Geometric Structures for Sialon Ceramic Solid End Mills and Its Performance in High-Speed Milling of Nickel-Based Superalloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Workpiece and Ceramic Tools
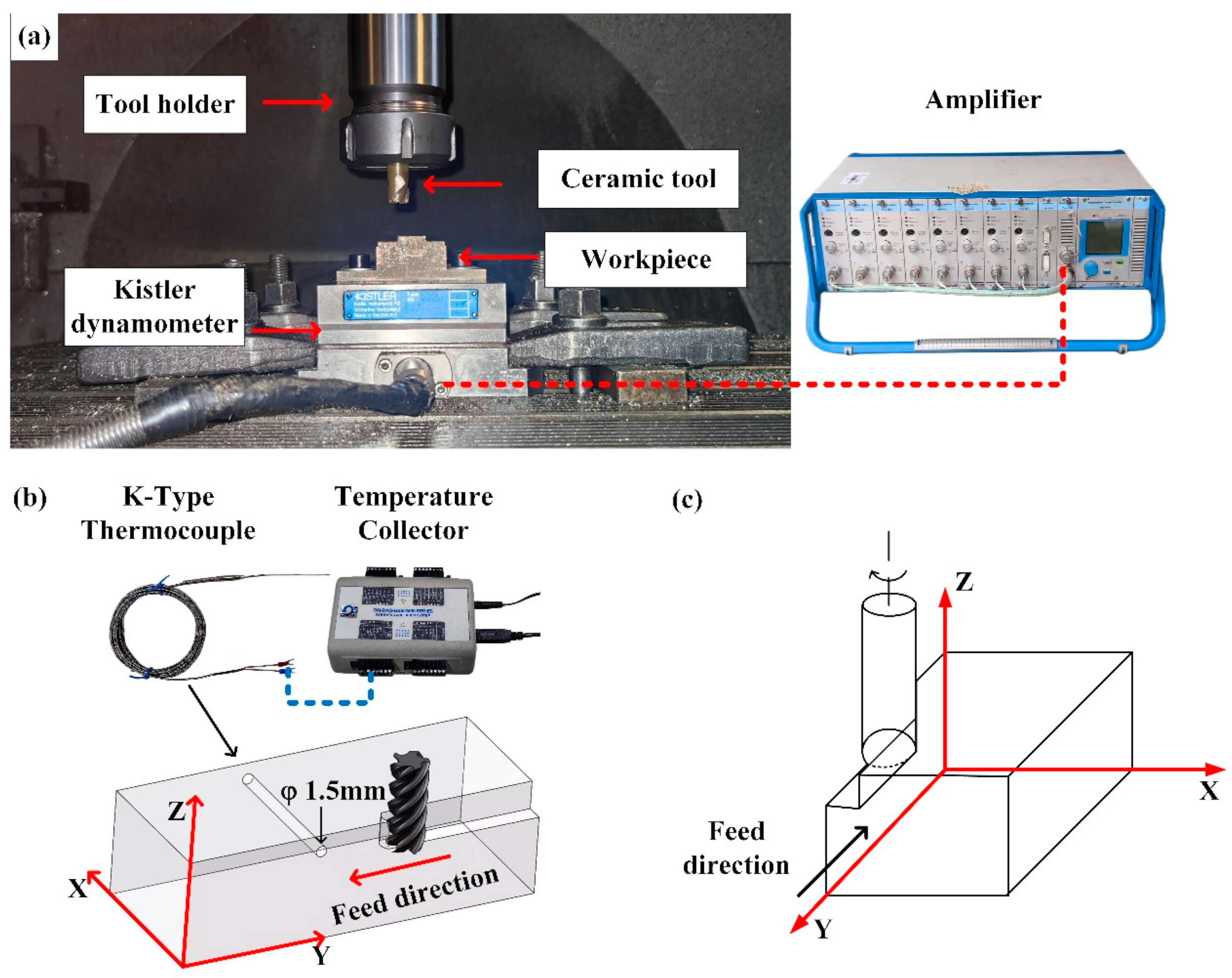
2.2. Milling Scheme and Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussions
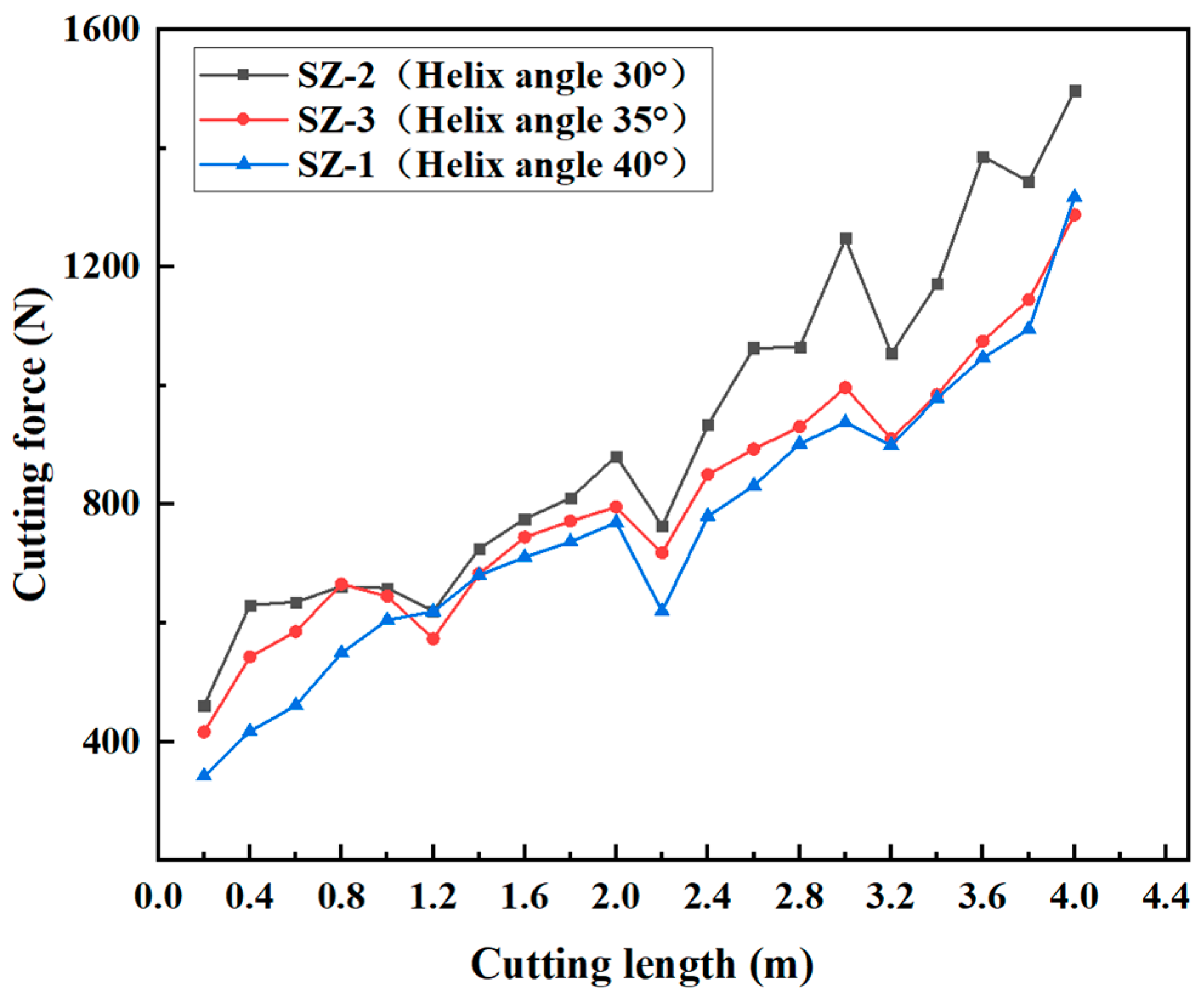
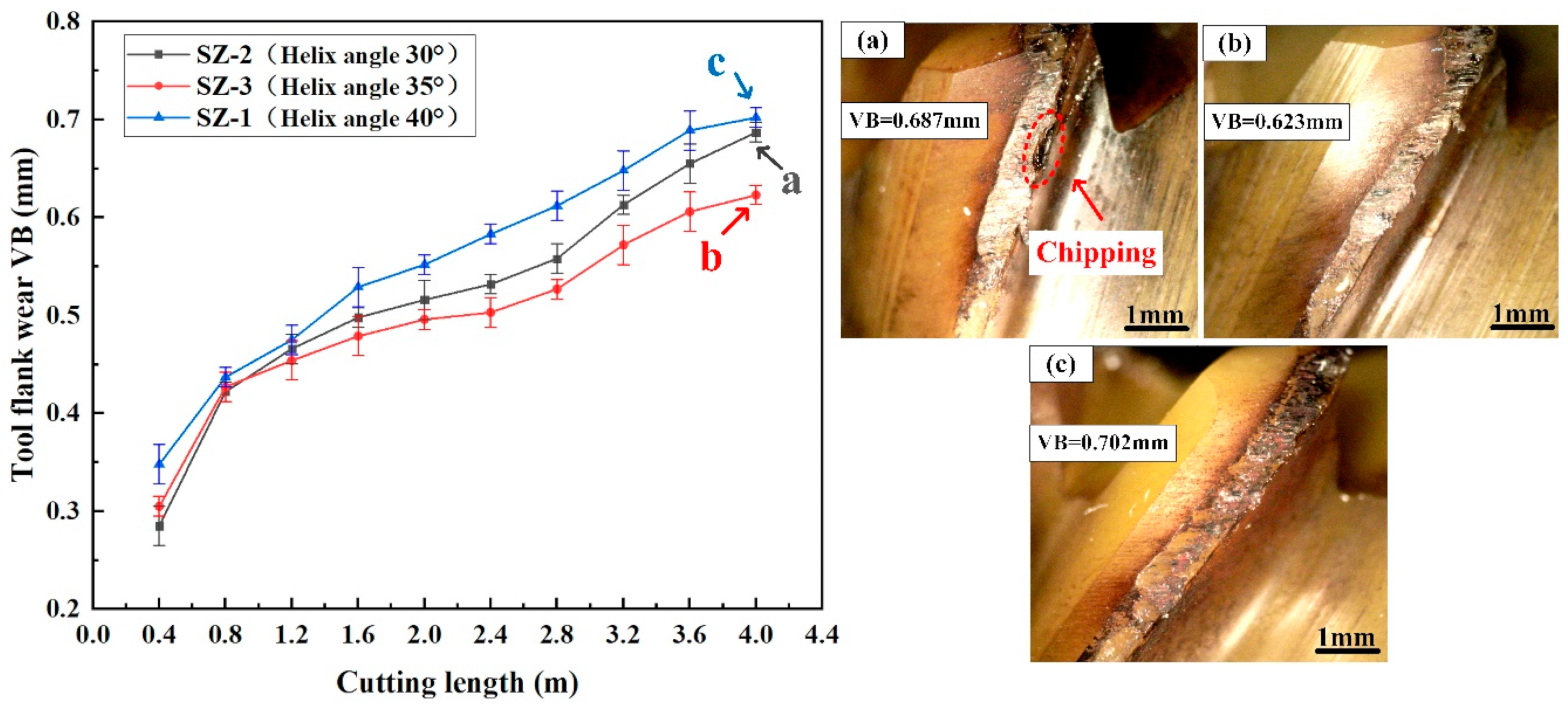
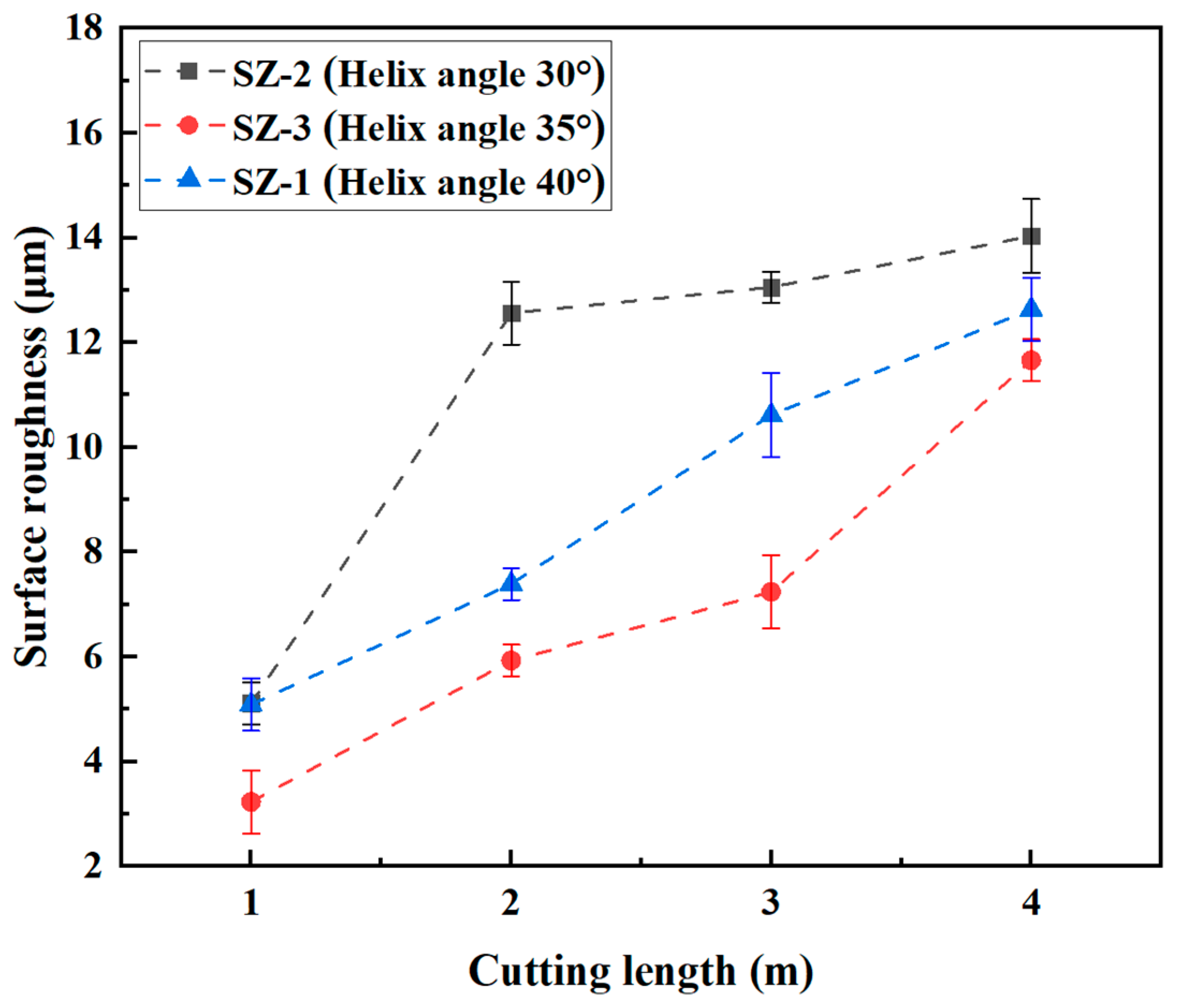
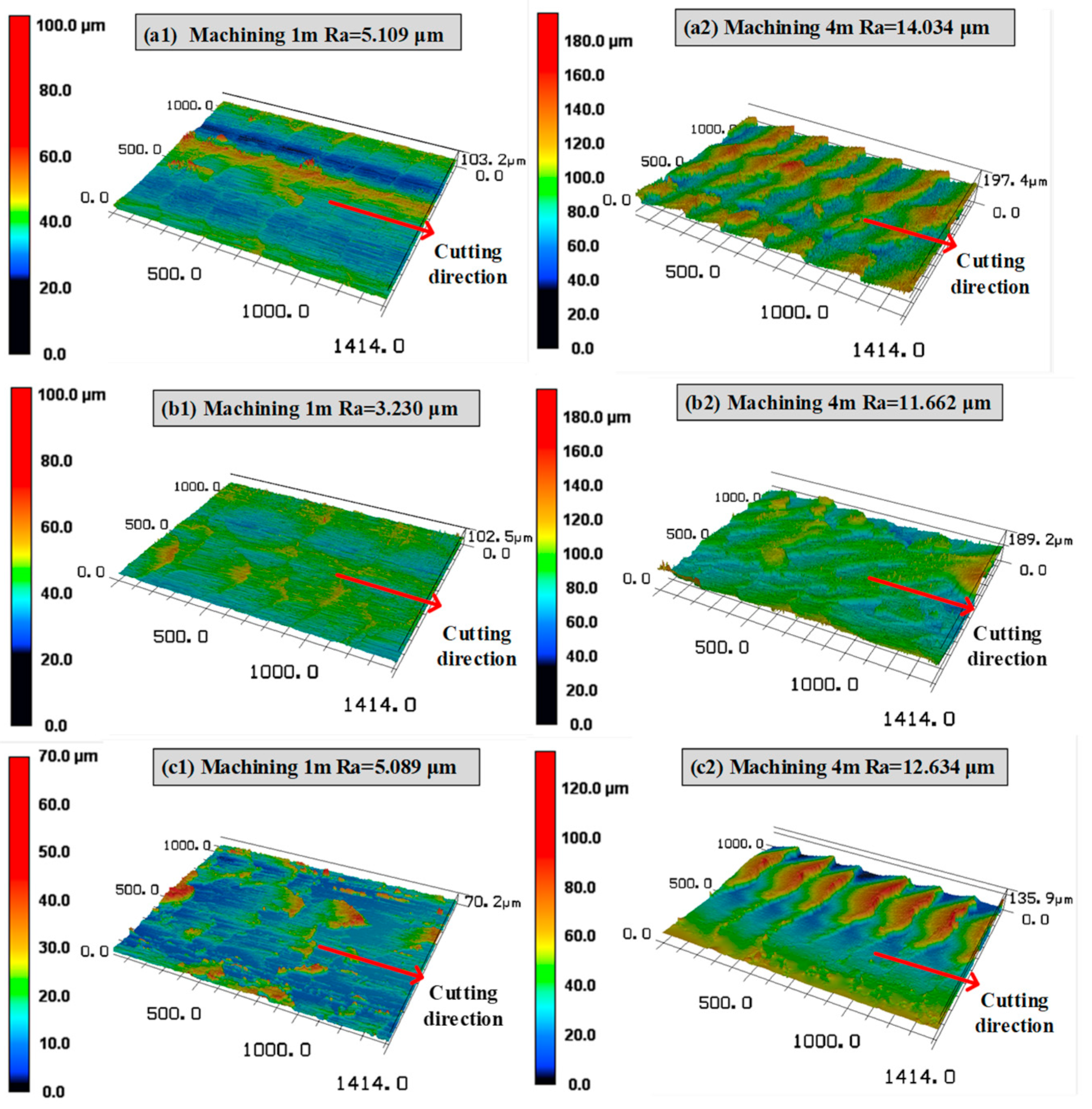
3.1. Effect of Helix Angle on the Cutting Performance of Sialon Ceramic End Mills
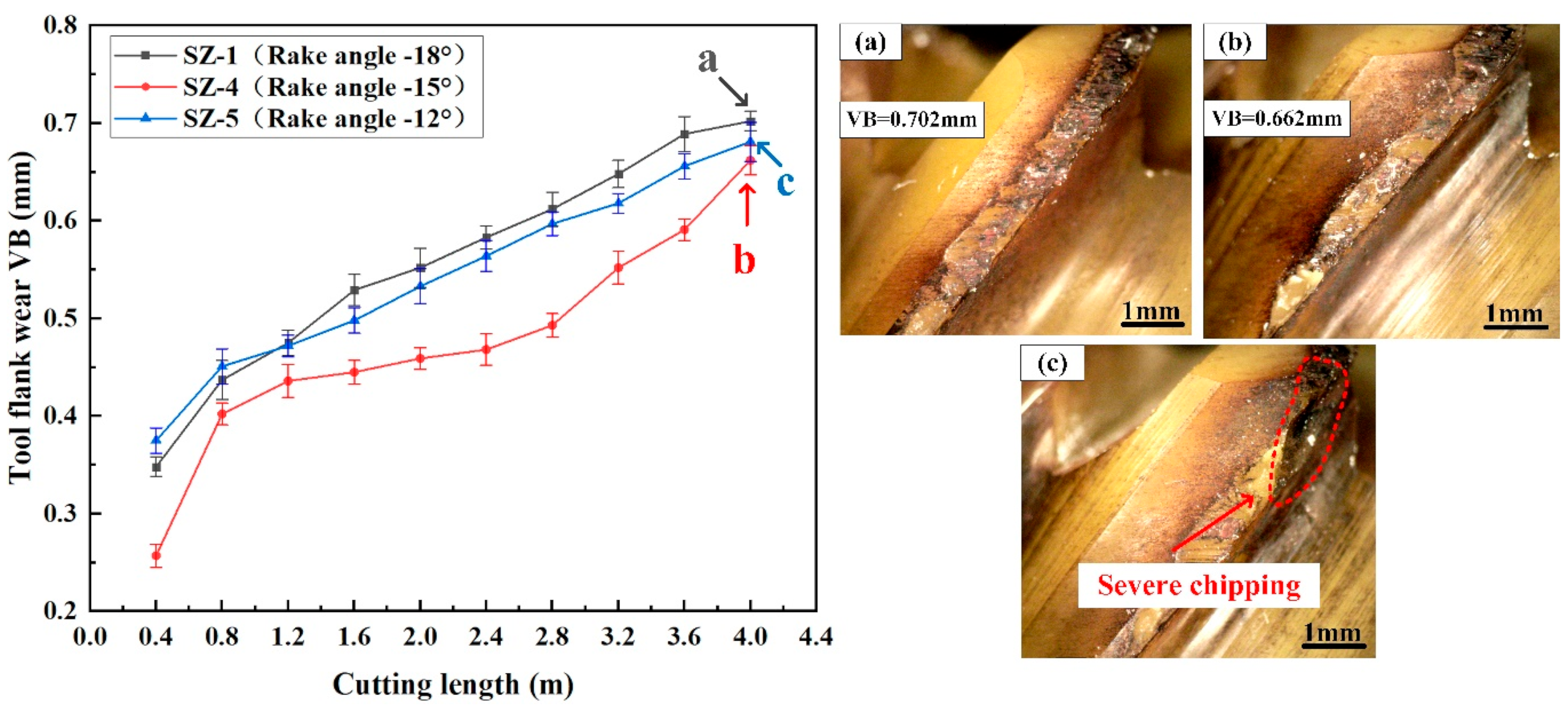
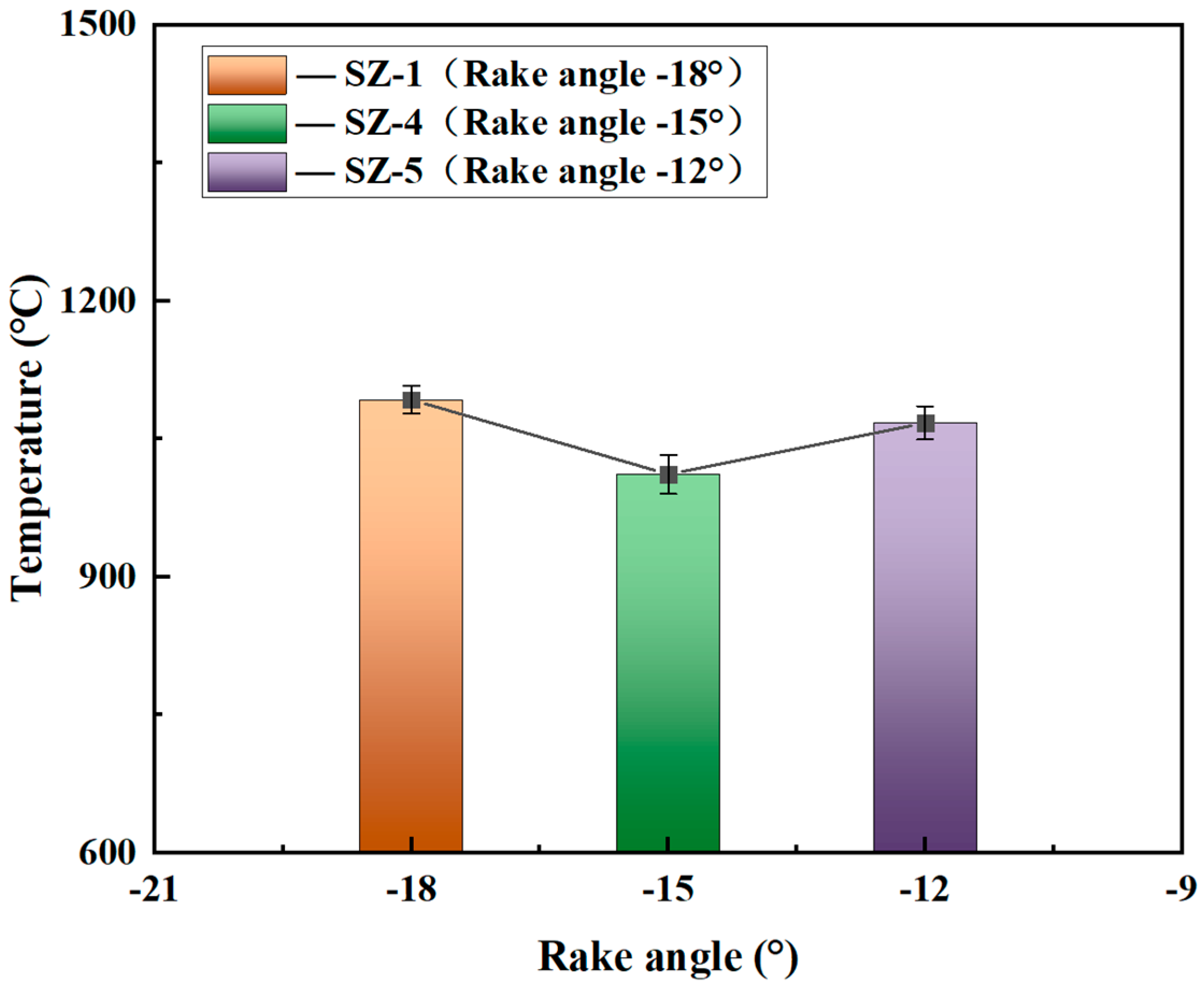
3.2. Effect of Rake Angle on the Cutting Performance of Sialon Ceramic End Mills
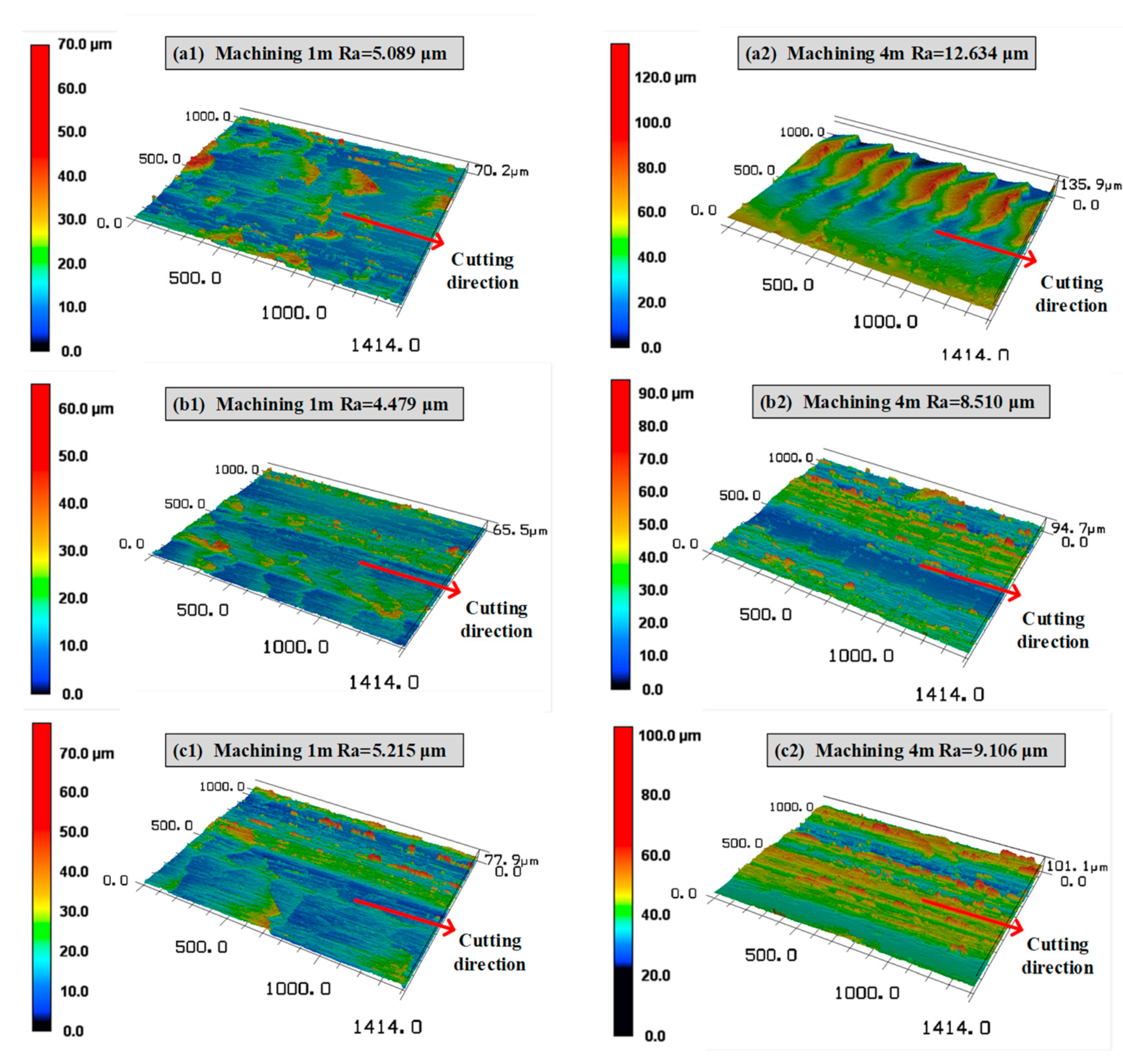
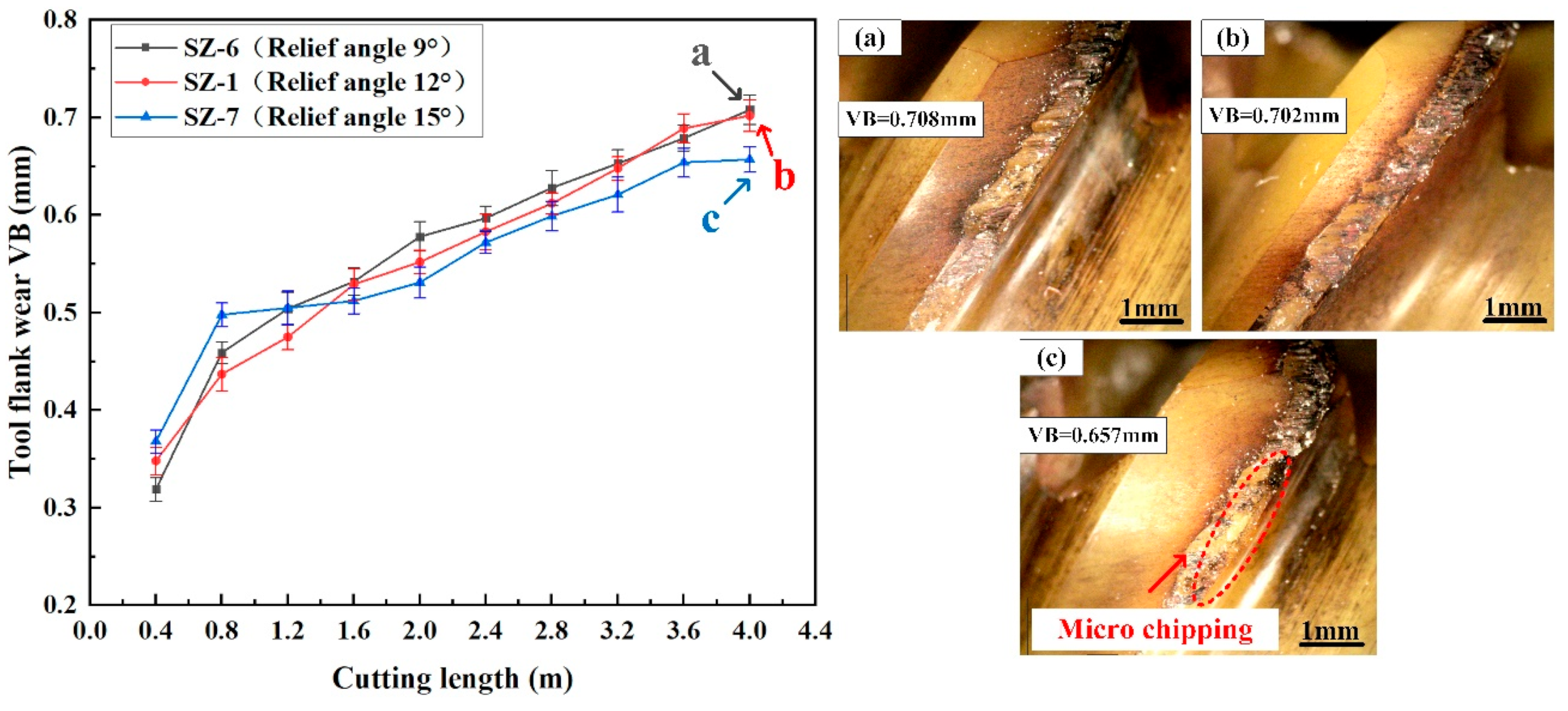
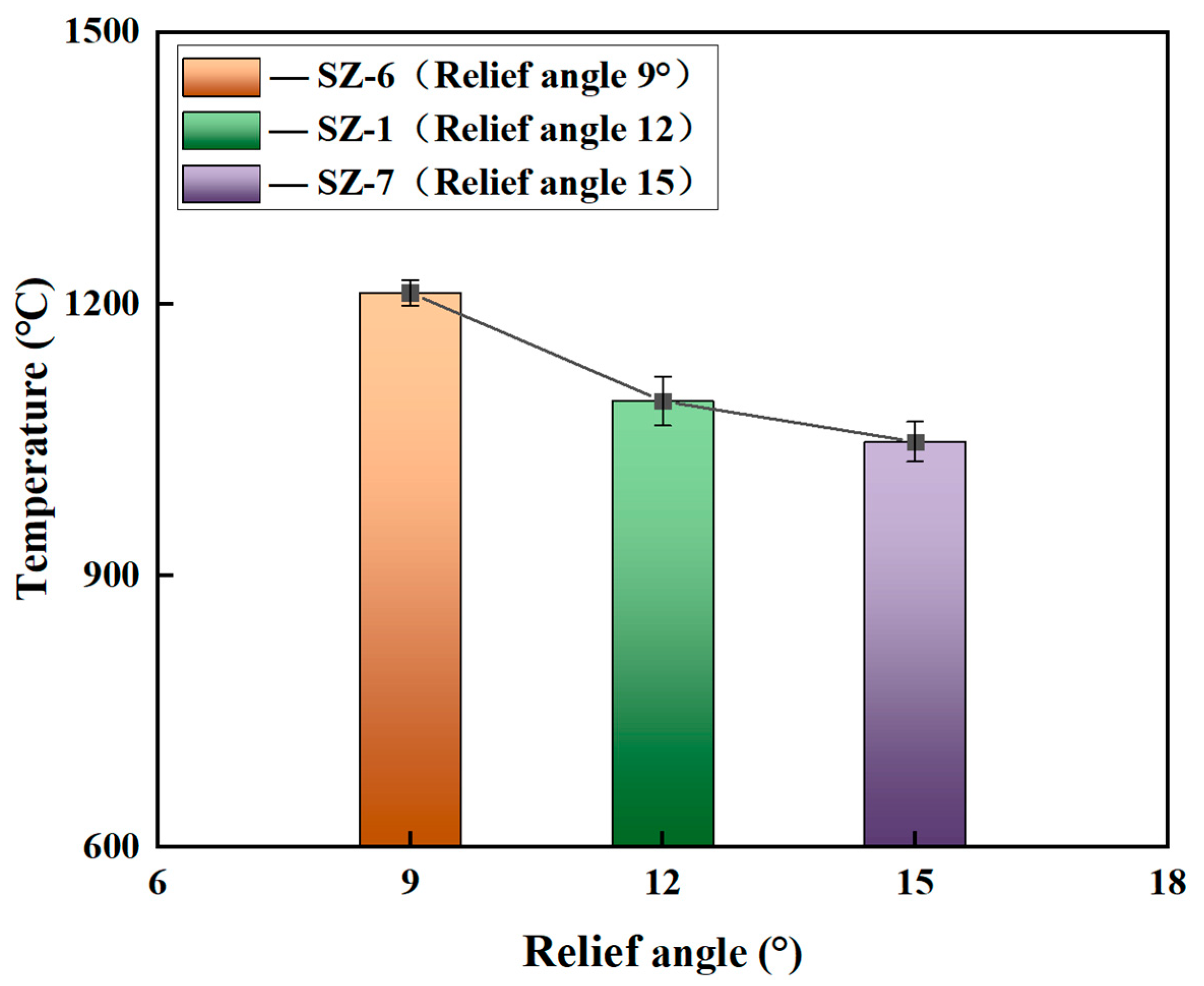
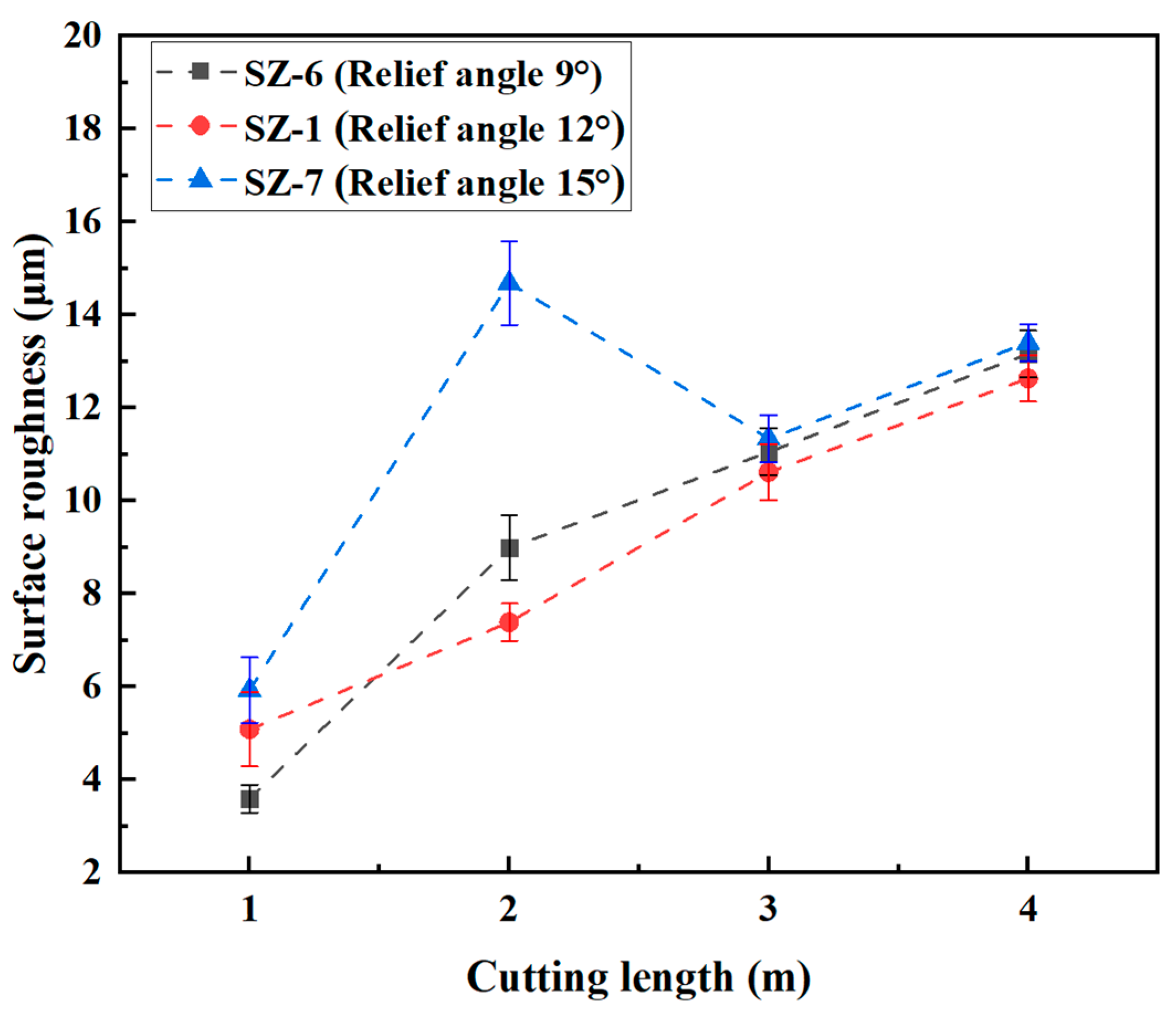
3.3. Effect of Relief Angle on the Cutting Performance of Sialon Ceramic End Mills
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- As the helix angle of the ceramic end mill increases, the cutting force and temperature gradually decrease. When the helix angle reaches 35°, the ceramic end mill exhibits the lowest wear and the best surface quality, along with low cutting force and temperature.
- (2)
- As the rake angle of the ceramic end mill increases, the flank wear and the quality of the machined surface of the workpiece initially decrease and then increase. When the rake angle of the ceramic end mill is −15°, it exhibits the lowest cutting force and temperature during cutting, along with good machined surface quality.
- (3)
