The Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Lithium-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials via Mg-Al Co-Doping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
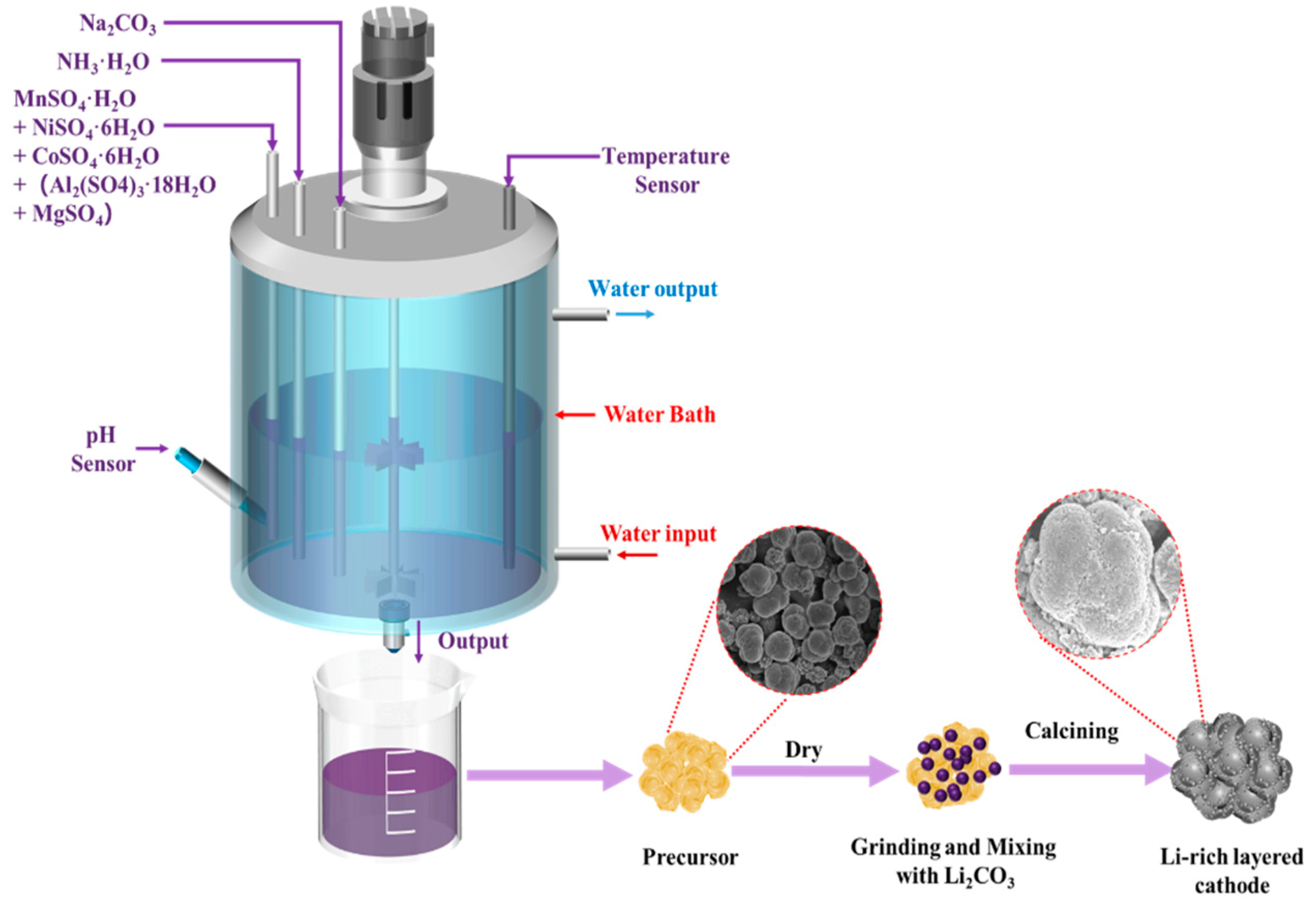
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Phase Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Performance Test
3. Results and Discussion
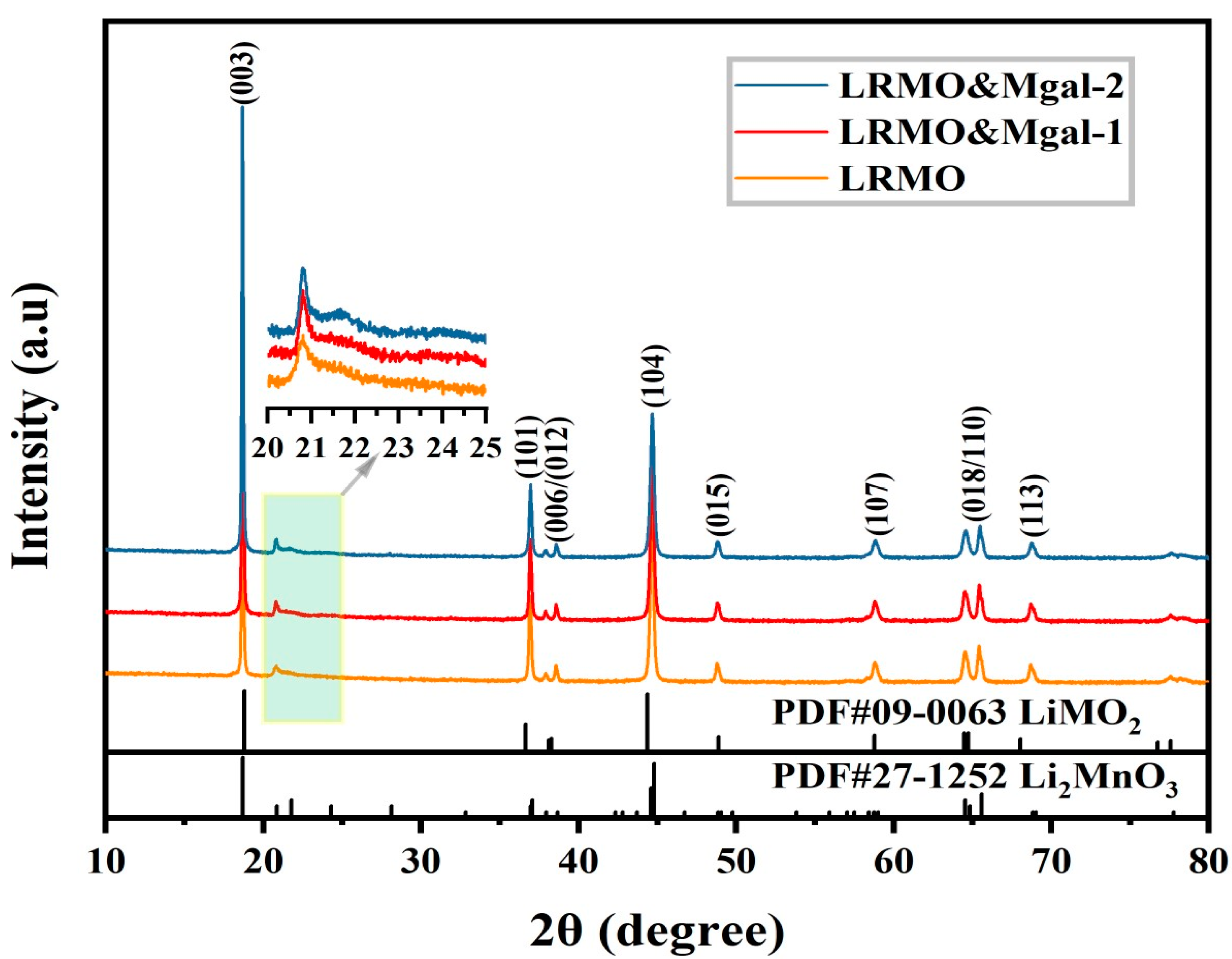
3.1. Structure and Composition Characterization of Mg-Al Co-Doped LMR
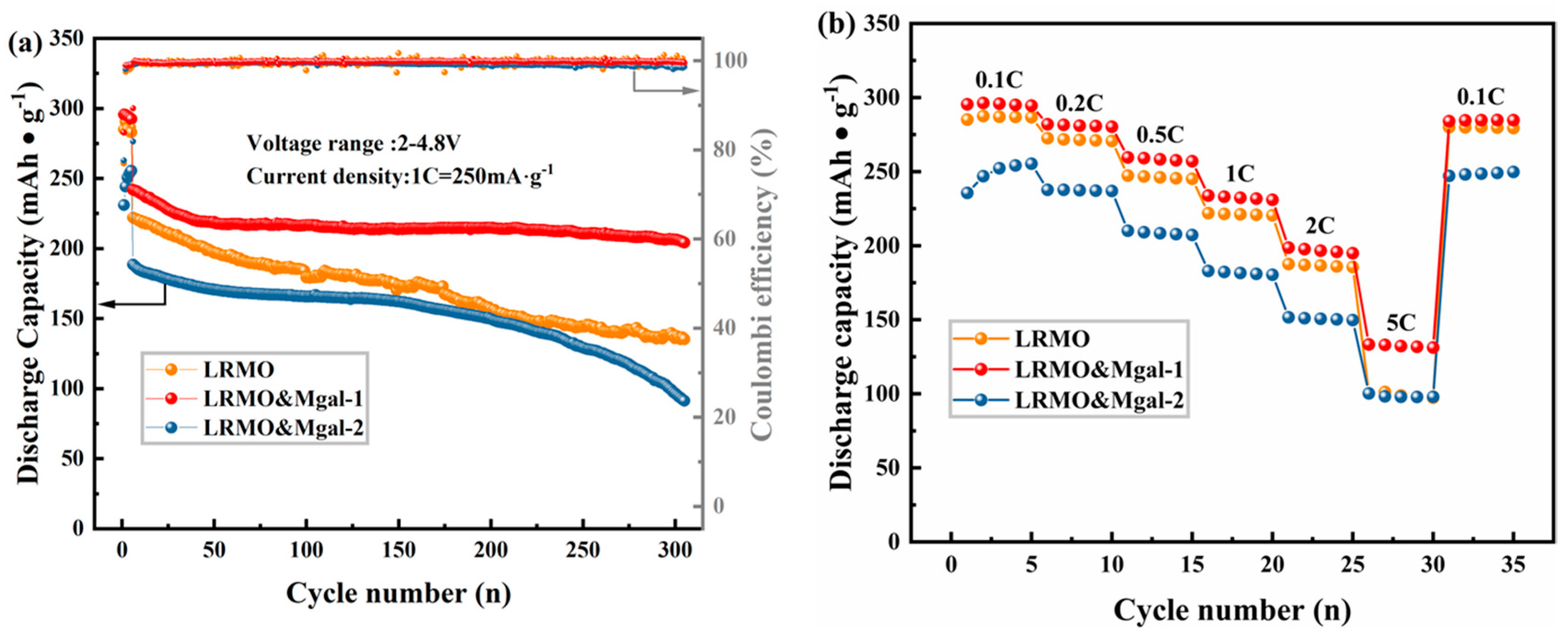
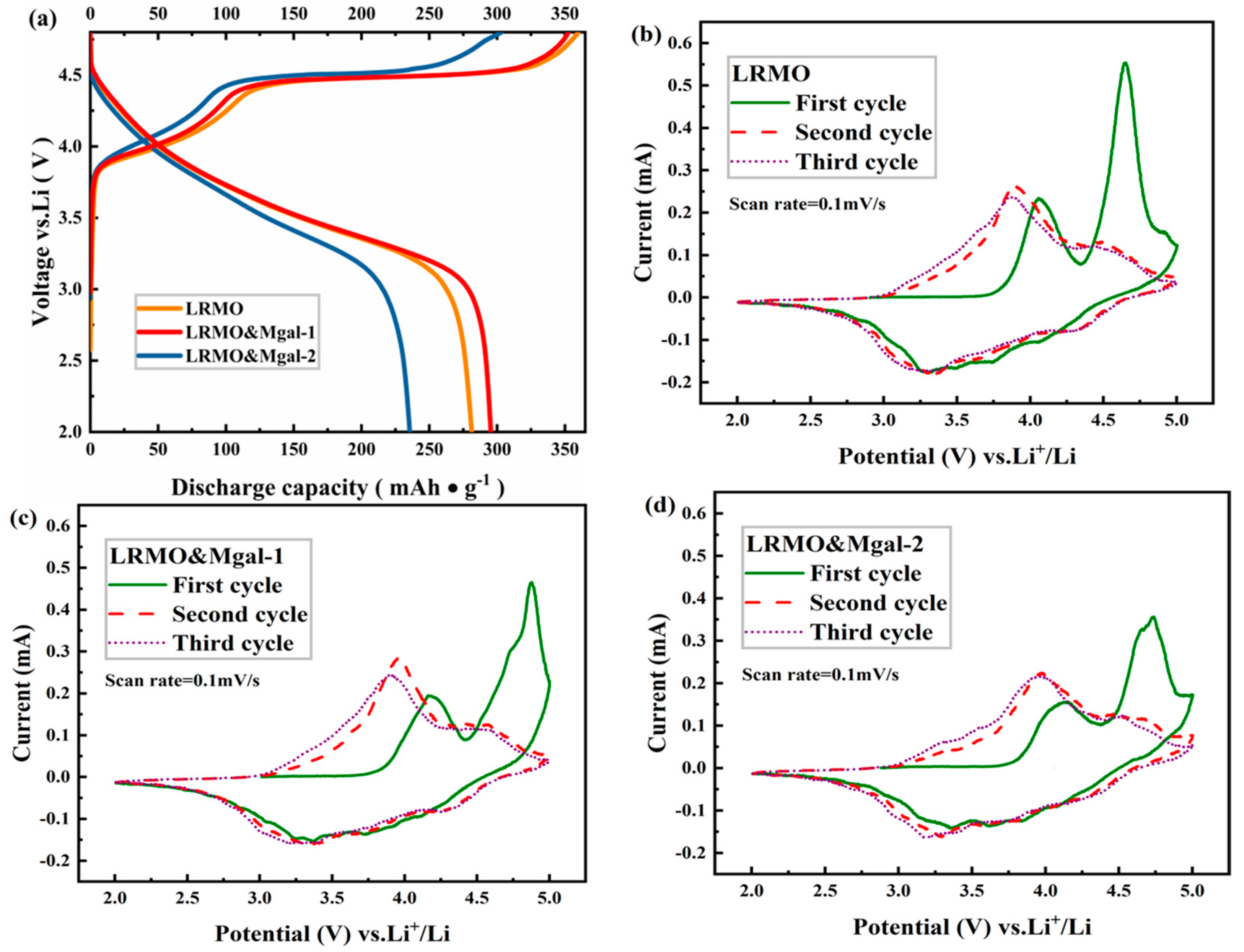
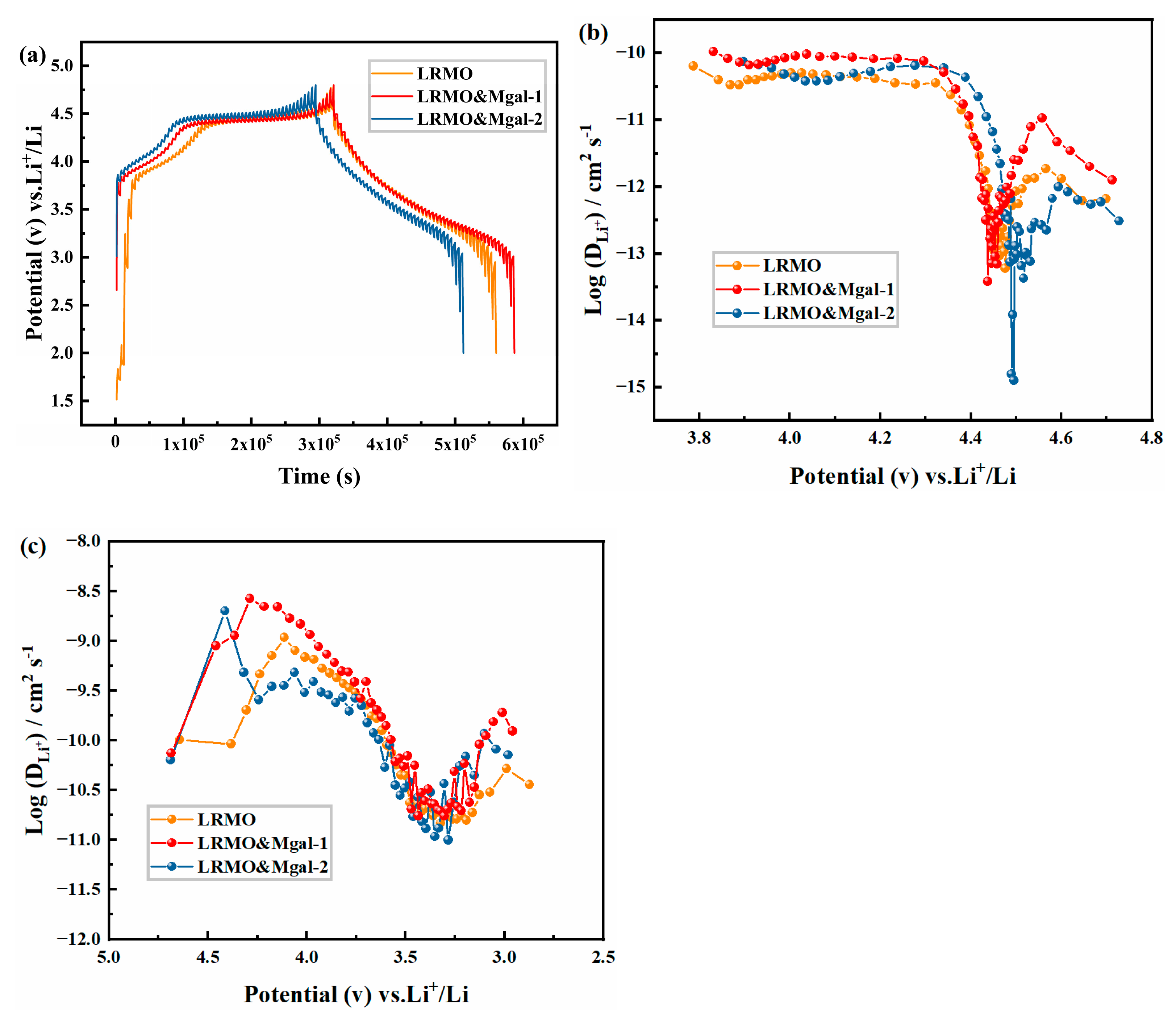
3.2. Electrochemical Properties of LMR-Based Materials
4. Conclusions
- The Mg-Al co-doped lithium-rich manganese-based cathode materials exhibit an enhanced layered structure. The mixing degree in the doped samples is further reduced compared to the original samples. The layer spacing of LRMO&Mgal-1 material increases, which is favorable for the lithium-ion transport;
- SEM results reveal that the Mg-Al co-doped cathode material appears dense after sintering, which is effective in resisting erosion by by-products. TEM and EDS results indicate that the material is a well-developed layer structure with uniform element distribution after Mg-Al tiny co-doping. XPS results further highlight an increased average oxidation state of Mn and enhanced Mn4+ content, contributing to the alleviation of the Jahn–Teller effect;
- The specific discharge capacity retention remained at 84.4% for the LRMO&Mgal-1 sample, even after 300 charge/discharge cycles at 1 C. The material exhibits excellent rate performance, achieving a specific capacity of 133.3 mAh·g−1 under high-current conditions of 5 C. The impedance test and GITT analysis indicate that the Li+ diffusion kinetics of the LRMO&Mgal-1 sample were effectively improved with Mg-Al tiny co-doping. These findings suggest that the addition of trace amounts of Mg-Al through co-doping has the potential to significantly improve the electrochemical properties of Li-rich Mn-based cathode materials.