Chloride Corrosion Resistance of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete and Its Application in Subsea Tunnel Linings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Test Methods for Accelerated Chloride Corrosion of SFRC
2.1. Chloride Ion Diffusion Method
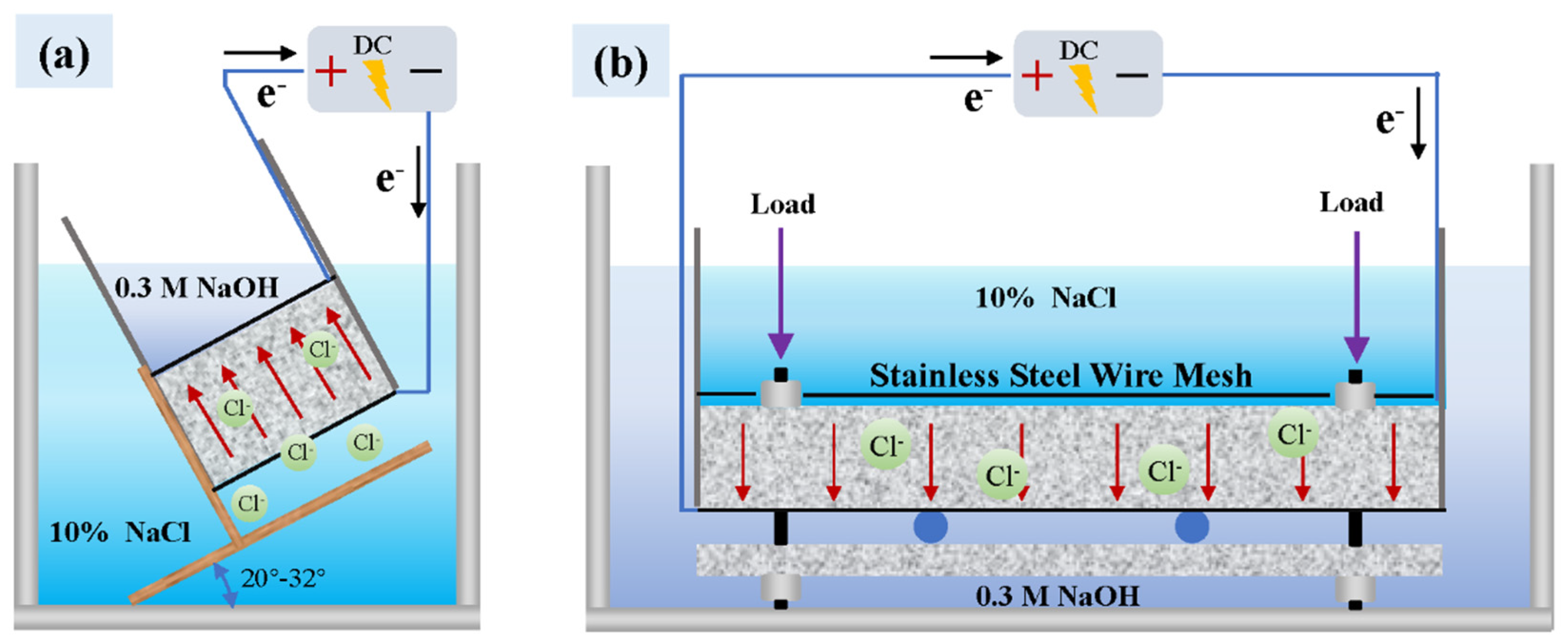
2.2. External Electric Field Migration Method
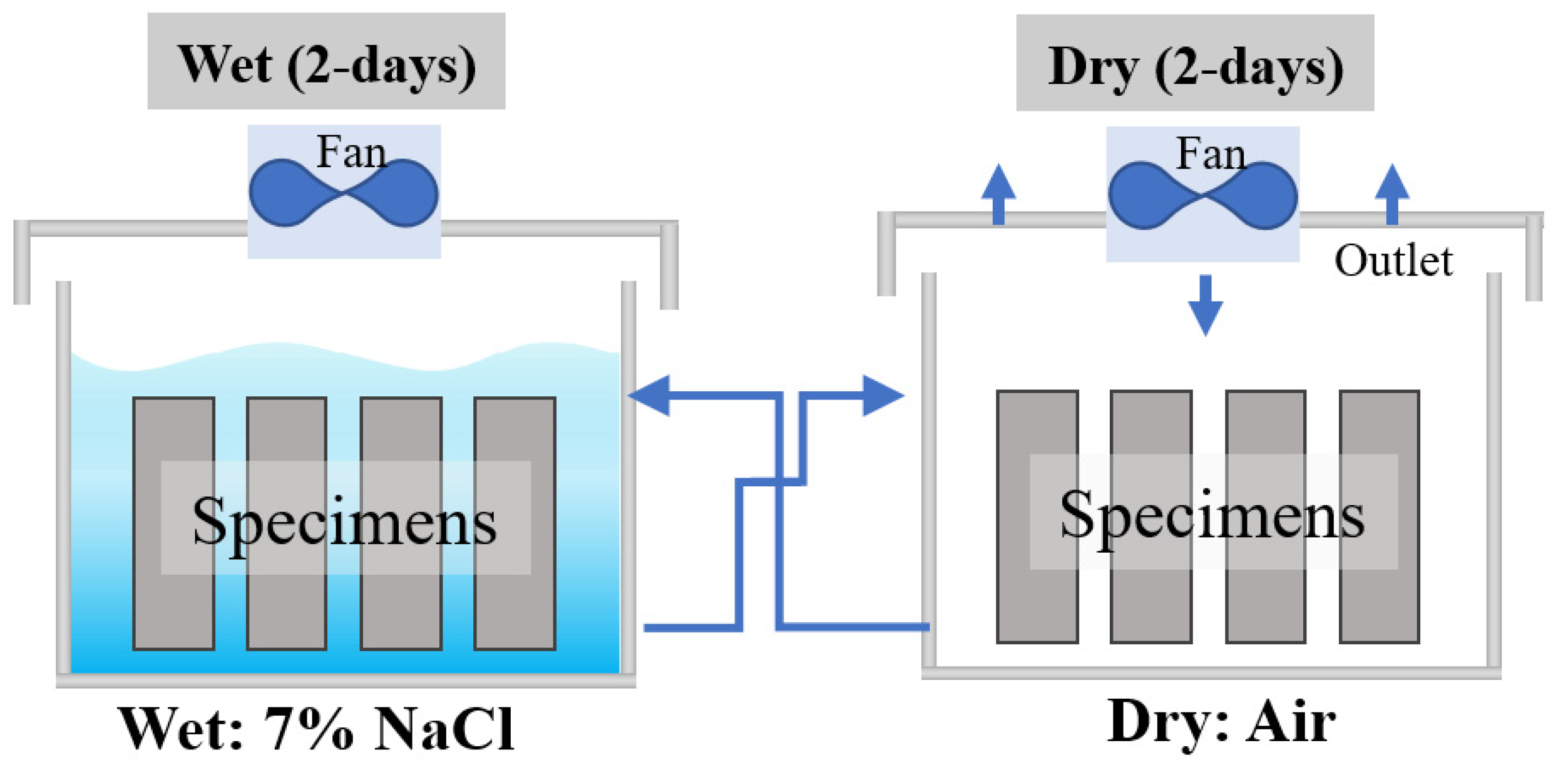
2.3. Pre-Corrosion Method
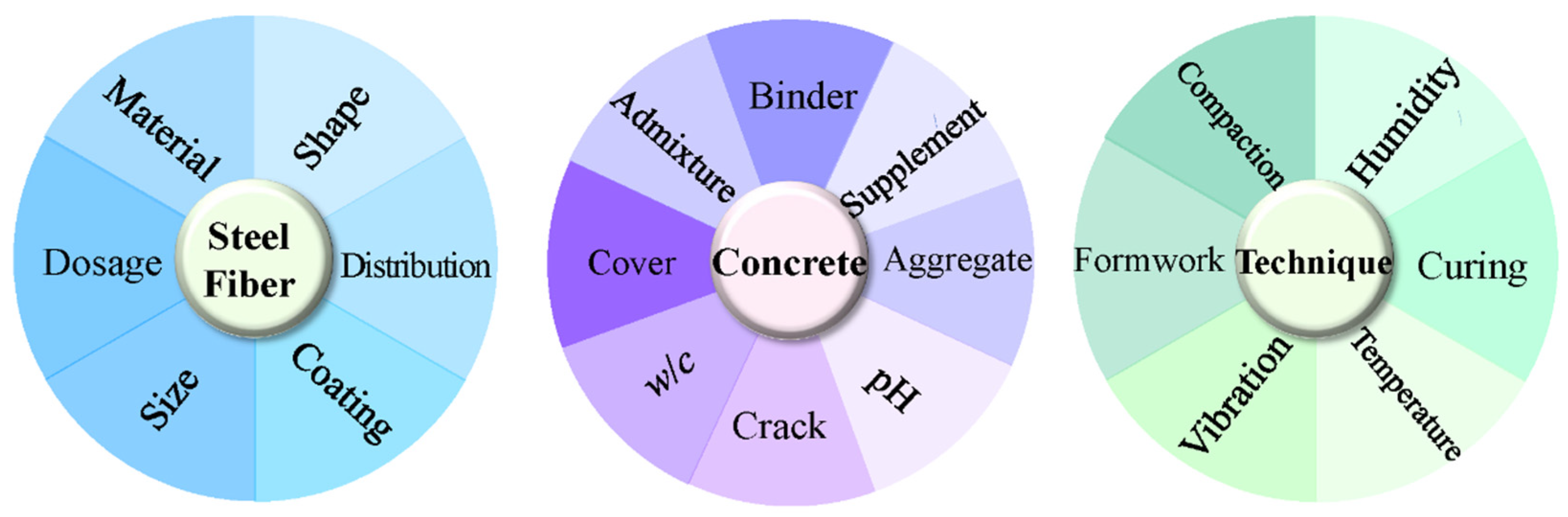
3. The Influence of Steel Fibers on the Chloride Corrosion Resistance of SFRC
3.1. Types of Steel Fibers
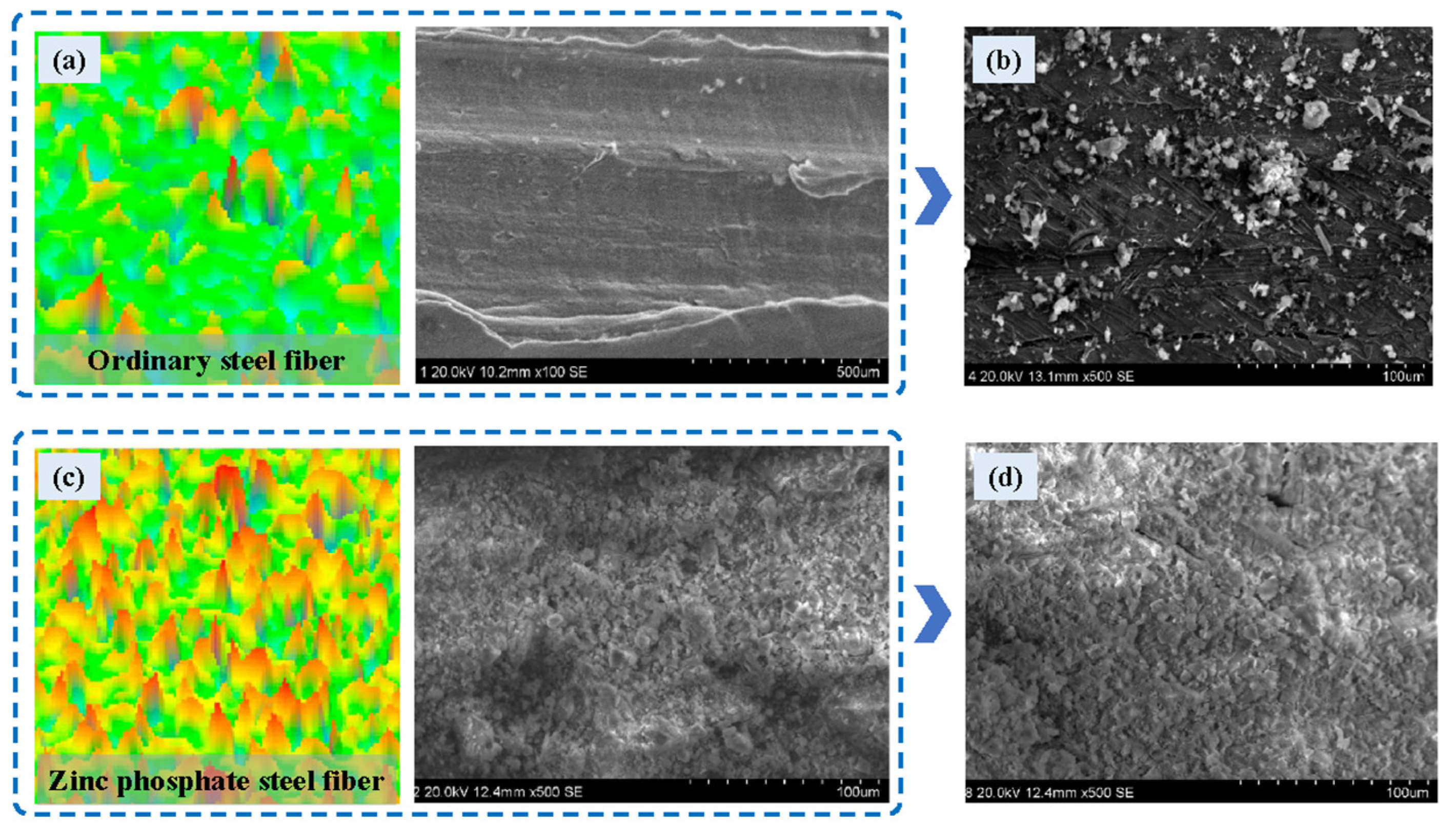
3.2. Surface Coatings for Steel Fibers
3.3. Shape of Steel Fibers
3.4. Dosage of Steel Fibers
4. Application and Challenges of SFRC in Subsea Tunnel Engineering
4.1. SFRC Application Cases in Subsea Tunnels
4.2. Challenges in the Application of SFRC in Subsea Tunnel Engineering
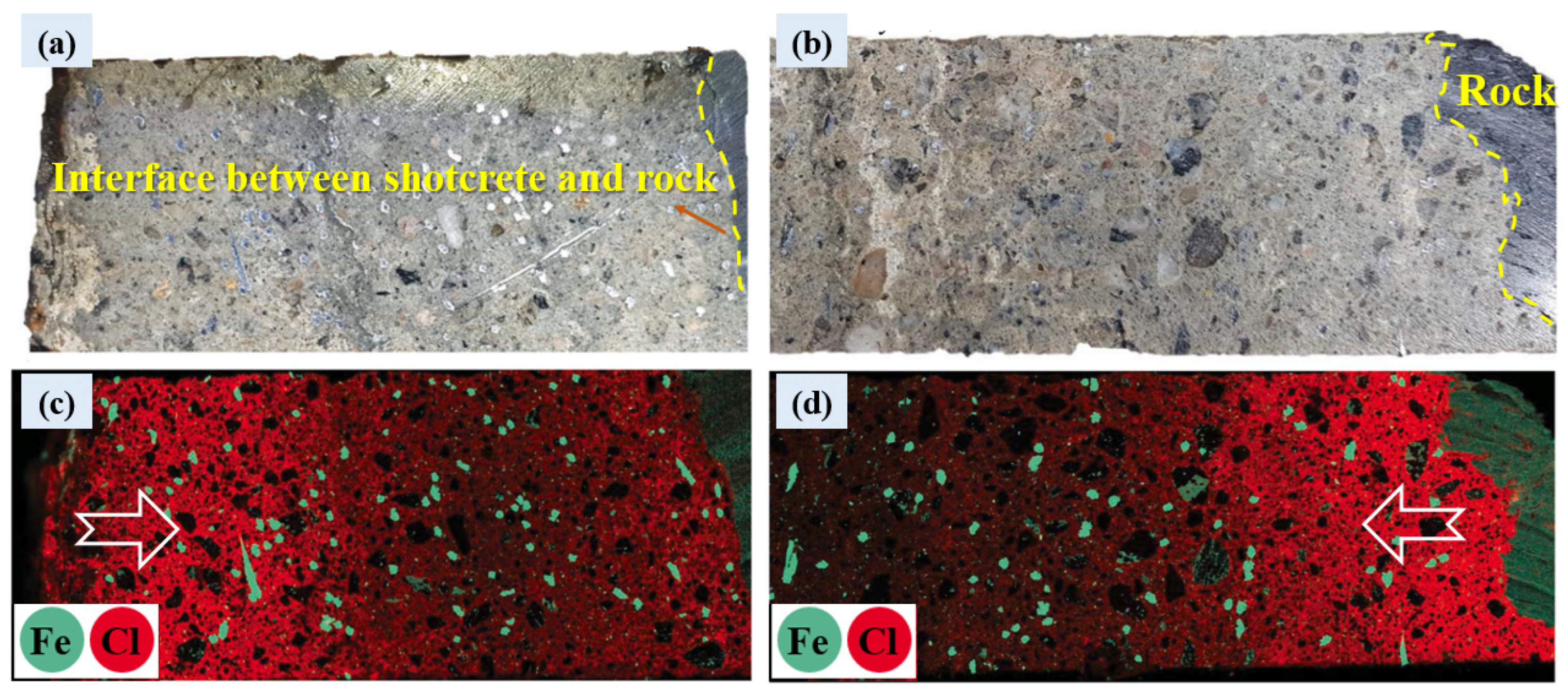
4.2.1. Multi-Directionality of Chloride Corrosion
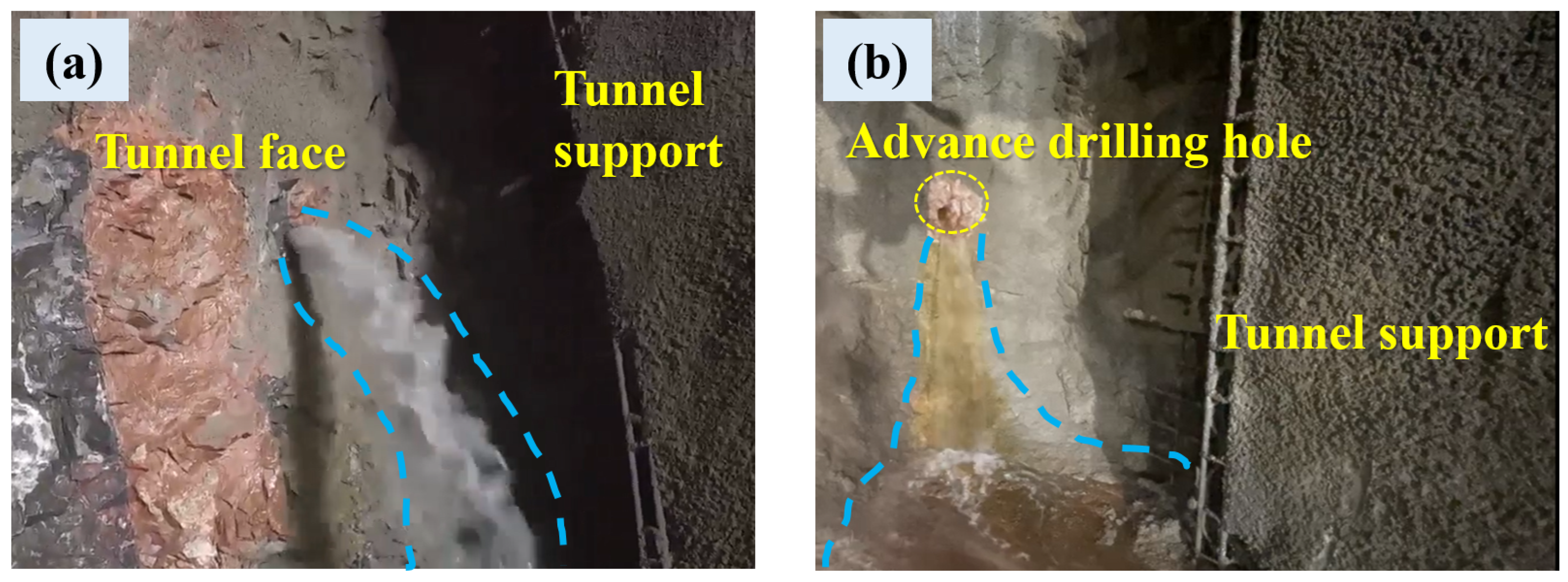
4.2.2. Diversity of Chloride Sources for Corrosion
4.2.3. Non-Uniform Distribution of Steel Fibers
4.2.4. Complexity of the Tunnel Service Environment
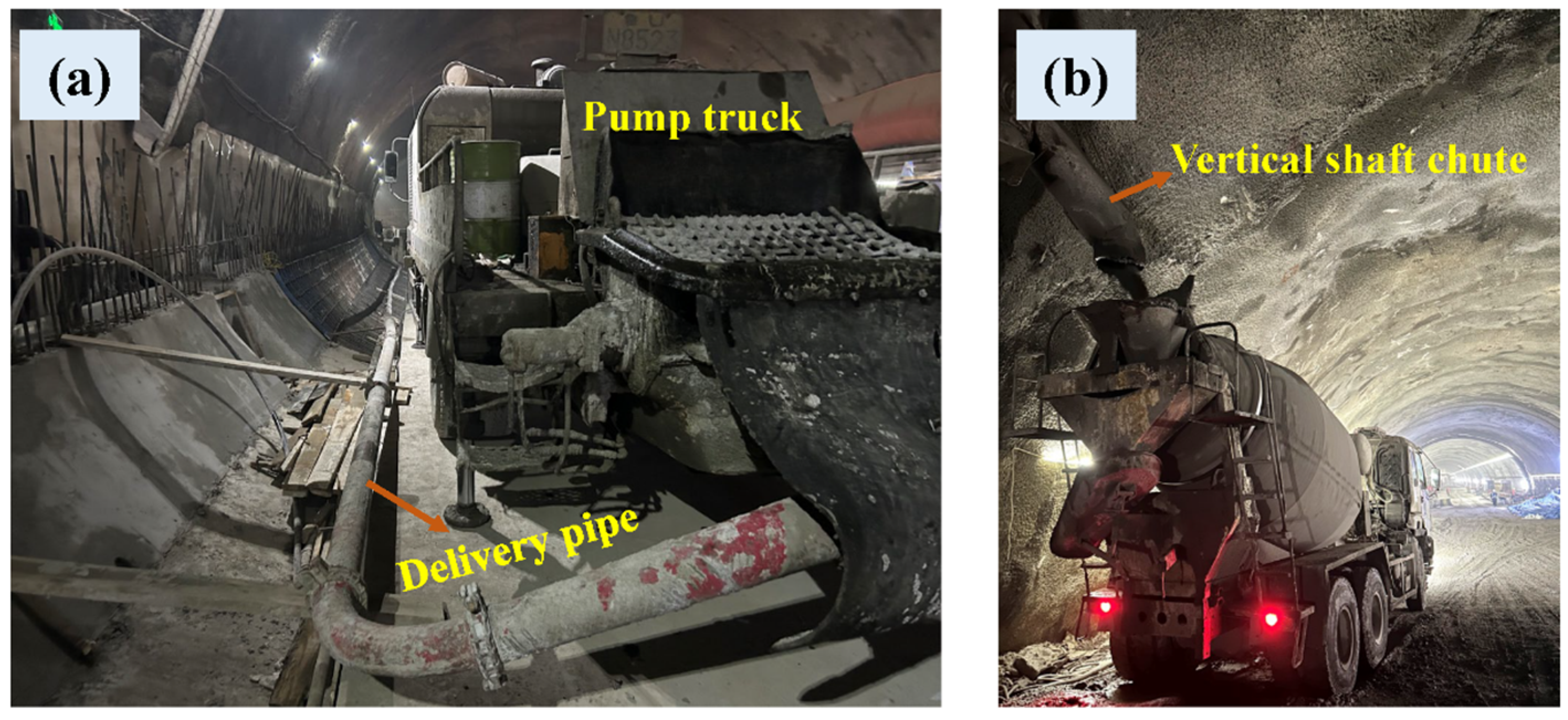
4.3. The Fabrication, Industrial Testing, and Market Share of SFRC in Subsea Tunnel Engineering
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, M.N.; Yu, L.; Guo, X.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, C.H. Experimental and numerical research on the influence of steel arch frame corrosion on security of supporting system in subsea tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 120, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, L.; Kropp, J.; Cleland, D.J. Assessment of the durability of concrete from its permeation properties: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2001, 15, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulikowski, J.; Kozubal, J. The Durability of a Concrete Sewer Pipeline Under Deterioration by Sulphate and Chloride Corrosion. In Proceedings of the 25th Russian-Polish-Slovak Seminar on Theoretical Foundation of Civil Engineering, Zilina, Slovakia, 11–16 July 2016; Elsevier Science Bv: Zilina, Slovakia, 2016; pp. 698–705. [Google Scholar]
- Cassiani, J.D.; Dugarte, M.; Arteta, C.A.; Kessler, S. Durability assessment of a tunnel structure with two-sided chloride ingress-A case study located in a tropical environment. Struct. Concr. 2022, 23, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.M.; Xue, Y.G.; Fu, K.; Kong, F.M.; Han, M.; Zhou, B.H.; Guo, Y.B. Assessing and predicting surrounding rock settlement troughs in the subsea tunnel: A case study of Haicang Tunnel. Mar. Geores. Geotechnol. 2024, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.L.; Fang, Q. Technologies for large cross-section subsea tunnel construction using drilling and blasting method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 141, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.H.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.P.