Contamination of Substrate-Coating Interface Caused by Ion Etching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Primary cleaning process: external mechanical and chemical pretreatment of the substrate surface prior to the insertion in the deposition chamber in order to roughly remove contaminants (such as grease, oxides).
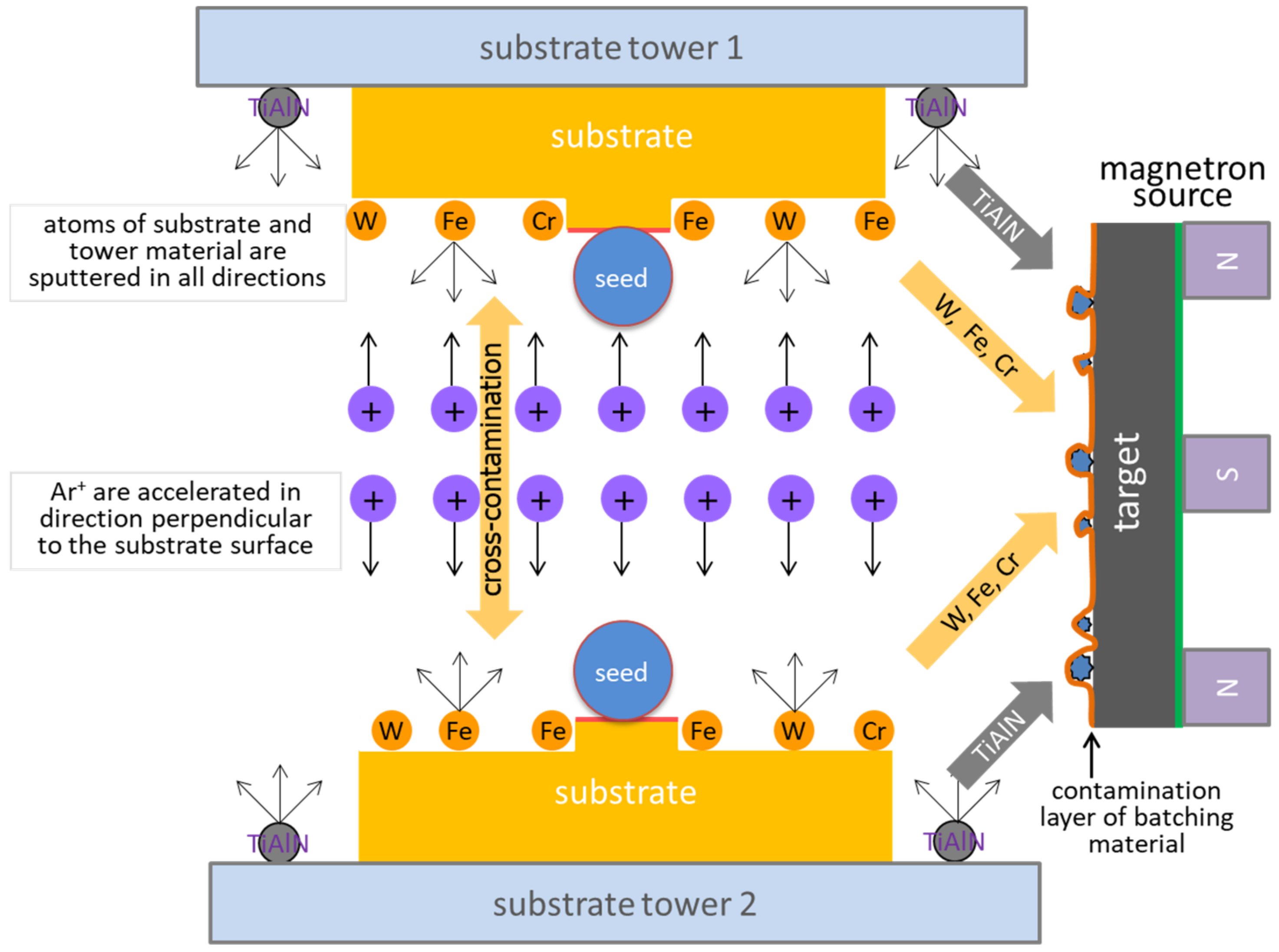
- In situ pre-treatment (heating and ion etching) of the substrate before the coating deposition process in order to remove the contamination that has formed since the primary cleaning process had been performed. Ion bombardment also creates a number of new nucleation sites for the coating atoms, which significantly improves chemical bonds between the substrate atoms and the condensing atoms. The ion etching also increases the roughness of the substrate surface and thus strengthens the coating–substrate interface.
