Surface Aging Effect on Tire/Pavement Noise Medium-Term Evolution in a Medium-Size City
Abstract
:1. Introduction
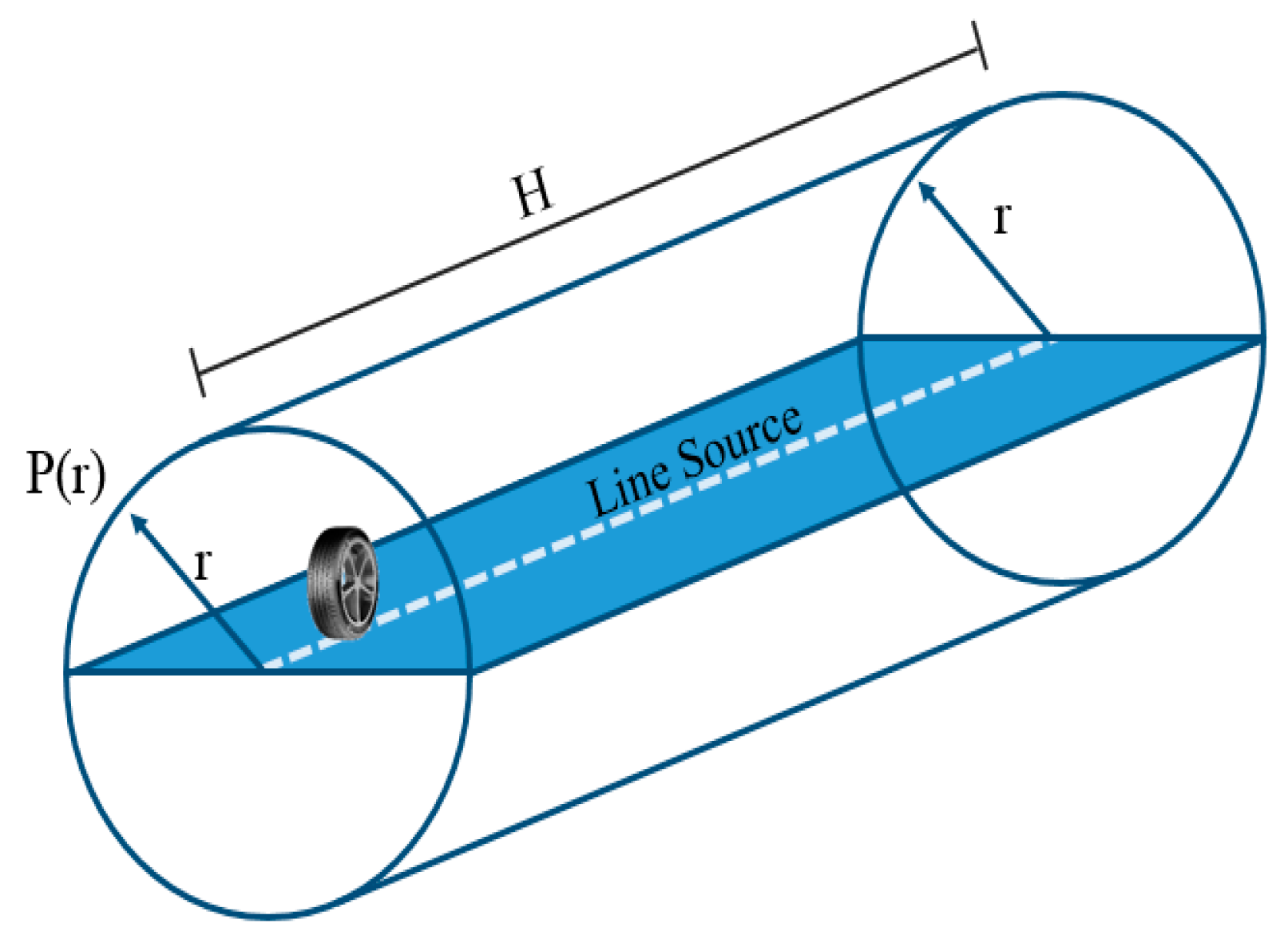
2. Environmental Noise Levels from Close ProXimity (CPX) Noise Levels
Lp(d) − Lp(r) = 10·log (r/d)
3. Project Selection
4. Experimental Study
4.1. Tire/Pavement Sound Measurements
4.2. Surface Profile Measurements
5. Analysis of Measurements and Discussion
5.1. Surface Assessment: Evolution of Tire/Pavement Noise Levels (CPX)
5.2. Rolling Noise Mapping at 50 km/h and Environmental Noise Levels (Environmental Noise Directive (END))
- (a)
- The attenuation due to the ground absorption or green walls: this effect could have some importance at great distance, such as at the right side of the studied section, where there are no buildings that block the noise propagation.
