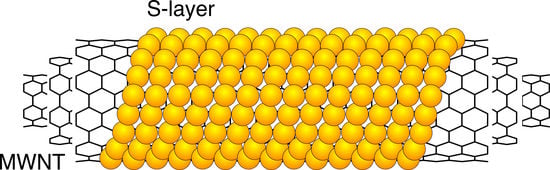
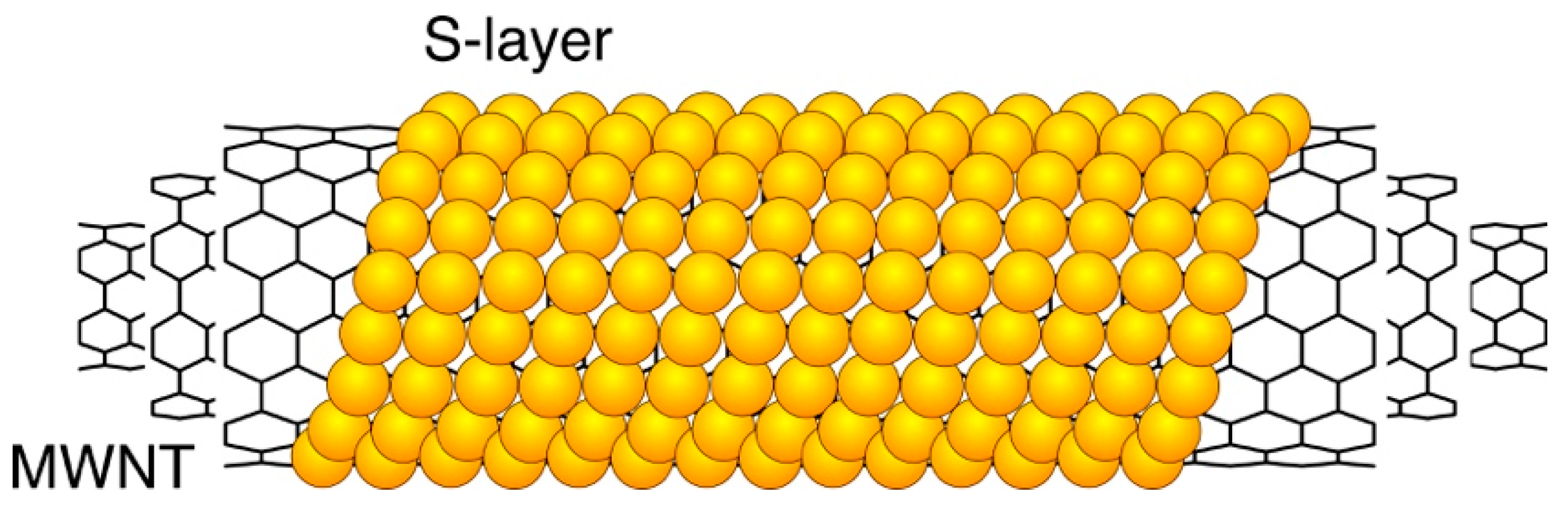
S-Layer Protein Coated Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Wild Type and Recombinant S-Layer Fusion Protein Solutions
2.2. Coating of -COOH Functionalized MWNTs with S-Layer Proteins
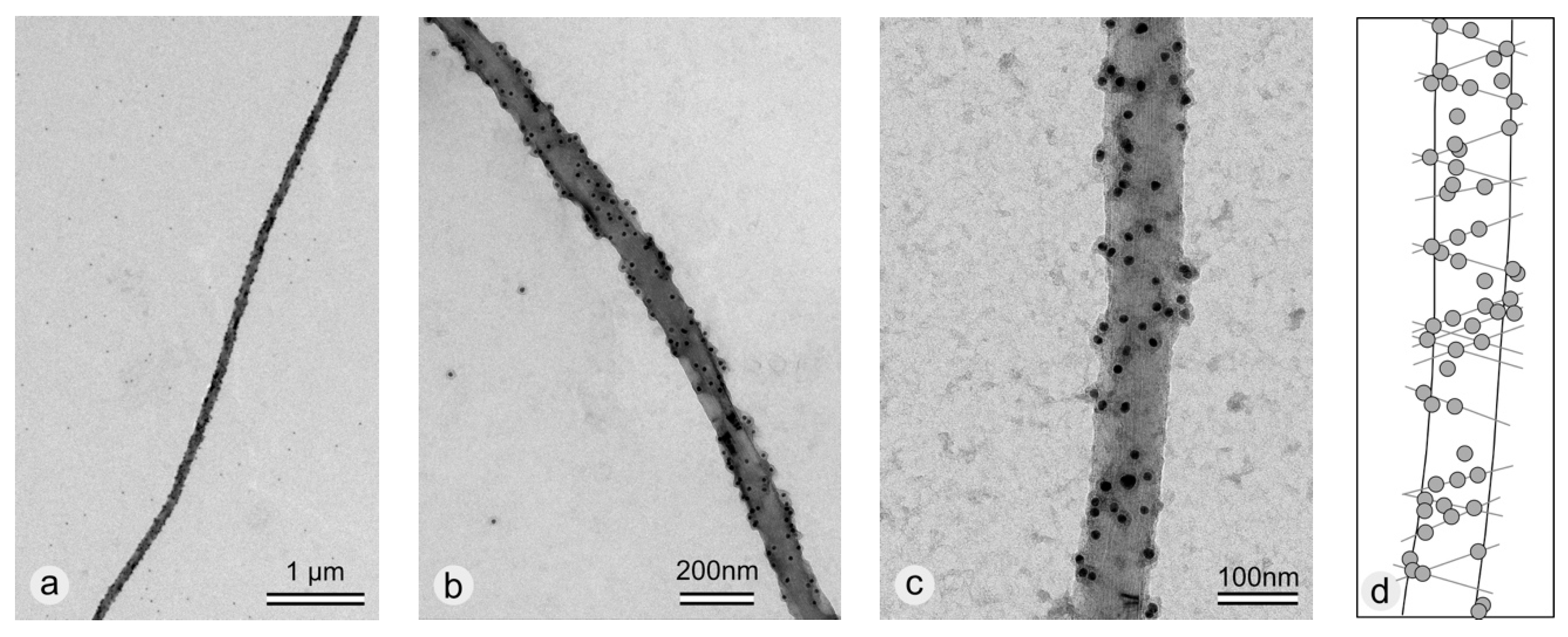
2.3. Immuno Gold Labeling of rSbpA31-1068GG Coated -COOH Functionalized MWNTs
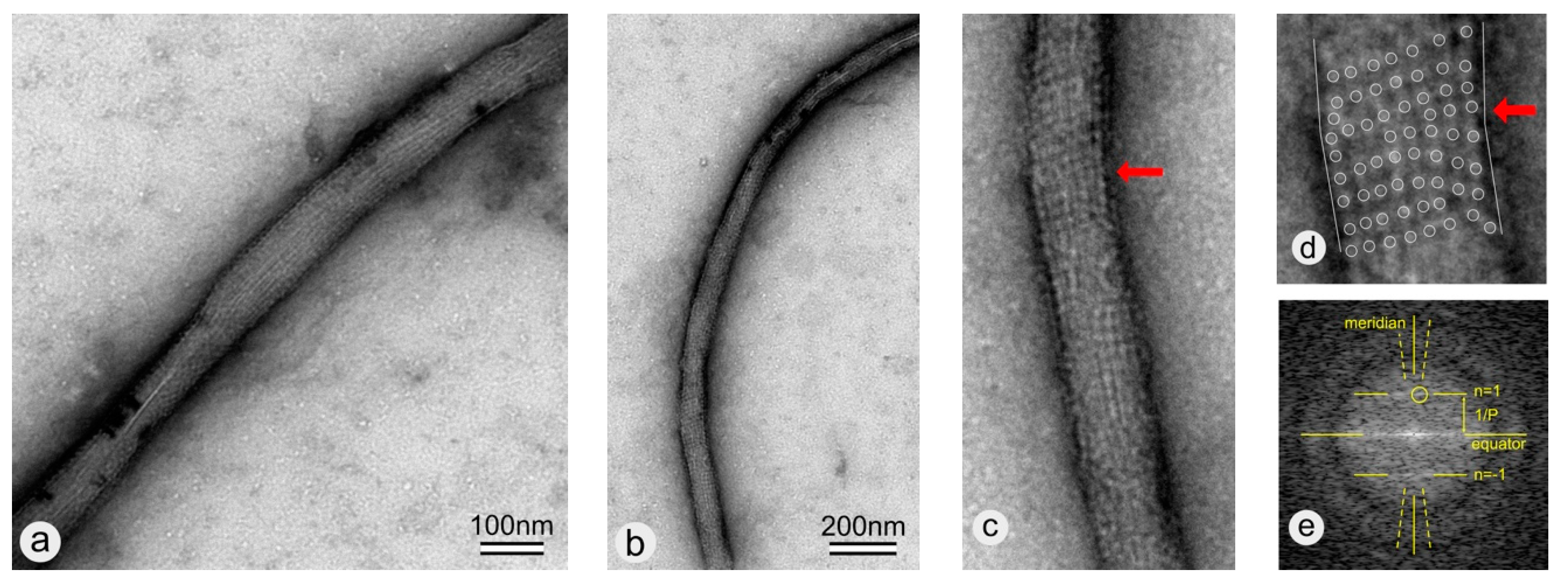
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Negative Staining, and Image Processing
2.5. Preparation of Bucky Paper and Scanning Electron Microscopy
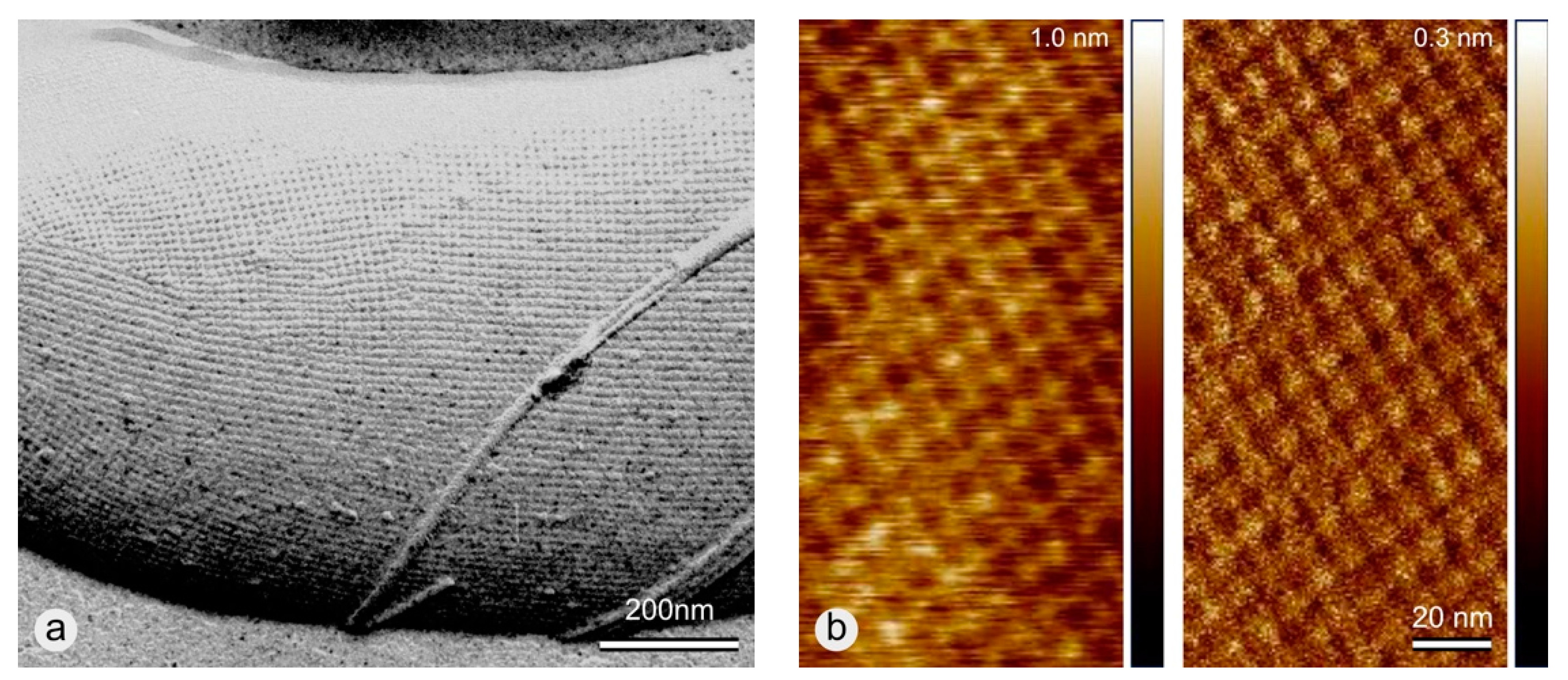
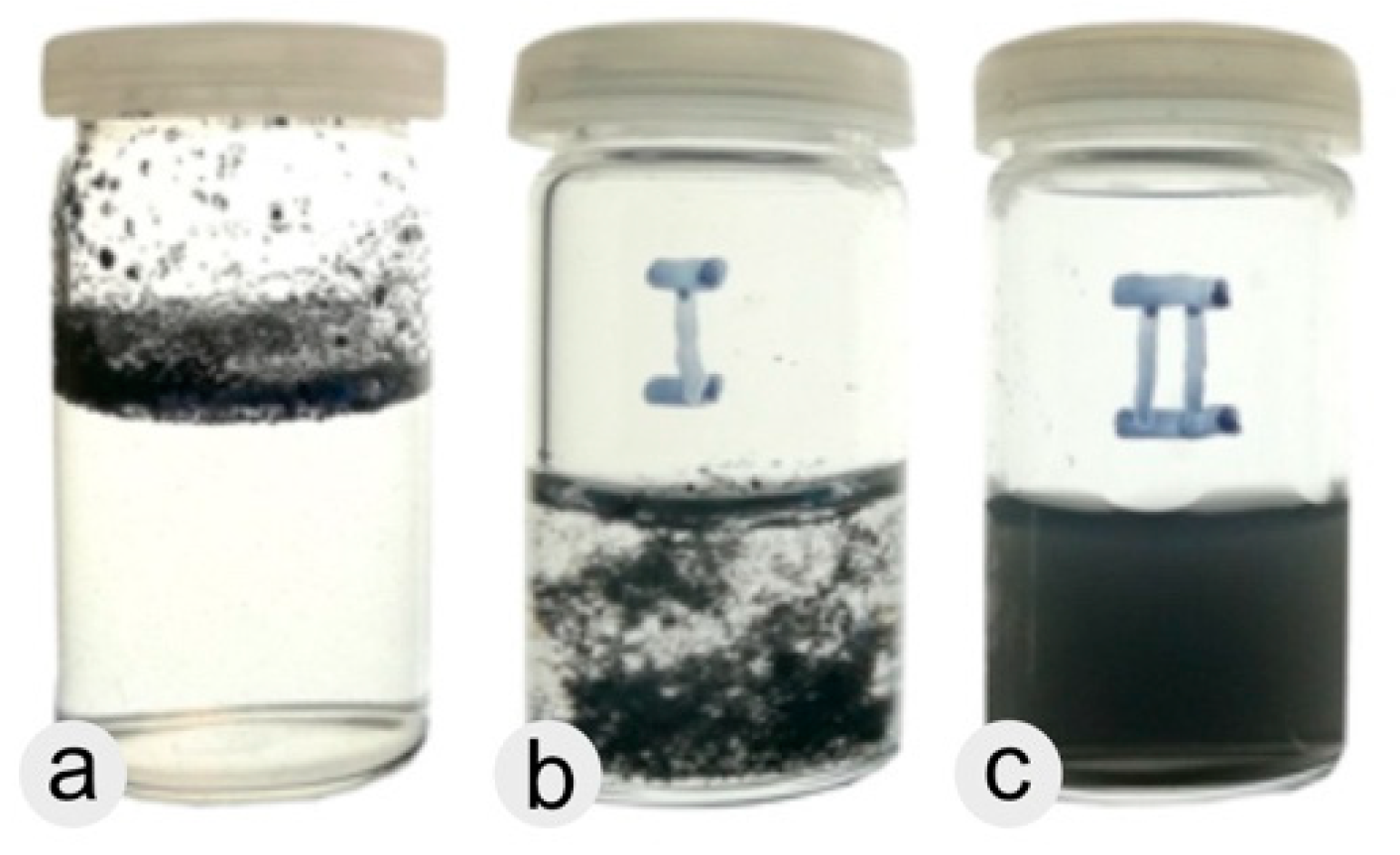
3. Results
3.1. Bucky Paper
3.2. Coating of -COOH Functionalized MWNTs with wtSbpA S-Layer Protein
3.3. Coating of -COOH Functionalized MWNTs with rSbpA31-1068GG Fusion Protein
3.4. Dispersion of -COOH Functionalized MWNTs by Addition of Triton-X 100
4. Discussion
5. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Saito, R. Physics of Carbon Nanotubes. Carbon 1995, 33, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouris, P.; Chen, Z.H.; Perebeinos, V. Carbon-based electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Carbon nanotubes-properties and applications: A review. Carbon Lett. 2013, 14, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, K.; Reddy, R.; Reddy, N. A review on protein functionalized carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Biomater. Func. 2015, 13, E301–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A. Functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Burghard, M. Chemically functionalized carbon nanotubes. Small 2005, 1, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Kharisov, B.I.; de Casas Ortiz, E.G. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes in water and non-aqueous solvents. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24812–24852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvaresi, M.; Zerbetto, F. The Devil and Holy Water: Protein and Carbon Nanotube Hybrids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posseckardt, J.; Zhang, J.W.; Mertig, M. Mobility of a supported lipid bilayer on dispersed single-walled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Status Solidi A 2016, 213, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haft, M.; Gronke, M.; Gellesch, M.; Wurmehl, S.; Buchner, B.; Mertig, M.; Hampel, S. Tailored nanoparticles and wires of Sn, Ge and Pb inside carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2016, 101, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.B.; Peairs, M.J.; Venton, B.J. Review: Carbon nanotube based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.S.; Wang, H.C.; Huang, Y.J.; Zhao, Z.X.