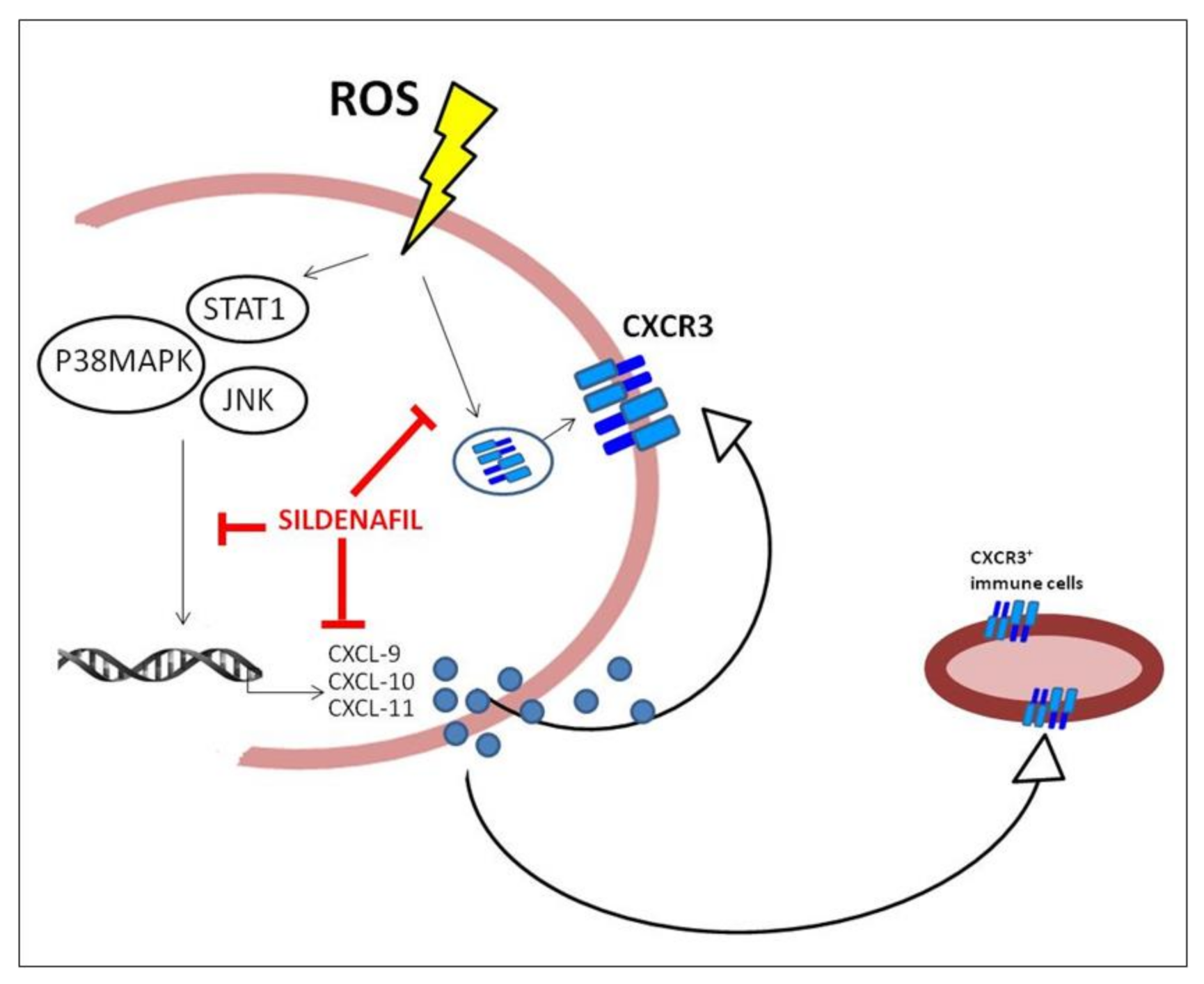
Sildenafil Counteracts the In Vitro Activation of CXCL-9, CXCL-10 and CXCL-11/CXCR3 Axis Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species in Scleroderma Fibroblasts
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Cultures and Treatments
2.3. Cytokine Secretion Assay
2.4. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.5. Protein Content Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sildenafil Reduced CXCL-9, CXCL-10 and CXCL-11 Secretion Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in SSc Fibroblasts
3.2. Sildenafil Impaired the Activation of Intracellular Pathways Underlying Chemokines Expression in SSc Fibroblasts
3.3. Sildenafil Reduced p-CRYAB (Ser59)/CRYAB Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in SSc Fibroblasts
3.4. Sildenafil Reduced CXCR3 Plasma Membrane Localization Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in SSc Fibroblasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varga, J.; Abraham, D. Systemic sclerosis: A prototypic multisystem fibrotic disorder. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, P.; Maślińska, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Łagun, Z.; Malewska, A.; Roszkiewicz, M.; Nitskovich, R.; Szymańska, E.; Walecka, I. Systemic sclerosis—Multidisciplinary disease: Clinical features and treatment. Reumatologia 2019, 57, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Ross, R.; Abignano, G.; Antinozzi, C.; Marampon, F.; Di Luigi, L.; Buch, M.; Riccieri, V.; Lenzi, A.; Crescioli, C.; et al. Muscle Damage in Systemic Sclerosis and CXCL10: The Potential Therapeutic Role of PDE5 Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Soffritti, I.; D’Accolti, M.; Bortolotti, D.; Rizzo, R.; Sighinolfi, G.; Giuggioli, D.; Ferri, C. HHV-6A Infection and Systemic Sclerosis: Clues of a Possible Association. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colletti, M.; Galardi, A.; de Santis, M.; Guidelli, G.M.; Di Giannatale, A.; Di Luigi, L.; Antinozzi, C. Exosomes in Systemic Sclerosis: Messengers between Immune, Vascular and Fibrotic Components? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabrielli, A.; Svegliati, S.; Moroncini, G.; Pomponio, G.; Santillo, M.; Avvedimento, E.V. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of scleroderma: The Murrell’s hypothesis revisited. Semin. Immunopathol. 2008, 30, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielli, A.; Svegliati, S.; Moroncini, G.; Amico, D. New insights into the role of oxidative stress in scleroderma fibrosis. Open Rheumatol. J. 2012, 6, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloranta, M.-L.; Franck-Larsson, K.; Lövgren, T.; Kalamajski, S.; Rönnblom, A.; Rubin, K.; Alm, G.V.; Rönnblom, L. Type I interferon system activation and association with disease manifestations in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechomska, M.; Huigens, C.A.; Hügle, T.; Stanly, T.; Gessner, A.; Griffiths, B.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Hambleton, S.; O’Reilly, S.; van Laar, J.M. Toll-like receptor-mediated, enhanced production of profibrotic TIMP-1 in monocytes from patients with systemic sclerosis: Role of serum factors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farina, G.A.; York, M.R.; Di Marzio, M.; Collins, C.A.; Meller, S.; Homey, B.; Rifkin, I.R.; Marshak-Rothstein, A.; Radstake, T.R.; Lafyatis, R. Poly(I:C) drives type I IFN- and TGFbeta-mediated inflammation and dermal fibrosis simulating altered gene expression in systemic sclerosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2583–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rabquer, B.J.; Tsou, P.S.; Hou, Y.; Thirunavukkarasu, E.; Haines, G.K., 3rd; Impens, A.J.; Phillips, K.; Kahaleh, B.; Seibold, J.R.; Koch, A.E. Dysregulated expression of MIG/CXCL9, IP-10/CXCL10 and CXCL16 and their receptors in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scala, E.; Pallotta, S.; Frezzolini, A.; Abeni, D.; Barbieri, C.; Sampogna, F.; de Pita, O.; Puddu, P.; Paganelli, R.; Russo, G. Cytokine and chemokine levels in systemic sclerosis: Relationship with cutaneous and internal organ involvement. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 138, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescioli, C.; Corinaldesi, C.; Riccieri, V.; Raparelli, V.; Vasile, M.; del Galdo, F.; Valesini, G.; Lenzi, A.; Basili, S.; Antinozzi, C. Association of circulating CXCL10 and CXCL11 with systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1845–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, T. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in scleroderma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 140, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, S.; Fujii, H.; Kaburagi, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Serum concentrations of the CXC chemokines interleukin 8 and growth-regulated oncogene-alpha are elevated in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lacotte, S.; Brun, S.; Muller, S.; Dumortier, H. CXCR3, Inflammation, and Autoimmune Diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loenhout, J.; Peeters, M.; Bogaerts, A.; Smits, E.; Deben, C. Oxidative Stress-Inducing Anticancer Therapies: Taking a Closer Look at Their Immunomodulating Effects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalec, L.; Choudhury, B.K.; Postlethwait, E.; Wild, J.S.; Alam, R.; Lett-Brown, M.; Sur, S. CCL7 and CXCL10 orchestrate oxidative stress-induced neutrophilic lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnett, C.F.; Machado, R.F. Sildenafil in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brueckner, C.S.; Becker, M.O.; Kröncke, T.; Huscher, D.; Scherer, H.U.; Worm, M.; Burmester, G.; Riemekasten, G. Effect of sildenafil on digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis: Analysis from a single centre pilot study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 69, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Della Rossa, A.; Doveri, M.; D’Ascanio, A.; Tavoni, A.; Consensi, A.; Neri, R.; Bazzichi, L.; Bombardieri, S. Oral sildenafil in skin ulcers secondary to systemic sclerosis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 40, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsaie, S.; Khalili, H.; Karimzadeh, I.; Dashti-Khavidaki, S. An old drug for a new application: Potential benefits of sildenafil in wound healing. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 15, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gürsoy, K.; Oruç, M.; Kankaya, Y.; Ulusoy, M.G.; Koçer, U.; Kankaya, D.; Gürsoy, R.N.; Çevik, Ö.; Öğüş, E.; Fidanci, V. Effect of topically applied sildenafil citrate on wound healing: Experimental study. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 14, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hachulla, E.; Hatron, P.Y.; Carpentier, P.; Agard, C.; Chatelus, E.; Jego, P.; Mouthon, L.; Queyrel, V.; Fauchais, A.L.; Michon-Pasturel, U.; et al. Efficacy of sildenafil on ischaemic digital ulcer healing in systemic sclerosis: The place-bo-controlled SEDUCE study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1009–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luigi, L.; Sgrò, P.; Duranti, G.; Sabatini, S.; Caporossi, D.; del Galdo, F.; Dimauro, I.; Antinozzi, C. Sildenafil Reduces Ex-pression and Release of IL-6 and IL-8 Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species in Systemic Sclerosis Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 30, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luigi, L.; Duranti, G.; Antonioni, A.; Sgrò, P.; Ceci, R.; Crescioli, C.; Sabatini, S.; Lenzi, A.; Caporossi, D.; del Galdo, F.; et al. The Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor Sildenafil Improves DNA Stability and Redox Homeostasis in Systemic Sclerosis Fibroblasts Exposed to Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Galdo, F.; Sotgia, F.; de Almeida, C.J.; Jasmin, J.