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.F. Theoretical analysis of erosion degradation and safety assessment of submarine shield tunnel segment based on ion erosion. Geomech. Eng. 2024, 37, 599–614. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.S.; Shen, J. Experimental Investigation on Deterioration Mechanisms of Concrete under Tensile Stress-Chloride Ion-Carbon Dioxide Multiple Corrosion Environment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, D.; Angst, U. Corrosion Caused Costs on Civil Engineering Structures of the Swiss Road Networks. Beton-Stahlbetonbau 2020, 115, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacic, S. Microbial Biofilm Communities Associated with Degradation of Sprayed Concrete in Subsea Tunnels; Chalmers Tekniska Hogskola: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ye, T.; Zhu, Z.; Pan, Y.T.; Wu, Z. Time-varying analysis of deterioration by chloride ion erosion for subsea tunnels under wave loads. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 45, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, S. Structural and Durability Performance of Precast Segmental Tunnel Linings; The University of Western Ontario: London, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.J.; Ding, W.Q.; Mosalam, K.M.; Günay, S.; Soga, K. Comparison of the structural behavior of reinforced concrete and steel fiber reinforced concrete tunnel segmental joints. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 68, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Boyd, A.J.; Lee, J.Y. Durability performance of fiber-reinforced concrete in severe environments. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 2379–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Pan, J.; Xing, W.J.; Li, M.J.; Geng, J.Y.; He, C. Experimental study on the high water pressure erosion mechanism and its influence on the submarine shield tunnel concrete segments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.T.; Huang, X.H.; Wang, Z.R.; Chen, L. Experimental study on the shear performance of a prestressed anchored jointed rock-like mass under different corrosion levels. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 158, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.P.; Tarakbay, A.; Memon, S.A.; Tang, W.C.; Cui, H.Z. Methods of accelerating chloride-induced corrosion in steel-reinforced concrete: A comparative review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.K. Stray current induced corrosion of steel fibre reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, S.Q. Effect of chloride-induced corrosion on bond performance of various steel fibers in cracked SFRC. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 140, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Fu, C.Q.; Ye, H.L.; Jin, X.Y. Corrosion of steel embedded in mortar and concrete under different electrolytic accelerated corrosion methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez Jiménez, C. Corrosion Durability Service Life of Calcium Silicate-Based Reinforced Concrete. Master’s Thesis, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Berrocal, C.G.; Lundgren, K.; Löfgren, I. Corrosion of steel bars embedded in fibre reinforced concrete under chloride attack: State of the art. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 80, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.S.; He, C.; Kang, X.Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.M.; Xu, G.W. Effects of sustained load and reinforcement spacing on the evolution and spatial characteristics of corrosion damages in RC segmental specimens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.Q.; Ye, H.L.; Jin, N.G.; Huang, Y.X. Chloride Penetration in Reinforced Concrete Beams under Combined Sustained Loading and Drying-Wetting Cycles. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.J.; Xiang, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.; Liu, M.W.; Ju, X.L.; Zhang, W.X. A Review of Durability Issues of Reinforced Concrete Structures Due to Coastal Soda Residue Soil in China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.G.; Zhao, Y.X.; Ban, J.X.; Wang, Y.Z.; Shen, P.L.; Lu, J.X.; Poon, C.S. Enhancing the corrosion resistance of recycled aggregate concrete by incorporating waste glass powder. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 137, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.H.; Chen, Q.Q.; Xue, Y.G.; Su, M.X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.H.; Zhou, B.H. A new method for risk assessment of water inrush in a subsea tunnel crossing faults. Mar. Geores. Geotechnol. 2022, 40, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.J.; Lin, W.T. Effects of silica fume and steel fiber on chloride ion penetration and corrosion behavior of cement-based composites. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 2013, 28, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordtest. NT Build 443 Concrete Hardened: Accelerated Chloride Penetration; Nordtest NT Build: Espoo, Finland, 1995; Volume NT Build 443. [Google Scholar]
- Mangat, P.S.; Gurusamy, K. Chloride diffusion in steel fiber reinforced marine concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1987, 17, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Sharma, U.K. Calibration of Accelerated Corrosion Regime for Short Square RC Columns Reinforced with Polypropylene and/or Steel Fibers. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 4499–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Wu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.L. Relationship of corrosion of concrete reinforcement to accelerated corrosion current. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Constr. Mater. 2019, 172, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.M.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Manzur, T. Structural performance of fiber reinforced lightweight self-compacting concrete beams subjected to accelerated corrosion. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.S.; Ji, Y.S.; Shah, S.P. Comparison of two accelerated corrosion techniques for concrete structures. Aci Struct. J. 2007, 104, 344–347. [Google Scholar]
