Titanium Carbide Coating for Hafnium Hydride Neutron Control Rods: In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. In Situ XRD Diffraction of the HfHx Samples
3. Results
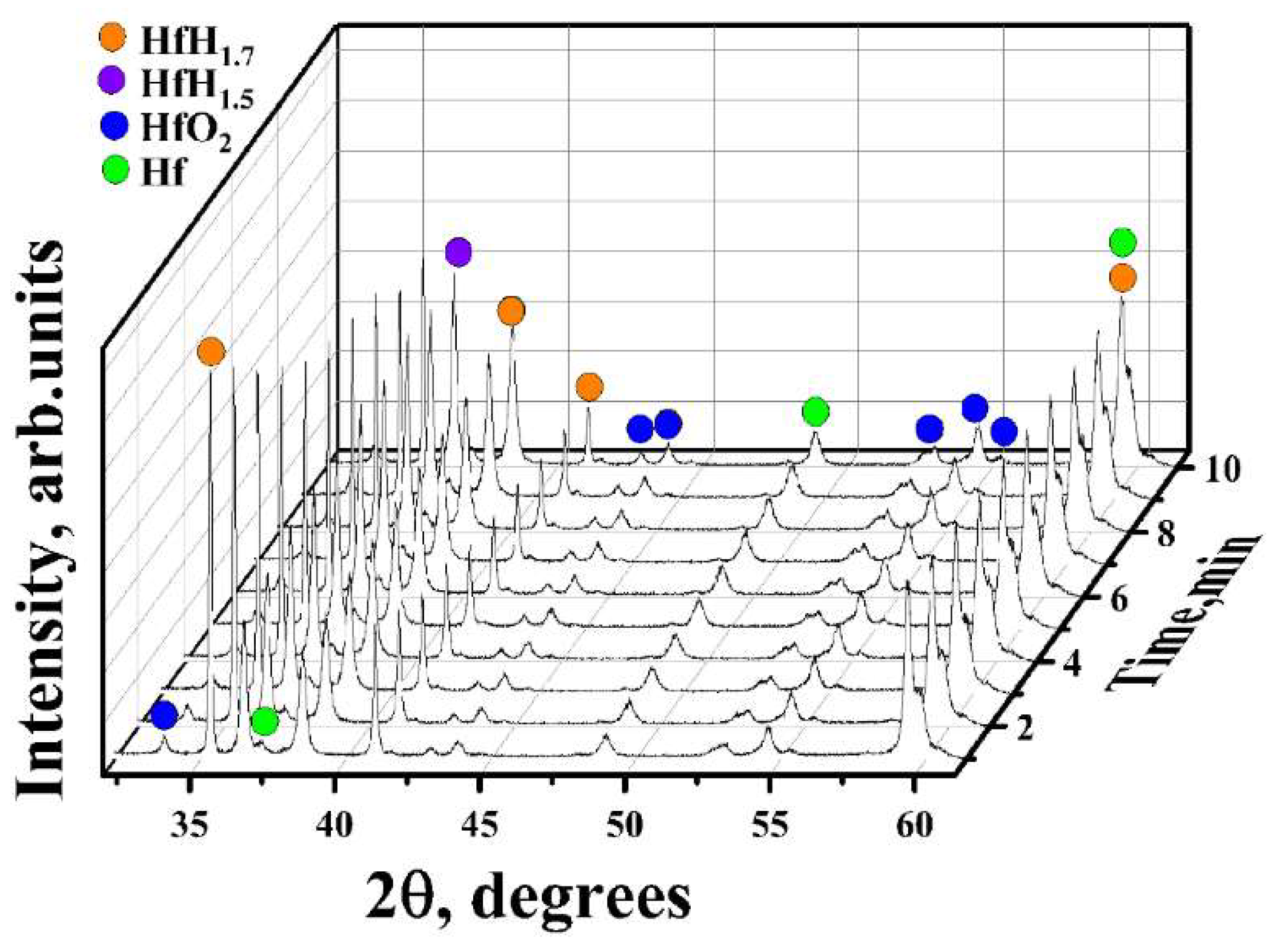
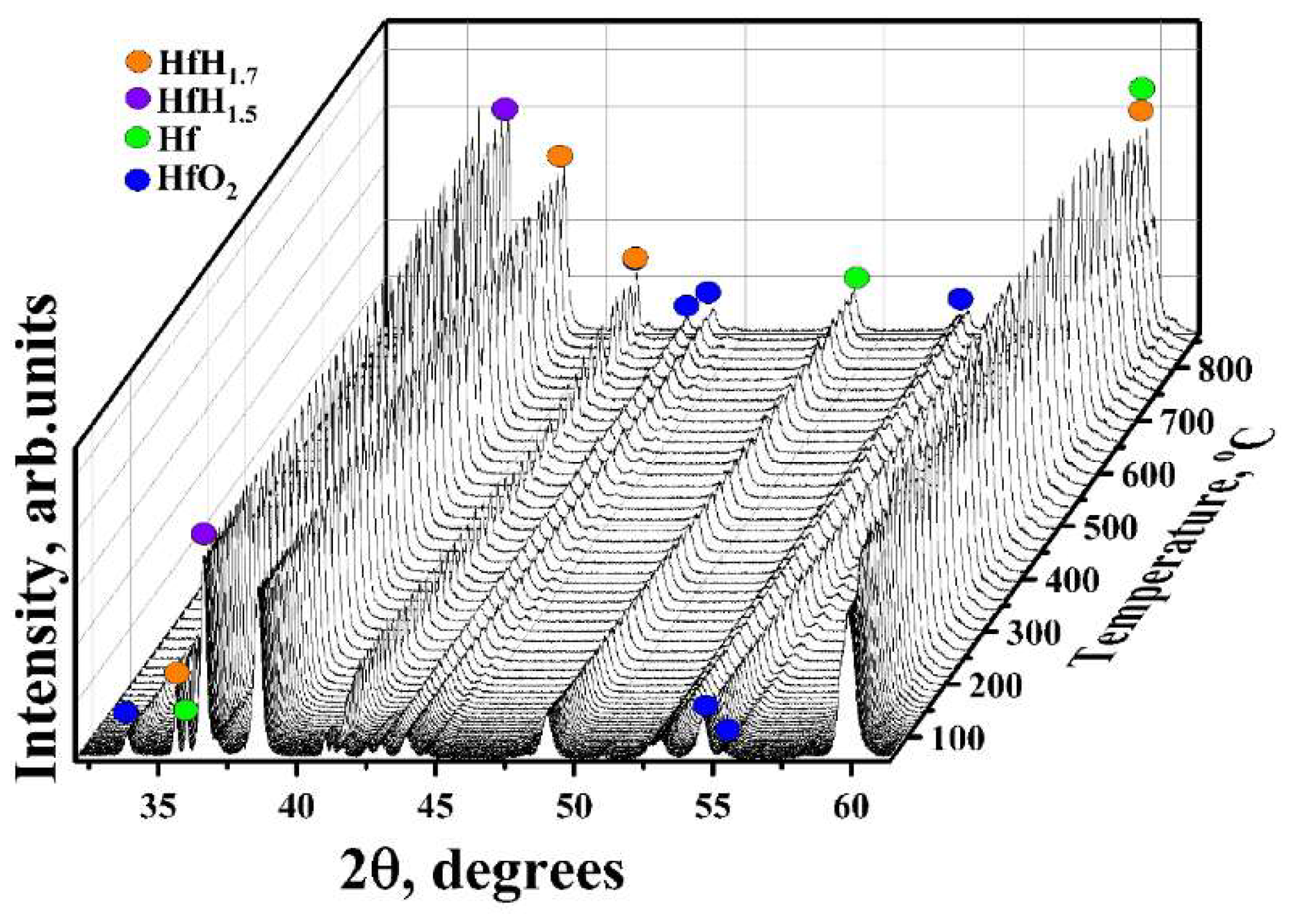
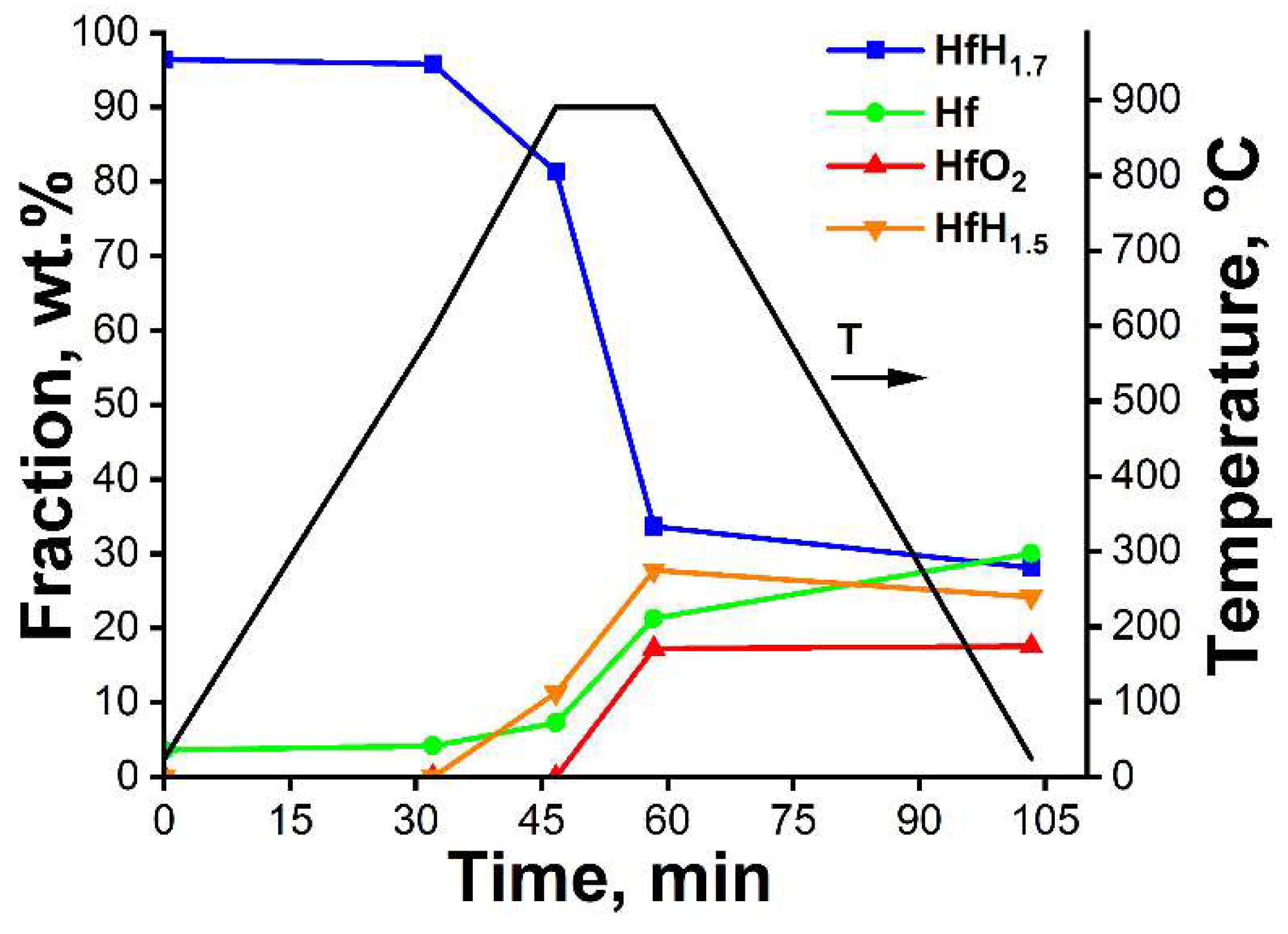
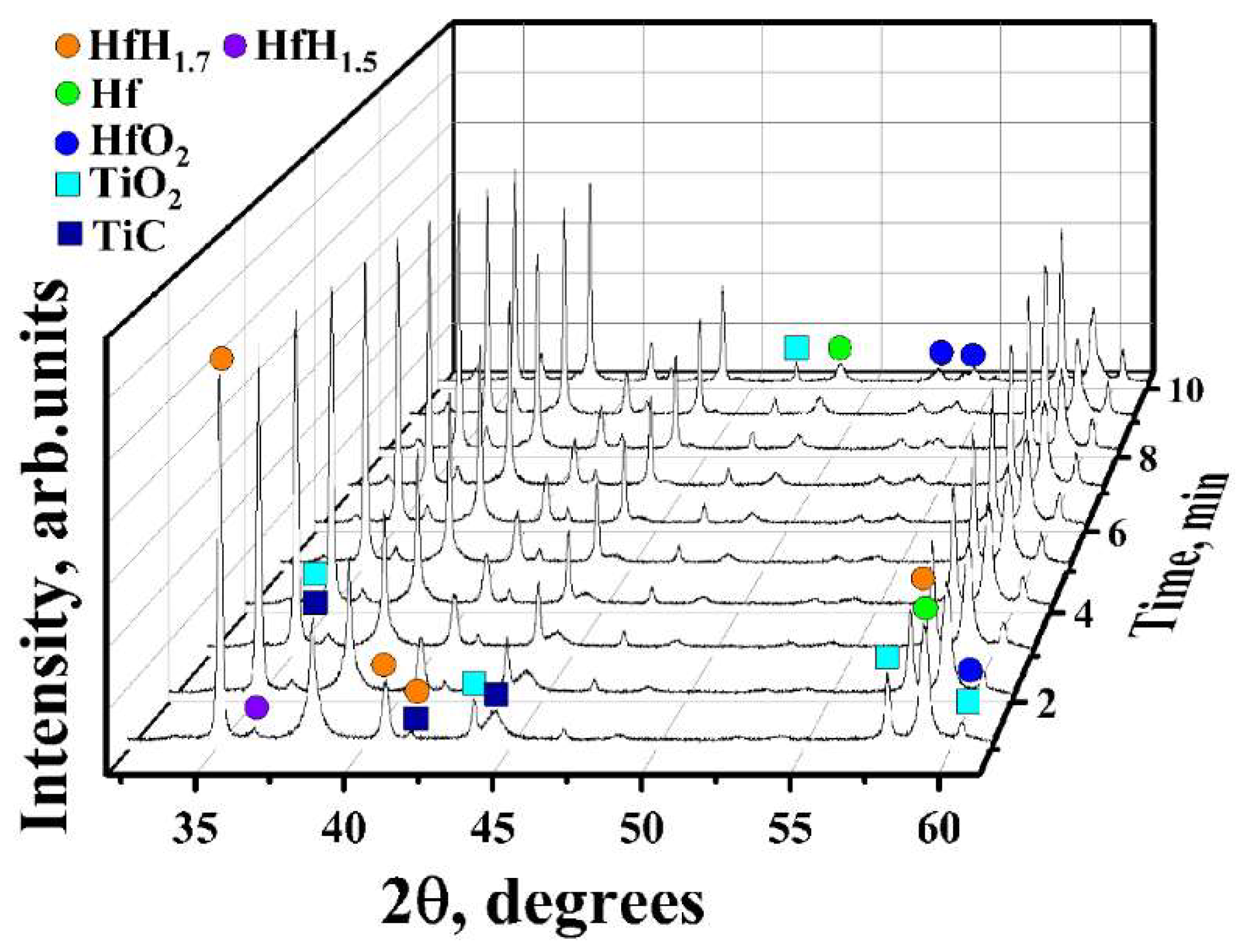
