Electronic Structures and Magnetic Properties of Co/Mn Co-Doped ZnO Nanowire: First-Principles LDA+U Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
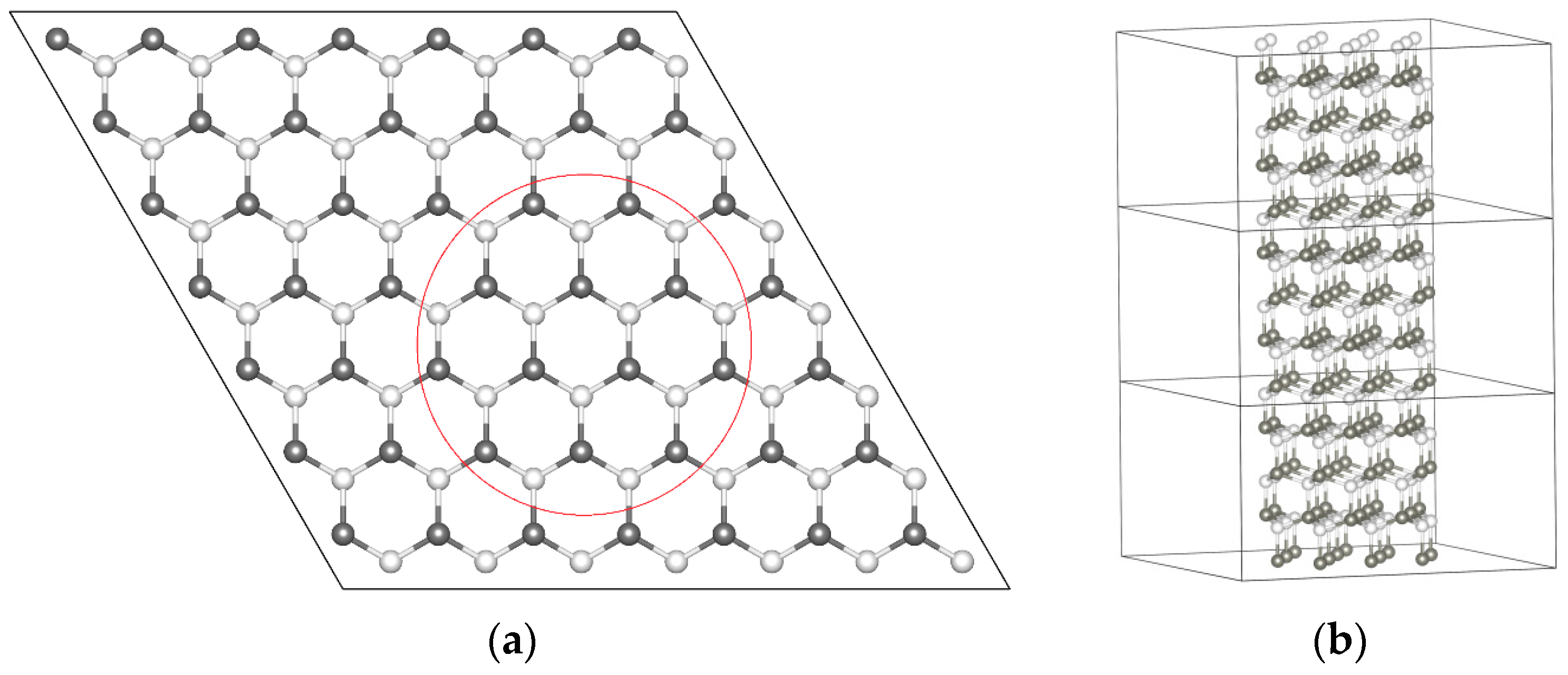
2. Theoretical Model and Calculation Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geometric Structure and Stability Analysis
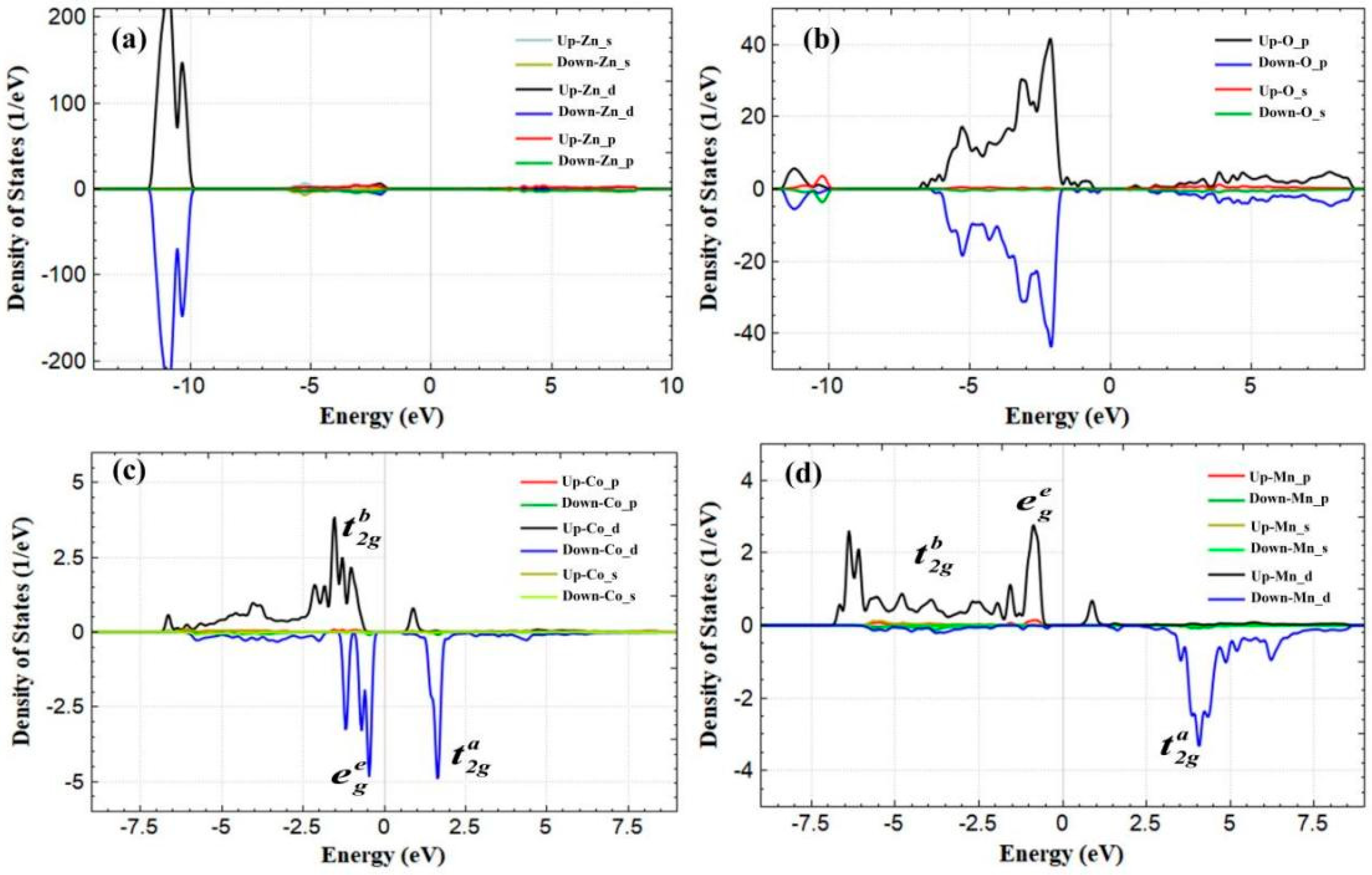
3.2. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ando, K.O. Seeking room-temperature ferromagnetic semiconductors. Science 2006, 312, 1883–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.F. Applications of modern ferroelectrics. Science 2007, 315, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Bergqvist, L.; Kudrnovský, J.; Dederichs, P.H.; Eriksson, O.; Turek, I.; Sanyal, B.; Bouzerar, G.; Katayama-Yoshida, H.; Dinh, V.A.; et al. First-principles theory of dilute magnetic semiconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2014, 82, 1633–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, M.H.N.; Zheng, R.K.; Li, S.; Ringer, S.R. First-principles investigation of electrical and magnetic properties of ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductors codoped with H. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H. Properties of ferromagnetic III–V semiconductors. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, T.; Ohno, H.; Matsukura, F.; Cibert, J.; Ferrand, D. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 2000, 287, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.K.; Wong, G.K.L.; Yu, P.; Kawasaki, M.; Ohtomo, A.; Koinuma, H.; Segawa, Y. Room-temperature ultraviolet laser emission from self-assembled ZnO microcrystallite thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 3270–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pazhanivelu, V.; Selvadurai, A.P.B.; Zhao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, R.; Murugaraj, R. Room temperature ferromagnetism in Mn doped ZnO:Co nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2016, 481, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhan, W.S.; Wang, W.G.; Xiao, J.Q. Room temperature ferromagnetism in two-step-prepared co-doped ZnO bulks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 022508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathiotakis, N.N.; Andriotis, A.N.; Menon, M. Codoping: A possible pathway for inducing ferromagnetism in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 193311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.B.; Shi, L.J.; Zou, B.S. Magnetic exciton relaxation and spin-spin interaction by the time-delayed photoluminescence spectra of ZnO: Mn nanowires. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 10353–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Wang, T.C.Y.; Tang, J.S.; Nie, T.X.; Jiang, W.J.; Chu, C.P.; Arafin, S.; He, L.; Afsal, M.; Chen, L.J.; et al. Electric-field control of ferromagnetism in Mn-doped ZnO nanowires. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geburt, S.; Röder, R.; Kaiser, U.; Chen, L.M.; Chu, M.H.; Ruiz, J.S.; Criado, G.M.; Heimbrodt, W.; Ronning, C. Intense intra-3d luminescence and waveguide properties of single co-doped ZnO nanowires. Phys. Status Solidi 2013, 7, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, G.Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Li, Y. Solution synthesis, optical and magnetic properties of Zn1-xCoxO nanowires. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3733–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, J.; Kong, W.; Ye, B. Coexistence of superparamagnetism and ferromagnetism in co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline films. Scr. Mater. 2013, 69, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, J.J.; Barrero, C.A.; Punnoose, A. Combination of defects plus mixed valence of transition metals: A strong strategy for ferromagnetic enhancement in ZnO nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 8969–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.Q.; Dai, Y.Q.; Han, B.Q.; Zhu, W.L.; Li, X.C.; Li, C.B. Enhanced gas-sensitivity and ferromagnetism performances by the Ni doping induced oxygen vacancies in (Mn, Ni) codoped ZnO nanorods. Appl. Sur. Sci. 2019, 490, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, L.; Anjum, S.; Waseem, S.; Javed, S.; Ramay, S.M.; Atiq, S. Effect of Co and Ni codoping on the structural, magnetic, electrical and optical properties of ZnO. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 84, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Gu, Y.S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Facile synthesis of highly uniform Co/Mn-codoped ZnO nanowires: Optical, electrical, and magnetic properties. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.B.; Yuan, C.S.; Lu, M.H.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhu, S.N.