- Mangat, P.S.; Gurusamy, K. Corrosion-resistance of steel fibers in concrete under marine exposure. Cem. Concr. Res. 1988, 18, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangat, P.S.; Gurusamy, K. Long-term properties of steel fibre reinforced marine concrete. Mater. Struct. 1987, 20, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangat, P.S.; Gurusamy, K. Permissible crack widths in steel fibre reinforced marine concrete. Mater. Struct. 1987, 20, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, S.; Vallarasu Manoharan, S.; Sengottian, T. Corrosion Effects on the Strength Properties of Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete Containing Slag and Corrosion Inhibitor. Int. J. Corros. 2014, 2014, 595040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazao, C.; Camoes, A.; Barros, J.; Gonçalves, D. Durability of steel fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 80, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhao, J.; You, P.B. Durability of steel fibre-reinforced recycled coarse aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouch, S.U.; Forth, J.P.; Granju, J.L. Surface corrosion of steel fibre reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granju, J.L.; Balouch, S.U. Corrosion of steel fibre reinforced concrete from the cracks. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff, Â.G.; Pilakoutas, K.; Lynsdale, C.; Neocleous, K. Corrosion Durability of Recycled Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete. Intersections 2009, 6, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Wen, D.J.; Xie, P. Bending Toughness of Zinc Phosphate Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete before and after Corrosion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Structures and Building Materials, Guangzhou, China, 7–9 January 2011; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Guangzhou, China, 2011; p. 1762. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.P.; Jung, M.S.; Kim, M.; Ann, K.Y. Corrosion risk of steel fibre in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazao, C.; Barros, J.; Camoes, A.; Alves, A.C.; Rocha, L. Corrosion effects on pullout behavior of hooked steel fibers in self-compacting concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Meson, V.; Geiker, M.; Fischer, G.; Solgaard, A.; Jakobsen, U.H.; Danner, T.; Edvardsen, C.; Skovhus, T.L.; Michel, A. Durability of cracked SFRC exposed to wet-dry cycles of chlorides and carbon dioxide—Multiscale deterioration phenomena. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 135, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.K.; Liu, R.Q.; Qi, W.H.; Yang, Y.Q. Corrosion Resistance of Concrete Reinforced by Zinc Phosphate Pretreated Steel Fiber in the Presence of Chloride Ions. Materials 2020, 13, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J. Steady-State Chloride Diffusion Coefficient and Chloride Migration Coefficient of Cracks in Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Li, W.J.; Zhou, X.; Guo, L. Multi-scale peridynamic investigation of chloride penetration in concrete under drying-wetting cycles. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2023, 155, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Liu, J.H.; Xue, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.H.; Ji, H.G. Corrosion Behavior of Steel Fibers in Reactive Powder Concrete with High Volume of Mineral Admixtures. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 2020, 35, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wen, X.D.; Feng, L. Temperature Effect on Corrosion Behavior of 304LN Stainless Steel and Carbon Steel Rebars in Chloride Contaminated Concrete Pore Solution Using Electrochemical Method. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 10844–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Li, S.H.; Yu, Q.L. Salt scaling resistance of pre-cracked ultra-high performance concrete with the coupling of salt freeze-thaw and wet-dry cycles. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 146, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Joukhadar, N.; Pantazopoulou, S.J. Effectiveness of UHPFRC cover in delaying bar corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangat, P.S.; Molloy, B.T. Size effect of reinforcement on corrosion initiation. In Proceedings of the 5th RILEM Symposium on Fibre-Reinforced Concretes (FRC), Lyon, France, 13–15 September 2000; RILEM Publications: Lyon, France, 2000; pp. 691–701. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.N.; Yu, L.; Tian, Y.; Yan, G.F. Influence of high humidity and salt-rich spray environment on ventilation effect in urban undersea road tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 94, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Meson, V.; Fischer, G.; Solgaard, A.; Edvardsen, C.; Michel, A. Mechanical Performance of Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete Exposed to Wet-Dry Cycles of Chlorides and Carbon Dioxide. Materials 2021, 14, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Neves, R. Assessment of Fiber Corrosion Influence in the Flexural Performance of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Niu, D.T. Influence of freeze-thaw cycles and sulfate corrosion resistance on shotcrete with and without steel fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaif, A.; Bernal, S.A.; Guadagnini, M.; Pilakoutas, K. Freeze-thaw resistance of steel fibre reinforced rubberised concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 195, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Keddam, M.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Pérez, M.C.; Rangel, C.M.; Takenouti, H. Electrochemical behaviour of steel rebars in concrete:: Influence of environmental factors and cement chemistry. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 3905–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maaddawy, T.A.; Soudki, K.A. Effectiveness of impressed current technique to simulate corrosion of steel reinforcement in concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.L.; Fu, C.Q.; Jin, N.G.; Jin, X.Y. Performance of reinforced concrete beams corroded under sustained service loads: A comparative study of two accelerated corrosion techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.Q.; Jin, N.G.; Ye, H.L.; Liu, J.M.; Jin, X.Y. Non-uniform corrosion of steel in mortar induced by impressed current method: An experimental and numerical investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.F.; Pei, G.D.; Chen, L.J.; Duan, K.; Zhang, F.L.; Su, R.K.L. Effects of Chloride, Humidity, and Concrete Mix on the Electrochemical Parameters of Steel Reinforcement Corrosion. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.P. Chloride transport in concrete—Measurement and prediction. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ranger, M.; Hasholt, M.T. Relationship between Chloride Migration, Bulk Electrical Conductivity and Formation Factor of Blended Cement Pastes. Nord. Concr. Res. 2023, 69, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.F.; Long, F.B.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, Z. Improved Rapid Chloride Migration Test for Chloride Diffusion Coefficient of Concrete Based on the Image Processing Technique. J. Test. Eval. 2023, 51, 4068–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Sorensen, H.E. Precision of the Nordic test methods for measuring the chloride diffusion/migration coefficients of concrete. Mater. Struct. 2001, 34, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.S.; Li, Z.L.; Zhang, W.Z.; Liu, J.; Xie, R.B.; Tang, L.P.; Zhu, J.H. Iodide and chloride ions diffusivity, pore characterization and microstructures of concrete incorporating ground granulated blast furnace slag. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordtest. NT Build 492 Concrete, Mortar and Cement-Based Repairmaterials: Chloride Migration Coefficient from Non-Steady Statemigration Experiments; Nordtest: Espoo, Finland, 1999; Volume NT Build 492. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50082-2009; Standard for Test Methods of Long-Term Performanceand Durability of Ordinary Concrete. China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Liu, Q.F.; Pei, G.D.; Hou, H.T.; Chen, Y.Q. Probabilistic similarity of non-uniform corrosion pattern between natural corrosion and accelerated experiment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hadi, M.N.S.; Gao, D.Y.; Zhao, L.P. Experimental study on the properties of corroded steel fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 79, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.; Jen, G.; Ostertag, C.P. Enhancing corrosion resistance of reinforced concrete structures with hybrid fiber reinforced concrete. Corros. Sci. 2015, 92, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazao, C.; Díaz, B.; Barros, J.; Bogas, J.A.; Toptan, F. An experimental study on the corrosion susceptibility of Recycled Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 96, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 39147-2020; Steel Fiber for Concrete. China Iron and Steel Association: Beijing, China, 2020.