3.1. In Situ XRD Study of the Uncoated HfHx Sample
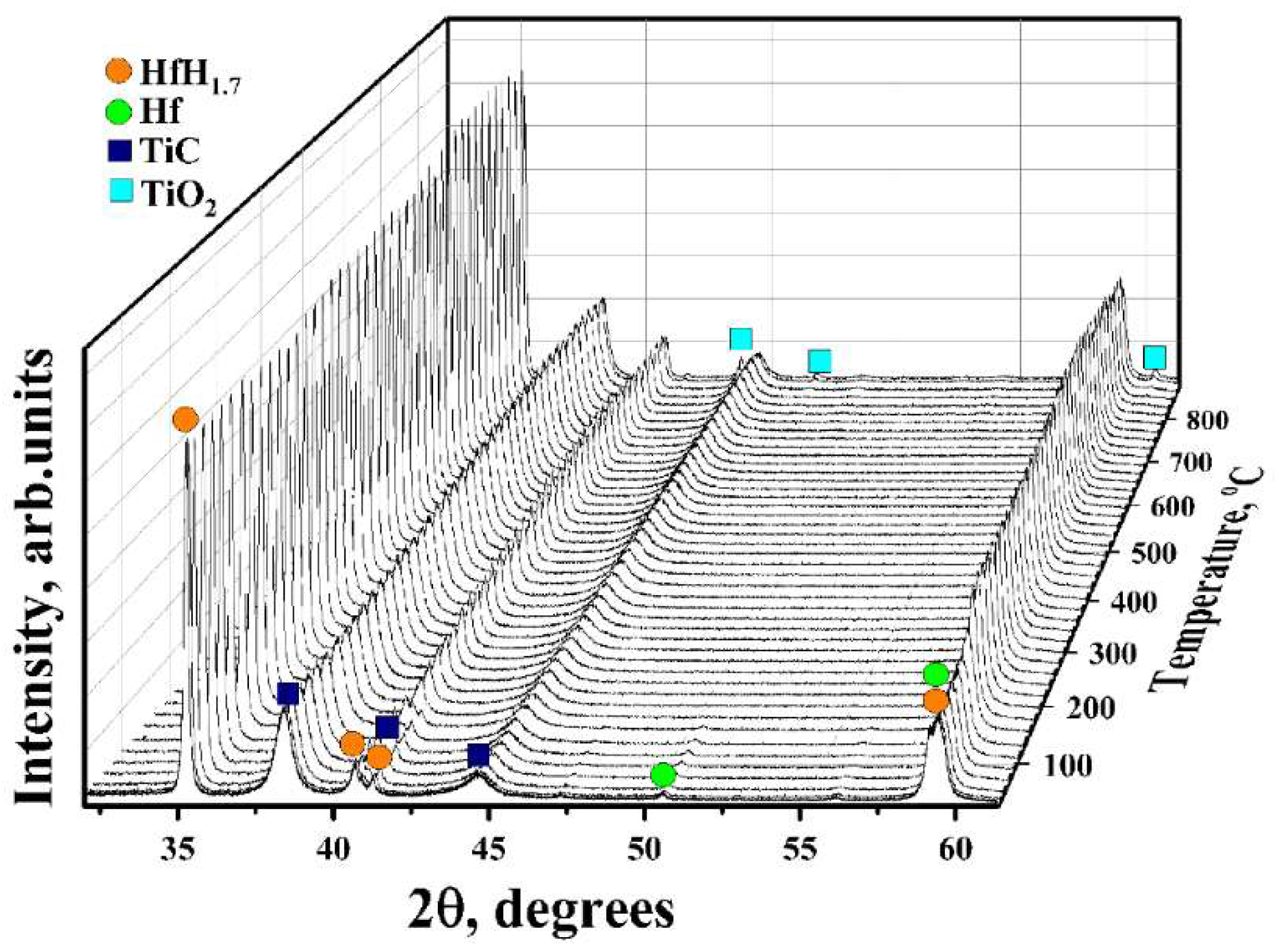
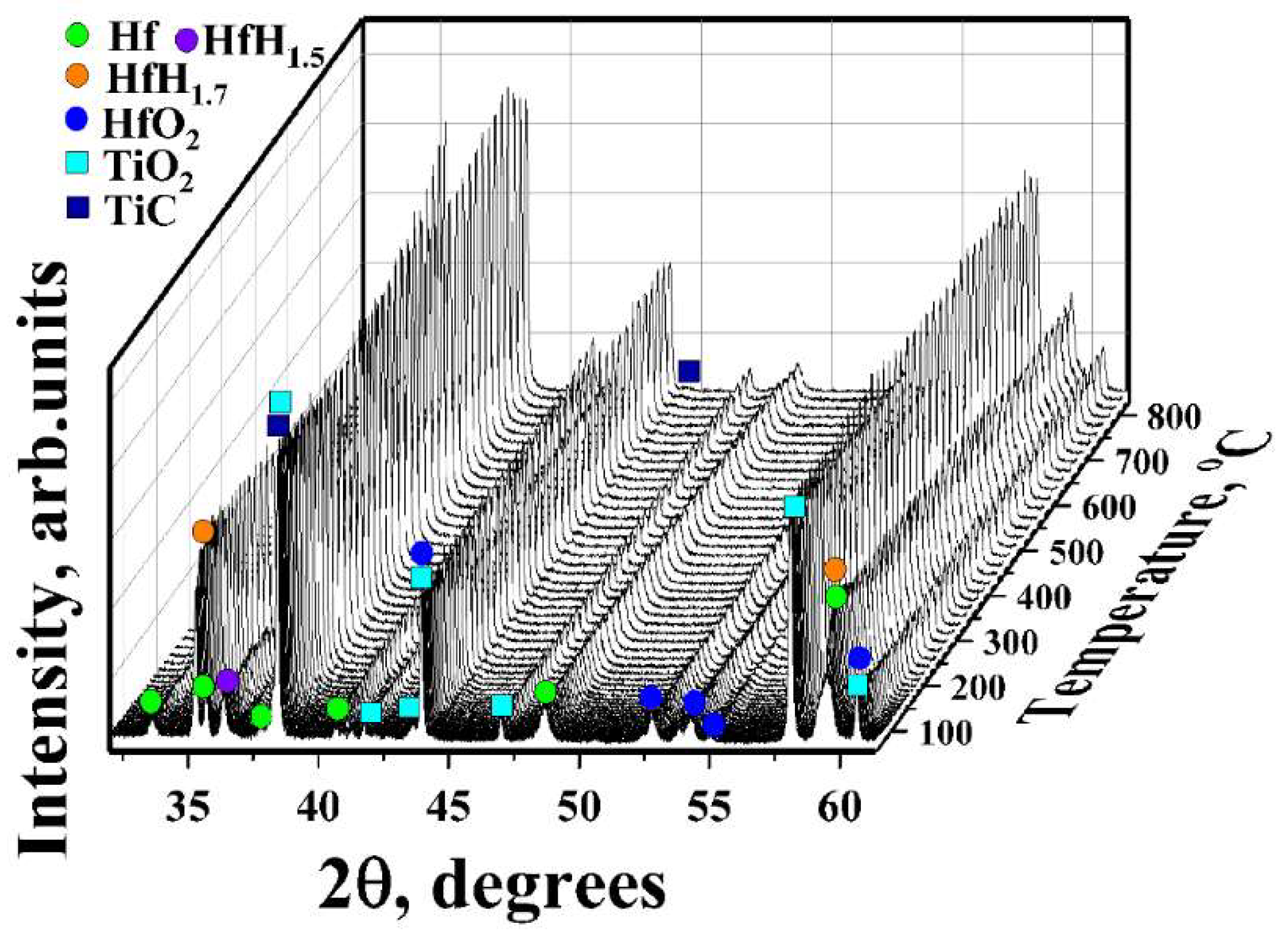
