Abstract
Eliminating and controlling fungal biodeterioration is one of the most important challenges of easel painting conservation. Historically, the pathologies produced by biodeterioration agents had been treated with non-specific products or with biocides specially designed for conservation but risky for human health or the environment due to their toxicity. In recent years, the number of research that studied more respectful solutions for the disinfection of paintings has increased, contributing to society’s efforts to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Here, an overview of the biodeterioration issues of the easel paintings is presented, critically analyzing chemical and eco-sustainable approaches to prevent or eradicate biodeterioration. Concretely, Essential Oils and light radiations are studied in comparison with the most used chemical biocides in the field, including acids, alcohols, and quaternary ammonium salts. This review describes those strategies’ biocidal mechanisms, efficiency, and reported applications in vitro assays on plates, mockups, and real scale. Benefits and drawbacks are evaluated, including workability, easel painting material alterations, health risks, and environmental sustainability. This review shows innovative and eco-friendly methods from an easel painting conservation perspective, detecting its challenges and opportunities to develop biocontrol strategies to substitute traditional chemical products.
1. Introduction
Cultural Heritage (CH) materials are susceptible to being complexly damaged physically, chemically, and aesthetically by the growing and metabolic activities of living beings, as investigators know as biodeterioration [1]. Many studies have been performed concerning vegetal or microbiological biodeterioration on inorganic materials, such as mural paintings [2,3,4,5], stone buildings [6,7,8,9], or stone sculptures [10,11,12,13,14]. Easel painting biodeterioration is a less-studied topic, although, in the last ten years, there has been more interest in their biological control and prevention [15,16,17,18,19,20].
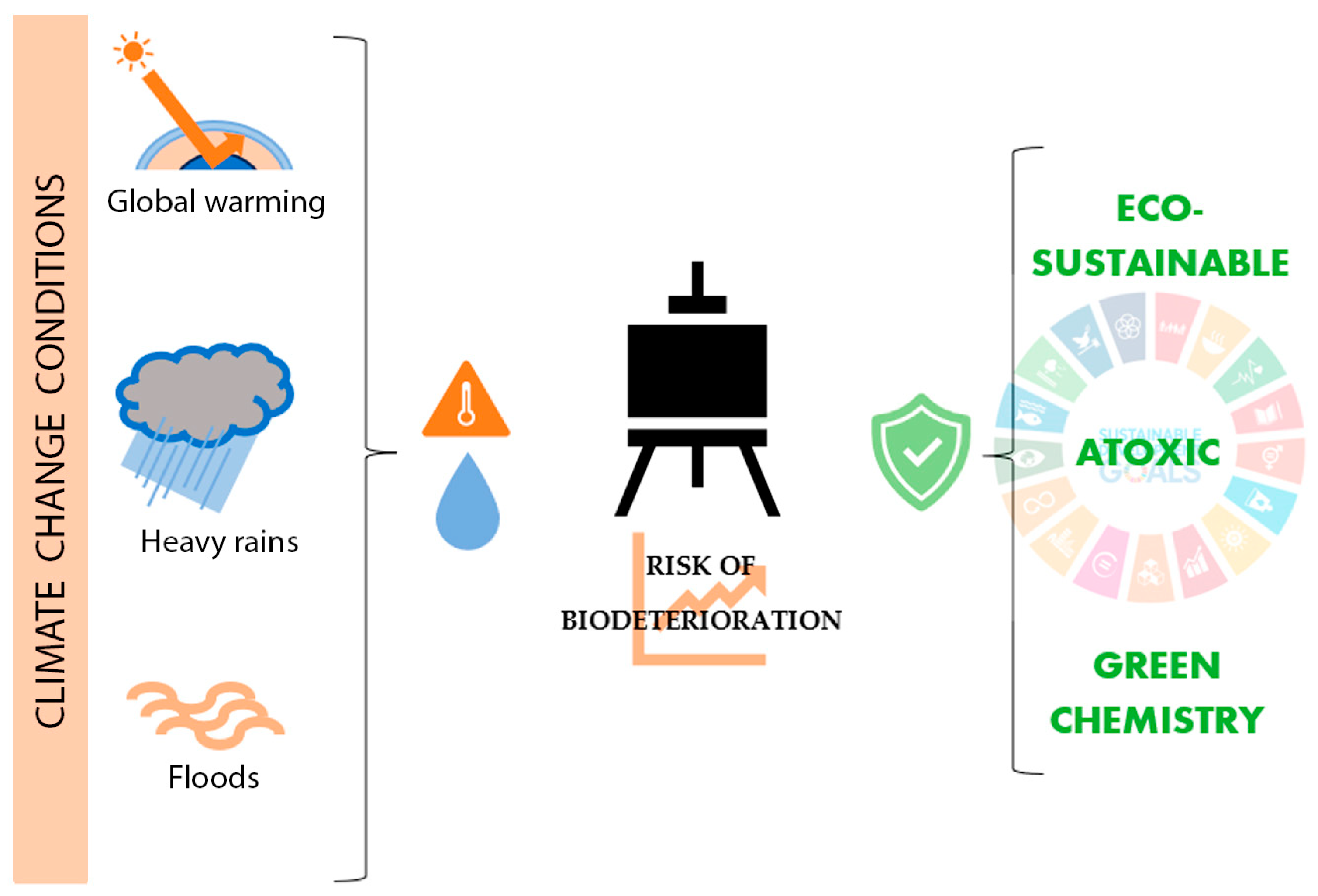
Different investigations worldwide conclude that issues such as climate change and global warming contribute to damaging historical buildings, archaeological sites, museums, and collections physically, chemically, or biologically [21,22,23]. In this way, new analysis and control methodologies are recently being discussed and developed [24,25]. Concerning biodeterioration, climate change phenomena such as seasonal variations, heavy rain, and global warming raise the risk of microbiological growth in tangible CH due to increased moisture and temperature (Figure 1) [22,26,27]. Due to this biodeterioration damage, biocides, which are generally toxic for humans and the environment, are frequently required.
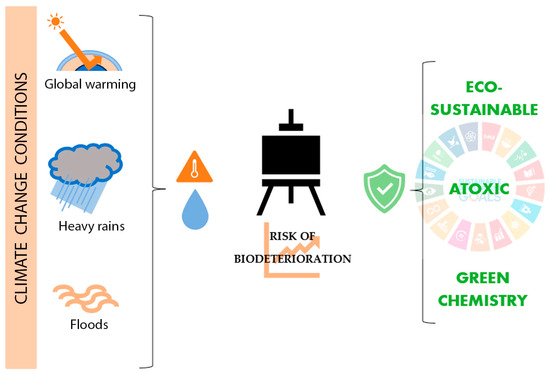
Figure 1.
Influence of climate change on easel painting biodeterioration and current trends on its treatment.
Investigating new eco-sustainable and atoxic solutions for CH biodeterioration found broad support in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). SDGs are a group of 17 objectives and 169 targets approved by the United Nations that aim to achieve a fair, healthy, and equal society [28]. Between these 17 objectives, CH plays an important part in SDG No. 11.4, which recognizes it as a fundamental part of human relations and their necessity to be protected. Furthermore, SDGs establish issues directly related to Good Health and Well-Being (SDG No. 4), Climate Action (SDG No. 13), Life Below Water (SDG No. 14), and Life on Land (SDG No. 15) [29]. In this context of promoting new, eco-sustainable, and non-toxic solutions for society’s needs, CH conservation should be an active part (Figure 1). Applied to CH conservation, Turo and Medeghini, 2021 [30] defined Sustainability as “all actions aimed at developing protective materials and/or analytical methodologies that fall into the green chemistry family”. Green chemistry, moreover, is understood as products or methodologies that do not use substances that are dangerous to humans or the environment [31,32]. In recent years, different investigations reported the benefits of natural origin biocides as Essential oils (EOs) or new physical biocide approaches, such as light radiations as antimicrobial treatments in CH, exported from other disciplines such as medicine, pharmacy, or food industry.
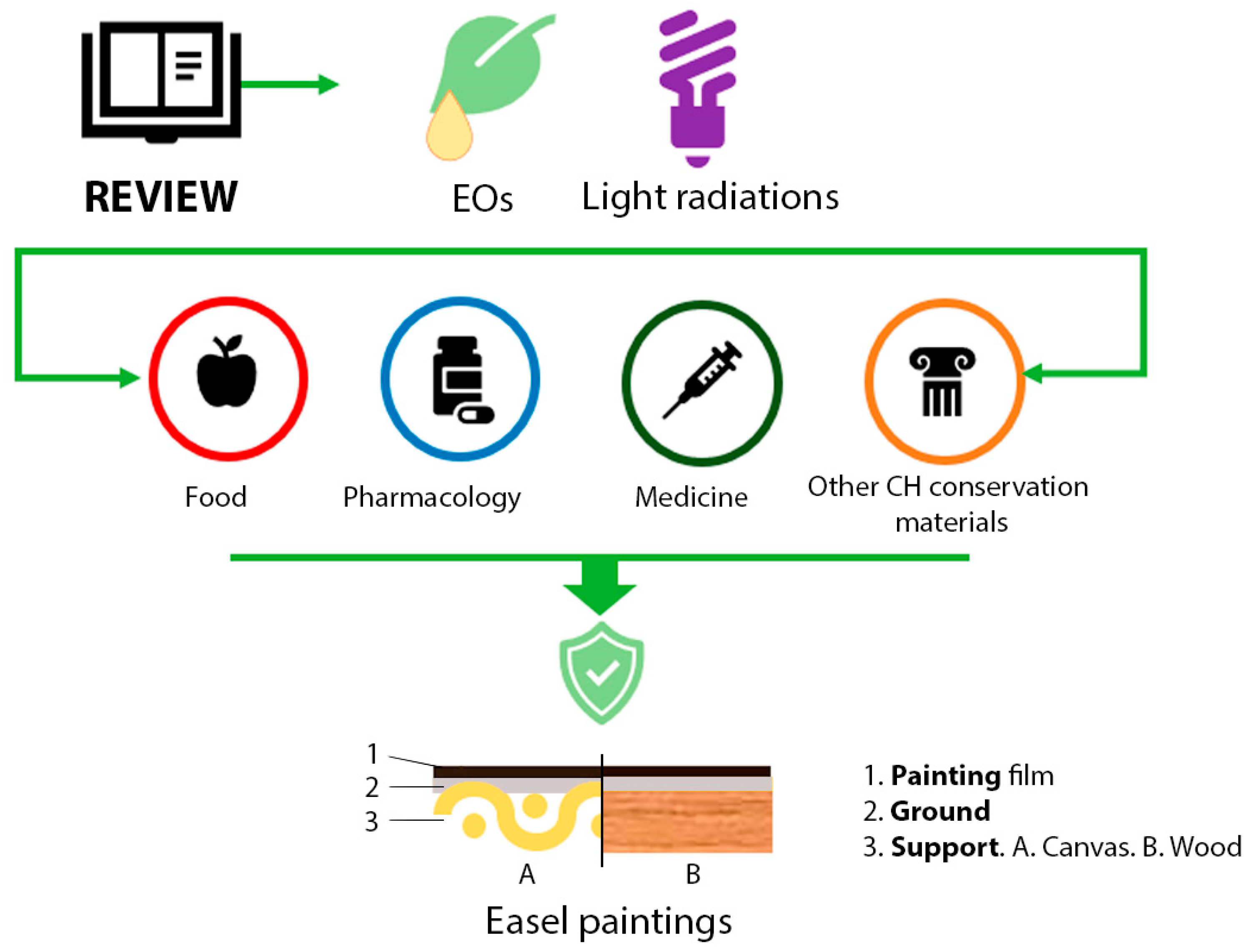
Although easel paintings refer to other supports such as stone [33], metal [34], glass [35], or other techniques, such as gum or proteinaceous binders [36], oil on canvas or wood is the most popular. Due to their historical popularity and their susceptibility to biodeterioration, this paper aims to overview the state of the art of EOs and light radiations as treatment solutions for this type of artwork conservation. In addition, this review analyzes critically their possibilities and future perspectives based on their application in other CH materials or other fields of knowledge (Figure 2).
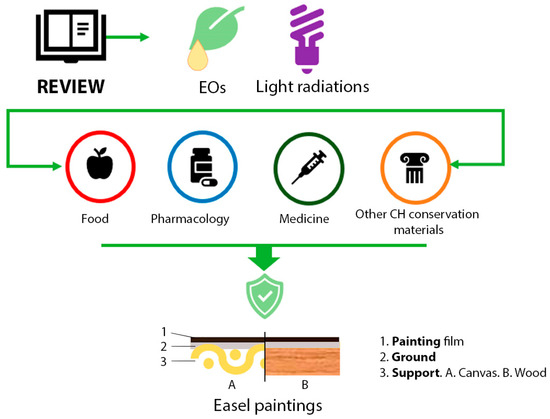
Figure 2.
Graphical representation of the investigation aim. Essential oils (EOs); Cultural Heritage (CH).
The bibliography research for this investigation was based on a Boolean search on Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, using different formulas with the following keywords: “essential oils”, “light radiations”, “Cultural Heritage”, “easel paintings”, “oil on canvas painting”, “biodeterioration”, “antifungal”, “disinfection”. Critical analysis was performed using the SWOT system (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats). The investigation search included all the published papers until December 2023.
2. Fungal Biodeterioration of Easel Paintings
Historical easel paintings have a mixture of materials and layers, increasing their conservation complexity. Materials such as cellulose on the support, rabbit skin glue, egg yolk, linseed oil, or varnishes on the polychromy are some organic materials that can compound an easel painting, although the painting layer also contains inorganic pigments [37,38]. These organic materials can be degraded by fungi if the environmental conditions are favorable (Figure 3). More common fungi are mesophiles, whose ideal conditions revolve around 20–30 °C and a Relative Humidity (RH) higher than 70%, and pH conditions between 4 and 6 [18,20,39,40,41].
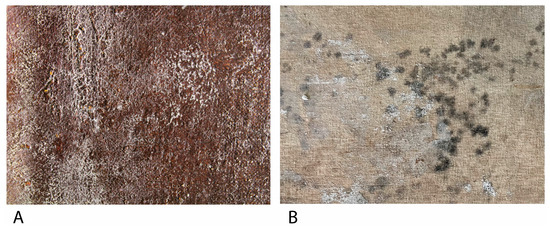
Figure 3.
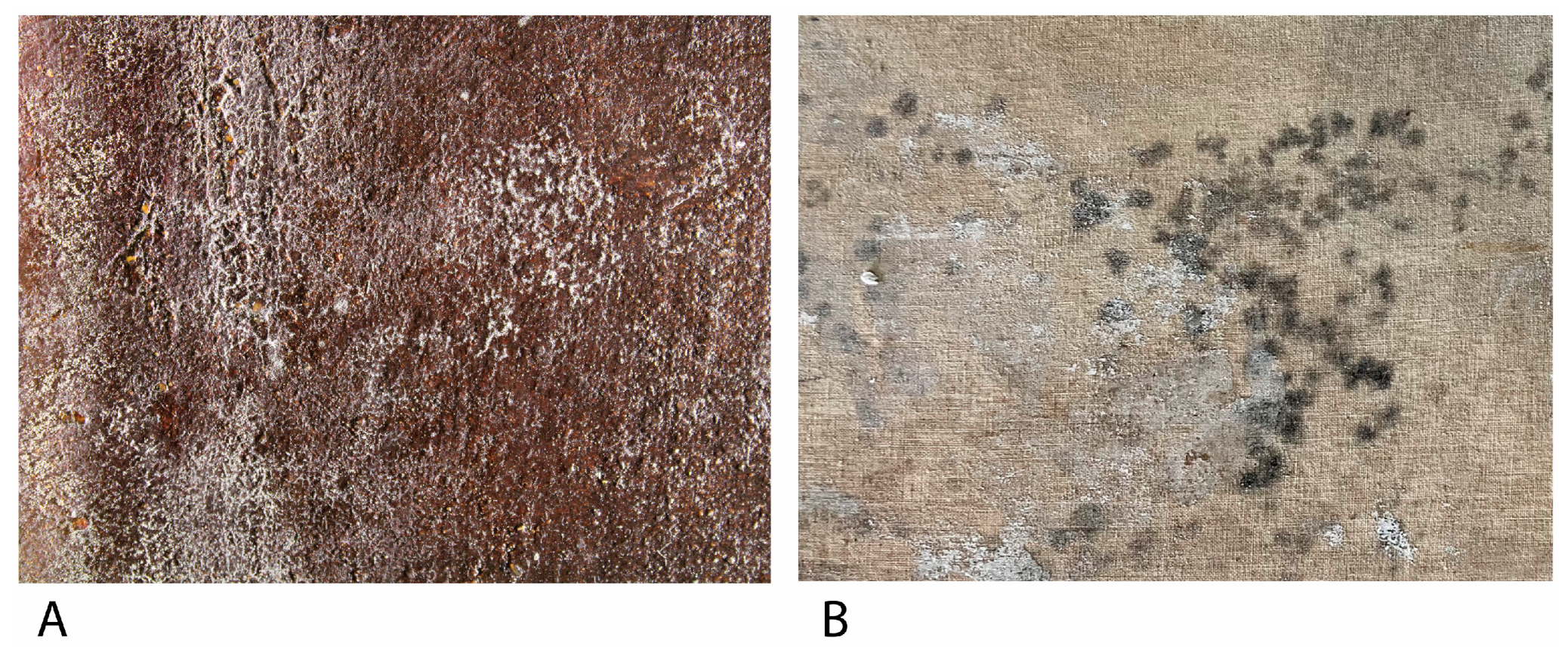
(A) Filamentous fungi growth on the obverse a Bartolomé Mongrell’s oil on canvas painting (Museu Municipal d’Alzira, València, Spain). (B) Fungal growth on the reverse of Santos Juanes Church’s (València, Spain) oil on canvas marouflage.
In the specific literature about fungal biodeterioration of easel painting, there are many fungal families that can grow on this kind of surface, of which the most prevalent are exposed in Table 1. All those fungi are mostly from the phylum Ascomycota, although there are fungi from the phylum Basidiomycota or Mucoromycota, which are three types of filamentous fungi. Filamentous fungi are formed by hyphae—large cell filaments—that generally have walls between them and are called coenocytic hyphae. Depending on their function, this kind of fungi has two different types of structures: vegetative mycelium, which penetrates the substrate and absorbs nutrients, and aerial mycelium and fruitful bodies, which are responsible for reproductive function [42] (Figure 4).

Table 1.
Most common fungal species on easel painting.

