Gene Expression Changes after Parental Exposure to Metals in the Sea Urchin Affect Timing of Genetic Programme of Embryo Development
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sea Urchin Sampling and Exposure to Metals
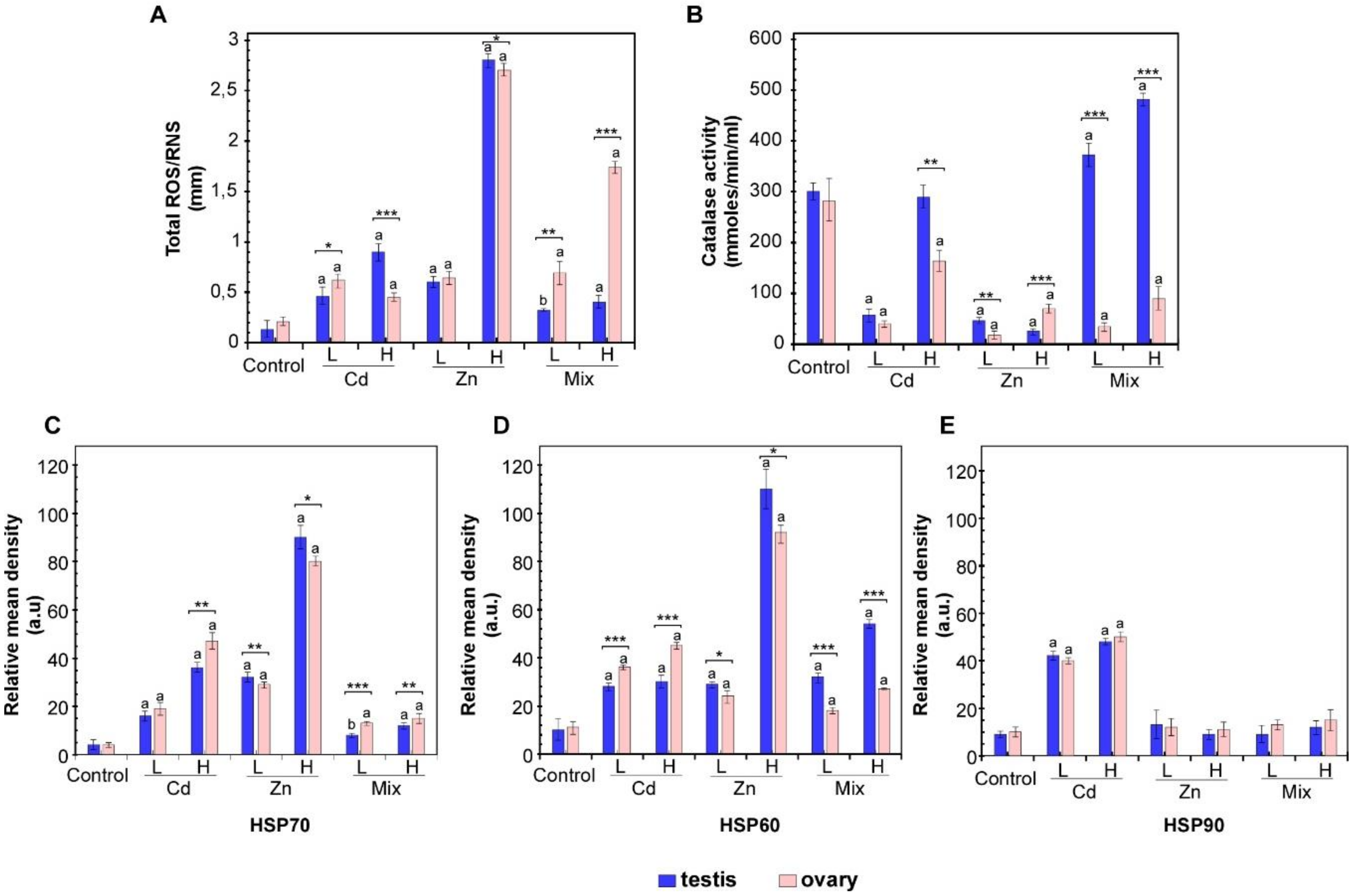
2.2. Protein Extraction, SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analyses
2.3. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection and Catalase Activity
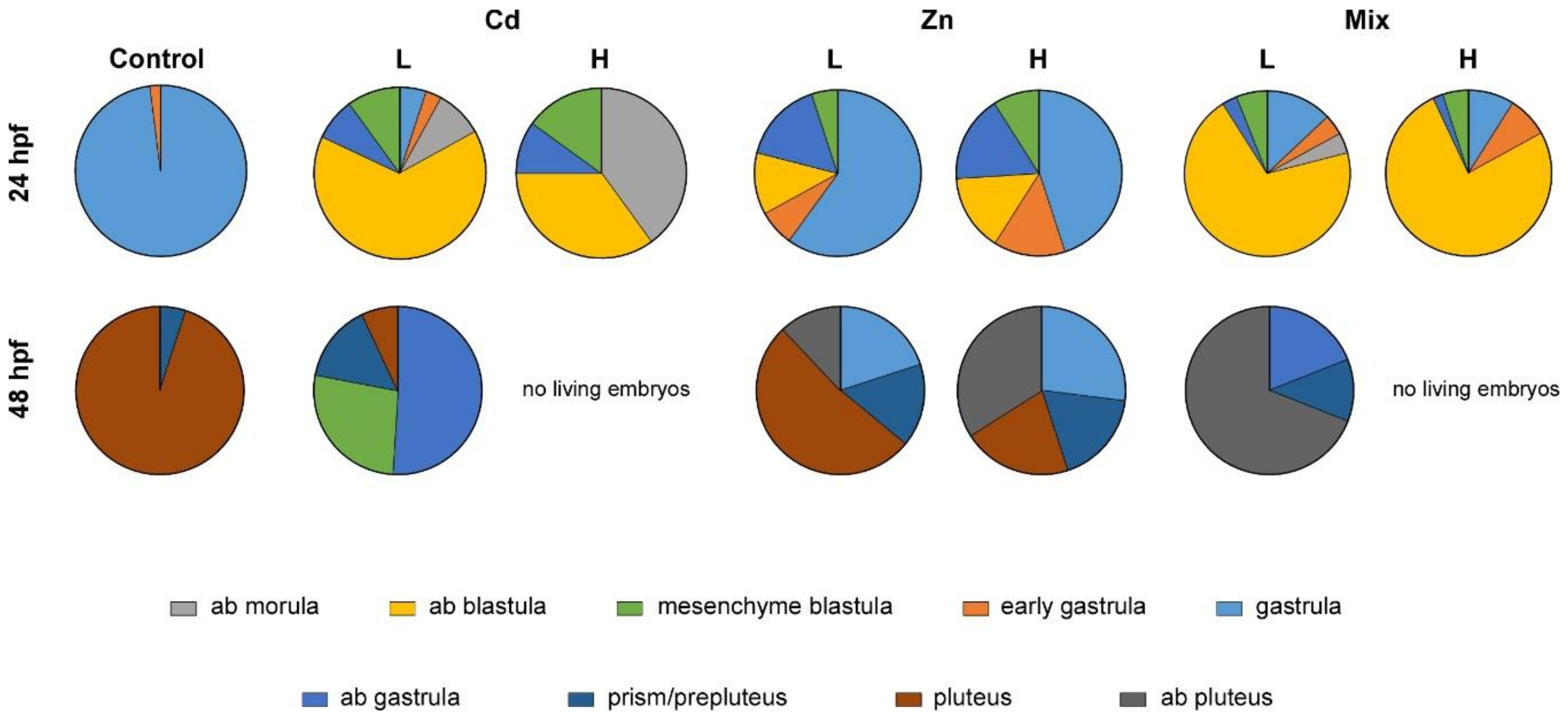
2.4. Embryo Culture and Morphological Analysis
2.5. RNA Purification and First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
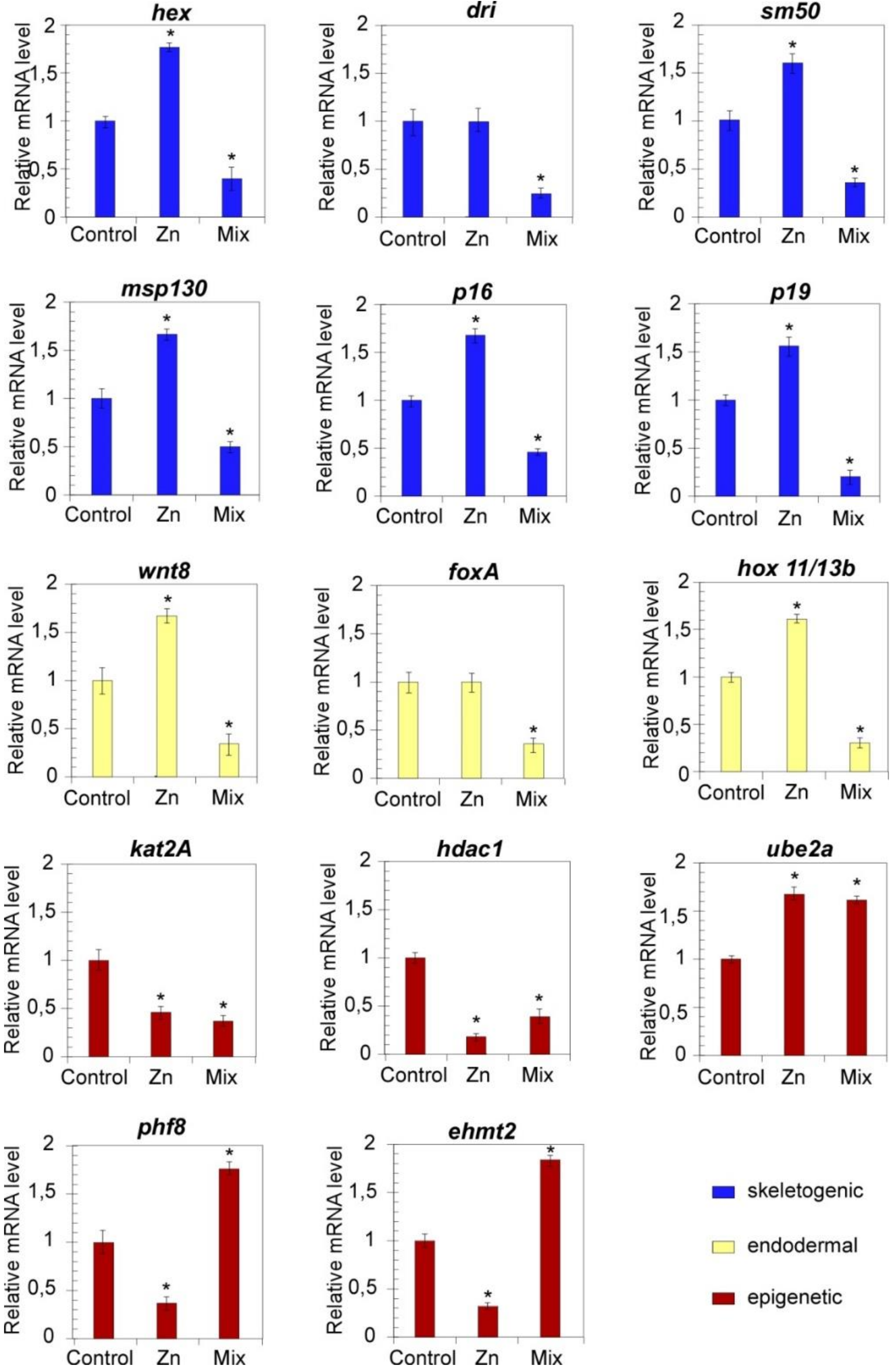
2.6. Gene Expression Profiling by Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Metal Exposures on the Stress Response of P. lividus Reproductive Tissues
3.2. Effects of Metal Exposures on the Offspring of Conditioned P. lividus
3.3. Pathway-Centered Gene Expression Profiling
3.3.1. Expression Profiles of Development Regulators
3.3.2. Expression Profiles of Transcriptional Regulators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marshall, D.J. Transgenerational plasticity in the sea: Context-dependent maternal effects across the life history. Ecology 2008, 89, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonduriansky, R.; Day, T. Nongenetic Inheritance and Its Evolutionary Implications. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, L.N.S.; Mark, F.C.; Strobel, A.; Lokmer, A.; John, U.; Mathias Wegner, K. Transgenerational effects persist down the maternal line in marine sticklebacks: Gene expression matches physiology in a warming ocean. Evol. Appl. 2016, 9, 1096–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelson, J.M.; Munday, P.L. Transgenerational plasticity mitigates the impact of global warming to offspring sex ratios. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2954–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, P.; Anderson, K.; Thompson, E.L.; Melwani, A.; Parker, L.M.; Ross, P.M.; Raftos, D.A. Rapid transcriptional acclimation following transgenerational exposure of oysters to ocean acidification. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4836–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosin, A.; Lehner, B. Mechanisms, timescales and principles of trans-generational epigenetic inheritance in animals. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2016, 36, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L. Transgenerational acclimation of fishes to climate change and ocean acidification. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonduriansky, R. Rethinking heredity, again. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldo, M.J.; Locatelli, Y.; O’Neill, C.; Mermillod, P. Impacts of and interactions between environmental stress and epigenetic programming during early embryo development. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2015, 27, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tabou De-Leon, S.; Davidson, E.H. Gene regulation: Gene control network in development. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2007, 36, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.H. Emerging properties of animal gene regulatory networks. Nature 2010, 468, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.E. Development in context: The timely emergence of eco-devo. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.F. Ecological developmental biology: Environmental signals for normal animal development. Evol. Dev. 2012, 14, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Nicosia, A.; Cuttitta, A.; Gianguzza, F.; Ragusa, M.A. An intronic cis-regulatory element is crucial for the alpha tubulin Pl-Tuba1a gene activation in the ciliary band and animal pole neurogenic domains during sea urchin development. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard-Ashby, M.; Materna, S.C.; Brown, C.T.; Chen, L.; Cameron, R.A.; Davidson, E.H. Gene families encoding transcription factors expressed in early development of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev. Biol. 2006, 300, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, E.; Wessel, G.M. In the beginning... Animal fertilization and sea urchin development. Dev. Biol. 2006, 300, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, A.G. Of sea urchins and worms: Development and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, M.A.; Nicosia, A.; Costa, S.; Casano, C.; Gianguzza, F. A Survey on Tubulin and Arginine Methyltransferase Families Sheds Light on P. lividus Embryo as Model System for Antiproliferative Drug Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E. The Regulatory Genome; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; ISBN 9780120885633. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, G.E.; Todgham, A.E. Living in the Now: Physiological Mechanisms to Tolerate a Rapidly Changing Environment. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Ortega-Martínez, O.; Thorndyke, M. Impact of near-future ocean acidification on echinoderms. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, M.A.; Costa, S.; Cuttitta, A.; Gianguzza, F.; Nicosia, A. Coexposure to sulfamethoxazole and cadmium impairs development and attenuates transcriptional response in sea urchin embryo. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, M.; Nicosia, A.; Costa, S.; Cuttitta, A.; Gianguzza, F. Metallothionein Gene Family in the Sea Urchin Paracentrotus lividus: Gene Structure, Differential Expression and Phylogenetic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matranga, V.; Pinsino, A.; Randazzo, D.; Giallongo, A.; Dubois, P. Long-term environmental exposure to metals (Cu, Cd, Pb, Zn) activates the immune cell stress response in the common European sea star (Asterias rubens). Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 76, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, I.S.; Davidson, E.H. Assessing regulatory information in developmental gene regulatory networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5862–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, D.A.; Runcie, D.E.; Babbitt, C.C.; Haygood, R.; Nielsen, W.J.; Wray, G.A. The Impact of Gene Expression Variation on the Robustness and Evolvability of a Developmental Gene Regulatory Network. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildor, T.; De-Leon, S.B.-T. Comparative Study of Regulatory Circuits in Two Sea Urchin Species Reveals Tight Control of Timing and High Conservation of Expression Dynamics. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henikoff, S.; Greally, J.M. Epigenetics, cellular memory and gene regulation. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R644–R648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.M.; Rougeulle, C. Developmental epigenetics: Phenotype and the flexible epigenome. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.F.; Li, W. LncRNA Functions as a New Emerging Epigenetic Factor in Determining the Fate of Stem Cells. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyko, F. The DNA methyltransferase family: A versatile toolkit for epigenetic regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, V.; Röttinger, E.; Lapraz, F.; Besnardeau, L.; Lepage, T. Left-right asymmetry in the sea urchin embryo is regulated by nodal signaling on the right side. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessodes, N.; Haillot, E.; Duboc, V.; Röttinger, E.; Lahaye, F.; Lepage, T. Reciprocal Signaling between the Ectoderm and a Mesendodermal Left-Right Organizer Directs Left-Right Determination in the Sea Urchin Embryo. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapraz, F.; Haillot, E.; Lepage, T. A deuterostome origin of the Spemann organiser suggested by Nodal and ADMPs functions in Echinoderms. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anello, L.; Cavalieri, V.; Di Bernardo, M. Developmental effects of the protein kinase inhibitor kenpaullone on the sea urchin embryo. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 204, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turturici, G.; La Fiora, V.; Terenzi, A.; Barone, G.; Cavalieri, V. Perturbation of Developmental Regulatory Gene Expression by a G-Quadruplex DNA Inducer in the Sea Urchin Embryo. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 4391–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, F.C.; Verlaque, M. Chapter 13 Ecology of Paracentrotus lividus. Dev. Aquac. Fish. Sci. 2007, 37, 243–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.G.; Chan, F.; Menge, B.A.; Hofmann, G.E. Transcriptomic responses to ocean acidification in larval sea urchins from a naturally variable pH environment. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.G.; Pespeni, M.H.; Hofmann, G.E.; Palumbi, S.R.; Sanford, E. Transcriptomic responses to seawater acidification among sea urchin populations inhabiting a natural pH mosaic. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2257–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, O.; Castellano, I.; Cirino, P.; Romano, G.; Palumbo, A. Maternal exposure to cadmium and manganese impairs reproduction and progeny fitness in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.; Johnson, K.M.; Kelly, M.W.; Hofmann, G.E. Transcriptomics reveal transgenerational effects in purple sea urchin embryos: Adult acclimation to upwelling conditions alters the response of their progeny to differential pCO2 levels. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 1120–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strader, M.E.; Wong, J.M.; Hofmann, G.E. Ocean acidification promotes broad transcriptomic responses in marine metazoans: A literature survey. Front. Zool. 2020, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, M.; Bennici, C.; Biondo, G.; Masullo, T.; Monastero, C.; Tagliavia, M.; Torri, M.; Costa, S.; Ragusa, M.A.; Cuttitta, A.; et al. Aberrant gene expression profiles in Mediterranean sea urchin reproductive tissues after metal exposures. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Shi, D.; Ding, J.; Yin, D.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Y. Transgenerational effects of ocean warming on the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotto, L.; Domeneghetti, S.; Rosani, U.; Manfrin, C.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Raccanelli, S.; Pallavicini, A.; Venier, P. DNA Damage and Transcriptional Changes in the Gills of Mytilus galloprovincialis Exposed to Nanomolar Doses of Combined Metal Salts (Cd, Cu, Hg). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Soto, M.C.; Tovar-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Rodellas, V.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Basterretxea, G. Seasonal variation and sources of dissolved trace metals in Maó Harbour, Minorca Island. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wah Chu, K.; Chow, K.L. Synergistic toxicity of multiple heavy metals is revealed by a biological assay using a nematode and its transgenic derivative. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 61, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamateris, R.E.; Rafiq, K.; Ettensohn, C.A. The expression and distribution of Wnt and Wnt receptor mRNAs during early sea urchin development. Gene Expr. Patterns 2010, 10, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, M.A.; Costa, S.; Gianguzza, M.; Roccheri, M.C.; Gianguzza, F. Effects of cadmium exposure on sea urchin development assessed by SSH and RT-qPCR: Metallothionein genes and their differential induction. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Amado, J.; Silva, A.X.; Manzi, C.; Nespolo, R.F.; Cárdenas, L. Differential expression of stress candidate genes for thermal tolerance in the sea urchin Loxechinus albus. J. Therm. Biol. 2017, 68, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, A.; Bennici, C.; Biondo, G.; Costa, S.; Di Natale, M.; Masullo, T.; Monastero, C.; Ragusa, M.A.; Tagliavia, M.; Cuttitta, A. Characterization of Translationally Controlled Tumour Protein from the Sea Anemone Anemonia viridis and Transcriptome Wide Identification of Cnidarian Homologues. Genes 2018, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnau, M.; Biondo, R.; Temara, A.; Bouquegneau, J.M.; Jangoux, M.; Dubois, P. Distribution of heavy metals in the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus from the Mediterranean Posidonia oceanica ecosystem: Seasonal and geographical variations. J. Sea Res. 1998, 39, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.H.; Collins, K.J. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Sea Urchin Tissues From Egypt, Ireland and United Kingdom. Chem. Ecol. 1995, 10, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soualili, D.; Dubois, P.; Gosselin, P.; Pernet, P.; Guillou, M. Assessment of seawater pollution by heavy metals in the neighbourhood of Algiers: Use of the sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus, as a bioindicator. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, G.L.; Cicero, N.; Bartolomeo, G.; Rando, R.; Vadalà, R.; Santini, A.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Dugo, G.; Salvo, A. Assessment and Monitoring of Fish Quality from a Coastal Ecosystem under High Anthropic Pressure: A Case Study in Southern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Anderson, A.; Lortie, M.; Parsons, R.; Bodnarn, A. Oxidative damage and cellular defense mechanisms in sea urchin models of aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 63, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.L.; Zeng, L.; Xu, M.Y.; Shen, B.; Wu, C.W. Different effects of low- and high-dose waterborne zinc on Zn accumulation, ROS levels, oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in the liver of large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarengo, A.; Canesi, L.; Pertica, M.; Poli, G.; Moore, M.N.; Orunesu, M. Heavy metal effects on lipid peroxidation in the tissues of mytilus gallopro vincialis lam. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. 1990, 97, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.M.; Dringen, R.; Robinson, S.R. Zinc stimulates the production of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits glutathione reductase in astrocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, D.R. Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, G.W.; Di Giulio, R.T. Prooxidant and antioxidant mechanisms in aquatic organisms. Aquat. Toxicol. 