Effect of Displacement Degree of Distal Chevron Osteotomy on Metatarsal Stress: A Finite Element Method
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
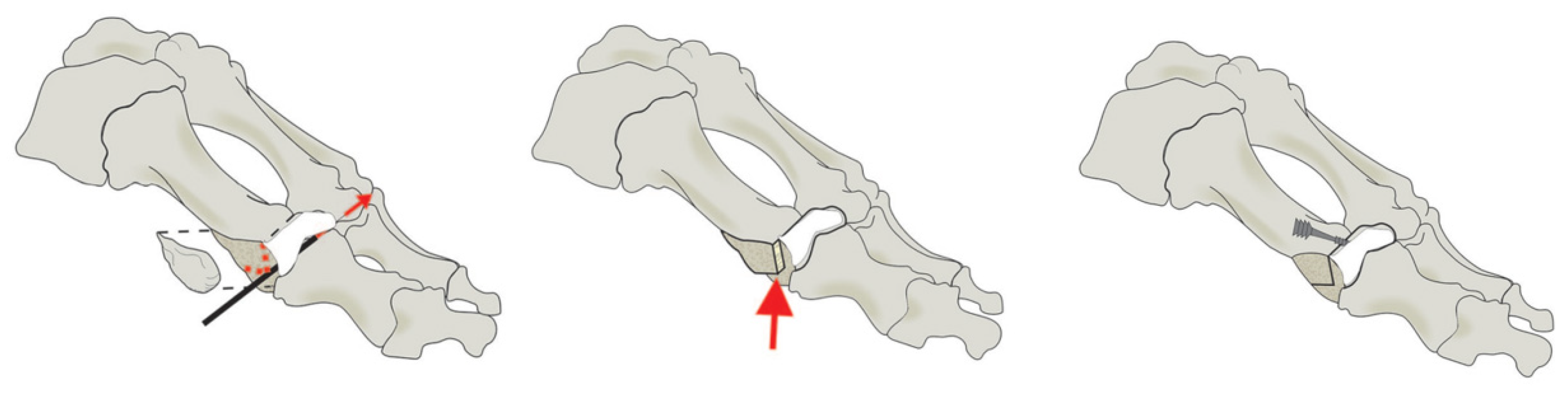
2.1. Data Acquisition
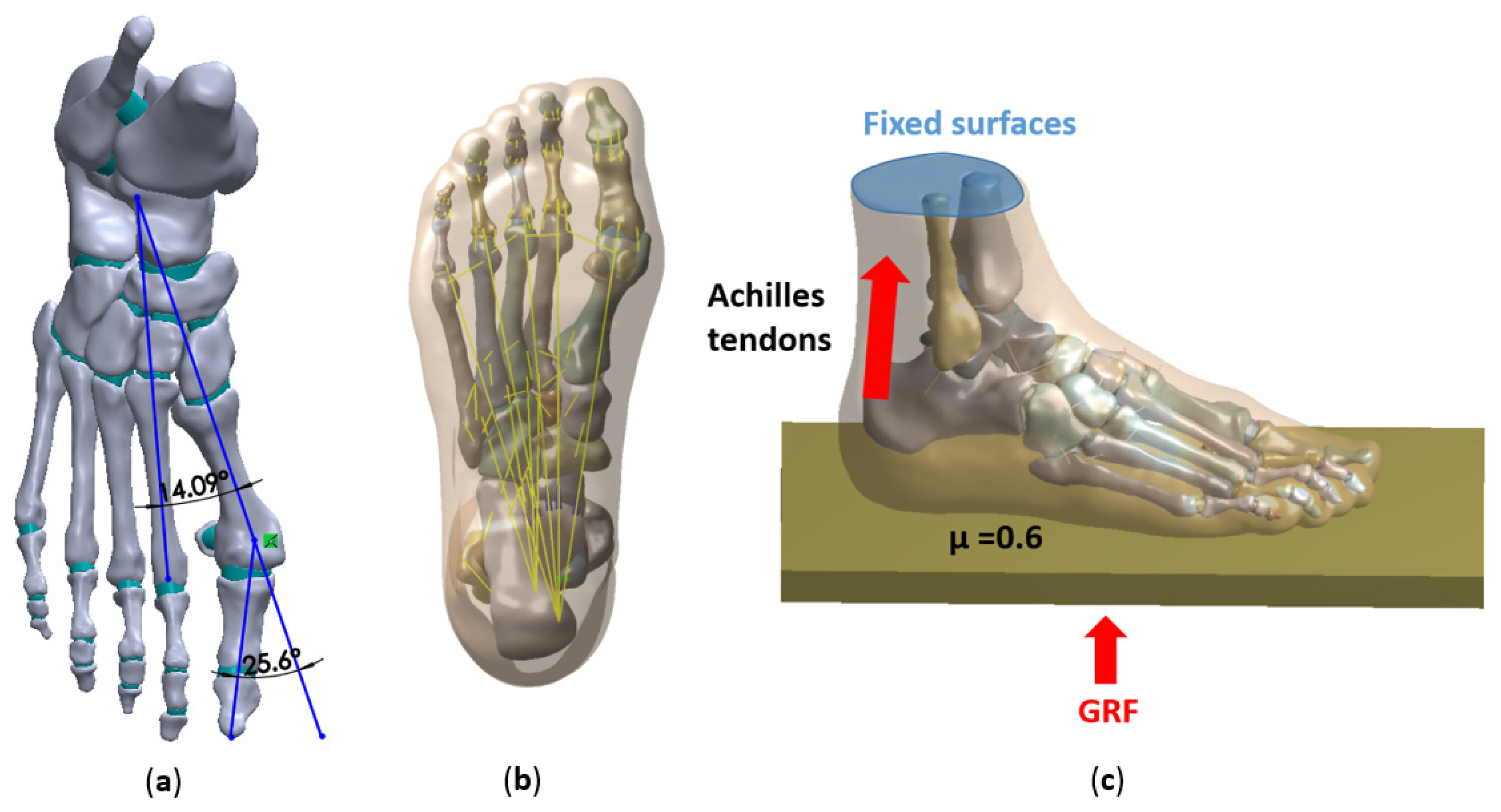
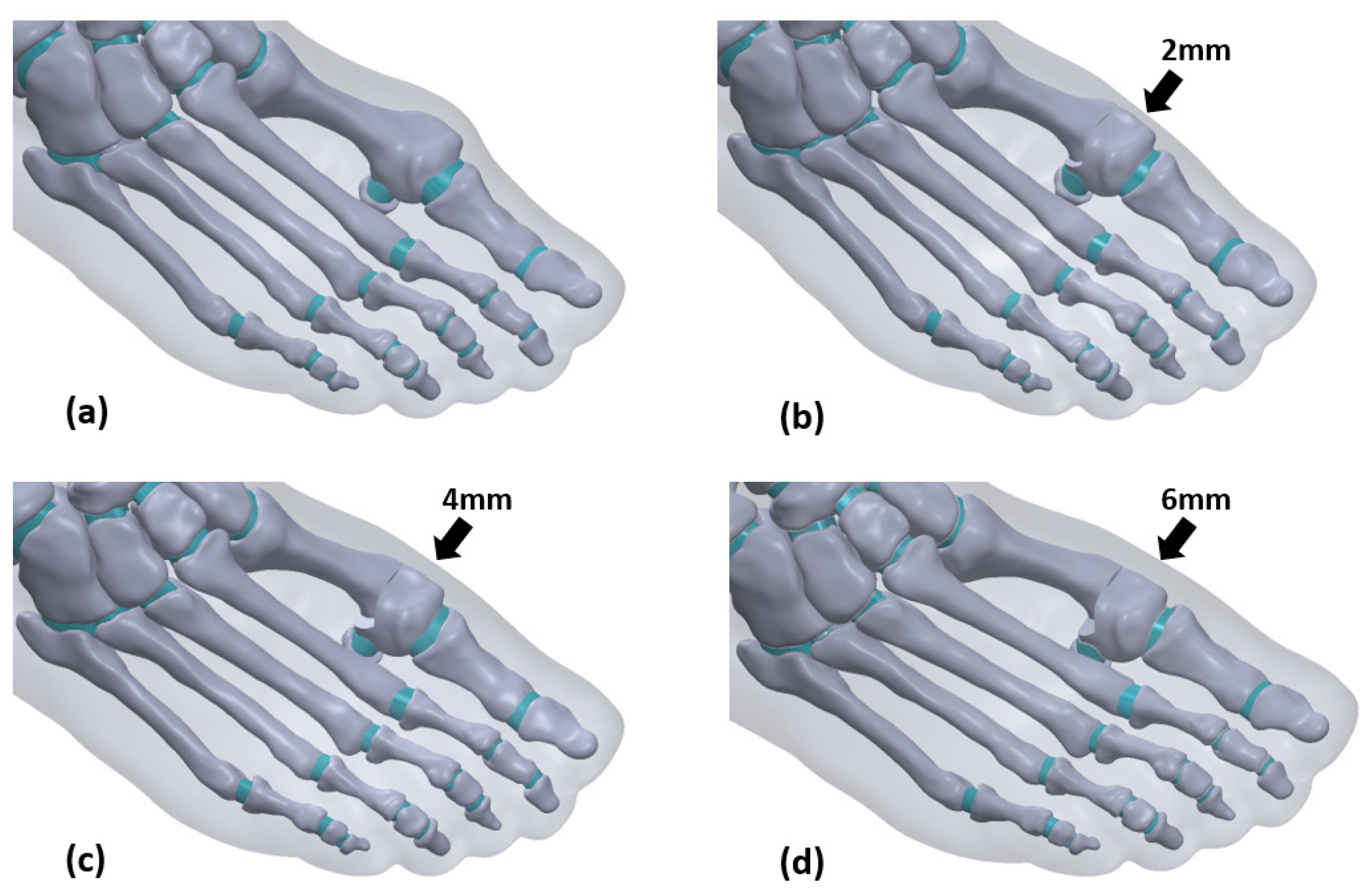
2.2. Model Construction
2.3. Boundary, Loading Conditions
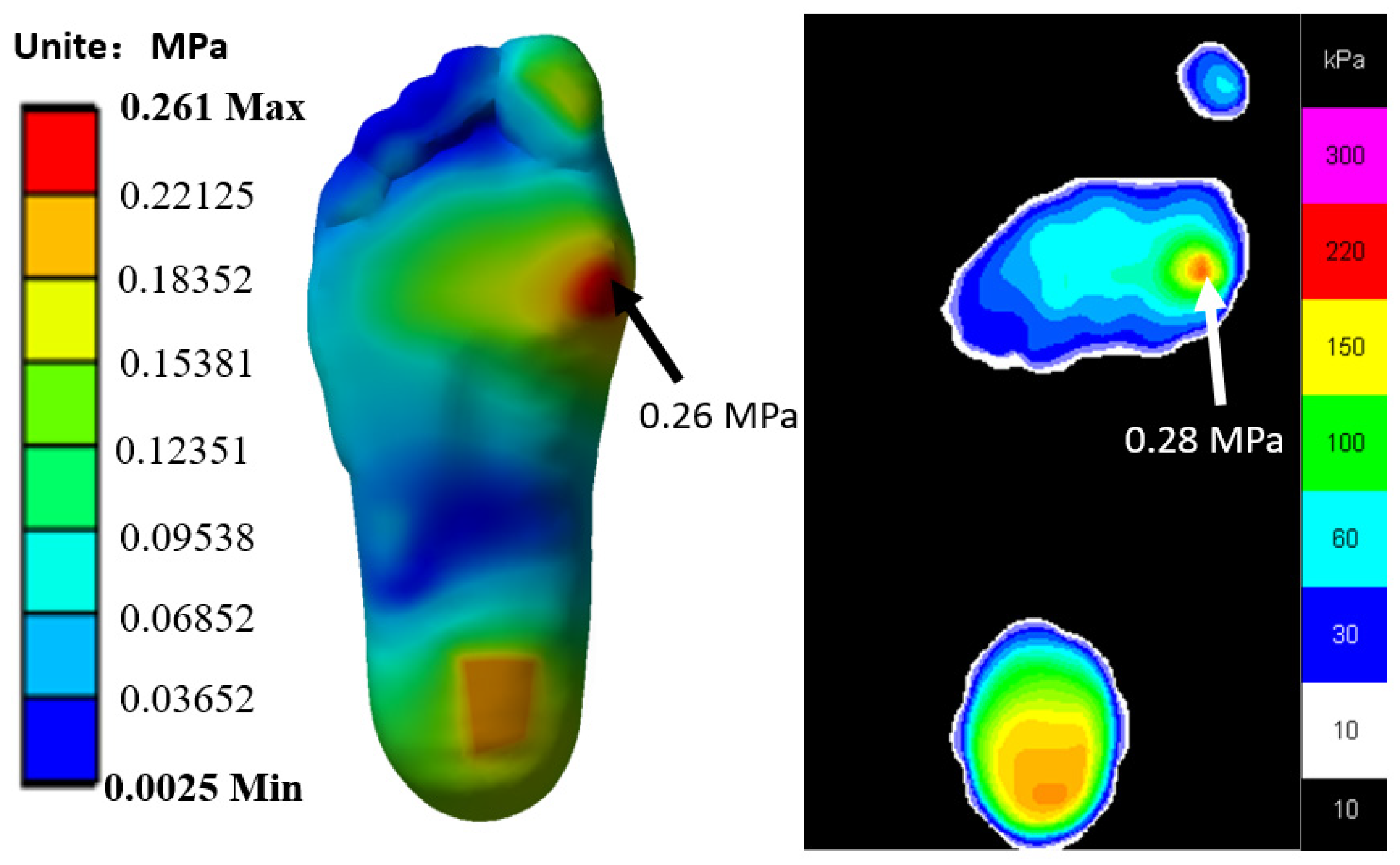
2.4. Validation of the FE Models
3. Results
3.1. Model Building
3.2. Verification Result
3.3. The Stress of the Metatarsals
3.4. The Stress of the First Metatarsophalangeal Articular Cartilage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ying, J.; Xu, Y.; István, B.; Ren, F. Adjusted Indirect and Mixed Comparisons of Conservative Treatments for Hallux Valgus: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, I.M.; Rubio, E.R.; Bosch, M.N.; González, M.S.; Paz, G.B.; Llabrés, A.J. Scarf and Akin osteotomies for moderate and severe hallux valgus: Clinical and radiographic results. Foot Ankle Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Foot Ankle Surg. 2008, 14, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldecker, U. Metatarsalgia in hallux valgus deformity: A pedographic analysis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Foot Ankle Surg. 2002, 41, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Lord, S.R. The contribution of foot problems to mobility impairment and falls in community-dwelling older people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2001, 49, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, Q. A Current Review of Foot Disorder and Plantar Pressure Alternation in the Elderly. Phys. Act. Health 2020, 4, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partio, N.; Mäenpää, H.; Huttunen, T.; Haapasalo, H.; Laine, H.J.; Mattila, V.M. Incidence