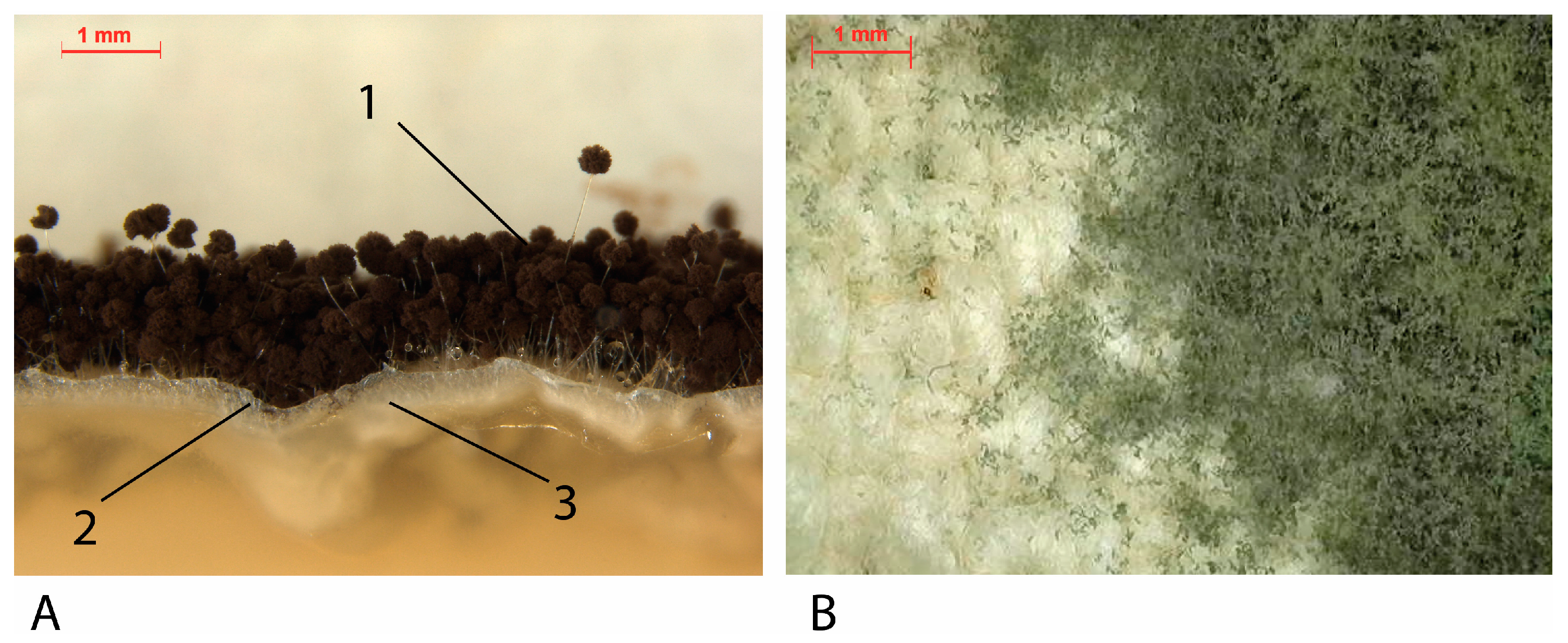
Figure 4.
(A) Cross-section of A. niger cultivated in agar. (1) Fruitful bodies (dark parts): spores-production structures. (2) Aerial mycelium: white hyphae on surface. (3). Vegetative mycelium: white hyphae into the agar medium. (B) Penicillium spp. fruitful bodies and areal mycelium on a cotton canvas mock-up.
The development of fungal strains damages easel painting materials in different ways, causing a multitude of pathologies depending on the substrate and the strain [57]. Generally, fungal growth produces acidification, chromatic changes, structural damage across chemical mechanisms—liberation of fatty acids and enzymatic action— and mycelium growth [19] (Figure 5). Microbial deterioration usually affects the painting support in the first instance, reaching and colonizing the pictorial layers in later phases [58]. The organic nature of these materials presents a large carbon source for microorganisms, which makes them susceptible to biological attack. In addition, the presence of glues or coating pastes applied as sizing treatments increases that susceptibility. Aesthetical damages are generally related to pigment production. Ascomycota strains such as A. niger produces azanigerones B and C—yellow [59]—or other colors from pale yellow to brown [60]. Cladosporium sp. and Fusarium sp. produce anhydrofusarubin—red [61,62]—or A. versicolor produces asperversin—yellow [63]. Red-orange, β-carotene, is the most produced pigment by Mucoromycota as a preventive measure for stress oxidative damages [64].
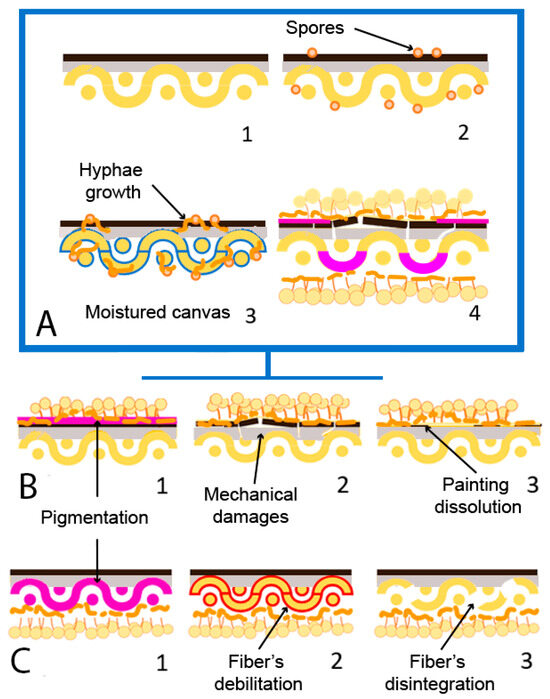
Figure 5.
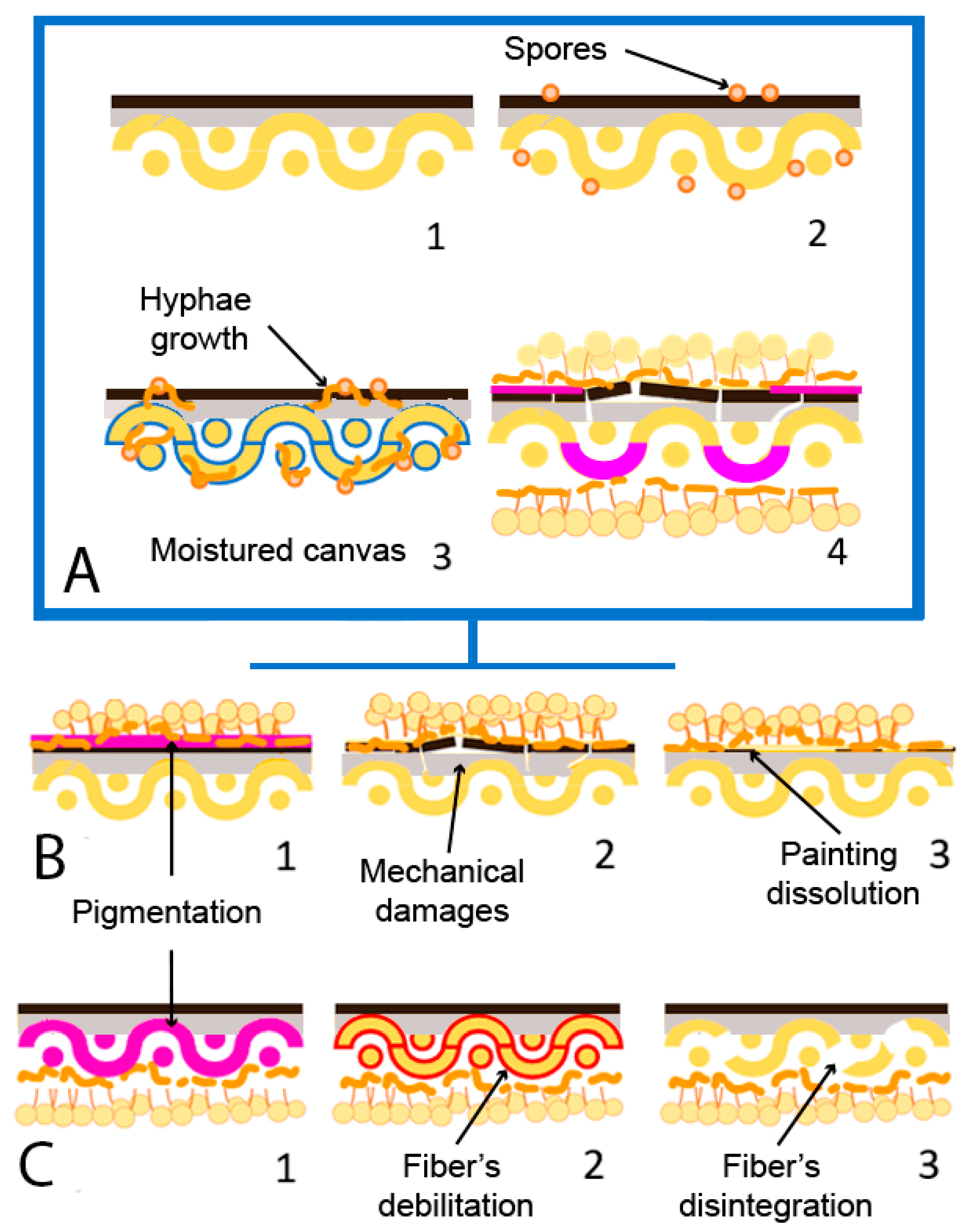
Fungal biodeterioration mechanism and damages on canvas painting (adapted from Poyatos et al., 2018 [19]). (A) (1) Non-biodeteriorated oil on canvas painting; (2) presence of fungal spores (orange) on the surface; (3) moisture of canvas (blue) due to RH increase and fungal development. (4) Biodeteriorated painting. (B) Damages on painting strata; (1) Pigmentation (pink); (2) mechanical damage of painting film; (3) dissolution of painting film. (C) Damages on canvas support; (1) pigmentation (pink); (2) fiber’s debilitation (red); (3) fiber’s disintegration.
2.1. Fungal Biodeterioration of Wood on Easel Paintings
Wood was the most important painting support until canvas popularization in the 16th century. It presents well-known biodeterioration problems due to its use in different industries or as a construction material [65]. Wood fungal biodeterioration can be classified as white rot, brown rot (exclusively by Basidiomycota), and soft rot (generally Ascomycota), depending on the produced damages [66,67]. Brown rot fungi feed on cellulose and produce brown pigmentation and structural damage on wood, while white rot fungi also feed on lignin and produce discoloration [68]. Soft rot fungi can produce lignin and cellulose, penetrating the surface at various centimeters, producing cavities and erosion [67]. Recently, Afifi et al., 2023 [69] detected biodeterioration damages produced by Aspergillus sp., such as discoloration or hyphae penetration into the wooden support of mock-ups based on a historical stucco (Sultan al-Ashraf Qaytbay Mausoleum, Egypt).
2.2. Fungal Biodeterioration of Textile Fibers on Easel Paintings
Starting in the 17th century, textile fibers began to expand as the main artistic support due to their lower cost or technical characteristics, such as the possibility of producing larger and lighter formats, the contribution of texture, or the ease of transport and storage [19,70]. The historical textiles usually used are made of natural fiber fabrics, such as cotton, hemp, linen, or jute. These fabrics’ main component is cellulose, which comes from the plant fibers from which the materials are obtained [58,71]. For example, cotton comprises seed fibers, while flax or jute are made from phloem fibers [58]. The main component of the cell walls of tissues of plant origin is cellulose. Cellulose is a polysaccharide formed by a crystalline region with great resistance to biodeterioration and an amorphous region easily attacked by microorganisms, in which the biological attack usually begins [72]. The fungal deterioration of tissues happens mainly due to the production capacity of intracellular and extracellular hydrolytic enzymes and organic acids, using natural fibers as a carbon source for their growth and development. These enzymes are cellulases, breaking cellulose’s intramolecular bonds and obtaining glucose molecules [71,72]. That is, they decrease the degree of polymerization of the cellulose molecules [73]. This can cause fiber breakage and thinning and, therefore, a decrease in the individual resistance of the fibers and the textile [72].
In addition, organic acids produce minerals for some phototrophs and have a wide variety of pigments, being the first alteration of fungal biodeterioration and complex to eliminate. Therefore, the amount of cellulose in the tissues will be decisive regarding their vulnerability to being colonized by micro-organisms. Of the fabrics widely used as pictorial textile supports, cotton is the material that has the highest amount of cellulose (90%), followed by linen (80%), hemp (77%), and finally, jute (60%) [58,71]. Factors such as composition or fiber and the structural and chemical characteristics of the textile influence the risk of biodeterioration. Increasing the amount of cellulose—in addition to pectins or pentoses—on the textile composition will increase the biodeterioration susceptibility, too. However, some substances are present in textiles that few microorganisms cannot metabolize, such as lignin [71,74]. Structurally and chemically, the cellulose chains’ length, degree of polymerization and crystallinity, the fibers’ orientation or the threads’ thickness, and their chemical, photochemical, and mechanical degradation must be considered [19,71,75,76].
2.3. Fungal Biodeterioration of Oil Binders in Easel Paintings
On polychromies, fungal biodeterioration affects the chemical and physical stability: while fatty acids acidify the surface, esterases and lipases disaggregate the pictorial layer, damaging the oil medium and producing resistance loss, fracture, and detachments in extreme cases [19,77,78]. Therefore, enzyme liberation supposes triacylglycerols hydrolyzation by lipases and the aqueous part hydrolyzation by esterases, favoring the mycelium growth, which produces microcracks [54,79]. As ideal conditions for fungal growth—high RH—are also prejudicial for easel paintings because of the different mechanical behavior between layers [80], a synergy between biodeterioration agents and other types of alteration is caused, such as moisture, dust, or environmental contaminants [81]. Contrary to support, pictorial films have more factors in the biodeterioration mechanisms, such as pigments. Paintings with Pb, Zn, Cr, or Cd are more resistant to fungal biodeterioration, while earth pigments are more susceptible [82,83]. Different investigations studied the effect of fungal strains isolated from easel paintings. Salvador et al., 2017 [15] analyzed the biodeterioration of different Giorgio Marini (1836–1905) portraits conserved in museums or private collections in Évora, Portugal. Strains of Aspergillus sp., Cladosporium sp., Penicillium sp., and Mucor sp. were isolated, attributing their growth to the presence of proteinaceous binders and inadequate climate conditions. Even in outdoor environments, Poyatos-Jiménez et al., 2021 [41] evaluated the biodeterioration of a collection of paintings placed on different Cloisters of Quito, Ecuador. In their study, authors isolated strains of Aspergillus sp., Mucor sp., Cladosporium sp., or Penicillium sp. They attributed their biodeterioration pathologies to the semi-tropical environment where the paintings are exhibited.
3. Chemicals Biocides Frequently Used in Easel Painting
Biocides are, according to the European Regulation No. 52/2012—which controls their commercialization—a chemical substance used to control organisms that are damaging to persons, animals, or objects. On CH, most used biocides are organic or inorganic compounds, such as phenols, acids, quaternary ammonium salts (QACs), alcohols (ethanol) or nitrogen-containing compounds, and inorganic compounds like urea derivatives, heavy metals salts, and, recently, metal nanoparticles (NPs) (Table 2) [84]. Depending on their structure, biocides have different biological mechanisms affecting target organisms, but most do not present long-term effectiveness and help new micro-organisms proliferate thanks to microbial resistance. Furthermore, products with these compounds can damage artistic materials. Chemical products used as biocides are divided into oxidative (oxidizing the cell structure) and non-oxidative (inhibiting vital enzyme production), being the second group the most used on CH conservation [85,86].
The biocide mechanism of phenol compounds is characterized by disrupting the fungal cell membrane by ergosterol enzyme inhibition and an oxidative action, supposing the increase in ROS (reactive oxygen species) levels and cell stress [87,88]. The boric acid antifungal mechanism disrupts oxidative metabolism, decreasing ergosterol synthesis and affecting the hyphae by its growth inhibition [89]. On the other hand, low molecular weight QAC biocide activity resides on the cationic immobilization because of the combination of the QAC’s positive charge with the negative charge of the fungal cell, producing disorder of charges, the membrane cell disruption, cytoplasmatic compounds liberation and cell lysis [90,91]. Koestler et al., 1993 [92] reported the use of orthophenylphenol (Lysol, Reckitt Benckiser, Parsippany, NJ, USA), inorganic compounds such as sulfuryl fluoride (Vikane, Douglas Products, Liberty, MO, USA), and QAC mixtures (BioMet 66, M&T Chemicals Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA) in North American museums in the last years of the 20th century, although nowadays they are not used. Their study analyses the negative effects of these products on paintings, demonstrating that these materials produced gloss, color, or topography changes, in contrast with gas N, which was also tested.

Table 2.
Description of most used chemical biocide on oil on canvas conservation treatments on consulted bibliography [85,93,94,95,96,97,98].
Table 2.
Description of most used chemical biocide on oil on canvas conservation treatments on consulted bibliography [85,93,94,95,96,97,98].
| Biocidal Group | Biocide | Composition | Mechanisms of Action | Treatment Location | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Ethanol | CH₃CH₂OH | Non-oxidative/Oxidative Cell membrane damage ROS increase | Reverse/Obverse | Disinfection |
| QACs Azoles | Biotin R | N-octyl-isothiazolinone (3%–5%) þ 3-iodopro–p-2-ynyl N-butylcarbamate (10%–25%) | Non-oxidative Cationic immobilization Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition | Reverse/Obverse | Disinfection |
| QACs Azoles Acids | Biotin T | di-n-decyl-dimethylammoniumchloride 40%–60%, 2-N-octil-2H-isotiazol-3-one 7%–10%, Isopropanol 15%–20%, formic acid (1%–2.5%) | Non-oxidative Cationic immobilization Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition | Reverse/Obverse | Disinfection |
| QACs Alcohol | Preventol RI50/RI80 | Alkyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium Chloride; (50%), isopropyl alcohol (2%)/Alkyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride; (80%), isopropyl alcohol (2%) | Non-oxidative Cationic immobilization Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition | Reverse | Prevention/Disinfection |
| Phenols | Preventol ON | Sodium-2-phenylphenolate | Non-oxidative/Oxidative Ergosterol production inhibition and ROS increase | Obverse | Prevention |
| Metal NP’s’s | ZnO NP’’s | ZnO | Oxidative ROS increase | Obverse | Prevention |
| Acids | Boric acids | H3BO3 | Non-oxidative Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition | Support | Prevention/Disinfection |
In addition, authors such as Di Vito et al., 2022 [93] reflected the traditional use of QAC products, such as Biotin R, Biotin® T (CTS, Vicenza, Italy), Preventol RI50, or Preventol RI80 (Lanxess, Cologne, Germany). Villarquide, 2005 [94] reported using 3% Preventol RI50 for canvas reverse treatment. Villarquide, 2005 [94] also reported the use of phenol liquids derivates for reverse disinfection in different concentrations: pentachlorophenol (Mystox LPL, Catomance, Nottingham, UK) 5% on White Spirit, orthophenylphenol (Lysol, Reckitt Benckiser, Parsippany, NJ, USA) 0.5%–1% on distilled water, and dichlorophen (Permicide, Athea Laboratories®, Milwaukee, WI, USA). In terms of preservation, Romero-Noguera et al., 2020 [95] tested the efficacy of the addition of some biocides on colophony, sandarac, and Manila copal varnishes using biocides reported by Caneva et al., 1998; Nugari and Salvadori, 2003; and Salthammer and Schieweck, 2006 [99,100,101]: benzalkonium chloride, orthophenyl phenol (Preventol ON, Lanxess, Cologne, Germany), and tributyltin naphthenate (Metatin N, Acima Chemical Industries, Buchs, Switzerland). Spreading and incorporating the biocides into the varnish were the methodologies followed and had positive results on the tested fungal strains (Pennicilium chrysogenum, Chrysonilia sitophila, and Phoma herbarum), with different efficiencies depending on the biocide, the varnish and the method of application. Boric acid is applied in industrial wood as a protective measure, being more effective against brown rot fungi than white rot, as reported by Estevez-Fregoso et al., 2021 [102]. In CH, boric acid is used as a curation treatment for canvas conservation, as Guillén et al. reported in 2011 [103].