3.2. In Situ XRD Study of the TiC-Coated HfHx Sample
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
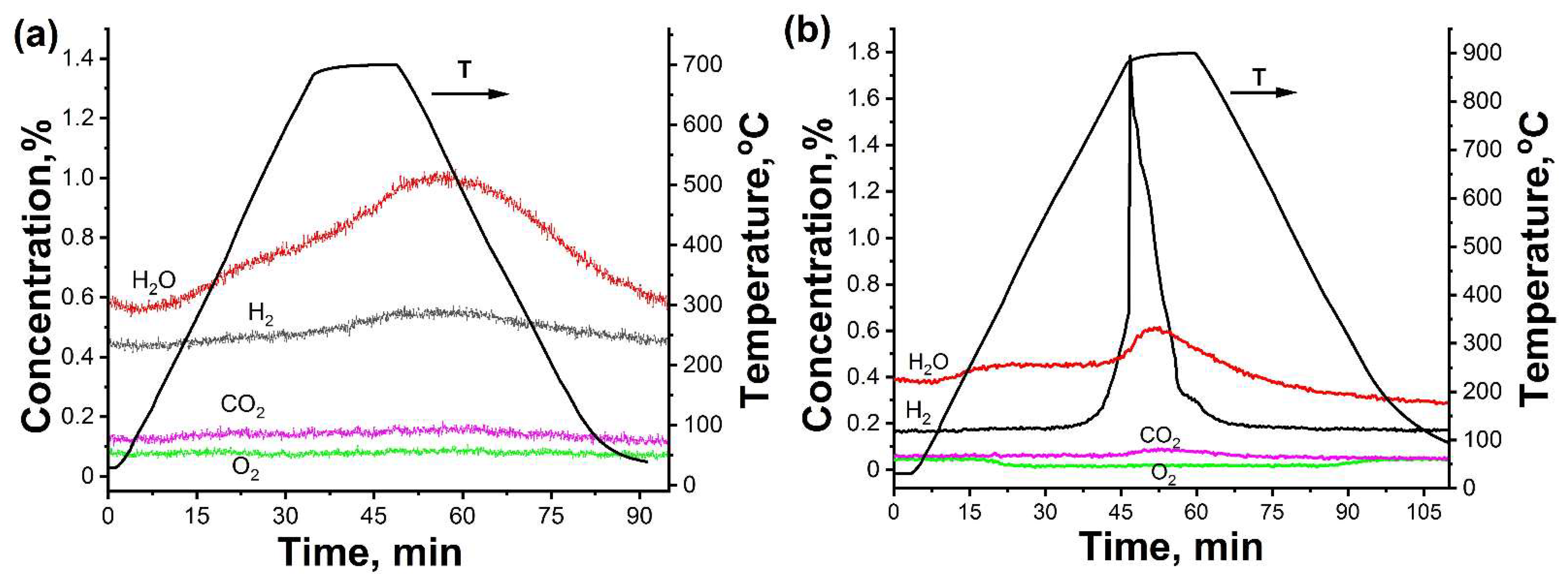
- In the case of the uncoated HfHx sample, the HfH1.7 phase was decomposed to the HfH1.5 and Hf phases, followed by an intensive hydrogen release starting from 700 °C.
- (2)
- The formation of an outer HfO2 layer can limit hydrogen release from hafnium hydrides, but it was only observed after a significant decrease in hydrogen flow from the uncoated HfHx sample.
