Light-Field Optimization of Deep-Ultraviolet LED Modules for Efficient Microbial Inactivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
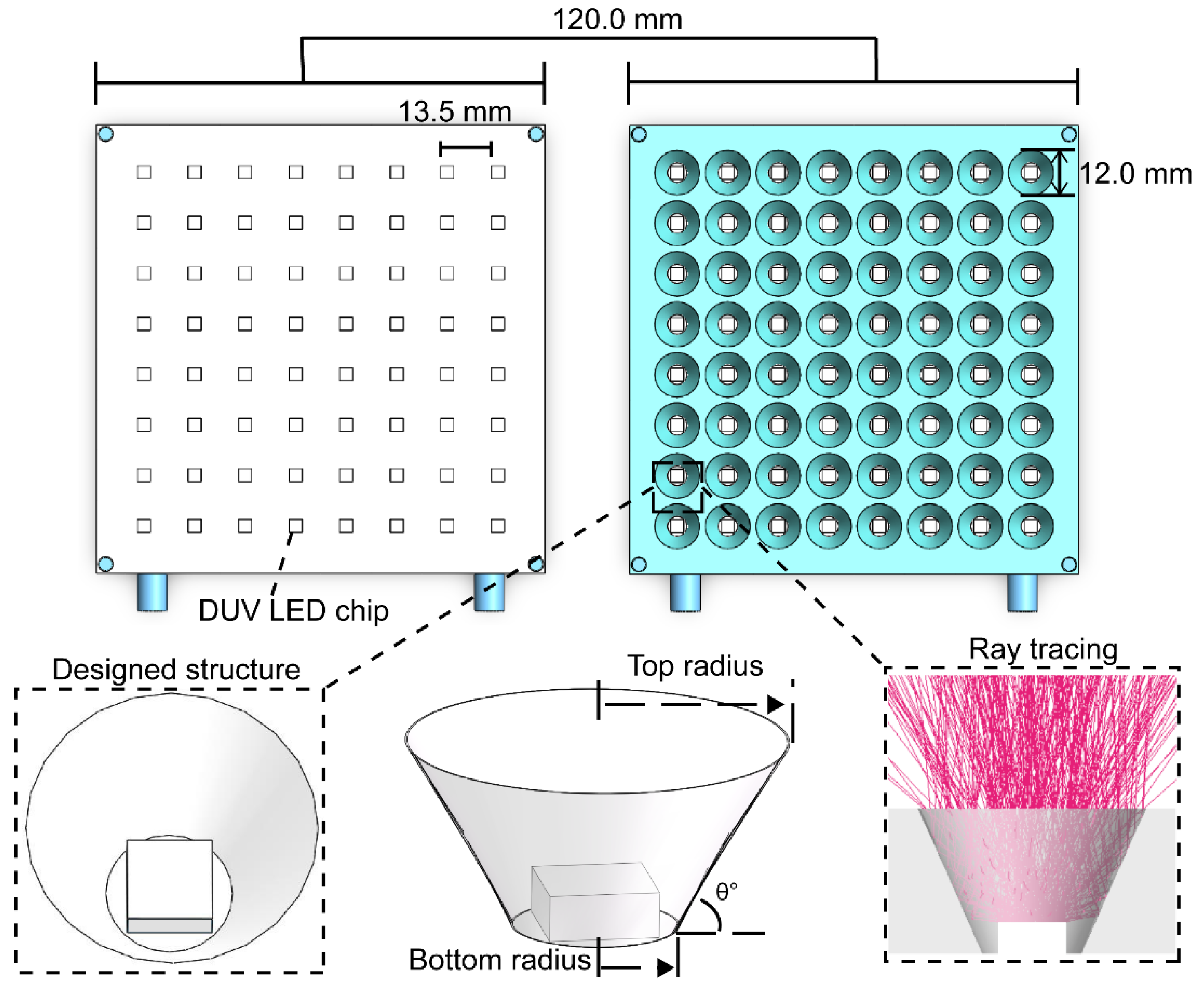
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
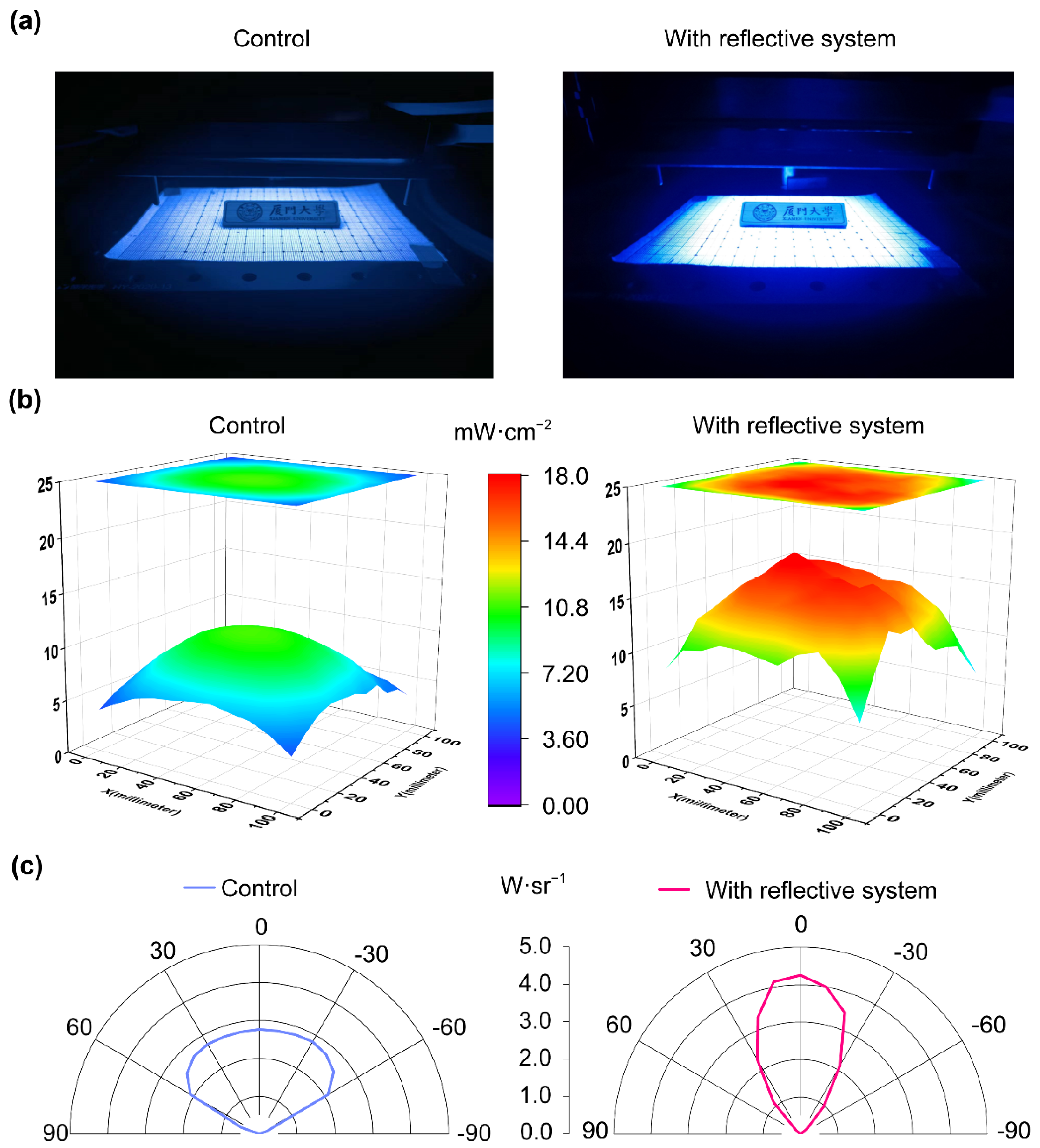
3.1. Preliminary Test
3.2. Optical Simulation and Measurement
3.3. Microbial Inactivation Test
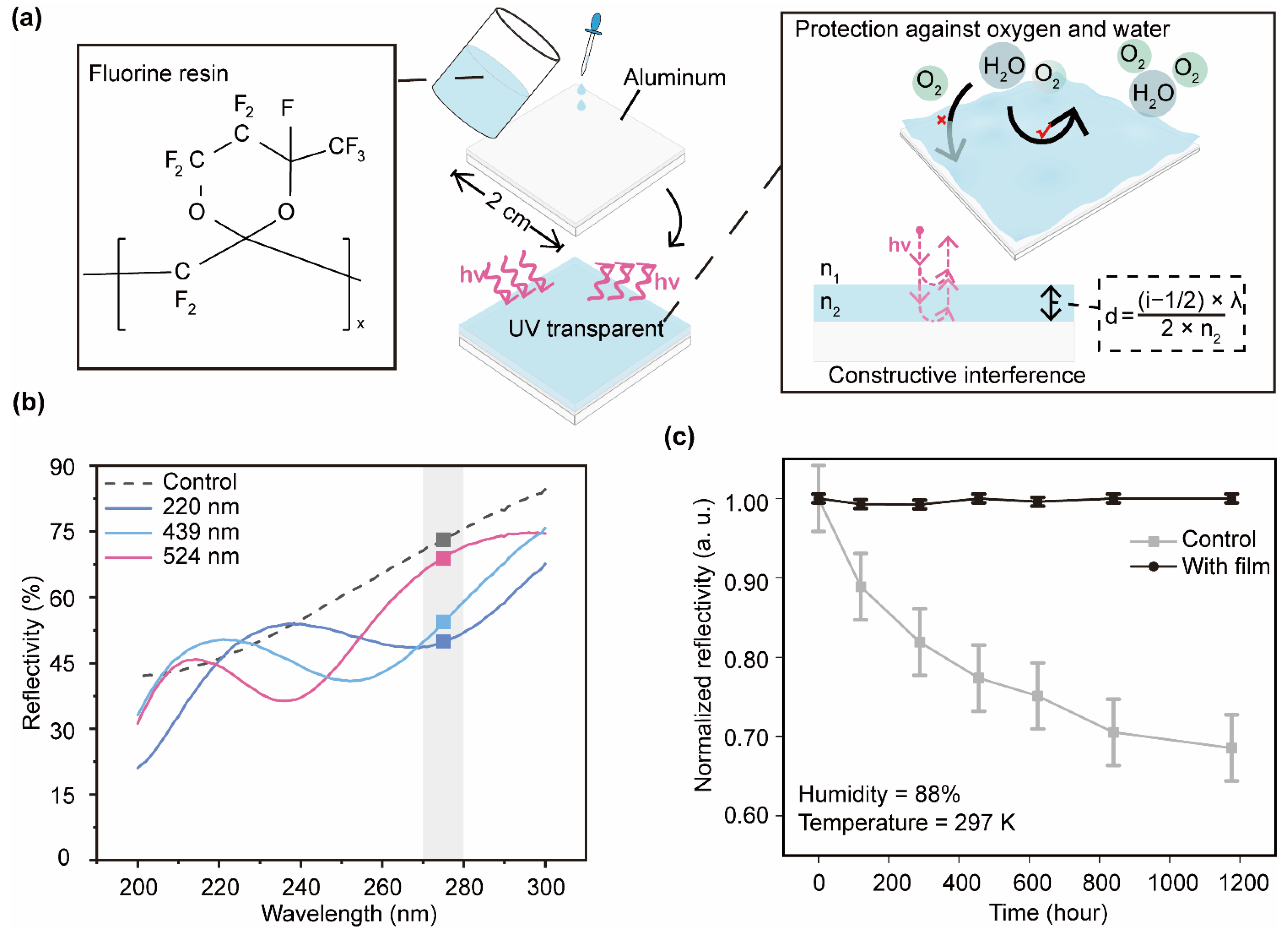
3.4. Fabrication and Verification of the Protective Film
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clerck, H. Emergence of Zaire Ebola virus disease in Guinea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, E.B. Zika virus outside Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wu, T.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z. The SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: What we know. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.I.; Prince, T.; Anderson, E.R.; Casas-Sanchez, A.; Smith, S.L.; Cansado-Utrilla, C.; Solomon, T.; Griffiths, M.J.; Acosta-Serrano, Á.; Turtle, L.; et al. Methods of inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 for downstream biological assays. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1462–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, W.; Li, D.; Yuan, Y.; Tong, W.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Rong, X.; Wang, T.; et al. Sec-Eliminating the SARS-CoV-2 by AlGaN Based High Power Deep Ultraviolet Light Source. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.; Cotton, C. The Ultraviolet Disinfection Handbook; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2008; pp. 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Raeiszadeh, M.; Adeli, B. A Critical Review on Ultraviolet Disinfection Systems against COVID-19 Outbreak: Applicability, Validation, and Safety Considerations. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasin, M.; Bianco, A.; Pareschi, G.; Cavalleri, A.; Cavatorta, C.; Fenizia, C.; Galli, P.; Lessio, L.; Lualdi, M.; Tombetti, E. UV-C irradiation is highly effective in inactivating SARS-CoV-2 replication. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Zheng, J.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Yin, J.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; Kang, J. Deep-ultraviolet photonics for the disinfection of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (Delta and Omicron) in the cryogenic environment. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2023, 6, 220201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Liang, S.; Sun, X.; Ben, J.; Qu, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lan, K.; Li, D. Rapid inactivation of human respiratory RNA viruses by deep ultraviolet irradiation from light-emitting diodes on a high-temperature-annealed AlN/Sapphire template. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2023, 6, 230004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Demir, H.V. Bright Future of Deep-Ultraviolet Photonics: Emerging UVC Chip Scale Light-Source Technology Platforms, Benchmarking, Challenges, and Outlook for UV Disinfection. ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Loeb, S.; Kim, J.-H. LED revolution: Fundamentals and prospects for UV disinfection applications. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneissl, M.; Seong, T.-Y.; Han, J.; Amano, H. The emergence and prospects of deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode technologies. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, N.; Cai, D.; Lin, W.; Huang, K.; Li, S.; Kang, J. Multiple fields manipulation on nitride material structures in ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagedorn, S.; Walde, S.; Susilo, N.; Netzel, C.; Tillner, N.; Unger, R.-S.; Manley, P.; Ziffer, E.; Wernicke, T.; Becker, C.; et al. Improving AlN Crystal Quality and Strain Management on Nanopatterned Sapphire Substrates by High-Temperature Annealing for UVC Light-Emitting Diodes. Phys. Status Solidi A 2020, 217, 1900796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Deng, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, L.; Ding, X. Solid–Liquid Hybrid-State Organic Lens for Highly Efficient Deep Ultraviolet Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Photonics Res. 2022, 3, 2100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Q.; Yu, Q.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Study on the Light Field Regulation of UVC-LED Disinfection for Cold Chain Transportation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.; Lewis, P.; North, P. Monte Carlo ray tracing in optical canopy reflectance modelling. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 18, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, G.; Waylonis, J.E. Optical constants and reflectance and transmittance of evaporated aluminum in the visible and ultraviolet. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1961, 51, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatalov, M.; Chitnis, A.; Yadav, P.; Hasan, F.; Khan, J.; Adivarahan, V.; Maruska, H.P.; Sun, W.H.; Khan, M.A. Thermal analysis of flip-chip packaged 280 nm nitride-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 201109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. The Ministry of Health’s Notice on the Issuance of the “Technical Standard for Disinfection” (2002 Edition). 2002. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/cms-search/xxgk/getManuscriptXxgk.htm?id=16508 (accessed on 3 March 2023). (In Chinese)
