The Bone Buttress Theory: The Effect of the Mechanical Loading of Bone on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material & Methods
2.1. Reporting of In Vivo Experiments
2.2. Specimens
2.3. Adaptation Phase
2.4. Surgical Procedure
2.5. Primary Stability Measurements
2.6. Healing Caps
2.7. Randomisation of Samples
2.8. Biomechanical Stimulus
2.9. Sacrifice
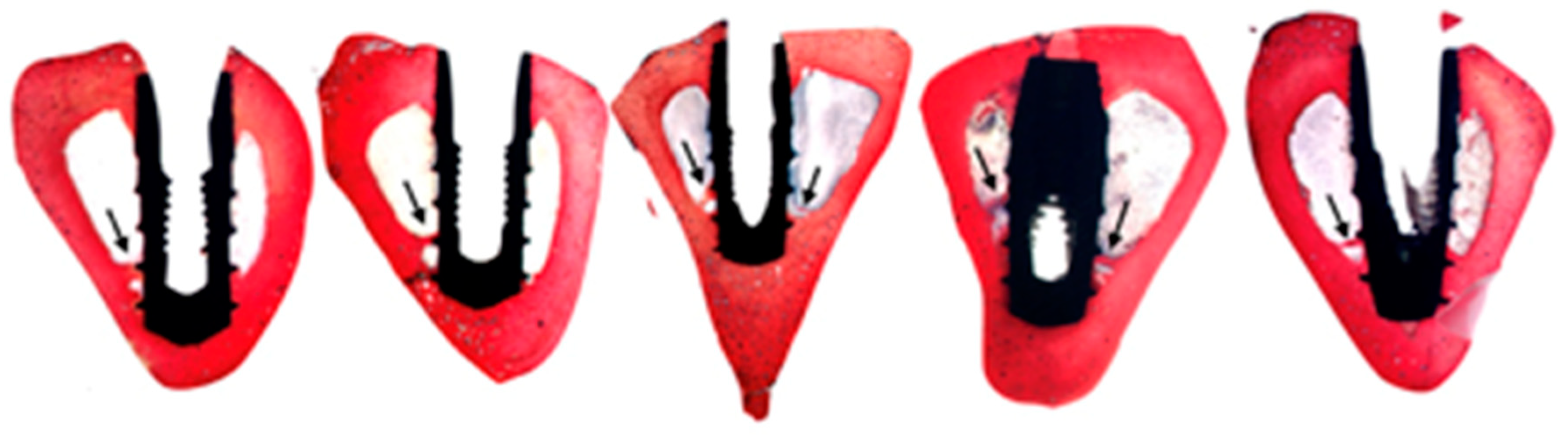
2.10. Histological Processing
2.11. Histomorphometrical Analysis
- -
- % BIC: percentage of bone-to-implant contact in the region of interest (ROI). The BIC was analysed exclusively in the coronal area of the implant, specifically in the area surrounding its neck. The apical anchorage zone was not included given that its relationship with the implant was more heterogeneous, and, unlike the coronal area, it was impossible to control during surgery.
- -
- New bone formation (mm2): the amount of newformed bone on the surface of the implant.