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.L.; Huang, X.; Li, F. Enhanced high rate performance of Li[Li0.17Ni0.2Co0.05Mn0.58−xAlx]O2−0.5x cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49651–49656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Q.; Wang, Y. High-capacity full lithium-ion cells based on nanoarchitectured ternary manganese–nickel–cobalt carbonate and its lithiated derivative. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14947–14956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezaal, M.A.; Qu, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, R.; Xuejiao, J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, W.; Lei, L. Promoting the cyclic and rate performance of lithium-rich ternary materials via surface modification and lattice expansion. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 93048–93056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, N.; Wu, F.; Lee, J.T. Li-ion battery materials: Present and future. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wei, X.; Yang, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xing, Y.; Liu, G. Synthesis, structure and electrochemical properties of lithium-rich cathode material Li1.2Mn0.6Ni0.2O2 microspheres. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 81565–81572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shunmugasundaram, R.; Doig, R.; Dahn, J.R. In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study of Layered Li–Ni–Mn–Co Oxides: Effect of Particle Size and Structural Stability of Core–Shell Materials. Chem. Mater. 2015, 28, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Gwon, H.; Jung, S.-K.; Ku, K.; Kang, K. Review—Lithium-Excess Layered Cathodes for Lithium Rechargeable Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A2447–A2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Tao, J.; Chen, Z.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Z. Surface heterostructure induced by TiO2 modification in Li-rich cathode materials for enhanced electrochemical performances. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 353, 135959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gao, Y.; Liang, X. Slightly Fluorination of Al2O3 ALD Coating on Li1.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2 Electrodes: Interface Reaction to Create Stable Solid Permeable Interphase Layer. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A2021–A2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Lu, H.; Su, Y.; Li, N.; Bao, L.; Chen, S. Preparation and electrochemical characterization of Li(Li0.17Ni0.2Co0.05Mn0.58)O2 coated with LiAlO2. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 40, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Li, T. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of Zn-doped Li-rich layered Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2 cathode material. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 11396–11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yuan, D.; Qian, J.; Ai, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y. Enhanced high-rate capability and cycling stability of Na-stabilized layered Li1.2[Co0.13Ni0.13Mn0.54]O2 cathode material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11397–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, T.; Schipper, F.; Erickson, E.M.; Susai, F.A.; Markovsky, B.; Aurbach, D. Structural and Electrochemical Aspects of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 Cathode Materials Doped by Various Cations. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Huang, D.; He, Y.-B.; Zhao, S.-X. Mg2+ doping into Li sites to improve anionic redox reversibility and thermal stability of lithium-rich manganese-based oxides cathode. Mater. Today Energy 2022, 29, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yin, C.; Jia, K.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Z. Stabilization effects of Al doping for enhanced cycling performances of Li-rich layered oxides. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 13845–13852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.; Song, C.; Chen, L.; Li, M. The effect on the properties of each element in the Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 material by the incorporation of Al. Ionics 2020, 26, 5951–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Wu, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, E.; Yu, H. Thermal Stability Enhancement through Structure Modification on the Microsized Crystalline Grain Surface of Lithium-Rich Layered Oxides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8306–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, G. An appropriate amount of new spinel phase induced by control synthesis for the improvement of electrochemical performance of Li-rich layered oxide cathode material. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 330, 135240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Kang, F. A Simple Dual-Ion Doping Method for Stabilizing Li-Rich Materials and Suppressing Voltage Decay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13996–14004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B.H. EXPGUI, a graphical user interface for GSAS. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, L.; Chen, R. Structure Evolution from Layered to Spinel during Synthetic Control and Cycling Process of Fe-Containing Li-Rich Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5601–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; E, Y.; Fan, L.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, S. A new route for the electrodeposition of platinum–nickel alloy nanoparticles on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 5873–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zeng, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; He, H.; Chen, X.; He, A. Electrochemical performance of the Li-rich layered Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 cathode material influenced by Fe3+ doping. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 910, 164862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Zhang, M.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Qian, D.; Liu, H.; Hy, S.; Chen, Y.; An, K.; et al. Gas-solid interfacial modification of oxygen activity in layered oxide cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Dual-Site Doping Strategy for Enhancing the Structural Stability of Lithium-Rich Layered Oxides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 16407–16417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Ohta, K.; Hou, X.; Kimura, Y.; Tsuruta, K.; Tamenori, Y.; Aso, R.; Yoshida, H.; Amezawa, K. Oxygen defect engineering for the Li-rich cathode material Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2−δ. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 9, 3657–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galakhov, V.R.; Demeter, M.; Bartkowski, S.; Neumann, M.; Ovechkina, N.A.; Kurmaev, E.Z.; Lobachevskaya, N.I.; Mukovskii, Y.M.; Mitchell, J.; Ederer, D.L. Mn 3s exchange splitting in mixed-valence manganites. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Bastos, S.S.T.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Delgado, J.J.; Figueiredo, J.L. Carbon Monoxide Oxidation Catalysed by Exotemplated Manganese Oxides. Catal. Lett. 2009, 134, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, L.; Sorrentino, A.; Marini, C.; Ramanan, N.; Heinis, D.; Olszewski, W.; Mullaliu, A.; Birrozzi, A.; Laszczynski, N.; Giorgetti, M.; et al. Role of Manganese in Lithium- and Manganese-Rich Layered Oxides Cathodes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Guo, H.; Li, X.; Jing, Q.; Yang, Z. Effect of Mg doping on the structural and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode materials. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 182, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Shang, K.H.; He, W.; Ai, X.P.; Cao, Y.L.; Yang, H.X. Magnesium-Doped Li1.2[Co0.13Ni0.13Mn0.54]O2 for Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode with Enhanced Cycling Stability and Rate