The Implication of Benzene–Ethanol Extractive on Mechanical Properties of Waterborne Coating and Wood Cell Wall by Nanoindentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
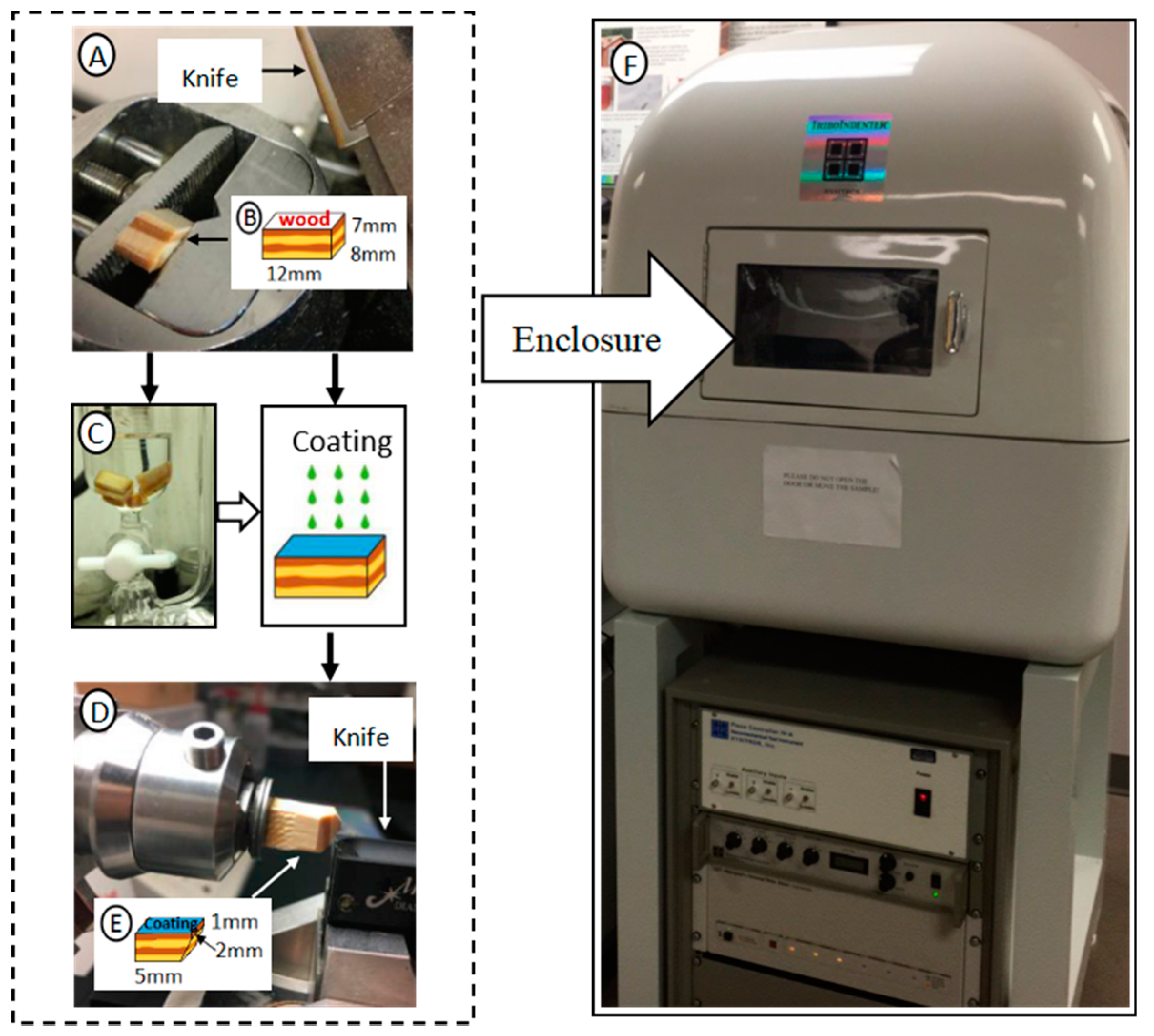
2.2. Sample Preparation by Ethanol-Toluene Extraction
2.3. Coating Process
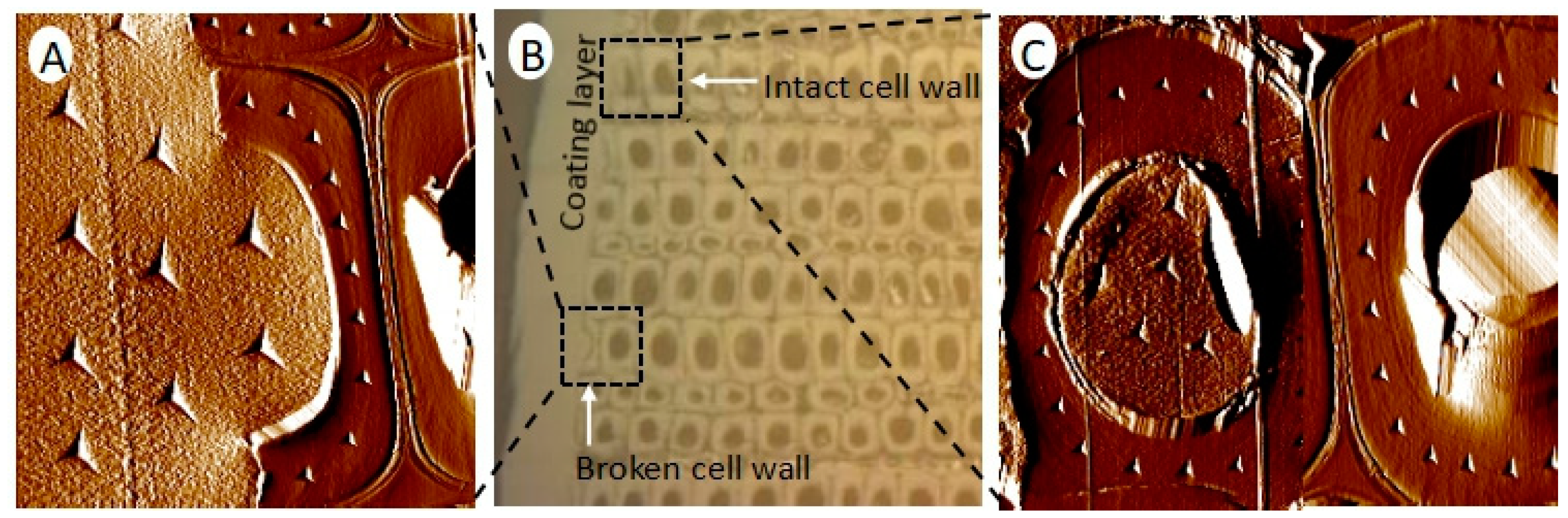
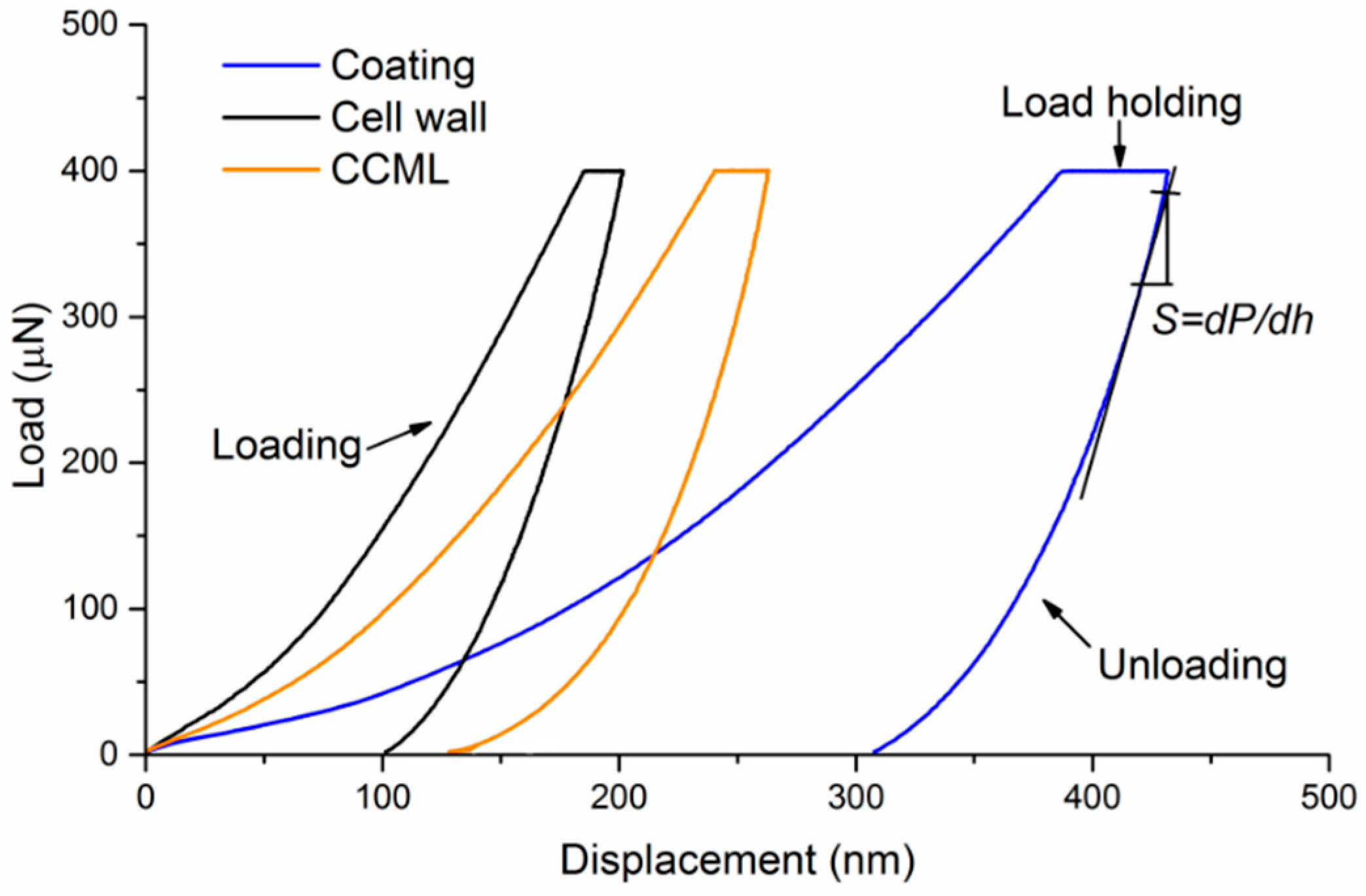
