Wear and Corrosion Resistance of ZrN Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Alloy for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
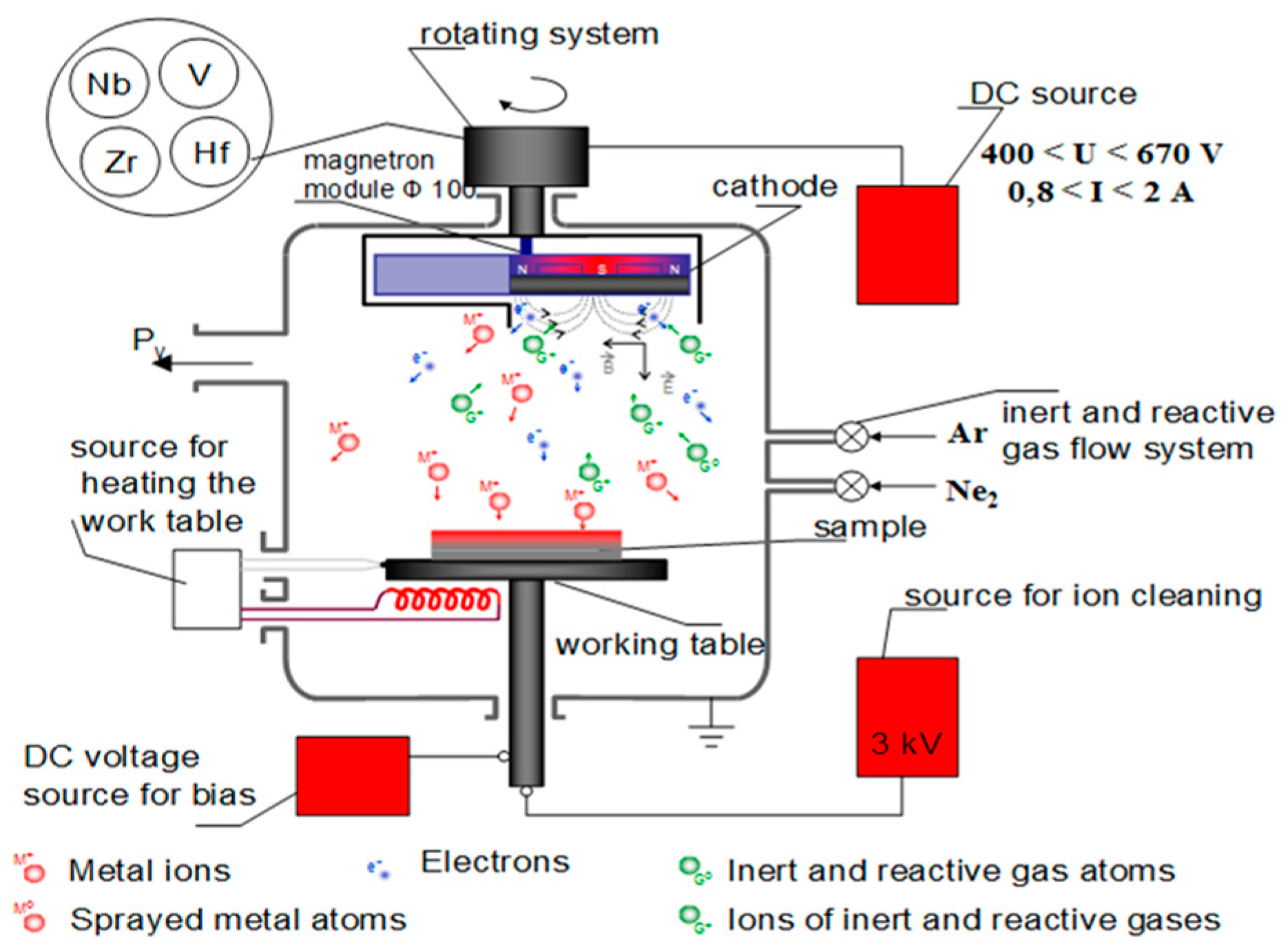
2.1. ZrN Films Deposition
- Cathode cleaning—This process includes sputter cleaning of the Ti6Al4V substrates by Ar+ plasma to eliminate oxide layers from their surface and ensure a purity of the process. Also, it is necessary to decrease the surface roughness, which has a negative effect on the obtained coating’s properties. This process of high energetic ion bombardment is carried out at the following conditions:
- A working pressure (the working gas is Ar)—before the deposition process, the vacuum chamber was evacuated to a base pressure of PAr = 8 Pa;
- A discharge voltage U = 950 V;
- A discharge current I = 0.1 A;
- A temperature t° = 230 °C;
- A cleaning time t = 10 min.
- Deposition of intermediate pure Zr layer in order to enhance the adhesion between the coatings and the substrate—This process is evaluated at the following conditions:
- A working pressure (the working gas is Ar) PAr = 9 × 10−2 Pa;
- A discharge voltage U = 460 V;
- A discharge current I = 1 A;
- A temperature t° = 250 °C;
- Deposition time t = 3 min.