Although the ethanol biocide mechanism needs to be clarified, it is reported that it can also damage the membrane cell and coagulate proteins, supposing cell lysis [104]. Furthermore, it is more efficient when mixed with water (70% for total antifungal activity on paper samples), which can be related to the protein coagulate/denaturation effect. However, surfaces cleaned with ethanol are faster recolonized, probably because of their non-sporicidal activity and the spread of spores during the cleaning process [104,105]. Calvo, 2002 [106] reported the traditional use of ethanol for textile support disinfection.
Abbas et al., 2012 [107] analyzed the antifungal capacities of inorganic compounds, such as heavy metals compounds: mercury (II) chloride (HgCl2), copper (II) acetate (Cu(CH3COO)2), cadmium (II) chloride (CdCl2); and urea ((NH2)2CO) being more effective the inorganic salts of heavy metals. In recent years, there have been experiences of using TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles [96,108] on coating materials applied to paintings or cellulose materials, such as paper or wood [109,110], as a green solution for biological growth preservation. Franco-Castillo et al., 2021 [111] reported that the antifungal activities of ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles are their photocatalytic capacities, with some differences. Generally, both can create ROS from O2 or H2O molecules in the atmosphere, such as superoxide anions radicals, hydroxide radicals, and hydrogen peroxide, which can kill micro-organisms across oxidative reactions on the membrane cell. For these reactions, and the difference between both, TiO2 nanomaterials need UV radiation or solar light, while ZnO nanoparticles are effective even in dark conditions.
In addition to the biocides mentioned above, some authors suggest using azoles [97]. These antifungals avoid ergosterol biosynthesis in the fungal membrane cell, inhibiting the enzyme P-450 sterol 14α-demethylase. On organic materials conservation, such as easel paintings, Sameño Puerto, 2018 [97] reports that the most used antifungal products are azole derivates or mixtures, such as Biotin T—in combination with QAC’s—Biotin R and Rocima GT (Lanxess, Cologne, Germany)—added to QAC’s and formaldehyde [112], on cellulosic materials.
The problem of some of the traditional biocides used in easel painting conservation and restoration processes and exposed in this chapter is their toxicity, which is noted by the safe use recommendations in each Safety Data Sheet. Although the use of Personal Protective Equipment is necessary for all curative treatments—even when natural biocides are being used—and the conventional biocides concentrations generally are low, the toxicity for humans, non-target organisms, and the environment opened in the last 10 years, new investigation lines for the study and use of green biocides on CH conservation [113,114,115]. In European Regulation No. 528/2012 [116], the use of QACs is permitted in concentrations between 100 and 250 ppm (mL/L) and, higher than 6%, can be prejudicial for skin, eyes, or mucosa [70]. Other products, such as azole derivates, have been reported as a risk for aquatic forms of life because of the river’s contamination [117], while phenols can damage humans in different ways, producing acute or chronic injuries [118]. The high toxicity of heavy metals, such as copper or mercury, on humans or sea organisms has also been reported [119,120]. Recently, an interesting investigation published by Casorri et al., 2023 [98] reviewed the literature on the toxicity of different chemical biocide products used in CH conservation, pointing out natural biocides as good alternatives due to synthetic biocide’s health risks. In addition, the high hygroscopicity of textile fibers of easel paintings makes it impossible to apply treatments in the liquid phase. This can lead to excessive wetting and penetration and an increase in the dimensions of the textile, creating such harmful alterations as the detachment of the pictorial layers. For this reason, fungal disinfection on textile supports is usually applied with dry treatments or gelled solutions [121]. The characteristics and needs of pictorial textile support is among the first factors to consider in searching for effective and harmless alternatives.
4. Essential Oils as a Green Biocide
EOs are liquids and volatile organic compounds (low molecular content) extracted from plant regions such as flowers, peels, stems, or seeds. EOs result from the secondary plant metabolism participating in different biological mechanisms of the plant [122]. They have different functions in defense plant activity, such as antimicrobial mechanisms. Generally, EOs contain 20 to more than 100 single components, of which only 2 to 4 are in high concentrations (20%–70%) [123,124]. Mono (C10) and sesquiterpenes (C15), such as carbohydrates, phenols, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and ketones, are their main components, being 80%–90% of the EOs. However, each has different structures, defining the EO peculiarities [123,125,126]. More than 150 types of EOs can be extracted from 30,000 different plants, varying in composition depending on the species, the organ, and the season [125], and are used in multiple fields, such as medicine, agroalimentary, or pharmacological industries because of their antimicrobial, antitumor, antioxidant, antidiabetic, or insecticidal capacities [123,127,128]. EOs can be extracted by steam distillation, solvent extraction, cohobation, and maceration, although there are more effective methods, such as supercritical fluid, microwave-assisted extraction, and ultrasound-assisted extraction [122,128].
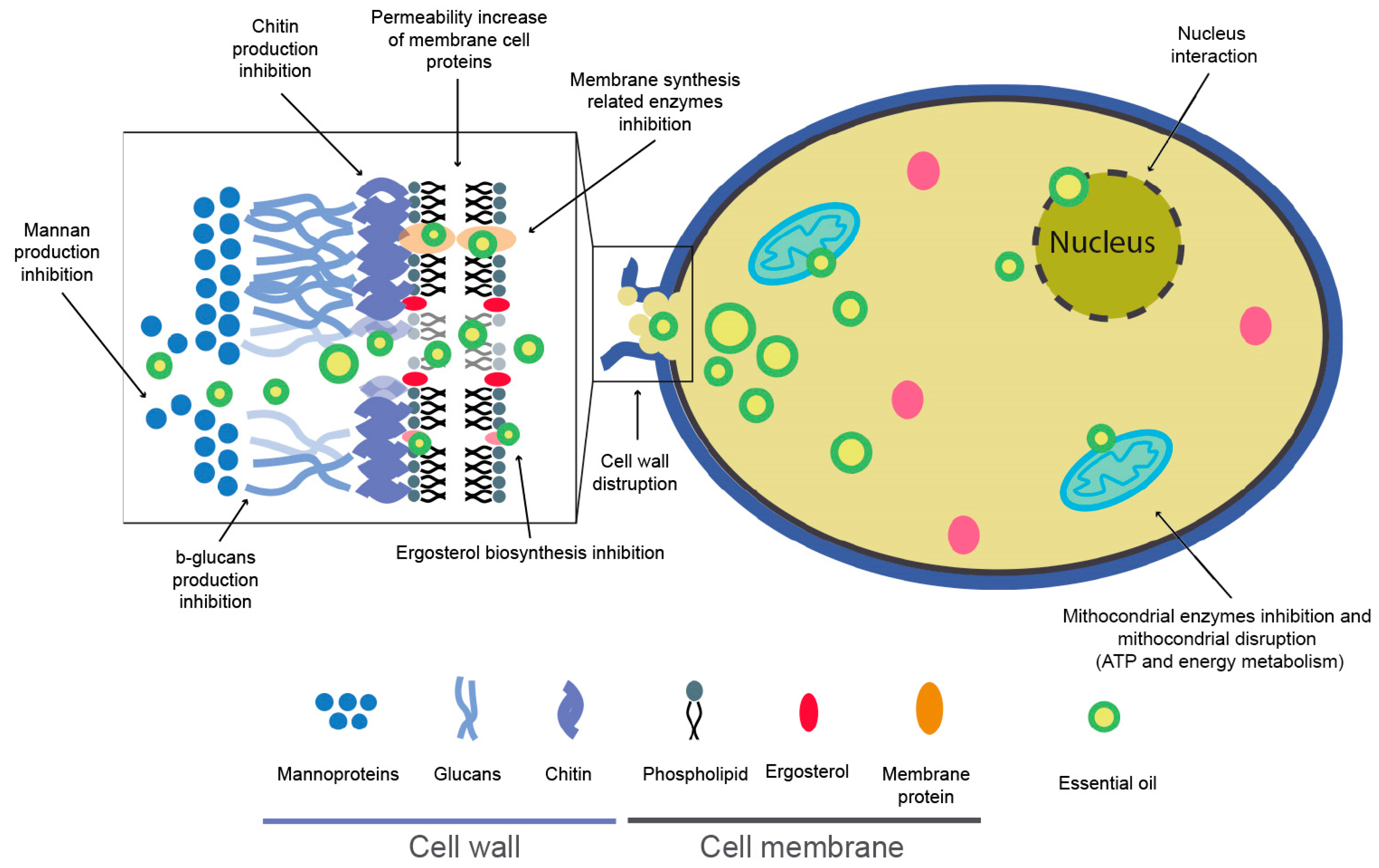
EO components such as hydrocarbons, alcohols, phenols, lactones, esters, or aldehydes are responsible for antimicrobial activities, probably acting each component in its own way [129]. The antifungal mechanism of EOs can be influenced by the lipophilic nature and low molecular weight of terpenes/terpenoids, allowing cell membrane disruption, sporulation inhibition, and germination [130]. The cell membrane and cell wall are the main structural elements of fungal cells and are composed mainly of ergosterol, chitin, b-glucans, and mannan, respectively. EO compounds can inhibit and stop the production of these substances, which causes cell disruption and death. Furthermore, EOs affect one of the most critical cell organelles, the mitochondria, where ATP biosynthesis and the respiration process succeed and coagulate the cytoplasm. EOs can damage this organelle, producing a variation in the biological activity and causing cell death (Figure 6) [126,130,131,132,133,134,135,136].
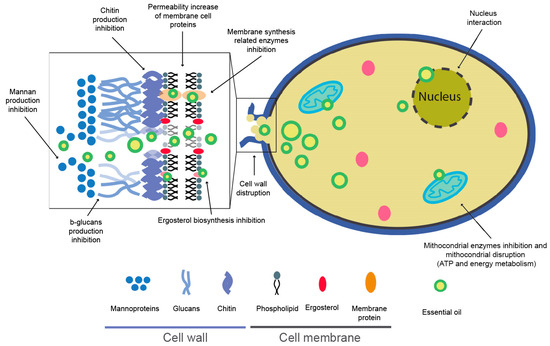
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of possible essential oils (EOs) biocide mechanism [123,126,127,130,131,134,135,136].
EO toxicity and its current legislation are complex and discussed further in the critical comparison section. The reason is that although the EO toxicity is considered low to moderate in mammalians (LD50: 800–3000 mg·kg−1 in rodents) [136], there are components of EOs that are toxic also in small (LD50 0.1–1 g/kg [137]) [138] and huge doses (lethal doses of 350 g to a 70 kg adult [137]). In this way, it is reported that some components, such as carvacrol, pulegone, safrole, psoralen, bergapten, thujone, camphor, pinocamphone, and cinnamaldehyde, can produce skin sensitization, dermatitis, or neurological or endocrine issues [137,138,139,140]. Therefore, EO safety is based on their chemical structure and dose, and in comparison, chemical biocides used in conservation are a less hazardous alternative [114].
4.1. EOs Application on Easel Painting Conservation
The use of essential oils in easel painting conservation treatments is emerging, and there are few references. For this reason, this chapter overviews different investigations about the study of EO application on easel paintings and related materials, including wood, textiles, and polychromies (Table 3). Recent references, according to the use of EOs in easel paintings, are generally in vitro studies on plates or mock-ups [49,55,141,142] and, in just one, applied the EOs in vivo [47].

Table 3.
Use of EO on easel painting conservation.
Elsayed and Sabana, 2018 [49] tested the effect of EOs extracted from Origanum majorana, Cinnamomum camphora, Syzygium aromaticum, and Ocimum basilicum (Elnekity, Mansoura, Egypt) at 20%–60% for plates assays and 40%–80% on mock-ups against stock strains of A. alternata, and A. niger (Plant Pathology Department, Mansoura University, Egypt). In their investigation, the authors used the poisoned food method as an in vitro antifungal test (20%–60% EO concentration) on plates and mock-ups, simulating archaeological oil paintings (40%–80% EO concentration). The best in vitro plate results were achieved by the highest concentration in all essential oils and strains: S. aromaticum and C. camphora against A. alternata at 60% obtained 76.00% and 74.44% of inhibition, respectively. In comparison, at the same concentration, both EOs against A. niger achieved 61.89% and 74.78% of inhibition. The authors sprayed the different EOs on the surface of mock-ups as a preventive treatment. After the inoculation and incubation of both strains, the best result was achieved with C. camphora (80%) obtaining an inhibition of 98% on A. alternata and 95.6% on A. niger. All essential oils at 80% concentration achieved <90% of spores’ mortality.
Gatti et al., 2021 [141] tested S. aromaticum (buds, Fitomedical, Binasco, Italy) and Origanum vulgare EOs (flowers, Fitomedical, Binasco, Italy) diluted with ethanol 70% at a 2:1 ratio against fungal strains isolated from a Giovanni Maria Mossa’s oil on canvas painting: P. chrysogenum, Penicillium sp., Cephalotheca foveolata, A. versicolor, Cladosporium parahalotolerans, and other fungi from Trichocomaceae and Chaetomiaceae families. Using an in vitro test on agar plates, the authors tested the effect of both EOs in contact (disk diffusion assay) and contactless (vapor phase, overturning the agar plate, and adding the EOs on the lid). In the contact test, both EOs showed high antifungal activity against P. chrysoenum, C. foveolata, Cephaloteca sp., A. versicolor, and Chaetomiaceae. However, O. vulgare EO performed better in the rest of the strains. Because of that, this EO was chosen for the contactless test. Due to the high antifungal activity of the O. vulgare volatile compounds, the inhibition was higher than the contact test on the same strains (P. chrysogenum, Aspergillus sp., A. versicolor, and C. foveolata).
Furthermore, Martin Rey, 2017 [70] studied the incorporation of Melaleuca alternifolia (leaves), Rosmarinus officinalis, and Thymus vulgaris EOs and R. officinalis and T. vulgaris extracts (Manuel Riesgo SA, Madrid, Spain) as conservative substances into synthetic and semisynthetic adhesive mixtures (Plextol B500, Synthomer plc, London, UK, Klucel G, CTS España, Getafe, Spain) for canvas reinforcement. In the study, the author inoculated different biocide-adhesive dried films (7% of EOs concentration) with A. niger, P. crysogenum, and C. globosum from a stock collection. Regarding antifungal abilities, all EOs and extracts tested in the study showed fungal growth total inhibition after four weeks of incubation. Similarly, Lee et al., 2018 [142] tested the addition of Cymbopogon nardus EO (Anshin camphor oil, Ltd., Hsinchu, Taiwan) on a gelatin solution, a very common adhesive used in oil on canvas consolidation. At 0.5% and 1%, the EO inclusion achieved the total inhibition of a stock A. niger strain (Colección Española de Cultivos Tipo, Valencia, Spain) after four weeks of incubation on adhesive films and tung oil-on-wood mock-ups treated with the adhesive mixture. However, as the authors reported, the results obtained on the mock-up test are influenced by the antifungal effect of tung oil.
In the research of Minotti et al., 2022 [47], the authors develop a treatment methodology for “Il Silenzo”, a Jacopo Zucchi oil painting conserved at the Uffizi Museum. In their study, the authors test EOs and Hydrolates (Hys) from Monarda didyma and Monarda fistulosa (Dept. of Agricultural and Food Sciences, University of Bologna, Italy), EO from Cinnamomum zeylanicum (bark, PRANAROM International, Ghislenghien, Belgium), and Hys from Citrus aurantium (Erboristeria Magentina s.r.l., Turin, Italy). Fungal strains were isolated from the painting and identified as: A. alternata, A. niger, A. pullulans, C. globosum, C. cladosporiorides and P. citrinum. To improve the hydrophilicity of the EO, the treatment was performed using an EO–Hy oil in water (o/w) emulsion. The authors used a broth microdilution susceptibility test to determine that C. zeylanicum EO and C. aurantium Hy achieved the best performance. The highest Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Fungicide Concentration (MFC) were 0.008% v/v and 0.125% v/v and 6.25% v/v and 3.12% v/v, respectively, on all strains tested. Zucchi’s painting was applied by spraying the o/w emulsion, where the oil phase was composed of the EO–Hy mixture.
Elsayed et al., 2023 [143] tested self-extracted essential oils from seeds, leaves, stems, or fruits of Piper nigrum, Capsicum annuum, Cinnamomum verum, Zingiber officinale, and C. camphora on A. niger, A. flavus, C. halotolerans, and N. goegapense isolated from different objects of Egyptian CH, among which were three oil paintings. Using in vitro contactless assay on oil on canvas painting mock-ups, the authors reported that P. nigrum L. EO achieved the most important inhibition against A. flavus (98.81%), C. halotolerans (97.68%), and N. goegapense (99.85%), while EO of Z. officinale achieve the best results against A. niger (98.21%). The same results were achieved in terms of spore death.
On an oil-on-wood painting from the Saqqara excavation (Giza, Egypt), Geweely et al., 2019 [55] studied 12 different EOs (Natural Oils Department, National Research Center in Dokki, Egypt) as antifungal agents at concentrations of 0.125 µL/mL, 0.25 µL/mL, 0.5 µL/mL, 0.75 µL/mL, 1 µL/mL, using a similar in vitro methodology to Elsayed and Shabana, 2018. All EOs were tested on 16 species of fungi isolated from the studied objects. Aspergillus sp. was the genera with the highest frequency of occurrence. They conclude that the best EOs for the inhibition of the growth of tested fungi are T. vulgaris (MIC: 0.25–0.75 µL/mL), S. aromaticum (MIC: 0.5–1.0 µL/mL), and Pelargonium odorantissimum (geranium) (MIC: 0.5–1.0 µL/mL), improving their antifungal activity when increasing its concentration.
On wood, Pop et al., 2020 [144] tested Eugenia caryophyllata (buds, Steaua Divina Ilfov, Romania) EO applied by brush at 5%–10% in ethanol on samples of Fagus sylvatica wood. At the same concentrations as Diffusit S (Wolman, Sinzheim, Germany) at 10% and Biotin T (CTS, Vicenza, Italy) at 5%, E. cayophyllata EO achieved the best results. However, any biocide achieves total inhibition after 23 days. Although it is not a CH-related investigation, some interesting conclusions about wood protection can be attached from Salem et al., 2016 [145]. In this paper, the authors test the efficacy of self-extracted Eucalyptus camaldulensis (leaves) and Pinus rigida (wood) EOs on the vapor phase (at concentrations of 5000 ppm, 2500 ppm, 1250 ppm, 625 ppm, 312.5 ppm, and 156.25 ppm) as prevention treatment against A. alternata, F. subglutinans, C. globosum, A. niger, and Trichoderma viride on Pinus sylvestris, Pinus rigida and Fagacea sylvativa wood samples. Authors find a complete inhibition of A. alternata, F. subglutinans, C. globosum, A. niger, and T. viride using P. rigida EO at 5000 ppm, while all strains grew completely at 156.5 ppm except for C. globosum. E. camaldulensis EO just reduced the growth of C. globosum at 5000 pm and 156.25 ppm and F. subglutinans at 5000 ppm. No inhibition effect was found in A. niger and T. viride with E. camaldulensis EO.
