Assessments of the Ecological and Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Topsoils of Different Land Uses: A Case Study in Peninsular Malaysia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site Descriptions and Soil Collection
2.2. Metal Analysis
2.2.1. Acid Digestions for Topsoil
2.2.2. Quality Control for Heavy Metal Analysis
2.3. Data Treatment
2.3.1. Geoaccumulation Index
2.3.2. Contamination Factor
2.3.3. Pollution Load Index (PLI)
2.3.4. Ecological Risk Index
2.3.5. Potential Ecological Risk Index
3. Human Health Risk Assessment
Data Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Potentially Toxic Metals in Topsoils
4.2. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals Pollution
4.2.1. Geoaccumulation Index
4.2.2. Pollution Load Index
4.2.3. Ecological Risk and Potentially Ecological Risk Index
4.3. Comparisons of PERI with Other Studies
4.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, X.-S.; Ding, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Yu, S. Incorporating Bioaccessibility into Human Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Urban Park Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.-M.; Fu, R.-B.; Liu, H.-Q.; Guo, X.-P. Current Knowledge from Heavy Metal Pollution in Chinese Smelter Contaminated Soils, Health Risk Implications and Associated Remediation Progress in Recent Decades: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 286, 124989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K. Soil Pollution: Sources, Management Strategies and Health Effects; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-5361-3942-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, M.; Geik, K.; Lee, W.; Hayet, R. Landfill Leachate as a Source of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) to Malaysian Waters. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2005, 29, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Wong, C.H. Assessment Cu, Ni and Zn Pollution in the Surface Sediments in the Southern Peninsular Malaysia Using Cluster Analysis, Ratios of Geochemical Nonresistant to Resistant Fractions, and Geochemical Indices. Environ. Asia 2011, 4, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Pang, B.H. Assessment of Cu, Pb, and Zn Contamination in Sediment of North Western Peninsular Malaysia by Using Sediment Quality Values and Different Geochemical Indices. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 183, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.K.; Pang, B.H. Anthropogenic Concentrations of Cd, Ni and Zn in the Intertidal, River and Drainage Sediments Collected from North Western Peninsular Malaysia. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 19, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Hoodaji, M.; Tahmourespour, A.; Amini, H. Assessment of Copper, Cobalt and Zinc Contaminations in Soils and Plants of Industrial Area in Esfahan City (in Iran). Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Shoiful, A.; Kindaichi, T. Pollutant Removal from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions with a Combined Electrochemical Oxidation and Adsorption Method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DoE Malaysia. Malaysia Environmental Quality Report 2014; Department of Environment, Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, M.P.; Takada, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Ohno, K.; Yamada, J.; Kouno, E.; Kumata, H. Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Rivers and Estuaries in Malaysia: A Widespread Input of Petrogenic PAHs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Ismail, A.; Cheng, W.H.; Tan, S.G. Crystalline Style and Tissue Redistribution in Perna Viridis as Indicators of Cu and Pb Bioavailabilities and Contamination in Coastal Waters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 63, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, N.Y.M.J.; Abas, M.R.B.; Rahman, N.A.; Tahir, N.M.; Rushdi, A.I.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Levels and Distributions of Organic Source Tracers in Air and Roadside Dust Particles of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimon, A.; Jusoh, K.; Mahir, A.R.; Ismail, B.S. Comparative Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Selected Vegetables, Their Availability and Correlation in Lithogenic and Nonlithogenic Fractions of Soils from Some Agricultural Areas in Malaysia. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2009, 3, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Yacoob, A.; Cheng, W.H. Distribution of Heavy Metal Concentrations in Different Soft Tissues and Shells of the Bivalve Psammotaea Elongata and Gastropod Faunus Ater Collected from Pantai Sri Tujuh, Kelantan; Universiti Malaysia Terengganu (UMT): Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.K.; Shuhaimi-Othman, M.; Hoon, L.P. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Fanworth (Cabombafurcata) from Lake Chini, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 4, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Maah, M.J.; Yusoff, I. Heavy Metals Accumulation in Plants Growing in Ex Tin Mining Catchment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, S.; Ahmed, K.