Preparation of New Vanadium Base Composite Conversion Coating on 6061 Aluminum Alloy Surface for Sports Equipment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Conversion Coating Preparation
2.2. Characterization of Surface Morphology and Composition
2.3. Characterization of Wettability
2.4. Characterization of Corrosion Resistance
3. Results and Discussion
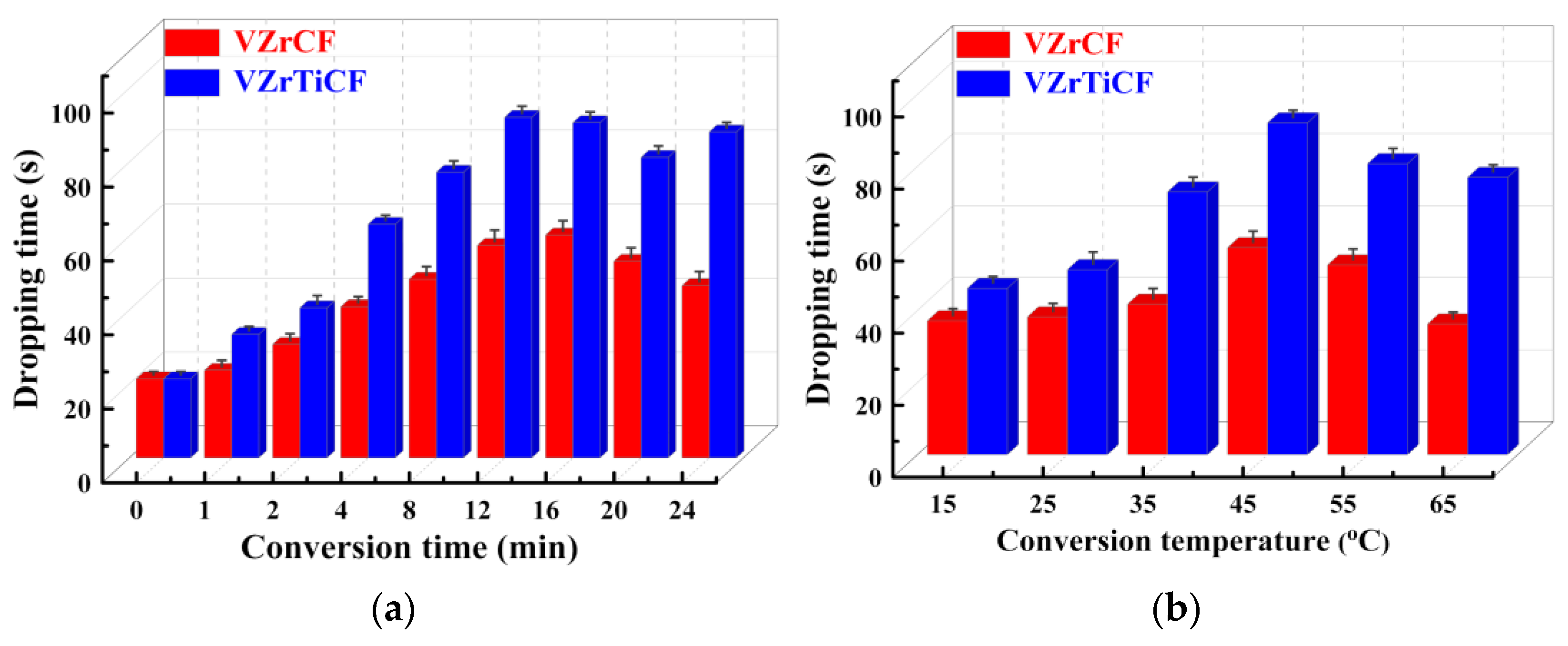
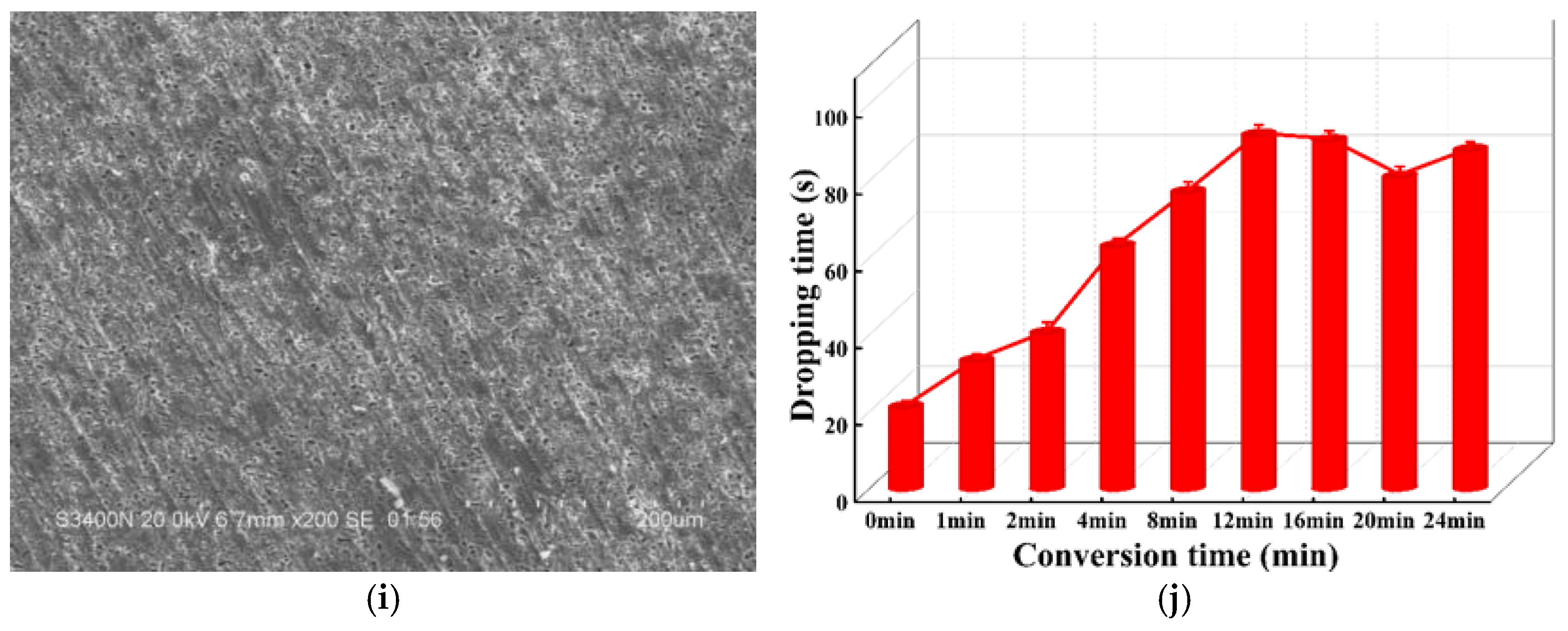
3.1. Effect of Conversion Parameters
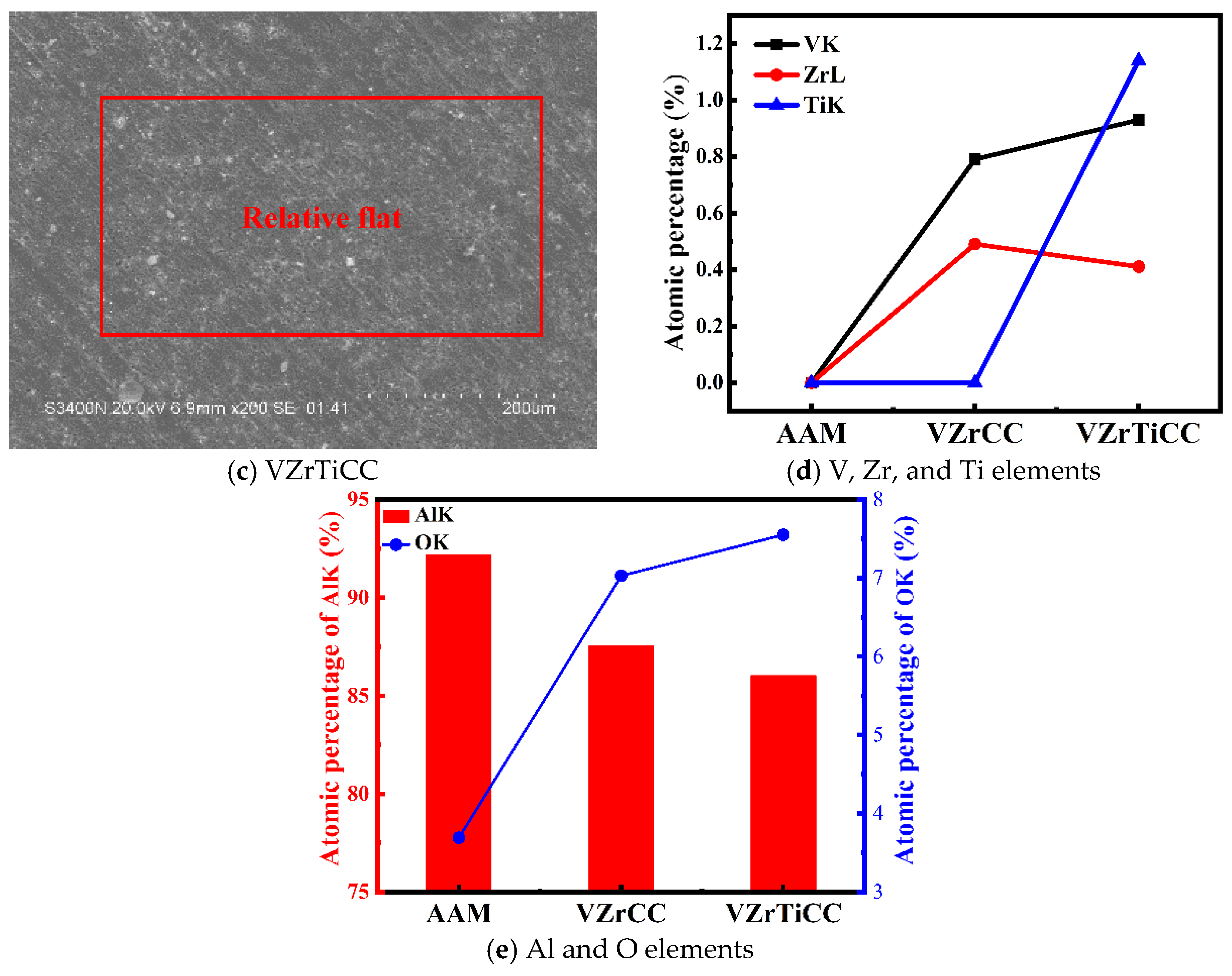
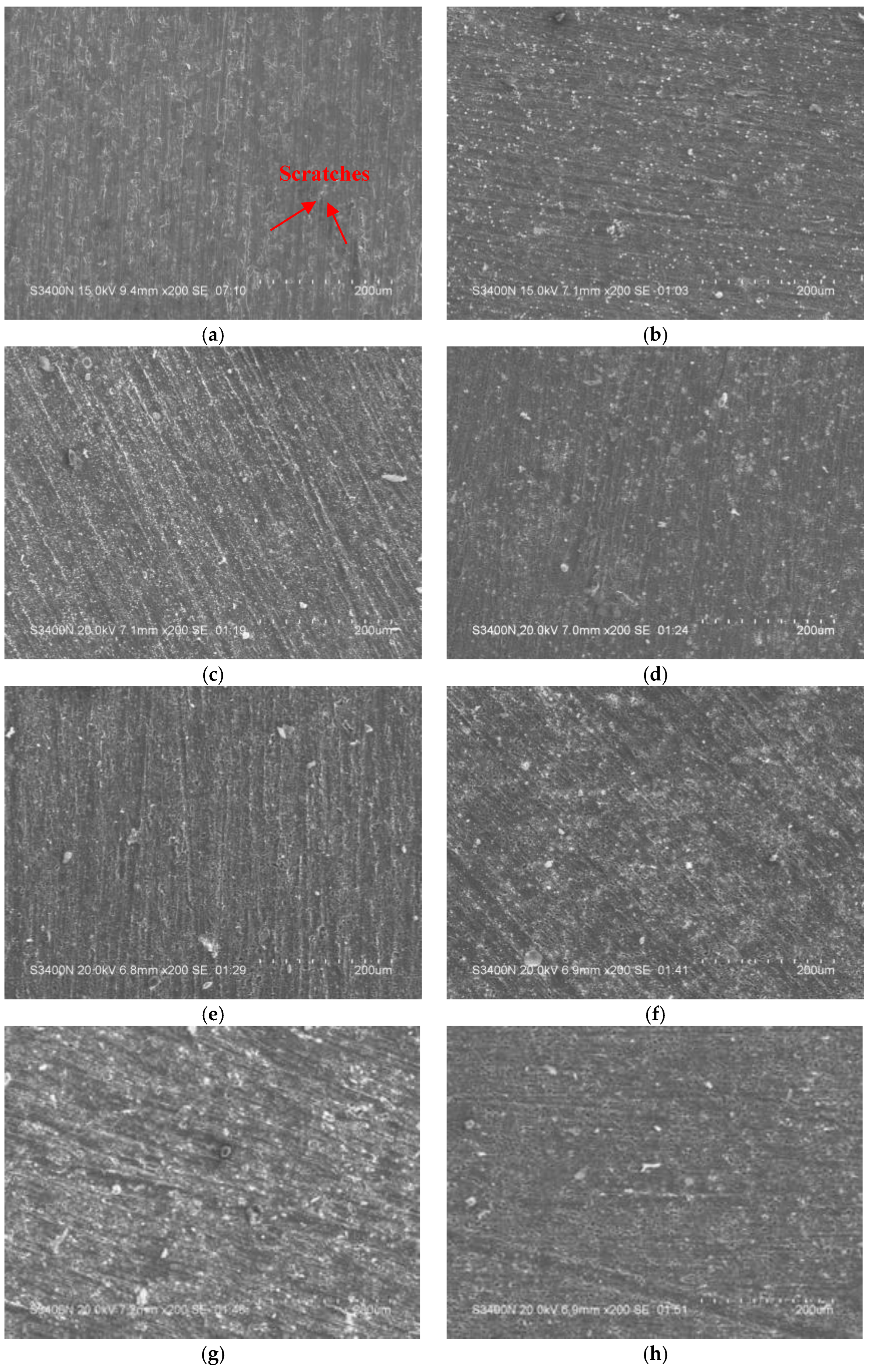
3.2. Morphology and Composition Analysis
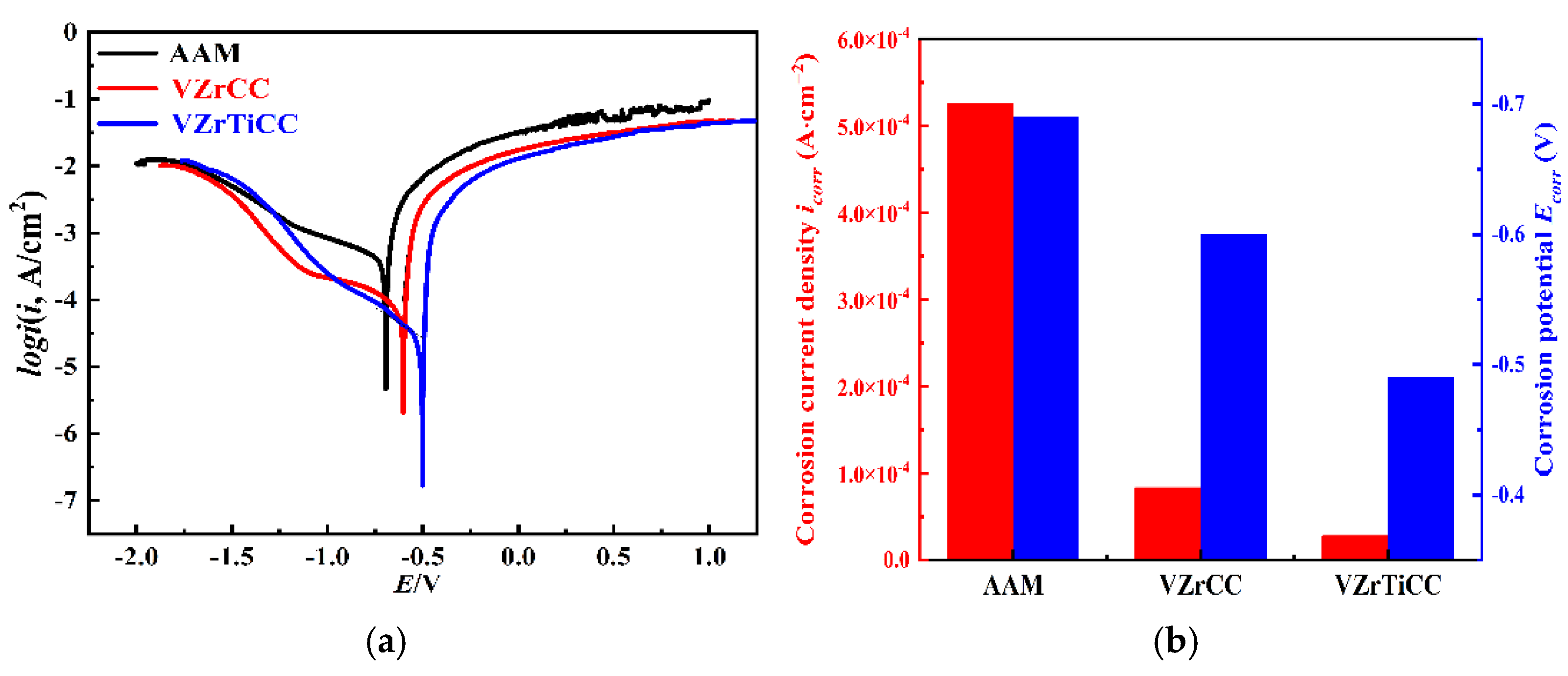
3.3. Corrosion Resistance Analysis
3.3.1. Electrochemical Analysis
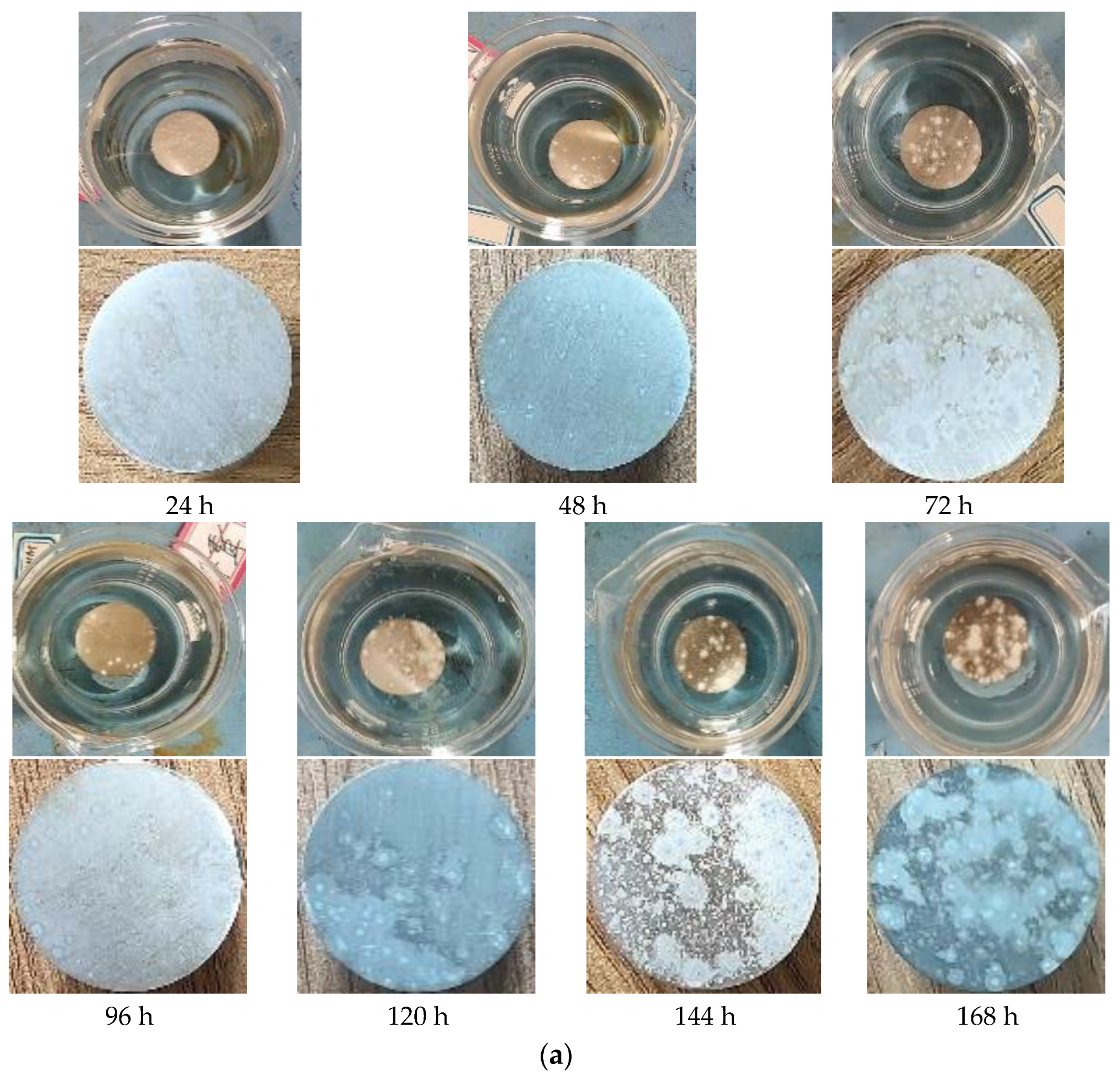