-F.; Musick, M.; Lisanti, M.P.; Jiménez, S.A. Decreased expression of caveolin 1 in patients with systemic sclerosis: Crucial role in the pathogenesis of tissue fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illert, A.L.; Kawaguchi, H.; Antinozzi, C.; Bassermann, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; von Klitzing, C.; Hiwatari, M.; Peschel, C.; de Rooij, D.G.; Morris, S.W.; et al. Targeted inactivation of nuclear interaction partner of ALK disrupts meiotic prophase. Development 2012, 139, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marampon, F.; Antinozzi, C.; Corinaldesi, C.; Vannelli, G.B.; Sarchielli, E.; Migliaccio, S.; Di Luigi, L.; Lenzi, A.; Crescioli, C. The phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor tadalafil regulates lipidic homeostasis in human skeletal muscle cell metabolism. Endocrine 2018, 59, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimauro, I.; Scalabrin, M.; Fantini, C.; Grazioli, E.; Valls, M.R.B.; Mercatelli, N.; Parisi, A.; Sabatini, S.; Di Luigi, L.; Caporossi, D. Resistance training and redox homeostasis: Correlation with age-associated genomic changes. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antinozzi, C.; Marampon, F.; Sgrò, P.; Tombolini, V.; Lenzi, A.; Crescioli, C.; Di Luigi, L. Comparative study of testosterone and vitamin D analogue, elocalcitol, on insulin-controlled signal transduction pathway regulation in human skeletal muscle cells. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, E.; Nardozi, D.; Antinozzi, C.; Faieta, M.; Di Cecca, S.; Caggiano, C.; Fukuda, T.; Bonanno, E.; Zhenkun, L.; Maldonado, A.; et al. H2AFX and MDC1 promote maintenance of genomic integrity in male germ cells. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs.214411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimauro, I.; Antonioni, A.; Mercatelli, N.; Grazioli, E.; Fantini, C.; Barone, R.; Macaluso, F.; Di Felice, V.; Caporossi, D. The early response of αB-crystallin to a single bout of aerobic exercise in mouse skeletal muscles depends upon fiber oxidative features. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioni, A.; Dimauro, I.; Fantini, C.; Barone, R.; Macaluso, F.; Di Felice, V.; Caporossi, D. αB-crystallin response to a pro-oxidant non-cytotoxic environment in murine cardiac cells: An “in vitro” and “in vivo” study. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 20, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, S.; Mercatelli, N.; Dimauro, I.; Jackson, M.; Paronetto, M.P.; Caporossi, D. Alpha B-crystallin induction in skeletal muscle cells under redox imbalance is mediated by a JNK-dependent regulatory mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 86, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheiro, T.; Horta, S.; van Roon, J.A.G.; Santiago, M.; Salvador, M.J.; Trindade, H.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; da Silva, J.A.P.; Paiva, A. Increased frequencies of circulating CXCL10-, CXCL8- and CCL4-producing monocytes and Siglec-3-expressing myeloid dendritic cells in systemic sclerosis patients. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antinozzi, C.; Sgrò, P.; Di Luigi, L. Advantages of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors in the Management of Glucose Me-tabolism Disorders: A Clinical and Translational Issue. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 7078108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, J.; Raska, M.; Kriegova, E.; Goodman, S.B. Inflammation and its resolution and the musculoskeletal system. J. Orthop. Transl. 2017, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, C.D.; Barone, F.; Nayar, S.; Bénézech, C.; Caamano, J. Stromal Cells in Chronic Inflammation and Tertiary Lymphoid Organ Formation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 715–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescioli, C.; Sottili, M.; Bonini, P.; Cosmi, L.; Chiarugi, P.; Romagnani, P.; Vannelli, G.B.; Colletti, M.; Isidori, A.M.; Serio, M.; et al. Inflammatory response in human skeletal muscle cells: CXCL10 as a potential therapeutic target. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 91, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svegliati, S.; Cancello, R.; Sambo, P.; Luchetti, M.; Paroncini, P.; Orlandini, G.; Discepoli, G.; Paterno, R.; Santillo, M.; Cuozzo, C.; et al. Platelet-derived growth factor and reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulate Ras protein levels in primary human fibroblasts via ERK1/2. Amplification of ROS and Ras in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 28, 36474–36482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsushita, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Serum chemokine and cytokine levels as indicators of disease activity in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 30, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferri, C.; Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Giuggioli, D.; Colaci, M.; Manfredi, A.; Frascerra, S.; Franzoni, F.; Galetta, F.; et al. CXCL10 (α) and CCL2 (β) chemokines in systemic sclerosis—A longitudinal study. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luster, A.D. Chemokines—Chemotactic Cytokines That Mediate Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Baggiolini, M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, M.; van Bon, L.; Preti, C.; Rossato, M.; Beretta, L.; Radstake, T.R.D.J. Earliest Phase of Systemic Sclerosis Typified by Increased Levels of Inflammatory Proteins in the Serum. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Mayes, M.D.; Tan, F.K.; Wu, M.; Reveille, J.D.; Harper, B.E.; Draeger, H.T.; Gonzalez, E.B.; Assassi, S. Correlation of interferon-inducible chemokine plasma levels with disease severity in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragusa, F. MIG chemokine in systemic sclerosis. MIG in Systemic sclerosis. Clin. Ter. 2018, 169, e178–e183. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, H.; Shimada, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Serum levels of a Th1 chemoattractant IP-10 and Th2 chemoat-tractants, TARC and MDC, are elevated in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2004, 35, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luigi, L.; Corinaldesi, C.; Colletti, M.; Scolletta, S.; Antinozzi, C.; Vannelli, G.B.; Giannetta, E.; Gianfrilli, D.; Isidori, A.M.; Migliaccio, S.; et al. Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor Sildenafil Decreases the Proinflammatory Chemokine CXCL10 in Human Cardiomyocytes and in Subjects with Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Inflammation 2016, 39, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevi, F.; Campolo, F.; Naro, F.; Zolla, L. The cardioprotective effect of sildenafil is mediated by the activation of malate dehydrogenase and an increase in the malate-aspartate shuttle in cardiomyocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 127, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Sepúlveda, A.; Esquinca-González, A.; Benavides-Suárez, S.A.; Sordo-Lima, D.E.; Caballero-Islas, A.E.; Cabral-Castañeda, A.R.; Rodríguez-Reyna, T.S. Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies, beyond the Fibroblast. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, Y.; Cheong, Y.-K.; Kim, N.-H.; Chung, H.-T.; Kang, D.G.; Pae, H.-O. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Reactive Oxygen Species: How Can ROS Activate MAPK Pathways? J. Signal. Transduct. 2011, 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottili, M.; Cosmi, L.; Borgogni, E.; Sarchielli, E.; Maggi, L.; Francalanci, M.; Vannelli, G.B.; Ronconi, E.; Adorini, L.; Annunziato, F.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of BXL-01-0029, a less hypercalcemic vitamin D ana-logue, in human cardiomyocytes and T cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 15, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groover, M.K.; Richmond, J.M. Potential therapeutic manipulations of the CXCR3 chemokine axis for the treatment of in-flammatory fibrosing diseases. F1000Research 2020, 5, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimauro, I.; Mercatelli, N.; Caporossi, D. Exercise-induced ROS in heat shock proteins response. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 98, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimauro, I.; Antonioni, A.; Mercatelli, N.; Caporossi, D. The role of αB-crystallin in skeletal and cardiac muscle tissues. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, E.; Yesilada, A.K.; Sevim, K.Z.; Sumer, O.; Tatlidede, H.S.; Sakiz, D. Effect of sildenafil citrate on secondary healing in full thickness skin defects in experiment. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2014, 115, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Gene Name | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CXCL-9 | CTGTTCCTGCATCAGCACCAAC | TGAACTCCATTCTTCAGTGTAGCA |
| CXCL-10 | TTCCTGCAAGCCAATTTTGT | ATGGCCTTCGATTCTGGATT |
| CXCL-11 | GAGTGTGAAGGGCATGGCTA | ACATGGGGAAGCCTTGAACA |
| β-ACTIN | CTGAACCCCAAGGCCAAC | AGCCTGGATAGCAACGTACA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antinozzi, C.; Sgrò, P.; Marampon, F.; Caporossi, D.; Del Galdo, F.; Dimauro, I.; Di Luigi, L. Sildenafil Counteracts the In Vitro Activation of CXCL-9, CXCL-10 and CXCL-11/CXCR3 Axis Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species in Scleroderma Fibroblasts. Biology 2021, 10, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060491
Antinozzi C, Sgrò P, Marampon F, Caporossi D, Del Galdo F, Dimauro I, Di Luigi L. Sildenafil Counteracts the In Vitro Activation of CXCL-9, CXCL-10 and CXCL-11/CXCR3 Axis Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species in Scleroderma Fibroblasts. Biology. 2021; 10(6):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060491
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntinozzi, Cristina, Paolo Sgrò, Francesco Marampon, Daniela Caporossi, Francesco Del Galdo, Ivan Dimauro, and Luigi Di Luigi. 2021. "Sildenafil Counteracts the In Vitro Activation of CXCL-9, CXCL-10 and CXCL-11/CXCR3 Axis Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species in Scleroderma Fibroblasts" Biology 10, no. 6: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060491
APA StyleAntinozzi, C., Sgrò, P., Marampon, F., Caporossi, D., Del Galdo, F., Dimauro, I., & Di Luigi, L. (2021). Sildenafil Counteracts the In Vitro Activation of CXCL-9, CXCL-10 and CXCL-11/CXCR3 Axis Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species in Scleroderma Fibroblasts. Biology, 10(6), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060491









