Application of Rejuvenators in Asphalt Binders: Classification and Micro- and Macro-Properties
Abstract
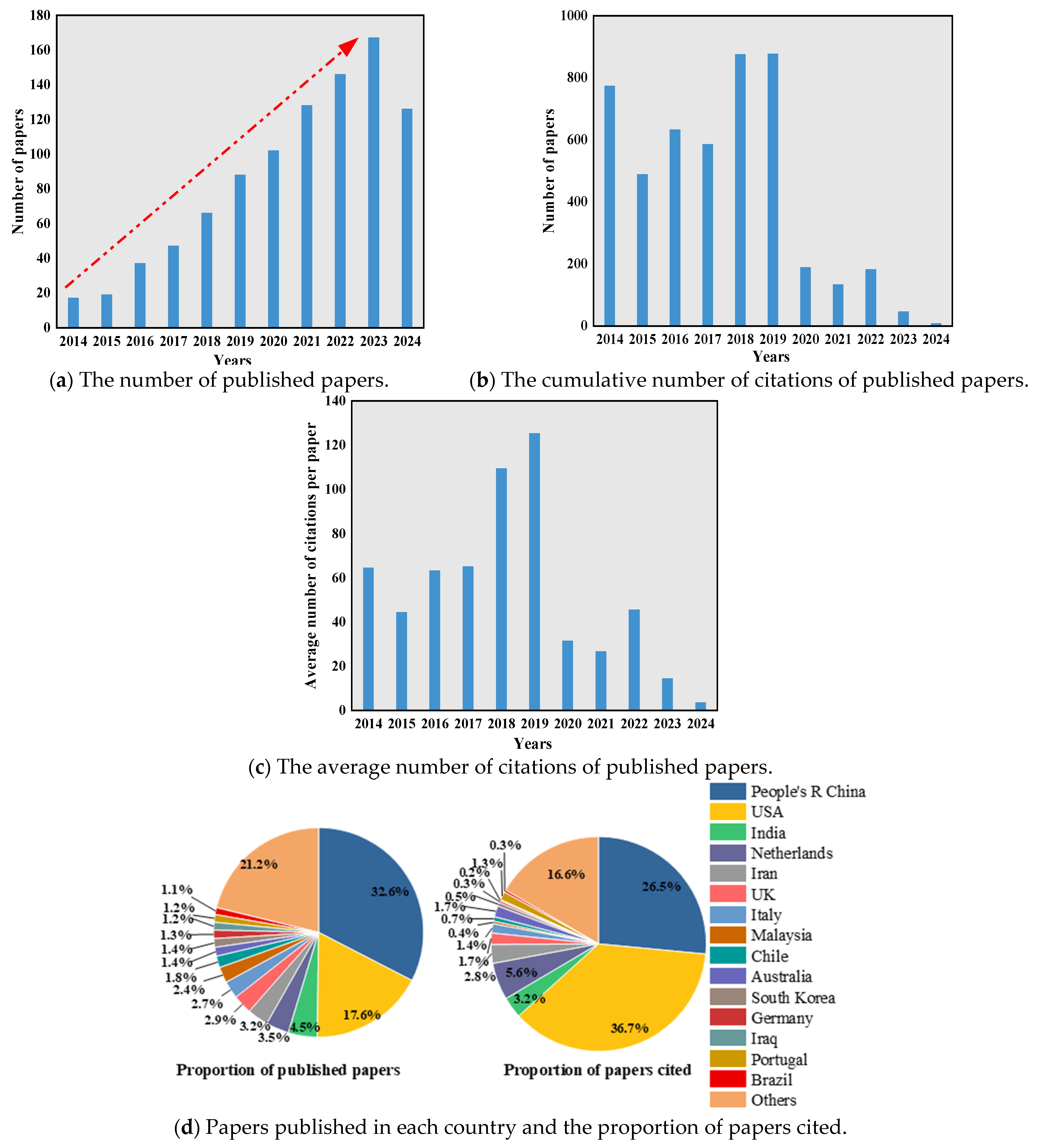
1. Introduction
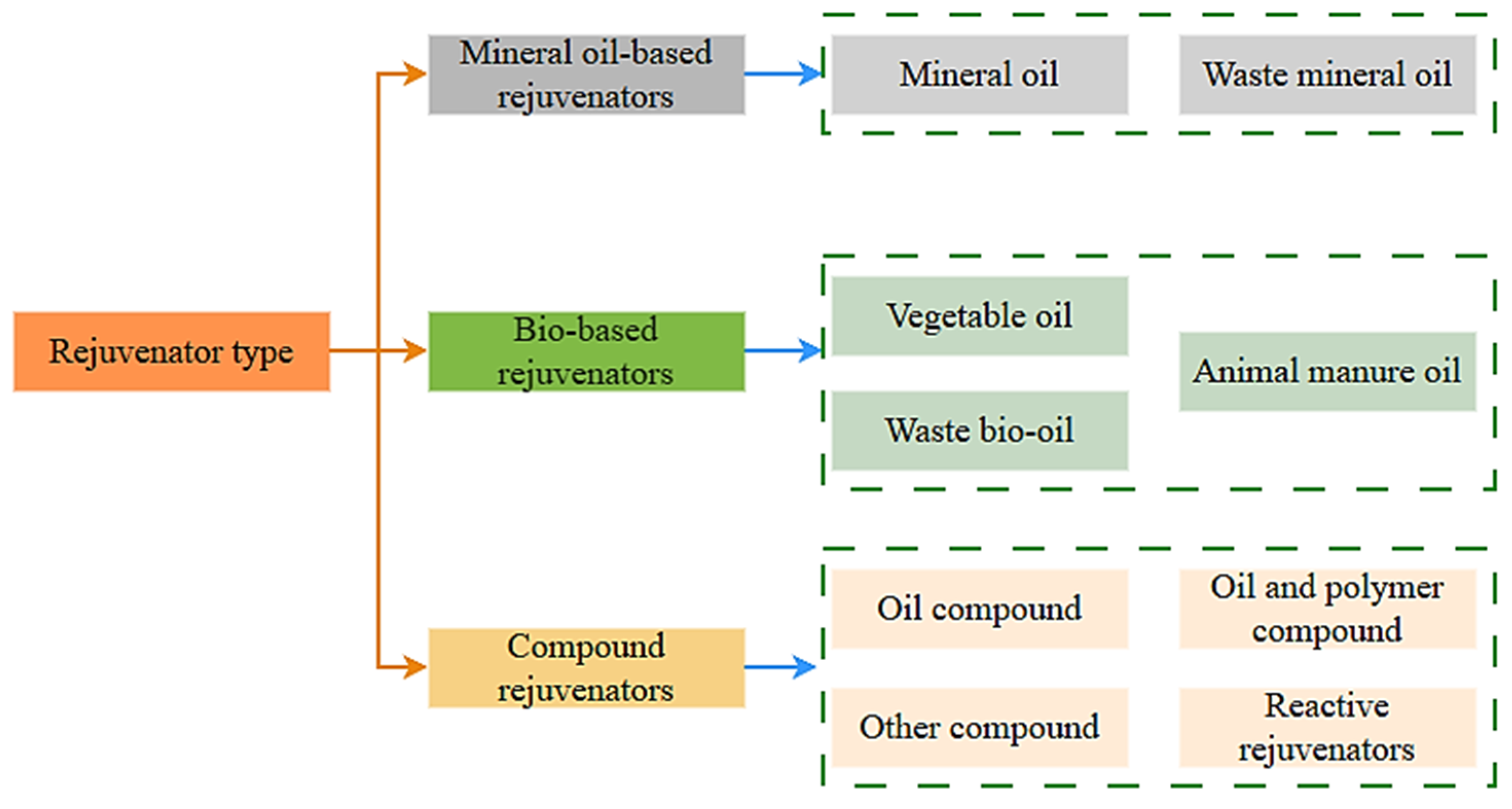
2. Classification of Rejuvenators
2.1. Mineral Oil-Based Rejuvenators
2.1.1. Mineral Oil
2.1.2. Waste Mineral Oil
2.2. Bio-Based Rejuvenators
2.2.1. Vegetable Oil
2.2.2. Animal Manure Oil
2.2.3. Waste Bio-Oil
2.3. Compound Rejuvenators
2.3.1. Oil Compound Rejuvenators
2.3.2. Oil and Polymer Compound Rejuvenators
2.3.3. Reactive Rejuvenators
- (a)
- Epoxy system
- (b)
- Isocyanate system
2.3.4. Other Compound Rejuvenators
3. Micro-Properties of Rejuvenated Asphalt
