Tuning the Electrical Properties of Tungsten Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WOx Film Synthesis Conditions
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reactivity of O2 with Respect to W Target
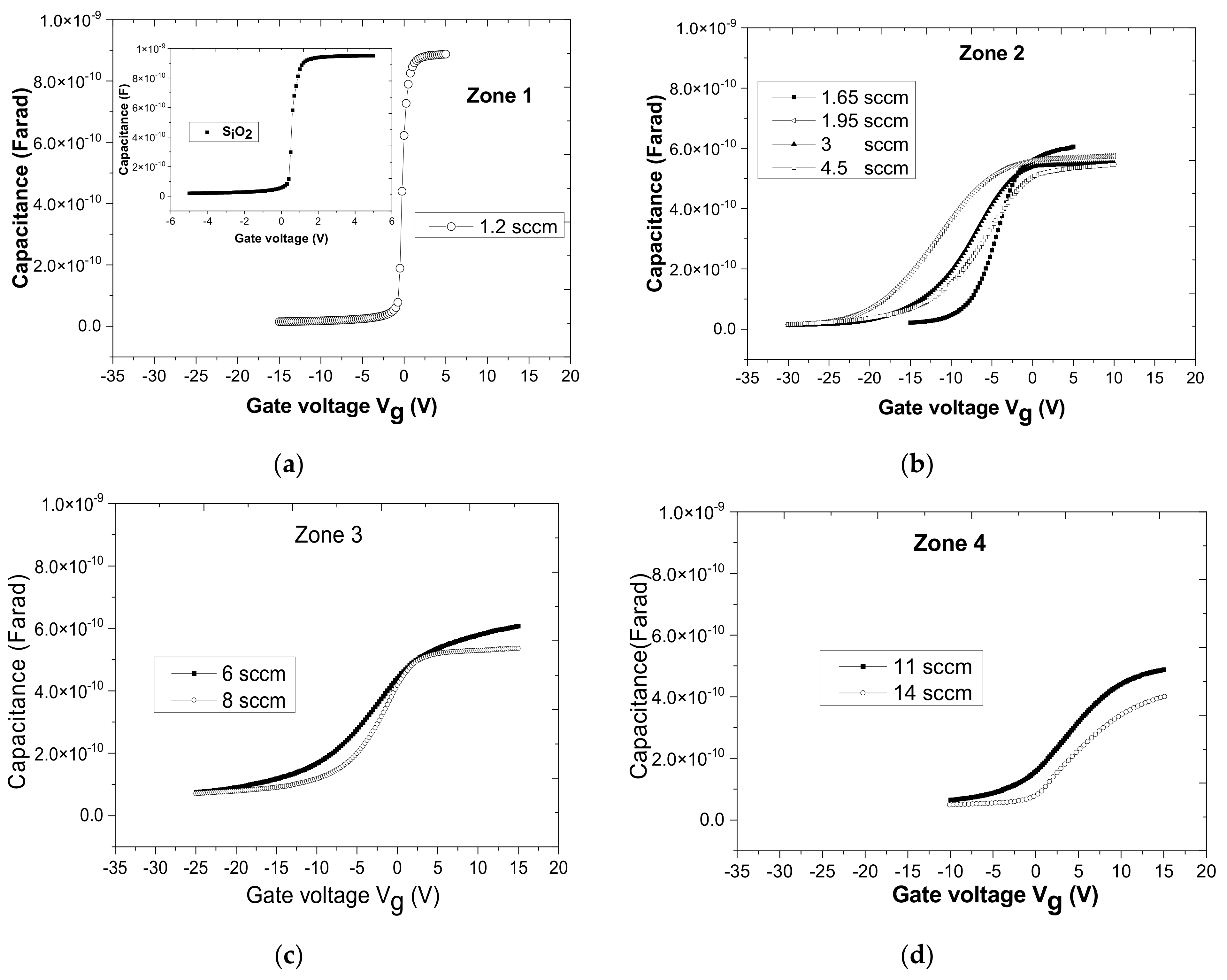
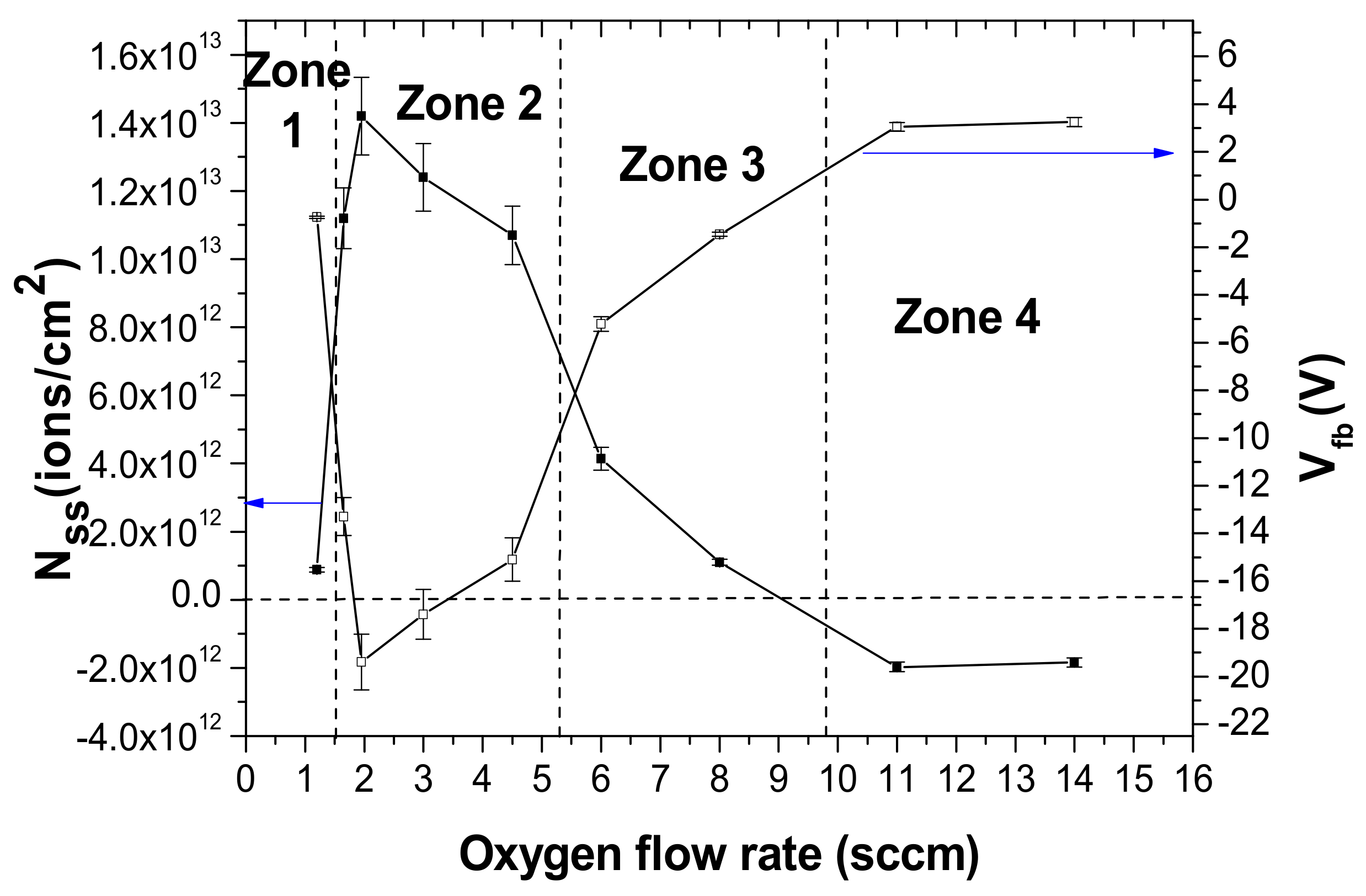
- Zone 1:
- Zone 2:
- Zone 3:
- Zone 4: Q (O2) ≥ 9.5 sccm
3.2. Synthesis of WOx Films
3.3. Chemical Composition
3.4. Optical Properties
3.4.1. Optical Transmittance
3.4.2. Optical Band Gap
3.5. Electrical Properties
3.5.1. Electrical Resistivity
3.5.2. MOS Structures
4. Description of the Formation of the Different WOx Film Zones
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaneko, H.; Nagao, F.; Miyake, K. Preparation and properties of the dc reactively sputtered tungsten oxide films. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 63, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.G. Oxide electrochromics: Why, how, and whither. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.T.; Ranjbar, M. Atmospheric flame vapor deposition of WO3 thin films for hydrogen detection with enhanced sensing characteristics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 21248–21255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucke, F.G.K. Electrochromic mirrors with variable reflectance. Sol. Energy Mater. 1987, 16, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.G.; Azens, A.; Heszler, P.; Kish, L.B.; Österlund, L. Nanomaterials for benign indoor environments: Electrochromics for “smart windows”, sensors for air quality, and photo-catalysts for air cleaning. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutov, E. MOS structures with amorphous tungsten trioxide for capacitive humidity sensors. Semiconductors 2008, 42, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojier, K.; Zolghadr, S.; Teimoori, F.; Goudarzi, S. Fabrication and characterization of porous WO3 thin film as a high accuracy cyclohexene sensor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 118, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitzke, D.W.; Cholant, C.M.; Landarin, D.M.; Lucio, C.S.; Krüger, L.U.; Gündel, A.; Flores, W.H.; Rodrigues, M.P.; Balboni, R.D.C.; Pawlicka, A.; et al. Electrochemical properties of WO3 sol-gel thin films on indium tin oxide/poly(ethylene terephthalate) substrate. Thin Solid Film. 2019, 683, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy, V.H.V.; Jo, I.-R.; Kang, S.-H.; Ahn, K.-S. Amorphous-crystalline dual phase WO3 synthesized by pulsed-voltage electrodeposition and its application to electrochromic devices. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 94, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Abe, Y.; Kawamura, M.; Sasaki, K. Effects of oxygen gettering and target mode change in the formation process of reactively RF sputtered WO x thin films. Vacuum 2002, 66, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Costa, M.F.; Almeida, B.; Teixeira, V.; Gago, J.; Roman, E. Structural and optical characterization of WO3 deposited on glass and ITO. Vacuum 2002, 64, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.H.; Mohamed, H.A.; Abd El Ghani, H.A. Development of structural and optical properties of WOx films upon increasing oxygen partial pressure during reactive sputtering. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2011, 406, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Salut, R.; Cote, J.