- (3)
- The TiC coating can be used as a protective layer for the HfHx sample at high temperatures (700 °C). However, this coating was partially oxidized into TiO2 at higher temperatures, and then, after some period, was not protective.
- (4)
- Due to the failure of the TiC coating, the fast hydrogen release from the TiC-coated HfHx samples was observed at 900 °C.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simeone, D.; Gosset, D.; Quirion, D.; Deschanels, X. Study of B4C microstructure evolution under neutron irradiation by X-ray diffraction profiles analysis. J. Nucl. Mater. 1999, 264, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Buiron, L.; Sciora, P.; Kooyman, T. Designs of control rods with strong absorption ability for small fast reactors. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2020, 368, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risovany, V.D.; Zakharov, A.V. Next generation control rods for fast neutron nuclear reactors. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1475, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konashi, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Terai, T.; Yamawaki, M.; Kurosaki, K.; Itoh, K. Development of advanced control rod of hafnium hydride for fast reactors. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants, Reno, NV, USA, 4–8 June 2006; pp. 2213–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, G.L.; Donnelly, R.G.; Martin, W.R. Irradiation Behavior of Boron Carbide. Nucl. Technol. 1972, 16, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konashi, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Itoh, K.; Hirai, M.; Sato, J.; Kurosaki, K.; Suzuki, A.; Matsumura, Y.; Abe, S. Study on an innovative fast reactor utilizing hydride neutron absorber—Final report of phase I study. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants 2010, ICAPP 2010, Anaheim, CA, USA, 8–12 June 2010; pp. 2098–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Risovaniy, V.D.; Zaharov, A.V.; Klochkov, E.P.; Varlashova, E.E.; Suslov, D.N.; Ponomarenko, A.B.; Scheglov, A.V. Dysprosium and hafnium base absorbers for advanced WWER control rods. In Proceedings of the Technical Committee Meeting, Control Assembly Materials for Water Reactors: Experience, Performance and Perspectives, Vienna, Austria, 12–15 October 1998; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Shirayanagi, H.; Fukumoto, T.; Shiga, S. Advanced control rods for Japanese BWR Plants Proceedings, IAEA. In Proceedings of the Technical Committee Meeting on Advances in Control Rod Assembly Materials for Water Reactors, Vienna, Austria, 29 November–2 December 1993; p. 135. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, T.; Konashi, K. Development of hydride absorber for fast reactor—Application of hafnium hydride to control rod of large fast reactor. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2009, 46, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, H.; Shallenberger, J.; Hollein, D.; Hott, C. Development of hafnium and comparison with other pressurized water reactor control rod materials. Nucl. Technol. 1982, 59, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Moriwaki, H.; Ohkubo, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Konashi, K. Application of hafnium hydride control rod to large sodium cooled fast breeder reactor. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2014, 278, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbert-Banti, S.; Viretto, A.; Barrachin, M.; Tanguy, C.; Steinbrück, M.; Stuckert, J. Hafnium oxidation at high temperature in steam. J. Nucl. Mater. 2021, 550, 152901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Kurosaki, K.; Muta, H.; Uno, M.; Konashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Thermal conductivity of hafnium hydride. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2009, 46, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Konashi, K. Investigation on electronic, mechanical and thermal properties of Hf–H system. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 443, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dottor, M.; Crivello, J.C.; Laversenne, L.; Joubert, J.M. Experimental determination of the H–Hf phase diagram using in situ neutron diffraction. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 937, 168353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetegrove, M.; Duarte, M.J.; Taube, K.; Rohloff, M.; Gopalan, H.; Scheu, C.; Dehm, G.; Kruth, A. Preventing Hydrogen Embrittlement: The Role of Barrier Coatings for the Hydrogen Economy. Hydrogen 2023, 4, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Kang, L.; Zhang, P.; Bai, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, B.; Xu, Y. TiC–Fe gradient coating with high hardness and interfacial adhesion strength on cast iron prepared by in-situ solid-phase diffusion method. Vacuum 2023, 215, 112336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Kumar, R. Investigation on wear behaviour of TiC/Co/Y2O3 metal matrix composite coating developed on AZ91D Mg alloy by plasma transferred arc cladding process. Mater. Lett. 2024, 355, 135457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Bi, W.; Li, C.; Sun, X.; Ma, G.; Wu, D. TiC ceramic coating reinforced 304 stainless steel components fabricated by WAAM-LC integrated hybrid manufacturing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 465, 129635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razumov, N.; Masaylo, D.; Kovalev, M.; Volokitina, E.; Mazeeva, A.; Popovich, A. Structure and Wear Resistance of Composite TiC-NiMo Coating Produced by L-DED on Ti-6Al-4V Substrate. Metals 2023, 13, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Iseki, M. Fast neutron damage in TiC1−x. J. Nucl. Mater. 