- EN 14889-1:2006; Fibres for Concrete—Part 1: Steel Fibres—Definitions, Specifications and Conformity. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- O’Brien, C.; McBride, A.; Zaghi, A.E.; Burke, K.A.; Hill, A. Mechanical Behavior of Stainless Steel Fiber-Reinforced Composites Exposed to Accelerated Corrosion. Materials 2017, 10, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.H.; Lee, B.W.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, K.M.; Park, I.M. Effect of Mn addition on corrosion properties of biodegradable Mg-4Zn-0.5Ca-xMn alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 695, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.P.; Xia, J.; Wang, B.S.; Xiang, H.L. Effect of Cold Rolling and Subsequent Annealing on the Corrosion Resistance of Ag-Containing CD4MCu Duplex Stainless Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, Y. Evaluating the chemical stability and performance of zinc phosphate-coated steel fibers in concrete corrosion simulations. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Dutta, B.K.; Panigrahi, S.C. Influence of coating on short steel fiber reinforcements on corrosion behavior of aluminium base short steel fiber reinforced composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2796–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.G.; Yang, Y.P. An Experimental Study on Corrosion Resistance and Bond Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Structures with Various Fibers. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 5593–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wen, D.J.; Wang, H.W. Influence of corrosion on the interface between zinc phosphate steel fiber and cement. Mater. Corros. 2012, 63, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cheng, Z.J.N.; Yu, J.J.; Guo, X.N.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, W.Q. Mechanical performance enhancement of UHPC via ITZ improvement using graphene oxide-coated steel fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 157, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Guo, P.W.; Meng, W.A. Tailoring of steel fiber surface by coating cellulose nanocrystal for enhanced flexural properties of UHPC. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 154, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoniem, A.; Nour, L.A. Experimental investigation into the properties of crumb rubberized concrete incorporating corrugated round steel fibers. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2024, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Ming, J.; Sun, W. Accelerated Corrosion Behavior of Steel in Concrete Subjected to Sustained Flexural Loading Using Electrochemical Methods and X-Ray Computed Tomography. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Meson, V.; Michel, A.; Solgaard, A.; Fischer, G.; Edvardsen, C.; Skovhus, T.L. Corrosion resistance of steel fibre reinforced concrete—A literature review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Liang, N.X.; Cao, Y.W.; Wang, P.M. Performance and Microstructure of Steel Fiber Reinforced Mortar. In Proceedings of the 6th International Speciality and Fibre Conference on Reinforced Materials, Yantai, China, 23–25 April 2010; Ci-Premier Pte Ltd.: Yantai, China, 2010; p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.Y.; Zhong, X.G.; Zhao, C.; Peng, X.; Yang, Q.Y. Experimental study on compressive behaviors and meso-scale structure of SFRFC based on CT scanning technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 387, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.M.; Song, G.F.; Du, H.; Li, X.; Liu, J.K.; Wei, Y. Mesoscale FE analysis of thermal conductivity of steel fiber-reinforced cementitious materials considering fiber-matrix interface and pore effects. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 142, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, K.H.; Dinesh, S.V.; Shreelakshmi. Effect of steel fibers and recycled concrete aggregates on the mechanical behaviour of concrete. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2024, 15, 2743–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, O.; Ozbay, E.; Atis, C.D.; Lachemi, M.; Hossain, K.M.A. Effects of milled cut steel fibers on the properties of concrete. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 2783–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, D.T.; Miao, Y.Y. Influence of steel fibre on micropore structure of concrete. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Fan, F.F.; Lai, J.X.; Xie, Y.L. Steel fiber reinforced concrete: A review of its material properties and usage in tunnel lining. Structures 2021, 34, 1080–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Soliman, A.M.; Nehdi, M.L. Experimental study on settlement and punching behavior of full-scale RC and SFRC precast tunnel lining segments. Eng. Struct. 2014, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, J. The strengthening theory of steel fiber reinforced concrete and its application in tunnel engineering: A review. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. 2024, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manquehual, C.J.; Jakobsen, P.D.; Holter, K.G.; De Weerdt, K.; Danner, T.; Bruland, A. Comparison of the condition of steel fiber-reinforced shotcrete with water-glass and alkali-free activators after more than 20 years of service in a subsea road tunnel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horny, U.; Bayer, L.; Schiesser, K.; Kliem, O. Metro Doha Green Line: Fibre reinforced tunnel linings—Design and construction experience. Geomech. Tunn. 2021, 14, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manquehual, C.J.; Jakobsen, P.D.; Holter, K.G.; De Weerdt, K.; Bruland, A. Investigation of leaching in steel fiber-reinforced shotcrete exposed to fresh and saline groundwater in a subsea road tunnel. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 163, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J. Development Trends in World Tunneling Technology: Safe, Economical, Green and Artistic. Tunn. Constr. 2021, 41, 693–696. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C. Study on Dynamic Damage Assessment Method of Fiber Concrete for Urban Underground Engineering; Shandong Jianzhu University: Jinan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, L. Challenges and Technological Innovations in the Jiaozhou Bay Second Submarine Tunnel Project. Mod. Tunn. Technol. 2024, 61, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.F.; Wang, F.; Long, Y.Y.; Zhao, X. Investigation of steady water inflow into a subsea grouted tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 80, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.T.; Schmitt, T.; Perloff, D.; Wu, N.; Yu, T.Y.; Wang, X.W. Nondestructive corrosion detection using fiber optic photoacoustic ultrasound generator. Measurement 2015, 62, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Chen, E.; Li, W. A review on corrosion detection and protection of existing reinforced concrete (RC) structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.K.; Pradhan, B. Effect of cation type of chloride salts on corrosion behaviour of steel in concrete powder electrolyte solution in the presence of corrosion inhibitors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.K.; Pradhan, B. Impact of Cation Type of Chloride Salts on Diffusion Behavior and Binding Capacity of Chloride Ions in Concrete Containing Sodium Nitrite and Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borosnyói, A.; Erdélyi, A. De-Icing Salt Scaling Damage Kinetics of Fibre Reinforced Concretes Made with High Bond Crimped Steel Fibres. Period. Polytech.-Civ. Eng. 2015, 59, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Xue, Y.G.; Li, G.K.; Su, M.X.; Qiu, D.H.; Kong, F.M.; Zhou, B.H. Using Bayesian network and Intuitionistic fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process to assess the risk of water inrush from fault in subsea tunnel. Geomech. Eng. 2021, 27, 605–614. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.G.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, S.C.; Qiu, D.H.; Su, M.X.