- Deposition process of ZrN coatings—During the process, Ti6Al4V substrates were heated up to a temperature of 250 °C. The process took place in Ar-N2 atmosphere. The inert Ar and reactive N2 gases mixture was introduced into the chamber by means of valves. The inert Ar and reactive N2 gas flows were regulated by vacuum meter indicators to determine the working pressure values. The experiments for the production of ZrN films were performed according to the following parameters:
- A nitrogen pressure PN2 = 5.6 × 10−3 Pa;
- A working pressure PAr/N2 = 1.1 × 10−1 Pa;
- A voltage U = 480 V;
- A bias voltage—zirconium nitride coatings were deposited at bias voltages of −50 V, −80 V, −110 V and −150 V;
- A constant current I = 1 A;
- A deposition time t= 60 min.
2.2. Structural Characterization
2.3. AFM Investigations
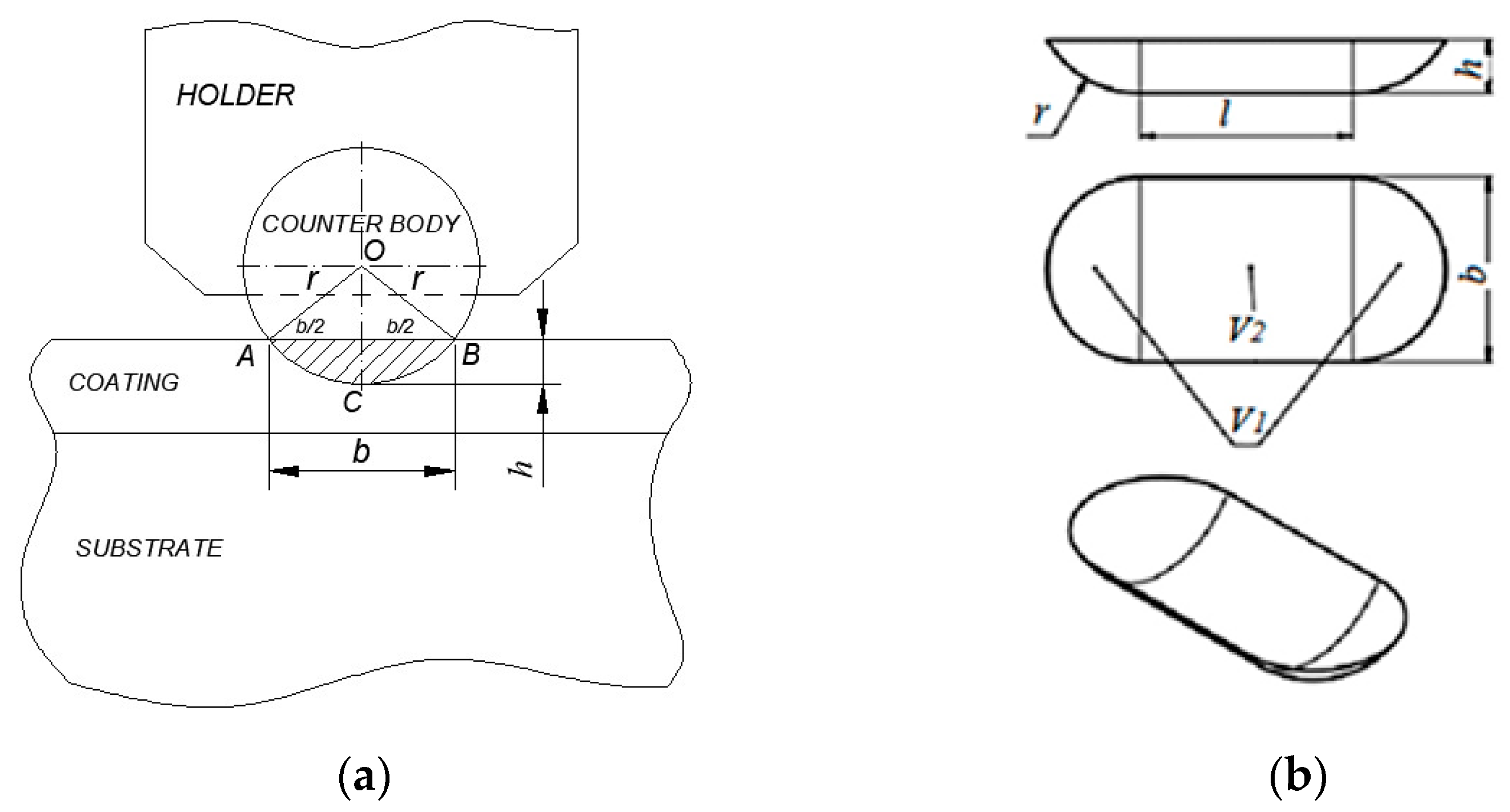
2.4. Wear Resistance Investigations
2.5. Corrosion Resistance Investigations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Method
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
3.5. Wear Resistance
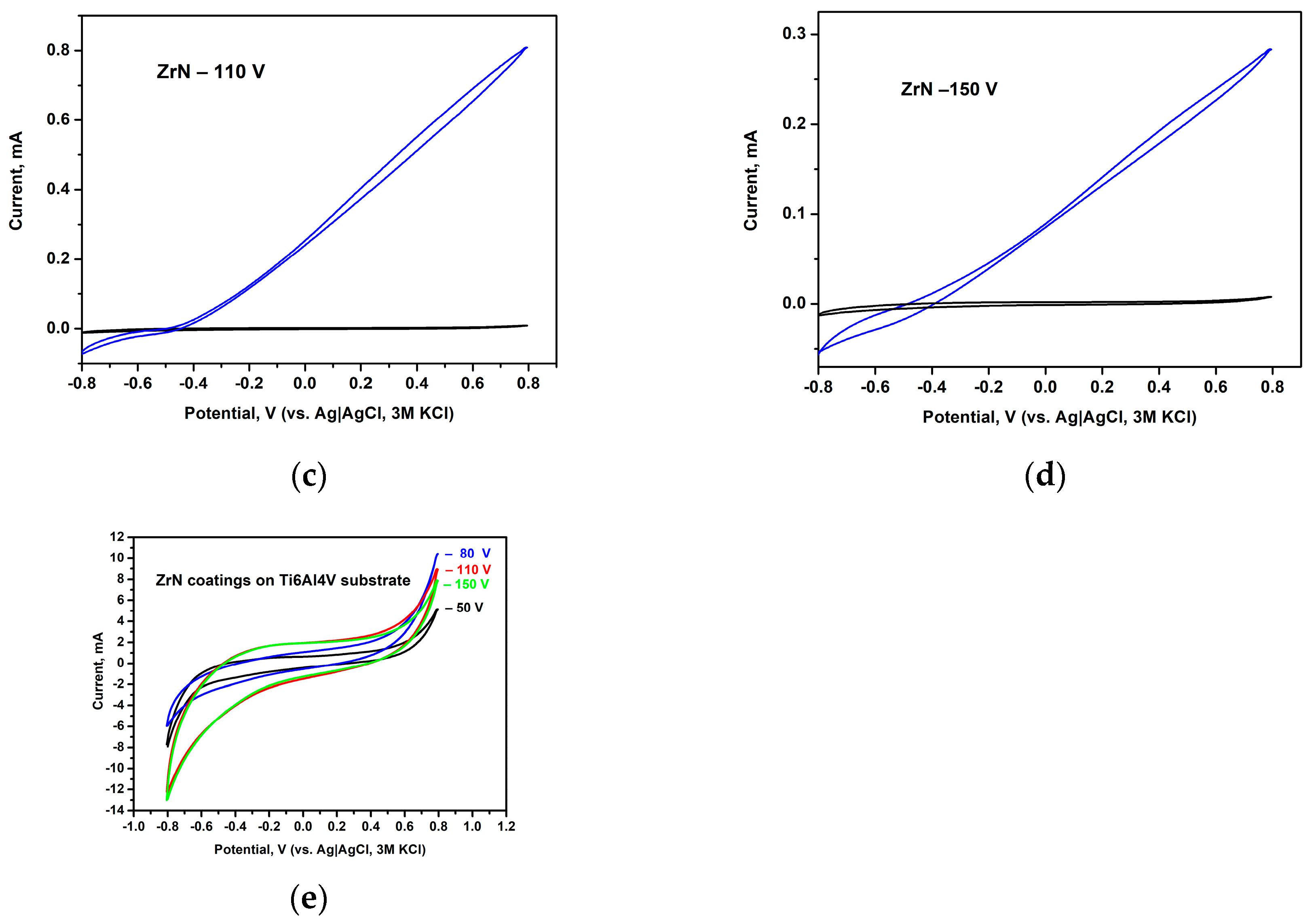
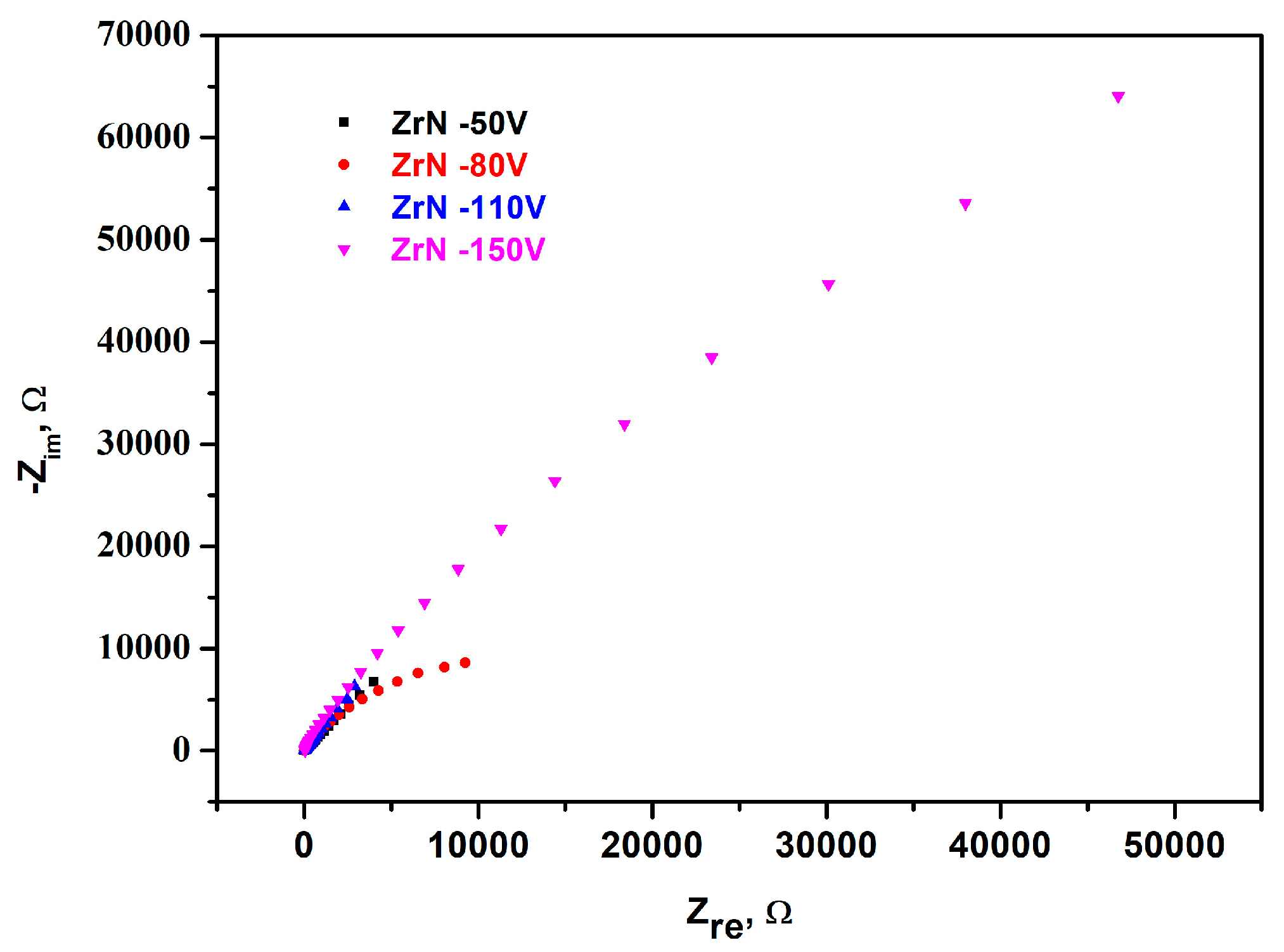
3.6. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, B.; Leong, K. Scaffolding in tissue engineering: General approaches and tissue-specific considerations. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.; Bazaka, K.; Crawford, R. 5-Metallic biomaterials: Types and advanced applications. In Metallic Biomaterial, 4th ed.; Biomaterials Science: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 121–147. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Tong, X.; Ma, X. Surface modification techniques of titanium and titanium alloys for biomedical orthopaedics applications: A review. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 22, 11333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chu, P.; Ding, C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Engin. R Rep. 2004, 47, 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganya, M.; Moshokoa, M.; Obadele, B.; Olubambi, P.; Machaka, R. The microstructural and mechanical characterization of the β-type Ti-11.1Mo-10.8Nb alloy for biomedical applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 655, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Khan, Z.; Siddiquee, A. Beta Titanium Alloys: The Lowest Elastic Modulus for Biomedical Applications: A Review. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Inter.J. Mater. Metal. Engin. 2014, 8, 822–827. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Rack, H. Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—A materials science perspective. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1621–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Metal ion release from metal implants. Mater. Sci. Engin. C 2004, 24, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepicka, M.; Gradzka-Dahlke, M. Surface modification of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy for biomedical applications and its effect on tribological performance—A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2016, 46, 86–103. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, W.; Yu, G.; Huang, J. Corrosion resistance of ZrN films on AISI 304 stainless steel substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 167, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudderth, L.; Perez-Nunez, D.; Keiser, D.; McDevitt, S. Fabrication of ZrN barrier coatings for U-Mo microspheres via fluidized bed chemical vapor deposition using a metalorganic precursor. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 202, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Hung, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, D.; Pilliar, R.; Wang, R. Improving fretting corrosion resistance of CoCrMo alloy with TiSiN and ZrN coatings for orthopedic applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 114, 104233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, D.; Bernardi, J.; Amorim, C.; Souza, F.; Spinelli, A.; Giacomelli, F.; Carlos, A.; Baumvola, I.; Basso, R. Effect of deposition temperature on microstructure and corrosion resistance of ZrN thin films deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaochen, L.; Jian, Z.; Ruihua, Z.; Shangchao, F.; Daqin, Y. Effects of sputtering pressure on microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrN films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Mater. Res. Bul. 2018, 105, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, T.; Lapitskaya, V.; Khabarava, A.; Chizhika, S.; Warcholinski, B.; Gilewicz, A. The influence of nitrogen on the morphology of ZrN coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 522, 146508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larijani, M.; Tabrizi, N.; Norouzian, S.; Jafari, A.; Lahouti, S.; Hosseini, H.H.; Afshari, N. Structural and mechanical properties of ZrN films prepared by ion beam sputtering with varying N2/Ar ratio and substrate temperature. Vacuum 2006, 81, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, D.; Hernandez-Bravo, R.; Ruden, A.; Espinosa-Arbelaez, D.; Gonzalez-Carmona, J.; Mujica, V. Mechanical, tribological and electrochemical behavior of Zr-based ceramic thin films for dental implants. Ceram. Inter. 2023, 49, 2102–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylyev, M.; Mordyuk, B.; Sidorenko, S.; Voloshko, S.; Burmak, A.; Kruhlov, I.; Zakiev, V. Characterization of ZrN coating low-temperature deposited on the preliminary Ar+ ions treated 2024 Al-alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 361, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-Gomez, J.; Sandhi, K.; Yang, Q. Wear and corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline TaN, ZrN, and TaZrN coatings deposited on biomedical grade CoCrMo alloy. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 130, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Liu, C.; Huo, K.; Tang, G.; Tian, X.; Chu, P. Corrosion behavior of ZrN/Zr coated biomedical AZ91 magnesium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 2554–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan-Han, H.; Huan-Ping, T.; Fu-Hsing, L. Formation of zirconia coatings on ZrN-coated substrates by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 269, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaogang, Z.; XiaoXu, Y.; Feifei, X.; Kwang-Ho, K.; Zhigang, S. Influence of substrate bias on microstructure and morphology of ZrN thin films deposited by arc ion plating. Trans. Nonfer. Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, s115–s119. [Google Scholar]