1988, 152, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Guinan, M.W.; Iida, T.; Iseki, M. Fusion neutron irradiation of TiC. J. Nucl. Mater. 1985, 133–134, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, E.; Slavov, L.; Demir, E.; Abdurakhimov, B.A.; Doroshkevich, A.S.; Aliyev, O.A.; Jabarov, S.H.; Valizade, A.H.; Mauyey, B.; Horodek, P.; et al. Microstructural evolution of TiC nano powders under fast neutron irradiation: A multi-technique analysis. Vacuum 2023, 215, 112338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larhlimi, H.; Ghailane, A.; Makha, M.; Alami, J. Magnetron sputtered titanium carbide-based coatings: A review of science and technology. Vacuum 2022, 197, 110853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Kurosaki, K.; Muta, H.; Uno, M.; Konashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Thermomechanical properties of hafnium hydride. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudinin, V.A. Hot target magnetron sputtering enhanced by RF-ICP source: Microstructure and functional properties of CrNx coatings. Vacuum 2022, 200, 111020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, D.; Bu, H.; Deng, L.; Liu, H.; Yuan, P.; Du, P.; Song, H. XRD-based quantitative analysis of clay minerals using reference intensity ratios, mineral intensity factors, Rietveld, and full pattern summation methods: A critical review. Solid Earth Sci. 2018, 3, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, M.H. Hafnium-hydrogen. Solid State Phenom. 1996, 49, 331–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrtanov, M.; Garanin, G.; Kashkarov, E.; Pushilina, N.; Kudiiarov, V.; Murashkina, T. Laboratory X-ray diffraction complex for in situ investigations of structural phase evolution of materials under gaseous atmosphere. Metals 2020, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrtanov, M.; Kudiiarov, V.; Kashkarov, E.; Shmakov, A.; Vinokurov, Z.; Babikhina, M.; Zolotarev, K.V. Application of synchrotron radiation for In Situ XRD investigation of zirconium hydrides formation at gas-phase hydrogenation. Phys. Procedia 2016, 84, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, N.; Tsuchiya, B.; Oku, M.; Shikama, T.; Wagatsuma, K. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study on initial oxidation of hafnium hydride fractured in an ultra-high vacuum. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 6844–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavarini, S.; Bes, R.; Millard-Pinard, N.; Cardinal, S.; Peaucelle, C.; Perrat-Mabilon, A.; Garnier, V.; Gaillard, C. A comparative study of TiN and TiC: Oxidation resistance and retention of xenon at high temperature and under degraded vacuum. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 014906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Kozeki, M. Oxidation of TiC at low temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Jo, I.; Kim, H.; Kwon, H.T.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, S.B. Effect of TiC addition on surface oxidation behavior of SKD11 tool steel composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 415, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Hashino, T. Solubility and diffusivity of hydrogen and deuterium in alpha-hafnium at high temperatures. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1990, 2, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| QTi, W/cm2 | QC, W/cm2 | t, h | h, µm | Ub, V | js, mA/cm2 | Tmax, °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15.7 | 23.6 | 2.5 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | −50 | 10 | 253 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sidelev, D.V.; Pirozhkov, A.V.; Mishchenko, D.D.; Syrtanov, M.S. Titanium Carbide Coating for Hafnium Hydride Neutron Control Rods: In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study. Coatings 2023, 13, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122053
Sidelev DV, Pirozhkov AV, Mishchenko DD, Syrtanov MS. Titanium Carbide Coating for Hafnium Hydride Neutron Control Rods: In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study. Coatings. 2023; 13(12):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122053
Chicago/Turabian StyleSidelev, Dmitrii V., Alexey V. Pirozhkov, Denis D. Mishchenko, and Maxim S. Syrtanov. 2023. "Titanium Carbide Coating for Hafnium Hydride Neutron Control Rods: In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study" Coatings 13, no. 12: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122053
APA StyleSidelev, D. V., Pirozhkov, A. V., Mishchenko, D. D., & Syrtanov, M. S. (2023). Titanium Carbide Coating for Hafnium Hydride Neutron Control Rods: In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study. Coatings, 13(12), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122053