-M.; Billard, A.; Martin, N. Structure, composition and electronic transport properties of tungsten oxide thin film sputter-deposited by the reactive gas pulsing process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 205, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regragui, M.; Jousseaume, V.; Addou, M.; Outzourhit, A.; Bernéde, J.C.; El Idrissi, B. Electrical and optical properties of WO3 thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2001, 397, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sasaki, A.; Oozu, H.; Aoki, K.; Kakushima, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Sugii, N.; Wakabayashi, H.; Tsutsui, K.; et al. Electron transport mechanism of tungsten trioxide powder thin film studied by investigating effect of annealing on resistivity. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M.; Chandrasekaran, J.; Balaji, M.; Kathirvel, P. Investigation of microstructural, optical and dc electrical properties of spin coated Al:WO3 thin films for n-Al:WO3/p-Si heterojunction diodes. Optik 2017, 145, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ni, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Bao, S.; Jin, P. The optical properties of low infrared transmittance WO3−x nanocrystal thin films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering under different oxygen ratios. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 57757–57763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltakesmez, A.; Tekmen, S.; Güzeldir, B. Temperature dependent current- and capacitance-voltage characteristics of W/n-Si structures with two-dimensional WS2 and three-dimensional WO3 interfaces deposited by RF sputtering technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 118, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Lü, H.-L. Interfacial characteristics of Al/Al2O3/ZnO/n-GaAs MOS capacitor. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 076701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terman, L.M. An investigation of surface states at a silicon/silicon oxide interface employing metal-oxide-silicon diodes. Solid-State Electron. 1962, 5, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keithley Instruments, Inc. C-V Characterization of MOS Capacitors Using the Model 4200-SCS Semiconductor Characterization System; Keithley Application Note Number 2896; Keithley Instruments, Inc.: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schroder, D.K. Semiconductor Material and Device Characterization, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ridaoui, M. Fabrication et Caractérisation de MOSFET III-V à Faible Bande Interdite et Canal Ultra Mince thèse, N° 42401. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Des Sciences et Technologies de Lille, Lille, France, Université de Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Li, G.; Xia, Y. Influence of hysteresis effect on properties of reactively sputtered TiAlSiN films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 431, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meeuwissen, A.; Bosco, G.B.F.; van der Kolk, E. Optical and structural characterization of Tm2O3, TmN, and TmOxNy thin films grown by direct-current reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2021, 717, 138450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossnagel, S.M.; Cuomo, J.J.; Westwood, W.D. Handbook of Plasma Processing