- -
- % of immature bone matrix: the proportion of the area of newformed bone that is immature, with disorganised collagen fibres.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Vertical Bone Growth
3.2. Implant Stability
3.3. Bone to Implant Contact
3.4. Bone Neoformation
3.5. Bone Disposition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schenk, R.K.; Buser, D. Osseointegration: A reality. Periodontology 2000 1998, 17, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhinelander, F.W. Tibial blood supply in relation to fracture healing. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1974, 105, 34–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Chávarri-Prado, D. The functional loading of implants increases their stability: A retrospective clinical study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghimire, S.; Miramini, S.; Richardson, M.; Mendis, P.; Zhang, L. Role of dynamic loading on early stage of bone fracture healing. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 1768–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Sanchez, I.; Sanz-Martin, I.; Figuero, E.; Sanz, M. Clinical efficacy of immediate implant loading protocols compared to conventional loading depending on the type of the restoration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 964–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallucci, G.O.; Hamilton, A.; Zhou, W.; Buser, D.; Chen, S. Implant placement and loading protocols in partially edentulous patients: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 106–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norton, M.R. The influence of insertion torque on the survival of immediately placed and restored single-tooth implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Gotfredsen, K.; Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J. Bone reactions adjacent to titanium implants subjected to static load. A study in the dog (I). Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kim, S.; Lim, S.; Ong, J.L. Histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of early and immediately loaded implants in the dog mandible. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 15, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podaropoulos, L.; Veis, A.A. Bone reactions around dental implants subjected to progressive static load: An experimental study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.E.; Toh, C.G.; Siar, C.H.; Swaminathan, D. Histologic and histomorphometric evaluation of peri-implant bone subjected to immediate loading: An experimental study with Macaca fascicularis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2002, 17, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Romanos, G.E.; Toh, C.G.; Siar, C.H.; Wicht, H.; Yacoob, H.; Nentwig, G.H. Bone-implant interface around titanium implants under different loading conditions: A histomorphometrical analysis in the Macaca fascicularis monkey. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiskott, H.W.; Cugnoni, J.; Scherrer, S.S.; Ammann, P.; Botsis, J.; Belser, U.C. Bone reactions to controlled loading of endosseous implants: A pilot study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuma, M.; Harada, S.; Kurokawa, F.; Takashima, F.; Miyauchi, S.; Maruyama, T. Experimental study on the functional adaptation to aluminum oxide, hydroxyapatite and titanium implants. J. Osaka Univ. Dent. Sch. 1987, 27, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Deporter, D.A.; Watson, P.A.; Pilliar, R.M.; Howley, T.P.; Winslow, J.A. Histological evaluation of a functional endosseous, porous-surfaced, titanium alloy dental implant system in the dog. J. Dent. Res. 1988, 67, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisi, P.; Rebaudi, A. Peri-implant bone reaction to immediate, early, and delayed orthodontic loading in humans. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2005, 25, 317–329. [Google Scholar]
- Lanyon, L.E. Analysis of surface bone strain in the calcaneus of sheep during normal locomotion. Strain analysis of the calcaneus. J. Biomech. 1973, 6, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyon, L.E. Experimental support for the trajectorial theory of bone structure. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1974, 56, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, W.; Snyder, B. Toward a quantitative formulation of Wolff’s law in trabecular bone. In Mechanical Properties of Bone; Cowin, S., Ed.; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 43–68. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, J. On the significance of the architecture of the spongy substance for the question of bone growth. Centralblatt für die Meichinschen Wissenschaften 1869, 54, 849–851. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, J. The classic: On the significance of the architecture of the spongy substance for the question of bone growth: A preliminary publication. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3077–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, R.B.; Burr, D.B.; Sharkey, N.A.; Fyhrie, D.P. Skeletal Tissue Mechanics. Skeletal Tissue Mechanics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, C.H.; Robling, A.G.; Duncan, R.L.; Burr, D.B. Do bone cells behave like a neuronal network? Calcif. Tissue Int. 2002, 70, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyhrie, D.P.; Carter, D.R. A unifying principle relating stress to trabecular bone morphology. J. Orthop. Res. 1986, 4, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traini, T.; Degidi, M.; Caputi, S.; Strocchi, R.; Di Iorio, D.; Piattelli, A. Collagen fiber orientation in human peri-implant bone around immediately loaded and unloaded titanium dental implants. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, J.; Traini, T.; Thams, U.; Piattelli, A.; Zoller, J.E. Peri-implant bone organization under immediate loading state. Circularly polarized light analyses: A minipig study. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traini, T.; Neugebauer, J.; Thams, U.; Zöller, J.E. Peri-Implant Bone Organization under Immediate Loading Conditions: Collagen Fiber Orientation and Mineral Density Analyses in the Minipig Model. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2010, 1, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, D.Y.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, N. Humanized animal exercise model for clinical implication. Pflugers Arch. 2014, 466, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlin, E.D. A rheologic model for cortical bone. A study of the physical properties of human femoral samples. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1965, 83, 1–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hexeberg, E.; Biology, C. Effects of endurance training on left ventricular performance: A study in anaesthetized rabbits. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1995, 154, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaustad, S.E.; Rolim, N.; Wisløff, U. A valid and reproducible protocol for testing maximal oxygen uptake in rabbits. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2010, 17, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Zucker, I.H. Exercise training normalizes sympathetic outflow by central antioxidant mechanisms in rabbits with pacing-induced chronic heart failure. Circulation 2007, 115, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misch, C. Implantología Contemporánea, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, E.; Kydd, W.L. Bite force duration: A diagnostic procedure for mandibular dysfunction. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1988, 60, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, K.; Naert, I.; Geris, L.; Vander Sloten, J.; Puers, R.; Duyck, J. The effect of micro-motion on the tissue response around immediately loaded roughened titanium implants in the rabbit. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2007, 115, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jingyun, H.A.N.; Jianxia, H.O.U.; Gang, Z.; Chao, W.; Yubo, F.A.N. A histological and biomechanical study of bone stress and bone remodeling around immediately loaded implants. Sci. China Life Sci. 2014, 57, 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, C.T.; Lanyon, L.E. Regulation of bone formation by applied dynamic loads. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1984, 66, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hert, J. Acceleration of the growth after decrease of load on epiphyseal plates by means of spring distractors. Folia Morphol. 1969, 17, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Duyck, J.; Rønold, H.J.; Van Oosterwyck, H.; Naert, I.; Vander Sloten, J.; Ellingsen, J.E. The influence of static and dynamic loading on marginal bone reactions around osseointegrated implants: An animal experimental study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, C.; Gross, T.; Qin, Y.X.; Fritton, S.; Guilak, F.; McLeod, K. Differentiation of the bone-tissue remodeling response to axial and torsional loading in the turkey ulna. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1996, 78, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.X.; McLeod, K.J.; Guilak, F.; Chiang, F.P.; Rubin, C.T. Correlation of bony ingrowth to the distribution of stress and strain parameters surrounding a porous-coated implant. J. Orthop. Res. 1996, 14, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, T.; Hagiwara, Y. Influence of lateral-oblique cyclic loading on abutment screw loosening of internal and external hexagon implants. Dent. Mater. J. 2009, 28, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kern, M.; Strub, J.R.; Lu, X.Y. Wear of composite resin veneering materials in a dual-axis chewing simulator. J. Oral Rehabil. 1999, 26, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.R. The timing and mechanism of the human masticatory stroke. Arch. Oral Biol. 1965, 10, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, T.; Ayukawa, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sakai, N. Effect of post-osseointegration loading magnitude on the dynamics of peri-implant bone: A fi nite element analysis and in vivo study. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 63, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroshima, S.; Nakano, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Sasaki, M.; Inoue, M.; Yasutake, M.; Sawase, T. Optimally oriented grooves on dental implants improve bone quality around implants under repetitive mechanical loading. Acta Biomater. 2017, 15, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, M.; Kuroshima, S.; Aoki, Y.; Inaba, N.; Sawase, T. Ultrastructural alterations of osteocyte morphology via loaded implants in rabbit tibiae. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 4130–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marx, R.E.; Shellenberger, T.; Wimsatt, J.; Correa, P. Severely resorbed mandible: Predictable reconstruction with soft tissue matrix expansion (tent pole) grafts. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 60, 878–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, Y. Early loading of splinted implants in posterior mandible: Three-year results of a prospective multicenter study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoglan, M.; Tatli, U.; Kurtoglu, C.; Salimov, F.; Kurkcu, M. Effects of different loading protocols on the secondary stability and peri-implant bone density of the single implants in the posterior maxilla. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrom, M.; Lundgren, S.; Nilson, H.; Sennerby, L. Monitoring of implant stability in grafted bone using resonance frequency analysis. A clinical study from implant placement to 6 months of loading. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 34, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Degidi, M.; Daprile, G.; Piattelli, A.; Carinci, F. Evaluation of factors influencing resonance frequency analysis values, at insertion surgery, of implants placed in sinus-augmented and nongrafted sites. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2007, 9, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piattelli, A.; Corigliano, M.; Scarano, A.; Costigliola, G.; Paolantonio, M. Immediate loading of titanium plasma-sprayed implants: An histologic analysis in monkeys. J. Periodontol. 1998, 69, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkenke, E.; Lehner, B.; Weinzierl, K.; Thams, U.; Neugebauer, J.; Steveling, H.; Radespiel-Tröger, M.; Neukam, F.W. Bone contact, growth, and density around immediately loaded implants in the mandible of mini pigs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, A.; Mardas, N.; Dard, M.; Donos, N. Effect of immediate or delayed loading following immediate placement of implants with a modified surface. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manresa, C.; Echeverr, J.; Manresa, C. The comparison between implant stability quotient and bone-implant contact revisited: An experiment in Beagle dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.P.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.H. The relationship between initial implant stability quotient values and bone-to-implant contact ratio in the rabbit tibia. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2011, 3, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Sato, D.; Yoneda, S.; Ito, D.; Kondo, H.; Kasugai, S. Relevance of resonance frequency analysis to evaluate dental implant stability: Simulation and histomorphometrical animal experiments. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliephake, H.; Sewing, A.; Aref, A. Resonance frequency measurements of implant stability in the dog mandible: Experimental comparison with histomorphometric data. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Álvarez-Arenal, Á.; Gil-Mur, F.J.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Chávarri-Prado, D.; Chento-Valiente, Y.; Dieguez-Pereira, M. Relationship between insertion torque and resonance frequency measurements, performed by resonance frequency analysis, in micromobility of dental implants: An in vitro study. Implant. Dent. 2015, 24, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennerby, L.; Meredith, N. Implant stability measurements using resonance frequency analysis: Biological and biomechanical aspects and clinical implications. Periodontol. 2000 2008, 47, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, R.; Albrektsson, T.; Galli, S.; Prgomet, Z.; Tengvall, P.; Wennerberg, A. Osseointegration and foreign body reaction: Titanium implants activate the immune system and suppress bone resorption during the first 4 weeks after implantation. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Yuan, X.; Sadowsky, S.J.; Coyac, B.R.; Brunski, J.B.; Helms, J.A. Mechano-adaptive responses of alveolar bone to implant hyper-loading in a pre-clinical in vivo model. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Measured Parameter | Group A (Test) Mean (SD) | Group B (Control) Mean (SD) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torque (N/cm) | 27.00 (10.05) | 23 (10.05) | p = 0.279 |
| Primary stability (ISQ) | 71.50 (3.09) | 72.53 (3.67) | p = 0.262 |
| Secondary stability (ISQ) | 82.75 (4.91) | 78.33 (3.68) | p = 0.008 |
| ISQ increase | 11.5 (6.10) | 5.80 (5.97) | p = 0.006 |
| Measured Parameter | Group A (Test) Mean (SD) | Group B (Control) Mean (SD) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical bone growth (mm) | 1.26 (0.47) | 0.32 (0.46) | p ≤ 0.01 |
| Bone to implant contact (%) | 25.14 (5.24) | 18.87 (4.45) | p ≤ 0.01 |
| Areas of regenerated bone (%) | 280.50 (125.40) | 228.00 (141.40) | p = 0.121 |
| Immature bone matrix (%) | 15.38 (8.84) | 20.68 (9.53) | p ≤ 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chavarri-Prado, D.; Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Álvarez-Arenal, Á.; Dieguez-Pereira, M.; Pérez-Pevida, E.; Viteri-Agustín, I.; Estrada-Martínez, A. The Bone Buttress Theory: The Effect of the Mechanical Loading of Bone on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants. Biology 2021, 10, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010012
Chavarri-Prado D, Brizuela-Velasco A, Álvarez-Arenal Á, Dieguez-Pereira M, Pérez-Pevida E, Viteri-Agustín I, Estrada-Martínez A. The Bone Buttress Theory: The Effect of the Mechanical Loading of Bone on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants. Biology. 2021; 10(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleChavarri-Prado, David, Aritza Brizuela-Velasco, Ángel Álvarez-Arenal, Markel Dieguez-Pereira, Esteban Pérez-Pevida, Iratxe Viteri-Agustín, and Alejandro Estrada-Martínez. 2021. "The Bone Buttress Theory: The Effect of the Mechanical Loading of Bone on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants" Biology 10, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010012
APA StyleChavarri-Prado, D., Brizuela-Velasco, A., Álvarez-Arenal, Á., Dieguez-Pereira, M., Pérez-Pevida, E., Viteri-Agustín, I., & Estrada-Martínez, A. (2021). The Bone Buttress Theory: The Effect of the Mechanical Loading of Bone on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants. Biology, 10(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010012