3.1. Surface Micro-Structure
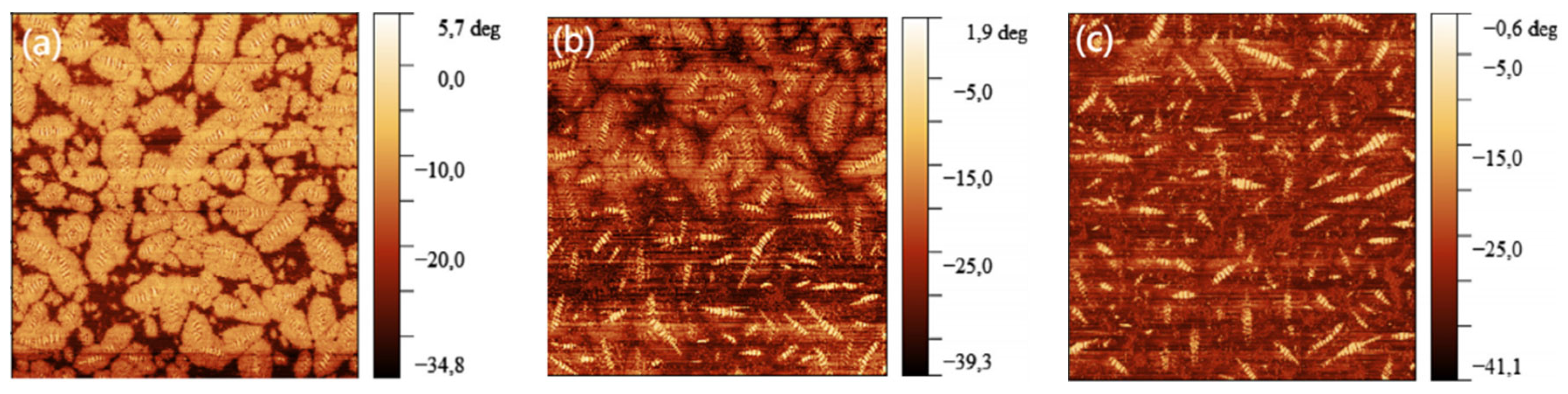
3.1.1. Atomic Force Microscope
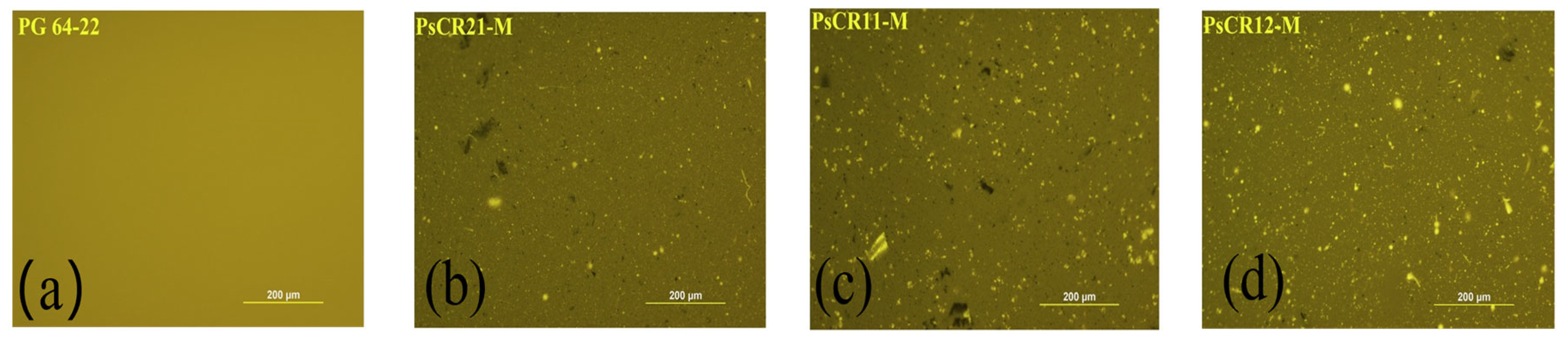
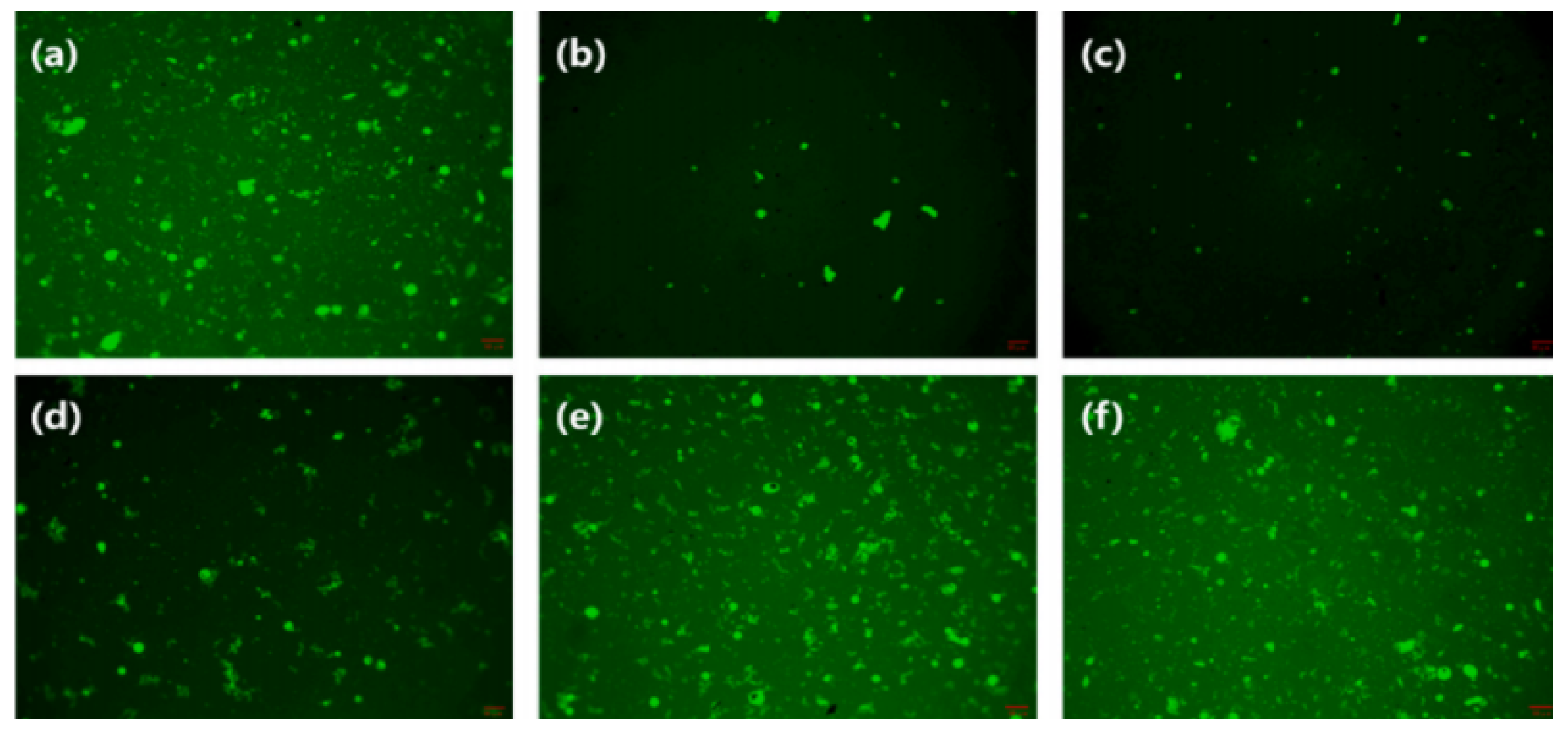
3.1.2. Fluorescence Microscope
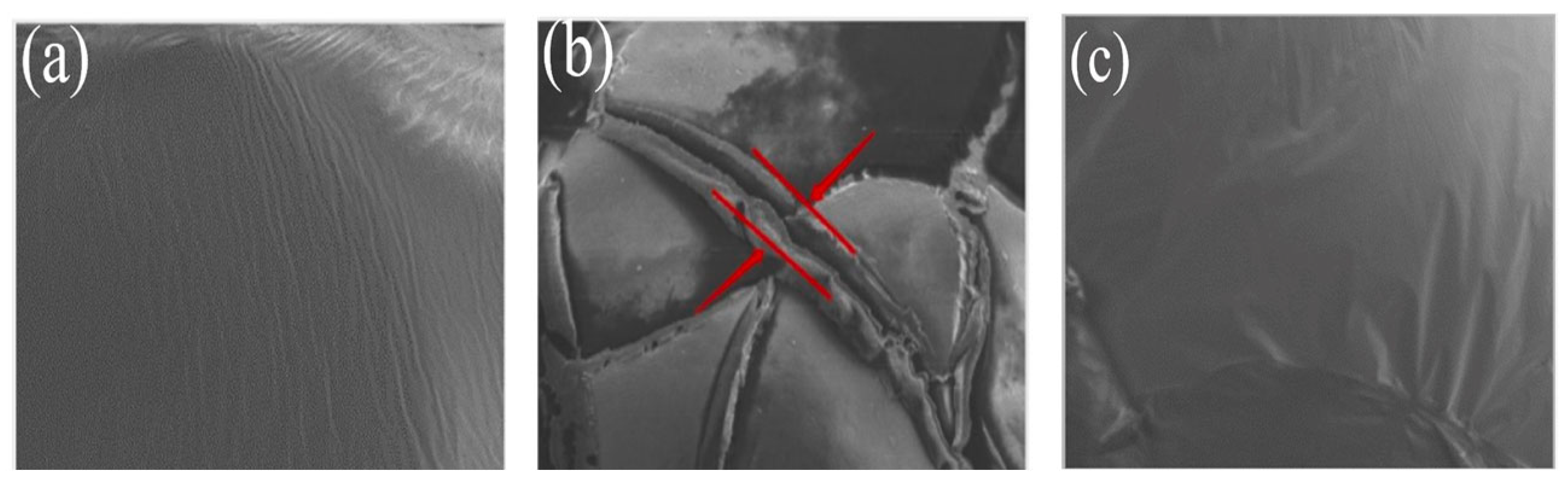
3.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscope
3.2. Functional Groups
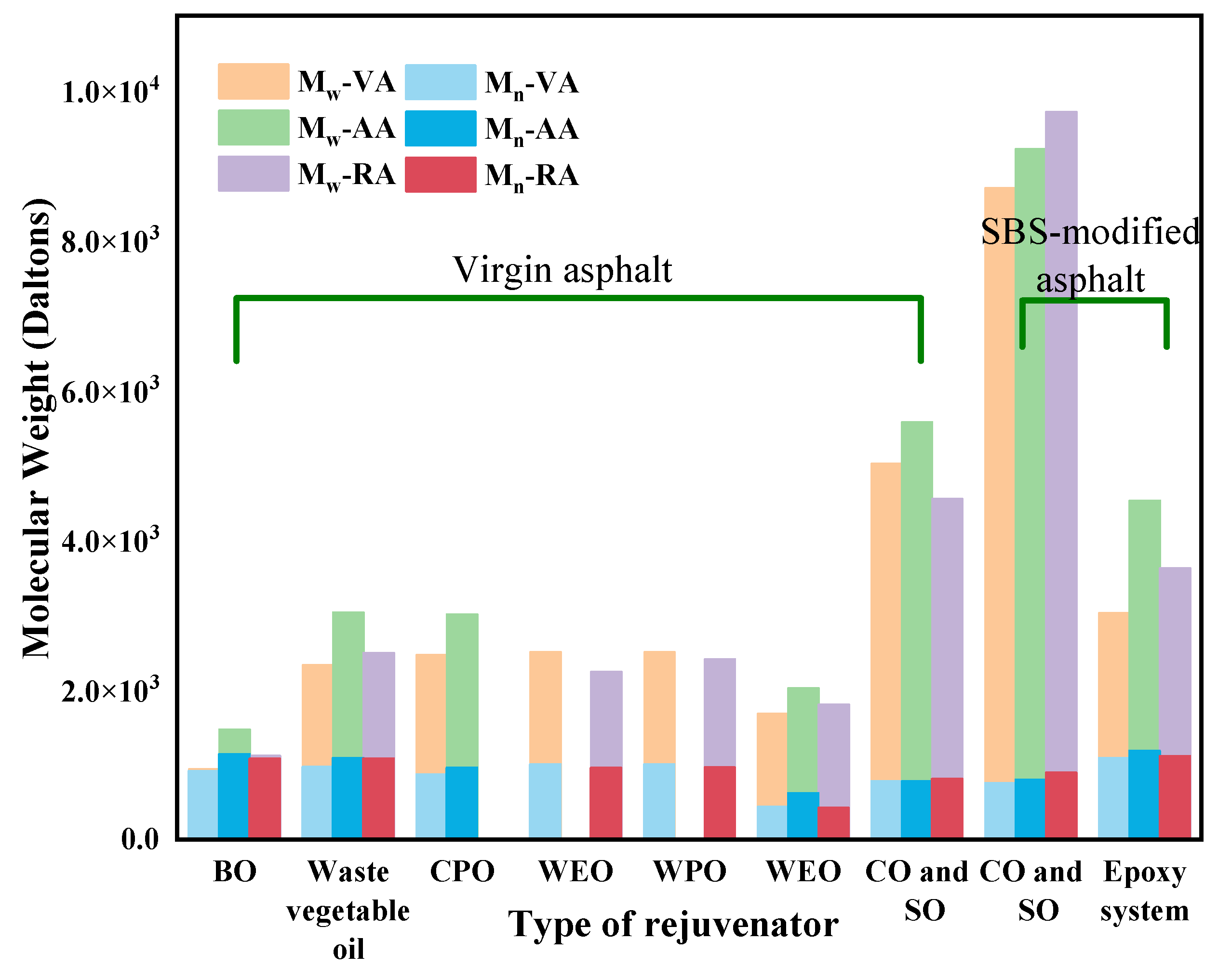
3.3. Molecular Weight
4. Macro-Properties of Rejuvenated Asphalt
4.1. Three Indicators
4.1.1. Penetration
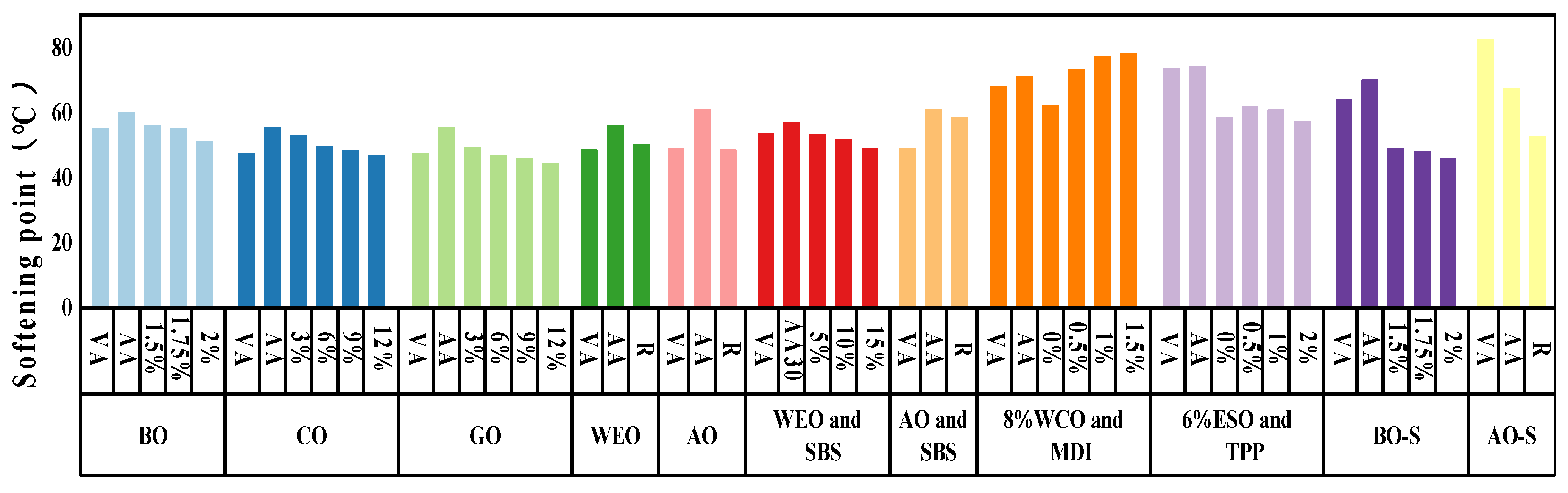
4.1.2. Softening Point
4.1.3. Ductility
4.2. High-Temperature Rheological Properties
4.3. Medium-Temperature Rheological Properties