- With the increase in the relief angle, the cutting temperature of the ceramic end mill gradually decreases, while the cutting force and the machined surface roughness show a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. When the relief angle of the ceramic end mill is 12°, it exhibits a lower cutting force and temperature, along with the best surface quality of the workpiece.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.B.; Li, W.; Jawahir, I.S. Surface integrity characterization and prediction in machining of hardened and difficult-to-machine alloys: A state-of-the-art research Review and analysis. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2009, 13, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, I.A.; EI-Baradie, M.A. Machinability of nickel-base super alloys: A general review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1998, 77, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, R.; Mannan, M.A. Machinability of nickel-based high temperature alloys. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2000, 4, 127–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.G.; Ramamoorthy, B.; Vijayaraghavan, L. Study on the machinability characteristics of superalloy Inconel 718 during high speed turning. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zou, B.; Huang, C.Z.; Xue, K.; Shi, Z.Y. Mechanical properties and microstructure of Al2O3-SiCw ceramic tool material toughened by Si3N4 particles. Ceram. Int. 2019, 46, 8845–8852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, E.Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.C.; Song, Q.H. Cutting performance, failure mechanisms and tribological properties of GNPs reinforced Al2O3/Ti(C,N) ceramic tool in high speed turning of Inconel 718. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 18859–18867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavko, D.; Borivoj, S.; Janez, K. Wear mechanisms of cutting tools in high-speed cutting processes. Wear 2001, 250, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Z.; Zeng, H.; Chen, X.Q. An experimental study of tool wear and cutting force variation in the end milling of Inconel 718 with coated carbide inserts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 180, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.; Attia, H.; Vargas, R.; Thomson, V. Wear mechanisms of WC coated and uncoated tools in finish turning of Inconel 718. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, P.C.; Santhanam, A.T.; Schlenkofer, U.; Shuster, A.F. Performance of PVD TiN, TiCN, and TiAlN coated cemented carbide tools in turning. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 1999, 17, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillez, A.; Schneider, F.; Dominiak, S.; Dudzinski, D.; Larrouquere, D. Cutting forces and wear in dry machining of Inconel 718 with coated carbide tools. Wear 2007, 262, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.W.; Zou, B.; Chen, W. Cutting performance of Silicon-based ceramic end milling tools in high-efficiency machining of GH4099 under dry condition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 118, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, T.; Enomoto, T. High Speed Machining of Inconel 718 Focusing on Tool Surface Topography of CBN Tool. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 1, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.M.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Z.J.; Cao, Q.Y. Cutting performance and wear mechanisms of Sialon–Si3N4 graded nano-composite ceramic cutting tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 58, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Zou, B.; Wang, J.C.; Wu, Y.; Huang, C.Z. Effect of the progressive tool wear on surface topography and chip formation in micro-milling of Ti–6Al–4V using Ti (C7N3)-based cermet micro-mill. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, H.; Kara, F.; Turan, S.; Kara, A. Novel SiAlON ceramics for cutting tool applications. Key Eng. Mater. 2003, 237, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterlich, B.; Bitsch, S.; Friederich, K. SiAlON based ceramic cutting tools. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, T.; Kubo, A.; Maekawa, K. Temperature and wear of cutting tools in high-speed machining of Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-6V-2Sn. Wear 1997, 202, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Zou, B.; Shi, Z.Y.; Huang, C.Z.; Li, L.; Liu, H.L.; Zhu, H.T.; Yao, P.; Liu, J.K. Wear patterns and mechanisms of sialon ceramic end-milling tool during high speed machining of nickel-based superalloy. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 5690–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.M.; Zhao, J.; Li, A.H.; Cui, X.B.; Zhou, Y.H. Failure Mechanisms of Graded Ceramic Tool in Ultra High Speed Dry Milling of Inconel 718. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaiekiya, F.; Aramesh, M.; Veldhuis, S.C. Chip formation and tribological behavior in high-speed milling of IN718 with ceramic tools. Wear 2020, 446, 203191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.W.; Zou, B.; Chen, P.; Huang, C.Z.; Guo, G.Q.; Liu, J.K.; Li, L.; Shi, Z.Y. Effect of MQL condition on cutting performance of high-speed machining of GH4099 with ceramic end mills. Tribol. Int. 2022, 167, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.F.; Huang, S.; Ding, H.T.; Chen, W.Y. Cutting performance and wear mechanism of Sialon ceramic tools in high speed face milling GH4099. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Xu, X.W.; Huang, X.H.; Ming, W.W.; An, Q.L.; Chen, M. Cutting performance and tool wear of SiAlON and TiC-whisker-reinforced Si3N4 ceramic tools in side milling Inconel 718. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 3096–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.; Alağaç, M.S.; Turan, S.; Kara, A.; Kara, F. Wear behavior of solid SiAlON milling tools during high speed milling of Inconel 718. Wear 2017, 378–379, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.H.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.B.; Gong, Z.C.; Dong, Y. Effect of cutting speed on cutting forces and wear mechanisms in high-speed face milling of Inconel 718 with Sialon ceramic tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 69, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, W.W.; Huang, X.H.; Ji, M.; Xu, J.Y.; Zou, F.; Chen, M. Analysis of cutting responses of Sialon ceramic tools in high-speed milling of FGH96 superalloys. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grguras, D.; Kern, M.; Pusavec, F. Suitability of the full body ceramic end milling tools for high speed machining of nickel based alloy Inconel 718. Procedia CIRP 2018, 77, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Sun, C.Y.; Liua, M.; Gao, F.S. Analysis of the optimization of tool geometric parameters for milling of Inconel 718. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 423, 012030. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.B.; Xu, C.G.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Z. Influence of Tool Geometrical Parameters in High Speed Cutting of Aluminum Alloy. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Changsha, China, 11–12 May 2010; pp. 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Hu, Y.N. Optimisation of tool angles and the relation between tool path and cutting force in high-speed milling with micro-end-mill. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2007, 28, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.F.; Zhang, L.W.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W. Constitutive Modeling of Dynamic Recrystallization Kinetics and Processing Maps of Solution and Aging FGH96 Superalloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 3728–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, F.; Marcus, S.; Friedrich, B. End milling of Inconel 718 using solid Si3N4 ceramic cutting tools. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Ondin, O.; Kivak, T.; Sarikaya, M.; Yildirim, C.V. Investigation of the influence of MWCNTs mixed nanofluid on the machinability characteristics of PH 13-8 Mo stainless steel. Tribol. Int. 2020, 148, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Zou, F.; Ming, W.W.; Xu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M. Wear mechanisms and effects of monolithic Sialon ceramic tools in side milling of superalloy FGH96. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 26813–26822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.K.; Jiang, F.; Yan, L.; Cheng, X. Optimizing the geometric parameters of cutting edge for finishing machining of Fe-Cr-Ni stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.; Ariffin, M.K.A.; Roshan, A. Finite Element Modeling of the Effect of Tool Rake Angle on Cutting Force and Tool Temperature during High Speed Machining of AISI 1045 Steel. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 939, 194–200. [Google Scholar]






| Ni | Cr | Co | W | Mo | Al | Ti | Fe |
| Bal | 18.92 | 6.37 | 5.83 | 4.02 | 1.98 | 1.21 | ≤2 |
| C | Mg | Si | Ce | Mn | S | P | B |
| ≤0.08 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.50 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.40 | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015 | ≤0.005 |
| Density (g·cm−3) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (HV) | Thermal Conductivity (W·(m·K)−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.47 | 210 | ≤1130 | ≥30 | ≤300 | 10.47 |
| Density (g/cm3) | Hardness (GPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa⋅m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.32 | 19.6 | 742.9 | 7.7 |
| Number | Diameter (mm) | Core Diameter (mm) | Flute and Full Length (mm) | Helix Angle (°) | Rake Angle (°) | First Relief Angle (°) | Second Relief Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZ-1 | 12 | 10 | 10 + 70 | 40 | −18 | 12 | 22 |
| SZ-2 | 12 | 10 | 10 + 70 | 30 | −18 | 12 | 22 |