4.2. Issues about the Effect of EOs on Easel Painting Materials
Due to the aesthetical, historical, or symbolic values of CH, there are different requirements for any material used in its conservation. Some of them are compatibility with artistic materials, reversibility—or retractability—and chemical, physical, and aging stability [146]. Their volatility and hydrophobicity make EO substances difficult to apply, although they are good alternatives for air control in their vapor phase [147,148]. As a hydrophobic material, it is difficult to obtain a stable mixture with water, the most used and preferred solvent in any conservation treatment, especially for cleaning purposes. Furthermore, their use on CH artifacts can pose a risk to their preservation in terms of binders and pigment solubility during the application or chromatic changes due to aging [141,149]. In the easel painting conservation-related bibliography, authors tested material properties such as mechanics, chemical stability, or colorimetry before and after EO treatments and artificial aging.
In terms of colorimetric changes, the study of Elsayed and Sabana, 2018 [49] determined no significant changes in non-biodeteriorated mock-ups (black, white, blue, red, yellow) treated with 80%–100% EO concentration after thermal aging. Color changes were appreciated in biodeteriorated mock-ups because of the fungal remains. In the same way, Minotti et al., 2022 [47] pointed out no changes in color on oil-on-canvas mock-ups after aging but some variations on tempera ones. Martin Rey, 2017 [70] reported in her investigation changes in the color of dried adhesive samples mixed with Cympopogon sp. and Mentha sp. EO.
Furthermore, Veneranda et al., 2018 [149] reported in an interesting paper that different EO constituents, such as eugenol, thymol, and cinnamaldehyde, were yellowing after two months of aging in sunlight and UV light, added to volumetric mass density changes in the case of cinnamaldehyde. Although non-molecular changes were detected in this study by Fourier Transformed Infrared (FTIR) in eugenol and thymol, truxillic and truxinic acids as photo-dimerization products appeared on the cinnamaldehyde spectra. The vapor phase methodology employed by Elsayed et al., 2023 [143] in their study showed non-significant changes in color values on non-biocolonized mock-ups. Furthermore, the use of P. nigrum L. EO vapor does not compromise the molecular structure of paintings, as was demonstrated with their FTIR analysis.
Martín Rey, 2017 [70], Lee et al., 2018 [142], and Doménech-Carbó et al., 2015 [150] reported the effect on the mechanical properties of EO-adhesive mixtures tested. First, the addition of EOs on Plextol–Klucel mixtures supposes a barrier effect, improving their moisture-loss stability and their reversibility due to the Tg reduction and their ductility increase. Furthermore, after their thermal aging, the adhesive mixture’s flexibility increased by 5% [70]. In the case of gelatin-based adhesive, the addition of Cymbopogon nardus EO and glycerol suppose an increase in viscosity—although lower than synthetic alternatives—and adhesion, in addition to the reduction of the Elastic modulus [142]. However, these effects are due to a synergy between EOs and glycerol [150].
Regarding mechanical properties, the food industry contributes interesting investigations about natural polymer–EO mixtures for edible coatings. Although these materials are not applied to artistic materials, they can be a reference for the mechanical responses of similar mixtures applied to easel painting. For example, Ganeson et al., 2022 [151] studied the functionality of edible films using cinnamon oil-gelatin emulsion and reported a decrease in their tensile strain and an increase in Young’s modulus. The authors explain this phenomenon as the result of increased interactions between the EO–surfactant and the polymeric network of gelatin.
5. Light Radiations as a Green Physical Biocide
Although chemical methods have been the most used to disinfect cultural heritage, other treatments, such as physical ones, have also been used. Physical methods produce a biocidal effect by altering the molecules of biodeteriogenic organisms, fracturing their chemical bonds, and causing modifications in the essential biopolymers and their enzymes. Within this typology of disinfection treatments, we can make two distinctions: the systems that are based on the application of electrical and electromagnetic radiation, such as ultraviolet or gamma radiation, and those that are based on the modification of physical parameters, such as pressure or temperature [71]. The overall advantages of all of them include the simplicity of application, their harmlessness to the environment and their users, and the fact that the development of genetically resistant populations is rare, as can happen with chemical biocides [103]. On the other hand, light radiation is currently widely used in treatments in other areas of study to stop biological propagation. It is also beginning to be applied within the conservation of historical monuments [152,153].
The application of electromagnetic radiation, such as gamma or ultraviolet (UV) radiation, has been extended for a multitude of actions during recent decades. These radiations have opened a new perspective as a disinfection treatment for fungi, molds, and insects that are harmful to the health of archivists, librarians, and restorers within the conservation of cultural heritage due to the inactivation capacity of nucleic acids of organisms [152] Electromagnetic sources, such as gamma, Rötgen, and UV radiation, have an energy range of weak interaction (102 to 107 electronvolts), which limits their penetration into materials, being one of the biggest drawbacks of this type of treatment, in addition to their activity limited to the exposure time [154].
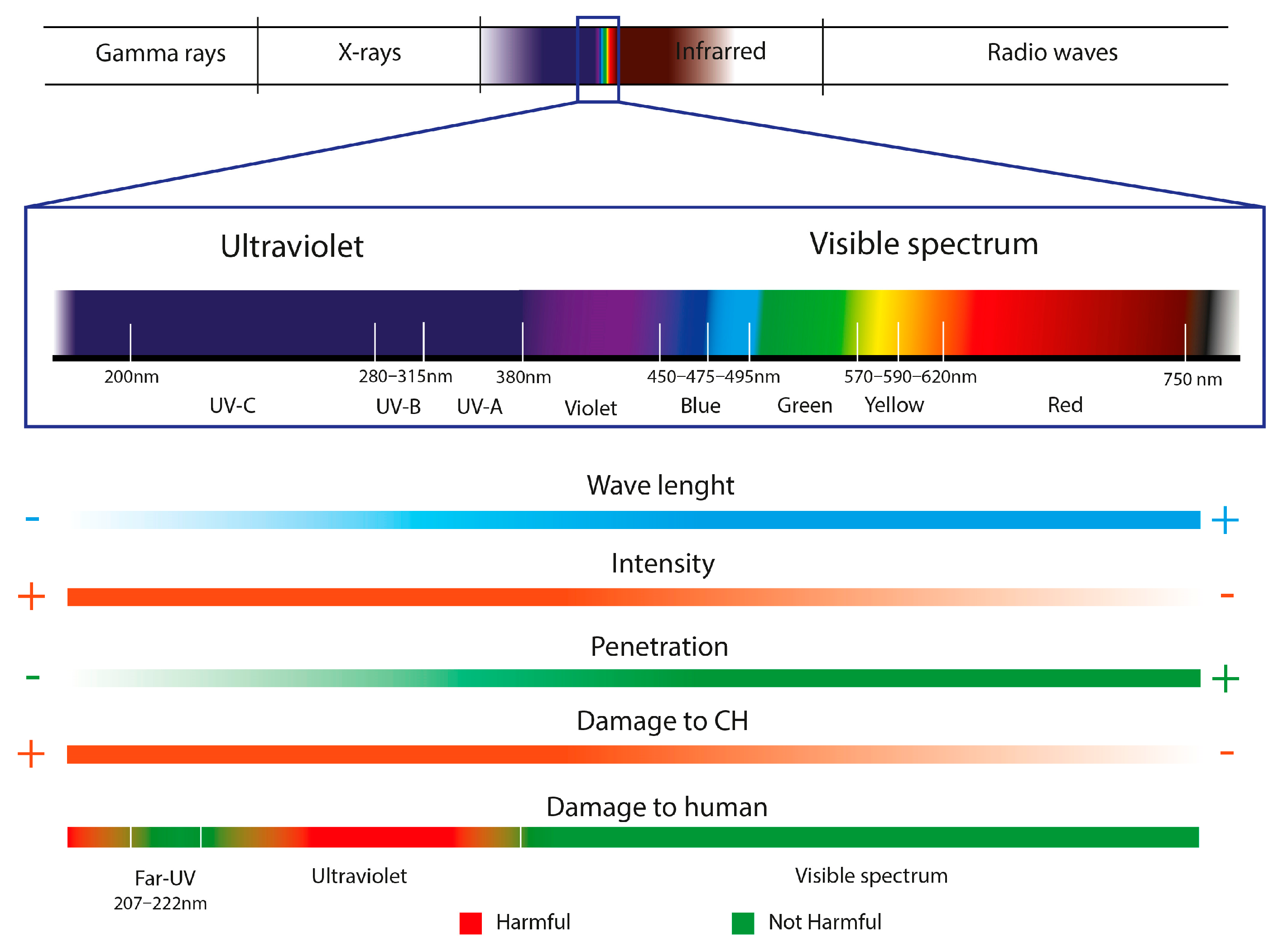
UV lighting is one of the most used radiations as an antimicrobial system in sterilizing different compounds, materials, and spaces, such as water and air, food, hospitals, microbiological laboratories, etc. [71,155,156]. Many studies demonstrate the infeasibility of propagation and metabolic activity, such as cyanobacteria, microalgae, and plants, after exposure to UV radiation. [157]. The biocidal capacity of UV lighting is directly related to its absorption by the nucleic acids of organisms. The dimers formed between the adjacent thymines of the polynucleotide chains of DNA and damage to the DNA/RNA are the main photoproducts of treating microorganisms exposed to UV radiation, which is summarized in chemical alterations that do not allow the development of biodeterogens. The microbiological inactivation capacity of this lighting will depend on several factors directly related to the radiation, such as its intensity, wavelength, and penetration. Other factors are the distance at which the object to be disinfected is located, environmental conditions, or the sensitivity of microorganisms to illumination. UV radiation is divided into four categories depending on its wavelength: UV-A (315 nm–380 nm), UV-B (280 nm–315 nm), UV-C (200 nm–280 nm), UV vacuum (100–200 nm), with the categories with lower values being those with the highest energy and lowest penetration [158].
The biocidal power of UV occurs in intensities between 200 nm and 300 nm. In the UV-C category, its maximum effectiveness is between 230 nm and 275 nm, with 254 nm of UV usually used for sterilization [156,159,160,161]. This radiation is considered dangerous for human health, as it is a potential cause of dermatitis, skin cancer, burns, peeling, etc. Been one of the main causes of its disuse in the treatment of heritage objects. Therefore, the use of protective equipment is essential [156]. Likewise, although it has great antimicrobial power at these intensities, its penetration is limited, making it impossible to inactivate the organisms that have penetrated deeply into the interior of the materials. In addition, exposure to ultraviolet lighting can cause chemical alterations, mainly in protein, cellulosic materials, and pigments, and aesthetic damage, such as chromatic changes and yellowing [71].
The devastating consequences generated in the health, economy, and education of human society due to the 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 encouraged research into disinfection systems for pathogens that are harmless to humans. Although 254 nm UV-C lighting is a good microorganism disinfection system, due to its harmful nature to human health, it is considered inadequate radiation for continuous application in indoor areas with an accumulation of people, such as schools, shops, offices, health centers, and hospitals [162]. Therefore, the challenge researchers face is implementing UV-C light in inhabited spaces [163]. Far-UVC illumination (200–230 nm) is being investigated as one of the alternatives to UV-C (254 nm). By presenting a penetration of the cells of microorganisms like UV-C (254 nm), its disinfection power is similar. Although its greatest advantage is its lower penetration into the skin’s cellular barriers, its harmlessness to mammals [162,164].
Researchers such as Buonanno et al., 2013 [165] et al. and Woods et al., 2015 [166] were pioneers in the study of Far-UVC (207–222 nm) as a substitute for skin antiseptics and the prevention of surgical infections. Determining that it is less harmful lighting than UV-B for the skin due to its limited penetration into human cells [165,166]. With the 2020 epidemic and the need to decontaminate areas contaminated by SARS-CoV-2, many researchers focused on verifying its effectiveness against the virus, among others, and its applicability in inhabited areas, concluding in its adequate viability [156,163,167]. Although the research being carried out around this lighting focuses mainly on the inactivation of bacteria and viruses, some of the lamps most currently used by different researchers such as Buonanno et al., 2020 [163], Narita et al., 2020 [156] or Panzures et al., 2023 [164], such as the Care222® Far-UVC Excimer Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) lamp, confirm its effectiveness against yeasts and fungi such as Candida spp., Penicillium expansum, and A. niger [168].
5.1. The Application of Light Radiation on Cultural Heritage
As indicated by Caneva et al., 2000, the chemical alterations UV lighting can cause in cellulosic and protein materials such as pigments mean that their use has been mainly reduced to stone, caves, and monuments [155,169]. In recent years, several researchers have used light radiation as a treatment against the proliferation of different organisms (Figure 7 and Table 4) [153,155,157,169,170,171,172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179]. Pfendler et al. 2019 [155] have proven that 254 nm UV illumination can eliminate mycelia of four fungi (Penicillium sp., Geomyces sp., Rhizomucor sp., Engydonyium album) of the six studied species found in French and Swiss caves, going so far as to affirm that it is a more economical, efficient, fast, and environmentally friendly treatment than chemical biocides [86,177]. Despite the little current information regarding the use of this treatment in easel paintings, authors such as Reverter-Carrión et al., 2018 [180] confirmed its efficiency for the disinfection of fungi recurrently present in paintings on canvas such as A. niger, although presenting greater resistance probably due to the UV absorption capacity of the melanin present in this fungus. Likewise, Borderie et al., 2014 [157] confirmed the suitability of applying UV-C treatment to eliminate other organisms, such as algae, without damaging prehistoric paintings composed of mineral pigments.
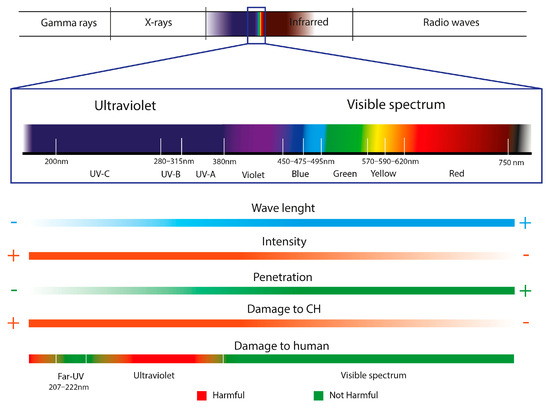
Figure 7.
Characteristics of light radiation used as a disinfectant treatment in Cultural Heritage (CH).
Likewise, the less energetic wavelengths within the UVR range (UV-A/UV-B) are also being tested for treating heritage monuments, mostly cyanobacteria [153,181,182]. Although UV-B rays have a lower energy power than UVC, the damage they cause is similar. Within the RUV range, UV-B (280–315 nm) includes the range of wavelengths most harmful to humans, which can cause everything from sunburn to skin cancer [182]. Pozo-Antonio and Sanmartín, 2018 [153] tested a treatment based on UV-B irradiation and the subsequent application of benzalkonium chloride on granite colonized by green algae and filamentous cyanobacteria, obtaining ideal results for the eradication of biofouling in granite, similar to those obtained with UV-C. The studies carried out on the application of UV-B in fungi are quite limited. For example, Selbmann et al., 2011 [183] studied the resistance of two Antarctic fungi, Cryomyces antarcticus and Cryomyces minteri, verifying their great resistance to this lighting due to the high resistance of Antarctic fungal strains. On the other hand, UV-A (315–380 nm) can also interfere with the cellular processes of organisms such as cyanobacteria [181]. Castenholz and García-Pichel, 2012 [182] indicate that UV-A presents similar effects to UV-B but with milder consequences, the main effects of the damage caused by radiation being the production of reactive oxygen that is also emitted by blue and violet waves.
During the last decade, it has been observed that outdoor lighting in stone monuments has biostatic effects on algae and cyanobacteria [184]. According to Mendez et al., 2023 [184], to minimize the impact that the lighting of monuments can have on animals, humans, and plants, this lighting should focus mainly on the yellow part of the spectrum (570–620 nm), using the smallest possible amount of blue light (380–495 nm), that is, low-energy lighting. A clear example of treatment using low-energy radiation is the Nerja Cave in Malaga (Spain), in which green lighting (500–555 nm) was applied to reduce biofilms composed of cyanobacteria and red and green algae [185]. Blue light (380–495 nm) has also been used in the Roman Catacombs of St. Callistus and Domitilla in Rome (Italy) to reduce bacterial biofilms [184,186,187]. Researchers like Sanmartín et al., 2021 [179] have gone further and combined radiation with low energy wavelengths and UVR. Specifically, the combination of UV-A and UV-B with red LED (670 nm) has been studied as a treatment for subaerial biofilms formed on the granite facades of the Xelmírez Palace and the Monastery of San Martiño de Pinario (Santiago de Compostela, Spain). Obtaining disparate results depends on the species of cyanobacteria and algae and the combination of radiation. Achieving stimulation of the proliferation of Isocystis sp. and Stichococcus bacillaris. Preventing the growth of Bracteacoccus minor, as with the application of UV-A with red LED [179].
5.2. Issues about the Effect of Light Radiations on the Textile of Paintings
In addition to its low penetration, as indicated by Caneva et al., 2000 [71], the most problematic disinfection treatment with light radiation (UV-C) is its chemical interaction with artistic materials. The most vulnerable pieces are those composed of pigments, cellulosic, and protein materials, such as easel paints [71]. Vaillant, 2003 [188] describes how UVR can precisely damage cellulosic supports, indicating that its action can cause the photolysis of cellulose molecules, their photo-oxidation, and the breaking of the chains, reducing the degree of polymerization and increasing reducing groups in the fabrics of paintings and paper works. Alterations may lead to modifications in these materials, such as increased hygroscopicity or decreased mechanical resistance.
As it is not a commonly used technique, there are no significant references to the degradation caused by UV-C disinfection in artistic fabrics. Despite this, in different industries, the study of the resistance to high-energy radiation of materials such as fabrics is recurrent, which allows us to deduce the degradation that canvas paint could suffer [189]. As Vaillant, 2003 [188] indicated, and Cuden et al., 2023 [189] reaffirmed, photodegradation is the main damage mechanism that UV produces in polymers due to its high energy concerning visible illumination, causing physicochemical modifications. The reduction in molecular weight caused by photodegradation can cause changes in physical properties such as extensibility and resistance and aesthetic changes such as color, texture, or brightness alterations [190]. It is also essential to know that the higher the energy of the UVR, the greater the degradation will be since it will more easily break the chemical bonds of the textile fibers [189]. These modifications are not immediately observable but develop over time, dependent on the radiation exposure conditions [189,191].
Another application of UV radiation that shows us its great degradation power on materials is aging regulations, which, for example, are frequently used to test the durability of materials. Regulations such as “ASTM G154-16: Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Nonmetallic Materials” [192] and “UNE 48-251-92: Paints and varnishes: Accelerated aging test. Method of exposure to alternating cycles of ultraviolet light and condensation” [193] establish the UV-A and UV-B lighting conditions applicable to materials for artificial aging. These regulations determine that the different wavelengths and intensities applied to materials can create a significant difference in their aging, in addition to the fact that the alterations are produced by repetitive exposure to said radiation.

Table 4.
Use of light radiations on Cultural Heritage (CH) materials conservation.
Table 4.