1991, 19, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, A.; Salamone, M.; Mazzola, S.; Cuttitta, A. Transcriptional and biochemical effects of cadmium and manganese on the defense system of octopus vulgaris paralarvae. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Abele, D.; Weihe, E.; Köhler, A. Sex-specific biochemical and histological differences in gonads of sea urchins (Psammechinus miliaris) and their response to phenanthrene exposure. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, L.D.; Livingstone, D.R. Antioxidant enzyme activities in embryologic and early larval stages of turbot. J. Fish. Biol. 1996, 49, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Yin, X.; Dou, S. Accumulation and oxidative stress biomarkers in Japanese flounder larvae and juveniles under chronic cadmium exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccheri, M.C.; Agnello, M.; Bonaventura, R.; Matranga, V. Cadmium induces the expression of specific stress proteins in sea urchin embryos. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, M.E.; Steinmann, R.; Fent, K. Different expression patterns of heat shock proteins hsp 60 and hsp 70 in zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) exposed to copper and tributyltin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 47, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sharma, A.; Mishra, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Chowdhuri, D.K. Heat shock proteins in toxicology: How close and how far? Life Sci. 2010, 86, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Faria, M.; Barata, C.; Pina, B. Transcriptional response of stress genes to metal exposure in zebra mussel larvae and adults. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harianto, J.; Nguyen, H.D.; Holmes, S.P.; Byrne, M. The effect of warming on mortality, metabolic rate, heat-shock protein response and gonad growth in thermally acclimated sea urchins (Heliocidaris erythrogramma). Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdoun, A.; Epel, D. Embryo stability and vulnerability in an always changing world. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M. Impact of Climate Change Stressors on Marine Invertebrate Life Histories with a Focus on the Mollusca and Echinodermata. In Climate Alert: Climate Change Monitoring and Strategy; University of Sydney Press: Sydney, Australia, 2010; pp. 142–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, K.N.; Lamare, M.D.; Burritt, D.J. Dietary pollutants induce oxidative stress, altering maternal antioxidant provisioning and reproductive output in the temperate sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, K.N.; Lamare, M.D.; Burritt, D.J. Maternal antioxidant provisioning mitigates pollutant-induced oxidative damage in embryos of the temperate sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Suckling, C.C.; Cavallo, A.; Mackenzie, C.L.; Thorne, M.A.S.; Davies, A.J.; Peck, L.S. Molecular mechanisms underpinning