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Miao, Z.Y.; Chen, Q.A.; Qiao, M.Q. Noncovalently functionalized multi-wall carbon nanotubes in aqueous solution using the hydrophobin HFBI and their electroanalytical application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.K.; Zheng, D.; Al-Rubeaan, K.; Luong, J.H.T.; Sheu, F.S. Advances in carbon nanotube based electrochemical sensors for bioanalytical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Guo, X.F. Carbon nanomaterials field-effect-transistor-based biosensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.O.; Maia, L.B.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Moura, I.; Moura, J.J.G.; Morais, S. Third-generation electrochemical biosensor based on nitric oxide reductase immobilized in a multiwalled carbon nanotubes/1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate nanocomposite for nitric oxide detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bukkitgar, S.D.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.; Reddy, K.R.; Shetti, N.P.; Reddy, C.V.; Sadhu, V.; Naveen, S. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Graphene Functionalized with Metal Oxide Nanostructures for Healthcare Applications. Chemistryselect 2019, 4, 5322–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Song, H.S.; Park, T.H.; Jang, J. Conducting Nanomaterial Sensor Using Natural Receptors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 36–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayu, M.B.; Pannell, M.J.; Labban, N.; Case, W.S.; Pollock, J.A.; Leopold, M.C. Functionalized carbon nanotube adsorption interfaces for electron transfer studies of galactose oxidase. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 125, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantarotto, D.; Singh, R.; McCarthy, D.; Erhardt, M.; Briand, J.P.; Prato, M.; Kostarelos, K.; Bianco, A. Functionalized carbon nanotubes for plasmid DNA gene delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5242–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, S.P.; Markovic, Z.M.; Kleut, D.N.; Romcevic, N.Z.; Trajkovic, V.S.; Dramicanin, M.D.; Markovic, B.M.T. A novel method for the functionalization of gamma-irradiated single wall carbon nanotubes with DNA. Nanotechnology 2009, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Schuster, B.; Egelseer, E.M.; Pum, D. S-layers: Principles and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 823–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Reassembly of S-layer proteins. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 312001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egelseer, E.M.; Ilk, N.; Pum, D.; Messner, P.; Schäffer, C.; Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. S-Layers, microbial, biotechnological applications. In Encyclopedia of Industrial Biotechnology: Bioprocess, Bioseparation, and Cell Technology; Flickinger, M.C., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 7, pp. 4424–4448. [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr, U.B. Self-assembly of the hexagonally and tetragonally arranged subunits of bacterial surface layers and their reattachment to cell walls. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1976, 55, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladenhauf, E.M.; Pum, D.; Wastl, D.S.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Phan, N.V.H.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer based biomolecular imprinting. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83558–83564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, D.; Kupcu, S.; Belton, D.J.; Perry, C.C.; Stoger-Pollach, M.; Sleytr, U.B.; Pum, D. Construction of silica-enhanced S-layer protein cages. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5689–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilk, N.; Egelseer, E.M.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer fusion proteins—Construction principles and applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völlenkle, C.; Weigert, S.; Ilk, N.; Egelseer, E.; Weber, V.; Loth, F.; Falkenhagen, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. Construction of a functional S-layer fusion protein comprising an immunoglobulin G-binding domain for development of specific adsorbents for extracorporeal blood purification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucisik, M.H.; Küpcü, S.; Breitwieser, A.; Gelbmann, N.; Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer fusion protein as a tool functionalizing emulsomes and CurcuEmulsomes for antibody binding and targeting. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 128, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, A.; Pum, D.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Sleytr, B.U. Magnetic beads functionalized with recombinant S-layer protein exhibit high human IgG-binding and anti-fouling properties. Curr. Top. Pept. Protein Res. 2016, 17, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Scheicher, S.R.; Kainz, B.; Kostler, S.; Reitinger, N.; Steiner, N.; Ditlbacher, H.; Leitner, A.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Ribitsch, V. 2D crystalline protein layers as immobilization matrices for the development of DNA microarrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Large-scale reconstruction of crystalline bacterial surface layer proteins at the air-water interface and on lipids. Thin Solid Films 1994, 244, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilk, N.; Vollenkle, C.; Egelseer, E.M.; Breitwieser, A.