Technology; Noyes Publcations: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, S.; Rizk, A.; Mousa, I. Physical parameters affecting deposition rates of binary alloys in a magnetron sputtering system. Vacuum 1998, 49, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parreira, N.M.G.; Polcar, T.; Cavaleiro, A. Characterization of W–O coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering with reactive gas pulsing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 5481–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S. Opportunities and challenges in science and technology of WO3 for electrochromic and related applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous Germanium. Phys. Status Solidi B 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffyberg, F.P.; Dwight, K.; Wold, A. Interband transitions of semiconducting oxides determined from photoelectrolysis spectra. Solid State Commun. 1979, 30, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, A.; Granqvist, C.G.; Wills, J.M. Electronic structure and optical properties of WO3, LiWO3, NaWO3 and HWO3. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 2436–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wijs, G.A.; de Groot, R.A. Structure and electronic properties of amorphous WO3. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 16463–16474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, A.; Yamada, S. Fundamental absorption edge of evaporated amorphous WO3 films. Appl. Phys. 1981, 24, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Borrero, P.P.; Sato, F.; Medina, A.N.; Baesso, M.L.; Bento, A.C.; Baldissera, G.; Persson, C.; Niklasson, G.A.; Granqvist, C.G.; da Silva, A.F. Optical band-gap determination of nanostructured WO3 film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 061909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; Kanth, B.R.; Devi, G.S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.K. Structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline WO3 thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migas, D.B.; Shaposhnikov, V.L.; Rodin, V.N.; Borisenko, V.E. Tungsten oxides. I. Effects of oxygen vacancies and doping on electronic and optical properties of different phases of WO3. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 093713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beainou, R.; Chargui, A.; Pedrosa, P.; Mosset, A.; Euphrasie, S.; Vairac, P.; Martin, N. Electrical resistivity and elastic wave propagation anisotropy in glancing angle deposited tungsten and gold thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet version 2005; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; Available online: http://www.hbcpnetbase.com (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Goldfarb, I.; Miao, F.; Yang, J.J.; Yi, W.; Strachan, J.P.; Zhang, M.-X.; Pickett, M.D.; Medeiros-Ribeiro, G.; Williams, R.S. Electronic structure and transport measurements of amorphous transition-metal oxides: Observation of Fermi glass behavior. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatten, R.; Chadwick, A.V.; Rougier, A.; Lindan, P.J.D. The Oxygen Vacancy in Crystal Phases of WO3. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3146–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Hossain, T.; Garces, N.Y.; Nepal, N.; Meyer, H.M.; Kirkham, M.J.; Eddy, C.R.; Edgar, J.H. Influence of Atomic Layer Deposition Temperatures on TiO2/n-Si MOS Capacitor. J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, N110–N114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoll, M.; Braunig, D.; Fahrner, W.R. Generation of Oxide Charge and Interface States by Ionizing Radiation and by Tunnel Injection Experiments. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1982, 29, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, B.J. C-V plotting: Myths and methods. Solid State Technol. 1993, 36, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Granqvist, C.G. Handbook of Inorganic Electrochromic Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hsieh, J.H.; Hung, M.-T.; Huang, B.Q. Electrochromic study on amorphous tungsten oxide films by sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2015, 587, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Cheong, H.M.; Tracy, C.E.; Mascarenhas, A.; Czanderna, A.W.; Deb, S.K. Electrochromic coloration efficiency of a-WO3−y thin films as a function of oxygen deficiency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-G.; Benson, D.K.; Tracy, C.E.; Deb, S.K.; Czanderna, A.W.; Bechinger, C. Chromic Mechanism in Amorphous WO3 Films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyer, L.; Fruchier, O.; Notingher, P.; Agnel, S.; Toureille, A.; Rousset, B. Analysis of Data Obtained Using the Thermal-Step Method on a MOS Structure—An Electrostatic Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiki, H.; Pierson, J.F.; Rousselot, C.; Martin, N.; Terwagne, G. Properties and electrochromic performances of reactively sputtered tungsten oxide films with water as reactive gas. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Q O2 (sccm) | Total Pressure (Pa) | Partial Oxygen Pressure (Pa) | Target Voltage (V) | Film Thickness (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 408 | 350 |
| 1.20 | 0.45 | 0.04 | 666 | 589 |
| 1.65 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 716 | 582 |
| 1.95 | 0.61 | 0.20 | 710 | 565 |
| 2.50 | 0.73 | 0.32 | 687 | 513 |
| 3.00 | 0.83 | 0.42 | 673 | 507 |
| 4.50 | 1.13 | 0.72 | 613 | 500 |
| 6.00 | 1.37 | 0.96 | 594 | 502 |
| 8.00 | 1.70 | 1.29 | 576 | 528 |
| 11.00 | 2.10 | 1.69 | 560 | 481 |
| 14.00 | 2.60 | 2.19 | 560 | 487 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
N’Djoré, K.B.J.-I.; Grafouté, M.; Makoudi, Y.; Hourani, W.; Rousselot, C. Tuning the Electrical Properties of Tungsten Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings 2022, 12, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020274
N’Djoré KBJ-I, Grafouté M, Makoudi Y, Hourani W, Rousselot C. Tuning the Electrical Properties of Tungsten Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings. 2022; 12(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020274
Chicago/Turabian StyleN’Djoré, Kouamé Boko Joël-Igor, Moussa Grafouté, Younes Makoudi, Waël Hourani, and Christophe Rousselot. 2022. "Tuning the Electrical Properties of Tungsten Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering" Coatings 12, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020274
APA StyleN’Djoré, K. B. J.-I., Grafouté, M., Makoudi, Y., Hourani, W., & Rousselot, C. (2022). Tuning the Electrical Properties of Tungsten Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Reactive Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings, 12(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020274