Use of light radiations on Cultural Heritage (CH) materials conservation.
| Light Radiations | Intensity/Exposition | CH Material/Country | Action | Microbiological Assays | Microorganism Strain | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-C (254 nm) | 85 ergs mm2 S−1/1, 3, 10, 15, 20, 30 min and 1, 6, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48 h | Sun Temple of Konark/India | Disinfection | In vitro test in Petri dishes | Tolypothrix byssoidea b | [170] |
| 0, 30, 60, 180 min (suspensions) 3, 6, 9 h (stones) | Domme, Laugerie-Haute and Jovelle caves/France | Disinfection | In vitro test in suspensions and in calcareous stones mock-ups | Klebsormidium flaccidum a Chlorophyceae Diniphyceae a | [172] | |
| 180 kJ m−2/periods of being on (30 min) and off (15 min) for 12 h | Moidons cave/France | Disinfection | In situ | C. minutissima Bracteacoccus sp. a Scenedesmus sp. a | [157] | |
| 150 and 300 kJ m2/4 and 8 h | Moidons cave/France | Disinfection and bleaching | In vitro test in suspensions and in situ | Chlorella minutissima a | [173] | |
| 150 kJ m−2/4 h | Moidons cave/France | Disinfection and bleaching | In vitro and in situ | Green algae | [169] | |
| 0, 1, 2, 5, 10, 15 min | Stone buildings/n.a | Disinfection | In vitro test in Petri dishes | Nostoc sp. b | [174] | |
| 4800 kJ m−2/62 h | Prehistoric caves/n.a | Disinfection | In vitro test in Petri dishes and limestone mock-ups | Bracteacoccus sp. a Phormidium sp. Verticillium sp. b Bryum argenteum d Bryum capillare d Barbula convolute d | [175] | |
| 30 kJ m−2/14 h | Moidons cave/France | Bleaching | In vitro in Petri dishes and in situ | Chlorella sp. a | [177] | |
| 646 kJ m−2/14 h | Monument Vicherey church/France | Disinfection | In situ | Algae and cyanobacteria | [194] | |
| 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 20, 30 kJ m−2/corresponding to 2.6, 5.2, 7.8, 10.4, 13, 26, and 39 min | Moidons cave/France | Disinfection | In vitro test in suspensions and Petri dishes | Chlorella vulgaris a | [178] | |
| 2, 10, 20 and 30 kJ m−2/2.6, 13, 26 and 39 min | Lascaux cave La Glacière cave Vicherey church/France | Disinfection | In vitro in suspension and Petri dishes and limestone mock-ups | Geomyces sp. c Rhizomucor sp. c Penicillium bilaiae c Engyodontium album c Ochroconis lascauxensis c | [155] | |
| UV-A/B/C + benzalkonium chloride (3% H2O) | 48 h | Granite of Rodas/Spain | Disinfection | Tests in naturally granite slab | Sporotetras polydermatica a | [153] |
| Red LED + UV-A/B | Daylight 16 h + darkness 4 h + different lights 4 h | Palace of Xelmírez and the Monastery of San Martiño Pinario/Spain | Disinfection | In vitro test in Petri dishes | Bracteacoccus minor a Pseudomuriella aurantica a Stichococcus bacillaris a Chlamydomons sp. a Isocystis sp. b Chlorella sp. a Aphanocapsa sp. b | [179] |
| Red light (630–650 nm) Blue light (460–480 nm) | 25 h | Christian catacombs of St. Domitilla and St. Callistus/Italia | Prevention | In vitro test in suspension | Eucapsis sp. b Scytonema julianum b Leptolyngbya sp. b Symphyonemosis sp. b | [171] |
| LED light + red, yellow, green and blue cellophane | 21 days with 12 h of darkness and 12 of light | Historical granite buildings/Spain | Prevention | In vitro test in suspensions | Bracteacoccus sp. a Chroococcus sp. b Isocystis sp. b Pseudocapsa dubia a | [176] |
Cultural Heritage and countries. n.a.: Non-available. Microorganism strain. a: Algae; b: cyanobacteria; c: fungi; d: moss.
6. Critical Comparison: Can EOs and Light Radiations Be a Good Alternative?
A modification of the SWOT analysis has been used to theoretically guarantee that EOs and/or light radiations can be a good alternative to traditional chemical biocides. In addition, their actual situation across the specific literature was analyzed. Thanks to this methodology, a picture of the real possibilities of these materials on easel painting conservation can be taken (Figure 8 and Figure 9).
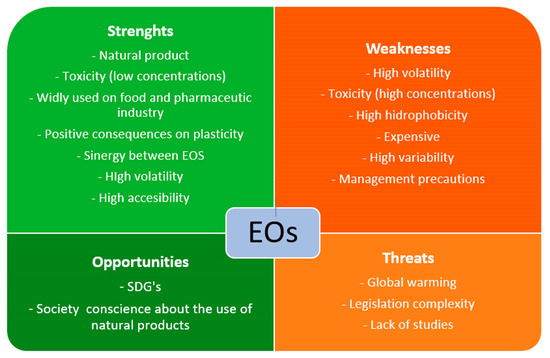
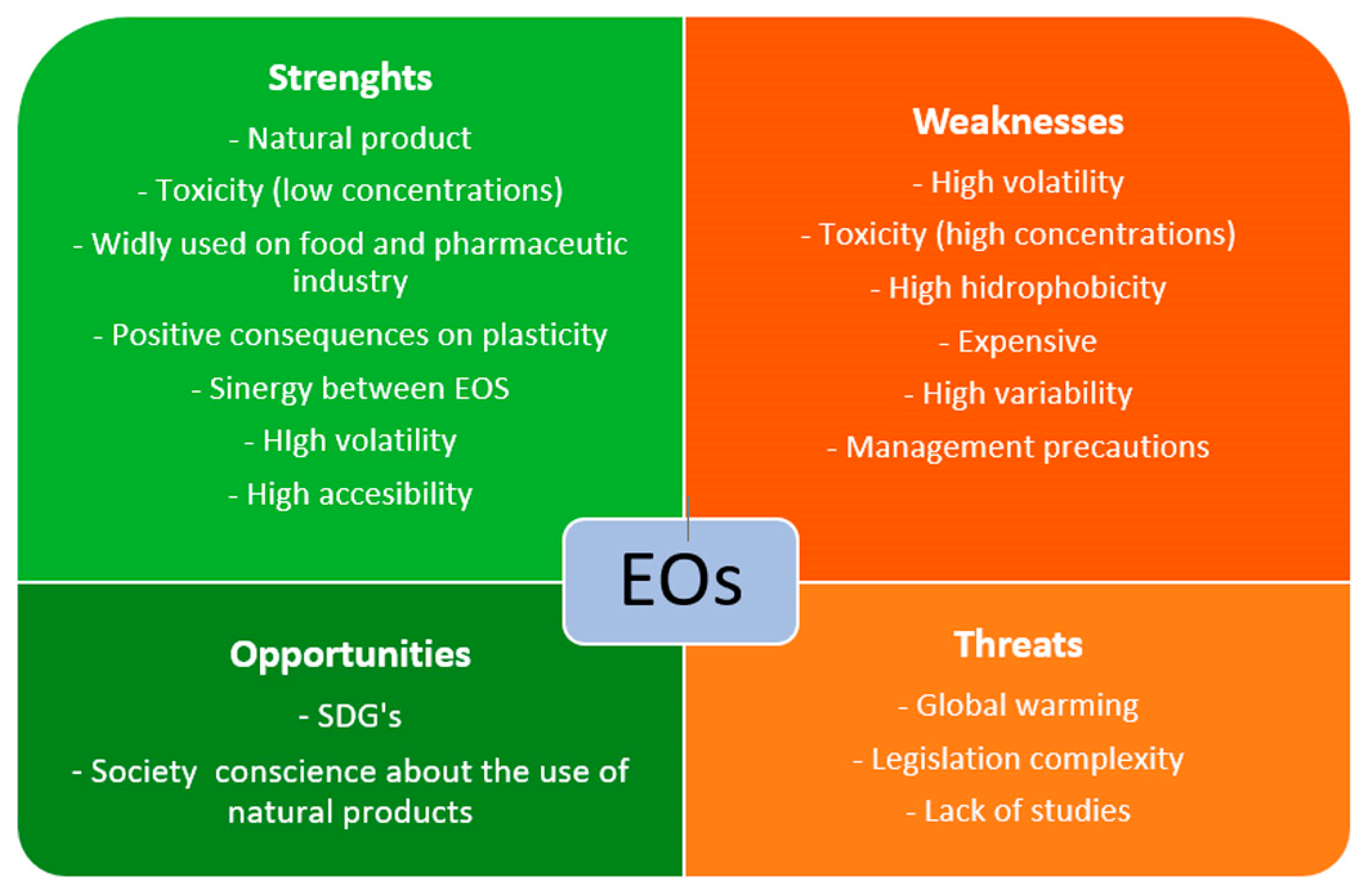
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of essential oils (EOs) SWOT analysis. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
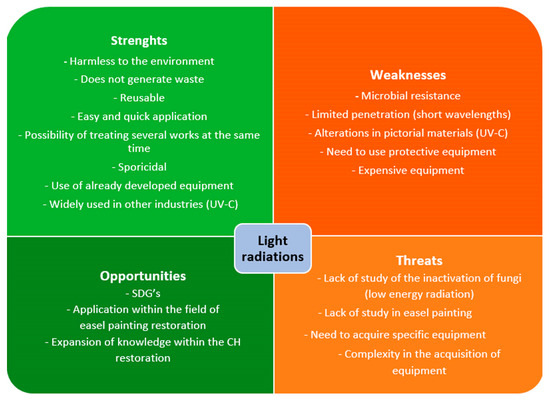
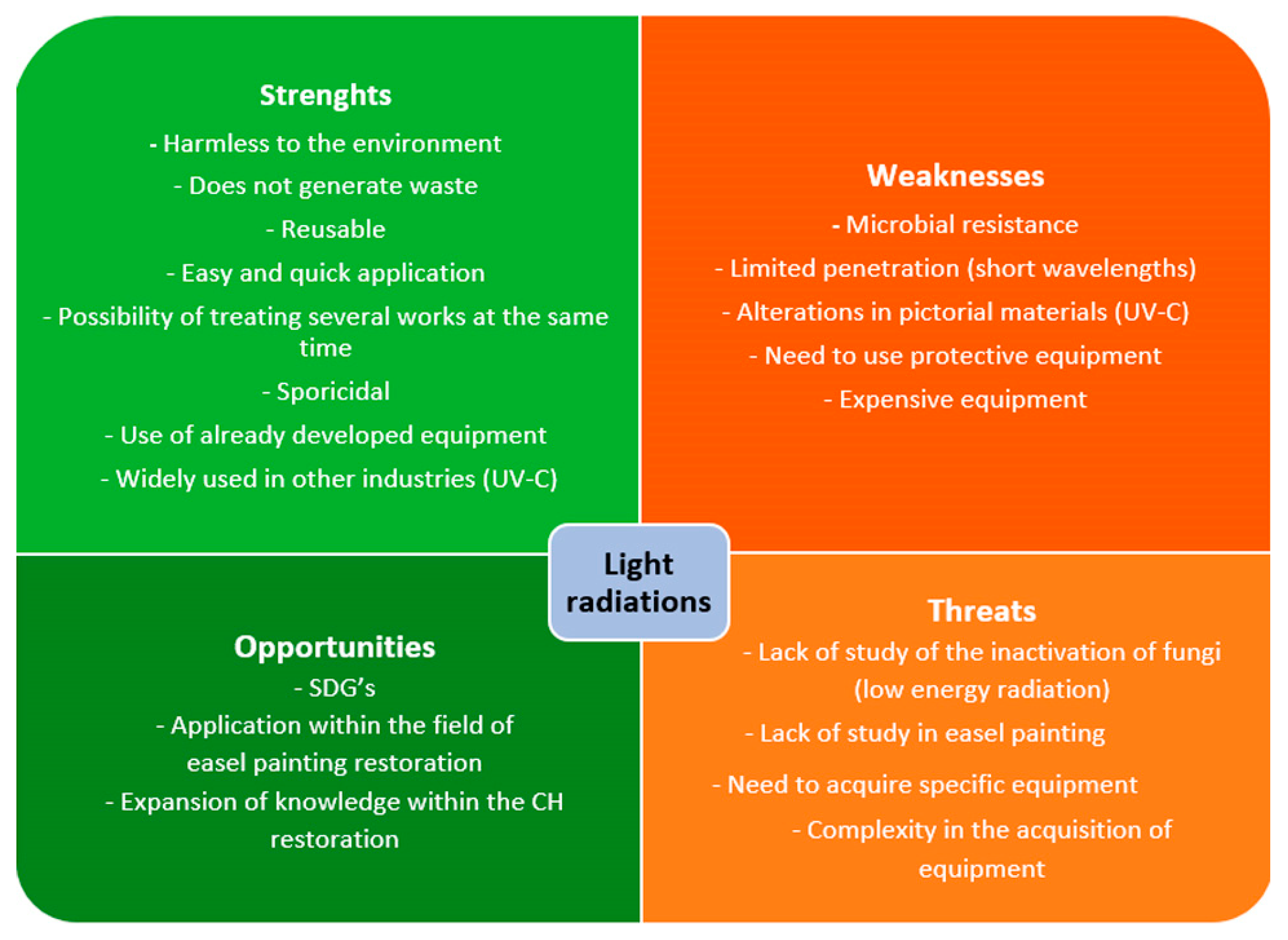
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of light radiations SWOT analysis. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs); Cultural Heritage (CH).
One of the most appreciable strengths of EOs is their natural origin. EOs are plant substances and have different functions, as explained before. In general, society wants to consume products as naturally as possible [195], and the tendency for conservation treatments has been similar in recent years. The use of “Green Chemistry” in conservation promotes the reduction and substitution of chemicals by eco-sustainable products, and in this way, EOs can be suitable substitutes for chemical biocides [1,196].
In contrast, one weakness of EOs is their high variability in terms of antimicrobial activity, which depends directly on the plant species, the origin region, the season of pick up, the part of the plant where EOs are extracted (leaves, buds, roots…), or even the method of EO extraction [197]. Furthermore, their effectiveness depends on the fungal species they treat. However, in front of this weakness, EOs can synergize with other EOs, achieving better biocide results than separately [198,199]. The hydrophobicity of EO compounds could be a weakness in easel painting conservation. As mentioned above, these inconveniences are related to their use in dilution with solvents for cleaning purposes or as preventive material in adhesive mixtures. Following “Green Chemistry” recommendations, restorers are used to choose water as a solvent in any treatment, and the inclusion of an oil phase supposes the addition of surfactants and low- or high-energy instruments to obtain an emulsion [200]. This is not always possible because of the adverse effects of some surfactants on painting surfaces. In addition, EOs as preservatives generally need encapsulation to improve their useful lives [201]. The high volatility of EOs can be a weakness and a strength. As an additive in an adhesive or a cleaning system, EOs will require a reduction of volatility to increase the mixture’s shelf-life. However, its high volatility is important in air cleaning or contactless treatments [141,147,202].
As Isman, 2020 [203] reported, EO price and availability depend on each other, which can be considered a weakness. EO commercialization has some issues that affect their cost due to the requirement of expensive production methods and the low yield of raw materials [204]. For example, 450 kg of Narcisus poeticus flowers yields between 350 g and 1 kg of EOs, depending on the extraction method [205]. As with any product, the large-produced, widely-used EOs are cheaper than those less used or demanded [203]. Taking, for example, Biotin T (CTS) and Origanum compacum, T. vulgaris, M. alternifolia, or S. aromaticum EOs (PRANAROM), the price range around 0.057 €/g for Biotin T, and around 1.30–1.60 €/g, 3.30–4.50 €/g, 0.60–0.70 €/g and 0.60–1.20 €/g for each EO, respectively (October 2023). In terms of availability, EOs can be found easily in pharmacies—although generally in small doses—while conservation biocides need to be ordered from specialized distributors, spending generally more time.
The biggest threats to EOs are probably legislation and regulation complexity related to their toxicity and global warming. The toxicity of EOs plays a two-sided role, and their concentration and appropriate management are the key [206], as also reported in Safety Data Sheets or leaflets. In other industries, such as pharmacy or food science, EOs are being applied in low concentrations as a treatment against fungal growth, among other utilities [207]. In those areas, products such as fruit are coated with EO edible films [208], or EO-based drugs are being produced [209]. In those applications for human consumption or health care, the safety of some EOs was proven and is considered GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) by the USA Food and Drugs Administration (FDA).
Furthermore, Institutions such as the European Medicinal Agency recognize EOs as pharmaceutical ingredients, subjecting them to different controls [210]. As was mentioned before, some studies warn about the toxicity of EOs, and legislation concerning EOs is complex insofar as there are no standardized controls, and they depend on their use [211]. In Europe, synthetic and natural biocides share the Regulation n° 528/2012. This Regulation establishes the possibility of increasing the number of commercially accepted biocides, above all natural ones that substitute synthetic ones, although it is a costly process [212,213].
Recently, there were different polemics about including some EOs as toxic in a revision of Regulation No. 1272/2008 [214] about the classification, labeling, and packaging of substances and mixtures. This revision aimed to consider it as “More than one constituent substance” (MOCS). As a result, EOs would have been considered toxic if one of their components had been considered this way. Finally, in October 2023, the European Parliament approved excluding that change from the final revision, considering [215]. Internationally, the World Health Organization (WHO) or the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations regulates the use of EOs, highlighting the WHO “Essential Medicine and Health Products Information Portal”, guidelines and volumes [211]. As Neagu et al. 2023 [210] reported, the FDA regulates the use of EOs as cleaners, fragrances, or drugs, restricting their sales with any curative or prevention intention. For this reason, the present investigation considers that low-toxicity EOs in small doses are a strength. Still, the caution of their management in pure for their dilution for being used in a conservation treatment must be considered as a weakness or even a threat.
As plants derivate, the effect of global warming and climate change on plant cultivation is critical for their production. This phenomenon can change the EO properties due to changes in some plant development [216]. Studies such as Laftouhi et al., 2023 [217] show the changes in the content of primary and secondary metabolites of R. officinalis EOs from Taounate, Morocco due to Tª or water variations; Cautela et al., 2021 [218] also demonstrate the effect of the drought of Citrus Bergamia EOs production in Calabria, Italy. However, the effect of EO production on the environment should be considered during fertilization, irrigation, and extraction to reduce their impact on nature and human health [219]. Apart from that, regarding material mechanics, their role as plasticizers is a strength, improving the elasticity of film-forming substances, such as adhesives used in easel painting conservation.
Opportunities for EOs in easel painting conservation are related to their natural origin and biocide properties. Today, society’s conscience about the importance of natural, sustainable products linked to the SDGs plays an important role in the industry, and restorers require effective, non-toxic solutions, as was mentioned above. Furthermore, the use of EOs can be a good option for dynamizing the circular economy, especially in the case of citrus, whose major component is Limonene, a high antimicrobial agent [220,221]. It is well-known that the EOs extracted from citrus are in the peel and seeds of the fruits, supposing their reuse for EOs extraction is a good way to reduce plant waste [222,223]. As plant derivates, EOs can contribute to climate change if they are cultivated in a responsible way. For this, ecological cultivation and using green EO extraction systems must be considered to reduce the environmental impact [224,225,226]. In this way, EOs can be a good opportunity to improve CO2 footprint reduction, promoting km0 cultivation, extraction, and consumption.
On the other hand, as indicated in Figure 9, one of the most notable points of the disinfection treatment with light radiation is its harmlessness to the environment. As artificial lighting is replicated from natural radiation, it does not produce pollution or generate waste when produced, respecting the environment [194]. In this way, it supports the SDGs, highlighting 12.4 “Climate action”, to which the implementation of UV would contribute since the use of chemical compounds would be reduced [29].