Capability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13014–13021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Dong, S.; Zeng, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, X.; Ma, L.; Hai, C.; Zhou, Y. Improving the electrochemical performances of Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 through cooperative doping of Na+ and Mg2+. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 414, 140169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Su, X.; Lei, D.; Qin, Y.; Wen, J.; Guo, F.; Wu, Y.A.; Rong, Y.; Kou, R.; Xiao, X.; et al. Approaching the capacity limit of lithium cobalt oxide in lithium ion batteries via lanthanum and aluminium doping. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Manthiram, A.; Wang, C. Lattice doping regulated interfacial reactions in cathode for enhanced cycling stability. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Zhou, D.; Hou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Bresser, D.; et al. Chemical and structural evolutions of Li–Mn-rich layered electrodes at different current densities. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 4137–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, D.; Liang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, N.; Tuo, K.; Lu, H.; Cai, X.; Mao, L.; et al. Study on electrochemical performance of Al-substitution for different cations in Li-rich Mn-based materials. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 394, 139136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Ai, L.; Fu, X.; Cui, X.; Shangguan, X. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of Mg–Al co-doped Li-rich Mn-based cathode materials. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 12004–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, H.; Croguennec, L.; Ménétrier, M.; Mannessiez, P.; Weill, F.; Delmas, C.; Belin, S. Operando X-ray Absorption Study of the Redox Processes Involved upon Cycling of the Li-Rich Layered Oxide Li1.20Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2 in Li Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5700–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, J.