Abstract
Stainless steel has become an integral part of modern engineering materials and daily life due to its mechanical efficiency, strength, recyclability, high resistance to oxidation and corrosive attack, which make it the ideal material for many kinds of applications. At the same time, steel suffers from certain types of corrosion, such as intergranular corrosion, or contact corrosion that develops when stainless steel comes into contact with carbon steel or another metal with a different electrochemical potential. Finally, pitting corrosion is a serious problem often occurring when stainless steel parts work in sea water. This paper provides a brief overview of methods for protecting stainless steel from corrosion using a new approach based on superhydrophobization of the surface of stainless steel using laser processing followed by the deposition of a layer of a substance with a low surface energy. The review discusses the mechanisms of corrosion protection by such coatings and the properties of superhydrophobic coatings presented in the literature. Superhydrophobic protective coatings on stainless steel have been shown to significantly reduce corrosion, with some demonstrating a decrease in corrosion current of up to 156 times. However, a more comprehensive analysis of the mechanisms contributing to this effect, as well as a comparison with anti-corrosion coatings on other metals, suggests that the combination of these mechanisms has the potential to create even more durable and effective surfaces for corrosion protection of stainless steel.
1. Introduction
Corrosion protection remains an acute problem of modern material science due to its economic, ecological, and safety consequences. The global impact of corrosion processes is estimated to be higher than 3% of global Gross Domestic Product, while application of available corrosion control practices may save not more than 35% of these losses [1]. Aside from the direct economic losses manifested in the necessity to repair or replace corroded elements, corrosion products often have a negative effect on the environment. Contamination by corrosion products is especially problematic in the case of water supply installations, where it may lead to serious contamination of drinking water and becomes hazardous to human health, both directly and through an effect on microorganisms [2]. Last but not least are the indirect consequences of corrosion resulting in technological disasters, damage to structures, and loss of human life [3]. That is why the challenge of economically and ecologically favorable protection of materials and equipment without compromising functional properties is of great interest for the material science community.
During recent decades, corrosion protection measures have been extensively explored and a few major approaches were formed. Among the most widely used, one can mention such approaches as modification of the chemical composition of a material itself by using additives that severely suppress corrosion rate [4], coating the surface with a protective layer with much higher chemical stability, and application of corrosion inhibitors [5], in addition to many others [6,7]. The main obstacle to employing corrosion protection techniques is the necessity to preserve the material’s structural, functional, and aesthetic properties. In particular, dopants that increase chemical stability may lead to worse mechanical stability; thick protective coatings alter surface characteristics such as surface conductivity, tribological and heat transfer properties and require special surface pretreatment for sufficient adhesion of a coating to the material.
Stainless steel is a widely-used material in a variety of applications due to its high corrosion resistance. However, under certain conditions, even stainless steel can be prone to corrosion. One approach to improving the corrosion resistance of stainless steel without detriment of structural properties is the use of superhydrophobic coatings. The development of superhydrophobic coatings for stainless steel has gained significant attention in recent years due to the potential for these coatings to provide long-term, durable corrosion protection with minimal maintenance requirements. The combination of water-repellent and anticorrosive properties makes these coatings attractive for a range of applications, including the medicinal, automotive and marine industries. However, there is still a need to further optimize the coating processes for improved performance and durability. As such, understanding the principles and properties of superhydrophobic coatings on stainless steel is important for the development of new corrosion protection technologies.
The structure of this review is as follows. First, we discuss the mechanisms that contribute to the corrosion protection by superhydrophobic coatings. Next, we review all known-to-us studies of corrosion protection properties of superhydrophobic coatings on stainless steel, and group them by alloy type. Following this, we discuss how these mechanisms operate in the reported results and offer generalizations based on our analysis of the literature. Finally, we provide our conclusions and outlook.
2. Mechanisms behind the Corrosion Protection by the Superhydrophobic Coatings
In this regard, ensuring a superhydrophobic state of the surface is one of the most promising approaches for the improvement of a material chemical stability. Superhydrophobic coatings are coatings with a very high contact angle >150° and a low roll-off angle <10° for water droplets, which are achieved by ensuring stable heterogeneous wetting state [8,9,10,11]. Being inspired by vivid examples found in nature, initially, the superhydrophobic coatings were fabricated by mimicking [12,13] or even templating the natural superhydrophobic surfaces [14] like butterfly wings or lotus leaves. An advance in theoretical understanding [11,15,16] of principles of design of superhydrophobic coatings, in particular the creation of multimodal roughness, ensuring appropriate curvature of texture elements [17] and lowering the surface energy, allowed passing to the creation of mass-scaled superhydrophobic coatings and opened the way to practical applications.
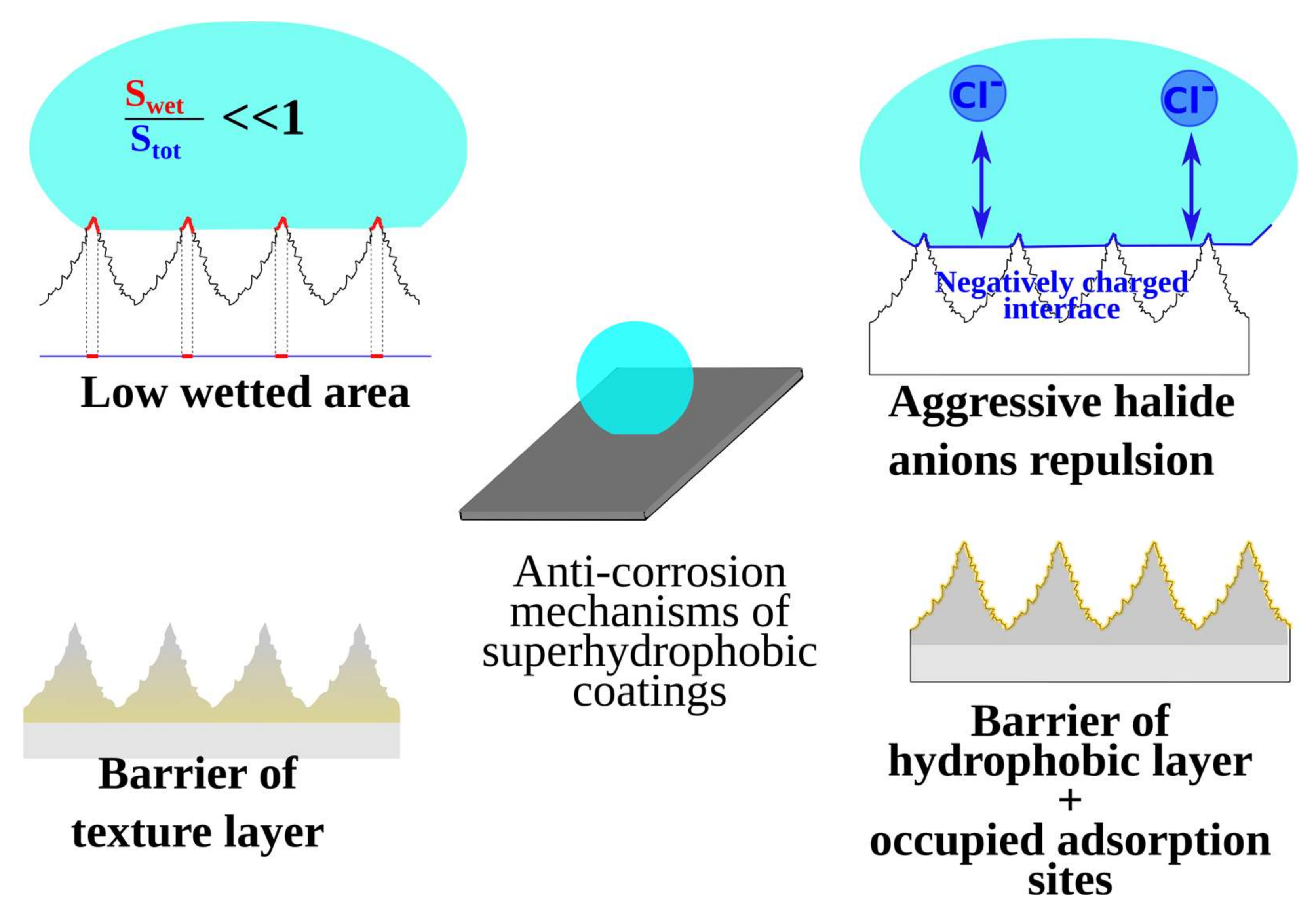
It was shown that aside from water repellence, many superhydrophobic coatings demonstrate anticorrosion [18], antibacterial [19], and anti-biofouling [20,21], as well as anti-icing [22] properties. Therefore, the area is experiencing a continued rapid growth in the number of new materials primarily focused on the design of polyfunctional coatings. Laboratory and industrial testing showed that well-prepared superhydrophobic coatings decrease corrosion rate by orders of magnitude by the modification of a thin surface layer without affecting bulk properties [23,24,25]. However, even coatings with very high contact angles and low roll-off angles may fail to demonstrate durable corrosion resistance [26,27,28]. Thorough analysis of the mechanisms behind the corrosion resistance of superhydrophobic coatings had shown that such protective properties cannot be explained only by the water repellence of such surfaces [29]. Indeed, literature data (see, for example, refs. [23,24,25,30,31]) report the superhydrophobic coatings on different metals for which the corrosion current shows to be 4–5 order of magnitude lower than that for the bare metal. At the same time, a decrease in the contact area due to capturing of air between an aqueous corrosive medium and the surface may only account for 2–2.5 orders. Thus, an explanation of the high protective properties requires the involvement of additional mechanisms (see Figure 1), discussed in recent studies [25,28,29,32,33]. One such mechanism is interface charging: for most hydrophobic materials, the isoelectric point is located deep inside the acid region of pH (around pH = 2–4) [34,35]. In other words, in neutral solutions, the interface between the aqueous medium and the superhydrophobic coating is negatively charged, causing a depletion of corrosively active anions, which is especially important when the coating is in contact with highly corrosive halide solutions. Additionally, molecules of hydrophobic agent compete with aggressive ions for adsorption sites, thus hindering the initiation of the corrosive reaction. Finally, often both the textured layer with multiscale features and the layer of hydrophobic agent act as barriers for charge transfer. That way, superhydrophobic coatings in which all these mechanisms are manifested demonstrate an extremely low corrosion rate.