4.4. Low-Temperature Rheological Properties
5. Macro-Properties of Rejuvenated Asphalt Mixture
5.1. High-Temperature Stability
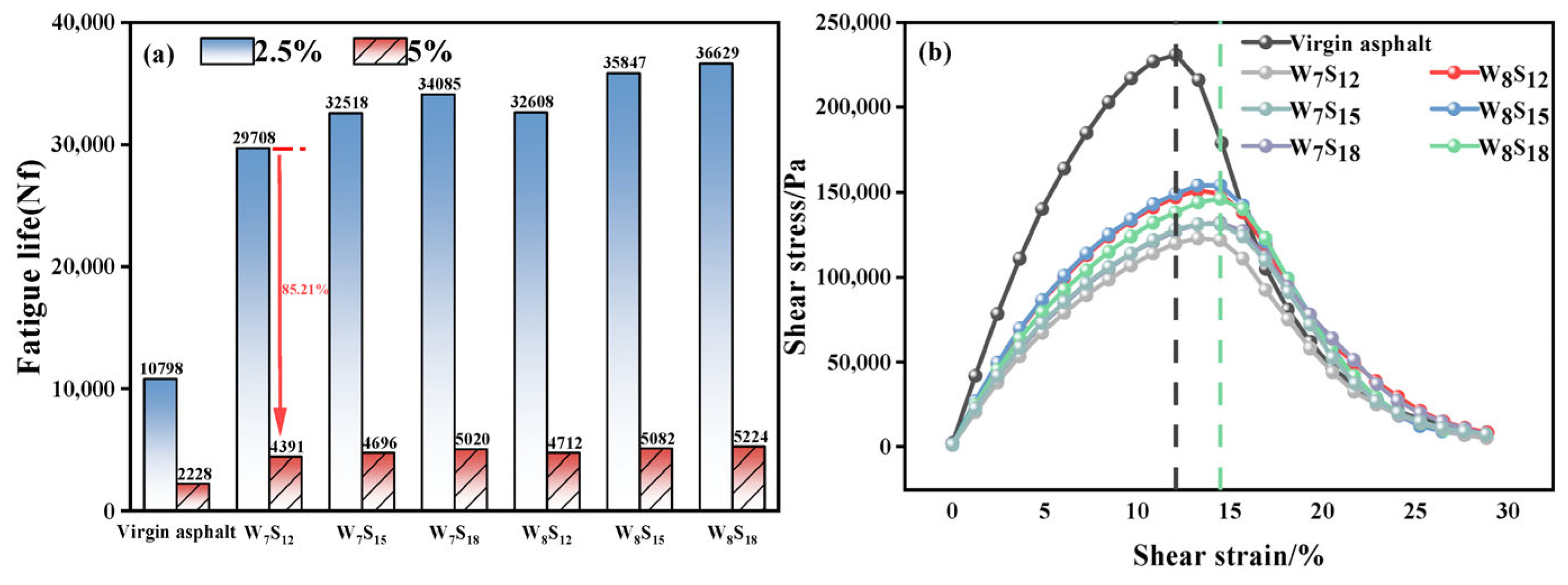
5.2. Fatigue Resistance
Low-Temperature Cracking Resistance
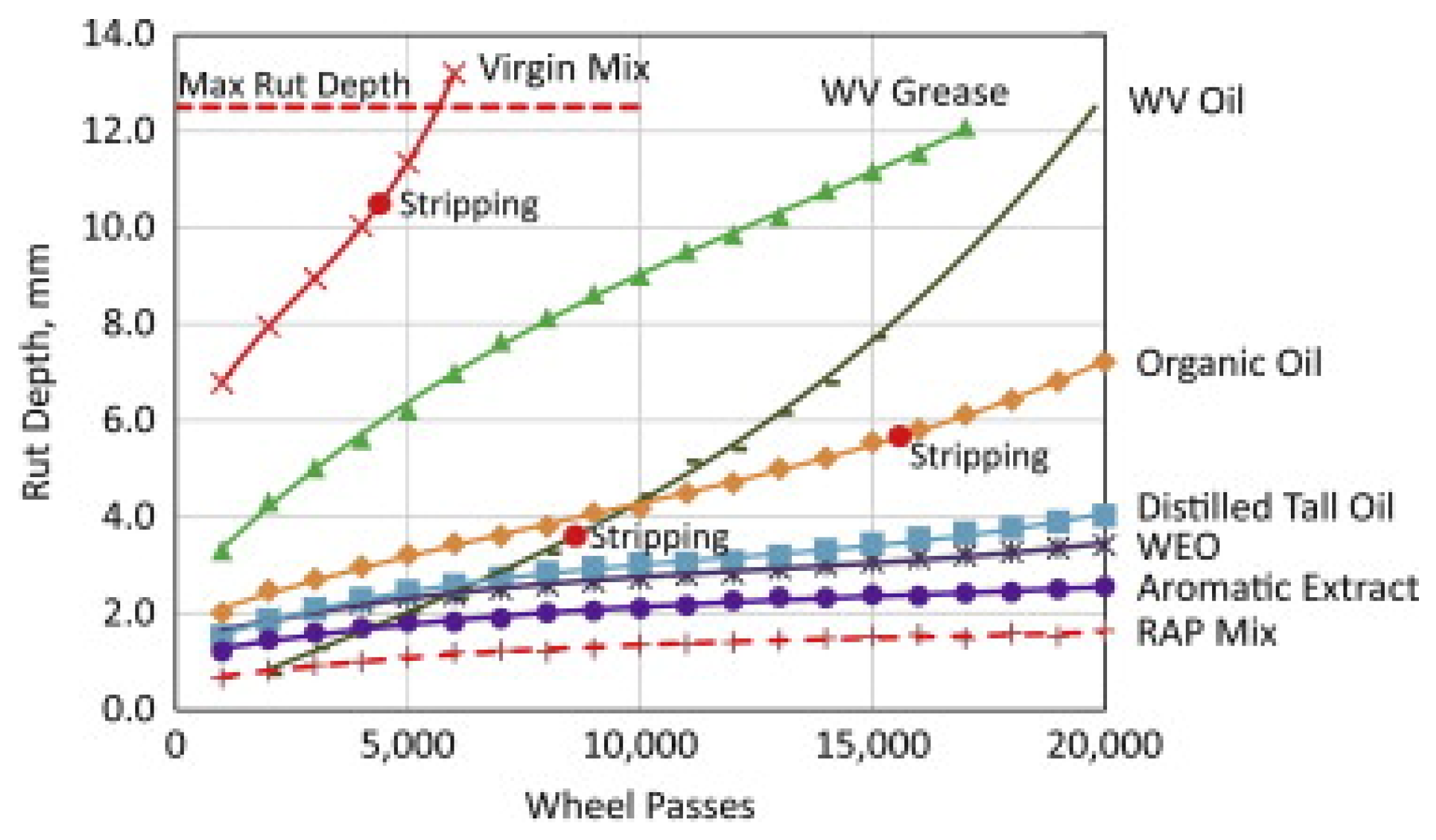
5.3. Water Stability
6. Technical Challenges and Future Recommendations
7. Conclusions
- Rejuvenators can be classified into mineral oil-based rejuvenators, bio-based rejuvenators, and compound rejuvenators according to differences in composition. Among these rejuvenators, mineral oil-based and bio-based rejuvenators are the most researched ones, and compound rejuvenators are the most promising ones for application.