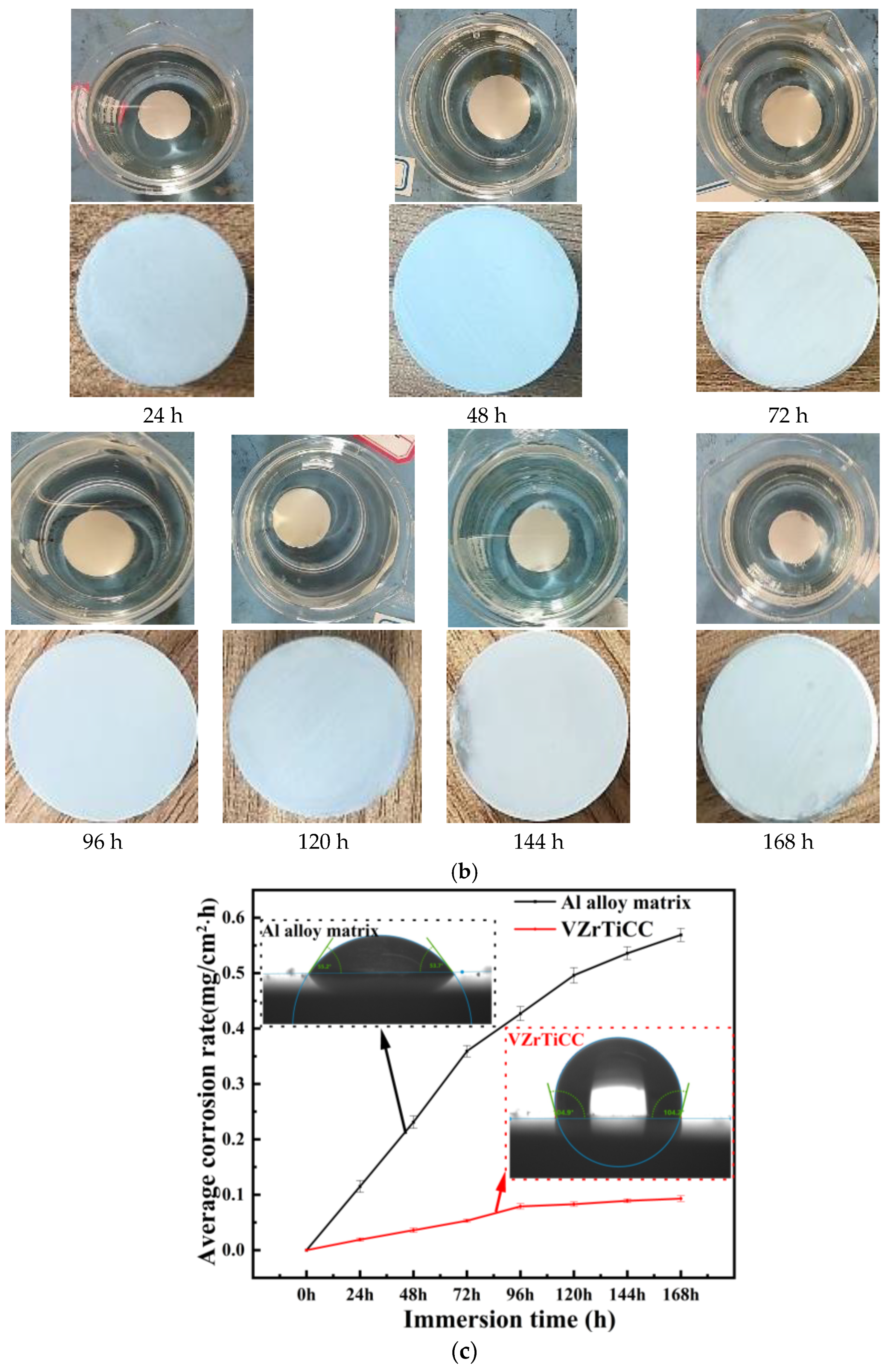
3.3.2. Full Immersion Test
3.4. Microscopic Morphology Evolution of VZrTiCC
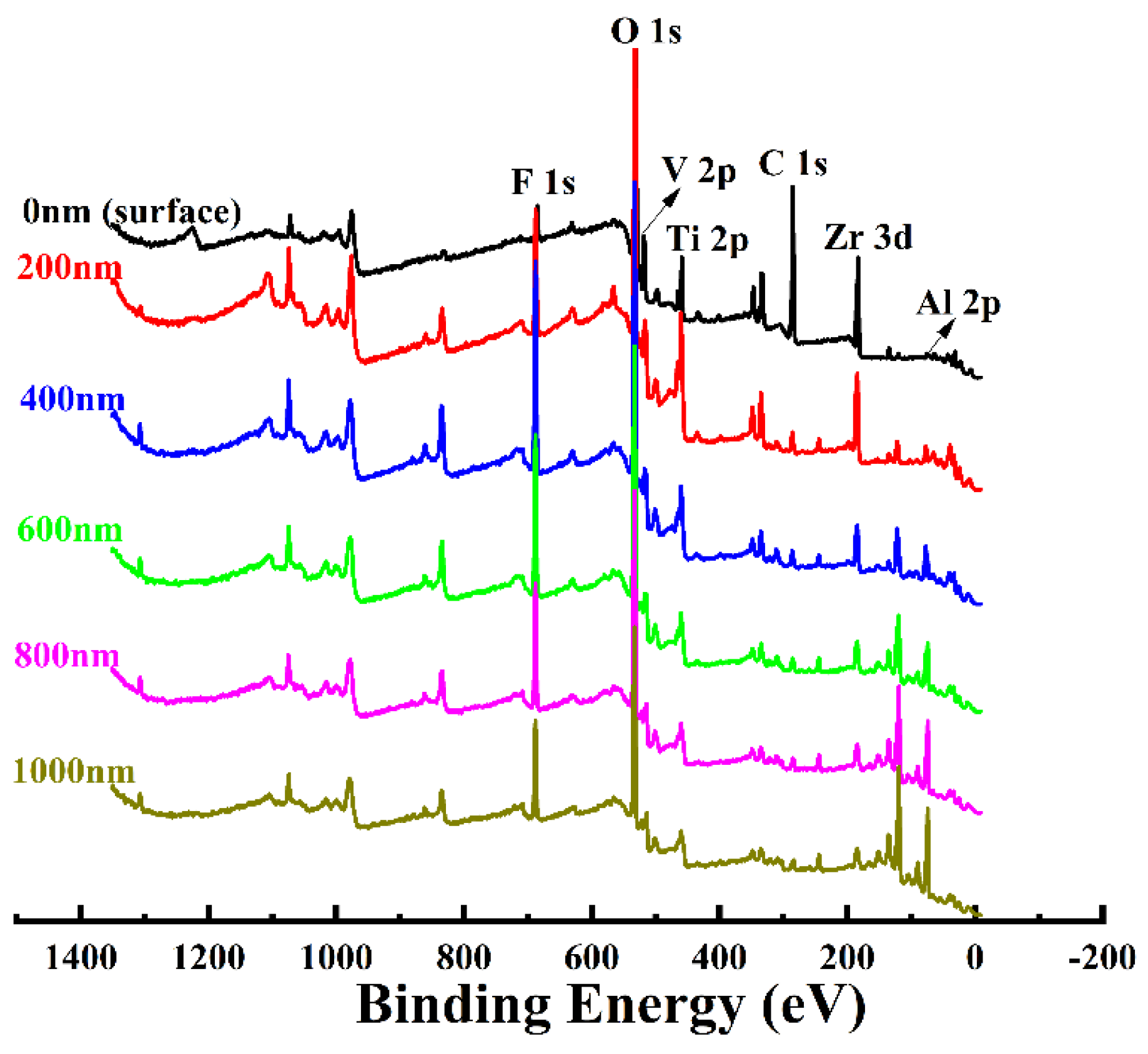
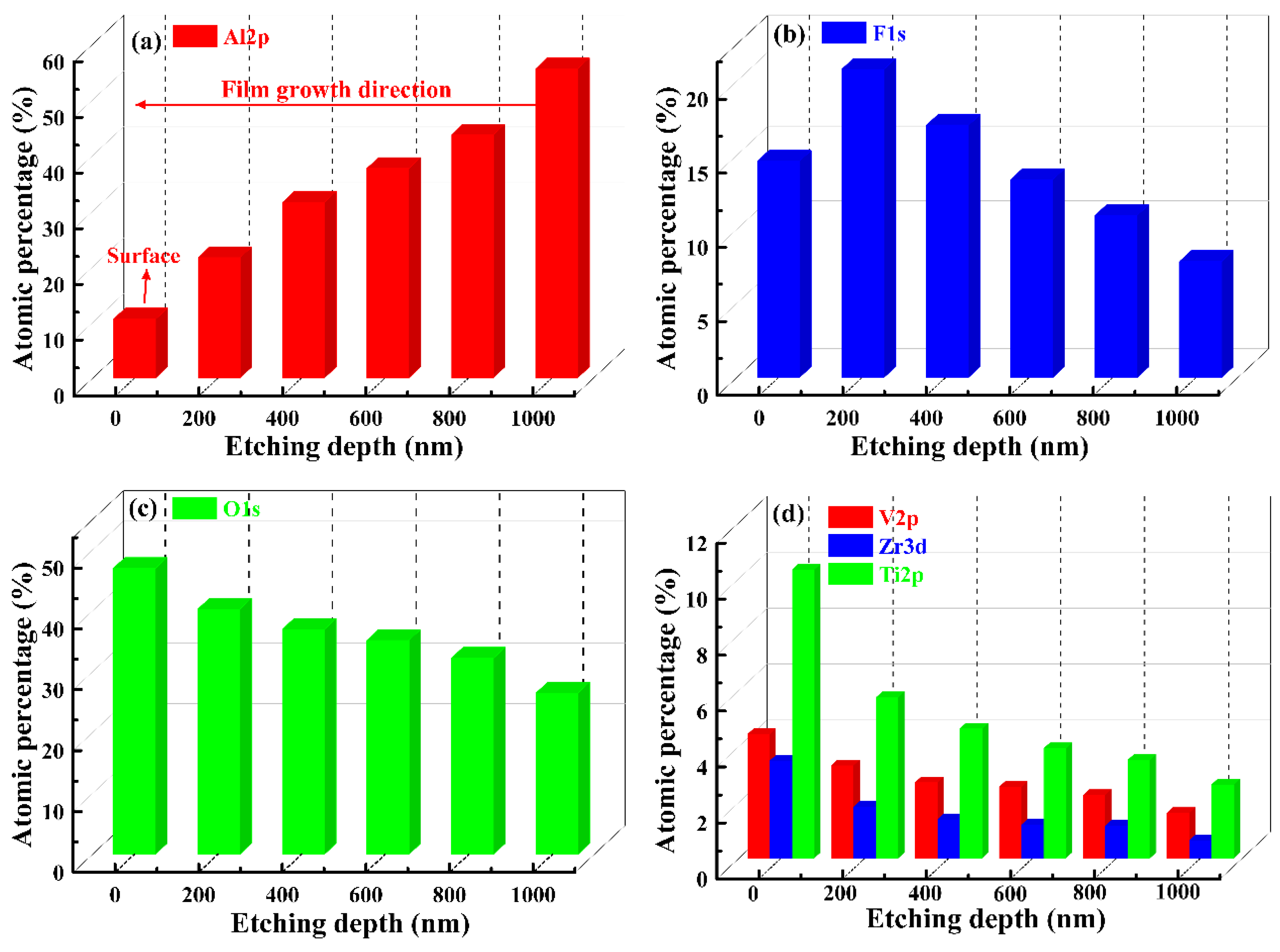
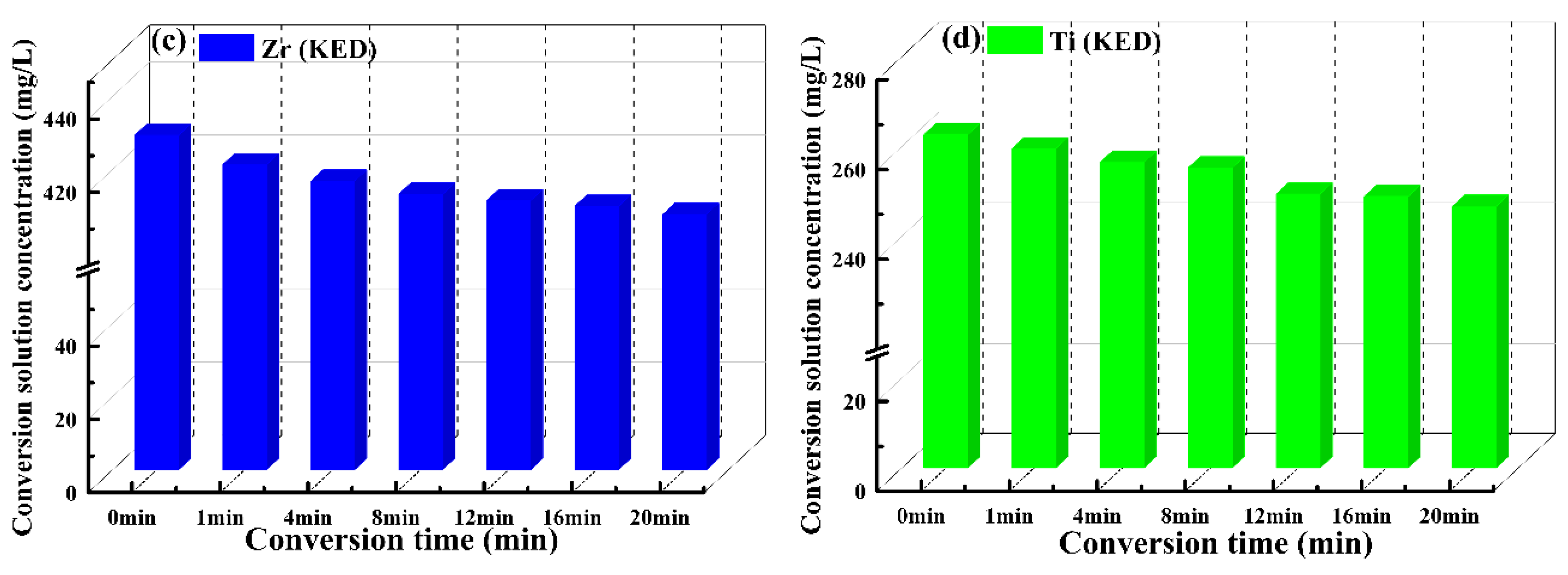
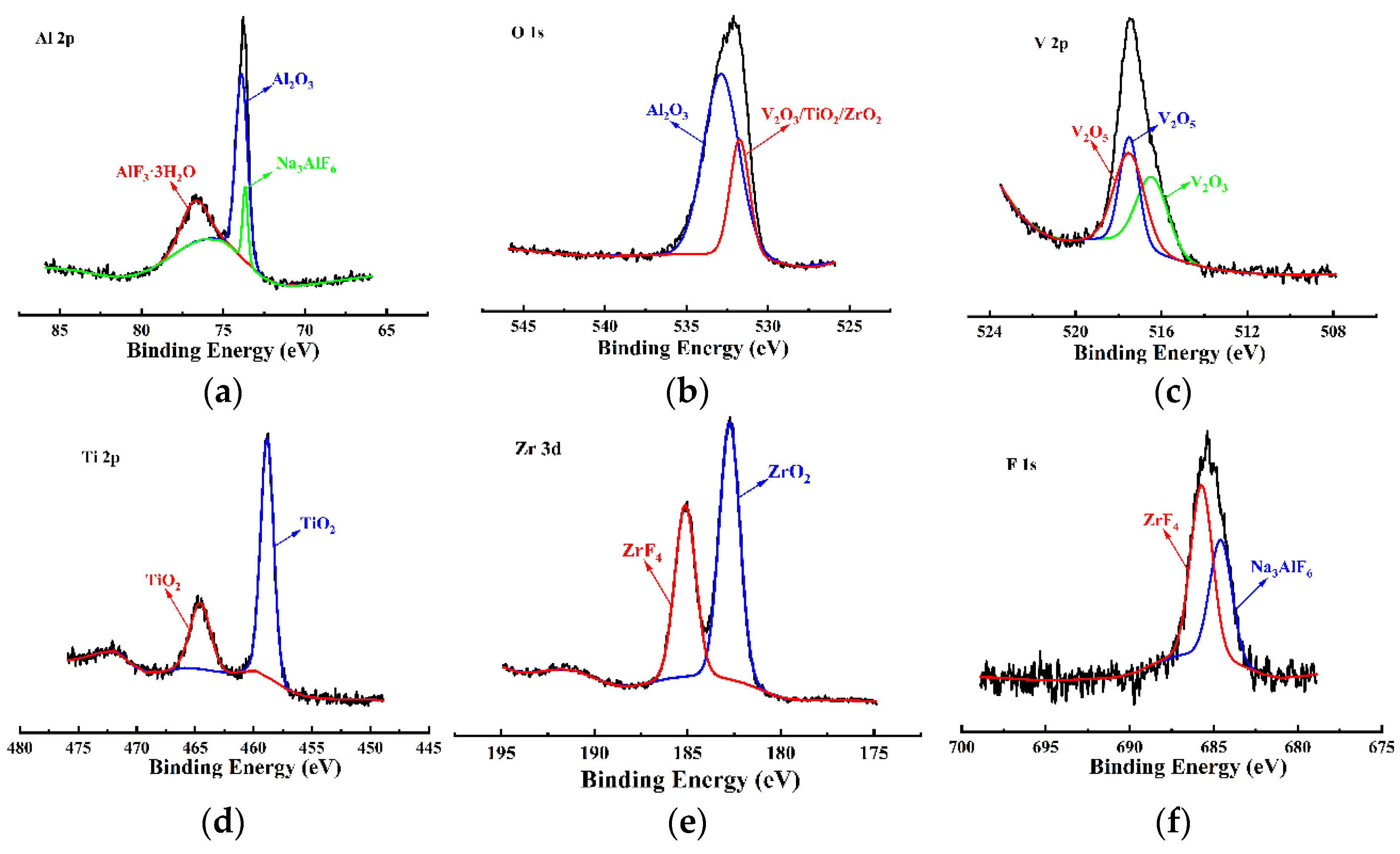
3.5. Elemental Composition Evolution of VZrTiCC
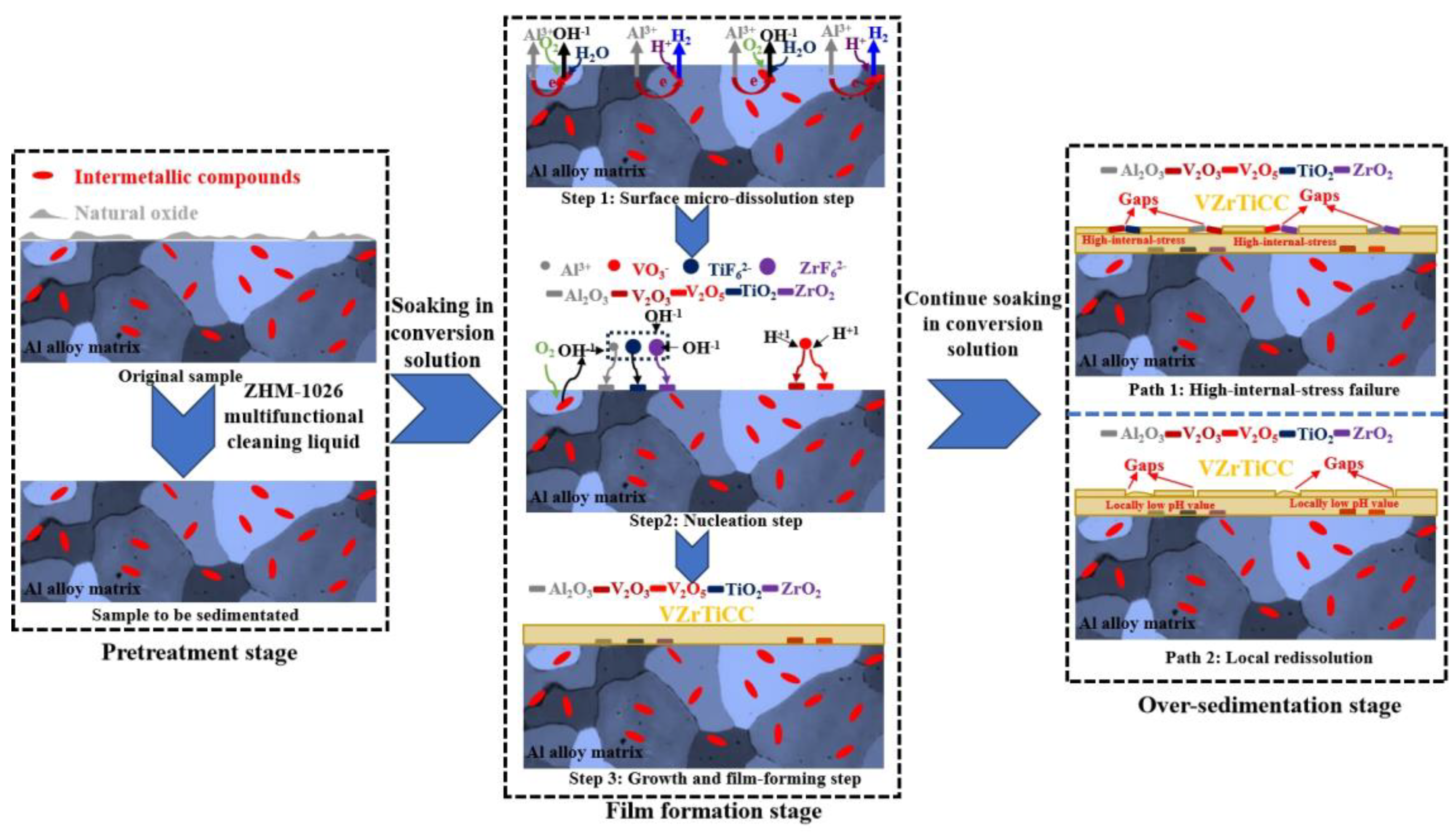