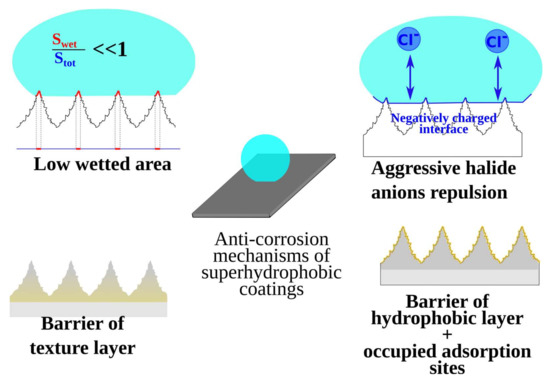
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of corrosion protection of superhydrophobic coatings in electrolyte solution.
The above analysis means that to ensure strong anticorrosion properties it is necessary to finely manage the uniformity of a coating–in particular, the chemical, phase, and morphology composition of the surface and pre-surface layers. Such level of structure control generally requires a multistep treatment which separately ensures properties of the substrate base, as well as form and composition of two or more types of texture elements (to provide multiscale roughness), thickness, and uniformity of adsorption of low surface energy film on top of the texture. Please note that as mentioned above, the presence of a top layer with low surface energy is one of the necessary conditions for obtaining the stable superhydrophobic state [11]. Therefore, approaches that allow imparting the multiple desired features are under active development. One such approach is the laser processing of materials surfaces, which allows combining laser chemical modification and surface texturing (LCMST) [24,36,37]. The LCMST flexibility originates in a wide range of physicochemical phenomena accompanying the interaction between the laser radiation and material’s surface. In particular, interaction of radiation with the surface leads to different mechanisms of surface texturing, which include mass transfer due to melting, boiling, and evaporation of material, ionization and density waves, interference of incident light and surface plasmon polaritons, formation of nanoparticles and their deposition with aggregation of freshly-created nanoparticles to nano- and microscale elements [38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. In addition, due to enhanced local temperatures of both surface and components of the laser plume, chemical reactions between the material substance and environment initiate the intense formation of new chemical compounds on the surface layer of the processed material [24,36,37,38,45]. Finally, fast heating followed by rapid cooling results in the evolution of the surface grain structure and improvement of the mechanical properties of the surface layer [46,47]. Variation of laser treatment regime, namely pulse energy, duration, and fluence, beam velocity, number of consecutive passes or pulses set in one spot, the distance between spots, as well as the environment (treatment in liquids or atmosphere with specific composition), allows utilizing the above-mentioned physicochemical processes to achieve desired properties of the coatings.
The fabrication of superhydrophobic coatings through laser treatment became especially useful for metals where the approach usually consists of two steps: surface morphology, chemical composition and structure modification via laser irradiation and then lowering the surface energy by adsorption of the layer of hydrophobic molecules with a thickness up to one monolayer. It should be noted that there are laser surface treatments aimed at increasing corrosion resistance but not associated with the creation of a superhydrophobic state of the surface. These approaches, which include laser alloying and cladding, where corrosion resistant dopant is mixed to the material and laser melting/heating that pursue to change volume microstructure, are generally out of the scope of this review; more information can be found in the recent review by Dudeja [48].
Due to distinction in laser peak power density, a set of phenomena accompanying pico- and femtosecond laser treatments, on the one hand, and nanosecond treatment on the other, differ vastly, and while all of these treatments can be used to achieve a superhydrophobic state, it is expedient to consider two groups of treatment separately. For the pico- and femto- second laser treatment, very high peak power simultaneously with very limited heat affected zone are characteristic: laser pulse may melt and evaporate material in the beam spot, while in the closest vicinity of the spot, the surface will not be even heated. Such features of short-pulse laser processing make it ideal for the fabrication of highly regular texture patterns [47], treating transparent materials like glasses [49] or materials and elements which cannot withstand bulk heating. For intensities below the ablation threshold, the morphology is determined by the interaction of light with surface plasmon polaritons and the resulted texture corresponds to laser-induced periodic surface structure (LIPSS) [39]. However, since usually LIPSS represent smooth ripples with the characteristic scale of about laser wavelength, to achieve multi-scale roughness with a second scale corresponding to the size of ablated area, the intensity of the radiation higher than ablation threshold is used, controlled by either energy of one pulse or the number of repetitive pulses [50]. Using this approach, the morphologies suitable for the preparation of superhydrophobic coatings were fabricated on many metals and alloys like steel [51], stainless steel [50,52], titanium [53], aluminum [54], copper [55], gold [56] and others.
The deposition of ablation products is often unwanted for LIPSS textures and special measures are used to avoid it [50]. In contrast, for the nanosecond laser treatment, the aggregation of nanoparticles formed in ablation plume into a fractal structure on the surface is an important phenomenon for obtaining multi-scale texture needed for stable superhydrophobicity [37,57]. Longer pulse duration and generally higher pulse energy lead to substantial and deep heating of the surface. High temperature intensifies chemical reactions and promotes reactions such as nitride [58] and oxynitride [37,59] formation that could hardly take place under other conditions. At the same time, deeper heat affected zone increases the thickness of the reacted and stirred layer, which can also be depleted or enriched with some components of the bulk material. In particular, the thickness of the barrier oxide layer on alumina after nanosecond laser treatment may reach hundreds of micrometers [37], which is difficult to obtain by other approaches. In the case of stainless steel, in addition to the formation of an oxide layer, the laser treatment can lead to an increase in the concentration of Cr in relation to Fe in the surface layer [60], with a corresponding effect on corrosion resistance.
Both ultrashort and nanosecond pulsed laser treatments were successfully used for the fabrication of superhydrophobicity based anti-corrosion coatings on metals. An important advantage of nanosecond laser treatment is the low cost of equipment at comparable power and surface processing speed, making the latter to be more economically feasible. Moreover, bearing in mind the peculiarities of anti-corrosion protection for such coatings discussed above, the nanosecond treatment is more advantageous due to its ability to create a thicker textured layer and significantly enhance the barrier properties of the surface layer by affecting phase and chemical composition.
Equally important in the creation of durable corrosion protection is the method of surface hydrophobization. Bare and oxidized metal surfaces are hydrophilic due to high surface energy. Thus, an increase in roughness after laser texturing, in accordance with Wenzel equation [61], may only lead to even better wettability and lower contact angles often reaching the superhydrophilicity threshold. Although quite a lot of studies report about “hydrophobization” by laser texturing, the thorough analysis shows that the lowering of the surface energy in these reports is not related to the laser treatment but explained by the adsorption of hydrophobic airborne contaminants [62,63].
Thus, to obtain stable superhydrophobicity, the textured surface of the metal needs to be hydrophobized. There are four main approaches for lowering surface energy presented in the literature: spontaneous hydrophobization through adsorption of airborne hydrocarbons, physical adsorption of a hydrophobic agent, chemisorption of hydrophobic agent, and coating the texture with a thick layer of hydrophobic material. The first three approaches aimed to create molecularly thin (monolayer or polylayer) adsorption film and thus can be considered as a treatment which does not change the morphology. In contrast, thick layer of hydrophobic material, for instance, polymer with a nanosized filler, may bring additional micro or nanostructure while concealing the initial nanostructure of the substrate.
Adsorption of airborne hydrocarbons is eco-friendly and happens without human intervention; this mechanism is often responsible for the self-healing of superhydrophobic properties. The spontaneous hydrophobization by airborne hydrocarbons is caused by highly nonequilibrium state of the surface after laser irradiation [62]. A thermodynamically driven tendency to decrease the surface energy promotes the adsorption of the hydrocarbons when the surface after laser treatment is stored for a long time in an open atmosphere or exposed to contaminated atmosphere at 60–150 °C for shorter times. It is worth noting that the increased temperature facilitates overcoming the energy barrier for adsorption and thus enhances the adsorption rate. However, the reproducibility of coating properties is low due to variations in the composition of atmospheric pollutants [62,64], and the coating is often characterized by the high density of wetting defects due to the non-uniformity of adsorbed layer.
The physical adsorption approach is based on the physical type of interaction between the substance with lower surface energy and the substrate, such as van der Waals forces or electrostatic interaction. This type of adsorption does not need the specific adsorption centers and generally produces uniform and reproducible coatings when deposited from a controlled atmosphere or solution of the hydrophobic agent in solvent.
It should be noted that the boundary between the two above-mentioned approaches is not clearly defined–there are examples in the literature when the surface was hydrophobized by atmospheric pollutants, but the atmosphere itself was deliberately polluted by paper [65] or silicone oil [66] decomposition products, efflux from polymer containers [67,68,69] or even vacuum pump oil vaporization [70]. These approaches, being relatively simple, have a major flaw: weak bonding of adsorbates or a non-uniform adsorbate layer make them prone to fast deterioration under chemical loads, especially under contact with corrosive media [71].
To overcome this issue, chemical adsorption approaches ensure the chemical bonding of hydrophobic agent with the surface. Often, to bind the adsorption centers or to increase their density on the substrate surface, special treatments like UV/O3 or exposure to air/oxygen plasma are used. The environmental friendliness and the cost of chemisorption approach depend on the hydrophobic agent used; harmless chemicals such as stearic acid [72,73,74] are relatively cheap and provide decently low surface energy, but bind to the surface only by one chemical bond and thus are not very stable against contact with corrosive media [71]. In contrast, some chemicals such as fluorinated organosilanes can form much more durable cross-linked layer on the surface with very low surface energy [71], but are sometimes expensive and the preparation process is not always environmentally safe.
A thick layer of low surface energy materials covering the surface may work as a charge and ion transfer barrier and can sufficiently inhibit the corrosion; however, it also changes surface properties such as hardness, conductivity, and heat transfer characteristics, friction and appearance. At the same time, such a layer covers the nanoscale roughness of the substrate and thus needs to ensure its own nano-level texture. Usually, it is achieved by either the addition of nanoparticles as fillers to the hydrophobic materials [75], or even the deposition of a thick layer of hydrophobized nanoparticles [76]; the difference between these two ways is more quantitative in terms of the amount of binder rather than qualitative. Being quite simple and often cheap, coatings based on the deposition of a thick layer manifest a set of common issues: low mechanical strength (much lower than that of the underlying metallic substrate), the removal of nanotexture under mechanical and chemical loads, and peeling of the hydrophobic layer. The additional drawbacks of a thick hydrophobic agent layer are related to poor adhesion to the substrate unless the suitable precursor layer was used, and possible mismatch in thermal expansion parameters of the substrate and the coating leading to the delamination of the coating at thermal stresses.
