Functional Attributes of Myco-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Endophytic Fungi: A New Implication in Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
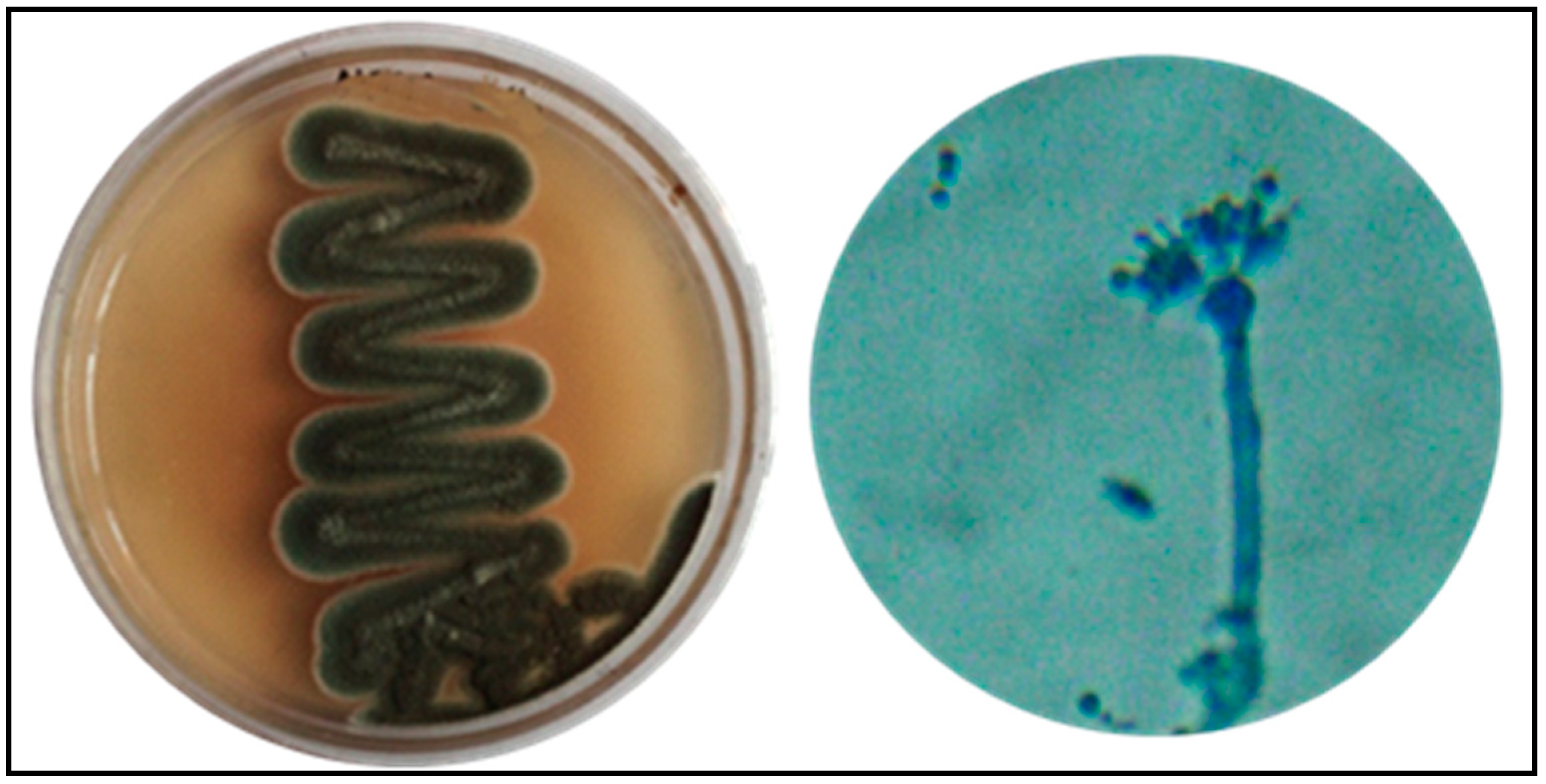
2.2. Isolation and Characterization of Endophytic Fungi
2.3. Preparation and Extraction of Culture Filtrate from P. oxalicum LA-1 Strain
2.4. Natural Products Analysis by GC-MS
2.5. Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Using Culture Filtrate of P. oxalicum LA-1 Strain (PoAgNPs)
2.6. Characterization of PoAgNPs
2.7. Hemolytic Activity of PoAgNPs