transgenerational plasticity in the green sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morroni, L.; Sartori, D.; Costantini, M.; Genovesi, L.; Magliocco, T.; Ruocco, N.; Buttino, I. First molecular evidence of the toxicogenetic effects of copper on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus embryo development. Water Res. 2019, 160, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matranga, V.; Zito, F.; Costa, C.; Bonaventura, R.; Giarrusso, S.; Celi, F. Embryonic development and skeletogenic gene expression affected by X-rays in the Mediterranean sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrella, S.; Romano, G.; Costantini, S.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Costantini, M. Toxic Diatom Aldehydes Affect Defence Gene Networks in Sea Urchins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, R.; Poma, V.; Costa, C.; Matranga, V. UVB radiation prevents skeleton growth and stimulates the expression of stress markers in sea urchin embryos. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Leon, S.B.T.; Davidson, E.H. Information processing at the foxa node of the sea urchin endomesoderm specification network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10103–10108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poustka, A.J.; Kühn, A.; Groth, D.; Weise, V.; Yaguchi, S.; Burke, R.D.; Herwig, R.; Lehrach, H.; Panopoulou, G. A global view of gene expression in lithium and zinc treated sea urchin embryos: New components of gene regulatory networks. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strader, M.E.; Kozal, L.C.; Leach, T.S.; Wong, J.M.; Chamorro, J.D.; Housh, M.J.; Hofmann, G.E. Examining the Role of DNA Methylation in Transcriptomic Plasticity of Early Stage Sea Urchins: Developmental and Maternal Effects in a Kelp Forest Herbivore. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strader, M.E.; Wong, J.; Kozal, L.; Leach, T.; Hofmann, G. Parental environments alter DNA methylation in offspring of the purple sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 517, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, Z. Histone Modification Patterns and Their Responses to Environment. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2014, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Zamudio, R.; Ha, H.C. Environmental epigenetics in metal exposure. Epigenetics 2011, 6, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, V.; Spinelli, G. Environmental epigenetics in zebrafish. Epigenet. Chromatin 2017, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhia, S.R.; Calabro, A.R.; Barile, F.A. Trace metals alter DNA repair and histone modification pathways concurrently in mouse embryonic stem cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Low (µg/L) L | High (µg/L) H |
|---|---|---|
| Cd2+ | 10 | 100 |
| Zn2+ | 40 | 200 |
| Mix | Cd-Zn (10 + 40) | Cd-Zn (100 + 200) |