- (b)
- The time gap between Lden and Lenv-CPtr measurements. Surface aging during this time interval was possible, especially if the road surface was considerably degraded in 2012. Nevertheless, the gap is not sufficiently large to say that this was a key factor.
- (c)
- Different noise source related to vehicle density. Figure 13b was elaborated from CPX measurement, which consider a vehicle producing noise at every point of Section 4 and at every second (linear noise source: busy lane). Nevertheless, there is not a vehicle producing noise at every point and every second in Section 4. As shown in Table 1, the annual average daily traffic is 11,157 vehicles/day (from gauging station B, Figure 4a). Considering the worst case (every vehicle during the 12 h of a day and none at evening and afternoon), there would be one vehicle producing noise every 3.9 s. Thus, the real noise source from traffic is not a linear noise source indeed, and therefore, noise at Figure 13b,c has been over estimated.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torija, A.J.; Genaro, N.; Ruiz, D.P.; Ramos-Ridao, A.; Zamorano, M.; Requena, I. Priorization of acoustic variables: Environmental decision support for the physical characterization of urban sound environments. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillermo, R.G.; Juan Miguel, B.M.; José, T.C.; David, M.G.; Pedro, A.M.; Valentín, G.M.; Rosendo, V.G.; Juan, A.M.S.; Carlos, P.G. Study on the relation between urban planning and noise level. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 111, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Bluhm, G.; Eriksson, C. Cardiovascular effects of environmental noise: Research in Sweden. Noise Health 2011, 13, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Das, P.P.; Foujdar, A. Association between road traffic noise and prevalence of coronary heart disease. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licitra, G.; Cerchiai, M.; Teti, L.; Ascari, E.; Fredianelli, L. Durability and variability of the acoustical performance of rubberized road surfaces. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 94, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, F.; Freitas, E.; Cunha, C.; Silva, C.; Lamas, J.; Mouta, S.; Santos, J.A. Traffic noise: Annoyance assessment of real and virtual sounds based on close proximity measurements. Transp. Res. Part D 2017, 52, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, V.F.; Paje, S.E. Study of the road surface properties that control the acoustic performance of a rubberized asphalt mixture. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 102, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donavan, P.R.; Rymer, B. Effects of aging on tire-pavement noise generation for concrete pavements of different textures. Transp. Res. Rec. 2011, 2233, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogrovejo, D.E.; Flintsch, G.W.; Izeppi, E.D.D.; McGhee, K.K.; Burdisso, R.A. Short-term effect of pavement surface aging on tire-pavement noise measured with onboard sound intensity methodology. Transp. Res. Rec. 2014, 2403, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, U.; Ejsmont, J.A. Tyre/Road Noise Reference Book; INFORMEX: Kisa, Sweden, 2002; ISBN 91-631-2610-9. [Google Scholar]