To summarize, lowering of the surface energy of textured surfaces is a well-studied problem and, depending on the application, one or another approach is expedient. Thus, for superhydrophobic coatings rarely contacting with water, the physical adsorption of hydrocarbons is enough; application of a thick layer of hydrophobic material is more suitable for prolonged contact with corrosive media without excessive mechanical and thermal loads. However, for polyfunctional coatings subjected to prolonged operation in an open atmosphere, and especially for those oriented to harsh conditions characteristic of aviation, marine or high-voltage industries, the most promising approach is applying of a layer of a chemically-adsorbed hydrophobic agent able to form the cross-linked polymer on the surface.
3. Protective Coatings on Stainless Steels
3.1. Establishing of Protective Propeties
Stainless steel is a widely-used alloy family employed in numerous industrial applications due to its high mechanical properties and good chemical stability in comparison to carbon steel. AISI 304 is the most common austenitic stainless steel. The presence of chromium (18%–20%) and nickel (8%–10%) in composition inhibits corrosion, however, it is still susceptible to pitting in chloride solutions such as seawater or biological fluids. For more harsh conditions, AISI 316 is used, which differs from AISI 304 by the presence of 2%–3% of molybdenum. While additions of chromium, nickel, and other compounds significantly inhibit the rate of corrosion, improving the chemical resistance of industrial stainless steel equipment, especially those in contact with atmospheric precipitation or seawater, the protection of stainless steel surface against corrosion is still of great interest. The majority of scientific papers in this area are devoted to the fabrication of superhydrophobic coatings on the most popular alloys such as AISI 316 and AISI 304 with relatively lower interest towards less-widely-used alloys. It is easy to find in the literature a number of studies where the coatings with extremely high water repellencies were fabricated. The developed multi-scale roughness with the elements of texture having convex curvature and low surface energy, allows getting quite routinely contact angles above 168° and roll-off angles less than 5°–7° [66,77,78,79,80].
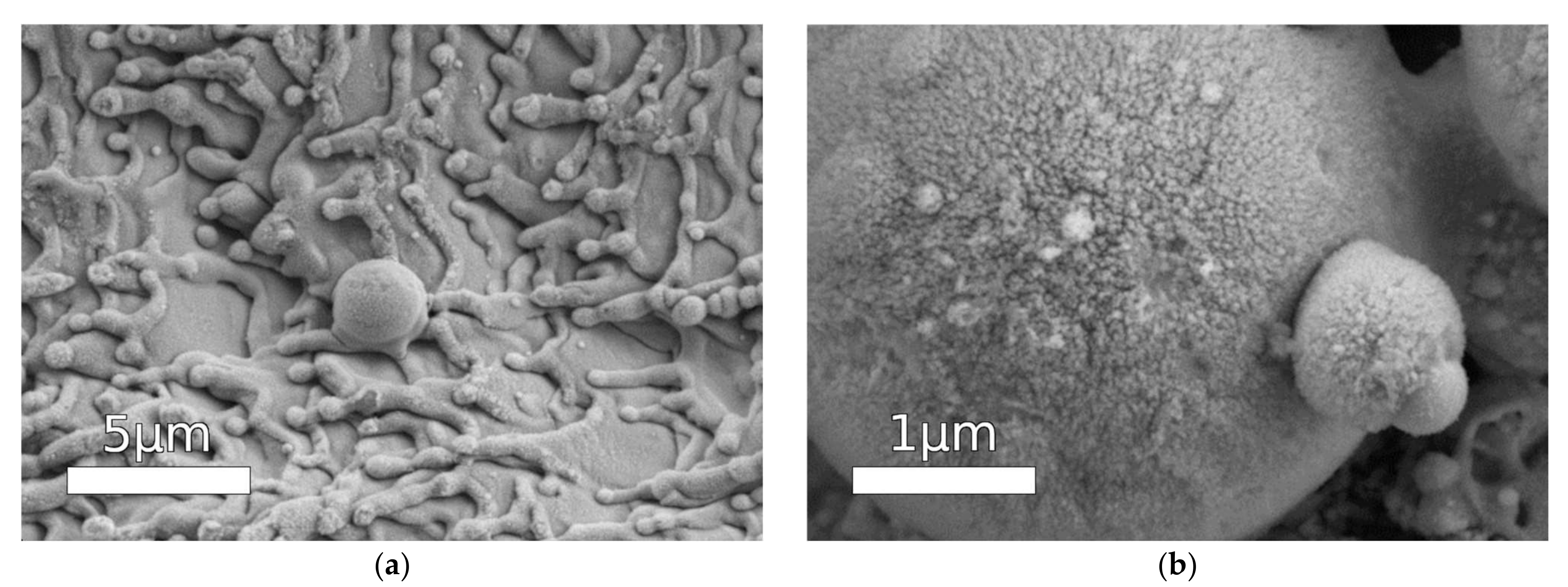
The detailed investigation of the resistance of some of such superhydrophobic coatings on stainless steel to different mechanical loads showed good preservation of a superhydrophobic state in conditions of prolonged abrasive wear and cavitation erosion [77,78] (see Figure 2). The analysis of chemical stability during prolonged contact with deionized water and chloride solutions indicates that the proper choice of laser treatment and hydrophobization methods allows achieving the preservation of the heterogeneous wetting regime with very high contact angles under prolonged contact with corrosive media [77,78,80]. Although high chemical resistance during immersion in a corrosive medium is the necessary condition for the corrosion resistance of the coating, it cannot always be considered an unambiguous indication on such resistance.
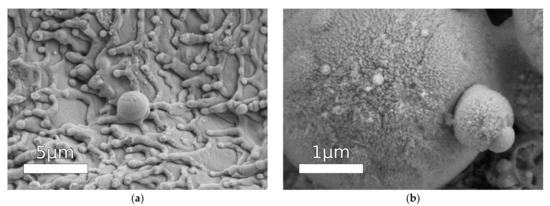
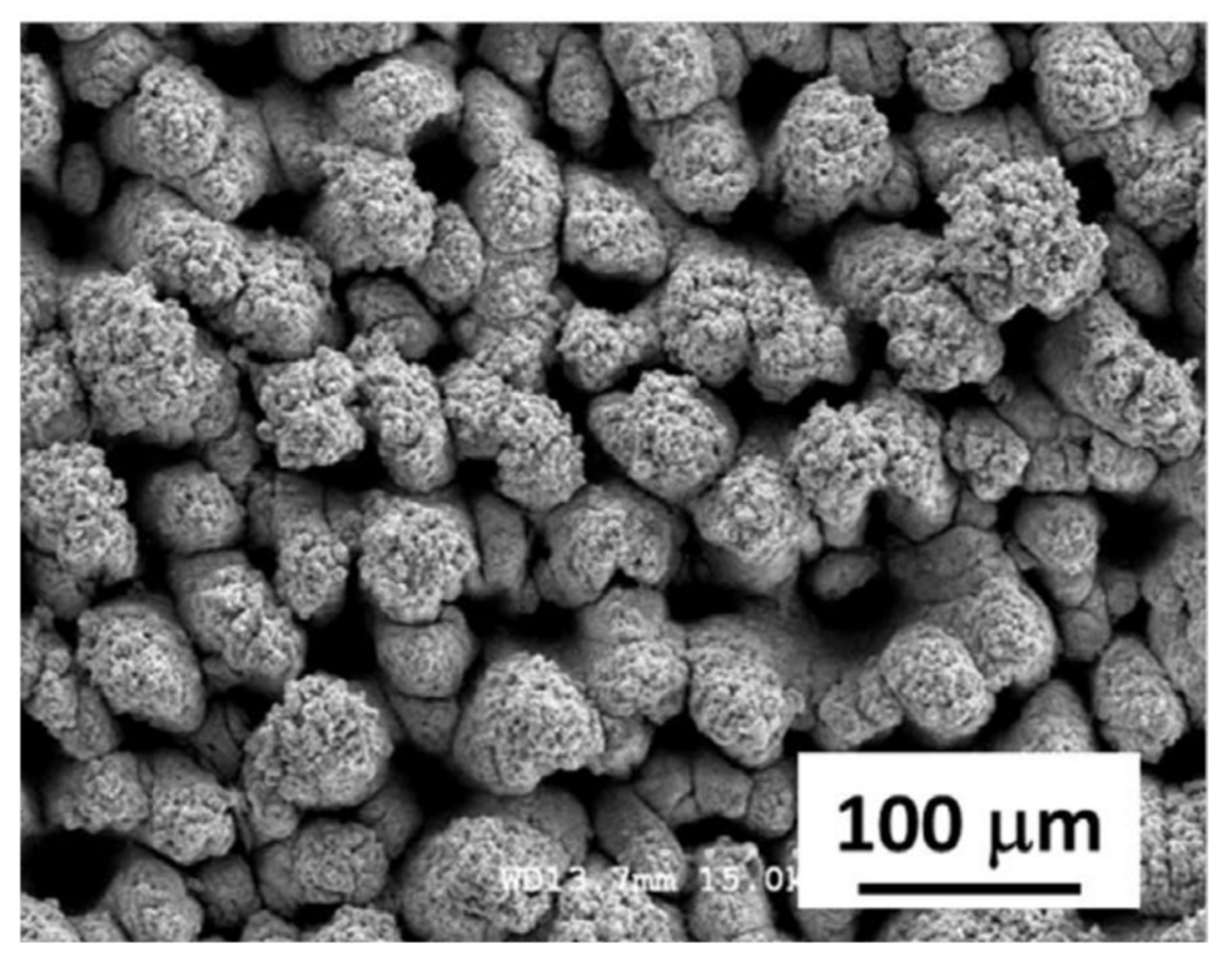
Figure 2.
SEM images of the surface of superhydrophobic stainless steel after 90 min of oscillating sand test, (a) survey image; (b) details of wear at high magnification (source: SEM images for Figure 4 from [78] obtained from authors, reprinted with permission from Pleiades Publishing, 2015).