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. Molecular characterization of the S-layer gene, sbpA, of Bacillus sphaericus CCM 2177 and production of a functional S-layer fusion protein with the ability to recrystallize in a defined orientation while presenting the fused allergen. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2002, 68, 3251–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavkov-Keller, T.; Howorka, S.; Keller, W. The structure of bacterial S-layer proteins. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011, 103, 73–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ren, Q.; Wu, Y.N.; Morris, V.K.; Rey, A.A.; Braet, F.; Kwan, A.H.; Sunde, M. Surface functionalization of carbon nanomaterials by self-assembling hydrophobin proteins. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Shin, S.H.; Bertozzi, C.R.; De Yoreo, J.J. Self-catalyzed growth of S layers via an amorphous-to-crystalline transition limited by folding kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16536–16541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Chung, S.; Sanii, B.; Comolli, L.R.; Bertozzi, C.R.; De Yoreo, J.J. Direct observation of kinetic traps associated with structural transformations leading to multiple pathways of S-layer assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12968–12973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitwieser, A.; Iturri, J.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Sleytr, U.B.; Pum, D. In Vitro Characterization of the Two-Stage Non-Classical Reassembly Pathway of S-Layers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Anisotropic crystal growth of the S-layer of Bacillus sphaericus CCM 2177 at the air/water interface. Colloids Surf. A 1995, 102, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, E.; Fronzes, R.; Garcia-Pino, A.; Van Gerven, N.; Papapostolou, D.; Pehau-Arnaudet, G.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Howorka, S.; Remaut, H. SbsB structure and lattice reconstruction unveil Ca2+ triggered S-layer assembly. Nature 2012, 487, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, B.; Haxton, T.K.; Shon, A.; Shin, S.H.; Whitelam, S.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M. Ion-specific control of the self-assembly dynamics of a nanostructured protein lattice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilk, N.; Kosma, P.; Puchberger, M.; Egelseer, E.M.; Mayer, H.F.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sára, M. Structural and functional analyses of the secondary cell wall polymer of Bacillus sphaericus CCM 2177 that serves as an S-layer-specific anchor. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 7643–7646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egelseer, E.M.; Leitner, K.; Jarosch, M.; Hotzy, C.; Zayni, S.