2.8. Antibacterial Activity of PoAgNPs
2.8.1. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) of PoAgNPs by the Microdilution Plate Method
2.8.2. Fluorescence-Based Study of the Bactericidal Activity of PoAgNPs
2.9. In Vitro Anticancer Activity
2.9.1. Cell Lines
2.9.2. MTT Assay
2.9.3. Dual Staining Assay (AO/EB Staining)
2.10. Larvicidal Activity of PoAgNPs
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Endophytic Fungi P. oxalicum Strain LA-1 (PoAgNPs)
3.2. GC-MS Analysis of Bioactive Compounds from Endophytic Fungi
3.3. Optimization and Characterization of PoAgNPs from Endophytic Fungi
3.3.1. UV Vis Spectroscopy Analysis
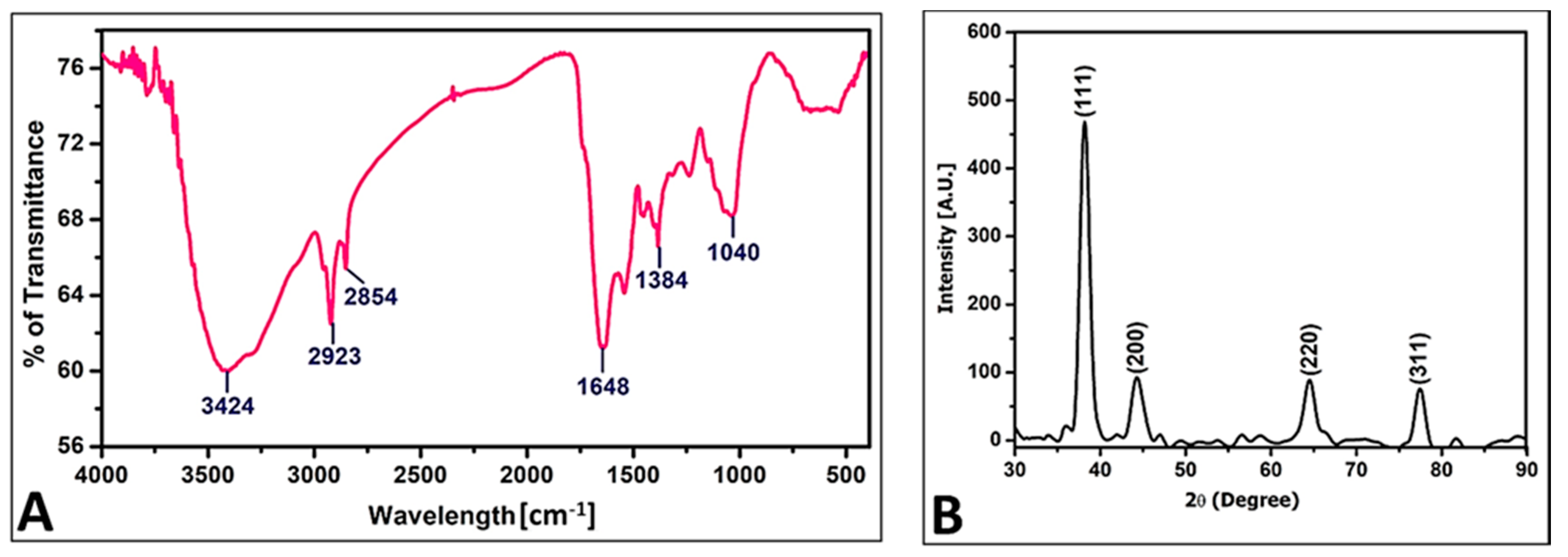
3.3.2. FT-IR Analysis of PoAgNPs
3.3.3. XRD Analysis of PoAgNPs
3.3.4. TEM and EDAX Analysis of PoAgNPs
3.3.5. Zeta Potential Analysis and DLS of PoAgNPs
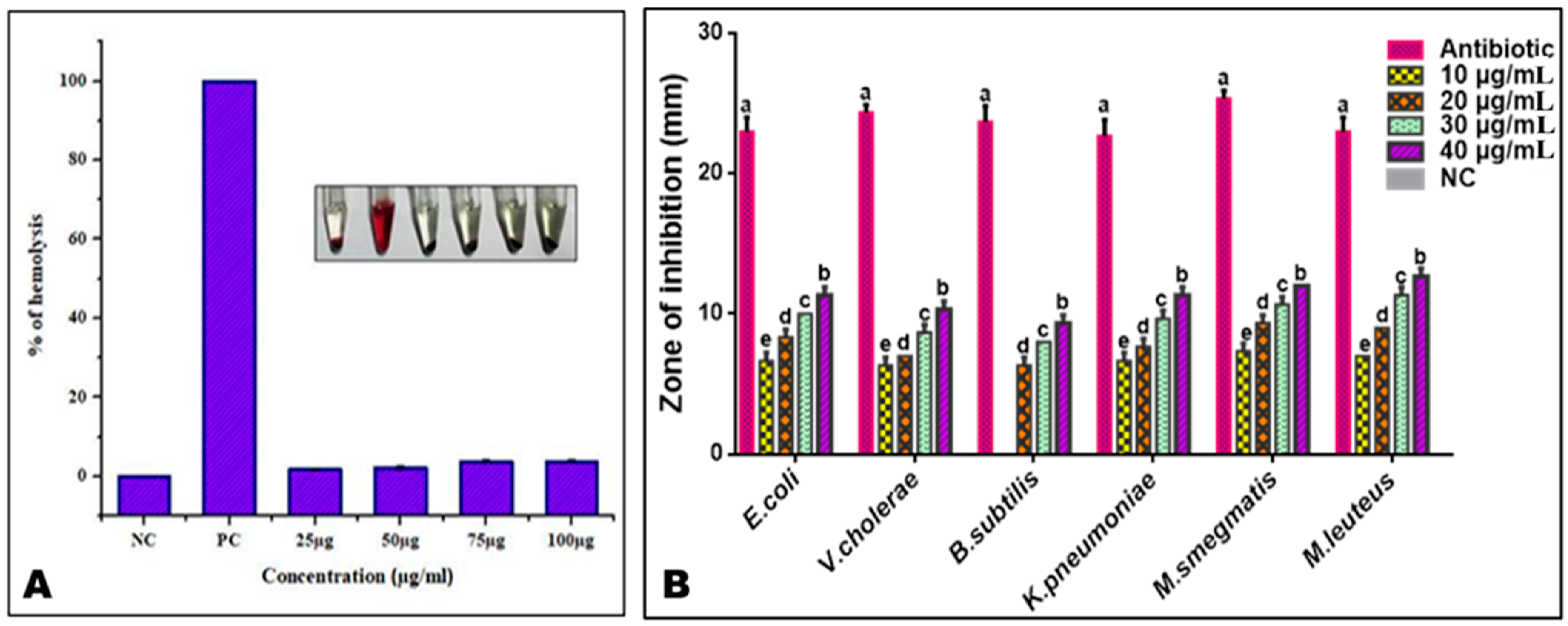
3.4. Hemolytic Activity of PoAgNPs
3.5. Antibacterial Studies of PoAgNPs
3.5.1. Antibacterial Activity
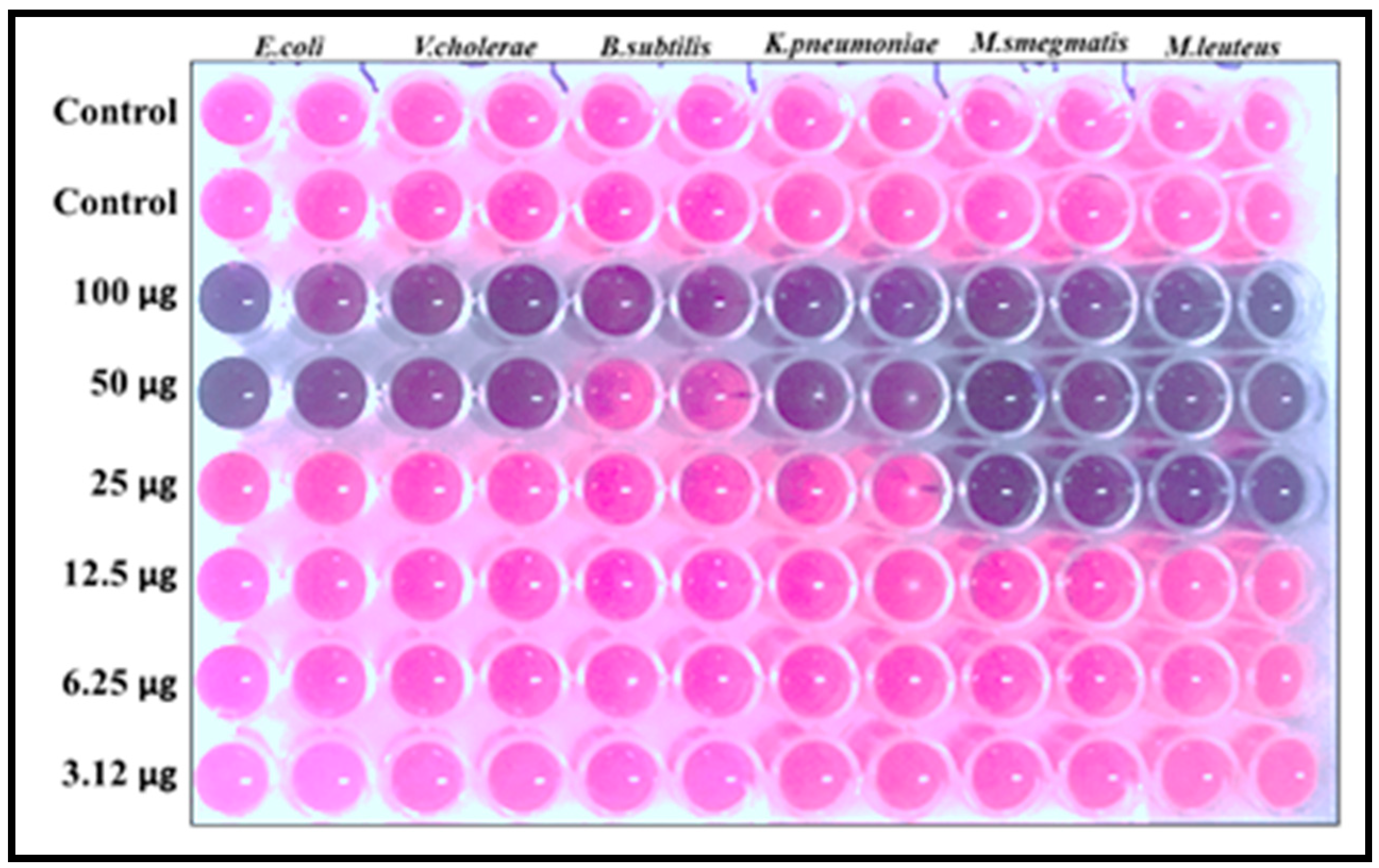
3.5.2. MIC and MBC Analysis
3.5.3. Confirmation of MIC by Resazurin Dye Assay
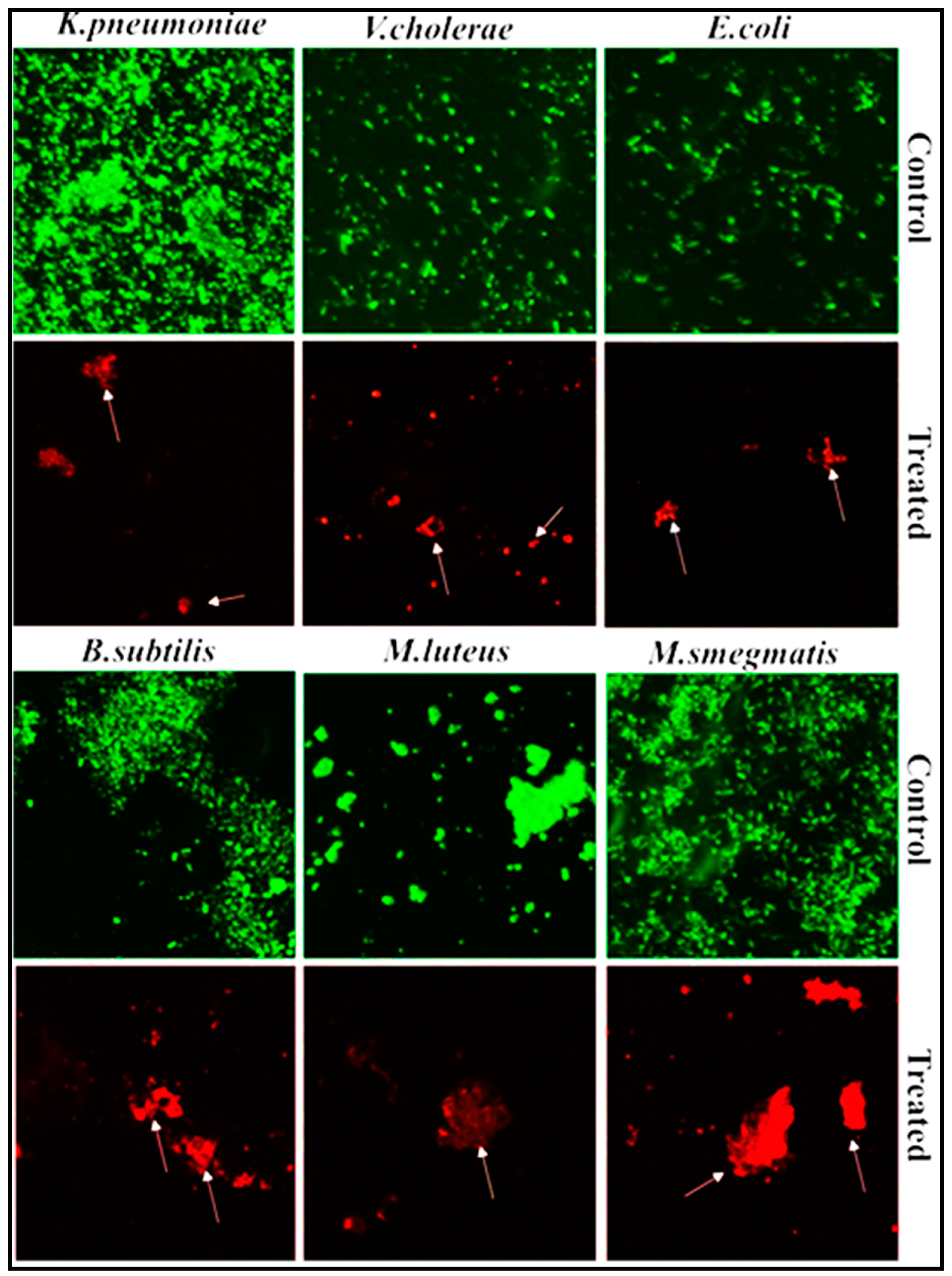
3.5.4. Fluorescence-Based Study of PoAgNPs against Bacterial Pathogens