- Liang, S.; Sun, W. Recent Advances in Packaging Technologies of AlGaN-Based Deep Ultraviolet Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group | Distance (cm) | Irradiance (mW/cm2) | Current (A) | Voltage (V) | Electrical Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 10 | 1.7765 | 0.996 | 41.823 | 42 |
| With reflective system | 10 | 3.8535 | 0.996 | 41.825 | 42 |
| Control | 10 | 3.8508 | 2.122 | 43.319 | 92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Ye, X.; Li, W.; Cheng, K.; Qu, S.; Kang, W.; Yin, J.; Kang, J. Light-Field Optimization of Deep-Ultraviolet LED Modules for Efficient Microbial Inactivation. Coatings 2024, 14, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050568
Huang J, Wang Q, Ye X, Li W, Cheng K, Qu S, Kang W, Yin J, Kang J. Light-Field Optimization of Deep-Ultraviolet LED Modules for Efficient Microbial Inactivation. Coatings. 2024; 14(5):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050568
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiaxin, Qingna Wang, Xiaofang Ye, Wenxiang Li, Keyang Cheng, Shanzhi Qu, Wenyu Kang, Jun Yin, and Junyong Kang. 2024. "Light-Field Optimization of Deep-Ultraviolet LED Modules for Efficient Microbial Inactivation" Coatings 14, no. 5: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050568
APA StyleHuang, J., Wang, Q., Ye, X., Li, W., Cheng, K., Qu, S., Kang, W., Yin, J., & Kang, J. (2024). Light-Field Optimization of Deep-Ultraviolet LED Modules for Efficient Microbial Inactivation. Coatings, 14(5), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050568