of hallux valgus primary surgical treatment. Finnish nationwide data from 1997 to 2014. Foot Ankle Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszka, H.; Gądek, A. Percutaneous Transosseous Suture Fixation of the Akin Osteotomy and Minimally Invasive Chevron for Correction of Hallux Valgus. Foot Ankle Int. 2020, 41, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barg, A.; Harmer, J.R.; Presson, A.P.; Zhang, C.; Lackey, M.; Saltzman, C.L. Unfavorable Outcomes Following Surgical Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformity: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. Vol. 2018, 100, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, X. The excessive length of first ray as a risk factor for hallux valgus recurrence. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trnka, H.J. Percutaneous, MIS and open hallux valgus surgery. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernois, J.; Redfern, D.J. Percutaneous Surgery for Severe Hallux Valgus. Foot Ankle Clin. 2016, 21, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalender, A.M.; Uslu, M.; Bakan, B.; Ozkan, F.; Erturk, C.; Altay, M.A.; Guner, S.; Kalender, M. Mitchell’s osteotomy with mini-plate and screw fixation for hallux valgus. Foot Ankle Int. 2013, 34, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, Y.A.; Mansour, A.M. Percutaneous distal metatarsal osteotomy versus distal chevron osteotomy for correction of mild-to-moderate hallux valgus deformity. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2012, 132, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badwey, T.M.; Dutkowsky, J.P.; Graves, S.C.; Richardson, E.G. An anatomical basis for the degree of displacement of the distal chevron osteotomy in the treatment of hallux valgus. Foot Ankle Int. 1997, 18, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Orcajo, E.; Bayod, J.; de Las Casas, E.B. Computational foot modeling: Scope and applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2016, 23, 389–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, M. Computational models of the foot and ankle for pathomechanics and clinical applications: A review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behforootan, S.; Chatzistergos, P.; Naemi, R.; Chockalingam, N. Finite element modelling of the foot for clinical application: A systematic review. Med. Eng. Phys. 2017, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Wang, Y.; Leung, A.K.-L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M. Finite element simulation on posterior tibial tendinopathy: Load transfer alteration and implications to the onset of pes planus. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 51, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Ni, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. Biomechanics of Foot and Ankle. In Frontier in Orthopaedic Biomechanics; Cheng, C.-K., Woo, S.L.-Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 219–263. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Lake, M.J.; Zeng, Y. Heel skin stiffness effect on the hind foot biomechanics during heel strike. Skin Res. Technol. 2010, 16, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Szymanowska, O.; Shen, S.; Zhao, X.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Effects of severe hallux valgus on metatarsal stress and the metatarsophalangeal loading during balanced standing: A finite element analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, D.W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.L.; Yan, F.; Peng, Y.; Tan, Q.; Ni, M.; Leung, A.K.; Zhang, M. Finite Element Analysis of Generalized Ligament Laxity on the Deterioration of Hallux Valgus Deformity (Bunion). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 571192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Pérez, E.; Simón-Pérez, C.; Alonso-Peña, D.; Pontón-Cortina, A.; Chicharro-Luna, E.; Martínez-Nova, A.; Navarro-Flores, E. Stiffness degree of ankle range of motion in diabetic patients with atypical amputation. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2020, 66, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzaroglou, C.; Bougas, P.; Panagiotopoulos, E.; Saridis, A.; Karanikolas, M.; Kouzoudis, D. Ninety-degree chevron osteotomy for correction of hallux valgus deformity: Clinical data and finite element analysis. Open Orthop. J. 2010, 4, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermans, J.J.; Beumer, A.; de Jong, T.A.; Kleinrensink, G.J. Anatomy of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis in adults: A pictorial essay with a multimodality approach. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiou, K.A.; Liu, G.T.; Lavery, L.A.; Lanctot, D.R.; Schenck, R.C., Jr. Biomechanical topography of human articular cartilage in the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1998, 348, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cheung, J.T.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, A.K.; Zhang, M. Development of a finite element model of female foot for high-heeled shoe design. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23 (Suppl. S1), S31–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkin, A. Structural Analysis of the Human Foot in Standing Posture. Ph.D. Thesis, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Nonlinear finite element analysis for musculoskeletal biomechanics of medial and lateral plantar longitudinal arch of Virtual Chinese Human after plantar ligamentous structure failures. Clin. Biomech. 