The most useful modern way to characterize corrosion resistance of the coating is to study the evolution of potentiodynamic polarization curves in time. This approach allows the obtaining of such characteristics as corrosion current and thus the corrosion rate, as well as corrosion potential and the impact of contact with a corrosive medium on the coating protective properties. In addition, the processing of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data by fitting an equivalent scheme allows the shedding of light on the processes occurring upon contact with corrosive media and estimating the electrochemical parameters of these processes, such as charge transfer and double electric layer characteristics, etc. Finally, the analysis of evolution of the above-mentioned characteristics can provide better understanding of long-term durability of the protective properties of the coating. It should be noted that the differences in details of the test such as the exact composition of corrosive media, temperature, time of relaxation to steady state, rate of potential increase, used electrodes and equipment make it somewhat difficult to compare characteristics obtained in different studies. At the same time, the comparison of treated and untreated samples obtained in one study is the most frequently-used option. That is why we will mention below electrochemical data for the coated and bare metals where available. Finally, some studies fall back to the simplest approach of monitoring the evolution of the sample appearance and detection of the time of emergence of visual corrosion traces. Such qualitative data can be used for the hints of whether the coating can manifest corrosion resistance or not.
3.2. AISI 316 Stainless Steel
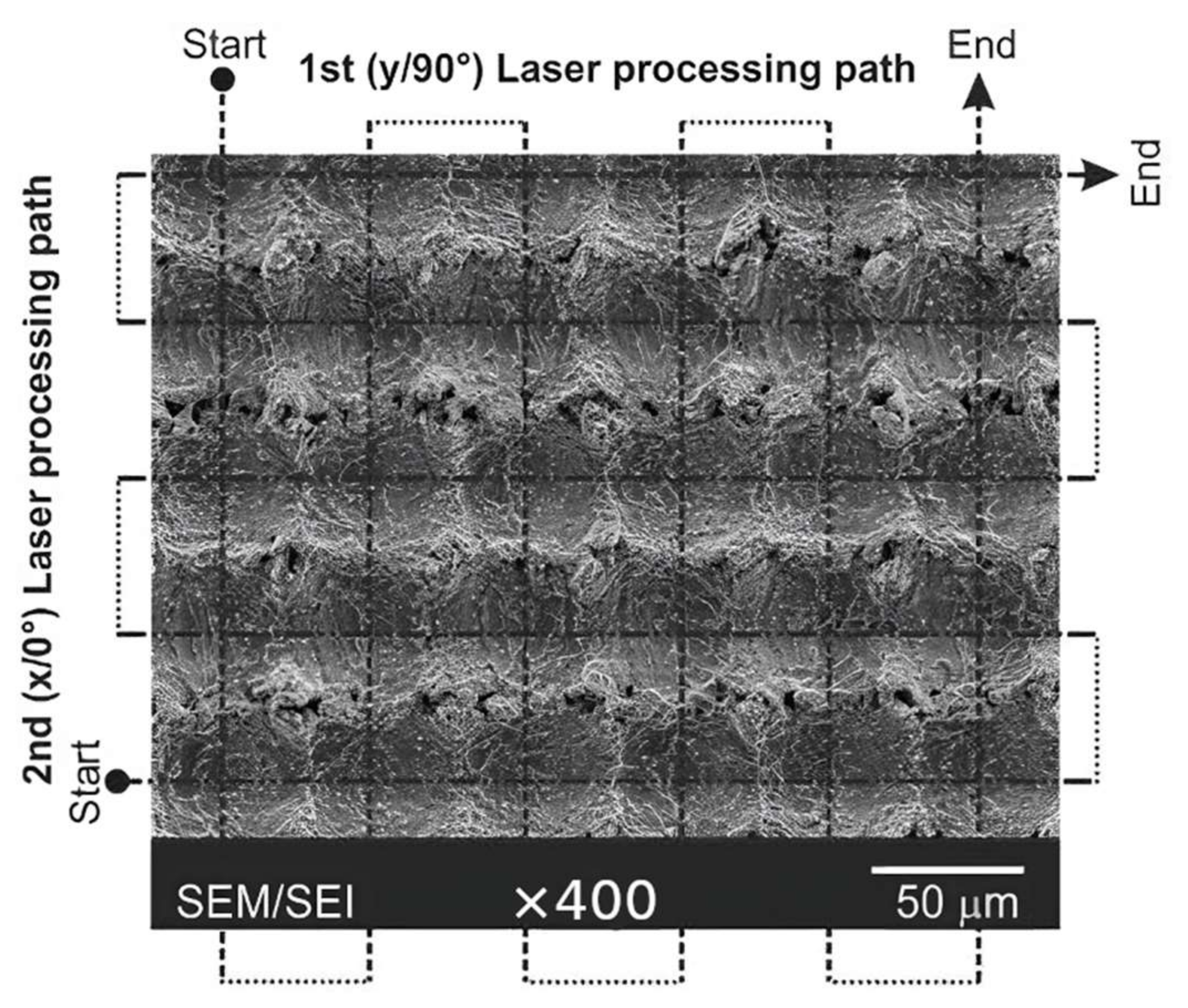
Now let us consider some results obtained in the field of laser processing for producing the superhydrophobic coatings to protect the stainless steel against corrosion. Trdan et al. [81] studied the effect of spontaneous hydrophobization of laser-treated samples of AISI 316 stainless steel on its corrosion properties. In this work, a 1064-nm laser with 40 nanosecond pulse duration was used to create square grid microtexture on the surface decorated by nanoparticles formed due to ablation (see Figure 3).
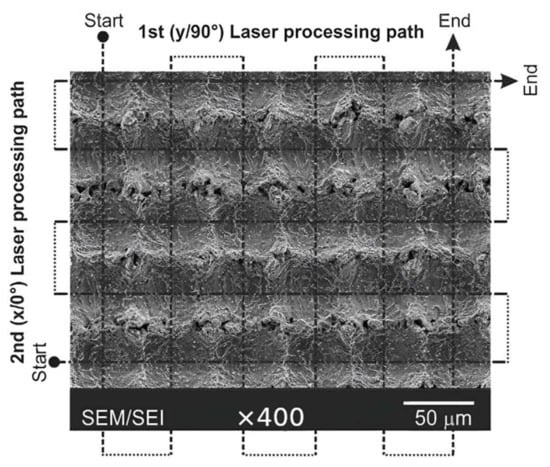
Figure 3.
SEM micrographs of laser-textured surfaces with direction of laser passes. Adapted/redrawn with permission from [81], Elsevier, 2017.
In agreement with the results of other studies, it was found that a just textured surface is superhydrophilic and has corrosion current orders higher than for the untreated samples. However, after a month of storing the samples obtained, superhydrophobicity (contact angle ~168°) and corrosion current decreased to about twice lower value compared to the untreated sample: 2.9 × 10−7 vs. 7.2 × 10−7 A/cm2 for bare stainless steel. It was found that corrosion lesions propagate along the axis corresponding to the latest laser texturing direction. In addition, the authors mentioned that the used laser treatment regime led to the inhibition of intergranular corrosion due to a more homogeneous microstructure. As was discussed in the literature [6], homogenization of the surface contacting with the corrosive liquid hinders the formation of corrosion pairs (i.e., of cathodic and anodic sites).
Chen et al. [82] used pulsed laser with wavelength of 355 nm and pulse duration of 20 ns to texture the surface of 316 stainless steel. It was found that at pulse frequency of 6.8 kHz and beam speed around 5 mm/s, there are two thresholds associated with the pulse energy: at 220 mW per pulse, an ablation process starts with main texture features determined by material evaporation, while at 570 mW per pulse, the main process determining the texture is deposition and aggregation of nanoparticles formed in the ablation process. The latter leads to the formation of highly-developed “reed leaf” structure. Subsequent hydrophobization by fluorooxysilane FAS-17 allowed the obtaining of the superhydrophobic state with contact angle of 157° and roll-off angle of 1°. Chemical adsorption of hydrophobic agent able to form cross-linked polymers led to substantially lower corrosion currents: 3.2 × 10−9 vs. 5.0× 10−7 A/cm2 for bare stainless steel. It is worth noting that both corrosion potential and the corrosion current showed very high stability during 168 h of immersion in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution, indicating durable protective properties of the prepared coating. This coating also demonstrated some mechanical resistance under the sandpaper abrasion test, retaining superhydrophobicity after 2.5 m abrasion length at the applied pressure of 12.5 kPa. Using the same type of laser and hydrophobic agent, but shorter laser pulses of 15 ns, Lu et al. [83] also obtained superhydrophobic coating (contact angle ~160°) with improved corrosion protection: corrosion current on the best sample was 2.8 × 10−8 vs. 2.0 × 10−6 A/cm2 for bare stainless steel. It was found that the dependence of corrosion inhibition efficiency was nonmonotonic, and passed through the maximum at laser fluence around 8 J/cm2, which correlated well with nonmonotonic dependence of the wetting properties on the laser treatment intensity.
Sun et al. [84] applied the other method of laser treatment to obtain corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic coating on 316 stainless steel. In particular, they used selective laser melting to weld stainless steel powder to the stainless steel substrate in such a way that it formed a microtexture of trapezoids hanging over the surface and decorated by spherical particles. Further hydrophobized by FAS, such coating demonstrated superhydrophobicity with contact angle about 160° and inhibition of corrosion with corrosion currents: 4.2 × 10−8 vs. 1.4 × 10−6 A/cm2 for bare stainless steel.
Laser treatment with wave length of 1064 nm and pulse duration of 50 ns was applied in the study of Yang et al. [85] to fabricate the corrosion resistant coating on 316 L stainless steel. After subsequent hydrophobization by FAS, the superhydrophobic sample demonstrated corrosion current one order of magnitude lower than the untreated sample: 4.7 × 10−7 vs. 4.6 × 10−6 A/cm2. However, long-term immersion into corrosive environments had shown that coating didn’t withstand 12 h of contact with 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. At the same time, the impregnation of the superhydrophobic surface by silicone oil to form so-called SLIPS (slippery liquid infused porous surface) led to the improvement of corrosion resistance. Corrosion currents for both initial state and upon many hours of contact with corrosive media were found to be significantly less: 1.6 × 10−8, 4.4 × 10−8, 5.1 × 10−8 and 1.4 × 10−7 A/cm2 for 0, 12, 24 and 72 h of contact, correspondingly. This behavior apparently indicates that the hydrophobization process in this case failed to form a uniform layer of hydrophobic agent. That way, wetting defects in as prepared coating broke the air cushions between the liquid and the surface, leading to quite high initial corrosion current and serving as centers for subsequent quick deterioration of the whole coating. One of the possible reasons for such behavior can be the deficiency of the chemical active centers for FAS adsorption. Seemingly, the additional O3/UV treatment of the surface after laser texturing and just before hydrophobization could increase the number of adsorption sites for FAS molecules and promote the formation of a dense and uniform hydrophobic layer with more durable corrosion resistance.