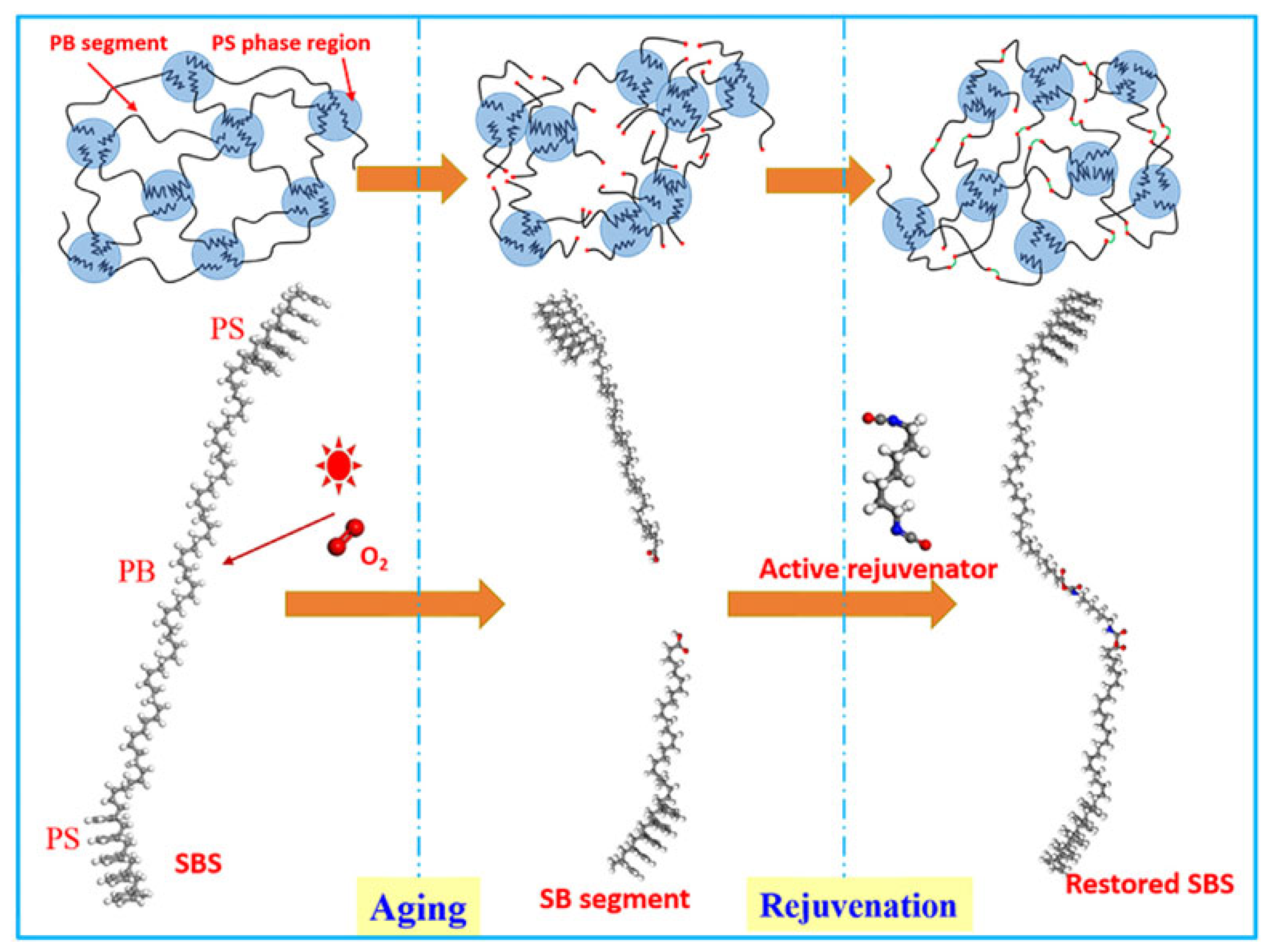
- Through micro-experiments, it can be found that mineral oil-based and bio-based rejuvenators, through physical dilution of aged virgin asphalt to upgrade its microscopic performance, can only restore the smoothness of aged asphalt without changing the microstructure of aged asphalt. Oil-based and polymer compound and reactive rejuvenators can not only restore the properties of asphalt through physical dilution but also reconstruct the original structure or form new structures by supplementing degraded modifiers and repairing broken modifiers. This can restore the properties of aging modified asphalt.