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Yu, Y.; Kang, F. Surface-Functionalized Coating for Lithium-Rich Cathode Material to Achieve Ultra-High Rate and Excellent Cycle Performance. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11891–11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Xia, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Zhang, W. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of nano TiO2(B)-coated Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13]O2 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12962–12968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, R.A.; Rees, G.J.; Pérez-Osorio, M.A.; Marie, J.-J.; Boivin, E.; Robertson, A.W.; Nag, A.; Garcia-Fernandez, M.; Zhou, K.-J.; Bruce, P.G. First-cycle voltage hysteresis in Li-rich 3d cathodes associated with molecular O2 trapped in the bulk. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Chu, Y.; Yu, J.; Qu, J.; Yang, S.; Tan, C.; Lai, F.; Jin, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Uniform amorphous MgxByOz coating combined with Vo for highly stable Li-Rich Mn-based cathode material. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, C.; Yu, B.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y.; Fu, Z.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z.; Guo, B.; Huang, Y.; et al. Fundamental mechanism revealed for lithium deficiencies engineering in a new spherical Li-Rich Mn-based layered Li1.23Mn0.46Ni0.246Co0.046Al0.015O2 cathode. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 418, 140379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, H.; Yan, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q. Mitigating capacity fade by constructing highly ordered mesoporous Al2O3/polyacene double-shelled architecture in Li-rich cathode materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13933–13945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, Y.-X.; Chen, F.; He, X.-D.; Yasmin, A.; Hu, Q.; Wen, Z.-Y.; Chen, C.-H. In situ formation of LiF decoration on a Li-rich material for long-cycle life and superb low-temperature performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11513–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