Kedia et al. [86] have treated 316 L stainless steel by 532 nm laser with 6 ns pulse duration, with subsequent wetting transition upon storage in an open atmosphere to obtain better corrosion resistance and improve the biocompatibility of implants. They have found that although the best treatment regime corresponding to maximum incident power resulted in a slightly higher corrosion current than the control sample, 4.2 × 10−7 vs. 3.2 × 10−7 A/cm2 for bare stainless steel, it led to better protection against pitting corrosion.
Seemingly, a thick layer of formed oxides was responsible for shifting the pitting potential towards more positive values. In addition, micro-groove patterns with nanostructures promoted bone cells adhesion, alignment, spreading, and contact guidance, thus demonstrating better biocompatibility. Presumably, the absence of the improvement in corrosion current was related to the poor and uneven hydrophobic layer on top of the texture, formed by spontaneous airborne organics deposition, as was explained above. Changing of the hydrophobization method to the adsorption of stearic acid would probably further increase corrosion resistance without sacrificing biocompatibility.
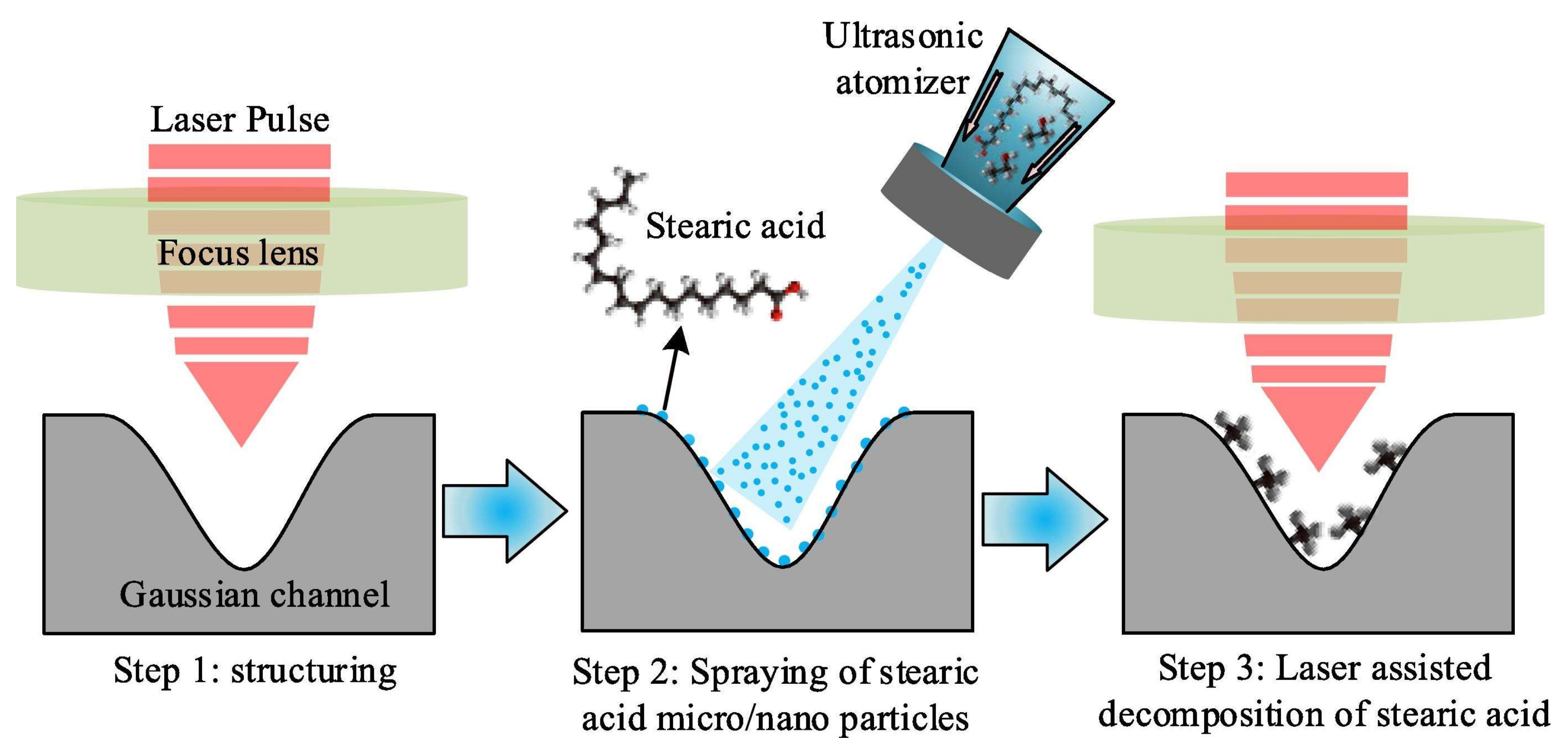
Tang et al. studied the effect of laser post-treatment of superhydrophobic coating on 316 L stainless steel [87]. First, the surface was textured by 1064 nm laser with 100 ns pulse duration to obtain micro- and nano- developed morphology. Then, the coating was hydrophobized by spreading of micro drops of ethanol solution with dissolved stearic acid. After ethanol evaporation, the superhydrophobicity was achieved. Finally, the superhydrophobic coating was additionally treated by laser with low intensity to partially decompose the stearic acid (see Figure 4).
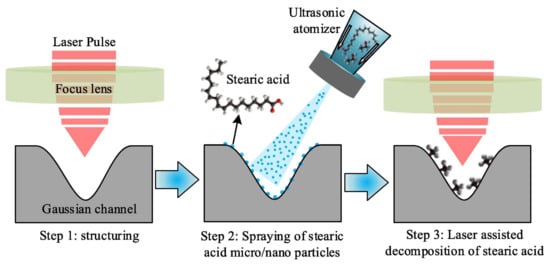
Figure 4.
A scheme of coating fabrication via laser texturing and laser-assisted decomposition of stearic acid. Reprinted with permission from [87], Elsevier, 2022.
It was found that post-treatment substantially increased corrosion protection: 2.2 × 10−8 vs. 3.3 × 10−7 vs. 1.6 × 10−6 A/cm2 for coating with post-treatment, without post-treatment, and for bare stainless steel, respectively. The authors suggested that decomposition of stearic acid produced long-chain alkanes which have stronger surface adsorption and stability. However, more plausible seems the hypothesis that during hydrophobization from the ethanol solution, some spots on the surface, especially inside deep pores, remained uncovered by stearic acid and thus served as corrosion development centers; at subsequent post-treatment, such spots could be covered by products of decomposition by redeposition from the vapor in a local high-temperature environment.
Short- and long-term corrosion resistance of laser treated 316 L stainless steel hydrophobized by either spontaneous airborne organics or deposition of the epoxy layers with or without FAS-TiO2 filler was studied by Conradi et al. [75]. Although the general tendency indicates improvement of the corrosion barrier upon deposition of the hydrophobic layers, the obvious advantages of FAS-TiO2 epoxy layers were detected just for freshly-prepared coatings and 3 subsequent months. After a year of storage, when the spontaneous hydrophobization was completed, the corrosion currents measured after 1 h of sample stabilization in electrolyte solution did not allow an unambiguous distinction between spontaneously- and intentively-hydrophobized structures. As was shown in the literature earlier [31,88,89], the prolonged contact of the coatings with electrolytes could better reveal the possible differences in stability and protective efficiency of two approaches.
3.3. AISI 304 Stainless Steel
Sun et al. [20] studied the durability of superhydropbobic coating on AISI 304 stainless steel fabricated via two-stage picosecond laser treatment followed by the deposition of oxysilane functionalized silica nanoparticles. It was found that neither micro-groove + LIPSS nor micro-pit + LIPSS textured surfaces retained superhydropbobic properties upon five weeks’ contact with seawater; presented micro-photographs indicated partial degradation of the texture due to corrosion. At the same time, surfaces remained hydrophobic, with micro-groove design being slightly better than micro-pit in both wetting and anti-biofouling performance.
Zhang et al. prepared a micro-pit based superhydropbobic coating on AISI 304 stainless steel using the pulsed laser with the wave length of 1064 nm and hexadecyltrimethoxysilane as the hydrophobic agent [90]. As expected, it was shown that superhydrophobic coating demonstrated better corrosion resistance than hydrobized but not textured stainless steel, and both were better than the untreated surface. The fact that the textured but not hydrophobized surface was between the superhydrophobic and hydrophobic smooth samples in terms of anticorrosion properties most likely indicates spontaneous hydrophobization by atmospheric pollution. This also indirectly explains why corrosion current on superhydropbobic coating was only 20 times lower than on untreated sample (which is quite a moderate result), 1.0 × 10−7 vs. 2.1 × 10−6 A/cm2: during preparation, no special treatment to clean the surface from adsorbed contaminants was applied, and it is therefore highly likely that most of the adsorption sites which could bind the hexadecyltrimethoxysilane molecules were occupied by less durable hydrocarbons.
Singh et al. studied the effect of surface microstructuing of AISI 304 stainless steel by femtosecond Ti:Sapphire laser with the wave length of 800 nm [91]. The used setup is quite unusual for surface treatment, due to low power and wide focus spot of 250 µm. That way, to get the surface textured, the authors had to use low beam velocity of the order of a hundred micrometers per second, corresponding to the effective number of pulses per spot in the range 750–30,000. The laser processing regime used in this study leads to the absorbed energy being much higher than the ablation threshold for stainless steel. Immediately after that treatment, the obtained superhydrophilic coating demonstrated much lower corrosion resistance than the untreated surface, while hydrophobization by atmospheric contaminations increased the corrosion protection and allowed it to almost reach the corrosion current corresponding to the untreated sample. Such a result is well aligned with the analysis discussed above.