- Anfosso-Lédée, F. Modeling the local propagation effects on tire-road noise: Propagation filter between CPX and CPB measurements. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–25 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bérengier, M.; Bendtsen, H.; Haider, M. A methodology to estimate the effect of pavement management on noise emission in urban areas. In Proceedings of the 19th International Congress on Acoustic, Madrid, Spain, 2–7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cesbron, J.; Klein, P. Correlation between tyre/road noise levels measured by the Coast-By and the Close-ProXimity methods. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 126, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Blokland, G.; Roovers, M.S. SILVIA Deliverable D14: Measurement Methods; Technical Report SILVIA-M+P-015-02-WP2-140705, SILVIA Project Report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, H.M.; Roovers, M.S. CPX-SPB/CPB Relation; Technical Report SILVIA-M+P-008-00-WP2-080904, SILVIA Project Report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, M.; Descornet, G. Noise Classification Methods for Urban Road Surfaces; Classification Methodology; F.D13, Project SILENCE; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Licitra, G.; Losa, M.; Alfinito, L.; Cerchiai, M. Correlation factor between statistical Pass-By and Close-ProXimity noise level on Italian roads. In Proceedings of the 19th International Congress on Acoustic, Madrid, Spain, 2–7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson, H. Test Method for the Whole Vehicle; Technical Report HAR11TR-020301-SP10; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Anfosso Lédée, F.; Dutilleux, G.; Conter, M. Compatibility of the ROSANNE noise characterization procedure for road surfaces with CNOSSOS-EU model. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise Congress, Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Skov, R.S.H. Analysis and comparison of methods, CPX and SPB, for measuring noise properties of road surfaces. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise Congress, Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gardziejczyk, W. The effect of time on acoustic durability of low noise pavements—The case studies in Poland. Transp. Res. Rec. Part D 2016, 44, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardziejczyk, W. Influence of road pavement macrotexture on tyre/road noise of vehicles. Baltic J. Road Bridge Eng. 2014, 9, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonin, R. Quiet road pavements: Design and measurement—State of the art. Acoust. Austral. 2016, 44, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Cerchiai, M.; Teti, L.; Ascari, E.; Bianco, F.; Chetoni, M. Performance assessment of low-noise load surfaces in the leopoldo Project: Comparison and validation of different measurement methods. Coatings 2015, 5, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M. Handbook of Acoustical Measurements and Noise Control, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Makarewicz, R. Cylindrical spreading due to downwind refraction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DGC. Dirección General de Carreteras (Ministerio de Fomento). Mapas Estratégicos de Ruido de las Carreteras de la Red del Estado Segunda Fase. 2012. 2013. (Strategic Noise Maps of Spanish Road Network). Retrieved 24 March 2018. Available online: http://sicaweb.cedex.es/mapas-consulta-fase2.php (accessed on 29 May 2018). (In Spanish).
- Carlos, I.M.; Luis, D.B.; Mario, S. Noise pollution in national parks: Soundscape and economic valuation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 123, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Feiteira Dias, J.L.; Picado-Santos, L.G.; Capitao, D.D. Mechanical performance of dry process fine crumb rubber asphalt mixture placed on the portuguese road network. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 73, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paje, S.E.; Luong, J.; Vázquez, V.F.; Bueno, M.; Miró, R. Road pavement rehabilitation using a binder with a high content of crumb rubber: Influence on noise reduction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, V.F.; Luong, J.; Bueno, M.; Teran, F.; Paje, S.E. Assessment of an action against environmental noise: Acoustic durability of a pavement Surface with crumb rubber. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, M.; Luong, J.; Terán, F.; Viñuela, U.; Vázquez, V.F.; Paje, S.E. Noise reduction properties of an experimental bituminous slurry with crumb rubber incorporated by the dry process. Coatings 2014, 4, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paje, S.E.; Bueno, M.; Terán, F.; Miró, R.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Martínez, A.H. Acoustic field evaluation of asphalt mixtures with crumb rubber. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paje, S.E.; Bueno, M.; Terán, F.; Viñuela, U.; Luong, J. Assessment of asphalt concrete acoustic performance in urban streets. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, M.; Viñuela, U.; Teran, F.; Paje, S.E.; Luong, J. A first step toward a close proximity noise map. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mioduszewski, P.; Gardziejczyk, W. Inhomogeneity of low-noise wearing courses evaluated by tire/road noise measurements using the close-proximity method. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 111, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, U. Road traffic noise—The influence of the road surface and its characterization. Appl. Acoust. 1987, 21, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; van Keulen, W.; Ceylan, H.; Cao, D.; van de Ven, M.; Molenaar, A. Pavement stiffness measurements in relation to mechanical impedance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, V.F.; Paje, S.E. Dynamic stiffness assessment of construction materials by the resonant and non-resonant methods. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2016, 35, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









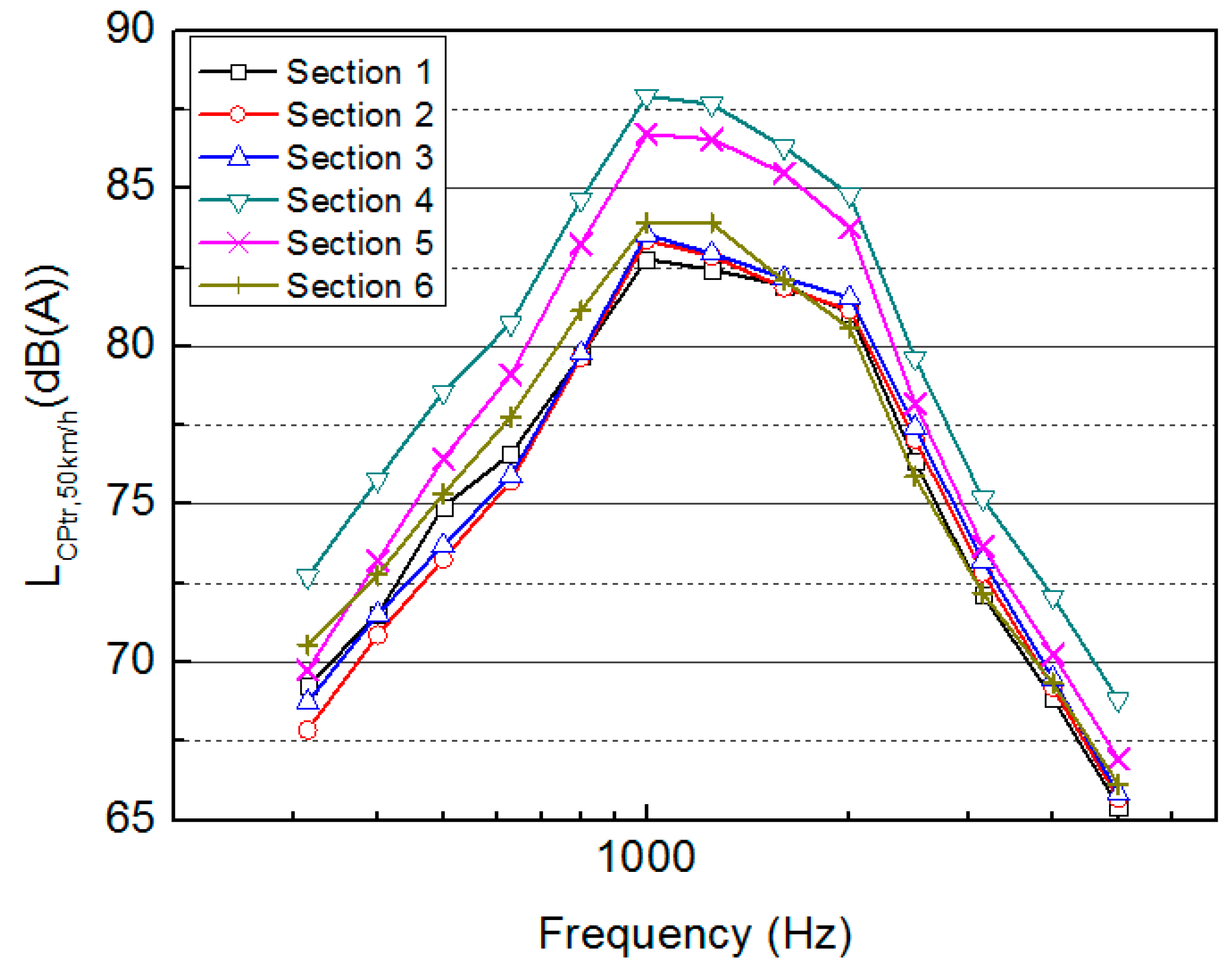


| Section | Street | Mixture Type (MAS, mm) | Age (Years) | Vehicles/Day | Use (Left/Right) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N-401 Toledo road | Slurry Seal (10) | >3 | 6200 | Dwellings/Business park |
| 2 | N-430C Ronda Toledo | Slurry Seal (10) | >10 | – | Dwellings/Schools, Univ. |
| 3 | N-430C Ronda Calatrava | Slurry Seal (10) | >10 | – | Dwellings/Schools, Univ. |
| 4 | N-430 Crossing | Asphalt Concrete (22) | >8 | 11,157 | Schools, Univ./Dwellings |
| 5 | N-430 Carrion road | Asphalt Concrete (22) | >8 | – | Business park/Business park |
| 6 | N-430 Ronda La Mata | Slurry Seal (10) | >10 | – | Schools/Dwellings |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez, V.F.; Terán, F.; Huertas, P.; Paje, S.E. Surface Aging Effect on Tire/Pavement Noise Medium-Term Evolution in a Medium-Size City. Coatings 2018, 8, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060206
Vázquez VF, Terán F, Huertas P, Paje SE. Surface Aging Effect on Tire/Pavement Noise Medium-Term Evolution in a Medium-Size City. Coatings. 2018; 8(6):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060206
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez, Víctor F., Fernando Terán, Pedro Huertas, and Santiago Expósito Paje. 2018. "Surface Aging Effect on Tire/Pavement Noise Medium-Term Evolution in a Medium-Size City" Coatings 8, no. 6: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060206
APA StyleVázquez, V. F., Terán, F., Huertas, P., & Paje, S. E. (2018). Surface Aging Effect on Tire/Pavement Noise Medium-Term Evolution in a Medium-Size City. Coatings, 8(6), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060206