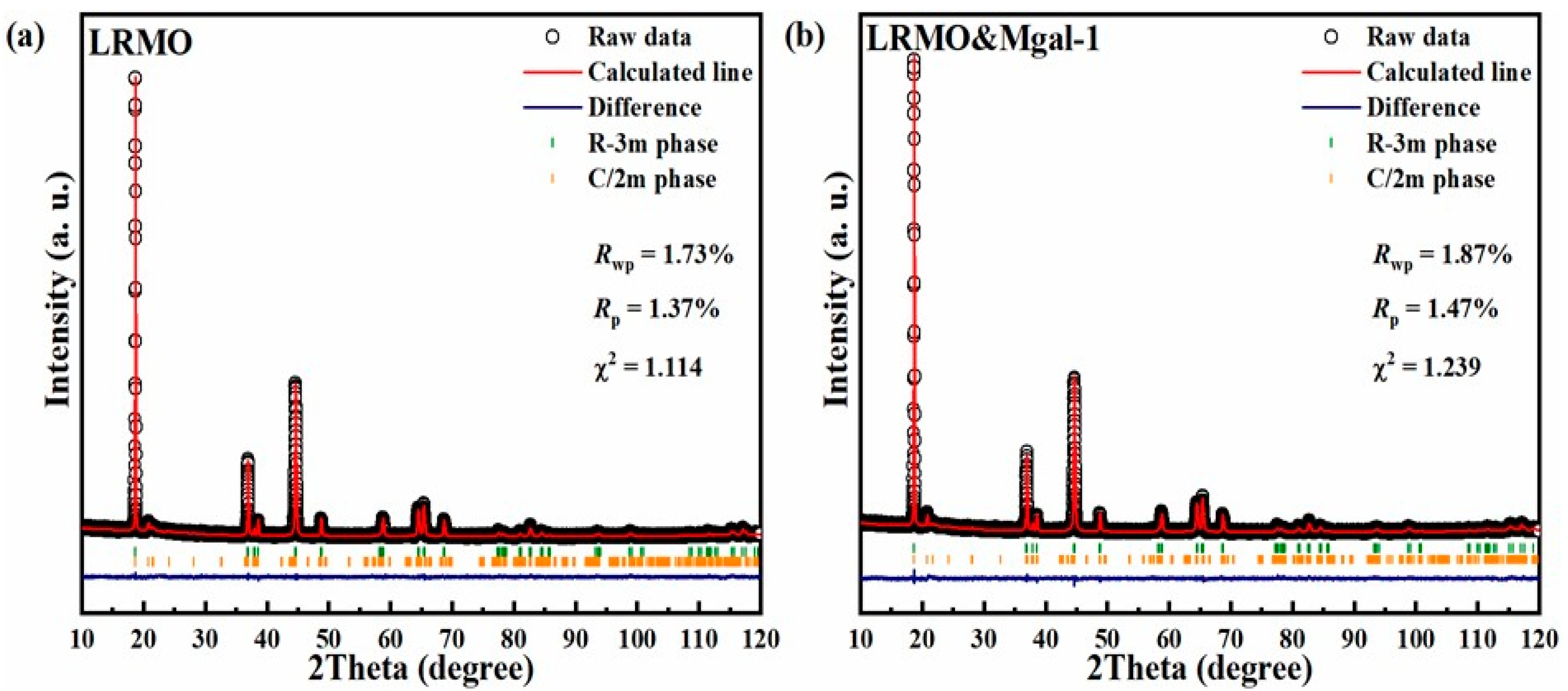




| Sample | a/Å | c/Å | c/a |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRMO | 2.851 (8) | 14.233 (6) | 4.9910 |
| LRMO&Mgal-1 | 2.852 (1) | 14.240 (4) | 4.9930 |
| Sample | Rs (Ω) | Rf (Ω) | Rct (Ω) | R (Ω) | σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRMO | 1.16 | 72.28 | 165.90 | 239.18 | 217.7 |
| LRMO&Mgal-1 | 1.15 | 47.30 | 74.26 | 121.56 | 179.3 |
| LRMO&Mgal-2 | 1.56 | 230.5 | 254.4 | 484.90 | 555.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.; Deng, W.; Zheng, X.; Lin, K.; Liu, M.; Zhu, G.; Lin, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, J. The Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Lithium-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials via Mg-Al Co-Doping. Coatings 2025, 15, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010003
Lu W, Deng W, Zheng X, Lin K, Liu M, Zhu G, Lin J, Wei Y, Wang F, Liu J. The Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Lithium-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials via Mg-Al Co-Doping. Coatings. 2025; 15(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Wanting, Wenhui Deng, Xiyan Zheng, Kunling Lin, Mengyuan Liu, Guozhang Zhu, Jingyi Lin, Yi Wei, Feng Wang, and Jiageng Liu. 2025. "The Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Lithium-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials via Mg-Al Co-Doping" Coatings 15, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010003
APA StyleLu, W., Deng, W., Zheng, X., Lin, K., Liu, M., Zhu, G., Lin, J., Wei, Y., Wang, F., & Liu, J. (2025). The Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Lithium-Rich Manganese-Based Cathode Materials via Mg-Al Co-Doping. Coatings, 15(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15010003