2.4. Nanoindentation
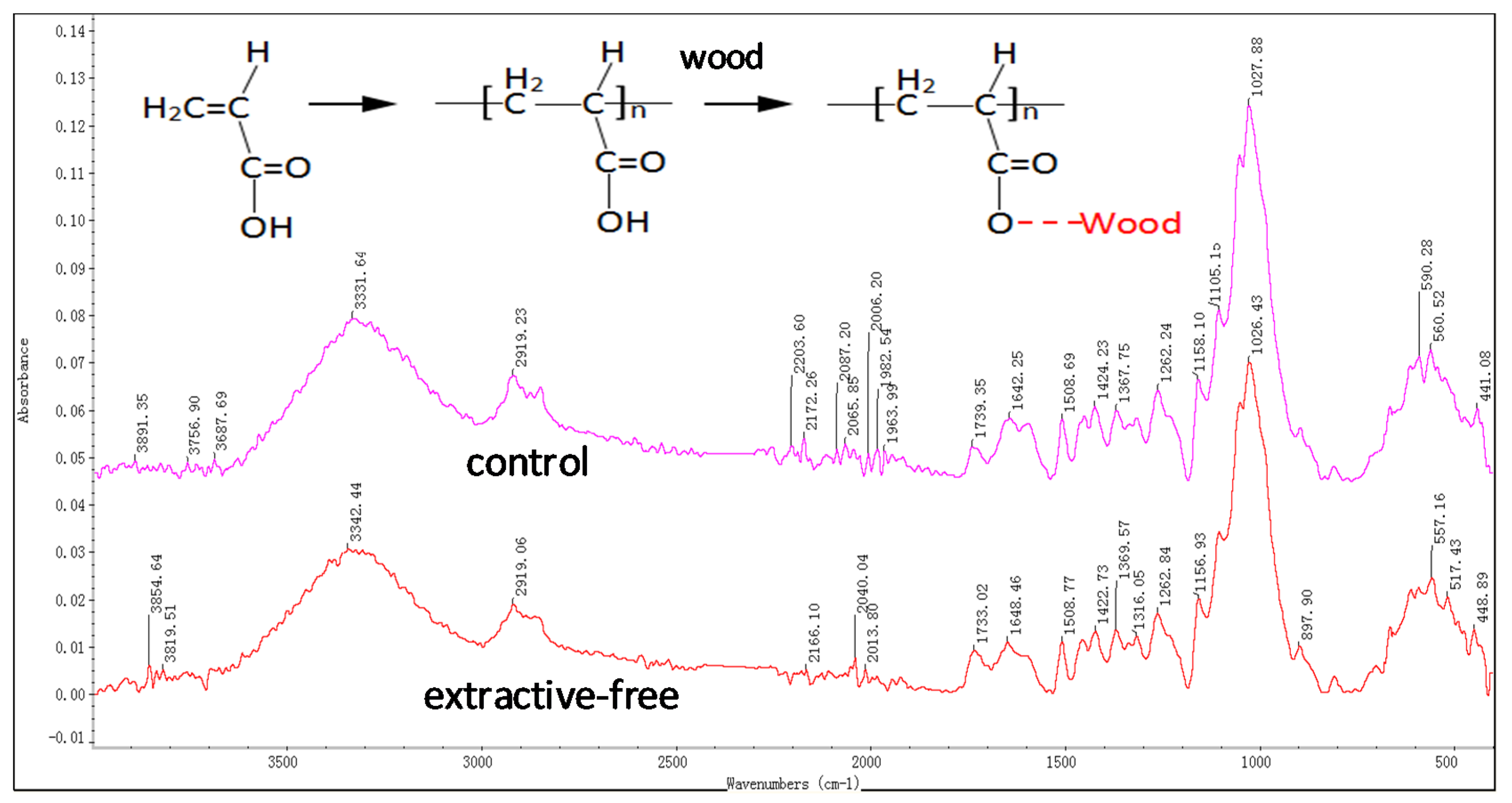
2.5. FT-IR Analysis
2.6. Specific Surface Area Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Analysis Combined with FT-IR
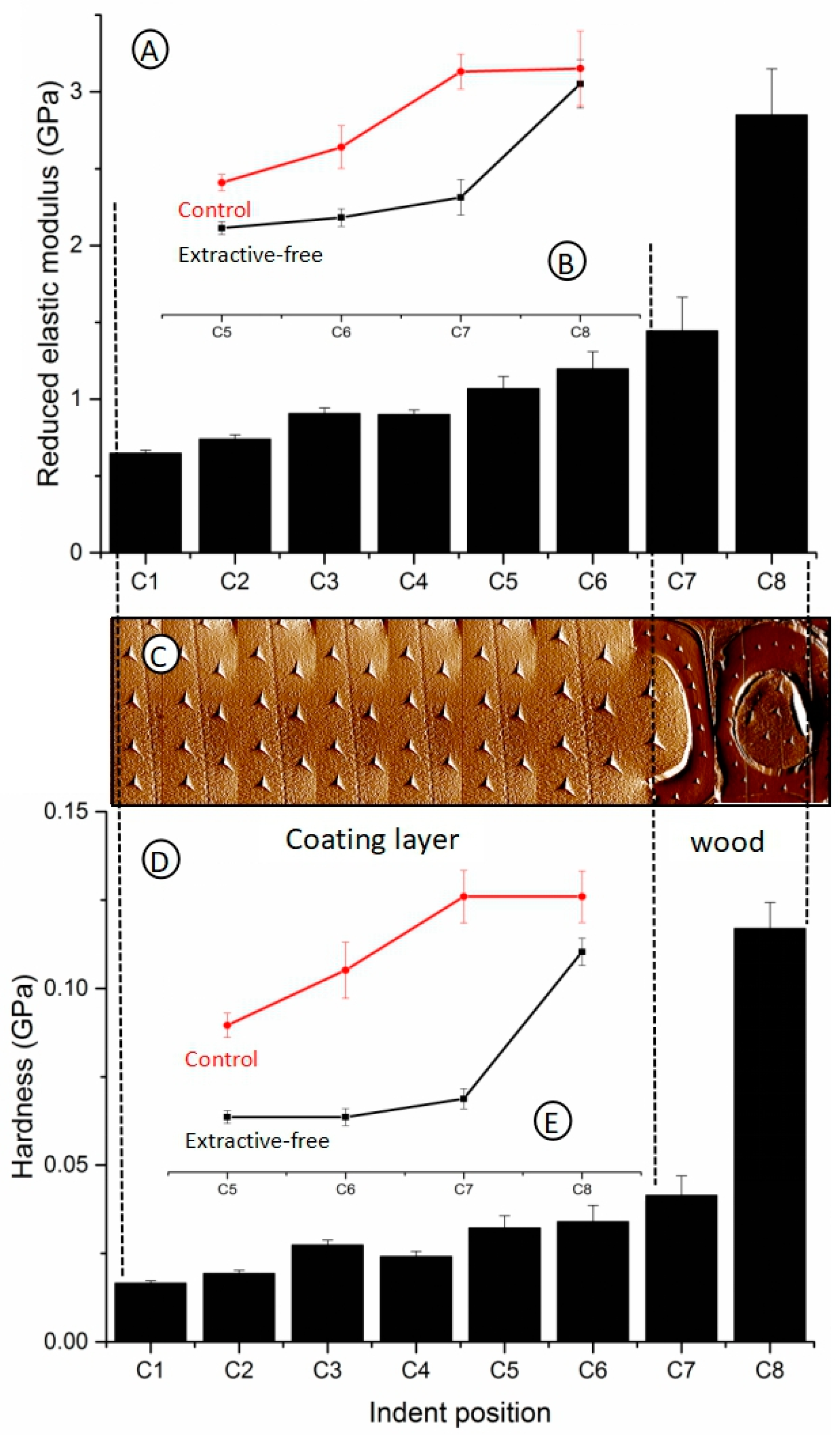
3.2. Reduced Elastic Modulus and Hardness of Coating Layer
3.3. Reduced Elastic Modulus and Hardness of Wood Cell Wall
4. Conclusions
- The elastic modulus and the hardness of acrylic coating decreased by 16% and 5% for extractive-free wood compared with the control wood, indicating that the extracted material prevented the coating from entering the wood cell wall cavities. However, the wood hardness in CCML layer decreased significantly, indicating that the water-based coating entered into the wood cell when the wood surface was extracted, resulting in a decline to its mechanical properties.
- The specific surface area of the extractive-free wood increased, and the specific surface area was positively correlated with the adsorption capacity, indicating that compared with the control wood, the adsorption ability of the extractive-free wood to the waterborne coating was enhanced.
- The surface characteristics of extractive-free wood changed greatly compared to a control. FT-IR analysis showed that the O–H bond in waterborne coatings combined with the wood extract to form stable structures, indicating that the extractive-free wood reacts with the waterborne coating and enhance the performance of the coating on the wood.
