Control of Polydimethylsiloxane Surface Hydrophobicity by Plasma Polymerized Hexamethyldisilazane Deposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
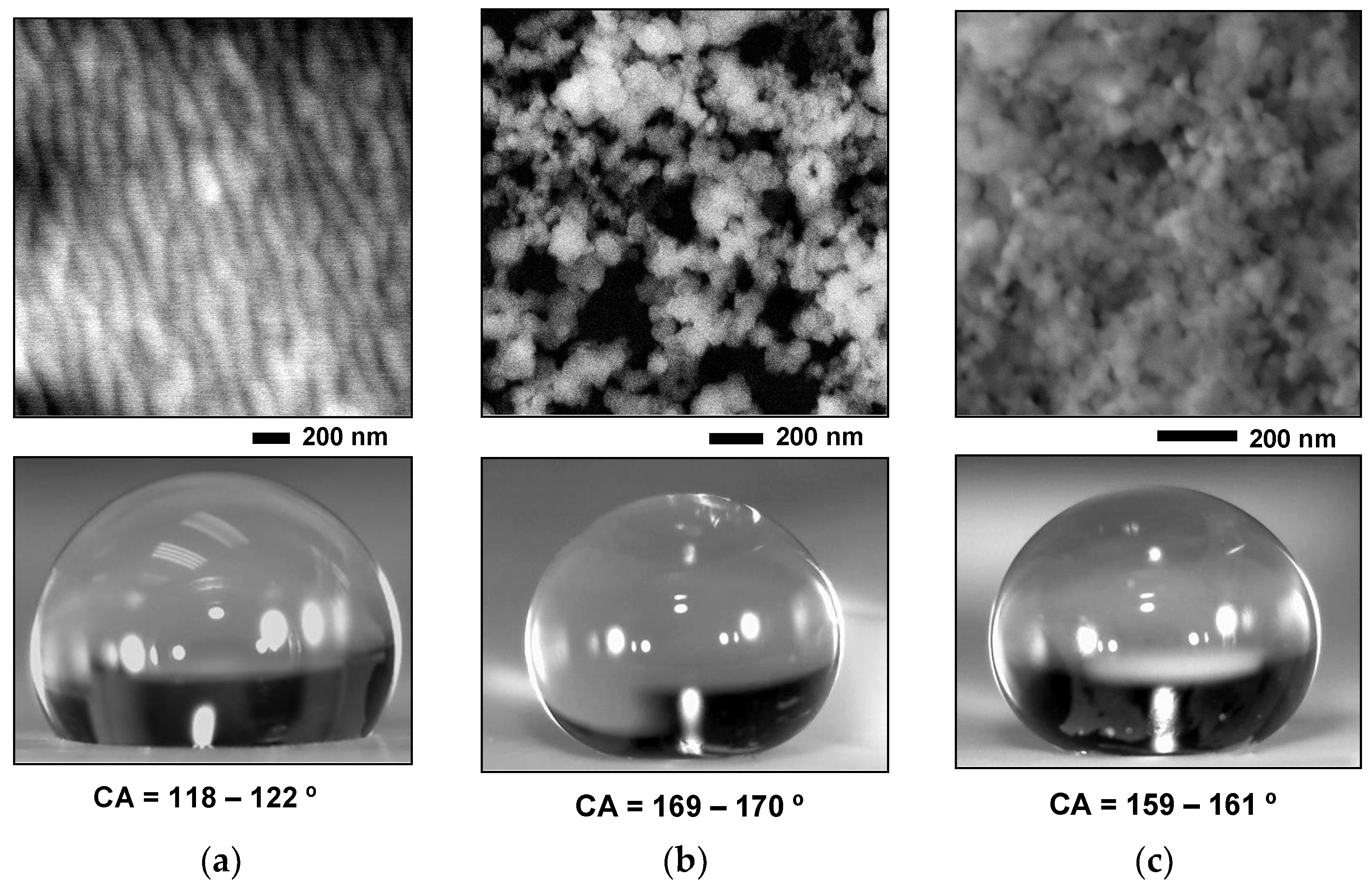
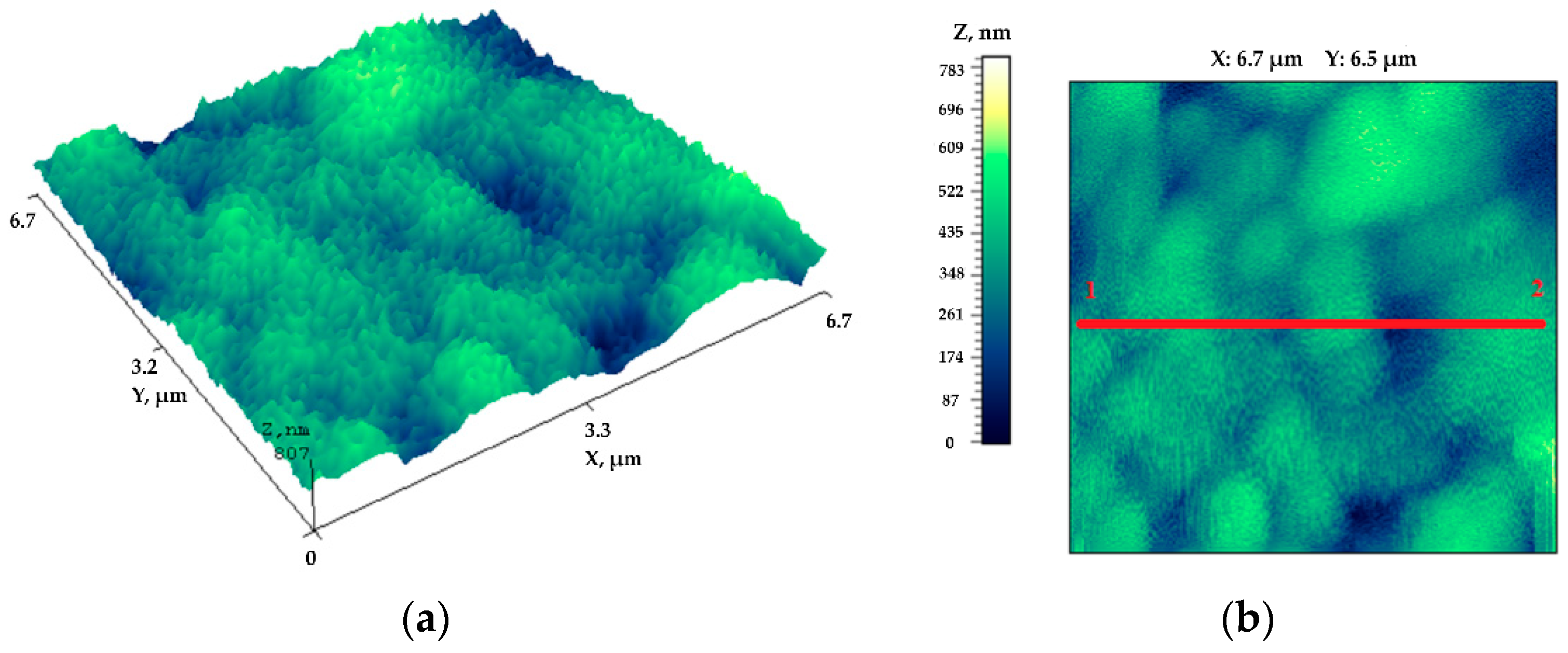
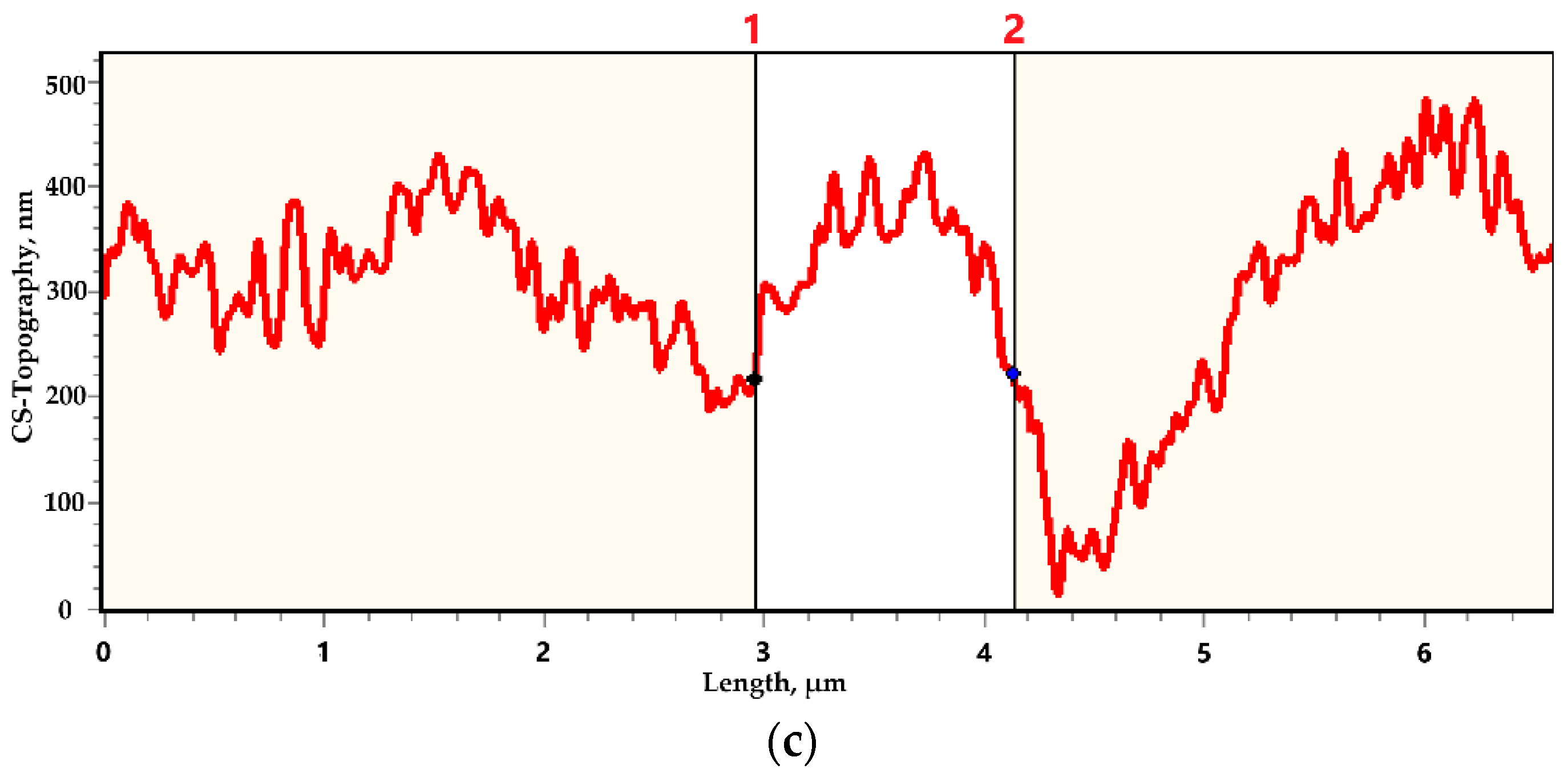
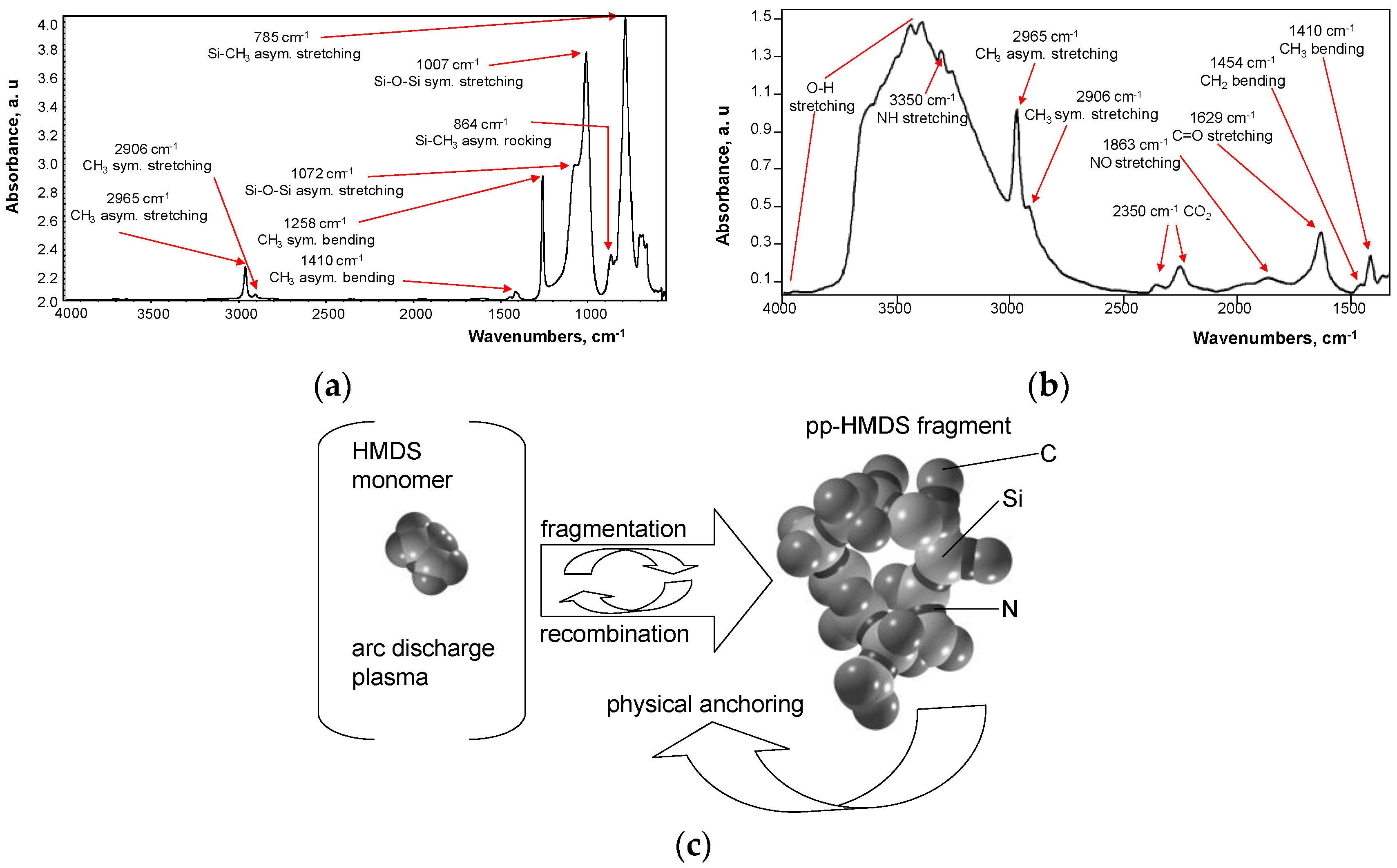
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Pi, P.; Wen, X.; Zheng, D.; Xu, M.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Z. A novel method to fabricate superhydrophobic surfaces based on well-defined mulberry-like particles and self-assembly of polydimethylsiloxane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3507–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, G.; Stevens, B. A cost-effective two-step method for enhancing the hydrophilicity of PDMS surfaces. BioChip J. 2014, 14, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.T.S.; Santos, A.S.F.; Santos, I.M.G.; Silva, M.R.S.; Bomio, M.R.D.; Longo, E.; Paskocimas, C.A.; Motta, F.V. TiO2/PDMS nanocomposites for use on self-cleaning surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 239, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropmann, A.; Tanguy, L.; Koltay, P.; Zengerle, R.; Riegger, L. Completely superhydrophobic PDMS surfaces for microfluidics. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8292–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, B.J.; Bharathidasan, T.; Anandan, C. Superhydrophobic oleophobic PDMS-silica nanocomposite coating. Surf. Innov. 2013, 1, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Bhushan, B. Transparent, wear-resistant, superhydrophobic and superoleophobic poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 488, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorasani, M.T.; Mirzadeh, H. In vitro blood compatibility of modified PDMS surfaces as superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpilowski, K.; Goncharuk, O. Hydrophobic properties of hexamethyldisilazane modified nanostructured silica films on glass: Effect of plasma pre-treatment of glass and polycondensation features. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 016409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protsak, I.; Pakhlov, E.; Tertykh, V.; Le, Z.-C.; Dong, W. A new route for preparation of hydrophobic silica nanoparticles using a mixture of poly(dimethylsiloxane) and diethyl carbonate. Polymers 2018, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazauskas, A.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Grigaliūnas, V.; Jucius, D.; Guobienė, A.; Prosyčevas, I.; Narmontas, P. Characterization of plasma polymerized hexamethyldisiloxane films prepared by arc discharge. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2014, 34, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, A.; Kulik, G.; Sage, D.; Barbieri, L.; Hoffmann, P. A snake-based approach to accurate determination of both contact points and contact angles. Colloid Surf. A 2006, 286, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, D.; Neyer, A.; Kuckuk, R.; Heise, H.M. Raman, mid-infrared, near-infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy of PDMS silicone rubber for characterization of polymer optical waveguide materials. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 976, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielens, F.; Gervais, C.; Lambert, J.F.; Mauri, F.; Costa, D. Ab initio study of the hydroxylated surface of amorphous silica: A representative model. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3336–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimoldi, E.; Zanini, S.; Siliprandi, R.; Riccardi, C. AFM and contact angle investigation of growth and structure of pp-HMDSO thin films. Eur. Phys. J. D 2009, 54, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benıtez, F.; Martınez, E.; Esteve, J. Improvement of hardness in plasma polymerized hexamethyldisiloxane coatings by silica-like surface modification. Thin Solid Films 2000, 377, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; Muller, R.S.; Tobias, C.W. Chemical surface modification of porous silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Lukac, P.J.; Yu, T.; Weiss, R.G. Reversible, room-temperature, chiral ionic liquids. Amidinium carbamates derived from amidines and amino-acid esters with carbon dioxide. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4761–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, R.Y.; Mota, R.P.; Batocki, R.; Santos, D.; Nicoleti, T.; Kostov, K.; Kayama, M.; Algatti, M.; Cruz, N.; Ruggiero, L. Plasma-polymerized hexamethyldisilazane treated by nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation technique. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 167, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Haag, R. Universal polymer coatings and their representative biomedical applications. Mater. Horiz. 2015, 2, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankauskaitė, V.; Narmontas, P.; Lazauskas, A. Control of Polydimethylsiloxane Surface Hydrophobicity by Plasma Polymerized Hexamethyldisilazane Deposition. Coatings 2019, 9, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010036
Jankauskaitė V, Narmontas P, Lazauskas A. Control of Polydimethylsiloxane Surface Hydrophobicity by Plasma Polymerized Hexamethyldisilazane Deposition. Coatings. 2019; 9(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankauskaitė, Virginija, Pranas Narmontas, and Algirdas Lazauskas. 2019. "Control of Polydimethylsiloxane Surface Hydrophobicity by Plasma Polymerized Hexamethyldisilazane Deposition" Coatings 9, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010036
APA StyleJankauskaitė, V., Narmontas, P., & Lazauskas, A. (2019). Control of Polydimethylsiloxane Surface Hydrophobicity by Plasma Polymerized Hexamethyldisilazane Deposition. Coatings, 9(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9010036