- Azibi, M.; Saoula, N.; Aknouche, H. The influence of substrate bias voltage on the electrochemical properties of ZrN thin films deposited by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering: Biomedical application. J. Electr. Engin. 2019, 70, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, G.; Brun, P.; Gardin, C.; Ferroni, L.; Bressan, E.; Meneghello, R.; Zavan, B.; Sivolella, S. Biocompatibility and antibacterial properties of zirconium nitride coating on titanium abutments: An in vitro study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slate, A.; Wickens, D.; Mohtadi, M.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.; West, G.; Banks, C.; Whitehead, K. Antimicrobial activity of Ti-ZrN/Ag coatings for use in biomaterial applications. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oganyan, M.; Vereschaka, A.; Volosova, M.; Gurin, V. Influence of the application of wear-resistant coatings on force parameters of the cutting process and the tool life during end milling of titanium alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, S.; Cygnar, M.; Cieślikowski, B. Analysis of the application of ZrN coatings for the mitigation of the development of fretting wear processes at the surfaces of push fit joint elements. Proc. Inst. Mechan. Engin. Part J. J. Engin. Tribol. 2019, 234, 1208–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wu, C. Mechanical properties and impact resistance of multilayered TiAlN/ZrN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 231, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabadzhiyska, S.; Kotlarski, G.; Shipochka, M.; Rafailov, P.; Ormanova, M.; Strijkova, V.; Dimcheva, N.; Valkov, S. Duplex Surface Modification of 304-L SS Substrates by an Electron-Beam Treatment and Subsequent Deposition of Diamond-like Carbon Coatings. Coatings 2022, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ma, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Feng, J. Preparation and toughening of a-Cur/c-ZrN nano-multilayer hard coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 483, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Wen, M.; Qu, C.; Hu, C.; Zheng, W. Preferred orientation, phase transition and hardness for sputtered zirconium nitride films grown at different substrate biases. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 2865–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kuppusami, P.; Khan, S.; Sudha, C.; Thirumurugesan, R.; Ramaseshan, R.; Divakar, E.; Mohandas, S. Dash, Influence of nitrogen flow rate on microstructural and nanomechanical properties of Zr-N thin films prepared by pulsed DC magnetron Sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kaliaraj, G. Multifunctional zirconium nitride/copper multilayer coatings on medical grade 316 L SS and titanium substrates for biomedical applications. J. Mechan. Behav. Biom. Mater. 2018, 77, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsson, J.; Brenning, N.; Lundin, D.; Helmersson, U. High power impulse magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2012, 30, 030801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devia, D.; Velez, J.; Parra, E. Bias voltage influence on the mechanical and tribological properties of titanium aluminum nitride coatings produced by triode magnetron sputtering. Rev. Matér. 2015, 20, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Detorhodge, A.; Chason, A. Stress and microstructure evolution of thick sputtered films. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2055–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Ehiasarian, A.; Wen, J.; Petrov, I. Interface microstructure engineering by high power impulse magnetron sputtering for the enhancement of adhesion. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 054301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, A.; Bejarano, J.; Gomez, G.; Prieto, M.; Cortéz, C.; Muñoz, J. Nanostructured multilayers of TiN/ZrN obtained by magnetron sputtering. Phys. Status Solidi 2007, 4, 4127–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Mehmood, M.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, F.; Shah, A. Structural and electrical resistivity characteristics of vacuum arc ion deposited zirconium nitride thin films. Mater. Sci. Semic. Process. 