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sára, M. The S-layer proteins of two Bacillus stearothermophilus wild-type strains are bound via their N-terminal region to a secondary cell wall polymer of identical chemical composition. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Györvary, E.S.; Stein, O.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Self-assembly and recrystallization of bacterial S-layer proteins at silicon supports imaged in real time by atomic force microscopy. J. Microsc. 2003, 212, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, G.; Siedlaczek, P.; Sinn, G.; Rennhofer, H.; Micusik, M.; Omastova, M.; Unterlass, M.M.; Wendrinsky, J.; Milotti, V.; Fedi, F.; et al. Acid Free Oxidation and Simple Dispersion Method of MWCNT for High-Performance CFRP. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S.; Lee, J.; Yuan, L.X.; Chae, S.R.; Peterson, V.K.; Minett, A.I.; Yin, Y.B.; Harris, A.T. Removal of natural organic matter in water using functionalised carbon nanotube buckypaper. Carbon 2013, 59, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.F. Disclinations. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRosier, D.J.; Moore, P.B. Reconstruction of 3-Dimensional Images from Electron Micrographs of Structures with Helical Symmetry. J. Mol. Biol. 1970, 52, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Rice, W.J.; Stokes, D.L. Fourier-Bessel Reconstruction of Helical Assemblies. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 482, 131–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, P.; Pum, D.; Sára, M.; Stetter, K.O.; Sleytr, U.B. Ultrastructure of the cell envelope of the archaebacteria Thermoproteus tenax and Thermoproteus neutrophilus. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 166, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, P.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Characterization of the ultrastructure and the self-assembly of the surface layer of Bacillus stearothermophilus strain NRS 2004/3a. J. Ultrastruct. Mol. Struct. Res. 1986, 97, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobeth, M.; Blecha, A.; Bluher, A.; Mertig, M.; Korkmaz, N.; Ostermann, K.; Rodel, G.; Pompe, W. Formation of tubes during self-assembly of bacterial surface layers. Langmuir 2011, 27, 15102–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali-Boucetta, H.; Nunes, A.; Sainz, R.; Herrero, M.A.; Tian, B.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K. Asbestos-like pathogenicity of long carbon nanotubes alleviated by chemical functionalization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.; Kaushal, R.; Tripathi, S.K.; Sharma, A.L.; Kaur, I.; Bharadwaj, L.M. Comparative study of carbon nanotube dispersion using surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallakpour, S.; Soltanian, S. Surface functionalization of carbon nanotubes: Fabrication and applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109916–109935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, K.; Singh, D.P.; Singh, S.; Dash, D.; Srivastava, O.N. Attachment of biomolecules (protein and DNA) to amino-functionalized carbon nanotubes. New Carbon Mater. 