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.F. Magnetic and transport properties of (Mn, Co) codoped ZnO films prepared by radio-frequency magnetron cosputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 053908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Jha, R. Analysis of structural, optical and magnetic properties of Fe/Co co-doped ZnO nanocrystals. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 8488–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J.J.; Barrero, C.A.; Punnoose, A. Evidence of ferromagnetic signal enhancement in Fe and Co codoped ZnO nanoparticles by increasing superficial Co3+ content. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 13203–13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Meng, D.W.; Liu, C.Z.; He, X.W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xie, J. Structure and ferromagnetism of Fe-doped and Fe-and Co-codoped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by homogeneous precipitation method. Mate. Lett. 2012, 86, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Li, G.; Duan, L.; Li, L.; Dou, X.; Zhang, L. Formation of ZnO nanosheets with room-temperature ferromagnetism by co-doping with Mn and Ni. Scripta Mater. 2009, 60, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Jha, R. Transition metal (Co, Mn) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Effect on structural and optical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.L.; Gu, Z.B.; Lu, M.H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.T.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, G.X.; Heng, H.; Chen, Y.F. Raman spectroscopy of (Mn, Co)-codoped ZnO films. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 123515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.R.; Qu, D.L.; Zhao, W.X.; Tong, Y.X. Electrochemical deposition of (Mn, Co)-codoped ZnO nanorod arrays without any template. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.S.; Koeseoglu, Y.; Guener, S.; Kazan, S.; Kocaman, B.; Ndikilar, C.E. Synthesis and characterization of Mn and Co codoped ZnO nanoparticles. Superlattice. Microst. 2015, 83, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jin, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H. Room temperature ferromagnetic Cr–Ni codoped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors synthesized by hydrothermal method under high pulsed magnetic field. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hongzhiwei Technology, Device Studio, Version 2021A, China, 2021. Available online: https://iresearch.net.cn/loudSoftware (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Dudarev, S.L.; Dudarev, G.A.; Savrasov, S.Y.; Humphreys, C.J.; Sutton, A.P. Electron-energy-loss spectra and the structural stability of nickel oxide: An LSDA+U study. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavender, A.T.; Varma, M.C.; Deb, S.; Hong, N.H. Tuning the band-gap of zinc oxide by first principle studies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1832, 120012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.G.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.F. Correlation effects on lattice relaxation and electronic structure of ZnO within the GGA+U formalism. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2013, 117, 26029–26039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, M. Magnetic and optical properties of Cu-doped ZnO nanosheet: First-principles calculations. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2013, 53, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössler, U. Energy Bands of Hexagonal II-VI Semiconductors. Phys. Rev. 1969, 184, 733–738. [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne, E.; Levin, I.; Wu, H.; Llobet, A. Magnetic structure of bixbyite alpha-Mn2O3: A combined DFT+U and neutron diffraction study. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 184413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cen, W.L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.B.; Wang, H.Q.; Weng, X.L. A theoretic insight into the catalytic activity promotion of CeO2 surfaces by Mn doping. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 5769–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez-Ornelas, J.I.; Perez, R.P.; Fernández-Escamilla, H.N.; Bracamontes, E.M.; Guerrero-Sánchez, J. Understanding the role of oxygen vacancies in the stability of ZnO (0001)-(1×3) surface reconstructions. J. Phys.Chem. C 2021, 125, 1932–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Katayama-Yoshida, H. First principles materials design for semiconductor spintronics. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2002, 17, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouni, N.; El Kenz, A.; Ez-Zahraouy, H.; Loulidi, M.; Benyoussef, A.; Bououdina, M. Stabilization of ferromagnetism in (Cr, V) co-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 340, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Fan, G.; Xing, H.; Zheng, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, L. Electronic structure and magnetism of V-doped AlN. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 331, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Dederics, P.H.; Katayama-Yoshida, H. Curie temperatures of III–V diluted magnetic semiconductors calculated from first principles. Europhys. Lett. 2003, 61, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
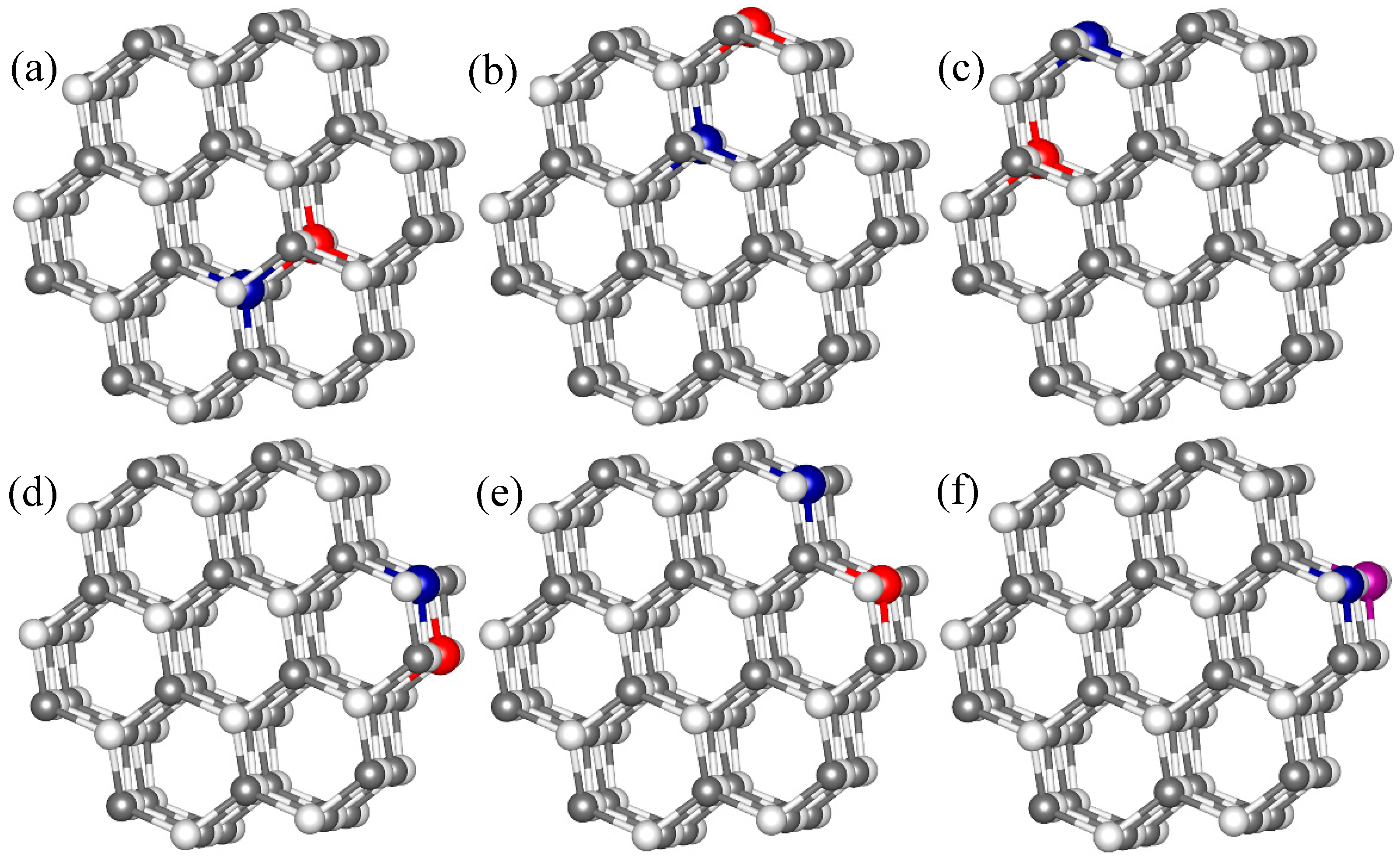


| ΔE(eV) | Δε(eV) | Coupling | dCo−O (Å) | dMn−O (Å) | dCo−Mn (Å) | μCo (μB) | μMn (μB) | μO (μB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.542 | 0.000 | FM | 1.815 | 1.863 | 2.407 | 2.94 | 5.08 | −0.346 |
| II | 0.236 | 0.118 | FM | 1.917 | 1.786 | 2.193 | 2.83 | 4.98 | −0.014 |
| III | 0.162 | 0.362 | FM | 1.778 | 1.731 | 2.669 | 2.80 | 4.96 | 0.033 |
| IV | 0.391 | 0.133 | FM | 1.763 | 1.680 | 3.211 | 2.86 | 5.01 | −0.136 |
| V | 0.145 | 0.397 | FM | 1.743 | 1.692 | 3.045 | 2.78 | 4.92 | 0.028 |
| VI | 0.107 | 0.417 | FM | 1.858 | 1.802 | 5.361 | 2.74 | 4.86 | 0.064 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Wu, Q.; Ning, J.; Zhang, B.; Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W. Electronic Structures and Magnetic Properties of Co/Mn Co-Doped ZnO Nanowire: First-Principles LDA+U Studies. Coatings 2023, 13, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13030567
Xue S, Zhang L, Liu G, Wu Q, Ning J, Zhang B, Yang S, Zhang F, Zhang W. Electronic Structures and Magnetic Properties of Co/Mn Co-Doped ZnO Nanowire: First-Principles LDA+U Studies. Coatings. 2023; 13(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Suqin, Lei Zhang, Gaihui Liu, Qiao Wu, Jing Ning, Bohang Zhang, Shenbo Yang, Fuchun Zhang, and Weibin Zhang. 2023. "Electronic Structures and Magnetic Properties of Co/Mn Co-Doped ZnO Nanowire: First-Principles LDA+U Studies" Coatings 13, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13030567
APA StyleXue, S., Zhang, L., Liu, G., Wu, Q., Ning, J., Zhang, B., Yang, S., Zhang, F., & Zhang, W. (2023). Electronic Structures and Magnetic Properties of Co/Mn Co-Doped ZnO Nanowire: First-Principles LDA+U Studies. Coatings, 13(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13030567