2015, 30, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, Y.; Mori, M.; Miyake, S.; Saito, K.; Asami, K. Characterization of Zr–Al–N films synthesized by a magnetron sputtering method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 193, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Oe, K.; Kaneuji, A.; Uozu, R.; Shintani, K.; Saito, T. Relationship between the surface roughness of material and bone cement: An increased “polished” stem may result in the excessive taper-slip. Materials 2021, 14, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, G.; Mendonça, D.; Aragao, F.; Cooper, L. Advancing dental implant surface technology—From micron- to Nanotopography—Review. Biomate. 2008, 29, 3822–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhong, X.; Wu, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Xia, Y.; Feng, Y.; He, J.; Chen, W. The effect of surface roughness and wettability of nanostructured TiO2 film on TCA-8113 epithelial-like cells. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 6155–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupetsov, V. Increasing the Wear Resistance of Details and Tools of Production Equipment; ZEA-Print: Smolyan, Bulgaria, 2018; pp. 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rupetsov, V. Experimental test stand for the study of coatings resistance. J. Food Packag. Sci. Techn. Technol. 2014, 1, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A. Analysis of relation between friction and wear. Inter. J. Mechan. Engin. Robot. 2014, 1, 603–606. [Google Scholar]
- Hadinezhad, M.; Elyasi, M.; Rajabi, M.; Abbasi, M. Study of the Effects of Slip Distance and Surface Roughness on Wear Rate. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Sarhan, A.; Yusuf, F.; Hamdi, M. Biomedical materials and techniques to improve the tribological, mechanical and biomedical properties of orthopedic implants-A review article. J. Alloys Comp. 2017, 714, 636–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




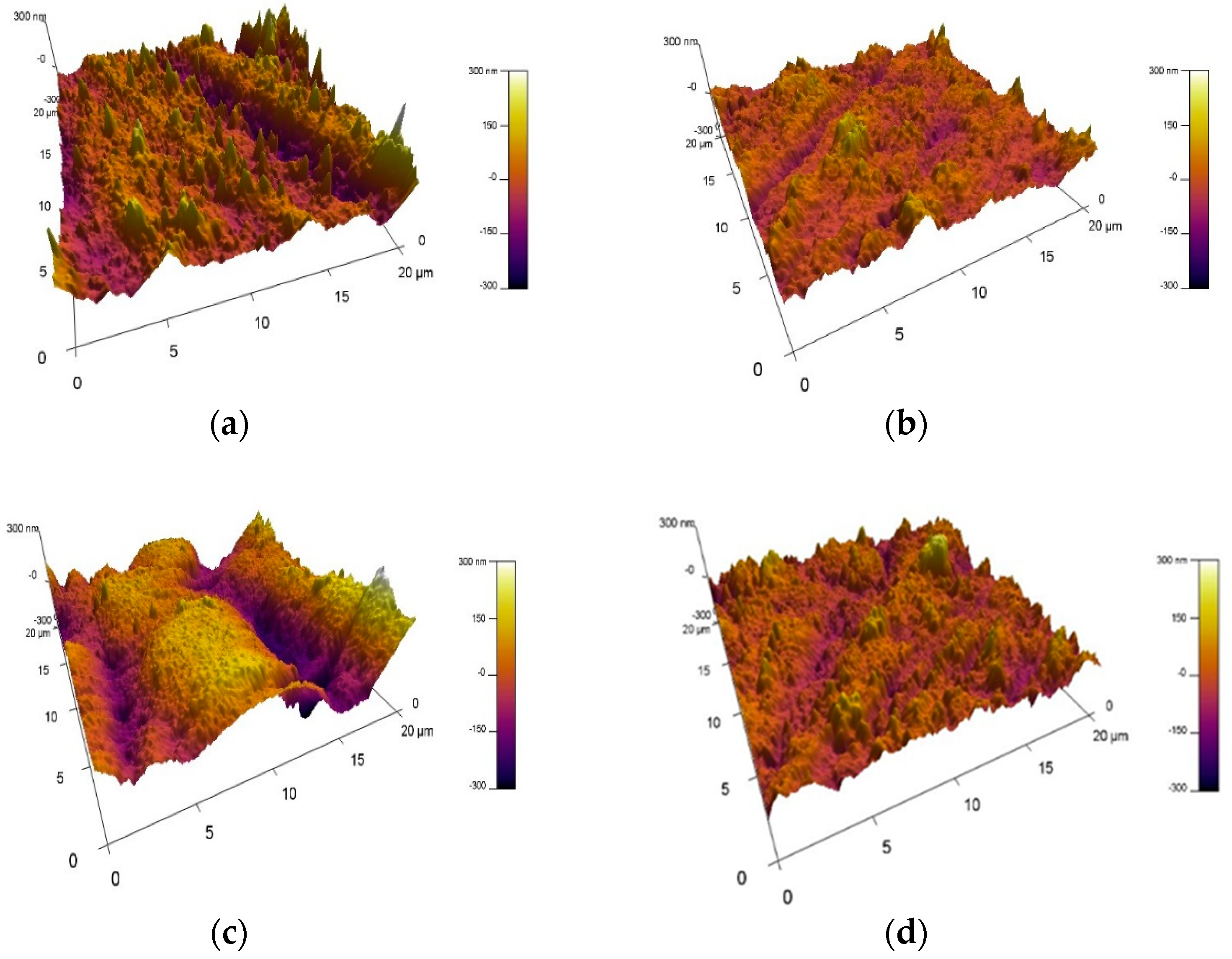
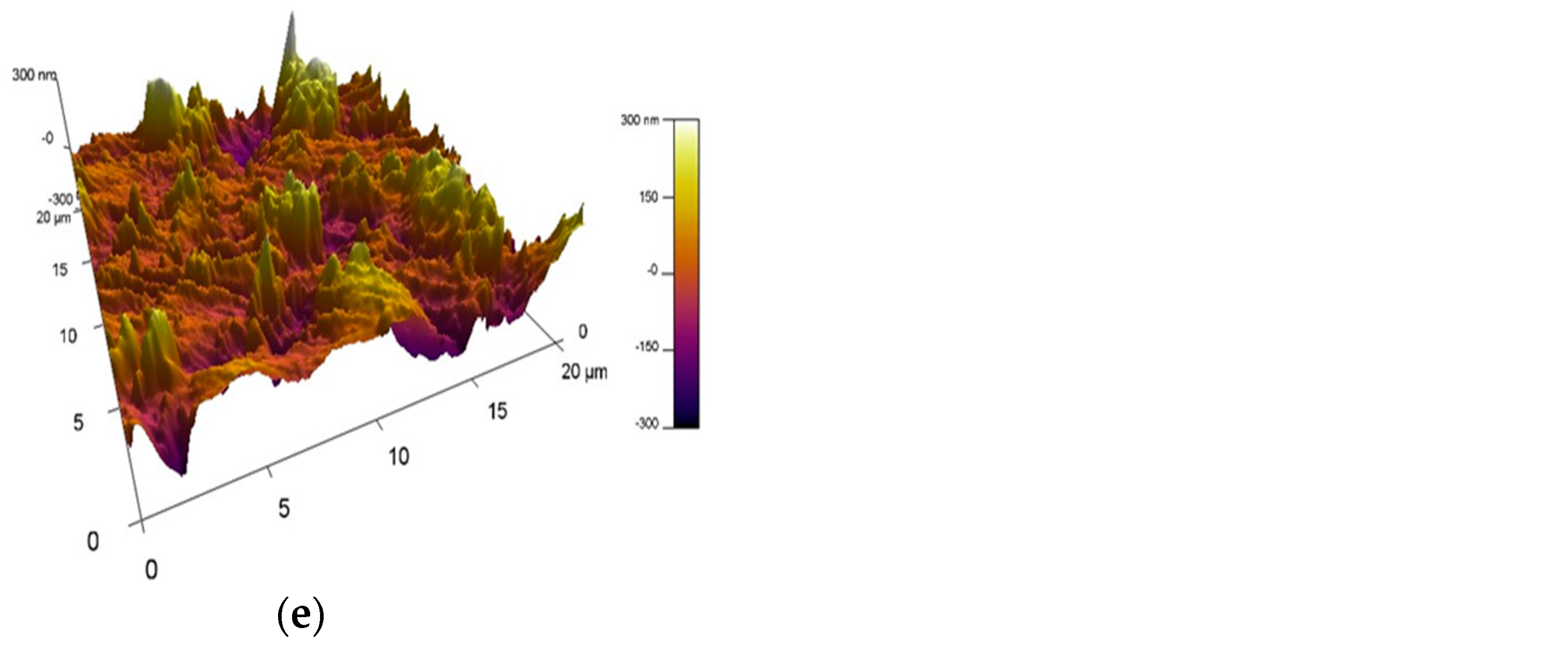