2009, 24, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, D.; Geckeler, K.E. pH-sensitive dispersion and debundling of single-walled carbon nanotubes: Lysozyme as a tool. Small 2006, 2, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.F.; Wang, M.J.; Li, J.H. Poly-L-lysine functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 15343–15346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Robinson, J.T.; Tabakman, S.M.; Yang, K.; Dai, H.J. Carbon materials for drug delivery & cancer therapy. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.; Raffa, S.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K. Cell-penetrating CNTs for delivery of therapeutics. Nano Today 2007, 2, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.E.; Ni, L.; Brown, W.R.; Joshi, K.S.; Chang, J.; Rosenberg, B.; Voss, E.W., Jr. The immunochemistry of sandwich ELISAs--VI. Greater than 90% of monoclonal and 75% of polyclonal anti-fluorescyl capture antibodies (CAbs) are denatured by passive adsorption. Mol. Immunol. 1993, 30, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. An Amperometric Glucose Sensor-Based on Isoporous Crystalline Protein Membranes as Immobilization Matrix. Anal. Lett. 1993, 26, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.; Hodl, C.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. A Multistep Enzyme Sensor for Sucrose Based on S-Layer Microparticles as Immobilization Matrix. Anal. Lett. 1994, 27, 849–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, A.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Klimant, I.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fibre-optic glucose biosensor using enzyme membranes with 2-D crystalline structure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1996, 11, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferner-Ortner-Bleckmann, J.; Gelbmann, N.; Tesarz, M.; Egelseer, E.M.; Sleytr, U.B. Surface-layer lattices as patterning element for multimeric extremozymes. Small 2013, 9, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitwieser, A.; Egelseer, E.M.; Moll, D.; Ilk, N.; Hotzy, C.; Bohle, B.; Ebner, C.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. A recombinant bacterial cell surface (S-layer)-major birch pollen allergen-fusion protein (rSbsC/Bet v1) maintains the ability to self-assemble into regularly structured monomolecular lattices and the functionality of the allergen. Protein Eng. 2002, 15, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, D.; Huber, C.; Schlegel, B.