2007, 22, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.T.-M.; Zhang, M.; Leung, A.K.-L.; Fan, Y.-B. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the foot during standing—A material sensitivity study. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, A.; Megido-Ravid, M.; Itzchak, Y.; Arcan, M. Biomechanical analysis of the three-dimensional foot structure during gait: A basic tool for clinical applications. J. Biomech. Eng. 2000, 122, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Crowninshield, R.D.; Cooper, R.R. An analysis of soft tissue loading in the foot—A preliminary report. Bull. Prosthet. Res. 1981, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.D.; Ren, X.J.; Li, J.S.; Lake, M.J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zeng, Y.J. Computer simulation of stress distribution in the metatarsals at different inversion landing angles using the finite element method. Int. Orthop. 2010, 34, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Chon, T.; Zhang, Y.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 136, 104745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, R.; Yang, M.; Gao, Y.; Ren, S.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Song, Y.; Huang, X.H.; Teo, E.C.; Zhu, J.; et al. A Simulation Analysis of Maternal Pelvic Floor Muscle. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. Cartilage Stiffness Effect on Foot Biomechanics of Chinese Bound Foot: A Finite Element Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayod López, J.; Becerro de Bengoa Vallejo, R.; Losa Iglesias, M.E.; Doblaré, M. Mechanical Stress Redistribution in the First Metatarsal Bone After Autologous Bone Harvesting. J. Am. Podiatr. Med Assoc. 