Reference
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, W.; Wu, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Q. GC/MS determination of bioactive constituents of benzene/ethanol extractive of leaves of two eucalyptus cultivars. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai, China, 16–18 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Peng, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Peng, W. Study on benzene/ethanol extractives of eucalyptus urophylla chips for bioenergy with high added value by Py-GC/MS. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Power & Energy Engineering Conference, Wuhan, China, 27–31 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Zhu, T.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, Z.; Li, K.; Li, N. Present situation and trend of wood extraction. For. Sci. Technol. 2004, 18, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wei, W.; Qiao, J. Determination of high-grade resource recovery of acetone extractives of masson pine (Pinus Massoniana L.) wood chips by Py-GC/MS. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai, China, 16–18 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, R.; Lucas, B.N.; Oliver, W.C.; Tsui, T.Y. Longitudinal hardness and Young’s modulus of spruce tracheid secondary walls using nanoindentation technique. J. Wood Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tian, G.; Wang, H.; Fei, B.; Wang, G. Mechanical characterization of single bamboo fibers with nanoindentation and microtensile technique. Holzforschung 2011, 65, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Jakes, J.E.; Frihart, C.R.; Beecher, J.F.; Moon, R.J.; Stone, D.S. Experimental method to account for structural compliance in nanoindentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, S.; Liao, C.; Meng, Y.; Pham, T. Nanoscale characterization of reed stalk fiber cell walls. BioResources 2013, 8, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, S.; Min, C.; Meng, Y.; Pham, T.; Ying, Y. Evaluation of the effects of compression combined with heat treatment by nanoindentation (NI) of poplar cell walls. Holzforschung 2014, 68, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Huang, C.; Meng, Y.; Fu, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q. Quasi-static and dynamic nanoindentation to determine the influence of thermal treatment on the mechanical properties of bamboo cell walls. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Effect of the penetration of isocyanates (pMDI) on the nanomechanics of wood cell wall evaluated by AFM-IR and nanoindentation (NI). Holzforschung 2017, 72, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanyan, V.; Galstian, T.; Riedl, B. Characterization of cellulose nanocrystals dispersion in varnishes by backscattering of laser light. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2015, 12, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custódio, J.E.P.; Eusébio, M.I. Waterborne acrylic varnishes durability on wood surfaces for exterior exposure. Prog. Org. Coat. 2006, 56, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklečić, J.; Blagojević, S.L.; Petrič, M.; Jirouš-Rajković, V. Influence of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on properties of waterborne polyacrylate coating exposed to outdoor conditions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 89, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.; Min, D.; Yong, Q. Effect of kraft pulping pretreatment on the chemical composition, enzymatic digestibility, and sugar release of moso bamboo residues. BioResources 2015, 10, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; He, J.; Du, L.; Min, D.; Yong, Q. Structural characterization of the lignins from the green and yellow bamboo of bamboo culm (Phyllostachys pubescens). J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2016, 36, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Swaboda, C.; Roessler, A.; Böttcher, H. Functionalising wood by nanosol application. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.-Q.; Bao, Y.-L.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, R.; Miyakoshi, T. Study on mechanical and electrical properties of cellulose nanofibrils/graphene-modified natural rubber. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 223, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Su, Y.; Shi, J.; Yuan, C.; Zhai, S.; Yong, Q. Revealing the effects of centuries of ageing on the chemical structural features of lignin in archaeological fir woods. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüneberger, F.; Künniger, T.; Zimmermann, T.; Arnold, M. Rheology of nanofibrillated cellulose/acrylate systems for coating applications. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonderegger, W.; Glaunsinger, M.; Mannes, D.; Volkmer, T.; Niemz, P. Investigations into the influence of two different wood coatings on water diffusion determined by means of neutron imaging. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2015, 73, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, A.; Corcione, C.E.; Frigione, M.; Pegoretti, A. Photocurable resin/nanocellulose composite coatings for wood protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 106, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboorani, A.; Auclair, N.; Riedl, B.; Landry, V. Physical and morphological properties of UV-cured cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) based nanocomposite coatings for wood furniture. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 93, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Lu, R.; Miyakoshi, T. Species and release characteristics of VOCs in furniture coating process. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Hayashi, S.; Xu, W.; Wu, Z.; Tanaka, S.; Sun, S.; Zhang, M.; Kanayama, K.; Umemura, K. A novel eco-friendly wood adhesive composed by sucrose and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate. Polymers 2018, 10, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gindl, W.; Dessipri, E.; Wimmer, R.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Using UV-microscopy to study diffusion of melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin in cell walls of spruce wood. Holzforschung 2002, 56, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnerth, J.; Gierlinger, N.; Keckes, J.; Gindl, W.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Actual versus apparent within cell wall variability of nanoindentation results from wood cell walls related to cellulose microfibril angle. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 4399–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Konnerth, J. Observation of the influence of temperature on the mechanical properties of wood adhesives by nanoindentation. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 714–717. [Google Scholar]
- Konnerth, J.; Valla, A.; Gindl, W. Nanoindentation mapping of a wood-adhesive bond. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 88, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckel, F.; Konnerth, J.; Kantner, W.; Moser, J.; Gindl, W. Tensile shear strength of UF and MUF-bonded veneer related todata of adhesives and cell walls measured by nanoindentation. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckel, F.; Konnerth, J.; Moser, J.; Kantner, W.; Gindl, W. Micromechanical properties of the interphase in pMDI and UF bond lines. Wood Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y.; Kjoller, K.; Roy, A.; Wang, S. In situ identification of the molecular-scale interactions of phenol-formaldehyde resin and wood cell walls using infrared nanospectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 76318–76324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcott, C.; Lo, M.; Hu, Q.; Dillon, E.; Prater, C.B. Nanoscale infrared spectroscopy of polymer composites. Am. Lab. 2014, 46, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, G.B.; Foerster, C.E.; Da Silva, S.L.R.; Lepienski, C.M. Nanomechanical properties of rough surfaces. Mater. Res. 2006, 9, 9159–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, S.; Cai, Z.; Young, T.M.; Du, G.; Li, Y. A novel sample preparation method to avoid influence of embedding medium during nano-indentation. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 110, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanokwijitsilp, T.; Traiperm, P.; Osotchan, T.; Srikhirin, T. Development of abrasion resistance SiO2 nanocomposite coating for teak wood. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 93, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.; Deng, Y. Temperature-dependent mechanical properties of wood-adhesive bondline evaluated by nanoindentation. J. Adhes. 2016, 93, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, N.P.; Meng, X.; Elam, J.W.; Martinson, A.B. Atomic layer deposition of metal sulfide materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xie, X.; Zhao, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of the effects of nanoclay on the mechanical properties of wood/phenol formaldehyde bondlines. Int. J. Adhes. 2017, 74, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, F.; Konnerth, J.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Mechanical properties of adhesives for bonding wood—A review. Int. J. Adhes. 2013, 45, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Du, G.; Hosseinaei, O.; Wang, S.; Wang, H. Mechanical properties of secondary wall and compound corner middle lamella near the phenol-formaldehyde (PF) adhesive bond line measured by nanoindentation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 236, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. The Implication of Benzene–Ethanol Extractive on Mechanical Properties of Waterborne Coating and Wood Cell Wall by Nanoindentation. Coatings 2019, 9, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070449
Wu Y, Sun Y, Yang F, Zhang H, Wang Y. The Implication of Benzene–Ethanol Extractive on Mechanical Properties of Waterborne Coating and Wood Cell Wall by Nanoindentation. Coatings. 2019; 9(7):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070449
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yan, Yingchun Sun, Feng Yang, Haiqiao Zhang, and Yajing Wang. 2019. "The Implication of Benzene–Ethanol Extractive on Mechanical Properties of Waterborne Coating and Wood Cell Wall by Nanoindentation" Coatings 9, no. 7: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070449
APA StyleWu, Y., Sun, Y., Yang, F., Zhang, H., & Wang, Y. (2019). The Implication of Benzene–Ethanol Extractive on Mechanical Properties of Waterborne Coating and Wood Cell Wall by Nanoindentation. Coatings, 9(7), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9070449



