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 5.47 | 20.86 | 3.94 | 62.23 | 2.66 | 0.48 | 1.73 | / |
| Fly ash | 42.86 | 36.75 | 8.65 | 5.23 | 0.49 | 0.43 | 0.24 | 5.35 |
| GGBS | 14.86 | 26.75 | 0.89 | 49.42 | 2.49 | 0.46 | 3.24 | 1.89 |
| Silica fume | 0.27 | 94.5 | 0.83 | 0.54 | / | / | 0.97 | 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Yong, H.; Lu, J.; Shu, C.; Wang, H. Influence of Coarse Aggregate Type on the Mechanical Strengths and Durability of Cement Concrete. Coatings 2021, 11, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091036
Wang L, Yong H, Lu J, Shu C, Wang H. Influence of Coarse Aggregate Type on the Mechanical Strengths and Durability of Cement Concrete. Coatings. 2021; 11(9):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091036
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lin, Han Yong, Jinyu Lu, Chunxue Shu, and Hui Wang. 2021. "Influence of Coarse Aggregate Type on the Mechanical Strengths and Durability of Cement Concrete" Coatings 11, no. 9: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091036
APA StyleWang, L., Yong, H., Lu, J., Shu, C., & Wang, H. (2021). Influence of Coarse Aggregate Type on the Mechanical Strengths and Durability of Cement Concrete. Coatings, 11(9), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11091036