2017, 107, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, D.; Larrainzar-Garijo, R.; De-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.B.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Bayod-López, J. Effectiveness of the Lapidus plate system in foot surgery: A PRISMA compliant systematic review. Int. Wound J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.; Teo, E.C.; Fekete, G.; Gu, Y. The influence of heel height on strain variation of plantar fascia during high heel shoes walking-combined musculoskeletal modeling and finite element analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 791238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo-López, P.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Rodríguez-Sanz, D.; Navarro-Flores, E.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; López-López, D. Fibularis tertius muscle in women & men: A surface anatomy cross-sectional study across countries. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biz, C.; Fosser, M.; Dalmau-Pastor, M.; Corradin, M.; Rodà, M.G.; Aldegheri, R.; Ruggieri, P. Functional and radiographic outcomes of hallux valgus correction by mini-invasive surgery with Reverdin-Isham and Akin percutaneous osteotomies: A longitudinal prospective study with a 48-month follow-up. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2016, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corless, J.R. A modification of the Mitchell procedure. J. Bone Joint Surg. B 1976, 58, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K. Chevron osteotomy of the first metatarsal: Patient selection and technique. Contemp. Orthop. 1981, 3, 707–711. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.A.; Cofield, R.H.; Morrey, B.F. Chevron osteotomy for hallux valgus. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1979, 142, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, D.W.; Leventen, E.O. A new osteotomy for hallux valgus: A horizontally directed “V” displacement osteotomy of the metatarsal head for hallux valgus and primus varus. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1981, 157, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, R.J.; Feffer, H.L. Modified chevron osteotomy of the first metatarsal. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1981, 157, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, P.J.; Lin, T.J. Hallux valgus. Med Clin. 2014, 98, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammarco, V.J.; Nichols, R. Orthotic management for disorders of the hallux. Foot Ankle Clin. 2005, 10, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jowett, C.R.; Bedi, H.S. Preliminary results and learning curve of the minimally invasive chevron akin operation for hallux valgus. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017, 56, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piqué-Vidal, C.; Solé, M.T.; Antich, J. Hallux valgus inheritance: Pedigree research in 350 patients with bunion deformity. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2007, 46, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Leung, A.K.-L. Functional restoration and risk of non-union of the first metatarsocuneiform arthrodesis for hallux valgus: A finite element approach. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3142–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Zhang, M.; Yu, J.; Leung, A.K.-L. Biomechanics of first ray hypermobility: An investigation on joint force during walking using finite element analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, J.; Dutheil, F.; Ugbolue, U.C. The Prevalence of Lower Extremity Injuries in Running and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. Phys. Act. Health 2021, 5, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