| SZ-3 | 12 | 10 | 10 + 70 | 35 | −18 | 12 | 22 |
| SZ-4 | 12 | 10 | 10 + 70 | 40 | −15 | 12 | 22 |
| SZ-5 | 12 | 10 | 10 + 70 | 40 | −12 | 12 | 22 |
| SZ-6 | 12 | 10 | 10 + 70 | 40 | −18 | 9 | 19 |
| SZ-7 | 12 | 10 | 10 + 70 | 40 | −18 | 15 | 25 |
| Cutting Speed/m·min−1 | Feed Rate/mm·z−1 | Axial Cutting Depth/mm | Radial Cutting Depth/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 0.04 | 4 | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, K.; Chen, P.; Liu, W.; Zou, B.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z. Geometric Structures for Sialon Ceramic Solid End Mills and Its Performance in High-Speed Milling of Nickel-Based Superalloys. Coatings 2023, 13, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091483
Xue K, Chen P, Liu W, Zou B, Li L, Chen W, Wang X, Xu Z. Geometric Structures for Sialon Ceramic Solid End Mills and Its Performance in High-Speed Milling of Nickel-Based Superalloys. Coatings. 2023; 13(9):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091483
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Kai, Peng Chen, Wenbo Liu, Bin Zou, Lei Li, Wei Chen, Xinfeng Wang, and Ziyue Xu. 2023. "Geometric Structures for Sialon Ceramic Solid End Mills and Its Performance in High-Speed Milling of Nickel-Based Superalloys" Coatings 13, no. 9: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091483
APA StyleXue, K., Chen, P., Liu, W., Zou, B., Li, L., Chen, W., Wang, X., & Xu, Z. (2023). Geometric Structures for Sialon Ceramic Solid End Mills and Its Performance in High-Speed Milling of Nickel-Based Superalloys. Coatings, 13(9), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13091483