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhou, B.H.; Tao, Y.F. Water inrush risk assessment for an undersea tunnel crossing a fault: An analytical model. Mar. Geores. Geotechnol. 2019, 37, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M.G.; Enfedaque, A.; Gálvez, J.C. On the prediction of the orientation factor and fibre distribution of steel and macro-synthetic fibres for fibre-reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 77, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Kaur, G.; Kunal. Strength and permeation properties of self-compacting concrete containing fly ash and hooked steel fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 103, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.G.; Gong, H.M.; Kong, F.M.; Yang, W.M.; Qiu, D.H.; Zhou, B.H. Stability analysis and optimization of excavation method of double-arch tunnel with an extra-large span based on numerical investigation. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2021, 15, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.J.; Zhou, M.T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.N.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.M. Effect of steel fiber shape and content on printability, microstructure and mechanical properties of 3D printable high strength cementitious materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, M.N.; Yu, L.; Guo, X.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Jiang, Y.T. Bond-slip behavior between corroded I-shaped steel and concrete in a subsea tunnel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 120, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Xue, Y.; Han, M.; Kong, F.; Fu, K.; Jiang, X. Large deformation characteristics and mechanism analysis of excavating shallow buried tunnel in reclamation areas. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2025, 84, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banthia, N.; Foy, C. Marine Curing of Steel Fiber Composites. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1989, 1, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Yang, L.; Kang, K.L.; Gao, D.Y.; Liu, G.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.S. Mechanical properties and corrosion mechanism of steel fiber reinforced concrete (SFRC) subjected to stray current. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, K.B.; Li, Y.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Cui, H.Z.; Liu, W. Corrosion behavior of steel fiber reinforced concrete under ambipolar stray current interference. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Wu, X.L.; He, G.X.; Shang, Q.F.; Xu, J.G.; Sun, Y.K. Mechanical Properties of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete by Vibratory Mixing Technology. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Sun, Y.K.; Xu, J.G.; Wang, B. The Effect of Vibration Mixing on the Mechanical Properties of Steel Fiber Concrete with Different Mix Ratios. Materials 2021, 14, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, A.U.; Akçaoglu, T.; Marar, K. Evaluation of workability parameters for hooked-end high strength steel fiber concrete mixes. Rev. Rom. Mat. 2020, 50, 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Grünewald, S.; Walraven, J.C. Parameter-study on the influence of steel fibers and coarse aggregate content on the fresh properties of self-compacting concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atis, C.D.; Karahan, O. Properties of steel fiber reinforced fly ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, A.; Folino, P.; Lima, C.; Martinelli, E.; Pepe, M. On the mechanical response of Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Concrete with Recycled and Industrial Steel Fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.T.; Wang, B.; Xu, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Hui, D.V.; Yuan, W.G.; Tang, H.F.; Zhao, J.J. Experimental study on recycled steel fiber-reinforced concrete under repeated impact. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fiber Type | Fiber Shape | L (mm) | D (mm) | Fiber Content (%) | Binder Content (kg/m3) | MS | w/c | Test Methods | Duration (d) | MFS (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME, LC, CR | H | 25 28.2 40 | 0.51 0.48 0.60 | 3 2.5 2.2 | 590 | None | 0.4 | CID (SSWDC) | 154, 304, 950, 1250 | / | [30] |
| ME, LC, CR | / | 25 28.2 40 | 0.51 0.48 0.60 | 3 2.5 2.2 | 590 | None | 0.4 | CID (SSWDC) | 640 | / | [35,36] |
| ME | / | 25 26.5 | 0.51 0.44 | 3.0 1.8 | 590 588 | Included | 0.4 | CID (SSWDC) | 900 450 | / | [37] |
| LC | H | 28.2 | 0.48 | 1.7 | 588 | Included | 0.4 | CID (SSWDC) | 450 | / | [37] |
| / | H | 60 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 449 | Included | 0.3 | CID (SWDC) | 28, 56, 90, 180 | 3.5 | [38] |
| / | H | 35 | 0.5 | 0.76 | 413 | None | 0.31 | EEFM | 1, 3 | 10 | [39] |
| / | H | 30.5 | 0.6 | 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 | 315–548 | None | 0.31–0.54 | CID (SWDC) | 30 | 3.5 | [40] |
| / | H, S | 30, 60 | 0.5, 0.75 | 0.51 | 250 | None | 0.7–0.78 | CID (SSWDC) | 90, 210 | 3.38 | [41] |
| / | H | 60 | 0.8 | 0.51 | 320 | None | 0.6 | CID (SSWDC) | 365 | 0.35 | [42] |
| / | H | 35, 60 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.5, 1 | 395, 558 | Included | 0.35, 0.55 | EEFM | 20 | 3.5 | [28] |
| / | C | / | / | 0.6 | 380 | None | 0.35 | CID (SWDC) | 28, 150 | 3 | [43] |
| / | H | 30 | 0.56 | 1 | 360, 444 | None | 0.44, 0.37 | CID (SWDC) | 810 | 8, 12 | [14] |
| ZP | W | 31 | 0.66 | 1 | 493.6 | None | 0.47 | CID (SWDC) | 30 | 5 | [44] |
| / | S | 15 | 0.39 | 2 | / | None | 0.4 | EEFM | 100 | 23 | [45] |
| / | H | 60 | 0.9 | / | 413 | None | 0.31 | CID (SWDC) | 7 | 3.5 | [46] |
| HC | H | 60 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 426.3 | Included | 0.34 | CID (SWDC) | 365, 730 | 3.5, 7 | [47] |
| ZP | S | 40 | 0.58 | 1 | 526 | Included | 0.58 | CID (SWDC) | 30 | 6 | [48] |
| Project | Tunnel Length (km) | Country | Application Locations | Construction Period | Application Scope | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nordkapp Tunnel | 6.8 | Norway | Shotcrete | 1995–1999 | Full line | [100] |
| Frøya Tunnel | 5.2 | Norway | Shotcrete | 1998–2000 | Full line | [102] |
| Metro Doha Green Line | 34 | The State of Qatar | PTLS | 2013–2014 | Full line | [101] |
| Qingdao Metro Line 1 | 8.1 | China | PTLS | 2015–2020 | Segmental | [103] |
| Qingdao Metro Line 1 | 8.1 | China | CPSL | 2015–2020 | Test section | [104] |
| Jiaozhou Bay Second Submarine Tunnel | 14.37 | China | PTLS, CPSL | 2020–2027 | Segmental | [105] |
| Classification | Test Items |
|---|---|
| Workability | Slump test, V-funnel test |
| Mechanical properties | Compressive strength test, flexural strength test, tensile strength test, impact toughness test, modulus of elasticity test |
| Long-term durability | Freeze–thaw resistance test, chloride ion penetration test, sulfate resistance test, water permeability test, carbonation test |
| Other performance | Chloride content test, air content test |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wei, L.; Cui, Q.; Shu, H.; Peng, W.; Gong, H.; Xue, Y.; Han, M. Chloride Corrosion Resistance of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete and Its Application in Subsea Tunnel Linings. Coatings 2025, 15, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020235
Liu J, Wei L, Cui Q, Shu H, Peng W, Gong H, Xue Y, Han M. Chloride Corrosion Resistance of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete and Its Application in Subsea Tunnel Linings. Coatings. 2025; 15(2):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020235
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiguo, Longhai Wei, Qinglong Cui, Heng Shu, Wenbo Peng, Huimin Gong, Yiguo Xue, and Min Han. 2025. "Chloride Corrosion Resistance of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete and Its Application in Subsea Tunnel Linings" Coatings 15, no. 2: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020235
APA StyleLiu, J., Wei, L., Cui, Q., Shu, H., Peng, W., Gong, H., Xue, Y., & Han, M. (2025). Chloride Corrosion Resistance of Steel Fiber-Reinforced Concrete and Its Application in Subsea Tunnel Linings. Coatings, 15(2), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15020235