- After substrate cleaning by ion etching, the coating adhesion strength can be further improved by deposition of a metallic interlayer, which is typically Cr or Ti. An interlayer minimizes internal stresses in the deposited coating and it can also dissolve oxides that remain on the substrate surface after ion etching [2].
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
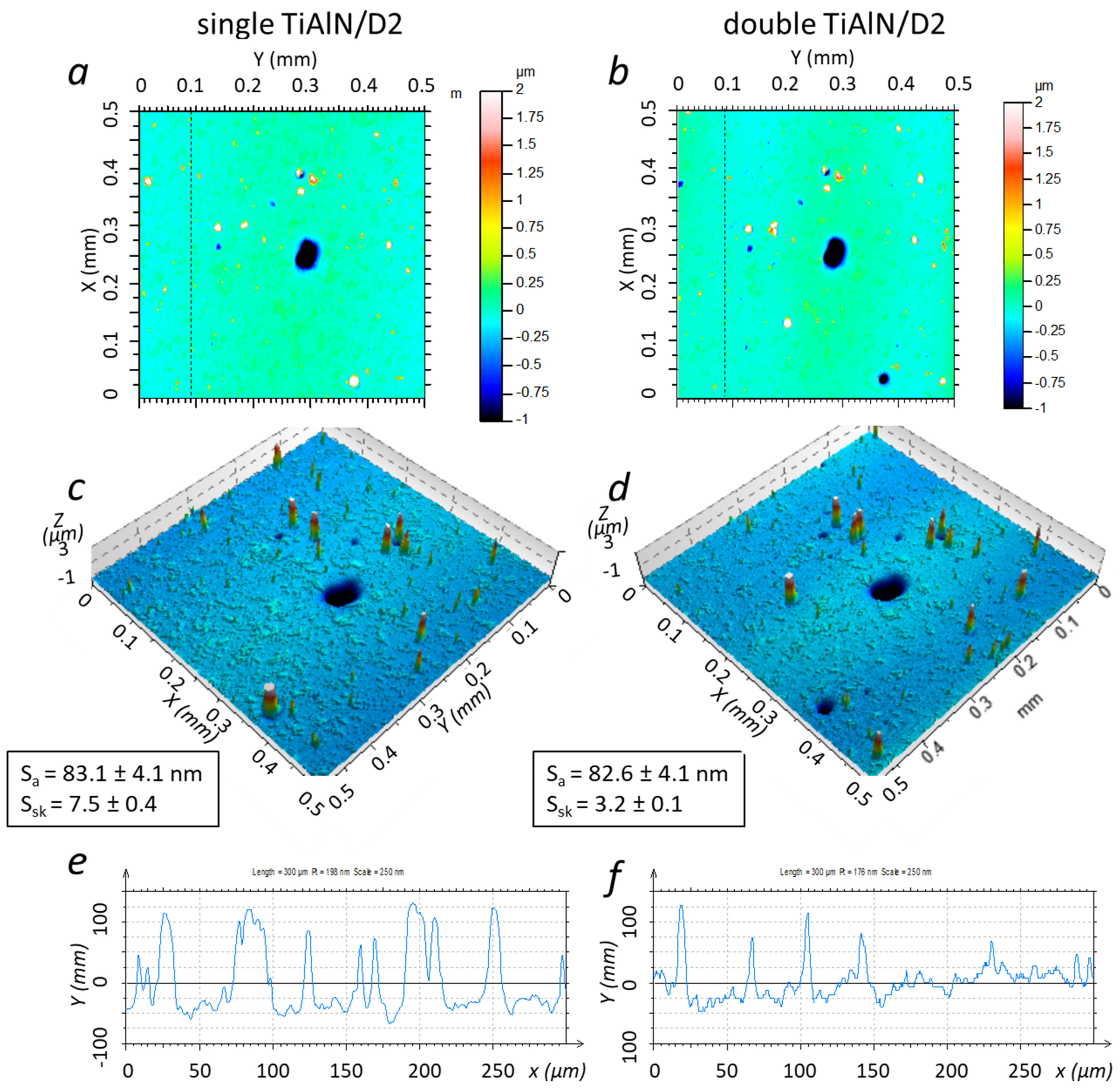
3.1. Surface Topography of Single and Double Layer TiAlN Coatings
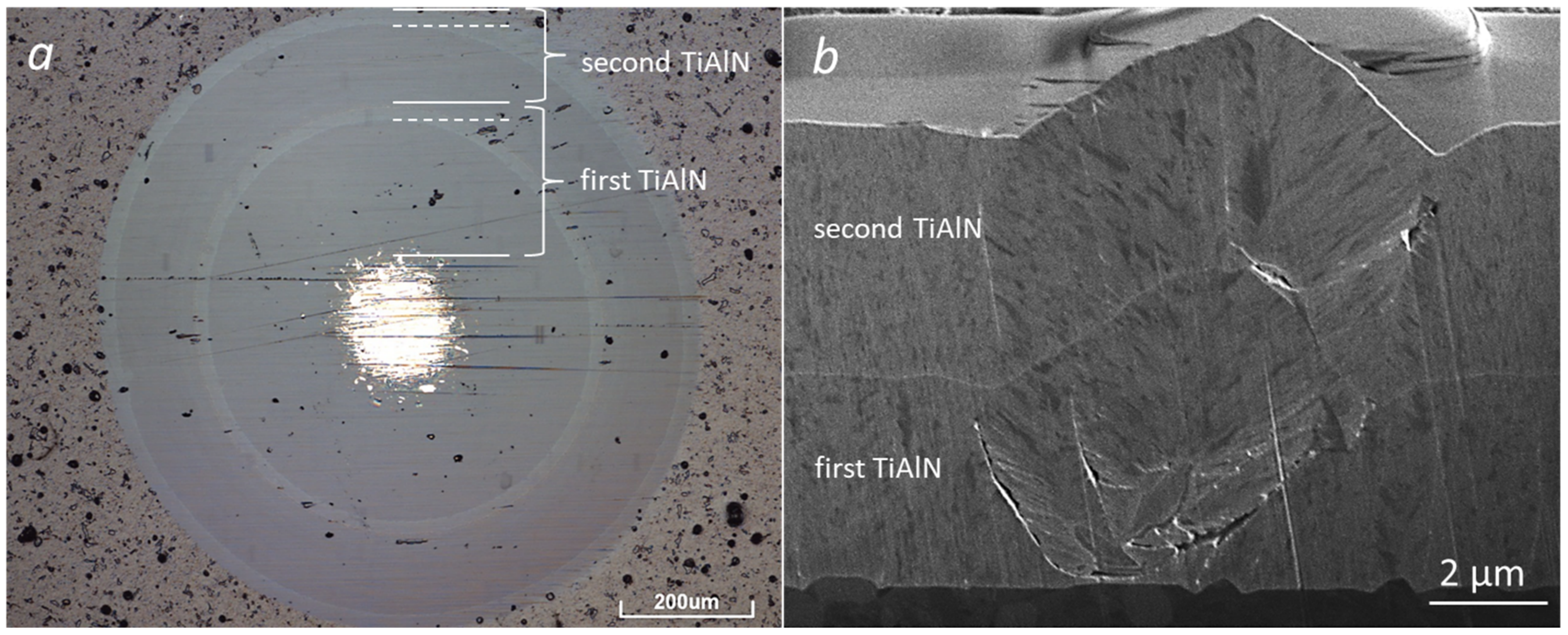
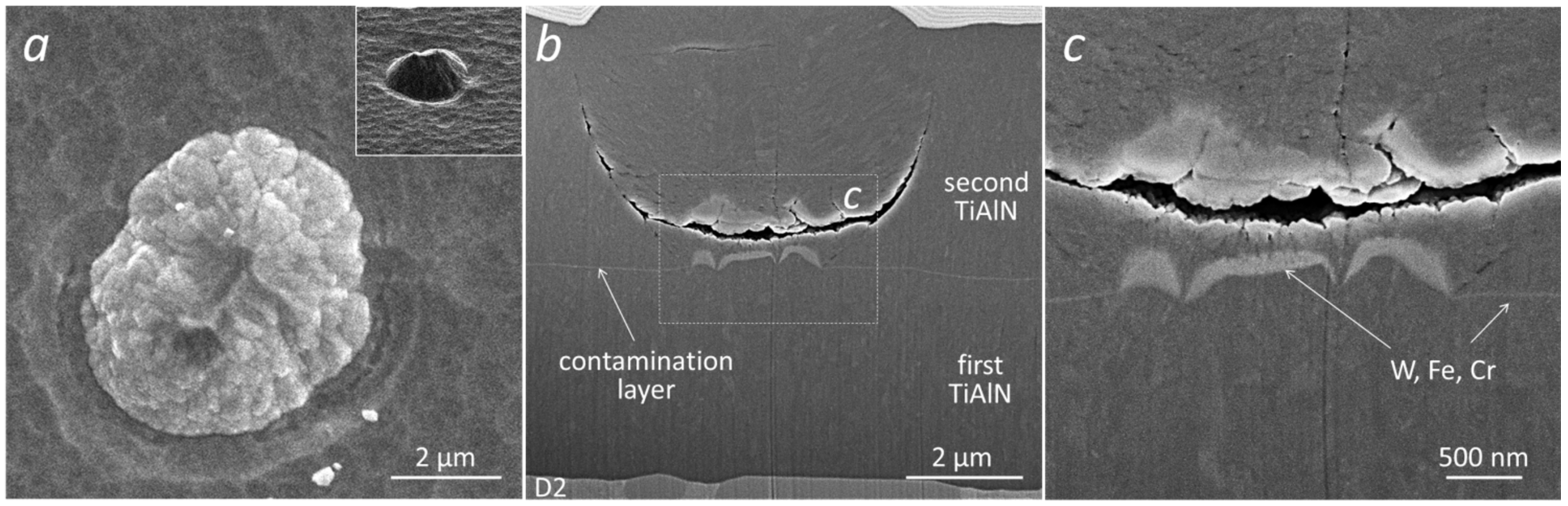
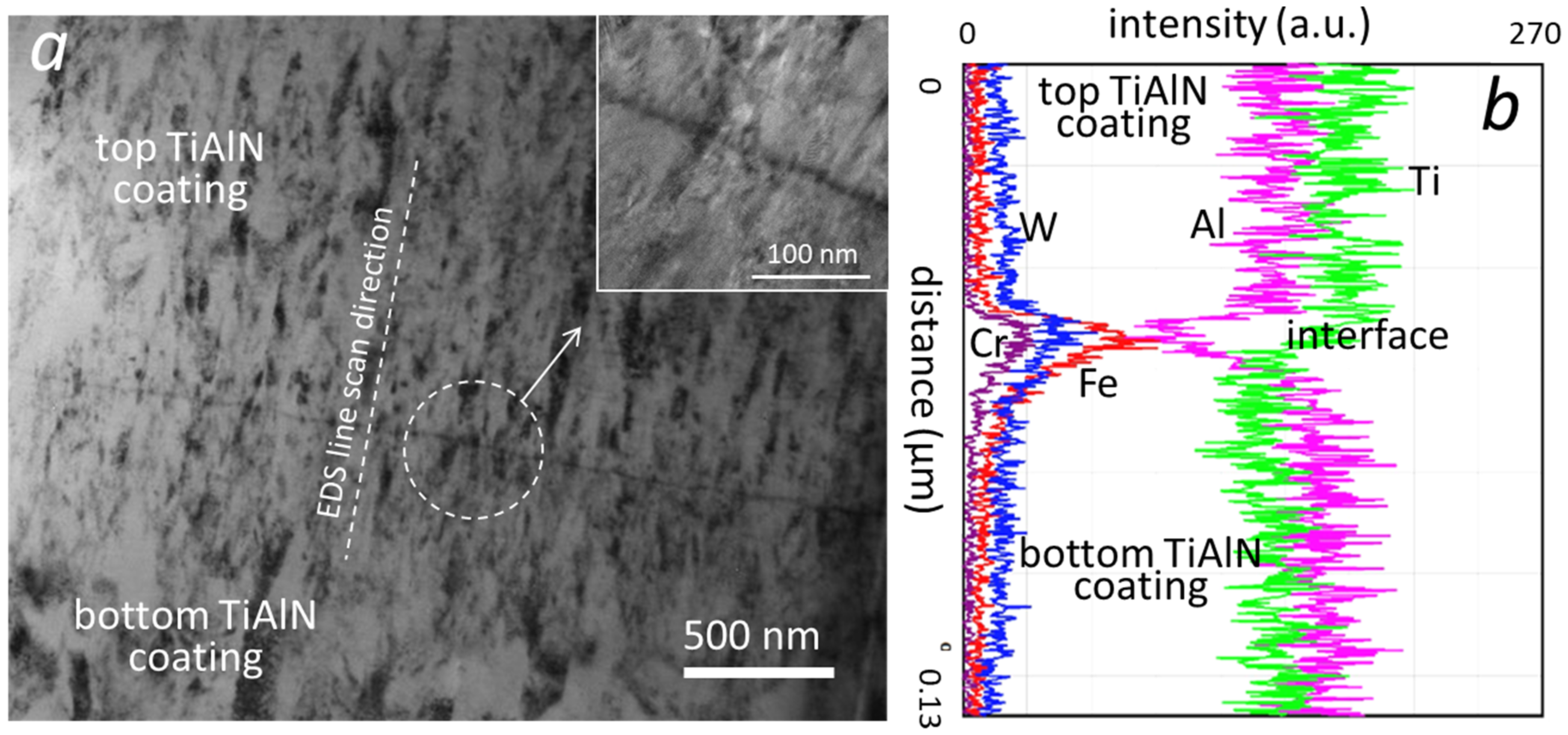
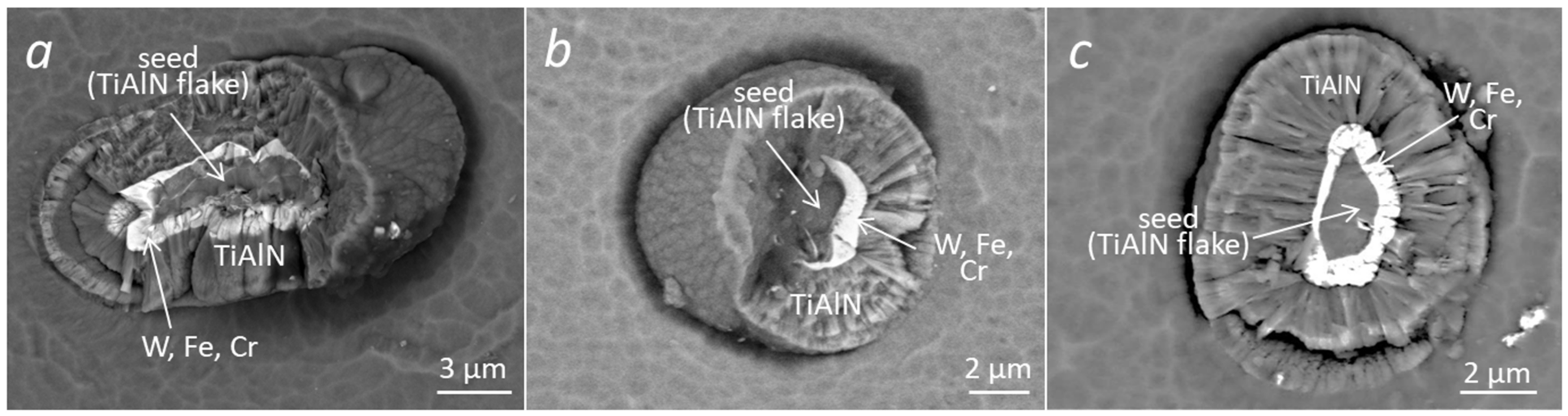
3.2. Contamination of the Interfacial Region in Double-Layer TiAlN Coating
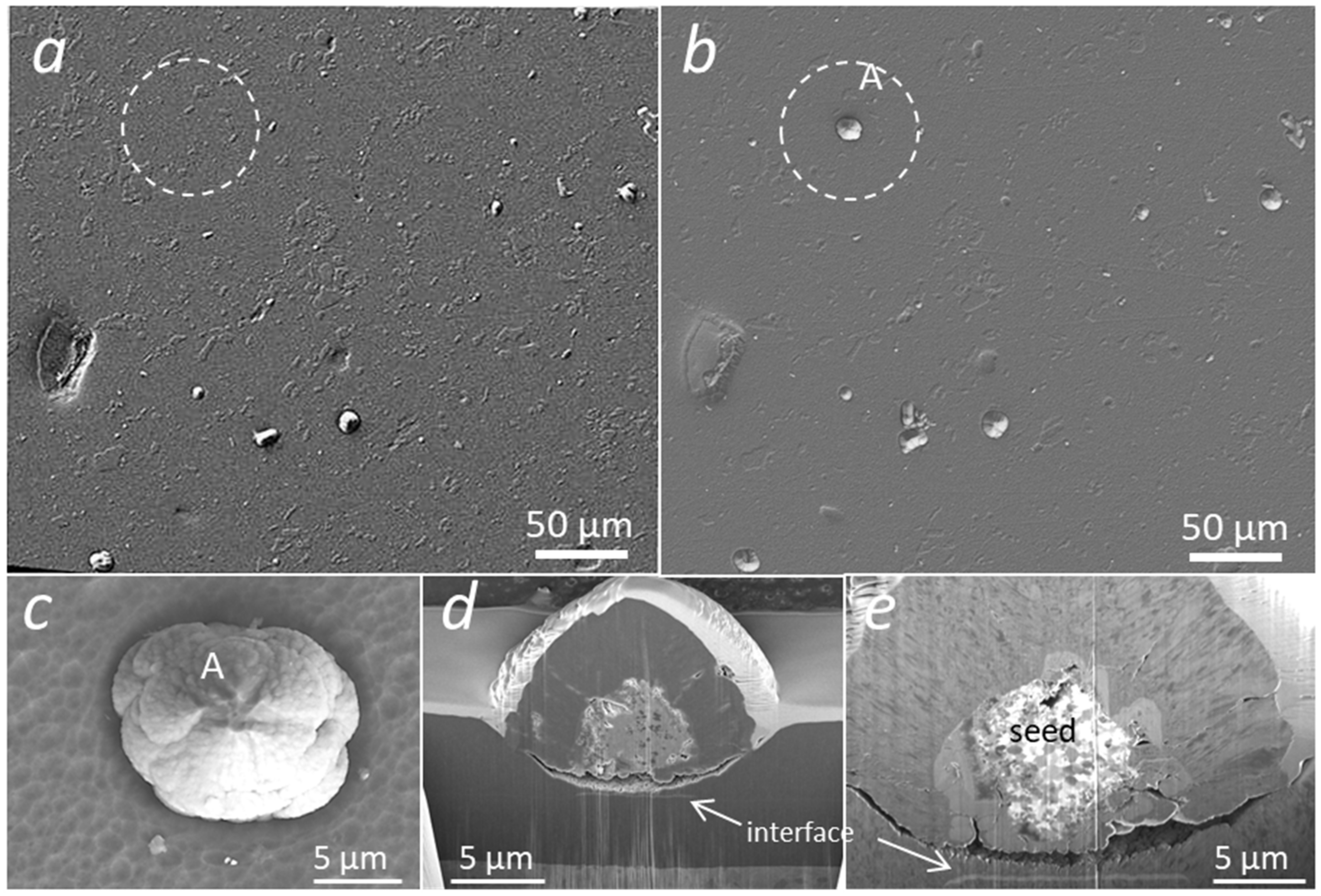
3.3. SEM Images of Broken Nodular Defects
3.4. Depth Distribution of Nodular Defects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Stappen, M.; Malliet, B.; De Schepper, L.; Stals, L.M.; Celis, J.P.; Roos, J.R. Influence of Ti intermediate layer on properties of TiN coatings deposited on various substrates. Surf. Eng. 1990, 6, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerth, J.; Wiklund, U. The influence of metallic interlayers on the adhesion of PVD TiN coatings on high-speed steel. Wear 2008, 264, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, H.E.; Schlier, R.E.; George, T.H.; Burger, R.M. Ion Bombardment-Cleaning of Germanium and Titanium as Determined by Low-Energy Electron Diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 1955, 26, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, D.M. Film deposition using acclerated ions. Electrochem. Technol. 1964, 2, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Panjan, P.; Drnovšek, A.; Gselman, P.; Čekada, M.; Panjan, M. Review of Growth Defects in Thin Films Prepared by PVD Techniques. Coatings 2020, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, P.; Drnovšek, A.; Mahne, N.; Čekada, M.; Panjan, M. Surface Topography of PVD Hard Coatings. Coatings 2021, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönjahn, C.; Lewis, D.B.; Münz, W.-D.; Petrov, I. Shortlisted substrate ion etching in combined steered cathodic arc–ubm deposition system: Effects on interface architecture, adhesion, and tool performance. Surf. Eng. 2000, 16, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehiasarian, A.P.; Wen, J.G.; Petrov, I. Interface microstructure engineering by high power impulse magnetron sputtering for the enhancement of adhesion. J. Appl. Phys 2007, 101, 054301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, M.D. A Short History of In Situ Cleaning in Vacuum for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). SVC Bull. Fall 2014, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Broitman, E.; Hultman, L. Adhesion improvement of carbon-based coatings through a high ionization deposition technique. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 370, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lattemann, M.; Ehiasarian, A.P.; Bohlmark, J.; Persson, P.A.O.; Helmersson, U. Investigation of high power impulse magnetron sputtering pretreated interfaces for adhesion enhancement of hard coatings on steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 6495–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovsepian, P.E.; Ehiasarian, A.P. Six strategies to produce application tailored nanoscale multilayer structured PVD coatings by conventional and High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering (HIPIMS). Thin Solid Films 2019, 688, 137409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehiasarian, A.P.; Münz, W.D.; Hultman, L.; Helmersson, U.; Petrov, I. High power pulsed magnetron sputtered CrNx films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 163–164, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassner, M.; Schalk, N.; Sartory, B.; Pohler, M.; Czettl, C.; Mitterer, C. Influence of Ar ion etching on the surface topography of cemented carbide cutting inserts. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 69, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Hagen, L.; Stangier, D.; Krabiell, M.; Schröder, P.; Tiller, J.; Krumm, C.; Sternemann, C.; Paulus, M.; Elbers, M. Influence of etching-pretreatment on nano-grained WC-Co surfaces and properties of PVD/HVOF duplex coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 374, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, M. Influence of substrate rotation and target arrangement on the periodicity and uniformity of layered coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, P.; Drnovšek, A.; Dražić, G. Influence of Growth Defects on the Oxidation Resistance of Sputter-Deposited TiAlN Hard Coatings. Coatings 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehn, H.A. Improvement of the corrosion resistance of PVD hard coating–substrate system. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 125, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, P.; Čekada, M.; Panjan, M.; Kek-Merl, D.; Zupanič, F.; Čurković, L.; Paskvale, S. Surface density of growth defects in different PVD hard coatings prepared by sputtering. Vacuum 2012, 86, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebastiani, M.; Piccoli, M.; Bemporad, E. Effect of micro-droplets on the local residual stress field in CAE-PVD thin coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 215, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, G.; Hultman, L.; Sundgren, J.E.; Greene, J.E.; Münz, W.D. Microstructures of TiN films grown by various physical vapour deposition techniques. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1991, 48, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maura e Silva, C.W.; Alves, E.; Ramos, A.R.; Sandu, C.S.; Cavaleiro, A. Adhesion failures on hard coatings induced by interface anomalies. Vacuum 2009, 83, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, G.K.; Hajicek, D.J. Cone Formation on Metal Targets during Sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 1971, 42, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintze, M.; Luciu, I. Nodule formation on sputtering targets: Causes and their control by MF power supplies. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 336, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwyn, G.S.; Weiss, C.A.; Sequedac, F.; Huang, C. Particle contamination formation in magnetron sputtering processes. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1997, 15, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Substrate | Sa (nm) | Ssk |