3.6. Formation Mechanism of VZrTiCC
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The optimal conversion time (CTI) and conversion temperature (CTE) for the VZrTiCC are 12 min and 45 °C. The VZrTiCC can significantly fill the scratches on the AAM surface, and its surface is relatively flat. The combination of a high Ecorr and the lowest icorr in the VZrTiCC underscores its exceptional electrochemical corrosion resistance, as evidenced from both thermodynamic and kinetic viewpoints. The higher wetting angle for the VZrTiCC makes the corrosive medium unable to corrode its surface efficiently. The VZrTiCC significantly reduces the ACR, with almost no corrosion spots on its surface, and its corrosion resistance is approximately 5 times higher than that of the AAM. This plays an important role in improving the service life of sports equipment.
- (2)
- The VZrTiCC primarily comprises six elements—V, Zr, Ti, Al, F, and O—and its surface phases mainly consist of metal oxides of corresponding elements and a small amount of fluoride. As the VZrTiCC grows from the inside out, the contents of the V, Zr, Ti, and O elements gradually increase, whereas the content of the Al element gradually decreases. The entire growth and sedimentation process shows significantly high Ti, medium V, and low Zr, and yet the unit sedimentation amount of the three conversion elements is Ti > Zr > V. The metal ion contents measured using ICP complemented the XPS results well.
