Effect of Vibrio-Derived Extracellular Protease vEP-45 on the Blood Complement System
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Expression and Purification of vEP-45 Protease
2.3. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Cleavage of C3, C4, and C5 by vEP-45 In Vitro
2.5. Cleavage of C3 and C5 by vEP-45 in Human Plasma
3. Results
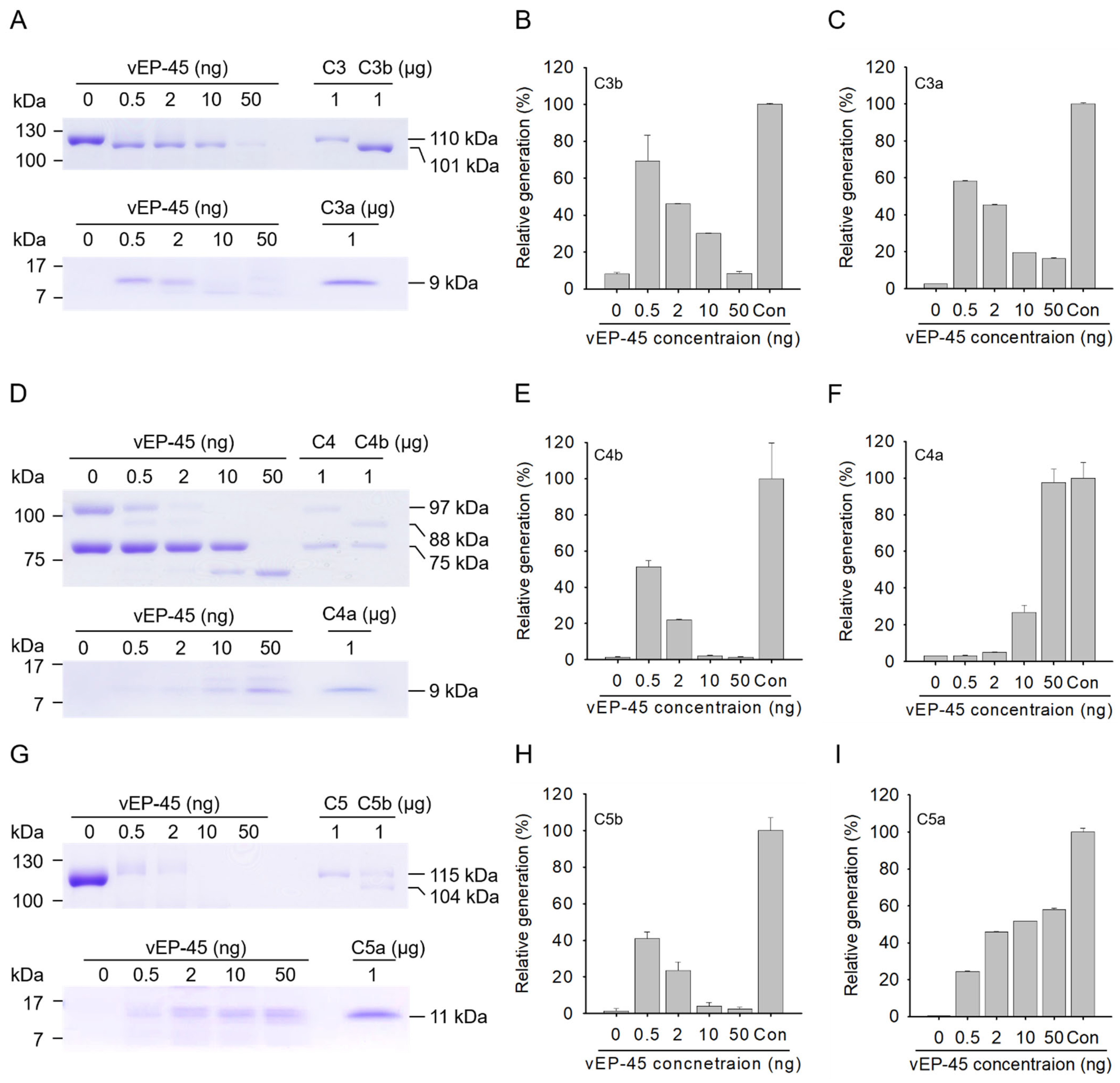
3.1. Cleavage of C3 by vEP-45
3.2. Cleavage of C4 by vEP-45 In Vitro
3.3. Cleavage of C5 by vEP-45 In Vitro
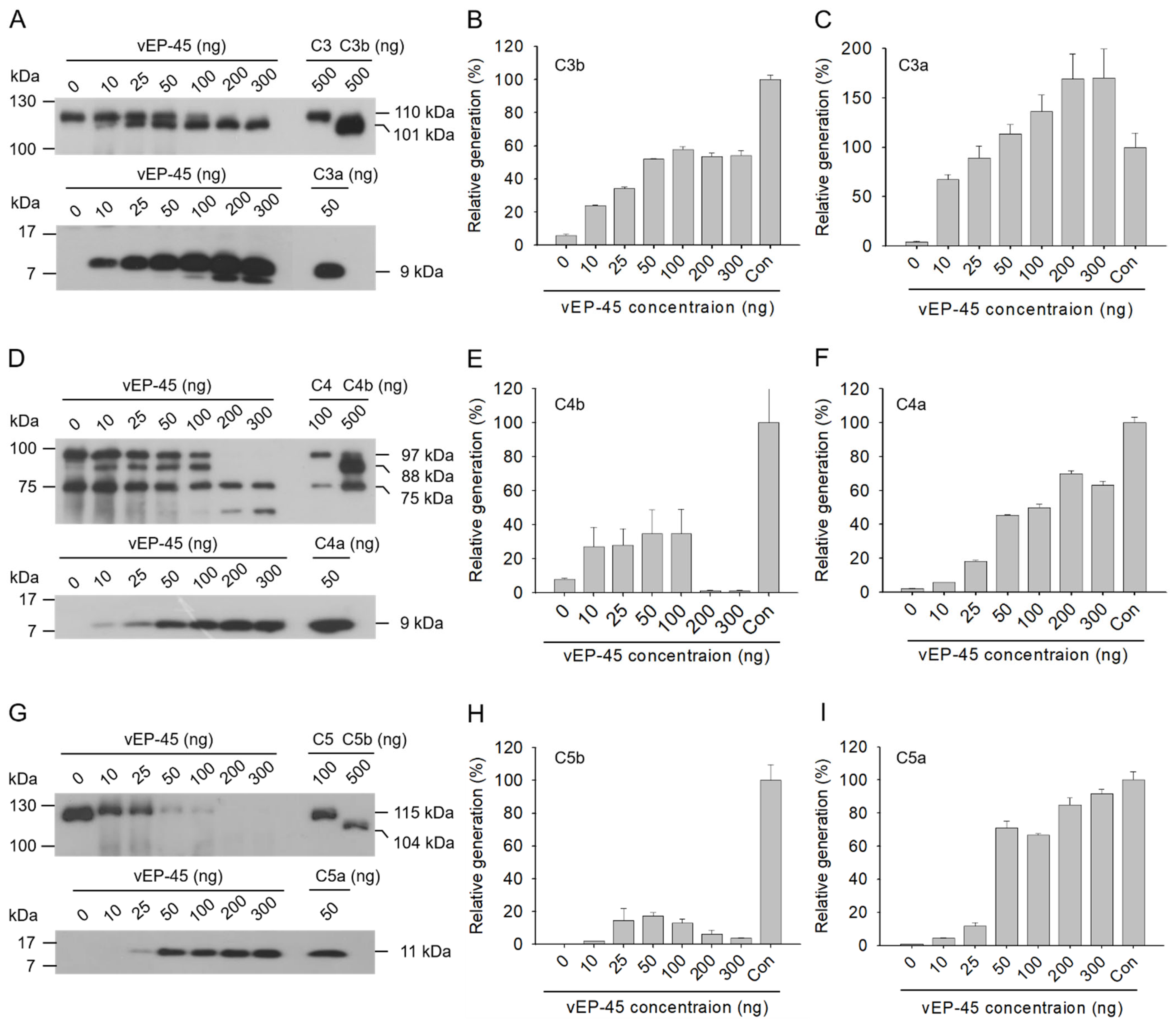
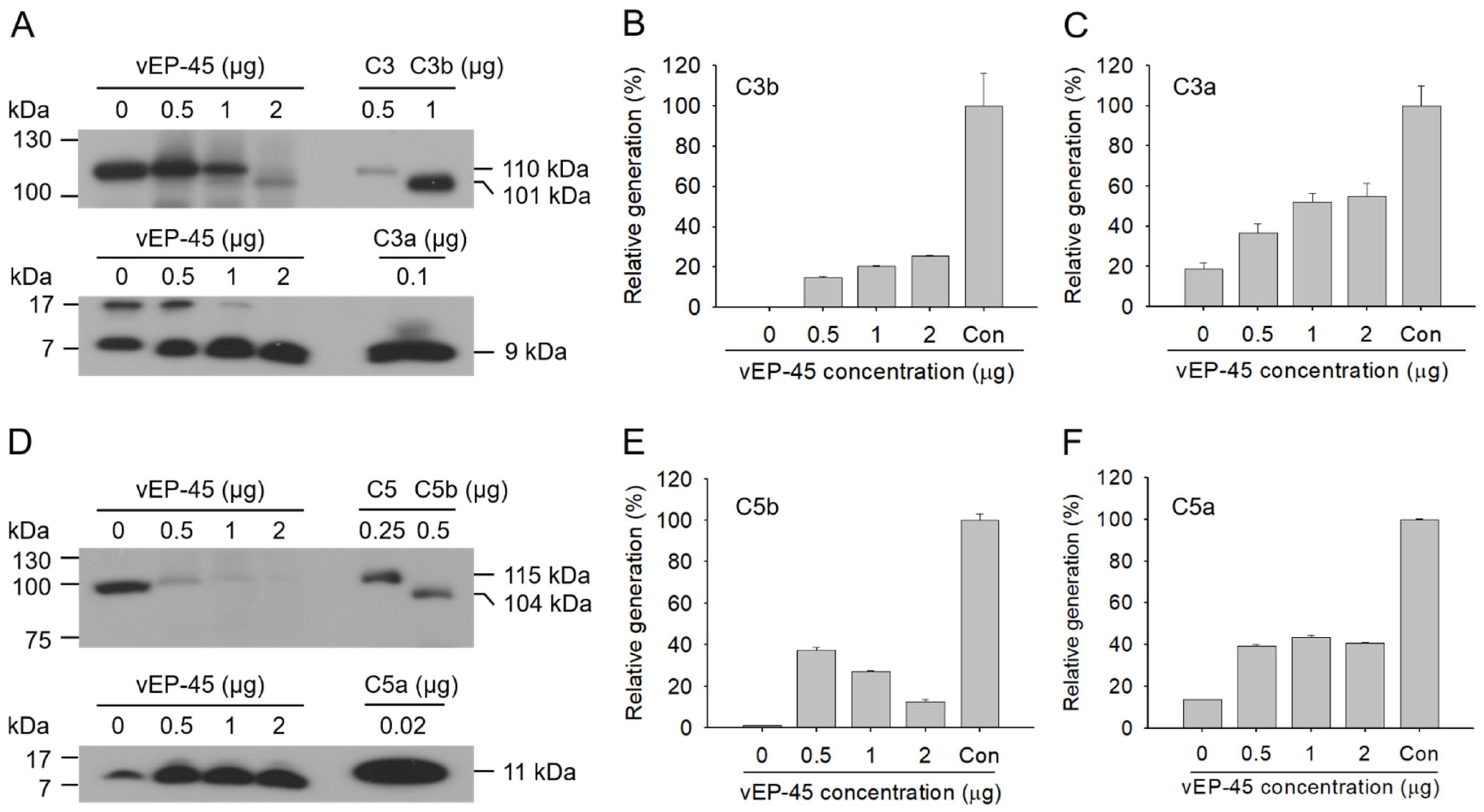
3.4. Activation of the Complement System in Human Plasma by vEP-45
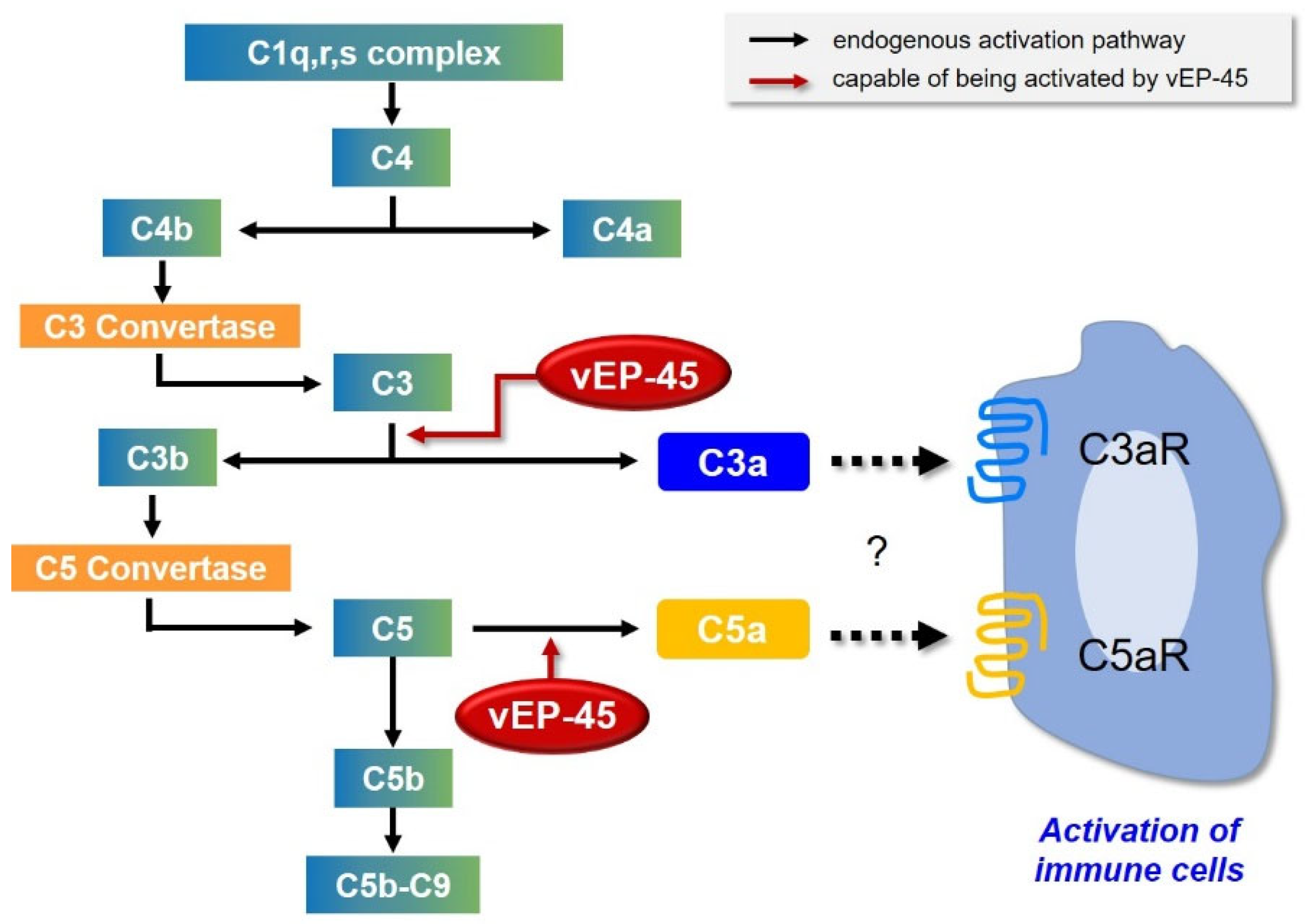
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oikonomopoulou, K.; Ricklin, D.; Ward, P.A.; Lambris, J.D. Interactions between coagulation and complement—Their role in inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 34, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, H.I.; Boral, I.; Bevington, A. Complement-coagulation cross-talk: A potential mediator of the physiological activation of complement by low pH. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.-C. Complement and its role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, J.V.; Ward, P.A. The complement system. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolev, M.; Le Friec, G.; Kemper, C. Complement—Tapping into new sites and effector systems. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merle, N.S.; Church, S.E.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement system part I—Molecular mechanisms of activation and regulation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar-Kharghan, V. The role of the complement system in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayilyan, K.; Kang, Y.; Dodds, A.; Sim, R. The complement system in innate immunity. In Innate Immunity of Plants, Animals, and Humans; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 219–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lambris, J.D. More than complementing Tolls: Complement–Toll-like receptor synergy and crosstalk in innate immunity and inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasque, P. Complement: A unique innate immune sensor for danger signals. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, N.S.; Noe, R.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement system part II: Role in immunity. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Chang, A.K.; Park, J.E.; Shin, S.Y.; Yoon, S.M.; Lee, J.S. Vibrio extracellular protease with prothrombin activation and fibrinolytic activities. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 19, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, A.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, J.E.; Acharya, P.; Park, I.-S.; Yoon, S.M.; You, H.J.; Hahm, K.-S.; Park, J.K.; Lee, J.S. Vibrio vulnificus secretes a broad-specificity metalloprotease capable of interfering with blood homeostasis through prothrombin activation and fibrinolysis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 6909–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Park, J.W.; Lee, W.; Lee, J.S. Pleiotropic effects of a vibrio extracellular protease on the activation of contact system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.-J.; Park, J.E.; Cho, Y.H.; Lim, D.S.; Lee, J.S. Effect of 7-Methylsulfinylheptyl Isothiocyanate on the Inhibition of Melanogenesis in B16-F1 Cells. Life 2021, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. The complement system and innate immunity. In Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, 5th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis, J.E.; Frank, M.M. The Human Complement System in Health and Disease; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Walport, M.J. Complement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambris, J.D. The multifunctional role of C3, the third component of complement. Immunol. Today 1988, 9, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisinger, M.J.; Goebeler, V.; Lu, Z.; Meixner, S.C.; Myles, T.; Pryzdial, E.L.; Conway, E.M. Thrombin generates previously unidentified C5 products that support the terminal complement activation pathway. Blood 2012, 120, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.