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. S-layer-streptavidin fusion proteins as template for nanopatterned molecular arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14646–14651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Liu, J.; Egelseer, E.M.; Moll, D.; Knoll, W.; Sleytr, U.B.; Sara, M. Heterotetramers formed by an S-layer-streptavidin fusion protein and core-streptavidin as a nanoarrayed template for biochip development. Small 2006, 2, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, B.; Steiner, K.; Moller, M.; Pum, D.; Schaffer, C.; Sleytr, U.B.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Absorption, steady-state fluorescence, fluorescence lifetime, and 2D self-assembly properties of engineered fluorescent S-layer fusion proteins of Geobacillus stearothermophilus NRS 2004/3a. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, B.; Steiner, K.; Sleytr, U.B.; Pum, D.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Fluorescence energy transfer in the bi-fluorescent S-layer tandem fusion protein ECFP-SgsE-YFP. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 172, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainz, B.; Steiner, K.; Sleytr, U.B.; Pum, D.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Fluorescent S-layer protein colloids. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3809–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunakey, S.J.G.; Coyle, B.L.; Thomas, A.; Xu, M.; Swift, B.J.F.; Baneyx, F. Selective Labeling and Decoration of the Ends and Sidewalls of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Using Mono- and Bispecific Solid-Binding Fluorescent Proteins. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, B.; Sleytr, U.B. Composite S-layer lipid structures. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 168, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Chen, F.; Huang, Z.L.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Cho, Y.K.; Fang, R.N.H.; et al. Biomembrane-Modified Field Effect Transistors for Sensitive and Quantitative Detection of Biological Toxins and Pathogens. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 3714–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbauer, M.; Küpcü, S.; Sticker, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Ertl, P. Exploitation of S-layer Anisotropy: pH-dependent Nanolayer Orientation for Cellular Micropatterning. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8020–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenton, W.