3.6. In-Vitro Anticancer Activity of PoAgNPs
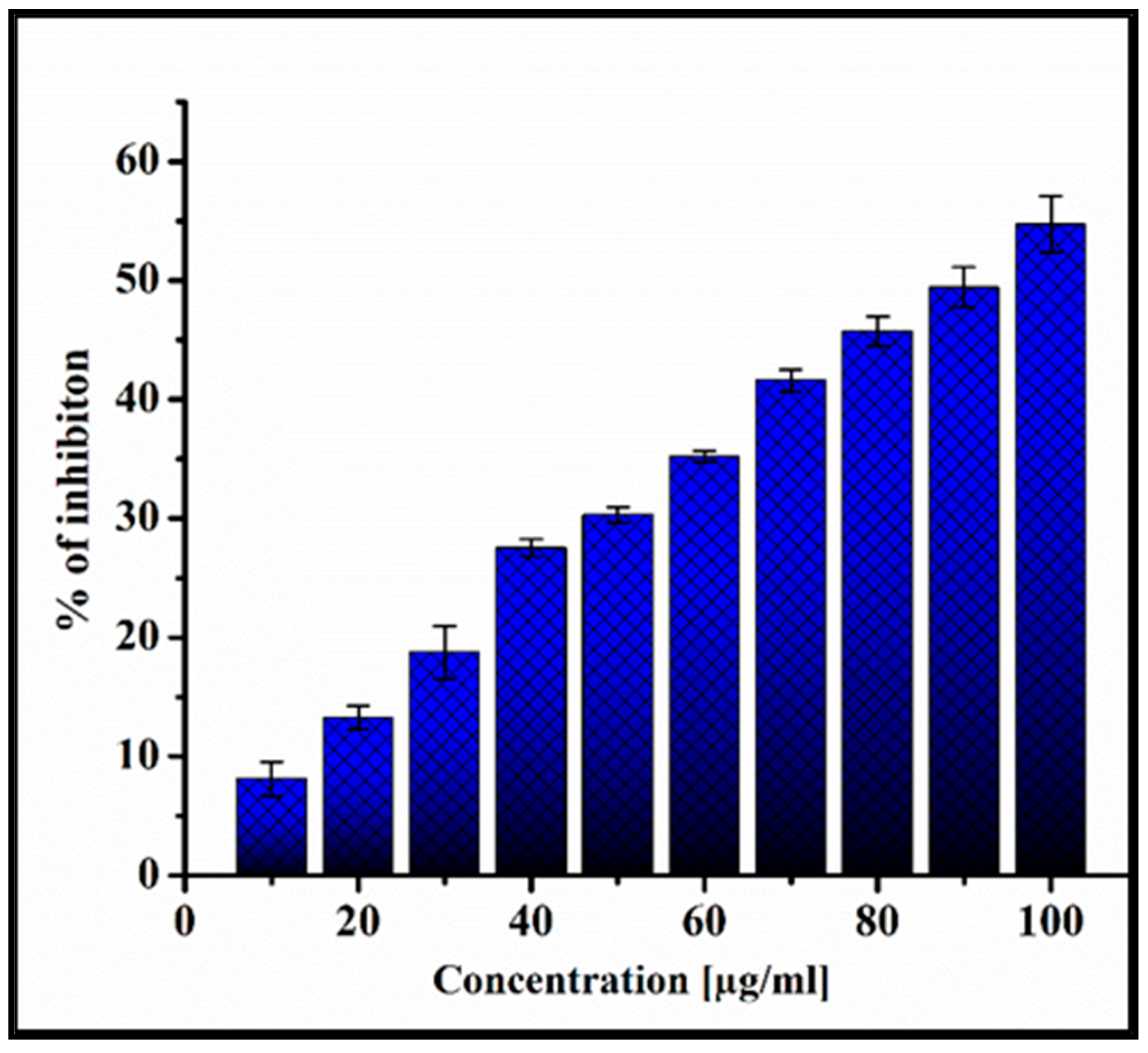
3.6.1. MTT Assay
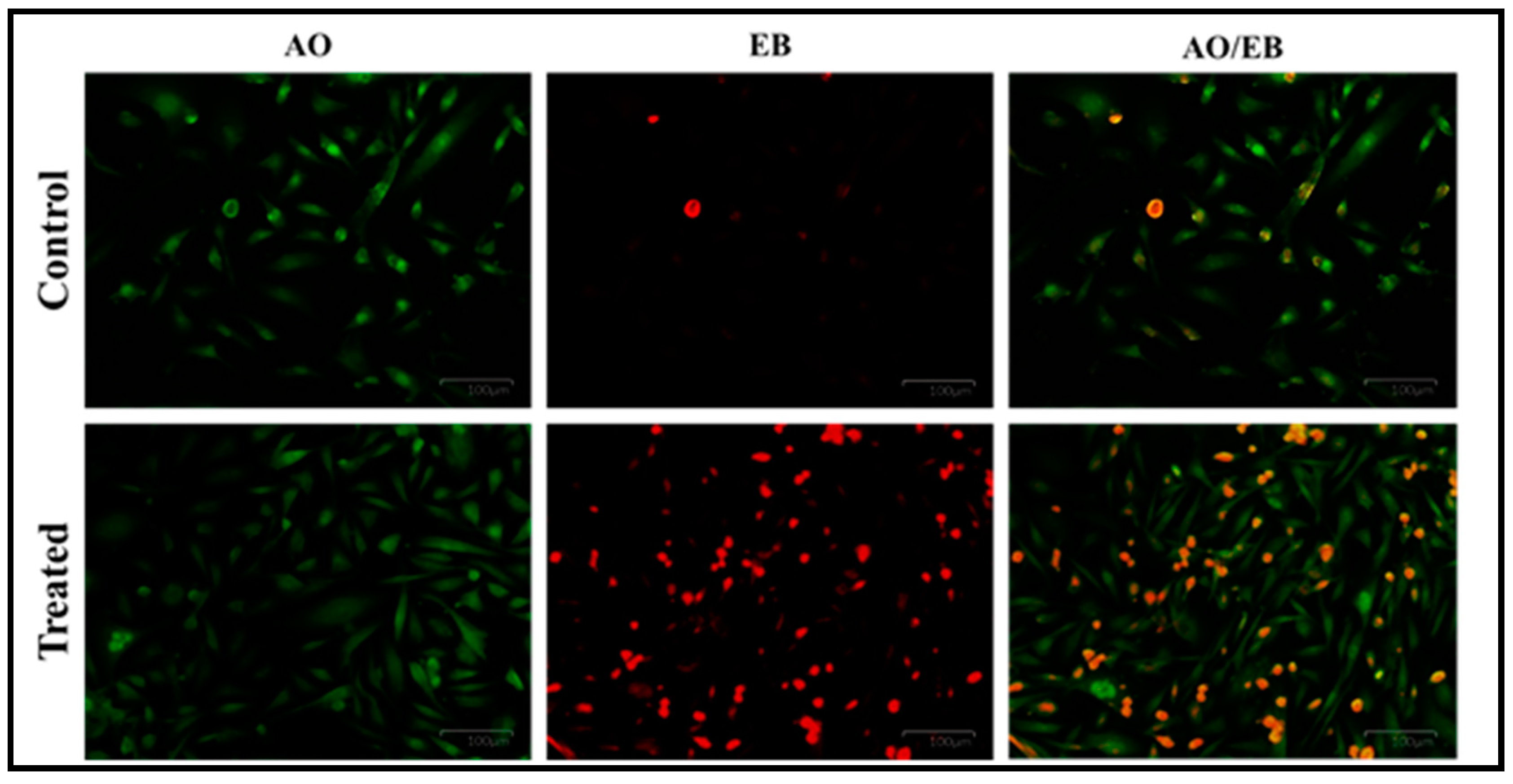
3.6.2. Dual Staining Assay (AO/EB)
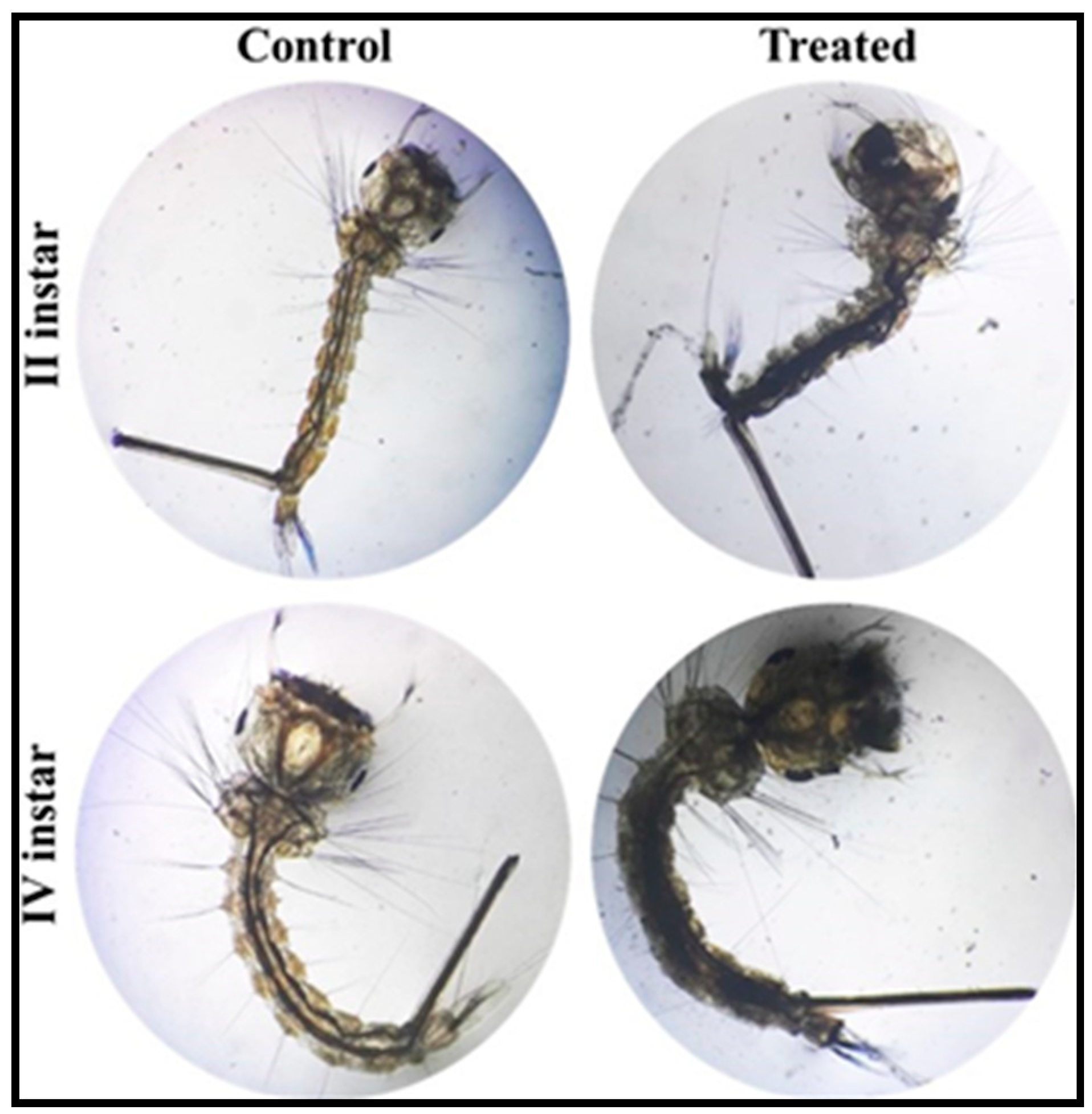
3.7. Larvicidal Activity of PoAgNPs against II and IV Instars Larvae of C. quinquefasciatus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meera, R. Nanostructures and their applications. Recent Res. Sci. Technol. 2012, 4, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon, B. Nanotechnology in agri-food production: An overview. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2014, 7, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ejad, R.M.; Karimi, S.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Plant-derived nanostructures: Types and applications. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 20–52. [Google Scholar]
- Marassi, V.; Di Cristo, L.; Smith, S.; Ortelli, S.; Blosi, M.; Costa, A.L.; Reschiglian, P.; Volkov, Y.; Prina-Mello, A. Silver nanoparticles as a medical device in healthcare settings: A five-step approach for candidate screening of coating agents. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curigliano, G.; Criscitiello, C. Successes and limitations of targeted cancer therapy in breast cancer. Prog. Tumor Res. 2014, 41, 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, P.; Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Nanocarriers for cancer-targeted drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo Clinic. Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer—Mayo Clinic. 2018. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/chemotherapy-for-breast-cancer/about/pac-20384931 (accessed on 11 May 2019).
