Omnidirectional SiO2 AR Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication Method
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Optical Simulation for Designing AR Coating
3. Results and Discussion
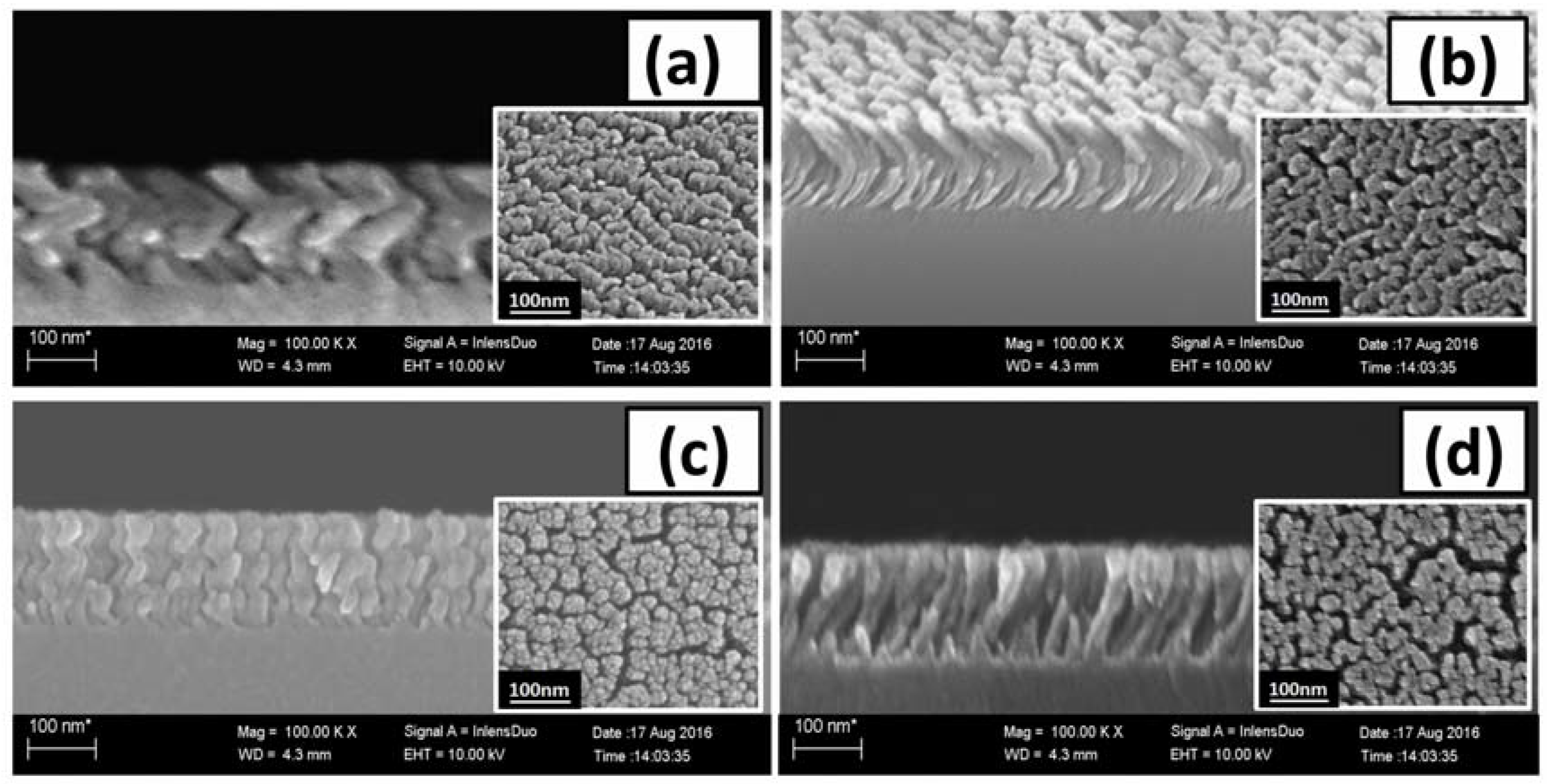
3.1. Morphological Study of SiO2 Single Layer Nanostructures
3.1.1. Nanozigzag, Nanohelix, Slanting and C-Shape SiO2 Nanofilms Fabrication
3.1.2. SiO2 Nanostructures Growth Mechanism
3.2. Refractive Index Analysis
3.3. Fabrication of SiO2 AR Coatings
3.4. AR Efficiency of SiO2 AR Coatings
3.5. Omnidirectional AR Efficiency of SiO2 AR Coatings
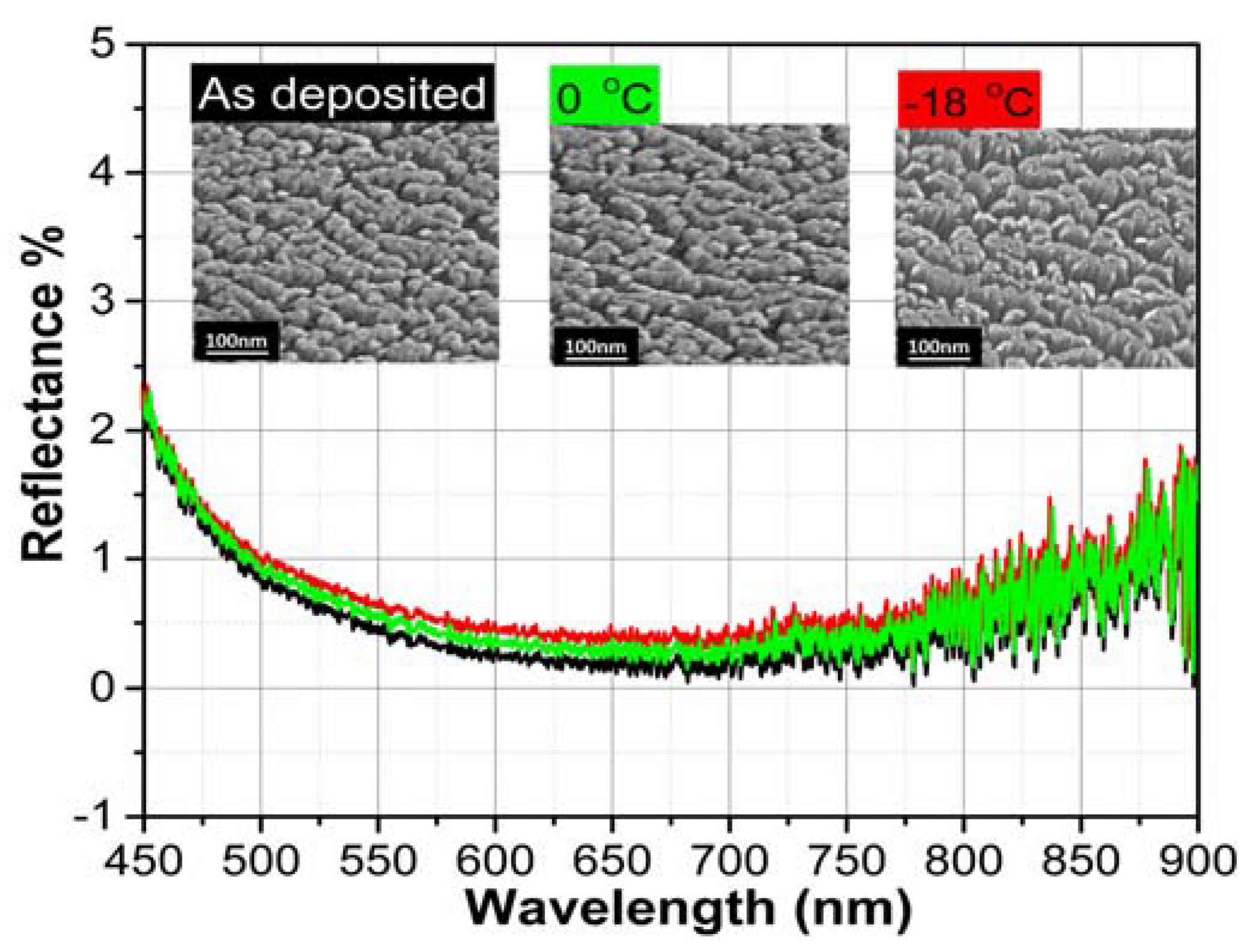
3.6. Negative Temperature Stability
3.7. Annealing Influence on AR Proficiency of SiO2 AR Coatings
3.8. Contact Angle Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Ding, R.; Xu, Y. Effect of post-treatment on ordered mesoporous silica antireflective coating. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50873–50881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Li, X.; Shen, J. Preparation and properties of ordered mesoporous silica antireflective coating with high strength. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; He, J. Antifogging and antireflection coatings fabricated by integrating solid and mesoporous silica nanoparticles without any post-treatments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlstrom, J.E.; Ade, P.A.R.; Aird, K.A.; Benson, B.A.; Bleem, L.E.; Busetti, S.; Chang, C.L.; Chauvin, E.; Cho, H.M.; Crawford, T.M. The 10 meter south pole telescope. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2009, 123, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelzenberg, M.D.; Boettcher, S.W.; Petykiewicz, J.A.; Turnerevans, D.B.; Putnam, M.C.; Warren, E.L.; Spurgeon, J.M.; Briggs, R.M.; Lewis, N.S.; Atwater, H.A. Enhanced absorption and carrier collection in Si wire arrays for photovoltaic applications. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Thompson, C.; Fleming, R.A. Antireflective Coating for Glass Applications and Method of Forming Same. U.S. Patent WO2014134594A1, 4 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Moghal, J.; Kobler, J.; Sauer, J.; Best, J.; Gardener, M.; Watt, A.A.R.; Wakefield, G. High-performance, single-layer antireflective optical coatings comprising mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 4, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; He, J. A novel precursor-derived one-step growth approach to fabrication of highly antireflective, mechanically robust and self-healing nanoporous silica thin films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Wei, T.; Lan, P.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Song, W. Investigation on antireflection coatings for Al:ZnO in silicon thin-film solar cells. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron. Opt. 2013, 124, 3392–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Dantan, J.Y.; Etienne, A.; Siadat, A.; Martin, P. Improved algorithm for tolerance allocation based on Monte Carlo simulation and discrete optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 56, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, E.H.S.D.C.; König, P.; Jilavi, M.H.; Oliveira, P.W.D.; Júnior, S.A. Carboxylic acids and esters as scaffold for cavities in porous single layer anti-reflective coatings of silica-titania with excellent optical and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2014, 5, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; He, J. Mechanically robust, humidity-resistant, thermally stable high performance antireflective thin films with reinforcing silicon phosphate centers. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 170, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khristyan, V.A.; Zagoruiko, Y.A.; Kovalenko, N.O.; Mateychenko, P.V.; Sofronov, D.S. Thermally stable antireflection coatings for active elements of ZnMgSe:Cr2+–laser: Preparation and properties. Funct. Mater. 2011, 18, 462–465. [Google Scholar]
- Doroshenko, M.E.; Osiko, V.V.; Jelínková, H.; Jelínek, M.; Šulc, J.; Němec, M.; Vyhlídal, D.; Čech, M.; Kovalenko, N.O.; Gerasimenko, A.S. Spectroscopic and laser properties of bulk iron doped zinc magnesium selenide Fe:ZnMgSe generating at 4.5–5.1 µm. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 19824–19834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Hadi, S.; Milakovich, T.; Bulsara, M.T.; Saylan, S. Design optimization of single-layer antireflective coating for GaAs1−xPx/Si Tandem Cells With x = 0, 0.17, 0.29, and 0.37. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2014, 5, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, S.; Milakovich, T.; Hadi, S.A.; Nayfeh, A.; Fitzgerald, E.A.; Dahlem, M.S. Multilayer antireflection coating design for GaAs 0.69 P 0.31/Si dual-junction solar cells. Sol. Energy 2015, 122, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Correa, R.; Morales-Acevedo, A.; Mora, A.; Pulzara, L.; Monsalve, J.M. Design of AlxGa1−xAs/GaAs/InyGa1−yAs triple junction solar cells with anti-reflective coating. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 37, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Wu, H.; Huai, X.; Zou, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Mechanically robust antireflective coatings. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, J.; Char, K. Thermally stable antireflective coatings based on nanoporous organosilicate thin films. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6737–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yan, H.; Li, D.; Qiao, L.; Han, S.; Yuan, X.; Liu, W.; Xiang, X.; Zu, X. TEM and STEM studies on the cross-sectional morphologies of Dual-/Tri-layer broadband SiO2 antireflective films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Hong, R. One-step sol-gel preparation of hydrophobic antireflective SiO2 coating on poly(methyl methacrylate) substrate. Mater. Lett. 2017, 208, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S.R.; Brett, M.J. Porous broadband antireflection coating by glancing angle deposition. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 4573–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Lan, P.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Tan, R.; Song, W.; Choy, K.L. Design, preparation, and durability of TiO2/SiO2 and ZrO2/SiO2 double-layer antireflective coatings in crystalline silicon solar modules. Sol. Energy 2013, 89, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Green, M.A. Optimized antireflection coatings for high-efficiency silicon solar cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1991, 38, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lan, P.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, L.; Lu, Y.; Dai, N.; Song, W. Sol-gel derived near-UV and visible antireflection coatings from hybridized hollow silica nanospheres. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 71, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; He, J. Facile fabrication of hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres for superhydrophilic and visible/near-IR antireflection coatings. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 8165–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Du, K.; Zhou, L.; Tu, H. Preparation of silica antireflective coating for UV-laser. Acta Opt. Sin. 1996, 16, 998–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Belleville, P.F.; Floch, H.G. Ammonia hardening of porous silica antireflective coatings. In Proc. SPIE 2288, Sol-Gel Optics III, Proceedings of SPIE’s 1994 International Symposium on Optics, Imaging, and Instrumentation, San Diego, CA, USA, 24-29 July 1994; Mackenzie, J.D., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; He, J. One-Pot fabrication of antireflective/antibacterial dual-function Ag NP-containing mesoporous silica thin films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 13, 11189–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, M.; Wojcieszak, D.; Domaradzki, J.; Kaczmarek, D.; Song, S.; Placido, F. TiO2/SiO2 multilayer as an antireflective and protective coating deposited by microwave assisted magnetron sputtering. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2013, 21, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuu, D.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, C.N.; Lee, H.H.; Huang, J.J. Properties of double-layer Al2O3/TiO2 antireflection coatings by liquid phase deposition. Thin Solid Films 2015, 584, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Lee, Y.T. Self-cleaning and antireflection properties of titanium oxide film by liquid phase deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 231, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.F.J.; Tu, H.M.; Su, T.L. Optimization of the electron-beam-lithography parameters for the moth-eye effects of an antireflection matrix structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 5303–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z. Bilayer SiO2 nanorod arrays as omnidirectional and thermally stable antireflective coating. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, G.S.; Bayón, R.; Germán, N.; Morales, A. Long-term durability of sol–gel porous coatings for solar glass covers. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 3157–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Wu, H.; Ma, L.; Hou, M.; Zhang, Z. HfO2 nanorod array as high-performance and high-temperature antireflective coating. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirolkar, M.; Kazemian Abyaneh, M.; Singh, A.; Tomer, A.; Choudhary, R.; Sathe, V.; Phase, D.; Kulkarni, S. Rapidly switched wettability of titania films deposited by dc magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Suzuki, S.; Odaka, H.; Hosono, H. Photocatalytic TiO2 thin film deposited onto glass by DC magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2001, 392, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, M.; Tomás, S.A.; Santoyo-Salazar, J.; Morales-Luna, M. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2–ZnO thin films deposited by dc reactive magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 2017, 12, 8831–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, M.; Tomás, S.A.; Morales-Luna, M.; Arvizu, M.A.; Tellez-Cruz, M.M. Optical, structural, and morphological properties of photocatalytic TiO2–ZnO thin films synthesized by the sol–gel process. Thin Solid Films 2015, 594, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Morphology | Deposition Angle (α) | Refractive Index (η) | Thickness (nm) dS | Thickness (nm) dE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer-1 | Layer-2 | Layer-1 | Layer-2 | Layer-1 | Layer-2 | Layer-1 | Layer-2 | |
| Nanozigzag | 0 | 80 | 1.45 | 1.173 | 65 | 130 | 70 | 130 |
| C-shape | 0 | 80 | 1.45 | 1.179 | 75 | 135 | 78 | 141 |
| Nanohelix | 0 | 80 | 1.45 | 1.18 | 60 | 142 | 56 | 147 |
| Slanting | 0 | 80 | 1.45 | 1.19 | 64 | 130 | 56 | 125 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, S.B.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z. Omnidirectional SiO2 AR Coatings. Coatings 2018, 8, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060210
Khan SB, Wu H, Zhang Z. Omnidirectional SiO2 AR Coatings. Coatings. 2018; 8(6):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060210
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Sadaf Bashir, Hui Wu, and Zhengjun Zhang. 2018. "Omnidirectional SiO2 AR Coatings" Coatings 8, no. 6: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060210
APA StyleKhan, S. B., Wu, H., & Zhang, Z. (2018). Omnidirectional SiO2 AR Coatings. Coatings, 8(6), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8060210