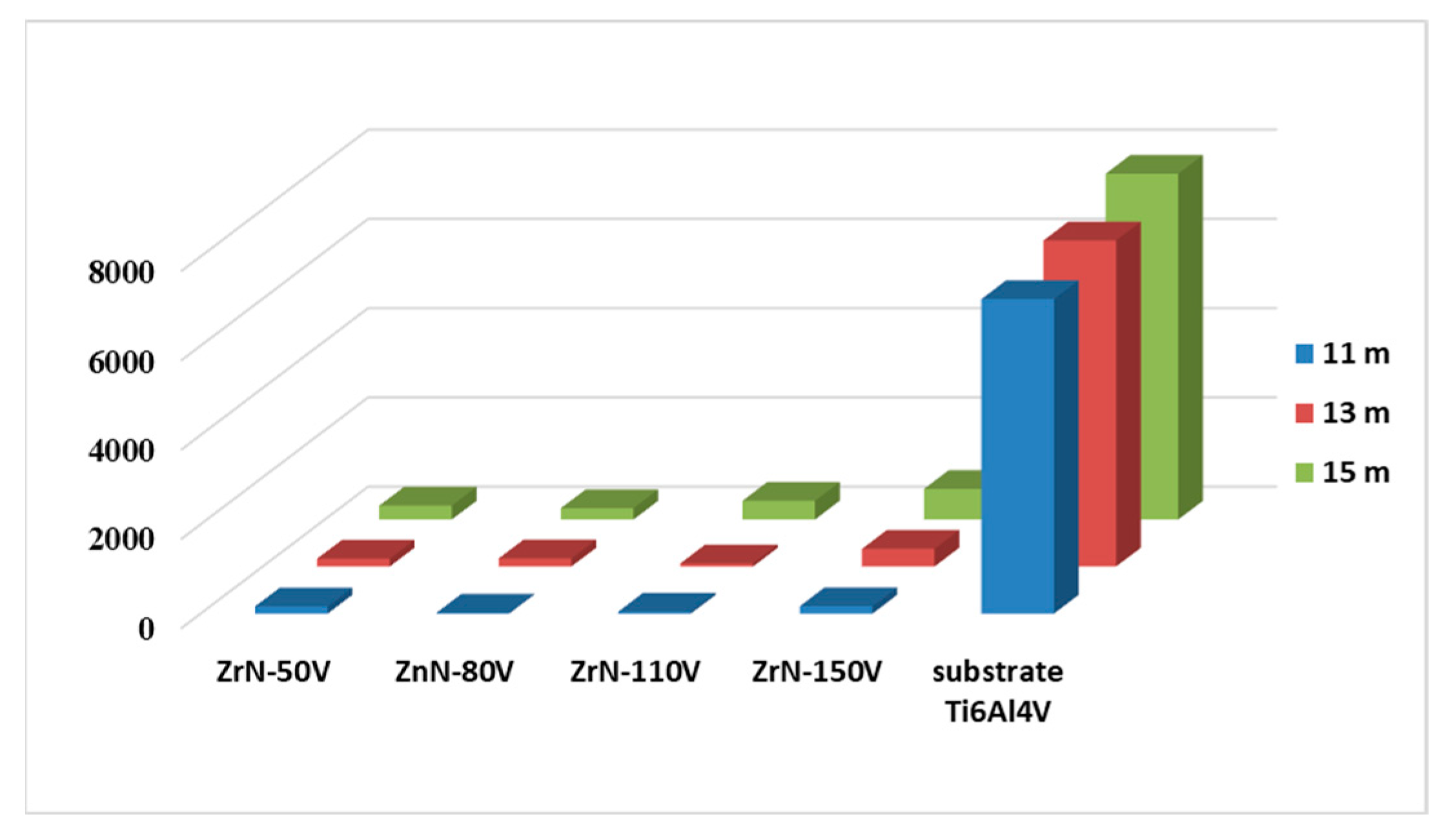


| Sliding Distance, m | Ti6Al4V | ZrN−50 V | ZrN−80 V | ZrN−110 V | ZrN−150 V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 38,780 | 892 | 119 | 246 | 925 |
| 13 | 45,518 | 1157 | 1187 | 458 | 2586 |
| 15 | 58,120 | 2339 | 1902 | 3142 | 5146 |
| Sliding Distance, m | Ti6Al4V | ZrN−50 V | ZrN−80 V | ZrN−110 V | ZrN−150 V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 7051 | 162 | 21 | 45 | 168 |
| 13 | 7310 | 178 | 182 | 70 | 398 |
| 15 | 7749 | 312 | 253 | 418 | 686 |
| No | Sample | OCP Measured in the Presence of 0.1 M NaCl |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ZrN−50 V | 168 mV |
| 2 | ZrN−80 V | −90 mV |
| 3 | ZrN−110 V | 93 mV |
| 4 | ZrN−150 V | 372 mV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabadzhiyska, S.; Dechev, D.; Ivanov, N.; Ivanova, T.; Strijkova, V.; Katrova, V.; Rupetsov, V.; Dimcheva, N.; Valkov, S. Wear and Corrosion Resistance of ZrN Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Alloy for Biomedical Applications. Coatings 2024, 14, 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111434
Rabadzhiyska S, Dechev D, Ivanov N, Ivanova T, Strijkova V, Katrova V, Rupetsov V, Dimcheva N, Valkov S. Wear and Corrosion Resistance of ZrN Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Alloy for Biomedical Applications. Coatings. 2024; 14(11):1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111434
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabadzhiyska, Stanislava, Dimitar Dechev, Nikolay Ivanov, Tatyana Ivanova, Velichka Strijkova, Vesela Katrova, Velko Rupetsov, Nina Dimcheva, and Stefan Valkov. 2024. "Wear and Corrosion Resistance of ZrN Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Alloy for Biomedical Applications" Coatings 14, no. 11: 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111434
APA StyleRabadzhiyska, S., Dechev, D., Ivanov, N., Ivanova, T., Strijkova, V., Katrova, V., Rupetsov, V., Dimcheva, N., & Valkov, S. (2024). Wear and Corrosion Resistance of ZrN Coatings Deposited on Ti6Al4V Alloy for Biomedical Applications. Coatings, 14(11), 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14111434