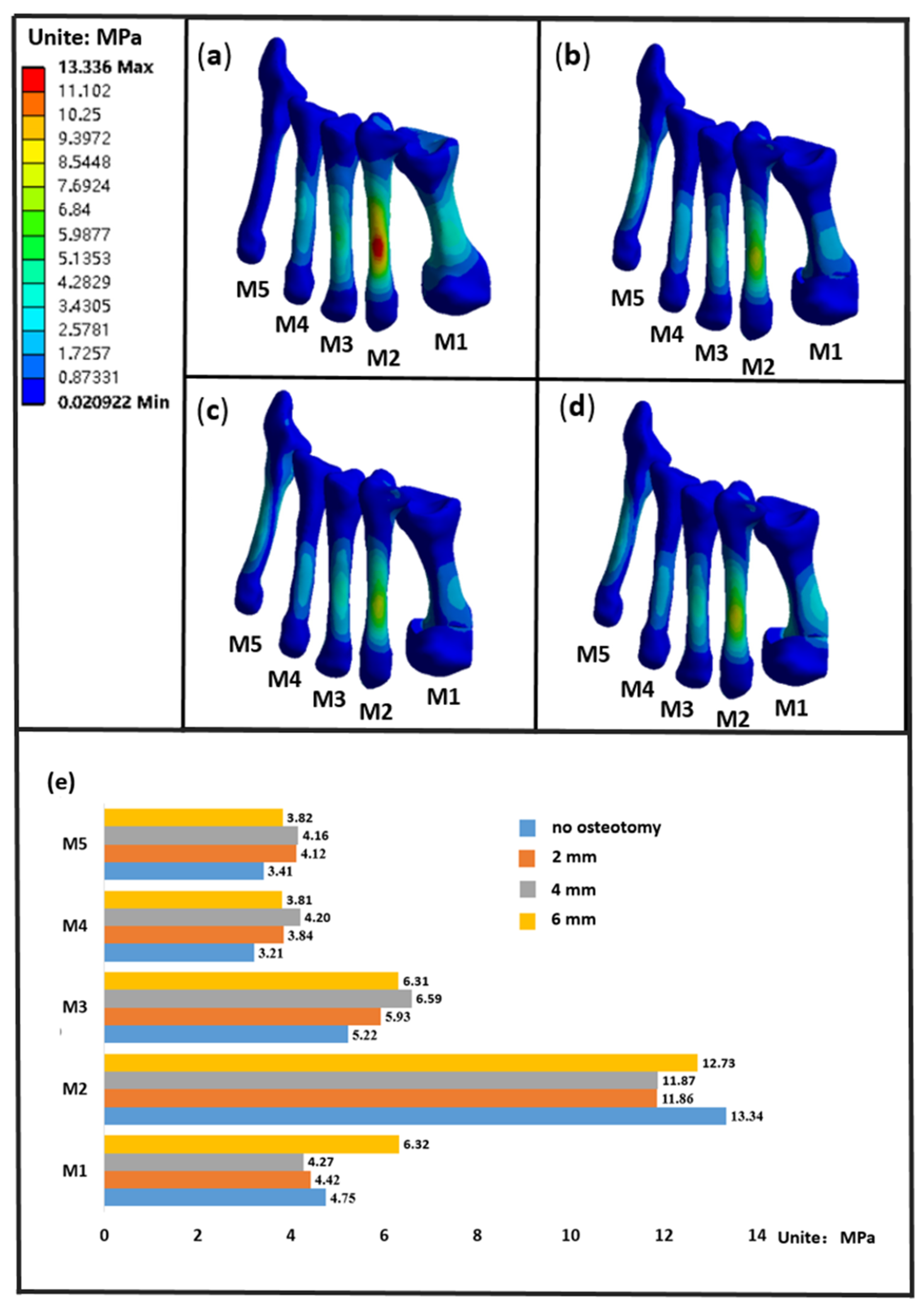
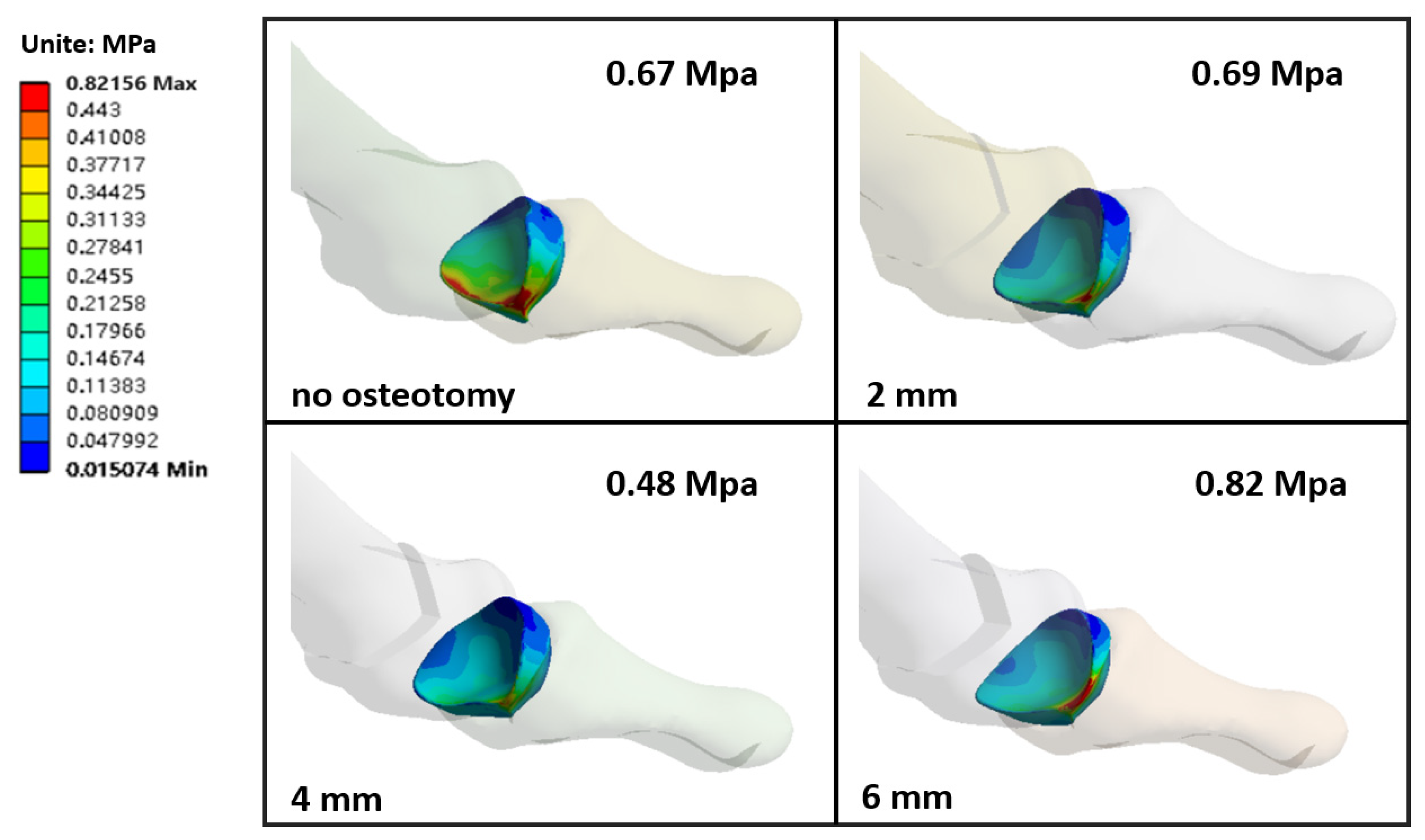
| Component | Yang’s Modulus E (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio (v) | Cross-Section Area (mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | 7300 | 0.3 | |
| Cartilage | 1 | 0.4 | |
| Ligament | 260 | 0.4 | 18.4 |
| Plantar Fascia | 350 | 0.4 | 58.6 |
| Plate | 17,000 | 0.4 |
| HVA | IMA | Nodes | Elements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| no osteotomy | 25.6° | 14.1° | 2061317 | 1391011 |
| 2 mm | 20.3° | 11.3° | 2059307 | 1389514 |
| 4 mm | 15.4° | 9.3° | 2059749 | 1390233 |
| 6 mm | 11.6° | 8.4° | 2055713 | 1387394 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Teo, E.C.; Gu, Y. Effect of Displacement Degree of Distal Chevron Osteotomy on Metatarsal Stress: A Finite Element Method. Biology 2022, 11, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010127
Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Huang J, Teo EC, Gu Y. Effect of Displacement Degree of Distal Chevron Osteotomy on Metatarsal Stress: A Finite Element Method. Biology. 2022; 11(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qiaolin, Yan Zhang, Jialu Huang, Ee Chon Teo, and Yaodong Gu. 2022. "Effect of Displacement Degree of Distal Chevron Osteotomy on Metatarsal Stress: A Finite Element Method" Biology 11, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010127
APA StyleZhang, Q., Zhang, Y., Huang, J., Teo, E. C., & Gu, Y. (2022). Effect of Displacement Degree of Distal Chevron Osteotomy on Metatarsal Stress: A Finite Element Method. Biology, 11(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010127