Indeed, superhydrophilic coatings have much higher contact area with corrosion media; in addition, it was shown that the laser-treated surface of 304 stainless steel is depleted of chromium [92], which inhibits the corrosion process. Corrosion current for hydrophobized coatings of about 12.7 × 10−6 vs. 7.6 × 10−6 A/cm2 for untreated surface, indicates that a non-uniform and weakly-bonded low surface energy layer cannot effectively protect the surface. This conclusion is further supported by the contact angle on treated sample as low as 144°. In this regard, it is quite unexpected that nanosecond laser treatment of 304 L stainless steel accomplished by Gupta et al. [19] demonstrated better performance of corrosion resistance: 1.2 × 10−8 vs. 1.5 × 10−7 A/cm2 for untreated surface, in addition to being much less hydrophobic with the contact angle around 110° corresponding to the homogeneous wetting regime of the textured surface by water. The distinctive feature of this study is an unnaturally low value of corrosion current for untreated sample, which can be explained by spontaneous deposition of organic contaminations on the bare sample during its storage. In that case, a low corrosion current for the laser-treated sample is seemingly related to the thick layer of oxides which could play a role of short-term corrosion barrier, and to the incomplete layer of organics deposited onto the surface after laser treatment as witnessed by the moderate contact angle of 110°.
Surprisingly good corrosion resistance was demonstrated in a paper by Zhu and Wu [68]. Laser treatment by 120 ns laser followed by hydrophobization by storage in sealing bags led to an enormous decrease in corrosion current: 7.2 × 10−10 vs. 1.3 × 10−6 A/cm2 for untreated surface. This result is somewhat difficult to assess given the lack of data on both the used laser treatment regime (no data on wavelength and ambiguous designation of beam speed) and the hydrophobization process.
In contrast, cauliflower ablation texture obtained by 800 nm laser with 120 fs pulse duration hydrophobized by perfluorooctylsilane (FOTS) demonstrated inexplicably high corrosion current values [93]. Despite the well-developed morphology (Figure 5), additional pre-treatment in piranha solution in order to remove contamination and expose the hydroxyl groups on the surface, and a proper procedure of hydrophobization and cross-linking, the coating demonstrated high corrosion current of 5.9 × 10−5 vs. 5.8 × 10−6 A/cm2 for untreated surface. Authors of the paper claim high corrosion durability based on stability of open circuit potential over long-term contact with NaCl solution; however, given the high corrosion current, it instead indicates reaching a steady state of intensive corrosion reaction. Most probably, this high corrosion rate is a result of incomplete drying of the samples in nitrogen flow after washing. In accordance with Kelvin equation, the equilibrium vapor pressure above concave interface, in particular above menisci in nano-pores of the highly developed surface, is much lower than that above flat surface. Therefore, without additional heating, the complete drying of capillary condensed water requires a very long time. If, as we believe, the surface had not been completely dried prior to the hydrophobization stage, it was not hydrophobized appropriately.
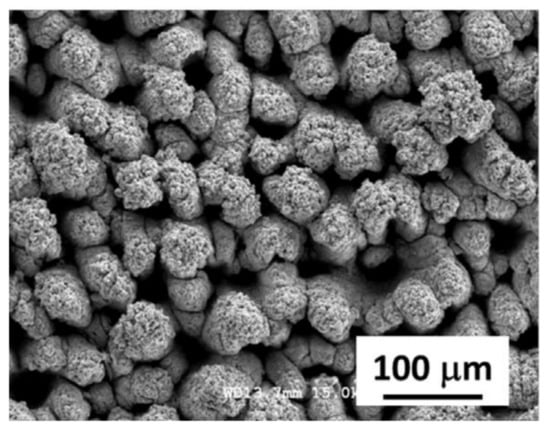
Figure 5.
An SEM image of cauliflower-like ablation texture. Reprinted with permission from [93], Wiley, 2018.
3.4. Less Common Stainless Steels
For AISI 420 stainless steel, which mainly consists of iron and 12%–14% of chromium, Pan et al. [72] showed that 515 nm laser treatment with 10 ps laser pulses followed by hydrophobization by stearic acid was able to produce the superhydrophobic coating with the contact angle as high as 163°. However, this coating was subjected to corrosion testing by immersion in a 0.5 M NaCl solution for 30 days with only evaluation of visual appearance. Despite the absence of visible corrosion traces after the prolonged contact with salt solution, it was not possible to affirm decent corrosion resistance.
Wang et al. [94] treated the surface of 1095 carbon steel by 1064 nm laser with 20 ns pulse duration. In their work, to obtain higher treatment speed, the authors used an untypically large distance of 600 µm between laser passes, for the laser spot size of around 50 µm. Under these conditions, parts of the initial surface were dissected by high-edged ditches. The authors used three different types of texture, which after hydrophobization by perfluorooctylsilane demonstrated the superhydrophobic state, characterized by different contact angles. It was found that the coating which presented the highest contact angle of ~160° showed the smallest corrosion current of 2.9 × 10−8 vs. 5.4 × 10−7 A/cm2 for bare steel.
It should be noted that examples of coatings with an improved corrosion resistance described above are in general the results of extensive treatment optimization; however, the latter often remains hidden in the published papers. Negative results are usually not published at all or only presented for the purpose of comparison with successful ones. Such bias is unfortunate since it prevents the community from learning from unsuccessful tries and thus leads to their repetition. Nevertheless, sometimes such results are published. In particular, Rafieazad et al. [95] tried to obtain corrosion resistant superhydrophobic coatings on the surface of 17–4 stainless steel by treatment with 1060 nm laser with 60 ns pulse duration, followed by hydrophobization of a mix of fluoroorganic compounds. Despite reaching ablation threshold and forming texture with deep trenches decorated by nanoparticles, the coating was not water-repellent enough to be considered superhydrophobic (contact angle of only about 145° was achieved) and failed to demonstrate corrosion inhibition: the corrosion current was 3.8 × 10−6 vs. 1.0 × 10−6 A/cm2 for bare 17–4 steel. Since the morphology of the obtained surface was quite developed, low contact angle and high corrosion current were most probably the results of issues during hydrophobization: low adsorption of hydrophobic agent to the surface because of inappropriate velocity of the dip-coating process, or the presence of a residual amount of alcohols from the hydrophobization stage during subsequent tests.
4. Discussion
The current state of superhydrophobicity-based anti-corrosion coatings reminds us of the parable of blind men and the elephant, where a group of blind men need to form an idea about the elephant while each blind man feels a different part of the elephant’s body. There are numerous variables that can be modified at each stage of the process for creating superhydrophobic surfaces, including texture creation, surface cleaning and drying, the formation of binding sites for hydrophobic molecules, and the hydrophobization step itself. However, the literature on this topic is limited and often conflicting, with only scattered reports of successful approaches. The available data is summarized in Table 1, where the corrosion inhibition efficiency is defined as a relative decrease in corrosion current for the best protective coating with respect to bare steel in a given report. The main parameters of the applied laser treatment, the used hydrophobic agent, and the achieved water contact angle are listed as well to briefly characterize the coating.

Table 1.
Protective properties of superhydrophobic coatings on laser-treated stainless steel presented in the literature.
It is important to consider the following aspects when analyzing these reports. While the process for creating these coatings may be technologically complex, it offers many advantages due to the versatility of the method of preparation and the variety of obtainable structures of the coating. These coatings belong to the category of passive protection, meaning that once applied, they should work for a long period of time without requiring active maintenance. The structures of these coatings, if correctly used, realize the strategies of self-healing corrosion protection systems, which take into account industrial demands and requirements and have been the trend in the recent years. This self-healing function is achieved through the encapsulation of hydrophobic agent within nanopores during the hydrophobization process [37]. If the hydrophobic layer is damaged or removed during harsh operating conditions, the thermodynamically-driven diffusion of the encapsulated hydrophobic molecules towards areas of high surface energy where the hydrophobic layer has been depleted can repair the damage [77,96]. Despite the incomplete and inconsistent nature of the available data on the topic of this brief review, we can cautiously make the following generalizations based on this information:
- Laser chemical modification is an effective method for creating protective coatings on various types of stainless steel with significantly reduced corrosion currents.
- Superhydrophobic coatings on stainless steel that offer corrosion resistance are typically produced through nanosecond laser treatment. In cases where lasers with shorter pulses are used, the irradiation regime is optimized to cause ablation and mass transfer rather than generating a LIPSS texture on the surface. This suggests that a relatively thick layer of stainless steel must be subjected to laser chemical modification in order to create a better protective barrier layer.
- Physical adsorption of airborne contaminants for hydrophobization is unreliable and generally does not provide long-term corrosion resistance for highly-developed stainless steel surfaces when exposed to corrosive media.
5. Conclusions
In this brief review, we have considered the applicability and efficiency of stainless steel protection against different types of corrosion based on the relatively new approach of surface superhydrophobization using laser surface processing and deposition of the hydrophobic agent.
It was discussed above that the anticorrosive superhydrophobic coatings obtained using laser processing work on the following basic principles. The first one is the water repelling effect which simply limits the effective contact area between the corrosive environment and the superhydrophobic material. As shown in the literature, the decrease in this effective contact area may reach as much as 99%. The second principle is the barrier effect initiated by the thermo-oxidation, due to the enhanced oxidation of the very top layer of the material under the laser surface melting and the deposition of ablation products onto the surface. Although, depending on the Pilling–Bedworth ratio [97], not all oxides give dense oxide layer and thus good barrier properties for the components of the corrosive medium, in essence, the charge transfer through these oxide layers is typically inhibited, while the further oxidation process is partially suppressed by decelerated mass transfer. Additionally, the laser processing in the special gaseous media allows chemical modification of the surface layer with the enrichment of the very top layer with the products of the chemical interaction between the material and atmospheric components, making it less prone to electrochemical reactions in corrosive media. The third principle is related to the chemisorption in contrast to a physisorption of the hydrophobic molecules. Chemisorbed molecules block the sites necessary for the adsorption of corrosion active species, like oxygen, halide anions, etc., resulting in suppressing the stages responsible for the development of the corrosion process. Finally, the fourth principle, based on the spontaneous decrease in the concentration of aggressive ions in the vicinity of the coating at pH ≥ 4, is based on the negative charging of a superhydrophobic coating in contact with an electrolyte. Note that in contrast to the superhydrophobic coating, a superhydrophilic one in neutral solutions is charged positively, thus promoting the enhanced concentration of anions in the double electric layer.