-F.; Ward, P.A. Role of C5a in inflammatory responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 821–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaskou, E.; Wilson, D.V.; Oo, Y.H. Innate immune cells in liver inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 949157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.W.; Woodruff, T.M. Complement: Bridging the innate and adaptive immune systems in sterile inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, A.; Bialas, A.R.; De Rivera, H.; Davis, A.; Hammond, T.R.; Kamitaki, N.; Tooley, K.; Presumey, J.; Baum, M.; Van Doren, V. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature 2016, 530, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avirutnan, P.; Hauhart, R.E.; Somnuke, P.; Blom, A.M.; Diamond, M.S.; Atkinson, J.P. Binding of flavivirus nonstructural protein NS1 to C4b binding protein modulates complement activation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inal, J.M.; Schifferli, J.A. Complement C2 receptor inhibitor trispanning and the β-chain of C4 share a binding site for complement C2. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5213–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetsel, R.A.; Kildsgaard, J.; Haviland, D.L. Complement anaphylatoxins (C3a, C4a, C5a) and their receptors (C3aR, C5aR/CD88) as therapeutic targets in inflammation. In Therapeutic Interventions in the Complement System; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 113–153. [Google Scholar]
- Kumakura, S.; Kamo, I.; Tsurufuji, S. Role of bradykinin in the vascular permeability response induced by carrageenin in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 93, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lysannm, B.; Henri, W.; Stefan, R.J.; Thomas, R.; Andy, T.L. Factor XII-deriven inflammatory reactions with implications for abaphlaxis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1115. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, S.H.; Park, J.E.; Cho, Y.H.; Lee, J.S. Effect of Vibrio-Derived Extracellular Protease vEP-45 on the Blood Complement System. Biology 2021, 10, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080798
Kwon SH, Park JE, Cho YH, Lee JS. Effect of Vibrio-Derived Extracellular Protease vEP-45 on the Blood Complement System. Biology. 2021; 10(8):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080798
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, So Hyun, Jung Eun Park, Yeong Hee Cho, and Jung Sup Lee. 2021. "Effect of Vibrio-Derived Extracellular Protease vEP-45 on the Blood Complement System" Biology 10, no. 8: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080798
APA StyleKwon, S. H., Park, J. E., Cho, Y. H., & Lee, J. S. (2021). Effect of Vibrio-Derived Extracellular Protease vEP-45 on the Blood Complement System. Biology, 10(8), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080798