- Mineral oil-based and bio-based rejuvenators are able to obviously enhance the low-temperature resistance of aged asphalt, although the high-temperature resistance is reduced by the presence of low-polarity molecules and excessive softening of the asphaltenes. Reactive rejuvenators can reconnect degraded SBS modifiers and rejuvenate aged virgin asphalt, which can recover the performance of aged SBSMA, even to the level of virgin sample. In addition, bio-based and mineral oil-based rejuvenators can also be modified to mitigate the loss of high-temperature resistance caused by excessive softening.
- Untreated waste bio-oil (excessive free fatty acids) and waste mineral oil (containing metal ions) rejuvenators can adversely affect the water stability of asphalt mixtures. In addition, compound rejuvenators are significantly better than bio-based and mineral oil-based rejuvenators in restoring high-temperature resistance and water stability to aged asphalt mixtures.
- Currently, this technology has not been applied widely to the field of engineering. In the future, it is essential to consider artificial intelligence combined with rejuvenator design and modify waste oil or modify current reactive rejuvenators to better rejuvenate aged asphalt.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RAP | Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement |
| SBS | Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene |
| SBSMA | SBS Modified Asphalt |
| AO | Aromatic Oil |
| WEO | Waste Engine Oil |
| WCO | Waste Cooking Oil |
| GO | Gutter Oil |
| SO | Soybean Oil |
| CO | Castor Oil |
| TO | Tung Oil |
| BO | Bio Oil |
| MO | Motor Oil |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| TAIC | Triallyl Isocyanate |
| MDI | 4,4-Diphenyl-ethane-diisocyanate |
| TDI | 2,4-Toluylene Diisocyanate |
| TGDOM | 4,4-Diphenyl-methane-diisocyanate |
| ESO | Epoxidized Soybean Oil |
| BUDGE | 1,4-Butanediol Di glycidyl Ether |
| TMPGE | Trimethylolpropane Tri glycidyl Ether |
| HDDGE | 1,6-Hexanediol Di glycidyl Ether |
| BDMA | N,N-Dimethylbenzylamine |
| RDGE | 2,2′-[1,3-Phenylenebis Oxyethylene)] Dioxirane |
| PEHA | 3,6,9,12-Tetraazatetradecane-1,14-diamine |
| TPP | Triphenylphosphine |
| DSR | Dynamic Shear Rheometer |
References
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, D.D.; Shan, J.H.; Ye, W.L.; Lu, H.H.; Sha, A.M. Experimental study of the performance of porous ultra-thin asphalt overlay. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xing, C.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Tang, S.; Cheng, H. Comparative analysis of four styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) structure repair agents in the rejuvenation of aged SBS-modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 476, 141232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltan, M.; Khaliqi, M.H. Effects of utilization of rejuvenator in asphalt mixtures containing recycled asphalt pavement at high ratios. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q. Design and construction of flexible base mixture ratio of recycled asphalt mixture. J. Sichuan Univ. Sci. Eng. 2006, 107–110. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/CNKI:SUN (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Zahoor, M.; Nizamuddin, S.; Madapusi, S.; Giustozzi, F. Sustainable asphalt rejuvenation using waste cooking oil: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.W.; Tang, S.X.; Chang, Z.B.; Han, Z.C.; Li, H.Z.Y.; Zhu, B.H. A comprehensive review on the plant-mixed cold recycling technology of emulsified asphalt: Raw materials and factors affecting performances. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 439, 137344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, Z.S.; Xu, M.; Feng, D.C. Mechanisms and research progress on biological rejuvenators for regenerating aged asphalt: Review and discussion. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Kazemi, M.; Fini, E. Research progress on resource utilization of waste cooking oil in asphalt materials: A state-of-the-art review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.B.; Hossain, K. Waste cooking oil as an asphalt rejuvenator: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Aging mechanism and effective recycling ratio of SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadshir, M.; Oldham, D.J.; Hosseinnezhad, S.; Fini, E.H. Investigating bio-rejuvenation mechanisms in asphalt binder via laboratory experiments and molecular dynamics simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.W.; Chang, Z.B.; Jiang, W.; Han, Z.C.; Li, M.C. Hot central-plant recycling technology: A systematic review on raw materials and performance-influencing factors. J. Traffic Transp. Eng.-Engl. Ed. 2025, 12, 1040–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseer, F.; Martin, A.E.; Arambula-Mercado, E. Use of recycling agents in asphalt mixtures with high recycled materials contents in the United States: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 974–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Chen, M.Z.; Wu, S.P.; Jiang, Q. Rheological properties and microscopic characteristics of rejuvenated asphalt using different components from waste cooking oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.W.; Li, M.C.; Yu, R.H.; Jin, T.; Zhu, B.H. Interfacial damage mechanisms in hot-recycled asphalt mixtures: A molecular dynamics study considering the blending level between virgin and aged asphalt. Fuel 2026, 404, 136345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Jiang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhao, K.; Li, Z. Minireview on the rejuvenation of aged Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene (SBS) modified bitumen: State-of-the-art and outlook. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 7634–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Tang, B. Effects of rejuvenator on performance-based properties of rejuvenated asphalt binder and mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Chen, R.; Xu, Z. Evaluation on Performance of Asphalt Rejuvenator Agent. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2007, 24, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Asli, H.; Ahmadinia, E.; Zargar, M.; Karim, M.R. Investigation on physical properties of waste cooking oil-rejuvenated bitumen binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Ding, R.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, K.; Cao, D.; Gao, A. Investigation on performance of mineral-oil-based rejuvenating agent for aged high viscosity modified asphalt of porous asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 395, 136285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Z.; Yan, Q.; Ji, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, A. The aging behavior of reclaimed asphalt mixture with vegetable oil rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hussain, U.B. Compound rejuvenation of polymer modified asphalt binder. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 25, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Mo, L.; Pan, C.; Riara, M.; Wei, M.; Zhang, J. Investigation of rejuvenation and modification of aged asphalt binders by using aromatic oil-SBS polymer blend. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tang, G.M.; Pan, S.L.; Ji, Z.Y.; Fang, L.; Zhang, C.L.; Cao, Z.L.; Zhou, X.X.; Jia, X.J. Application of reactive rejuvenator in aged SBS modified asphalt regeneration: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, M.; Yu, J.; Han, X.; Wang, R. Workability and Rheological Property Evolution of Active Rejuvenated Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene-Modified Bitumen in the Early Stage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 19129–19139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, J.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, L.; Chen, X. Applications of vegetable oils and their derivatives as bio-additives for use in asphalt binders: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 383, 131312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, S.; Du, X.; Tan, Y.; Luo, D. Study on effect of various rejuvenators on virgin asphalt binders suffering various aging conditions and the unified evaluation index. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 397, 132331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, O.d.M.M.; Silva, I.M.; Lucena, L.C.d.F.L.; Lucena, L.d.F.L.; Mendonca, A.M.G.D.; de Lima, R.K.B. Viability of recycled asphalt mixtures with soybean oil sludge fatty acid. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 349, 128728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, M.; Woszuk, A.; Ratajczak, M.; Franus, W. Properties of reclaimed asphalt pavement mixture with organic rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, M.; Nizamuddin, S.; Madapusi, S.; Giustozzi, F. Recycling asphalt using waste bio-oil: A review of the production processes, properties and future perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2021, 147, 1135–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, V.; Freire, A.C.; Neves, J. A review on the effect of RAP recycling on bituminous mixtures properties and the viability of multi-recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Pei, J.Z.; Cai, J.; Liu, T.; Wen, Y. Performance improvement and aging property of oil/SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 123735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Liu, Q.J.; Xu, Z.M.; Sun, X.W.; Zhao, S.Q. A novel characterization of furfural-extract oil from vacuum gas oil and its application in solvent extraction process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 152, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Martin, A.E.; King, G.; Glover, C.; Kaseer, F.; Arámbula-Mercado, E. Evaluation and classification of recycling agents for asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, B.; Tabatabaee, N.; Hajj, R. Use of linear amplitude sweep test as a damage tolerance or fracture test to determine the optimum content of asphalt rejuvenator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 123983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Jia, M.; Jiang, W.; Lou, B.W.; Jiao, W.X.; Yuan, D.D.; Li, X.Z.; Liu, Z.Z. High temperature property and modification mechanism of asphalt containing waste engine oil bottom. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Peng, A.H.; Wu, J.T.; Zhou, S.B. Waste engine oil influences on chemical and rheological properties of different asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Yaacob, H.; Satar, M.; Kamarudin, S.N.N.; Mahmud, M.Z.H.; Ismail, C.R.; Hassan, S.A.; Mashros, N. A review on the usage of waste engine oil with aged asphalt as a rejuvenating agent. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering and Science (IConMEAS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28–30 December 2020; pp. 2374–2380. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, R.Y.; Luo, H.Y.; Huang, X.M.; Zheng, Y.Z.Z.; Zhu, L.Y.; Liu, F.Y. Correlation analysis between mechanical properties and fractions composition of oil-rejuvenated asphalt. Materials 2022, 15, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Huang, X.; Tian, R.; Huang, J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, D.; Liu, B. Analysis of relationship between component changes and performance degradation of waste-oil-rejuvenated asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.J.; Ding, H.B.; Rahman, A.; Wang, W.Q. Damage characteristics of waste engine oil bottom rejuvenated asphalt binder in the non-linear range and its microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, S.; Wasiuddin, N.M.; Mohammad, L.N. Evaluation of bio-based and petroleum-based rejuvenator based on cracking susceptibility of hot mix asphalt with high RAP content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 371, 130725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, X.; Hasan, M.R.M. Preparation process of bio-oil and bio-asphalt, their performance, and the application of bio-asphalt: A comprehensive review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng.-Engl. Ed. 2020, 7, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.Y.; Xiao, F.P.; Wang, J.G.; Cong, L.; Amirkhanian, S. Productions and applications of bio-asphalts—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.Z.; Peng, Y.; You, L.Y. Use of tung oil as a rejuvenating agent in aged asphalt: Laboratory evaluations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ahmad, N.; Jamal, M.; Badin, G.; Suleman, M. Investigation into possibility of rejuvenating aged asphalt binder using mustard oil. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 1738–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, F.; Putman, B.; Leng, B.; Wu, S. High temperature properties of rejuvenating recovered binder with rejuvenator, waste cooking and cotton seed oils. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 59, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilema, M.; Bin Aman, Y.; Hassan, N.A.; Al-Saffar, Z.; Ahmad, K.; Rogo, K. Performance of aged asphalt binder treated with various types of rejuvenators. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.K.; Sahoo, U.C. Use of mahua oil for rejuvenation of the aged binder through laboratory investigations. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkashef, M.; Podolsky, J.; Williams, R.C.; Cochran, E. Preliminary examination of soybean oil derived material as a potential rejuvenator through superpave criteria and asphalt bitumen rheology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, H.X.; Ragauskas, A.J. Comparison for the compositions of fast and slow pyrolysis oils by NMR characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.; Lopez, G.; Amutio, M.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Bio-oil production from rice husk fast pyrolysis in a conical spouted bed reactor. Fuel 2014, 128, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnisa, F.; Daud, W.M.A.W.; Husin, W.N.W.; Sahu, J.N. Utilization possibilities of palm shell as a source of biomass energy in Malaysia by producing bio-oil in pyrolysis process. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; You, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Si, C.; Peng, C. Using bio-based rejuvenator derived from waste wood to recycle old asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 189, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S.C. Upcycle olive pomace as antioxidant and recycling agent in asphalt paving materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 330, 127217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Q.; Sha, A.M.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Z.Z.; Gao, J.; Zou, X.L.; Yuan, D.D. Study on the optimum rice husk ash content added in asphalt binder and its modification with bio-oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Tong, T. Physical-chemical properties of aged asphalt rejuvenated by bio-oil derived from biodiesel residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mills-Beale, J.; You, Z. Chemical characterization and oxidative aging of bio-asphalt and its compatibility with petroleum asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
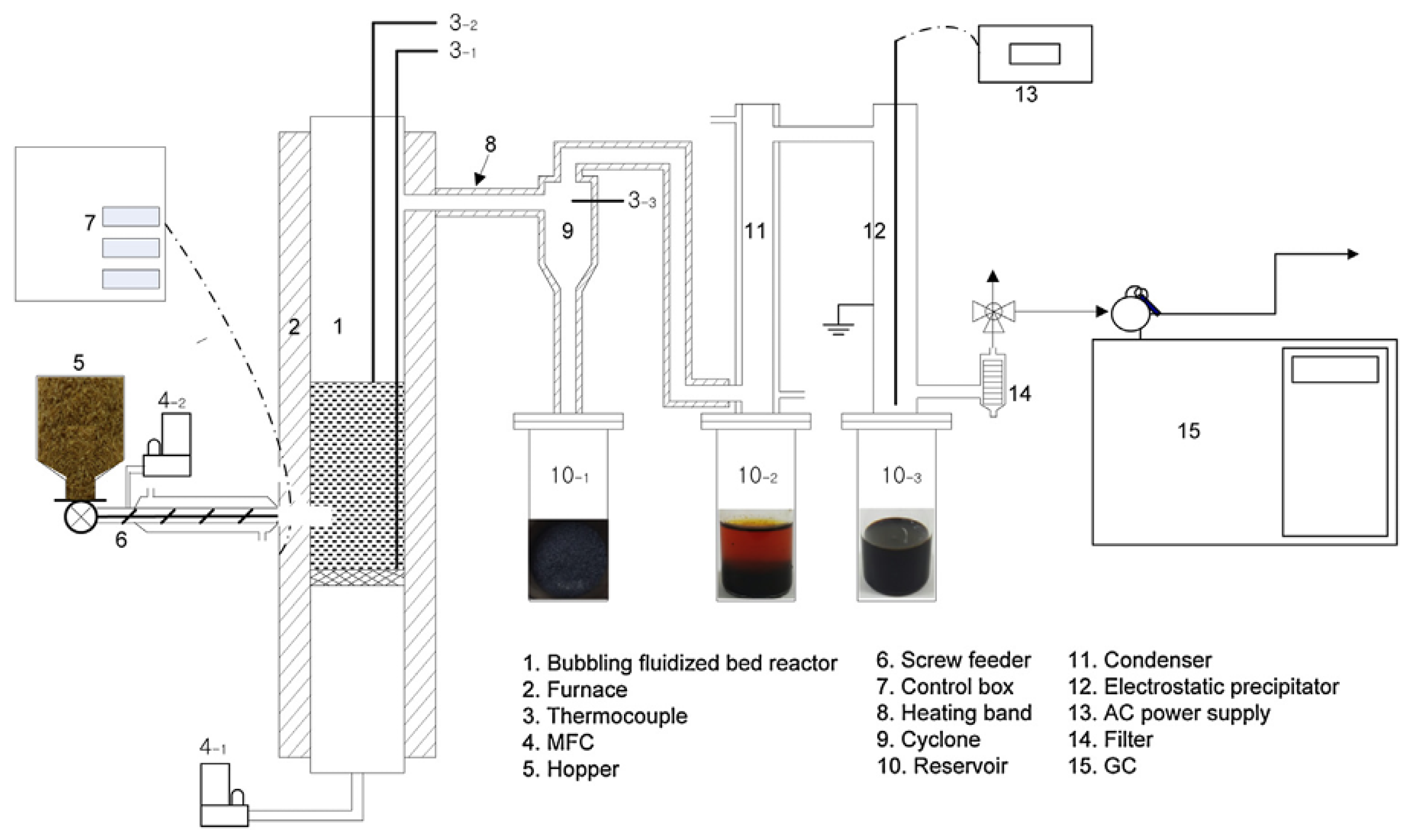
- Tran, Q.K.; Le, M.L.; Ly, H.V.; Woo, H.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-S. Fast pyrolysis of pitch pine biomass in a bubbling fluidized-bed reactor for bio-oil production. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, N.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H. Advances in bio-oil regenerated aged asphalt materials. China J. Highw. Transp. 2023, 36, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mills-Beale, J.; You, Z.P.; Fini, E.; Zada, B.; Lee, C.H.; Yap, Y.K. Aging influence on rheology properties of petroleum-based asphalt modified with biobinder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, E.H.; Kalberer, E.W.; Shahbazi, A.; Basti, M.; You, Z.; Ozer, H.; Aurangzeb, Q. Chemical characterization of biobinder from swine manure: Sustainable modifier for asphalt binder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, D.; Hung, A.; Parast, M.M.; Fini, E.H. Investigating bitumen rejuvenation mechanisms using a coupled rheometry-morphology characterization approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz, V.E.; Gökalp, I. Sustainable recovery of waste vegetable cooking oil and aged bitumen: Optimized modification for short and long term aging cases. Waste Manag. 2020, 110, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggers, V.; Wisniewski, A., Jr.; Madureira, L.; Barros, A.C.; Meier, H. Biofuels from waste fish oil pyrolysis: Continuous production in a pilot plant. Fuel 2009, 88, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Chen, M.Z.; Wen, J.; Leng, B.B.; Wu, S.P. Effect of waste edible animal oil on physical properties of aged asphalt. In Proceedings of the Annual Meetings of Chinese-Society’s-Building-Materials, Professional Committees of Stone and Aggregate and Utilization of Solid Waste, Wuhan, China, 28 November–1 December 2013; pp. 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Joni, H.H.; Al-Rubaee, R.H.A.; Al-zerkani, M.A. Rejuvenation of aged asphalt binder extracted from reclaimed asphalt pavement using waste vegetable and engine oils. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2019, 11, e00279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabaeei, A.M.; Al-Fakih, A.; Noura, S.; Yaghoubi, E.; Alaloul, W.; Al-Mansob, R.A.; Khan, M.I.; Yaro, N.S.A. Utilization of palm oil and its by-products in bio-asphalt and bio-concrete mixtures: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 337, 127552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Sun, W.; Zhu, H.; Tang, B. Investigation of rheological and chemical properties asphalt binder rejuvenated with waste vegetable oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Q.; Hu, Z.; Li, M.L.; Bai, T.; Xie, G.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, C. Investigation on the mechanism and performance of asphalt and its mixture regenerated by waste engine oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, H.; Fini, E.H.; You, Z.; Yang, X.; Gao, J.; Dong, S.; Jiang, G. Evaluation of the effect of bio-oil on the high-temperature performance of rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Bahadori, A.; Xin, J.; Zhang, K.; Muhunthan, B.; Zhang, J. Characteristics of bioepoxy based on waste cooking oil and lignin and its effects on asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Dong, R.; Tang, N. Development of a novel binder rejuvenator composed by waste cooking oil and crumb tire rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldagari, S.; Kabir, S.F.; Fini, E.H. Investigating aging properties of bitumen modified with polyethylene-terephthalate waste plastic. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 173, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Fu, C.; Lv, H. Chemical and rheological properties evaluation of a novel synchronous rejuvenated aged SBS modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 381, 135213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhao, Z.L.; Jin, D.Z. Physical and chemical evaluation of adhesion recovery property of aged high-viscosity asphalt based on specialized composite rejuvenators. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Yang, Z.; Lv, S.; Jin, J.; Zhang, S. Study on components selection and performance of bio-oil based asphalt rejuvenator based on softening and asphaltene deagglomeration effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavan, F.; Rajib, A.; Deng, S.; Lammers, P.; Fini, E.H. Investigation of balanced feedstocks of lipids and proteins to synthesize highly effective rejuvenators for oxidized asphalt. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7656–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltwati, A.; Mohamed, A.; Hainin, M.R.; Jusli, E.; Enieb, M. Rejuvenation of aged asphalt binders by waste engine oil and SBS blend: Physical, chemical, and rheological properties of binders and mechanical evaluations of mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltwati, A.; Al-Saffar, Z.; Mohamed, A.; Hainin, M.R.; Elnihum, A.; Enieb, M. Synergistic effect of SBS copolymers and aromatic oil on the characteristics of asphalt binders and mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 127026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.Y.; Feng, C.P.; Siddig, E.A.A. Effect of phenolic resin on the performance of the styrene-butadiene rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.G.; Li, C.X.; Xu, T. Multi-scale studies on interfacial system compatibility between asphalt and SBS modifier using molecular dynamics simulations and experimental methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ni, F.; Jin, J.; Zhou, Z. A comparison of rejuvenator and sryrene–butadiene rubber latex used in hot in-place recycling. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, X.; Jin, Y.; Lu, J.L.; Wan, L.; Li, Z.X. Performance restoration of aged SBS-modified asphalt in RAP via dry-process SBS modifier diffusion at the interface of aggregate-aged asphalt-virgin asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 453, 139022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Chen, M.; Yu, J.; Han, X. Preparation and characterization of active rejuvenated SBS modified bitumen for the sustainable development of high-grade asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.K.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.L.; Cong, R.S.; Fang, G.Y. Thermal properties of 1-hexadecanol/high density polyethylene/graphene nanoplates composites as form-stable heat storage materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 237, 111580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, T. Development of sustainable compound bio-oil rejuvenator and its rejuvenation mechanism on long-term aged asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Huang, R.; Fang, L.; Zhou, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ma, H.; Ji, Z. Novel rejuvenators for sustainable recycling of aged SBS modified bitumen: Performance evaluation and reactive mechanism analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Y.; Huang, B.S.; Bowers, B.F.; Zhao, S. Infrared spectra and rheological properties of asphalt cement containing waste engine oil residues. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.W.; Zhang, H.L.; Duan, H.H. Effect of catalytic-reactive rejuvenator on structure and properties of aged SBS modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, J.; Xue, L.; Zhang, C.; He, B.; Wu, M. Structure and performance evaluation on aged SBS modified bitumen with bi- or tri-epoxy reactive rejuvenating system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.C.K.; Zhu, B.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Tang, S.; Xing, C. Differences in rejuvenation mechanisms and physical properties of aged Styrene–Butadiene–Styrene (SBS)-modified bitumen by mono-epoxy and di-epoxy compounds. Polymers 2025, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zou, P.; Hu, M.; Cao, P. A novel WCO-MDI reactive rejuvenation method for aged SBS modified asphalt toward sustainable asphalt pavements. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.B.; Yu, J.Y.; Huang, X.Q.; Cao, Z.L.; Wang, R.Y.; He, P. Preparation of reactive chain extension rejuvenators and its application in the aged SBS modified bitumen sustainable recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Zhou, C.J.; Zou, P.; Hu, M.J.; Xu, Y.X. Shedding light on the rejuvenation mechanism of reactive compounds in aged SBS-modified asphalt through molecular dynamics and quantum chemical simulations. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Fu, Z.; Ma, F.; Liu, J.; Song, R.M.; Li, J.R.; Dai, J.S.; Li, C.; Wen, Y.L. Development on the rheological properties and micromorphology of active reagent-rejuvenated SBS-modified asphalt. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 16734–16751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Q.; Ma, T.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Hu, M.J.; Lu, T.; Siwainao, D.H. Dual self-repairing enhancement mechanisms of blocked dynamic isocyanate prepolymer on aging degradation and fatigue damages of high-content SBS-modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, J.; Xue, L.; He, B.; Du, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Effect of reactive rejuvenating system on physical properties and rheological characteristics of aged SBS modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, P.; Dai, J.; Ma, F.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, S. Rheological properties and microscopic mechanism of composite regenerated asphalt. Fuel 2025, 385, 134159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Hao, S.; Yao, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, H. Synergistic effects of epoxy polymer and rejuvenator in asphalt rejuvenation: A comprehensive performance analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 437, 137056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.X.; Jiang, X.L.; Shen, W.L.; Sreeram, A.; Ren, H.H.; Xu, X. Innovative use of polyurethane precursor to facilitate the reaction-rejuvenation of aged SBS-modified asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, J. Research on the aging and rejuvenation mechanisms of asphalt using atomic force microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, W.; Napiah, M.; Habib, N.Z.; Sutanto, M.H.; Alaloul, W.S.; Khan, M.I.; Musarat, M.A.; Memon, A.M. Modeling and design optimization of reclaimed asphalt pavement containing crude palm oil using response surface methodology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cui, Y.n.; Du, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q. Low-temperature performance and micro-structure of warm mix recycled composite aged asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 440, 137443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Huang, B.; Shu, X. Blending efficiency evaluation of plant asphalt mixtures using fluorescence microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Kabir, S.F.; Cao, L.; Luan, H.; Dong, Z.; Fini, E.H. Comparing effects of physisorption and chemisorption of bio-oil onto rubber particles in asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; He, H.W.; Zhang, P.; Lv, S.T.; Jiang, H.H.; Liu, H.F.; Peng, X.H. Laboratory investigation on performance and mechanism of polyphosphoric acid modified bio-asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Comprehensive review on the application of bio-rejuvenator in the regeneration of waste asphalt materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Xie, N.; Xia, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, P.; Ma, S.; Zhang, C.; Lv, S. Laboratory evaluation of different bio-oil recycled aged asphalts: Conventional performances and microscopic characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.M.R.; Arabani, M.; Hamedi, G.H. Performance of asphalt mixtures containing high reclaimed asphalt pavement and waste steel rolling oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 441, 137570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Yang, F.Y.; Zhang, F.; Zou, X.L.; Zhao, G.J. Diffusion and Regeneration Mechanism of Waste Composite Oils Rejuvenator in Aged Asphalt. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 36, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopedis, S.E.; Speight, J.G. Oxygen functions in asphaltenes. Fuel 1976, 55, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, Q.L.; Tao, J.L.; Ma, D.H.; Wang, Y.D. Aging mechanism of a diatomite-modified asphalt binder using Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Ma, F.; Liu, J.; Song, R.-M.; Fu, Z.; Dai, J.-S.; Li, C.; Wen, Y.-L. Development of a new rejuvenator for aged SBS modified asphalt binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Yaacob, H.; Satar, M.K.I.M.; Saleem, M.K.; Jaya, R.P.; Basar, N.; Radeef, H.R.; Hassan, N.A. Effects of maltene on the attributes of reclaimed asphalt pavement: Performance optimisation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, B.T.; Liulin, S.; Cai, S.X.; Tang, G.M.; Pan, S.L. Performance evaluation of multiple aging-regeneration of SBS-modified bitumen regenerated by a composite rejuvenator. Buildings 2024, 14, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Aggarwal, P. Application of natural and waste oils as rejuvenator in reclaimed asphalt pavement: A Review. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2023, 18, 805–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourkhaki, A.; Ameri, M.; Daryaee, D. Application of different modifiers for improvement of chemical characterization and physical-rheological parameters of reclaimed asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ge, C.; Quan, X.; Ma, T.; Ding, F.; Zhang, Y. Rheological analysis and chemical characterization of bio-rejuvenated laboratory-aged binders using partially epoxidized soybean oil with various epoxy values. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, X.; Li, X. Insights into permeability of rejuvenator in old asphalt based on permeation theory: Permeation behaviors and micro characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; You, Z.; Wang, H.; Ye, M.; Yap, Y.K.; Si, C. The impact of bio-oil as rejuvenator for aged asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, D.X.; Wen, Y.T. Effects of Environment-Friendly Rejuvenator on the Rheological Properties and Microstructure of Aged Asphalt. Transp. Res. Rec. 2024, 2678, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.M.; Sun, G.Q.; Sun, D.Q.; Yu, F.; Hu, M.J.; Lu, T. Application of gel permeation chromatography technology in asphalt materials: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278, 122386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liu, X.; Apostolidis, P.; Erkens, S.; Ren, S.; Xu, S.; Scarpas, T.; Huang, W. On the rejuvenator dosage optimization for aged SBS modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.N.; Wang, H.Z.; Yang, J.; Luo, S.; Liu, Y.X.; Huang, W.; Hu, J.; Xu, G.J.; Min, Z.H. Biomass waste to produce bio oil as rejuvenator for asphalt based on pyrolysis technology. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 2287695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Guo, C.; You, Z.; Xu, F.; Ma, W.; You, L.; Li, T.; Zhou, L.; Huang, S.; Ma, H.; et al. The effect of waste engine oil and waste polyethylene on UV aging resistance of asphalt. Polymers 2020, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Hasan, H.G.M.; Abdulmawjoud, A.A.; Bilema, M.; Alharthai, M. Tailored enhancement of reclaimed asphalt pavement with waste engine oil/vacuum residue blend as rejuvenating agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Z.; Gu, Y.; Xue, L. Effect of reactive rejuvenators on structure and properties of UV-aged SBS modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Investigation on microstructural damage properties of asphalt mixture using linear and damage-coupled viscoelastic model. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Muhunthan, B. Evaluation of the effects of waste engine oil on the rheological properties of asphalt binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Zhang, F.; Feng, Z.X.; Li, W.B.; Zou, X.L. Study on waste engine oil and waste cooking oil on performance improvement of aged asphalt and application in reclaimed asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 276, 122138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Leng, B.; Wu, S.; Sang, Y. Physical, chemical and rheological properties of waste edible vegetable oil rejuvenated asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Yang, H.; Shan, L.; Tian, S.; Shen, H. Novel composite rejuvenators development and comparative analyses of epoxy versus diisocyanate rejuvenators in rejuvenating aged SBS-modified asphalt binders. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 476, 143709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, J.J.; Yuan, D.D.; Wang, T.; Ling, X.W. Investigation of LAS-based fatigue evaluation methods for high-viscosity modified asphalt binders with high-content polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 422, 135810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Kumar, P.; Saboo, N. Effectiveness of rejuvenating agents (RAs): Analysis of mechanical restoration and long-term aging effects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 456, 139308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, C. Regenerative and Innovative Utilization of Coffee Residue and Waste Cooking Oil: Improving Rheological Properties of Recycled Asphalt. Buildings 2025, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, D.; Rajib, A.; Dandamudi, K.P.R.; Liu, Y.; Deng, S.; Fini, E.H. Transesterification of waste cooking oil to produce a sustainable rejuvenator for aged asphalt. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.T.; Liu, J.; Peng, X.H.; Liu, H.F.; Hu, L.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J.P. Rheological and microscopic characteristics of bio-oil recycled asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Li, J.; Zhu, W.; Xia, Y. Laboratory evaluation on residue in castor oil production as rejuvenator for aged paving asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Fan, G.; Lv, S.; He, F.; Fan, X.; Peng, X.; Liu, T.J.; Liu, H. The influence of SBS modification on the rheological property of asphalt before and after regeneration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Lu, R.; Liu, N.; Wu, W.; Yuan, D. A comprehensive review on the blending condition between virgin and RAP asphalt binders in hot recycled asphalt mixtures: Mechanisms, evaluation methods, and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 398, 136515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Poulikakos, L.; Frank, R. Influence of six rejuvenators on the performance properties of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) binder and 100% recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.F.; Bhusal, S.; Wen, B. Laboratory evaluation of waste cooking oil-based bioasphalt as an alternative binder for hot mix asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, A.D.; Forrester, M.J.; Staver, M.; Kuehl, B.W.; Hernandez, N.; Williams, R.C.; Cochran, E.W. Chemically mediated asphalt rejuvenation via epoxidized vegetable oil derivatives for sustainable pavements. Fuel 2024, 355, 129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yu, J.; Yi, J.; Sun, G.; Xu, S.; Han, X. Investigation of road performances of rejuvenated styrene-butadiene-styrene modified asphalt mixture. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryaee, D.; Ameri, M.; Mansourkhaki, A. Utilizing of waste polymer modified bitumen in combination with rejuvenator in high reclaimed asphalt pavement mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, M.C.; Chen, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cannone Falchetto, A.; Fang, M.; Gu, H.; Han, Z.; He, Z.; Hu, J.; et al. Review of advanced road materials, structures, equipment, and detection technologies. J. Road Eng. 2023, 3, 370–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M. Investigation on Micro-Properties of Bio-Rejuvenated Asphalt Mixture. Ph.D. Thesis, Southeast University, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, S.X.; Chen, G.F.; Yan, J.M.; Li, Z.Q.; Shen, W.L.; Gong, K.; Luo, Y. Combined use of polyurethane prepolymer and aromatic oil in physicochemical rejuvenation of aged SBS modified bitumen for performance recovery. Polymers 2023, 15, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Liang, M.; Jiang, H.G.; Wei, J.C.; Yao, Z.Y. Influence of different rejuvenating agents on rheological behavior and dynamic response of recycled asphalt mixtures incorporating 60% RAP dosage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryaee, D.; Habibpour, M.; Gulzar, S.; Underwood, B.S. Combined effect of waste polymer and rejuvenator on performance properties of reclaimed asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.B.; Mao, S.P.; Xu, S.; Yu, J.Y.; Cao, Z.L.; Wang, R.Y.; He, P.; Zeng, S.H. Effects of Reactive Chain Extension Rejuvenation Systems on the Viscosity-Temperature Characteristics, Rheological Properties, and Morphology of Aged Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene-Modified Bitumen. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 16474–16484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, Y.H.; Ding, Y.J.; Qiao, S.H.; Xi, Y. Design of asphalt rejuvenator structures based on data-driven methods. Fuel 2025, 380, 133024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, C.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, B.; Li, H.; Tang, S. Application of Rejuvenators in Asphalt Binders: Classification and Micro- and Macro-Properties. Coatings 2025, 15, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101177
Xing C, Zhou W, Zhu B, Li H, Tang S. Application of Rejuvenators in Asphalt Binders: Classification and Micro- and Macro-Properties. Coatings. 2025; 15(10):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101177
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Chengwei, Weichao Zhou, Bohan Zhu, Haozongyang Li, and Shixian Tang. 2025. "Application of Rejuvenators in Asphalt Binders: Classification and Micro- and Macro-Properties" Coatings 15, no. 10: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101177
APA StyleXing, C., Zhou, W., Zhu, B., Li, H., & Tang, S. (2025). Application of Rejuvenators in Asphalt Binders: Classification and Micro- and Macro-Properties. Coatings, 15(10), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101177