According to our review, while superhydrophobic coatings with high contact and roll-off angles have been developed for stainless steel [77], the creation of durable, corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic coatings on stainless steel with corrosion current that is three to six orders of magnitude lower than that of bare stainless steel surfaces—a typical protective efficiency characteristic of superhydrophobic anti-corrosion coatings on many other metals [24,88]—still remains a challenge.
The principles for creating superhydrophobic anticorrosive coatings outlined in this study have not yet been systematically studied for their potential to improve the protection of steel. However, we believe that their effectiveness will be demonstrated in the near future, leading to widespread adoption of this approach in practice. It should be noted that no previous efforts have been made to intentionally employ all of the anticorrosive mechanisms of superhydrophobic coatings on stainless steel in a synergistic manner, presenting an opportunity for further research in this area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.E., K.A.E. and L.B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, K.A.E.; writing—review and editing, A.M.E. and L.B.B.; visualization, K.A.E.; supervision, L.B.B.; project administration, A.M.E.; funding acquisition, A.M.E. and K.A.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation and the grant for young research groups MK-2124.2021.1.3.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Koch, G.; Varney, J.; Thompson, N.; Moghissi, O.; Gould, M.; Payer, J. International Measures of Prevention, Application, and Economics of Corrosion Technologies Study. NACE Int. 2016, 216, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kimbell, L.K.; Wang, Y.; McNamara, P.J. The Impact of Metal Pipe Materials, Corrosion Products, and Corrosion Inhibitors on Antibiotic Resistance in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7673–7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, C.M. The Impact of Corrosion on Society. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2952–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, J.R.; Inman, S.B.; Gerard, A.Y.; Taylor, C.D.; Windl, W.; Schreiber, D.K.; Lu, P.; Saal, J.E.; Frankel, G.S. Controlling the Corrosion Resistance of Multi-Principal Element Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2020, 188, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeev, Y.G.; Kuznetsov, Y.I. Inhibitory Protection of Steels from High-Temperature Corrosion in Acid Solutions. A Review. Part 1. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2020, 9, 394–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamashov, N.D. Theory of Corrosion and Protection of Metals; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Solis, C.D.; Vimalanandan, A.; Altin, A.; Mondragón-Ochoa, J.S.; Kreth, K.; Keil, P.; Erbe, A. Fundamentals of Electrochemistry, Corrosion and Corrosion Protection. In Soft Matter at Aqueous Interfaces; Lang, P., Liu, Y., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 917, pp. 29–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of Porous Surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Wetting on Hydrophobic Rough Surfaces: To Be Heterogeneous or Not to Be? Langmuir 2003, 19, 8343–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A.; Della Volpe, C.; Siboni, S.; Amirfazli, A.; Drelich, J.W. Contact Angles and Wettability: Towards Common and Accurate Terminology. Surf. Innov. 2017, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Hydrophobic Materials and Coatings: Principles of Design, Properties and Applications. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2008, 77, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Gao, N.; Barthlott, W. Mimicking Natural Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Grasping the Wetting Process: A Review on Recent Progress in Preparing Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latthe, S.; Terashima, C.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Developed by Mimicking Hierarchical Surface Morphology of Lotus Leaf. Molecules 2014, 19, 4256–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürstner, R.; Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C.; Walzel, P. Wetting and Self-Cleaning Properties of Artificial Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boinovich, L.; Emelyanenko, A. Principles of Design of Superhydrophobic Coatings by Deposition from Dispersions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2907–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emelyanenko, A.M. Superhydrophobic Materials and Coatings. From Basic Researches to Practical Applications. Colloid J. 2022, 84, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.; Emelyanenko, A. The Prediction of Wettability of Curved Surfaces on the Basis of the Isotherms of the Disjoining Pressure. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 383, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Gnedenkov, S.V.; Alpysbaeva, D.A.; Egorkin, V.S.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Sinebryukhov, S.L.; Zaretskaya, A.K. Corrosion Resistance of Composite Coatings on Low-Carbon Steel Containing Hydrophobic and Superhydrophobic Layers in Combination with Oxide Sublayers. Corros. Sci. 2012, 55, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Anandkumar, B.; Choubey, A.; George, R.P.; Ganesh, P.; Upadhyaya, B.N.; Philip, J.; Bindra, K.S.; Kaul, R. Antibacterial and Corrosion Studies on Nanosecond Pulse Laser Textured 304 L Stainless Steel Surfaces. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process 2019, 6, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Yang, H.; Xue, W.; He, A.; Zhu, D.; Liu, W.; Adeyemi, K.; Cao, Y. Anti-Biofouling Superhydrophobic Surface Fabricated by Picosecond Laser Texturing of Stainless Steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukolov, A.I.; Popova, T.N. Efficiency of the Use of Commercial Superhydrophobic Coatings in the Fields of Marine Industry. Colloid J. 2022, 84, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Ivanov, V.K.; Pashinin, A.S. Durable Icephobic Coating for Stainless Steel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2549–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanenko, A.M.; Boinovich, L.B.; Modestov, A.D.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Dvoretskaya, O.V. Corrosion Behavior of Superhydrophobic Coatings on Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy in Potassium Iodide Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, C659–C665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Chulkova, E.V.; Shiryaev, A.A.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Pulsed Laser Induced Triple Layer Copper Oxide Structure for Durable Polyfunctionality of Superhydrophobic Coatings. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1801099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanenko, K.A.; Chulkova, E.V.; Semiletov, A.M.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Palacheva, V.V.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Boinovich, L.B. The Potential of the Superhydrophobic State to Protect Magnesium Alloy against Corrosion. Coatings 2022, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; Arenas, M.A.; Perrie, W.; Dearden, G.; de Damborenea, J. Surface Texturing of Aluminium Alloy AA2024-T3 by Picosecond Laser: Effect on Wettability and Corrosion Properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 321, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Pan, J.; Cai, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Z. Degradation Mechanisms of Corrosion and Biofouling Resistance of Superhydrophobic Coatings in Harsh Marine Conditions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 173, 107222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Benedetti, A. Superhydrophobic Surfaces for Applications in Seawater. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Modestov, A.D.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Emelyanenko, K.A. Not Simply Repel Water: The Diversified Nature of Corrosion Protection by Superhydrophobic Coatings. Mendeleev Commun. 2017, 27, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J. Long-Term Corrosion Protection for Magnesium Alloy by Two-Layer Self-Healing Superamphiphobic Coatings Based on Shape Memory Polymers and Attapulgite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, T.; Chiba, S.; Watanabe, K.; Suzuki, H. Corrosion Resistance of Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide Container-Containing Magnesium Hydroxide Films Formed Directly on Magnesium Alloy by Chemical-Free Steam Coating. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Krishnan, A.V.; Ajith, A.; Shibli, S.M.A. Influence of Materials and Fabrication Strategies in Tailoring the Anticorrosive Property of Superhydrophobic Coatings. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 25, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yin, M.; Pu, J.; Yuan, N.; Ding, J. Superhydrophobic and Self-Healing Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide/Silane Composite Coatings on the Mg Alloy Surface with a Long-Term Anti-Corrosion Lifetime. Langmuir 2021, 37, 8129–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, R.; Freudenberg, U.; Schweiß, R.; Küttner, D.; Werner, C. Hydroxide and Hydronium Ion Adsorption—A Survey. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.A.; Pitchumani, R. A Study of Corrosion on Electrodeposited Superhydrophobic Copper Surfaces. Corros. Sci. 2021, 186, 109420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaola, A.O.; Bamidele, E.A.; Akisin, C.J.; Bello, I.T.; Oyatobo, A.T.; Abdulkareem, A.; Farayibi, P.K.; Asmatulu, E. Wettability Transition for Laser Textured Surfaces: A Comprehensive Review. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Modin, E.B.; Sayfutdinova, A.R.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Vasiliev, A.L.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Combination of Functional Nanoengineering and Nanosecond Laser Texturing for Design of Superhydrophobic Aluminum Alloy with Exceptional Mechanical and Chemical Properties. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10113–10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäuerle, D. Material Transformations, Laser Cleaning. In Laser Processing and Chemistry; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011; pp. 535–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Kunz, C.; Gräf, S. Bio-Inspired Functional Surfaces Based on Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures. Materials 2016, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugioka, K.; Cheng, Y. Ultrafast Lasers—Reliable Tools for Advanced Materials Processing. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakis, E. Nanomaterials by Ultrafast Laser Processing of Surfaces. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2012, 4, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratakis, E.; Bonse, J.; Heitz, J.; Siegel, J.; Tsibidis, G.D.; Skoulas, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Mimidis, A.; Joel, A.-C.; Comanns, P.; et al. Laser Engineering of Biomimetic Surfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2020, 141, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionin, A.A.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Samokhin, A.A. Material Surface Ablation Produced by Ultrashort Laser Pulses. Phys.-Uspekhi 2017, 60, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D.; Almeida, J.; Almeida, G.; Cardoso, M.; De Boni, L.; Mendonça, C. Ultrafast Laser Pulses for Structuring Materials at Micro/Nano Scale: From Waveguides to Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Photonics 2017, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kray, D.; Fell, A.; Hopman, S.; Mayer, K.; Willeke, G.P.; Glunz, S.W. Laser Chemical Processing (LCP)—A Versatile Tool for Microstructuring Applications. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 93, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusinski, J.; Kac, S.; Kopia, A.; Radziszewska, A.; Rozmus-Górnikowska, M.; Major, B.; Major, L.; Marczak, J.; Lisiecki, A. Laser Modification of the Materials Surface Layer—A Review Paper. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2012, 60, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Laser Tailoring the Surface Chemistry and Morphology for Wear, Scale and Corrosion Resistant Superhydrophobic Coatings. Langmuir 2018, 34, 7059–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudeja, J. Efficient Enhancement of Corrosion Resistance in Steel by Fiber Lasers. Res. Rev. Int. J. Multidiscip. 2018, 3, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Myers, N.; Bishop, G.