| Gene Name | Gene Symbol | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Forkhead box transcription factor a | foxa | CAGGTATGGGAAGCATGGGA GCGTATCTCATCGACATGGC |
| Homeodomain containing transcription factor Hox11/13b | hox11/13b | TTGCGACGTTCACAACAACT GTGAGATCGAGAGCCTGTGA |
| Wint8 | wnt8 | AAGTGTCATGGCGTCTCTGG ATGAGCTTGCCACTGACGAA |
| Deadringer-like | dri | TGGAAATAGACGAGAGGGGC GTGGTATCATGGTGGGTGGA |
| Hex homeodomain transcription factor | hex | TGAACCACCCTACTCCACTG GCCGCTCTATTTTGTCCGAG |
| Spicule matrix protein 50 | sm50 | GATGGCACACCAGCTTATCC CTGACGCTTCATGACTGGAG |
| Biomineralization protein p16 | p16 | AGCAGGAGCAGTCGGAGATAC CATCATCACTTCCCATATCGC |
| Biomineralization protein p19 | p19 | AGAGACCAGGCAGGAGACTAAG GTTGATGTCGAGCTTGTCTTTC |
| Mesenchyme-specific cell surface glycoprotein | msp130 | ATACATGGCAACCCAAGAAG CGATTCCAACGAAGATGAGT |
| Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 A | UBE2a | GATTTGAGGAGTGGAGGATTG AGCTGGCGGATCTTCTTGTA |
| Histone deacetylase | Hdac1 | TCACGCCAAGAAGTCAGAAG CCGTGGTGGATATCAATGTC |
| Histone acetyltransferase | kat2A | TGCAATGGATGGAAGAACC ATGTGCAGCAAGTTGATGG |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase | EHMT2 | GTGCAGGAGCTCTTGGTAATG ACAGAGAGGGTCGGAAAGTG |
| Histone lysine demethylase | phf8 | AGCAGTTGCCATTCCTTTTC CGACCCATTCACATTCCAC |
| 18S ribosomal RNA | 18s | GAATGTCTGCCCTATCAACTTTCG TTGGATGTGGTAGCCGTTTCTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masullo, T.; Biondo, G.; Natale, M.D.; Tagliavia, M.; Bennici, C.D.; Musco, M.; Ragusa, M.A.; Costa, S.; Cuttitta, A.; Nicosia, A. Gene Expression Changes after Parental Exposure to Metals in the Sea Urchin Affect Timing of Genetic Programme of Embryo Development. Biology 2021, 10, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020103
Masullo T, Biondo G, Natale MD, Tagliavia M, Bennici CD, Musco M, Ragusa MA, Costa S, Cuttitta A, Nicosia A. Gene Expression Changes after Parental Exposure to Metals in the Sea Urchin Affect Timing of Genetic Programme of Embryo Development. Biology. 2021; 10(2):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020103
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasullo, Tiziana, Girolama Biondo, Marilena Di Natale, Marcello Tagliavia, Carmelo Daniele Bennici, Marianna Musco, Maria Antonietta Ragusa, Salvatore Costa, Angela Cuttitta, and Aldo Nicosia. 2021. "Gene Expression Changes after Parental Exposure to Metals in the Sea Urchin Affect Timing of Genetic Programme of Embryo Development" Biology 10, no. 2: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020103
APA StyleMasullo, T., Biondo, G., Natale, M. D., Tagliavia, M., Bennici, C. D., Musco, M., Ragusa, M. A., Costa, S., Cuttitta, A., & Nicosia, A. (2021). Gene Expression Changes after Parental Exposure to Metals in the Sea Urchin Affect Timing of Genetic Programme of Embryo Development. Biology, 10(2), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020103