Likewise, unlike traditional chemical biocides with a single use, since lamps generate radiation, they can be reapplied multiple times without acquiring new equipment over a long period. For example, the UNE 48-251-92 regulation indicates that under conditions of use, the useful life of UV-A/UV-B lamps can reach 1600 to 1800 h.
On the other hand, applying the treatment with light radiation is simple for the user since it is unnecessary to carry out dissolutions or gelations, as in the case of chemical biocides. The affected parts or areas must be exposed to lighting for the required time. It can also treat multiple works or large, colonized surfaces in each treatment cycle. Furthermore, as it is a controlled treatment, only the affected area is treated without interfering with the environment [157].
Light radiation (UV-C) is commonly used for disinfection in different areas, such as clinical and food. For this reason, the equipment used for disinfection has already been designed, developed, and tested [71,156,194]. Therefore, developing new equipment for use in CH is not necessary; only its adaptation is.
The most notable strength of light radiation in CH, mostly UV-C, as an organism inactivation treatment is its negative effects on the viability and metabolic activity of organisms such as plants, microalgae, cyanobacteria, and fungi [155,157]. Likewise, authors such as Pfendler et al., 2018 [194] have verified that UV-C, besides achieving the inactivation of fungal mycelia, is also sporicidal and can be applied preventively and curatively. Also, this light has interesting effects on restoring monuments, caves, or sculptures, such as the bleaching of biofilms [227], which could also create unwanted decoloration of the tissues.
Likewise, one of the drawbacks that must be considered regarding the effectiveness of radiation treatment, specifically UV-C, is that fungi that contain pigments such as melanin can make them resistant to inactivation [194]. The low penetration of short wavelength radiation, which is most used in the inactivation of micro-organisms (UV-C) [87], can be a serious weakness due to the impossibility of eliminating internal colonization. The physicochemical and mechanical alterations caused by the different radiations when applied repeatedly to tissues can be one of the disadvantages of this treatment [71]. By modifying the characteristics of the tissues, they could become more prone to subsequent colonization due, for example, to the possible increase in sensitivity to humidity caused by the breakdown of cellulose bonds.
Non-visible radiation, such as UV, can also cause alterations in human health, causing damage to the skin and eyesight, except for Far-UV lighting and visible radiation that are not harmful to mammalian cells [162]. Therefore, using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as protective glasses and clothing opaque to UV penetration, is essential. Applicants’ exposure to this radiation should be as little as possible, as indicated by the UNE-EN ISO: 15858 regulations [228]. Although the durability of the lamps is extensive, their acquisition is only affordable for some restoration teams. For example, the equipment currently being created, such as the Care222® Far-UVC Excimer Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation (UVGI) lamp (222 nm), is complicated to acquire, and its cost is high.
One of its greatest threats is the lack of knowledge regarding disinfection treatment using light radiation in easel painting. The applications of light radiations are mostly reduced to the treatment of monumental heritage [179]. Likewise, the research has mostly analyzed its effectiveness against organisms other than fungi. And the research on fungi has yet to focus on fungal organisms from easel paintings. Therefore, whether these radiations effectively inactivate fungal mycelia and spores from easel paintings is unknown.
We can also identify the opportunities this new research line can offer. Treatment with light radiation for disinfection fungal agents in textile pictorial supports has yet to be studied, offering the possibility of opening a new line of research. It is an opportunity to develop an ecological, healthy, and non-harmful treatment for easel paintings, providing new knowledge to the conservation of painting on canvas and other CH objects.
7. Conclusions
Biodeterioration is a complex damage combination that includes aesthetical, physical, and chemical alterations due to biological activities, which can contribute to the loss of material and immaterial values of easel paintings. As was explained in the introduction of this investigation, climate change and global warming increase the risk of biodeterioration, and this challenge requires eco-suitable and non-toxic solutions. EOs are natural-origin substances with great biocidal activity, although their application in real cases is scarce. After analyzing the benefits and drawbacks of most used traditional and alternative biocides for easel painting conservation, it can be concluded that EOs are a good alternative to investigate further (Table 5). On the other hand, disinfection using light radiation is another ecological alternative. Despite this, they present significant problems in terms of penetration and alteration of the materials, so it is possible that in addition to causing damage to the tissues, they do not completely inactivate the organisms in the works. Therefore, a good alternative would be radiation with longer wavelengths, greater penetration, and lower intensity. Likewise, arduous research is necessary to verify the effectiveness of these radiations against the fungi usually present in paintings on canvas. EOs and light radiations are shown here as interesting eco-friendly methods for easel painting biocontrol. Further research will allow them to substitute traditional chemical products.

Table 5.
Analysis of benefits and drawbacks of most commonly used biocides and alternative biocides.
8. Perspectives
EO’s perspectives in easel painting conservation can include encapsulation, air diffusion, or nanoemulsions. Regarding prevention, EO encapsulation has some advantages compared to non-encapsulated ones. Its hydrophobicity, volatility, risk of binders solubilization, or colorimetric changes can be reduced, in addition to the increase of protection against degradation (UV light or oxidation) [128,229,230,231]. In addition, different treatments for easel painting conservation can be good alternatives for including encapsulated EOs as antifungal substances (e.g., varnishing). Due to the effectivity of their volatile compounds, EOs can be investigated as indoor air quality control agents for museum rooms or storage, taking as reference studies such as Díaz-Alonso et al., 2021 [147]. Regarding curation, using EO nanoemulsions or nano gels for fungal strain removal, adapted from other CH conservation disciplines, explored by Minotti et al., 2022 [47], is a potential investigation line. In this way, the versatility of emulsions or gels in terms of applicability and their well-known use in painting conservation cleaning treatments [232,233] could allow restorers to control the EO’s use to eliminate fungal contamination.
On the other hand, light radiation within easel painting conservation offers promising possibilities against biological colonization, although more investigations are required. The greatest challenge in applying these treatments is determining each light’s exposure times and fungal inhibition. Regarding fungal inactivation, wavelengths with less penetration but greater energy could play a fundamental role in paralyzing superficial fungal attacks, such as Far-UV or UV-C, commonly used for macro and microorganisms [156,234]. In canvas paintings with more developed fungal damage and greater fungal penetration, applying treatments with greater penetration, such as visible radiation or UV-A/B, would be necessary. One of the most beneficial options for human health would be using radiation that is not harmful to the skin and eyes, such as visible lighting or Far-UV [163], which would allow the application of the disinfection treatment without the need for specific protective equipment. In addition to being a curative treatment, determining the same parameters for the inactivation of fungal spores could open the doors to preventive treatments that would minimize biological development in works exposed to favorable climatic conditions. It must be considered that the recurrent application of light treatments such as UV can accelerate the aging of materials such as cellulose [189].
Future perspectives on both research lines must be focused on reducing risks, improving economic and environmental sustainability, and increasing easel painting compatibilities, biocide long-term effects, and efficacy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.B.-R. and S.M.-R.; Methodology, A.S.-L., H.O.-U. and P.B.-R.; Formal Analysis, A.S.-L. and H.O.-U.; Investigation, A.S.-L., H.O.-U., P.B.-R. and S.M.-R.; Resources, P.B.-R. and S.M.-R.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.S.-L., H.O.-U., P.B.-R. and S.M.-R.; Writing—Review and Editing, A.S.-L., H.O.-U., P.B.-R. and S.M.-R.; Supervision, P.B.-R. and S.M.-R.; Project Administration, P.B.-R. and S.M.-R.; Funding Acquisition, A.S.-L., H.O.-U., P.B.-R. and S.M.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación (PID2019-110616RB-I00 and PRE2020-093139) and Generalitat Valenciana (CIACIF/2022/179).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Russo, R.; Palla, F. Plant Essential Oils as Biocides in Sustainable Strategies for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, P.; Luca, D.D. A Metabarcoding Approach for the Study of Biodeterioration of Ancient Wall Paintings in an Italian Cave. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2204, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucconi, L.; Canini, F.; Isola, D.; Caneva, G. Fungi Affecting Wall Paintings of Historical Value: A Worldwide Meta-Analysis of Their Detected Diversity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Fiorentino, S.; Montanari, M.; Roversi Monaco, C.; del Bianco, A.; Vandini, M. Learning from the Past, Intervening in the Present: The Role of Conservation Science in the Challenging Restoration of the Wall Painting Marriage at Cana by Luca Longhi (Ravenna, Italy). Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suphaphimol, N.; Suwannarach, N.; Purahong, W.; Jaikang, C.; Pengpat, K.; Semakul, N.; Yimklan, S.; Jongjitngam, S.; Jindasu, S.; Thiangtham, S.; et al. Identification of Microorganisms Dwelling on the 19th Century Lanna Mural Paintings from Northern Thailand Using Culture-Dependent and-Independent Approaches. Biology 2022, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, B.; Young, M.E.; Turmel, A.; Fuentes, E. Role of Masonry Fabric Subsurface Moisture on Biocolonisation. A Case Study. Build. Environ. 2022, 210, 108690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröer, L.; de Kock, T.; Godts, S.; Boon, N.; Cnudde, V. The Effects of Cyanobacterial Biofilms on Water Transport and Retention of Natural Building Stones. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2022, 47, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.; Trovão, J.; Portugal, A. Phototrophic and Fungal Communities Inhabiting the Roman Cryptoporticus of the National Museum Machado de Castro (UNESCO Site, Coimbra, Portugal). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipper, P.J.A.; Skipper, L.K.; Dixon, R.A. A Metagenomic Analysis of the Bacterial Microbiome of Limestone, and the Role of Associated Biofilms in the Biodeterioration of Heritage Stone Surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.; Rosado, T.; Candeias, A.; Mirão, J.; Caldeira, A.T. A Change in Composition, a Change in Colour: The Case of Limestone Sculptures from the Portuguese National Museum of Ancient Art. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 42, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Song, W. Fungal Communities in the Biofilms Colonizing the Basalt Sculptures of the Leizhou Stone Dogs and Assessment of a Conservation Measure. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, D.; Bartoli, F.; Meloni, P.; Caneva, G.; Zucconi, L. Black Fungi and Stone Heritage Conservation: Ecological and Metabolic Assays for Evaluating Colonization Potential and Responses to Traditional Biocides. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.C.; Pintado, M.; Moreira, P.R. Sampling Methods for Outdoor Sculptures: Comparison of Swabs and Cryogels by Flow Cytometry as Novel Alternatives for Assessment and Quantification of Microbial Contamination. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 54, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.C.; Madureira, A.R.; Pintado, M.; Moreira, P.R. Biocontamination and Diversity of Epilithic Bacteria and Fungi Colonising Outdoor Stone and Mortar Sculptures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 3811–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, C.; Bordalo, R.; Silva, M.; Rosado, T.; Candeias, A.; Caldeira, A.T. On the Conservation of Easel Paintings: Evaluation of Microbial Contamination and Artists Materials. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2017, 123, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Pancaldi, S.; Baldisserotto, C.; Petrucci, F.; Impallaria, A.; Volpe, L.; D’Accolti, M.; Soffritti, I.; Coccagna, M.; Sassu, G.; et al. Characterization of Biodegradation in a 17 Th Century Easel Painting and Potential for a Biological Approach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, C.; Sandu, I.; Sandbakken, E.; Candeias, A.; Caldeira, A.T. Biodeterioration in Art: A Case Study of Munch’s Paintings. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavkler, K.; Humar, M.; Kržišnik, D.; Turk, M.; Tavzes, Č.; Gostinčar, C.; Džeroski, S.; Popov, S.; Penko, A.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; et al. A Multidisciplinary Study of Biodeteriorated Celje Ceiling, a Tempera Painting on Canvas. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 170, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyatos, F.; Morales, F.; Nicholson, A.W.; Giordano, A. Physiology of Biodeterioration on Canvas Paintings. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Miras, M.; Piñar, G.; Romero-Noguera, J.; Bolívar-Galiano, F.C.; Ettenauer, J.; Sterflinger, K.; Martín-Sánchez, I. Microbial Communities Adhering to the Obverse and Reverse Sides of an Oil Painting on Canvas: Identification and Evaluation of Their Biodegradative Potential. Aerobiologia 2013, 29, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicu, I.C.; Fatorić, S. Climate Change Impacts on Immovable Cultural Heritage in Polar Regions: A Systematic Bibliometric Review. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2023, 14, e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.S.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J.J. Climate Change Impacts on Cultural Heritage: A Literature Review. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyshkvarkova, E.; Sukhonos, O. Climate Change Impact on the Cultural Heritage Sites in the European Part of Russia over the Past 60 Years. Climate 2023, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A.; Sardella, A. Climate Change and Cultural Heritage: Methods and Approaches for Damage and Risk Assessment Addressed to a Practical Application. Heritage 2023, 6, 3578–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatorić, S.; Daly, C. Towards a Climate-smart Cultural Heritage Management. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2023, 14, e855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verticchio, E.; Frasca, F.; Matè, D.; Giammusso, F.M.; Sani, M.; Sebastiani, M.L.; Sclocchi, M.C.; Siani, A.M. Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on the Biodeterioration Risk in Historical Buildings of the Mediterranean Area: The State Archives of Palermo. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonthijun, P.; Mills, N.; Mills, N.; Yongsawas, R.; Sansupa, C.; Suwannarach, N.; Jaikang, C.; Motanated, K.; Chayapakdee, P.; Jongjitngam, S.; et al. Seasonal Variations in Fungal Communities on the Surfaces of Lan Na Sandstone Sculptures and Their Biodeterioration Capacities. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, L.; Trillo, C.; Makore, B.N. Cultural Heritage and Sustainable Development Targets: A Possible Harmonisation? Insights from the European Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Suistanable Development Goals; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Di Turo, F.; Medeghini, L. How Green Possibilities Can Help in a Future Sustainable Conservation of Cultural Heritage in Europe. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Cortés, J.F.; Miranda, R. Green Chemistry Metrics, A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.; Eghbali, N. Green Chemistry: Principles and Practice. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.H.; Pasian, C.; De Angelis, R.; Debono, N. Cleaning of Oil-on-Stone Wall Paintings: Lessons Learned from Easel Painting Conservation. Stud. Conserv. 2020, 65, P254–P257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corregidor, V.; Oliveira, A.R.; Rodrigues, P.A.; Alves, L.C. Paintings on Copper by the Flemish Artist Frans Francken II: PIXE Characterization by External Microbeam. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2015, 348, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayle, M.; Waugh, D.G.; Colston, B.J.; Lawrence, J. On the Study of Oil Paint Adhesion on Optically Transparent Glass: Conservation of Reverse Paintings on Glass. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumer, U.; Fiedler, I.; Bretz, S.; Ranz, H.-J.; Dietemann, P. Decorative Reverse-Painted Glass Objects from the Fourteenth to Twentieth Centuries: An Overview of the Binding Media. Stud. Conserv. 2012, 57, S18–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombini, M.P.; Degano, I.; Nevin, A. Analytical Approaches to the Analysis of Paintings: An Overview of Methods and Materials. In Cultural Heritage Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Văcar, C.L.; Mircea, C.; Pârvu, M.; Podar, D. Diversity and Metabolic Activity of Fungi Causing Biodeterioration of Canvas Paintings. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Pettitt, T.R.; Buenfeld, N.; Smith, S.R. A Critical Review of the Physiological, Ecological, Physical and Chemical Factors Influencing the Microbial Degradation of Concrete by Fungi. Build. Environ. 2022, 214, 108925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepero de García, M.C. Biologia De Hongos; Ediciones Unlandes: Bogotá, Colombia, 2012; ISBN 9586957942. [Google Scholar]
- Poyatos-Jiménez, F.; Morales, F.; Morales-Carrera, R.; Boffo, S.; Giordano, A.; Romero-Noguera, J. Fungal and Bacterial Biodeterioration of Outdoor Canvas Paintings: The Case of the Cloisters of Quito, Ecuador. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2021, 31, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, G.J.; Funke, B.R.; Case, C.L. Introducción a La Microbiología, 12th ed.; Editorial Médica Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2017; ISBN 9789500695404. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Noguera, J.; Bolívar-Galiano, F.C.; Ramos-López, J.M.; Fernández-Vivas, M.A.; Martín-Sánchez, I. Study of Biodeterioration of Diterpenic Varnishes Used in Art Painting: Colophony and Venetian Turpentine. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 62, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech-Carbó, M.T.; Bitossi, G.; de la Cruz-Cañizares, J.; Bolívar-Galiano, F.; López-Miras, M.d.M.; Romero-Noguera, J.; Martín-Sánchez, I. Microbial Deterioration of Mowilith DMC 2, Mowilith DM5 and Conrayt Poly(Vinyl Acetate) Emulsions Used as Binding Media of Paintings by Pyrolysis-Silylation-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 85, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K. Fungi: Their Role in Deterioration of Cultural Heritage. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2010, 24, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowski, G.; Vogt, O.; Ogonowski, J. Paint-Degrading Microorganisms. Czas. Tech. 2017, 2017, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Minotti, D.; Vergari, L.; Proto, M.R.; Barbanti, L.; Garzoli, S.; Bugli, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Sabatini, L.; Peduzzi, A.; Rosato, R.; et al. Il Silenzio: The First Renaissance Oil Painting on Canvas from the Uffizi Museum Restored with a Safe, Green Antimicrobial Emulsion Based on Citrus Aurantium Var. Amara Hydrolate and Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Essential Oil. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojevi, J.; Grbi, M.L. Moulds on Paintings in Serbian Fine Art Museums. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, Y.; Shabana, Y. The Effect of Some Essential Oils on Aspergillus Niger and Alternaria Alternata Infestation in Archaeological Oil Paintings. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2018, 18, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, L.; Sisti, M.; Campana, R. Evaluation of Fungal Community Involved in the Bioderioration Process of Wooden Artworks and Canvases in Montefeltro Area (Marche, Italy). Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbulie, J.; Obiajuru, I. Microbial Deterioration of Surface Paint Coatings. Glob. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2004, 10, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noohi, N.; Papizadeh, M. Study of Biodeterioration Potential of Microorganisms Isolated in the Paintings Storeroom of Mouze Makhsus Museum, Golestan Palace, Tehran. Stud. Conserv. 2022, 68, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seves, A.M.; Sora, S.; Ciferri, O. The Microbial Colonization of Oil Paintings. A Laboratory Investigation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1996, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciferri, O. Microbial Degradation of Paintings. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geweely, N.S.; Afifi, H.A.; Ibrahim, D.M.; Soliman, M.M. Efficacy of Essential Oils on Fungi Isolated from Archaeological Objects in Saqqara Excavation, Egypt. Geomicrobiol. J. 2019, 36, 148–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpalanozie, O.E.; Adebusoye, S.A.; Troiano, F.; Polo, A.; Cappitelli, F.; Ilori, M.O. Evaluating the Microbiological Risk to a Contemporary Nigerian Painting: Molecular and Biodegradative Studies. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 114, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterflinger, K.; Piñar, G. Microbial Deterioration of Cultural Heritage and Works of Art—Tilting at Windmills? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9637–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiano, P. Biodegradation of Cultural Heritage: Decay Mechanisms and Control Methods. In Proceedings of the 9th ARIADNE Workshop “Historic Material and Their Diagnostic” ARCCHIP, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–28 April 2002; pp. 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, R.; Conlan, X.A.; Goel, M. Fungi as a Potential Source of Pigments: Harnessing Filamentous Fungi. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.A.; Nazir, K.H.M.N.H.; Mahmud, M.; Mishra, P.; Ali, K.; Kabir, A.; Shahid, A.H.; Siddique, M.P.; Alim, A. Isolation and Identification of Natural Colorant Producing Soil-Borne Aspergillus Niger from Bangladesh and Extraction of the Pigment. Foods 2021, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulandari, A.P.; Examinati, R.R.I.N.; Madihah, H.D.; Andayaningsih, P.; Andayaningsih, P. Citotoxicity of Metabolites Produced by Endophytic Fungus Cladosporium Sp. Isolated from Marine Macroalgae on Invitro MCF7, Hela, and DU-145 Cell Lines. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.B.; Pedersen, T.B.; Nielsen, M.R.; Wimmer, R.; Muff, J.; Sørensen, J.L. Production and Selectivity of Key Fusarubins from Fusarium Solani Due to Media Composition. Toxins 2021, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.P.; Li, X.D.; Liu, X.H.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Ji, N.Y. Secondary Metabolites from an Algicolous Aspergillus Versicolor Strain. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzurendova, S.; Losada, C.B.; Dupuy-Galet, B.X.; Fjær, K.; Shapaval, V. Mucoromycota Fungi as Powerful Cell Factories for Modern Biorefinery. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierascu, R.C.; Doni, M.; Fierascu, I. Selected Aspects Regarding the Restoration/Conservation of Traditional Wood and Masonry Building Materials: A Short Overview of the Last Decade Findings. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournou, A. Wood Deterioration by Terrestrial Microorganisms. In Biodeterioration of Wooden Cultural Heritage; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 345–424. [Google Scholar]