- (3)
- The formation process of the VZrTiCC mainly includes three key stages: a pretreatment stage, film formation stage, and over-sedimentation stage. During the film formation stage, various metal oxide crystal nuclei are formed and undergo rapid two-dimensional growth. After the optimal CC is formed, it progresses to the sedimentation stage, where it disrupts the dynamic equilibrium of sedimentary reactions. In this stage, the conversion reaction results in the occurrence of cracks or dissolution due to the excessive internal growth stress or low local pH values.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramnath, B.V.; Elanchezhian, C.; Jaivignesh, M.; Rajesh, S.; Parswajinan, C.; Ghias, A.S.A. Evaluation of mechanical properties of aluminium alloy–alumina–boron carbide metal matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, A.; Yi, D.; Li, T.A. Review on Traditional Processes and Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Aluminum Alloy Microstructures, Mechanical Properties, Costs, and Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Hong, H.; Zhang, T. Long-Term Corrosion Behavior of 434 Stainless Steel Coatings on T6061 Aluminum Alloy in Chloride Environments. Coatings 2025, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Liao, X.; Lei, H.; Hao, D.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B. The Effect of Oxidation Time on the Organization and Corrosion Performance of 6061 Aluminum Alloy Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings. Coatings 2025, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, L.; Pesin, A.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; Tandon, P.; Kong, C.; Yu, H. Recent development of superplasticity in aluminum alloys: A review. Metals 2020, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, A.; Saha, D.; Singh, J.K.; Paswan, S.; Singh, D.D.N. Effect of Environmental Pollution on Corrosion Characteristics of 3003 Aluminium Alloy Exposed in Different Parts of India. Trans. Indian Inst. Metals 2017, 70, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Frankel, G.S. Transitions between pitting and intergranular corrosion in AA2024. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1193–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. The Use of Aluminum Alloys in Structures: Review and Outlook, Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; p. 105290. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.S.; Yue, X.; Li, Q.Y.; Peng, H.L.; Dong, B.X.; Liu, T.S.; Yang, H.Y.; Fan, J.; Shu, S.L.; Qiu, F. Development and applications of aluminum alloys for aerospace industry. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 944–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhurinskiy, D.V.; Dautov, S.S.; Shornikov, P.G.; Akhatov, I.S. Surface Modification of Aluminum 6061-O Alloy by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation to Improve Corrosion Resistance Properties. Coatings 2020, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, Y. Corrosion resistance of aluminum fluoride modified 6061 aluminum alloy. Mater. Lett. 2021, 298, 129932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Garcia, A.; Esquivel-Peña, V.; Genesca, J.; Montoya, R. Advances in galvanic corrosion of aluminum alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 449, 142227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchariková, L.; Liptáková, T.; Tillová, E.; Kajánek, D.; Schmidová, E. Role of chemical composition in corrosion of aluminum alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, S.; Capraz, M.Z.; Shrotriya, P.; Hebert, K.R. Oxide Microstructural Changes Accompanying Pore Formation During Anodic Oxidation of Aluminum. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Sambasivam, K.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Hashmi, M.S.J. A study of defects generation on Ni–Co substrate during electroplating and its minimisation through proper cleaning. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 6, 565–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.; Bijalwan, P.K.; Pathak, A.S.; Bhagat, A.N. A review on physical vapor deposition-based metallic coatings on steel as an alternative to conventional galvanized coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2022, 19, 403–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Shu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, Q.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Tan, X. Efficient Cr(VI) removal by pyrite/porous biochar: Critical role of potassium salt and sulphur. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Ghanbari, S.; Orooji, Y.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr (VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, M.-Y.; Akratos, C.S.; Pavlou, S.; Vayenas, D.V. Chromium removal in constructed wetlands: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 96, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, B.S.; Balaraju, J. Chromate (Cr6+)-free surface treatments for active corrosion protection of aluminum alloys: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2024, 21, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, S.; RV, H. Myco-remediation of chromium heavy metal from industrial wastewater: A review. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 13, 101740. [Google Scholar]
- Iannuzzi, M.; Frankel, G.S. Mechanisms of corrosion inhibition of AA2024-T3 by vanadates. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 2371–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golru, S.S.; Attar, M.M.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Morphological analysis and corrosion performance of zirconium based conversion coating on the aluminum alloy 1050. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 24, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, G.; Allen, F. Self-Healing, Chromate-free Conversion Coating for Magnesium Alloys. Met. Finish. 2012, 110, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Qian, X.; Li, B.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Tang, H. Investigation of the microstructure, growth mechanism, and corrosion behavior of a new Zr–Ti conversion coating on 6016 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 7585–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreatta, F.; Turco, A.; De Graeve, I.; Terryn, H.; De Wit, J.; Fedrizzi, L. SKPFM and SEM study of the deposition mechanism of Zr/Ti based pre-treatment on AA6016 aluminum alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 7668–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlien, J.; Walmsley, J.; Østerberg, H.; Nisancioglu, K. Formation of a zirconium-titanium based conversion layer on AA 6060 aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 153, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendialdua, J.; Casanova, R.; Barbaux, Y. XPS studies of V2O5, V6O13, VO2 and V2O3. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1995, 71, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Adamsen, K.C.; Li, Z. WO3 Monomers Supported on Anatase TiO2(101),-(001),and Rutile TiO2(110):A Comparative STM and XPS Study. J. Phys. Chem. C Nanomater. Interfaces 2022, 126, 2493–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | Cu | Mg | Mn | Fe | Si | Zn | Cr | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 0.16 | 1.01 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 0.05 | Bal. |
| Type of Conversion Solution | NaVO3 | H2ZrF6 | H2TiF6 | (NaPO3)6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V-Zr | 4.0 g/L | 2.8 mL/L | 0 mL/L | 0.4 g/L |
| V-Zr-Ti | 4.0 g/L | 3.0 mL/L | 2.2 mL/L | 0.4 g/L |
| Composition | CuSO4∙5H2O | HCl | NaCl |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 41 g/L | 13 mL/L | 35 g/L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Qian, X.; Huang, F.; Fang, Y. Preparation of New Vanadium Base Composite Conversion Coating on 6061 Aluminum Alloy Surface for Sports Equipment. Coatings 2025, 15, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050516
Wang Y, Qian X, Huang F, Fang Y. Preparation of New Vanadium Base Composite Conversion Coating on 6061 Aluminum Alloy Surface for Sports Equipment. Coatings. 2025; 15(5):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050516
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yiqun, Xuzheng Qian, Feng Huang, and Yingsong Fang. 2025. "Preparation of New Vanadium Base Composite Conversion Coating on 6061 Aluminum Alloy Surface for Sports Equipment" Coatings 15, no. 5: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050516
APA StyleWang, Y., Qian, X., Huang, F., & Fang, Y. (2025). Preparation of New Vanadium Base Composite Conversion Coating on 6061 Aluminum Alloy Surface for Sports Equipment. Coatings, 15(5), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050516