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. Study of Surface Wettability on Fused Silica by Ultrafast Laser-Induced Micro/Nano-Surface Structures. J. Manuf. Process 2022, 79, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faas, S.; Bielke, U.; Weber, R.; Graf, T. Scaling the Productivity of Laser Structuring Processes Using Picosecond Laser Pulses at Average Powers of up to 420 W to Produce Superhydrophobic Surfaces on Stainless Steel AISI 316L. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Jauch, C.; Azarhoushang, B. Application of an Ultrashort-Pulsed Laser for Generation of Super-Hydrophobic Surfaces. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 7, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serles, P.; Nikumb, S.; Bordatchev, E. Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Functionalized Surfaces by Picosecond Laser Texturing. J. Laser Appl. 2018, 30, 032505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, F.H.; Liauw, C.M.; Benson, P.S.; Li, L.; Whitehead, K.A. Production of Hybrid Macro/Micro/Nano Surface Structures on Ti6Al4V Surfaces by Picosecond Laser Surface Texturing and Their Antifouling Characteristics. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milles, S.; Soldera, M.; Voisiat, B.; Lasagni, A.F. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Ice-Repellent Surfaces on Pure Aluminium Using Single and Multiscaled Periodic Textures. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Fan, P.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Lin, C. Superhydrophobic and Colorful Copper Surfaces Fabricated by Picosecond Laser Induced Periodic Nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 311, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, S.A.; Akram, M.; Bhat, J.A.; Hayes, J.J.; Singh, S.C.; ElKabbash, M.; Guo, C. Creating Superhydrophobic and Antibacterial Surfaces on Gold by Femtosecond Laser Pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; Xue, X.; Liang, C.; Yang, J.; Xing, R. Superhydrophobic Stainless Steel Bipolar Plates with Fractal Structure for Fuel Cells by Nanosecond Laser Ablation. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2200706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozioł, P.E.; Antończak, A.J.; Szymczyk, P.; Stępak, B.; Abramski, K.M. Conductive Aluminum Line Formation on Aluminum Nitride Surface by Infrared Nanosecond Laser. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 287, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavisse, L.; Sahour, M.C.; Jouvard, J.M.; Pillon, G.; Marco de Lucas, M.C.; Bourgeois, S.; Grevey, D. Growth of Titanium Oxynitride Layers by Short Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser Treatment of Ti Plates: Influence of the Cumulated Laser Fluence. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5515–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szubzda, B.; Antończak, A.; Kozioł, P.; Łazarek, Ł.; Stępak, B.; Łęcka, K.; Szmaja, A.; Ozimek, M. Corrosion Resistance of the AISI 304, 316 and 321 Stainless Steel Surfaces Modified by Laser. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 113, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Shiryaev, A.A. Comment on “Nanosecond Laser Textured Superhydrophobic Metallic Surfaces and Their Chemical Sensing Applications” by Duong V. Ta, Andrew Dunn, Thomas J. Wasley, Robert W. Kay, Jonathan Stringer, Patrick J. Smith, Colm Connaughton, Jonathan D. Shephard (Appl. Surf. Sci. 357 (2015) 248–254). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 379, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y. Insights into the Wettability Transition of Nanosecond Laser Ablated Surface under Ambient Air Exposure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 533, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Huang, Z.; Sett, S.; Oh, J.; Cha, H.; Li, L.; Feng, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Orejon, D.; et al. Atmosphere-Mediated Superhydrophobicity of Rationally Designed Micro/Nanostructured Surfaces. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4160–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Lu, S.; Xu, W.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Controllable Fabrication of Stable Superhydrophobic Surfaces on Iron Substrates. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40657–40667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.G.; Chun, D.-M. Simple and Fast Surface Modification of Nanosecond-Pulse Laser-Textured Stainless Steel for Robust Superhydrophobic Surfaces. CIRP Ann. 2020, 69, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.T.; Garcia-Girón, A.; Romano, J.M.; Huerta-Murillo, D.; Jagdheesh, R.; Walker, M.; Dimov, S.S.; Ocaña, J.L. Influence of Ambient Conditions on the Evolution of Wettability Properties of an IR-, Ns-Laser Textured Aluminium Alloy. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39617–39627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, J. One-Step Fabrication of an Anti-Corrosion Superhydrophobic Surface on Stainless Steel. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 076404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pou, P.; del Val, J.; Riveiro, A.; Comesaña, R.; Arias-González, F.; Lusquiños, F.; Bountinguiza, M.; Quintero, F.; Pou, J. Laser Texturing of Stainless Steel under Different Processing Atmospheres: From Superhydrophilic to Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhlke, C.A.; Anderson, T.P.; Li, P.; Lucis, M.J.; Roth, N.; Shield, J.E.; Terry, B.; Alexander, D.R. Superhydrophobic Metallic Surfaces Functionalized via Femtosecond Laser Surface Processing for Long Term Air Film Retention When Submerged in Liquid; Klotzbach, U., Washio, K., Arnold, C.B., Eds.; SPIE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015; p. 93510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M. The Behaviour of Fluoro- and Hydrocarbon Surfactants Used for Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Coatings at Solid/Water Interface. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 481, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Cao, Y.; Xue, W.; Zhu, D.; Liu, W. Picosecond Laser-Textured Stainless Steel Superhydrophobic Surface with an Antibacterial Adhesion Property. Langmuir 2019, 35, 11414–11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shi, J.; Huang, J.; Hu, J.; Lai, Y.; Chen, Z. Rational Designed Structured Superhydrophobic Iron Oxide Surface towards Sustainable Anti-Corrosion and Self-Cleaning. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 127768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Xu, C.; Rao, Y.; Wang, K. Preparation of Intricate Nanostructures on 304 Stainless Steel Surface by SiO2-Assisted HF Etching for High Superhydrophobicity. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradi, M.; Sever, T.; Gregorčič, P.; Kocijan, A. Short- and Long-Term Wettability Evolution and Corrosion Resistance of Uncoated and Polymer-Coated Laser-Textured Steel Surface. Coatings 2019, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Baig, U.; Gondal, M.A.; Akhtar, S.; Zubair, S.M. Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Surfaces Prepared by Spray-Coating of Facile Synthesized Cerium(IV) Oxide Nanoparticles for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 462, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanenko, A.M.; Shagieva, F.M.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Boinovich, L.B. Nanosecond Laser Micro- and Nanotexturing for the Design of a Superhydrophobic Coating Robust against Long-Term Contact with Water, Cavitation, and Abrasion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelyanenko, A.M.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Boinovich, L.B. Synthesis of Wear-Resistant Superhydrophobic Coatings via Laser Micro- and Nanotexturing. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2015, 10, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.G.; Chun, D.-M. Ultrafast and Eco-Friendly Fabrication Process for Robust, Repairable Superhydrophobic Metallic Surfaces with Tunable Water Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 28348–28358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganne, A.; Maslakov, K.I.; Gavrilov, A.I. Anti-Icing Properties of Superhydrophobic Stainless Steel Mesh at Subzero Temperatures. Surf. Innov. 2017, 5, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trdan, U.; Hočevar, M.; Gregorčič, P. Transition from Superhydrophilic to Superhydrophobic State of Laser Textured Stainless Steel Surface and Its Effect on Corrosion Resistance. Corros. Sci. 2017, 123, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Yan, W.; Zhu, W.; Liu, H. Biomimetic Fabrication of Robust Self-Assembly Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Corrosion Resistance Properties on Stainless Steel Substrate. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 43937–43949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Guan, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y. Nanosecond Laser Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surface on 316L Stainless Steel and Corrosion Protection Application. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 604, 125259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Xing, K.; Yang, Z. Study on Selective Laser Melting 316L Stainless Steel Parts with Superhydrophobic Surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 533, 147445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y. A Contrastive Investigation on Anticorrosive Performance of Laser-Induced Super-Hydrophobic and Oil-Infused Slippery Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 138, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, S.; Bonagani, S.K.; Majumdar, A.G.; Kain, V.; Subramanian, M.; Maiti, N.; Nilaya, J.P. Nanosecond Laser Surface Texturing of Type 316L Stainless Steel for Contact Guidance of Bone Cells and Superior Corrosion Resistance. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 42, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, B.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z. Formation Mechanism of Superhydrophobicity of Stainless Steel by Laser-Assisted Decomposition of Stearic Acid and Its Corrosion Resistance. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 153, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Modestov, A.D.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Shiryaev, A.A.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Dvoretskaya, O.V.; Ganne, A.A. Corrosion Behavior of Superhydrophobic Aluminum Alloy in Concentrated Potassium Halide Solutions: When the Specific Anion Effect Is Manifested. Corros. Sci. 2016, 112, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wu, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y. Prediction of Film Performance by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Corros. Sci. 2015, 99, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, N.; Zou, J.; Lin, X.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, W.; et al. Super-Hydrophobicity and Corrosion Resistance of Laser Surface Textured AISI 304 Stainless Steel Decorated with Hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (HDTMS). Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, B.S.; Jha, P.; Mahanti, A.; Singh, K.; Kain, V.; Sinha, S. Surface Micro-Structuring of Type 304 Stainless Steel by Femtosecond Pulsed Laser: Effect on Surface Wettability and Corrosion Resistance. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Suryawanshi, S.R.; More, M.A.; Basu, S.; Sinha, S. Field Emission Study from an Array of Hierarchical Micro Protrusions on Stainless Steel Surface Generated by Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armelin, E.; Moradi, S.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Alemán, C. Designing Stainless Steel Surfaces with Anti-Pitting Properties Applying Laser Ablation and Organofluorine Coatings. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhuang, J.; Qi, H.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Y. Laser-Chemical Treated Superhydrophobic Surface as a Barrier to Marine Atmospheric Corrosion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 401, 126255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieazad, M.; Jaffer, J.; Cui, C.; Duan, X.; Nasiri, A. Nanosecond Laser Fabrication of Hydrophobic Stainless Steel Surfaces: The Impact on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance. Materials 2018, 11, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sataeva, N.E.; Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, K.A.; Domantovsky, A.G.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Laser-Assisted Processing of Aluminum Alloy for the Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Coatings Withstanding Multiple Degradation Factors. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 397, 125993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilling, N.B.; Bedworth, R.E. The Oxidation of Metals at High Temperatures. J. Inst. Met. 1923, 29, 529–591. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).