- Tang, X.; Cai, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, L. Paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles of star-shaped cholic ac-id-core PLA-TPGS copolymer for breast cancer treatment. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sonawnae, A.; Jena, P.; Mohanty, S.; Mallick, R.; Jacob, B. Toxicity and antibacterial assessment of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles on human pathogens and macrophage cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, F.X.; Chan, J.M.; Wang, A.Z.; Langer, R.S.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticles in medicine: Therapeutic applications and developments. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- El-Nour, K.M.A.; Eftaiha, A.; Al-Warthan, A.; Ammar, R.A. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.-S.; Chen, G. Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles by Microorganisms and Their Applications. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 270974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; Alves, O.L.; De Souza, G.I.H.; Esposito, E. Mechanistic aspects of biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by several Fusarium oxysporum strains. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moghaddam, A.B.; Namvar, F.; Moniri, M.; Tahir, P.M.; Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R. Nanoparticles Biosynthesized by Fungi and Yeast: A Review of Their Preparation, Properties, and Medical Applications. Molecules 2015, 20, 16540–16565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, G.; Daisy, B.; Castillo, U.; Harper, J. Natural Products from Endophytic Microorganisms. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.H.; Debbab, A.; Kjer, J.; Proksch, P. Fungal endophytes from higher plants: A prolific source of phytochemicals and other bioactive natural products. Fungal Divers. 2010, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabukumar, S.; Sathishkumar, G.; Rajkuberan, C.; Gobinath, C.; Asad, S.; Hodhod, M.S.; Fuad, A.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Isolation of limonoid compound (Hamisonine) from endophytic fungi Penicillium oxalicum LA-1 (KX622790) of Limonia acidissima L. for its larvicidal efficacy against LF vector, Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 24, 21272–21282. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkuberan, C.; Sudha, K.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Antibacterial and cytotoxic potential of silver nanopar-ticles synthesized using latex of Calotropis gigantea L. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, D. Facile synthetic nano-curcumin encapsulated Bio-fabricated nanoparticles induces ROS-mediated apoptosis and migration blocking of human lung cancer cells. Process. Biochem. 2020, 95, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, S.; Sonsudin, F.; Mainal, A.; Yahya, R.; Gopinath, V.; Vadivelu, J.; Alarjani, K.M.; Al Farraj, D.A.; Yehia, H.M. Phytosynthesis of biohybrid nano-silver anchors enhanced size dependent photocatalytic, antibacterial, anticancer properties and cytocompatibility. Process. Biochem. 2021, 101, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and Broth Dilution Methods to Determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concen-tration (MIC) of Antimicrobial Substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandan, R.; Anjali, R.; Beulaja, M.; Prabhu, N.M.; Koodalingam, A.; Saiprasad, G.; Chitra, P.; Arumugam, M. Synthesis, characterization, anti-proliferative and wound healing activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Caulerpa scalpelli-formis. Process Biochem. 2019, 79, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkuberan, C.; Prabukumar, S.; Muthukumar, K.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Carica papaya (Papaya) latex: A new paradigm to combat against dengue and filariasis vectors Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Porras-Alfaro, A.; Bayman, P. Hidden Fungi, Emergent Properties: Endophytes and Microbiomes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiran, G.S.; Priyadharsini, S.; Sajayan, A.; Ravindran, A.; Selvin, J. An antibiotic agent pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione,hexahydro isolated from a marine bacteria Bacillus tequilensis MSI45 effectively controls multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17837–17846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheoran, N.; Nadakkakath, A.V.; Munjal, V.; Kundu, A.; Subaharan, K.; Venugopal, V.; Rajamma, S.; Eapen, S.J.; Kumar, A. Genetic analysis of plant endophytic Pseudomonas putida BP25 and chemo-profiling of its antimicrobial volatile organic compounds. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 173, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Rathod, V.; Ninganagouda, S.; Herimath, J.; Kulkarni, P. Optimization and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticle by Endophytic Fungi Penicillium sp. Isolated from Curcuma longa (Turmeric) and Application Studies against MDR E. coli and S. aureus. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2014, 408021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amendola, V.; Bakr, O.M.; Stellacci, F. A Study of the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Silver Nanoparticles by the Discrete Dipole Approximation Method: Effect of Shape, Size, Structure, and Assembly. Plasmonics 2010, 5, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netala, V.R.; Kotakadi, V.S.; Bobbu, P.; Gaddam, S.A.; Tartte, V. Endophytic fungal isolate mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their free radical scavenging activity and anti-microbial studies. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, Y.; Yu, H.; He, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Wan, X.; Wang, L. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by the endophytic fungus Epicoccum nigrum and their activity against pathogenic fungi. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 36, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Mehata, M.S. Medicinal Plant Leaf Extract and Pure Flavonoid Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and their Enhanced Antibacterial Property. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, V.A.; Minaev, B.F. Spectroscopy study of silver nanoparticles fabrication using synthetic humic substances and their antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 108, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaidev, L.R.; Narasimha, G. Fungal mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rafie, M.; Shaheen, T.; Mohamed, A.; Hebeish, A. Bio-synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles onto cotton fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.; Saraswati, S.; Kundu, G.C.; Ahmad, A. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Humicola sp. and evaluation of their cytoxicity using normal and cancer cell lines. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 114, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Jyoti, K.; Patnaik, A.; Singh, A.; Chauhan, R.; Chandel, S.S. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using an endophytic fungal supernatant of Raphanus sativus. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masum, M.I.; Siddiqa, M.M.; Ali, K.A.; Zhang, Y.; Abdallah, Y.; Ibrahim, E.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Phyllanthus emblica Fruit Extract and Its Inhibitory Action Against the Pathogen Acidovorax oryzae Strain RS-2 of Rice Bacterial Brown Stripe. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashokraja, C.; Sakar, M.; Balakumar, S. A perspective on the hemolytic activity of chemical and green-synthesized silver and silver oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, J. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles: Structural Effects. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.K.; Deshmukh, S.D.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.K. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nano weapon against multi-drug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruden, S.; Hilpert, K.; Berditsch, M.; Wadhwani, P.; Ulrich, A.S. Synergistic Interaction between Silver Nanoparticles and Membrane-Permeabilizing Antimicrobial Peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3538–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gnanasekar, S.; Murugaraj, J.; Dhivyabharathi, B.; Krishnamoorthy, V.; Jha, P.K.; Seetharaman, P.; Sivaperumal, S. Anti-bacterial and cytotoxicity effects of biogenic palladium nanoparticles synthesized using fruit extract of Couroupita guianensis Aubl. J. Appl. Biomed. 2018, 16, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Caselli, A.; Canale, A. Nanoparticles for mosquito control: Challenges and constraints. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2017, 29, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, O.Y.; Shamova, O.V.; Orlov, D.S.; Pazina, T.Y.; Boldina, A.S.; Kokryakov, V.N. Study of antimicrobial and he-molytic activities of silver nanoparticles prepared by chemical reduction. Glass Phys. Chem. 2010, 36, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Jegadeesh, R.; Sri, N.A.M.; Priscilla, A.J.; Sabaratnam, V. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ganoderma neo-japonicum Imazeki: A potential cytotoxic agent against breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4399–4413. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Muthukumaran, P.; Ramachandran, R.; Balakumaran, M.; Kalaichelvan, P. Acalypha indica Linn: Biogenic synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effects against MDA-MB-231, human breast cancer cells. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, S.; Chandrasekaran, R. Biogenic nanoparticles: A comprehensive perspective in synthesis, characterization, application and its challenges. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, K.; Ragavendran, C.; Natarajan, D. Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Beauveria bassiana and its larvi-cidal, antibacterial, and cytotoxic effect on human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44972–44986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Fang, L.; Ling, J.; Ding, C.Z.; Kang, B.; Huang, C.Z. Nanotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to Red Blood Cells: Size Dependent Adsorption, Uptake, and Hemolytic Activity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| S. No. | Retention Time | % of Total | M.W. | M. Formula | Compound Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.394 | 3.111 | 310 | C16H29F3O2 | 3-trifluoroacetoxytetradecane |
| 2 | 16.801 | 1.446 | 238 | C16H30O | E-14-hexadecenal |
| 3 | 18.117 | 3.3 | 206 | C14H22O | Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- |
| 4 | 19.333 | 2.771 | 238 | C16H30O | E-14-hexadecenal |
| 5 | 20.963 | 3.225 | 186 | C12H10O2 | 1-naphthalene carboxylic acid, methyl ester |
| 6 | 21.274 | 1.525 | 238 | C16H30O | E-14-hexadecenal |
| 7 | 21.642 | 1.825 | 242 | C15H30O2 | Pentadecanoic acid |
| 8 | 21.32 | 1.211 | 210 | C11H18N2O2 | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 9 | 22.46 | 2.082 | 210 | C11H18N2O2 | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 10 | 22.522 | 1.784 | 496 | C27H52O4Si2 | 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid |
| 11 | 22.744 | 5.481 | 210 | C11H18N2O2 | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 12 | 22.872 | 4.745 | 210 | C11H18N2O2 | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 13 | 22.922 | 2.623 | 210 | C11H18N2O2 | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 14 | 23.091 | 5.819 | 210 | C11H18N2O2 | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 15 | 23.541 | 2.329 | 256 | C16H32O2 | n-hexadecanoic acid |
| 16 | 25.431 | 4.221 | 238 | C16H30O | E-14-hexadecenal |
| 17 | 25.896 | 2.479 | 226 | C12H22N2O2 | 2,5-piperazinedione, 3,6-bis(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 18 | 27.464 | 2.952 | 266 | C18H34O | 5-octadecenal |
| 19 | 29.421 | 1.632 | 210 | C11H18N2O2 | Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)- |
| 20 | 31.769 | 8.132 | 281 | C18H35NO | 9-octadecenamide, (Z)- |
| Bacterial Pathogens | Gram-Negative | Gram-Positive | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | V. cholerae | K. pneumoniae | B. subtilis | M. smegmatis | M. luteus | |
| MIC (µg/mL) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 25 | 25 |
| MBC (µg/mL) | >100 | 100 | >100 | >100 | 100 | >100 |
| Larvae Stages | LC50 (95% Fiducial Limits (LCL-UCL))(PPM) | LC90 (95% Fiducial Limits (LCL-UCL))(PPM) | Regression Equations | R Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| II instar | 1.673 (1.521–1.840) | 10.85 (9.12–13.27) | 27.688X + 7.138 | 0.82 |
| IV instar | 2.273 (2.059–2.515) | 16.24 (13.29–20.56) | 22.773X + 6.808 | 0.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seetharaman, P.K.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Periakaruppan, R.; Gnanasekar, S.; Sivaperumal, S.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Valis, M.; Kuca, K. Functional Attributes of Myco-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Endophytic Fungi: A New Implication in Biomedical Applications. Biology 2021, 10, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060473
Seetharaman PK, Chandrasekaran R, Periakaruppan R, Gnanasekar S, Sivaperumal S, Abd-Elsalam KA, Valis M, Kuca K. Functional Attributes of Myco-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Endophytic Fungi: A New Implication in Biomedical Applications. Biology. 2021; 10(6):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060473
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeetharaman, Prabu Kumar, Rajkuberan Chandrasekaran, Rajiv Periakaruppan, Sathishkumar Gnanasekar, Sivaramakrishnan Sivaperumal, Kamel A. Abd-Elsalam, Martin Valis, and Kamil Kuca. 2021. "Functional Attributes of Myco-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Endophytic Fungi: A New Implication in Biomedical Applications" Biology 10, no. 6: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060473
APA StyleSeetharaman, P. K., Chandrasekaran, R., Periakaruppan, R., Gnanasekar, S., Sivaperumal, S., Abd-Elsalam, K. A., Valis, M., & Kuca, K. (2021). Functional Attributes of Myco-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles from Endophytic Fungi: A New Implication in Biomedical Applications. Biology, 10(6), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060473