|---|---|---|
| bare ASP | 11.8 ± 0.6 | 10 ± 0.5 |
| ASP + TiAlN | 70.2 ± 3.5 | 8 ± 0.4 |
| ASP + TiAlN + TiAlN | 57.5 ± 2.8 | 3.1 ± 0.1 |
| bare D2 | 11.3 ± 0.6 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| D2 + TiAlN | 83.1 ± 4.1 | 7.5 ± 0.4 |
| D2 + TiAlN + TiAlN | 82.6 ± 4.1 | 3.2 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panjan, P.; Drnovšek, A.; Čekada, M.; Panjan, M. Contamination of Substrate-Coating Interface Caused by Ion Etching. Coatings 2022, 12, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060846
Panjan P, Drnovšek A, Čekada M, Panjan M. Contamination of Substrate-Coating Interface Caused by Ion Etching. Coatings. 2022; 12(6):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060846
Chicago/Turabian StylePanjan, Peter, Aljaž Drnovšek, Miha Čekada, and Matjaž Panjan. 2022. "Contamination of Substrate-Coating Interface Caused by Ion Etching" Coatings 12, no. 6: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060846
APA StylePanjan, P., Drnovšek, A., Čekada, M., & Panjan, M. (2022). Contamination of Substrate-Coating Interface Caused by Ion Etching. Coatings, 12(6), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12060846