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B.; Mann, S. Biocrystal templating of CdS superlattices using self-assembled bacterial S-layers. Nature 1997, 389, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieluweit, S.; Pum, D.; Sleytr, U.B. Formation of a gold superlattice on an S-layer with square lattice symmetry. Supramol. Sci. 1998, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertig, M.; Kirsch, R.; Pompe, W.; Engelhardt, H. Fabrication of highly oriented nanocluster arrays by biomolecular templating. Eur. Phys. J. D 1999, 9, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompe, W.; Mertig, M.; Kirsch, R.; Wahl, R.; Ciacchi, L.C.; Richter, J.; Seidel, R.; Vinzelberg, H. Formation of metallic nanostructures on biomolecular templates. Zeitschrift Fur Metallkunde 1999, 90, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Mertig, M.; Wahl, R.; Lehmann, M.; Simon, P.; Pompe, W. Formation and manipulation of regular metallic nanoparticle arrays on bacterial surface layers: An advanced TEM study. Eur. Phys. J. D 2001, 16, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queitsch, U.; Mohn, E.; Schaffel, F.; Schultz, L.; Rellinghaus, B.; Bluher, A.; Mertig, M. Regular arrangement of nanoparticles from the gas phase on bacterial surface-protein layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 113114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S. Self-assembly and transformation of hybrid nano-objects and nanostructures under equilibrium and non-equilibrium conditions. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryan, G.; Kim, Y.H.; Acharya, R.; Axelrod, K.; Jain, R.M.; Willis, L.; Drndic, M.; Kikkawa, J.M.; DeGrado, W.F. Computational design of virus-like protein assemblies on carbon nanotube surfaces. Science 2011, 332, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardharajula, S.; Ali, S.Z.; Tiwari, P.M.; Eroglu, E.; Vig, K.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Functionalized carbon nanotubes: Biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5361–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleutel, M.; Van Driessche, A.E.S. Role of clusters in nonclassical nucleation and growth of protein crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E546–E553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Breitwieser, A.; Siedlaczek, P.; Lichtenegger, H.; Sleytr, U.B.; Pum, D. S-Layer Protein Coated Carbon Nanotubes. Coatings 2019, 9, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080492
Breitwieser A, Siedlaczek P, Lichtenegger H, Sleytr UB, Pum D. S-Layer Protein Coated Carbon Nanotubes. Coatings. 2019; 9(8):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080492
Chicago/Turabian StyleBreitwieser, Andreas, Philipp Siedlaczek, Helga Lichtenegger, Uwe B. Sleytr, and Dietmar Pum. 2019. "S-Layer Protein Coated Carbon Nanotubes" Coatings 9, no. 8: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080492
APA StyleBreitwieser, A., Siedlaczek, P., Lichtenegger, H., Sleytr, U. B., & Pum, D. (2019). S-Layer Protein Coated Carbon Nanotubes. Coatings, 9(8), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9080492