- Goodell, B. Genetics and Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Benz, J.P., Schipper, K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-49923-5. [Google Scholar]
- Branysova, T.; Demnerova, K.; Durovic, M.; Stiborova, H. Microbial Biodeterioration of Cultural Heritage and Identification of the Active Agents over the Last Two Decades. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 55, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, H.A.M.; Mansour, M.M.A.; Hassan, A.G.A.I.; Salem, M.Z.M. Biodeterioration Effects of Three Aspergillus Species on Stucco Supported on a Wooden Panel Modeled from Sultan Al-Ashraf Qaytbay Mausoleum, Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Rey, S.; Durand Alegría, J.S.; Martín Martínez, J.M. Adhesivos Tack-Melt Atóxicos Para Su Empleo En Tratamientos Restaurativos de Pintura Sobre Tela: Tipificación y Análisis. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia, Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Caneva, G.; Nugari, M.P.; Salvadori, O. La Biología En La Restauración; Nerea: Hondarribia, Spain, 2000; ISBN 84-89569-48-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ranalli, G.; Zanardini, E.; Sorlini, C. Biodeterioration—Including Cultural Heritage. In Reference Module in Life Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Szostak-Kotowa, J. Biodeterioration of Textiles. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2004, 53, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneva, G.; Ceschin, S. Ecology of Biodeterioration. In Plant Biology for Cultural Heritage: Biodeterioration and Conservation; Caneva, G., Nugari, M.P., Salvadori, O., Eds.; The Getty Conservation Institute: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kavkler, K.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Zalar, P.; Demšar, A. Fungal Contamination of Textile Objects Preserved in Slovene Museums and Religious Institutions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 97, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, I.; Bogdanowicz, A.; Szczęsny, P.; Zielenkiewicz, U.; Laudy, A. Evaluation of Bacterial Diversity on Historical Silk Velvet Textiles from the Museum of King John III’s Palace at Wilanów, Poland. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 131, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, H.R. Biodegradation of Paints: A Current Status. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitbach, A.M.; Rocha, J.C.; Gaylarde, C.C. Influence of Pigment on Biodeterioration of Acrylic Paint Films in Southern Brazil. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2011, 8, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Miras, M.D.M.; Martín-Sánchez, I.; Yebra-Rodríguez, Á.; Romero-Noguera, J.; Bolívar-Galiano, F.; Ettenauer, J.; Sterflinger, K.; Piñar, G. Contribution of the Microbial Communities Detected on an Oil Painting on Canvas to Its Biodeterioration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecklenburg, M.F. Micro Climates and Moisture Induced Damage to Paintings. In Proceedings of the Conference on Micro Climates in Museums, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–23 November 2007; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zmeu, C.N.; Bosch-Roig, P. Risk Analysis of Biodeterioration in Contemporary Art Collections: The Poly-Material Challenge. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 58, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Miranda, A.S.; Doménech-Carbó, A.; Doménech-Carbó, M.T.; Osete-Cortina, L.; Bolívar-Galiano, F.; Martín-Sánchez, I. Analyzing Chemical Changes in Verdigris Pictorial Specimens upon Bacteria and Fungi Biodeterioration Using Voltammetry of Microparticles. Herit. Sci. 2017, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Cerrada, A.; García, S.; Andrés, M.S.; Abrusci, C.; Marquina, D. Application of Molecular Techniques to the Elucidation of the Microbial Community Structure of Antique Paintings. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barresi, G.; Cammarata, M.; Palla, F. Biocide. In Biotechnology and Conservation of Cultural Heritage; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 49–65. ISBN 9783319461687. [Google Scholar]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Wu, F.; Gu, J.-D.; Feng, H.; Shah, K.; Wang, W. Controlling Biodeterioration of Cultural Heritage Objects with Biocides: A Review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappitelli, F.; Cattò, C.; Villa, F. The Control of Cultural Heritage Microbial Deterioration. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, G.; Russell, A.D. Antiseptics and Disinfectants: Activity, Action, and Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Elisha, I.L.; van Vuuren, S.; Viljoen, A. Volatile Phenolics: A Comprehensive Review of the Anti-Infective Properties of an Important Class of Essential Oil Constituents. Phytochemistry 2021, 190, 112864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilanes-Martínez, M.A.; Coral-Garzón, A.; Cáceres, D.H.; García, A.M. Antifungal Activity of Boric Acid, Triclosan and Zinc Oxide against Different Clinically Relevant Candida Species. Mycoses 2021, 64, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, A.; Lin, Y. Antifungal Mechanisms of Polymeric Quaternary Ammonium Salts against Conidia of Fusarium Oxysporum f. Sp. Cubense, Race 4. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 165, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Niu, L.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Tay, F.R.; Chen, J. Quaternary Ammonium-Based Biomedical Materials: State-of-the-Art, Toxicological Aspects and Antimicrobial Resistance. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 71, 53–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koestler, R.J.; Parreira, E.; Santoro, E.D.; Noble, P. Visual Effects of Selected Biocides on Easel Painting Materials. Stud. Conserv. 1993, 38, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vito, M.; Vergari, L.; Mariotti, M.; Proto, M.R.; Barbanti, L.; Garzoli, S.; Sanguinetti, M.; Sabatini, L.; Peduzzi, A.; Bellardi, M.G.; et al. Anti-Mold Effectiveness of a Green Emulsion Based on Citrus aurantium Hydrolate and Cinnamomum zeylanicum Essential Oil for the Modern Paintings Restoration. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarquide, A. La Pintura Sobre Tela II. Alteraciones, Materiales y Tratamientos de Restauración; NEREA: San Sebastián, Spain, 2005; ISBN 84-89569-50-9. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Noguera, J.; Bailón-Moreno, R.; Bolívar-Galiano, F. Varnishes with Biocidal Activity: A New Approach to Protecting Artworks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Feky, O.M.; Hassan, E.A.; Fadel, S.M.; Hassan, M.L. Use of ZnO Nanoparticles for Protecting Oil Paintings on Paper Support against Dirt, Fungal Attack, and UV Aging. J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameño Puerto, M.; Martín Garcia, L.; Villegas Sánchez, R. El Biodeterioro En Edificios Del Patrimonio Cultural: Metodología de Evaluación de Tratamientos Biocidas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Sevilla, Sevilla, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Casorri, L.; Masciarelli, E.; Ficociello, B.; Ietto, F.; Incoronato, F.; Di Luigi, M.; Beni, C.; Pacioni, G. Natural Substances as Biocides in the Fungi Treatment on Artistic Products to Protect the Environment and Health of Restoration Workers. Ital. J. Mycol. 2023, 52, 89–111. [Google Scholar]
- Caneva, G.; Nugari, M.P.; Pinna, D.; Salvadori, O. Il Controllo Del Degrado Biologico; Nardini Editore: Florence, Italy, 1998; ISBN 9788840440392. [Google Scholar]
- Nugari, M.P.; Salvadori, O. Biodeterioration Control of Cultural Heritage: Methods and Products. In Molecular Biology and Cultural Heritage; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Schieweck, A.; Delius, W.; Siwinski, N.; Vogtenrath, W.; Genning, C.; Salthammer, T. Occurrence of Organic and Inorganic Biocides in the Museum Environment. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3266–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez-Fregoso, E.; Farfán-García, E.D.; García-Coronel, I.H.; Martínez-Herrera, E.; Alatorre, A.; Scorei, R.I.; Soriano-Ursúa, M.A. Effects of Boron-Containing Compounds in the Fungal Kingdom. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 65, 126714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillén, N.; Martín-Rey, S.; Pérez-Marín, E.; Castell-Agustí, M. Estudio Comparativo de Las Metodologías de Aplicación de Las Sustancias Fungicidas En Pintura Sobre Lienzo. Master’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de València, València, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sequeira, S.O.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Cabrita, E.J.; Macedo, M.F. Ethanol as an Antifungal Treatment for Paper: Short-Term and Long-Term Effects. Stud. Conserv. 2017, 62, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diomedi, A.; Chacón, E.; Delpiano, L.; Hervé, B.; Jemenao, M.I.; Medel, M.; Quintanilla, M.; Riedel, G.; Tinoco, J.; Cifuentes, M. Antisépticos y Desinfectantes: Apuntando al Uso Racional. Recomendaciones Del Comité Consultivo de Infecciones Asociadas a La Atención de Salud, Sociedad Chilena de Infectología. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2017, 34, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A. Conservación y Restauración de Pintura Sobre Lienzo; Ediciones del Serbal: Barcelona, Spain, 2002; ISBN 87-7628-390-3. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Z.; Ali, B.; Naseem Sabri, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Biocides against Different Microorganisms Isolated from Biodeteriorated Paints. Pak. J. Zool. 2012, 44, 576–579. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, A.; Gherardi, F.; Goidanich, S.; Delaney, J.K.; De La Rie, E.R.; Ubaldi, M.C.; Toniolo, L.; Simonutti, R. Highly Transparent Poly(2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline)-TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings for the Conservation of Matte Painted Artworks. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 84879–84888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harandi, D.; Ahmadi, H.; Mohammadi Achachluei, M. Comparison of TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles for the Improvement of Consolidated Wood with Polyvinyl Butyral against White Rot. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 108, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanth, A.P.; Soni, A.K. Application of Nanocomposites for Conservation of Materials of Cultural Heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 59, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Castillo, I.; Hierro, L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Seral-Ascaso, A.; Mitchell, S.G. Perspectives for Antimicrobial Nanomaterials in Cultural Heritage Conservation. Chem 2021, 7, 629–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasov, A.D.; Sazanova, K.V.; Hosid, E.G.; Tkachenko, T.S.; Alekseev, A.I.; Pchelin, I.M.; Galushkin, A.A. Experience of Using Antifungal Rocima GT for Protection of Paper from Biological Damage Caused by Fungi. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidanza, M.R.; Caneva, G. Natural Biocides for the Conservation of Stone Cultural Heritage: A Review. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 38, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, S.; Scrano, L.; Ventrella, E.; Bonomo, M.G.; Crescenzi, A.; Salzano, G.; Bufo, S.A. Natural Biocides to Prevent the Microbial Growth on Cultural Heritage. In Proceedings of the Conference Built Heritage 2013—Monitoring Conservation and Management, Milan, Italy, 18–20 November 2013; Boriani, M., Gabaglio, R., Gulotta, D., Eds.; ResearchGate: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bellotti, N.; Bogdan, S.; Deyá, C.; del Amo, B.; Romagnoli, R. Evaluación de Extractos Vegetales Como Agentes Antifúngicos Para Pinturas. In Proceedings of the 3er Congreso Iberoamericano y XI Jornada de Técnicas de Restaración y Conservación del Patrimonio, La Plata, Argentina, 16–18 October 2013; Travesa, L., Ed.; CONICET Dialoga: La Plata, Argentina, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Unión Europea. Reglamento (UE) No 528/2012 Del Parlamento Europeo y Del Consejo. Off. J. 2012, 167, 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat, J.; Singh, N.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. A Comprehensive Review on Environmental Toxicity of Azole Compounds to Fish. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Gami, A.; Yunus Shukor, M.; Abdul Khalil, K.; Aini Dahalan, F.; Khalid, A.; Aqlima Ahmad, S. Phenol and Phenolic Compounds Toxicity. J. Environ. Microbiol. Toxicol. 2014, 2, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, R.U. Toxic Heavy Metals: Materials Cycle Optimization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Acute Toxicity and Synergism of Binary Mixtures of Antifouling Biocides with Heavy Metals to Embryos of Sea Urchin Glyptocidaris Crenularis. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kareem, O. Evaluating the Combined Efficacy of Polymers with Fungicides for Protection of Museum Textiles against Fungal Deterioration in Egypt. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Sana, S.S.; Li, H.; Xing, Y.; Nanda, A.; Netala, V.R.; Zhang, Z. Essential Oils and Its Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anti-Oxidant Activity Applications: A Review. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugreet, B.S.; Suroowan, S.; Rengasamy, R.R.K.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Chemistry, Bioactivities, Mode of Action and Industrial Applications of Essential Oils. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyana, Y.; Putri, Y.S.E.; Solihah, D.S.; Lutfi, F.S.; Alqurashi, R.M.; Marta, H. Pickering Emulsions as Vehicles for Bioactive Compounds from Essential Oils. Molecules 2022, 27, 7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’agostino, M.; Tesse, N.; Frippiat, J.P.; Machouart, M.; Debourgogne, A. Essential Oils and Their Natural Active Compounds Presenting Antifungal Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Guha, P. A Review on Antifungal Activity and Mode of Action of Essential Oils and Their Delivery as Nano-Sized Oil Droplets in Food System. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4701–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Meenatchi, V.; Lin, L. Encapsulation of Essential Oil Components with Methyl-β-Cyclodextrin Using Ultrasonication: Solubility, Characterization, DPPH and Antibacterial Assay. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbahani, A.; Miladi, K.; Badri, W.; Sala, M.; Aït Addi, E.H.; Casabianca, H.; El Mousadik, A.; Hartmann, D.; Jilale, A.; Renaud, F.N.R.; et al. Essential Oils: From Extraction to Encapsulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 483, 220–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djilani, A.; Dicko, A. The Therapeutic Benefits of Essential Oils. In Nutrition, Well-Being and Health; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; Coppola, R.; Feo, V. De Essential Oils and Antifungal Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yan, R.; Shi, J.; Chen, J.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Antifungal and Mycotoxin Detoxification Ability of Essential Oils: A Review. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Woo, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.B.; Zheng, Y.; Chun, H.S. Antifungal Activity of Essential Oil and Plant-Derived Natural Compounds against Aspergillus Flavus. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yaoc, W. Analysis of the Synergistic Antifungal Mechanism of Small Molecular Combinations of Essential Oils at the Molecular Level. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Singh, V.K.; Das, S.; Prasad, J.; Kedia, A.; Upadhyay, N.; Dubey, N.K.; Dwivedy, A.K. Essential Oil Nanoemulsion as Eco-Friendly and Safe Preservative: Bioefficacy Against Microbial Food Deterioration and Toxin Secretion, Mode of Action, and Future Opportunities. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 751062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Paralikar, P.; Jogee, P.; Agarkar, G.; Ingle, A.P.; Derita, M.; Zacchino, S. Synergistic Antimicrobial Potential of Essential Oils in Combination with Nanoparticles: Emerging Trends and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 519, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucia, A.; Guzmán, E. Emulsions Containing Essential Oils, Their Components or Volatile Semiochemicals as Promising Tools for Insect Pest and Pathogen Management. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 287, 102330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vostinaru, O.; Codruta Heghes, S.; Filip, L. Safety Profile of Essential Oils. In Essential Oils—Bioactive Compounds, New Perspectives and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pinna, D. Can We Do without Biocides to Cope with Biofilms and Lichens on Stone Heritage? Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 172, 105437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar Chaurasia, P.; Lata Bharati, S.; Golla, U. A Mini-Review on the Safety Profile of Essential Oils. MOJ Biol. Med. 2022, 7, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzerstorfer, P.; Sandner, G.; Pitsch, J.; Mascher, B.; Aumiller, T.; Weghuber, J. Acute, Reproductive, and Developmental Toxicity of Essential Oils Assessed with Alternative in Vitro and in Vivo Systems. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, L.; Troiano, F.; Vacchini, V.; Cappitelli, F.; Balloi, A. An in Vitro Evaluation of the Biocidal Effect of Oregano and Cloves’ Volatile Compounds against Microorganisms Colonizing an Oil Painting—A Pioneer Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Martín-Rey, S.; Osete-Cortina, L.; Martín-Sánchez, I.; Bolívar-Galiano, F.; Doménech-Carbó, M.T. Evaluation of a Gelatin-Based Adhesive for Historic Paintings That Incorporates Citronella Oil as an Eco-Friendly Biocide. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 2320–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, Y.; Shabana, Y.; Elmitwalli, H.; Rashad, Y.; Sreenivasaprasad, P.; Mabrouk, N. Analytical Assessment of Some Essential Oils against Common Fungi Isolated from Egyptian Heritage Part I: Textiles and Oil Paintings. Sci. Cult. 2023, 9, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, D.M.; Timar, M.C.; Beldean, E.C.; Varodi, A.M. Combined Testing Approach to Evaluate the Antifungal Efficiency of Clove (Eugenia Caryophyllata) Essential Oil for Potential Application in Wood Conservation. Bioresources 2020, 15, 9474–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; Zidan, Y.E.; Mansour, M.M.A.; El Hadidi, N.M.N.; Abo Elgat, W.A.A. Antifungal Activities of Two Essential Oils Used in the Treatment of Three Commercial Woods Deteriorated by Five Common Mold Fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 106, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Kapoor, N.; Tiwari, A. Biotechnology to Restoration and Conservation. In Microbial Biotechnology Approaches to Monuments of Cultural Heritage; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 151–175. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Alonso, J.; Bernardos, A.; Regidor-Ros, J.L.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Bosch-Roig, P. Innovative Use of Essential Oil Cold Diffusion System for Improving Air Quality on Indoor Cultural Heritage Spaces. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 162, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, A.; Šovljanski, O.; Nikolić, V.; Pezo, L.; Aćimović, M.; Cvetković, M.; Stanojev, J.; Kuzmanović, N.; Markov, S. Screening of Antifungal Activity of Essential Oils in Controlling Biocontamination of Historical Papers in Archives. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneranda, M.; Blanco-Zubiaguirre, L.; Roselli, G.; Di Girolami, G.; Castro, K.; Madariaga, J.M. Evaluating the Exploitability of Several Essential Oils Constituents as a Novel Biological Treatment against Cultural Heritage Biocolonization. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech-Carbó, M.T.; Lee, Y.; Osete-Cortina, L.; Martín-Rey, S. Influence of Plasticizer and Biocide on the Functional Properties of Gelatin-Based Adhesives Used in Painting Consolidation. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 1774–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeson, K.; Razifah, M.R.; Mubarak, A.; Kam, A.; Vigneswari, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Improved Functionality of Cinnamon Oil Emulsion-Based Gelatin Films as Potential Edible Packaging Film for Wax Apple. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cemmi, A.; Di Sarcina, I.; D’Orsi, B. Gamma Radiation-Induced Effects on Paper Irradiated at Absorbed Doses Common for Cultural Heritage Preservation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 202, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Sanmartín, P. Exposure to Artificial Daylight or UV Irradiation (A, B or C) Prior to Chemical Cleaning: An Effective Combination for Removing Phototrophs from Granite. Biofouling 2018, 34, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, M.; Domenech-Carbó, M.T.; Valentín, N. Una Mirada Hacia La Conservación Preventiva Del Patrimonio Cultural; Universidad Politécnica de Valencia: Valenica, Spain, 2003; ISBN 84-9705-420-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pfendler, S.; Karimi, B.; Alaoui-Sosse, L.; Bousta, F.; Alaoui-Sossé, B.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Aleya, L. Assessment of Fungi Proliferation and Diversity in Cultural Heritage: Reactions to UV-C Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, K.; Asano, K.; Naito, K.; Ohashi, H.; Sasaki, M.; Morimoto, Y.; Igarashi, T.; Nakane, A. Ultraviolet C Light with Wavelength of 222 Nm Inactivates a Wide Spectrum of Microbial Pathogens. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderie, F.; Tête, N.; Cailhol, D.; Alaoui-Sehmer, L.; Bousta, F.; Rieffel, D.; Aleya, L.; Alaoui-Sossé, B. Factors Driving Epilithic Algal Colonization in Show Caves and New Insights into Combating Biofilm Development with UV-C Treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunayon, S.S.; Mui, K.-W.; Wong, L.-T. A Pilot Study on the Antimicrobial Efficacy of a Novel UV-LED System against Drainage Stack Bioaerosol Emissions during Flushing Episodes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; You, S.; Wei, L. Electro-Oxidation and UV Irradiation Coupled Method for in-Site Removing Pollutants from Human Body Fluids in Swimming Pool. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 464, 132963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuei, M.S.; Peleato, N.M. Factors Affecting Particle-Microorganism Association and UV Disinfection: Effect of Source Water, Organics, and Particle Characteristics. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, L. Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation: A Prediction Model to Estimate UV-C-Induced Infectivity Loss in Single-Strand RNA Viruses. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousha, O.; O’Mahoney, P.; Hammond, R.; Wood, K.; Eadie, E. 222 Nm Far-UVC from Filtered Krypton-Chloride Excimer Lamps Does Not Cause Eye Irritation When Deployed in a Simulated Office Environment. Photochem. Photobiol. 2023; Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, M.; Welch, D.; Shuryak, I.; Brenner, D.J. Far-UVC Light (222 Nm) Efficiently and Safely Inactivates Airborne Human Coronaviruses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzures, A. 222-Nm UVC Light as a Skin-Safe Solution to Antimicrobial Resistance in Acute Hospital Settings with a Particular Focus on Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Surgical Site Infections: A Review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, M.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Bigelow, A.W.; Trivedi, S.; Lowy, F.D.; Spotnitz, H.M.; Hammer, S.M.; Brenner, D.J. 207-Nm UV Light—A Promising Tool for Safe Low-Cost Reduction of Surgical Site Infections. I: In Vitro Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.A.; Evans, A.; Forbes, P.D.; Coates, P.J.; Gardner, J.; Valentine, R.M.; Ibbotson, S.H.; Ferguson, J.; Fricker, C.; Moseley, H. The Effect of 222-nm UVC Phototesting on Healthy Volunteer Skin: A Pilot Study. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2015, 31, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, D.; Buonanno, M.; Grilj, V.; Shuryak, I.; Crickmore, C.; Bigelow, A.W.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Johnson, G.W.; Brenner, D.J. Far-UVC Light: A New Tool to Control the Spread of Airborne-Mediated Microbial Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USHIO. Care222® Technology; USHIO: Tokyo, Japan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Borderie, F.; Alaoui-Sossé, B.; Aleya, L. Heritage Materials and Biofouling Mitigation through UV-C Irradiation in Show Caves: State-of-the-Art Practices and Future Challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4144–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, S.P.; Sahu, J.K. UV Protecting Pigment of the Terrestrial Cyanobacterium Tolypothrix Byssoidea. J. Plant Physiol. 1998, 153, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Albertano, P. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species upon Red Light Exposure of Cyanobacteria from Roman Hypogea. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 84, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderie, F.; Laurence, A.-S.; Naoufal, R.; Faisl, B.; Geneviève, O.; Dominique, R.; Badr, A.-S. UV–C Irradiation as a Tool to Eradicate Algae in Caves. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borderie, F.; Alaoui-Sehmer, L.; Bousta, F.; Alaoui-Sossé, B.; Aleya, L. Cellular and Molecular Damage Caused by High UV-C Irradiation of the Cave-Harvested Green Alga Chlorella Minutissima: Implications for Cave Management. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 93, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, P.; Villa, F.; Polo, A.; Silva, B.; Prieto, B.; Cappitelli, F. Rapid Evaluation of Three Biocide Treatments against the Cyanobacterium Nostoc Sp. PCC 9104 by Color Changes. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfendler, S.; Einhorn, O.; Bousta, F.; Khatyr, A.; Alaoui-Sossé, L.; Aleya, L.; Alaoui-Sossé, B. UV-C as a Means to Combat Biofilm Proliferation on Prehistoric Paintings: Evidence from Laboratory Experiments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21601–21609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, P.; Vázquez-Nion, D.; Arines, J.; Cabo-Domínguez, L.; Prieto, B. Controlling Growth and Colour of Phototrophs by Using Simple and Inexpensive Coloured Lighting: A Preliminary Study in the Light4Heritage Project towards Future Strategies for Outdoor Illumination. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 122, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfendler, S.; Munch, T.; Bousta, F.; Alaoui-Sosse, L.; Aleya, L.; Alaoui-Sossé, B. Bleaching of Biofilm-Forming Algae Induced by UV-C Treatment: A Preliminary Study on Chlorophyll Degradation and Its Optimization for an Application on Cultural Heritage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14097–14105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfendler, S.; Alaoui-Sossé, B.; Alaoui-Sossé, L.; Bousta, F.; Aleya, L. Effects of UV-C Radiation on Chlorella Vulgaris, a Biofilm-Forming Alga. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, P.; Méndez, A.; Carballeira, R.; López, E. New Insights into the Growth and Diversity of Subaerial Biofilms Colonizing Granite-Built Heritage Exposed to UV-A or UV-B Radiation plus Red LED Light. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 161, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter-Carrión, L.; Sauceda-Gálvez, J.N.; Codina-Torrella, I.; Hernández-Herrero, M.M.; Gervilla, R.; Roig-Sagués, A.X. Inactivation Study of Bacillus Subtilis, Geobacillus Stearothermophilus, Alicyclobacillus Acidoterrestris and Aspergillus Niger Spores under Ultra-High Pressure Homogenization, UV-C Light and Their Combination. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 48, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-J.; Kim, S.; Chung, Y.-H. Sensing and Responding to UV-A in Cyanobacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16303–16332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castenholz, R.W.; Garcia-Pichel, F. Cyanobacterial Responses to UV Radiation. In Ecology of Cyanobacteria II; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 481–499. [Google Scholar]
- Selbmann, L.; Isola, D.; Zucconi, L.; Onofri, S. Resistance to UV-B Induced DNA Damage in Extreme-Tolerant Cryptoendolithic Antarctic Fungi: Detection by PCR Assays. Fungal Biol. 2011, 115, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, A.; Prieto, B.; Aguirre i Font, J.M.; Sanmartín, P. Better, Not More, Lighting: Policies in Urban Areas towards Environmentally-Sound Illumination of Historical Stone Buildings That Also Halts Biological Colonization. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rosal Padial, Y.R.; Martínez-Manzanares, E.; Hernández Mariné, M.C. Análisis, Impacto y Evolución de Los Biofilms Fotosintéticos En Espeleotemas. El Caso de La Cueva de Nerja. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Málaga, Málaga, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, L.; Belleza, S.; Urzì, C.; De Leo, F. A Study for Monitoring and Conservation in the Roman Catacombs of St. Callistus and Domitilla, Rome (Italy). In The Conservation of Subterranean Cultural Heritage; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Urzì, C.; De Leo, F.; Bruno, L.; Pangallo, D.; Krakova, L. New Species Description, Biomineralization Processes and Biocleaning Applications of Roman Catacombs-Living Bacteria. In The Conservation of Subterranean Cultural Heritage; Saiz-Jimenez, C., Ed.; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Vaillant, N.; Valentín, N. Principios Básicos de La Conservación Documental y Causas de Su Deterioro; Ministerio de Educación y Cultura, Instituto del Patrimonio Histórico Español: Madrid, Spain, 1996; ISBN 84-8181-150-5. [Google Scholar]
- Čuden, A.P.; Urbas, R. Advances in Ultraviolet (UV) Ray Blocking Textiles. In Functional and Technical Textiles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 213–273. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Solis-Ramos, E.; Yi, Y.; Kumosa, M. UV Degradation Model for Polymers and Polymer Matrix Composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 154, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezelj, E.; Tomljenovic, A.; Cunko, R. Textiles for the Protection against Sun Radiation. Tekstil 2004, 53, 301–316. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G154-16; Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Nonmetallic Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- UNE 48-251-92; Pinturas y Barnices: Ensayo de Envejecimiento Acelerado. Método de Exposición a Ciclos Alternos de Luz Ultravioleta y Condensación. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2003; pp. 1–13.
- Pfendler, S.; Borderie, F.; Bousta, F.; Alaoui-Sosse, L.; Alaoui-Sosse, B.; Aleya, L. Comparison of Biocides, Allelopathic Substances and UV-C as Treatments for Biofilm Proliferation on Heritage Monuments. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 33, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, C.; Borsotto, P.; Barbieri, C.; Borsotto, P. Essential Oils: Market and Legislation. In Potential of Essential Oils; BoD—Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Schiavo, S.; De Leo, F.; Urzì, C. Present and Future Perspectives for Biocides and Antifouling Products for Stone-Built Cultural Heritage: Ionic Liquids as a Challenging Alternative. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.-J.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Thakur, K.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.-G.; Hu, F.; Wei, Z.-J. Recent Updates on the Chemistry, Bioactivities, Mode of Action, and Industrial Applications of Plant Essential Oils. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, M.; Cuzman, O.A.; Tosini, I.; Galeotti, M.; Sorella, F. Essential Oils Mixtures as an Eco-Friendly Biocidal Solution for a Marble Statue Restoration. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 163, 105280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchia, A.; Aureli, H.; Prestileo, F.; Ortenzi, F.; Sellathurai, S.; Docci, A.; Cerafogli, E.; Colasanti, I.A.; Ricca, M.; La Russa, M.F. In-Situ Comparative Study of Eucalyptus, Basil, Cloves, Thyme, Pine Tree, and Tea Tree Essential Oil Biocide Efficacy. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Gumus, C.E. Natural Emulsifiers—Biosurfactants, Phospholipids, Biopolymers, and Colloidal Particles: Molecular and Physicochemical Basis of Functional Performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delshadi, R.; Bahrami, A.; Tafti, A.G.; Barba, F.J.; Williams, L.L. Micro and Nano-Encapsulation of Vegetable and Essential Oils to Develop Functional Food Products with Improved Nutritional Profiles. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, C.M.; Bosch-Roig, P.; Moliner, B.C.; Miller, A.Z. Antifungal Properties of Oregano and Clove Volatile Essential Oils Tested on Biodeteriorated Archaeological Mummified Skin. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 61, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, M.B. Commercial Development of Plant Essential Oils and Their Constituents as Active Ingredients in Bioinsecticides. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadpour, E.; Can Karaça, A.; Fasamanesh, M.; Mahdavi, S.A.; Shariat-Alavi, M.; Feng, J.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Rehman, A.; Jafari, S.M. Application of Essential Oils as Natural Biopesticides; Recent Advances. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.G.; Pedro, L.G.; Scheffer, J.J.C. Factors Affecting Secondary Metabolite Production in Plants: Volatile Components and Essential Oils. Flavour Fragr. J. 2008, 23, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlec, A.F. Essential Oils in Wellness Centers: Overview on European Union Legislation, Potential Therapeutic Effects and Toxicity. Farmacia 2020, 68, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milagres de Almeida, J.; Crippa, B.L.; Martins Alencar de Souza, V.V.; Perez Alonso, V.P.; da Motta Santos Júnior, E.; Siqueira Franco Picone, C.; Prata, A.S.; Cirone Silva, N.C. Antimicrobial Action of Oregano, Thyme, Clove, Cinnamon and Black Pepper Essential Oils Free and Encapsulated against Foodborne Pathogens. Food Control 2023, 144, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palou, L.; Valencia-Chamorro, S.; Pérez-Gago, M. Antifungal Edible Coatings for Fresh Citrus Fruit: A Review. Coatings 2015, 5, 962–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, C.; Maurel, O.M.; Musumeci, T.; Bonaccorso, A.; Drago, F.; Souto, E.M.B.; Pignatello, R.; Carbone, C. Essential Oils: Pharmaceutical Applications and Encapsulation Strategies into Lipid-Based Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, R.; Popovici, V.; Ionescu, L.E.; Ordeanu, V.; Popescu, D.M.; Ozon, E.A.; Gîrd, C.E. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Different Samples of Five Commercially Available Essential Oils. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaili, T.M.; Dhanasekaran, D.K.; Zeb, F.; Faris, M.E.; Naja, F.; Radwan, H.; Cheikh Ismail, L.; Hasan, H.; Hashim, M.; Obaid, R.S. A Status Review on Health-Promoting Properties and Global Regulation of Essential Oils. Molecules 2023, 28, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betlej, I.; Andres, B.; Krajewski, K.; Kiełtyka-Dadasiewicz, A.; Boruszewski, P.; Szadkowska, D.; Zawadzki, J.; Radomski, A.; Borysiuk, P. The Effect of Ethanol Extracts and Essential Oils Obtained from Different Varieties of Mint on Wood Molding. Forests 2023, 14, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettraino, A.M.; Zikeli, F.; Humar, M.; Biscontri, M.; Bergamasco, S.; Romagnoli, M. Essential Oils from Thymus Spp. as Natural Biocide against Common Brown- and White-Rot Fungi in Degradation of Wood Products: Antifungal Activity Evaluation by in Vitro and FTIR Analysis. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2023, 81, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unión Europea. Reglamento (CE) No 1272/2008 Del Parlamento Europeo y Del Consejo, de 16 de Diciembre de 2008, Sobre Clasificación, Etiquetado y Envasado de Sustancias y Mezclas. Off. J. 2008, 335, 1–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Parlamento Europeo. INFORME Sobre La Propuesta de Reglamento Del Parlamento Europeo y Del Consejo Por El Que Se Modifica El Reglamento (CE) n.o 1272/2008 Del Parlamento Europeo y Del Consejo Sobre Clasificación, Etiquetado y Envasado de Sustancias y Mezclas. Plenary Sess. 2023, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes Filho, S.; dos Santos, M.S.; dos Santos, O.A.L.; Backx, B.P.; Soran, M.-L.; Opriş, O.; Lung, I.; Stegarescu, A.; Bououdina, M. Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts and Essential Oils. Molecules 2023, 28, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laftouhi, A.; Eloutassi, N.; Drioua, S.; Ech-Chihbi, E.; Rais, Z.; Abdellaoui, A.; Taleb, A.; Beniken, M.; Taleb, M. Impact of Water Stress and Temperature on Metabolites and Essential Oil of Rosmarinus officinalis (Phytochemical Screening, Extraction, and Gas Chromatography). J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cautela, D.; Pastore, A.; Ferrari, G.; Laratta, B.; D’Onofrio, N.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Servillo, L.; Castaldo, D. Global Warming Threatens the World Production of Bergamot Essential Oil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 113986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maham, S.G.; Rahimi, A.; Smith, D.L. Environmental Assessment of the Essential Oils Produced from Dragonhead (Dracocephalum moldavica L.) in Conventional and Organic Farms with Different Irrigation Rates. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 1070–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigiserova, D.A.; Tiruta-Barna, L.; Ahmadi, A.; Hamelin, L.; Thomsen, M. A Step Closer to Circular Bioeconomy for Citrus Peel Waste: A Review of Yields and Technologies for Sustainable Management of Essential Oils. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stashenko, E.; René Martínez, J. Essential Oils and the Circular Bioeconomy. In Essential Oils—Recent Advances, New Perspectives and Applications; Viskelis, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Panwar, D.; Saini, A.; Panesar, P.S.; Chopra, H.K. Unraveling the Scientific Perspectives of Citrus By-Products Utilization: Progress towards Circular Economy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchio, I.; Mandrone, M.; Tomasi, P.; Marincich, L.; Poli, F. Plant Secondary Metabolites: An Opportunity for Circular Economy. Molecules 2021, 26, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, B.; Monteiro, H.; Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A. Life Cycle Energy and Carbon Emissions of Essential Oil Extraction from Rosemary. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifarin, T.O.; Otunola, G.A.; Afolayan, A.J. Chemical Composition of Essential Oils Obtained from Heteromorpha Arborescens (Spreng.) Cham. And Schltdl Leaves Using Two Extraction Methods. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 9232810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radivojac, A.; Bera, O.; Zeković, Z.; Teslić, N.; Mrkonjić, Ž.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Putnik, P.; Pavlić, B. Extraction of Peppermint Essential Oils and Lipophilic Compounds: Assessment of Process Kinetics and Environmental Impacts with Multiple Techniques. Molecules 2021, 26, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvezdanović, J.; Cvetić, T.; Veljović-Jovanović, S.; Marković, D. Chlorophyll Bleaching by UV-Irradiation in Vitro and in Situ: Absorption and Fluorescence Studies. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AENOR UNE-EN ISO: 15858; Dispositivos UV-C Información Sobre Seguridad. Límites Admisibles Para La Exposición Humana. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–14.
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Encapsulation Strategies to Enhance the Antibacterial Properties of Essential Oils in Food System. Food Control 2021, 123, 107856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Piao, X. Use of Aromatic Plant-Derived Essential Oils in Meat and Derived Products: Phytochemical Compositions, Functional Properties, and Encapsulation. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.K.; Parikh, J.K. Advances and Trends in Encapsulation of Essential Oils. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoletti, A.; Barker, R.; Chelazzi, D.; Bonelli, N.; Baglioni, P.; Lee, J.; Angelova, L.V.; Ormsby, B. Reviving WHAAM! A Comparative Evaluation of Cleaning Systems for the Conservation Treatment of Roy Lichtenstein’s Iconic Painting. Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansonetti, A.; Bertasa, M.; Canevali, C.; Rabbolini, A.; Anzani, M.; Scalarone, D. A Review in Using Agar Gels for Cleaning Art Surfaces. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 44, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, M.; Ponnaiya, B.; Welch, D.; Stanislauskas, M.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Smilenov, L.; Lowy, F.D.; Owens, D.M.; Brenner, D.J. Germicidal Efficacy and Mammalian Skin Safety of 222-Nm UV Light. Radiat. Res. 2017, 187, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).