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun. Metal Speciation in Soil and Health Risk Due to Vegetables Consumption in Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Contamination Features and Health Risk of Soil Heavy Metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabukdhara, M.; Nema, A.K. Heavy Metals Assessment in Urban Soil around Industrial Clusters in Ghaziabad, India: Probabilistic Health Risk Approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 87, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution and Human Health Risk in Urban Soils of Steel Industrial City (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A Review of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution from Mines in China: Pollution and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, P.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J. Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Street Dusts from Different Functional Areas in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Peng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Luo, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; Yang, G.; Wan, H.; Wu, L. Levels and Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Urban Soils in Dongguan, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 148, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-G.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.-P. Metals in Exposed-Lawn Soils from 18 Urban Parks and Its Human Health Implications in Southern China’s Largest City, Guangzhou. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Munir, S.; Sajjad, M.; Li, G. Urban Park Soil Contamination by Potentially Harmful Elements and Human Health Risk in Peshawar City, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 165, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Non-Inverted U-Shaped Challenges to Regional Sustainability: The Health Risk of Soil Heavy Metals in Coastal China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, O.H.; Olayinka, O.O.; Tope-Ajayi, O.O.; Adekoya, A.S. Assessing Spatial Distribution, Potential Ecological and Human Health Risks of Soil Heavy Metals Contamination around a Trailer Park in Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2020, 10, e00650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Liu, E.; Yao, D.; Xiao, T.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C. Contamination, Oral Bioaccessibility and Human Health Risk Assessment of Thallium and Other Metal(Loid)s in Farmland Soils around a Historic TlHg Mining Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 758, 143577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, B.; Fan, C.; Zhao, P.; Shen, S. Human Health Risk from Soil Heavy Metal Contamination under Different Land Uses near Dabaoshan Mine, Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417–418, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guo, S.; Zeng, G.-M.; Li, F.; Gu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, W.; Peng, S. A New Exploration of Health Risk Assessment Quantification from Sources of Soil Heavy Metals under Different Land Use. Environ. Pollut. Barking Essex 1987 2018, 243, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Xiao, T.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Peng, J. Pollution and Health Risk Assessment of Toxic Metal(Loid)s in Soils under Different Land Use in Sulphide Mineralized Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, A.L.; Caravanos, J.; Blaise, M.J.; Jaeger, R.J. Distribution of Lead in Urban Roadway Grit and Its Association with Elevated Steel Structures. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Recommendations for Sieving Soil and Dust Samples at Lead Sites for Assessment of Incidental Ingestion; 20460. OLEM Directive 9200.1-128; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Yap, C.K.; Hatta, Y.; Edward, F.; Tan, S. Comparison of Heavy Metal Concentrations (Cd, Cu, Fe, Ni and Zn) in the Shells and Different Soft Tissues of Anadara Granosa Collected from Jeram, Kuala Juru and Kuala Kurau, Peninsular Malaysia. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2008, 31, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Tan, S. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Juru River Basin Receiving Industrial Effluents: The Need for Biochemical and Molecular Studies in the Edible Cockles Anadara Granosa. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2008, 37, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Noorhaidah, A.; Azlan, A.; Nor Azwady, A.A.; Ismail, A.; Ismail, A.R.; Siraj, S.S.; Tan, S.G. Telescopium Telescopium as Potential Biomonitors of Cu, Zn, and Pb for the Tropical Intertidal Area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halmi, M.I.E.; Gunasekaran, B.; Othman, A.R.; Kamaruddin, K.; Dahalan, F.A.; Ibrahim, N.; Shukor, M.Y. A Rapid Inhibitive Enzyme Assay for Monitoring Heavy Metals Pollution in the Juru Industrial Estate. Bioremediat. Sci. Technol. Res. 2015, 3, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Alshaebi, F.; Yaacob, W.Z.; Samsudin, A.; Alsabahi, E. Risk Assessment at Abandoned Tin Mine in Sungai Lembing, Pahang, Malaysia. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2009, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Zin, N.S.; Abdul Aziz, H.; Adlan, M.N.; Ariffin, A. Characterization of Leachate at Matang Landfill Site, Perak, Malaysia. Acad. J. Sci. 2012, 1, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, R.I.; Ibrahim, M.Z.; Abdullah, M.A.; Ishak, A.R. Characterization and Toxicity Study of Leachate from Closed Landfills in Selangor. Asia Pac. Environ. Occup. Health J. 2018, 4, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantarifard, A.; Yang, G.S. Energy Potential from Municipal Solid Waste in Tanjung Langsat Landfill, Johor, Malaysia. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 8560–8568. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Ismail, A.; Tan, S.G.; Omar, H. Correlations between Speciation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in Sediment and Their Concentrations in Total Soft Tissue of Green-Lipped Mussel Perna Viridis from the West Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.H.; Yap, C.K. Potential Human Health Risks from Toxic Metals via Mangrove Snail Consumption and Their Ecological Risk Assessments in the Habitat Sediment from Peninsular Malaysia. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Luo, X.; Pan, R.; Ouyang, T. Spatial Distribution, Pollution, and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Agricultural Surface Soil for the Guangzhou-Foshan Urban Zone, South China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Zhou, D.; Luo, G.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, C.; Deng, Y.; Lu, Q. Ecological Security and Health Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals on a Village-Level Scale, Based on Different Land Use Types. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3393–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The Composition of Earth’s Upper Crust, Natural Cycles of Elements, Natural Resources. In Elements and Their Compounds in the Environment; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 2–16. ISBN 978-3-527-61963-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ihedioha, J.N.; Ukoha, P.O.; Ekere, N.R. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil of a Municipal Solid Waste Dump in Uyo, Nigeria. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.; Deng, R.; Wang, Z. Distribution, Source Identification, and Ecological-Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Soil of Thallium Mine Area (Southwestern Guizhou, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 16556–16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varol, M.; Sünbül, M.R.; Aytop, H.; Yılmaz, C.H. Environmental, Ecological and Health Risks of Trace Elements, and Their Sources in Soils of Harran Plain, Turkey. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudi, M.; Ruan, H.D.; Wei, B.; Wang, L.; Tong, S.; Kong, C.; Yang, L. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Surface Soil in an Arid Region of Xinjiang, China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.C. Pollutant Source, Ecological and Human Health Risks Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils from Coal Mining Areas in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujre, N.; Rangan, L.; Mitra, S. Occurrence, Geochemical Fraction, Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Cadmium, Copper and Nickel in Soils Contaminated with Municipal Solid Wastes. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R. Effect of Different Industrial Activities on Soil Heavy Metal Pollution, Ecological Risk, and Health Risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.F.; Silva, N.F.; Oliveira, C.M.; Matos, M.J. Heavy Metals Contamination of Urban Soils—A Decade Study in the City of Lisbon, Portugal. Soil Syst. 2021, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the Assessment of Heavy-Metal Levels in Estuaries and the Formation of a Pollution Index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Qiao, Q.; Piper, J.D.A.; Huang, B. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution from a Fe-Smelting Plant in Urban River Sediments Using Environmental Magnetic and Geochemical Methods. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3057–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Ahmed, K.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun; Masunaga, S. Potential Ecological Risk of Hazardous Elements in Different Land-Use Urban Soils of Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Hasnain, S.I.; Banerjee, D.K. Grain Size and Geochemical Partitioning of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Damodar River—A Tributary of the Lower Ganga, India. Environ. Geol. 2003, 39, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshav Krishna, A.; Rama Mohan, K. Distribution, Correlation, Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Surface Soils around an Industrial Area, Hyderabad, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihedioha, J.N.; Abugu, H.O.; Ujam, O.T.; Ekere, N.R. Ecological and Human Health Risk Evaluation of Potential Toxic Metals in Paddy Soil, Rice Plants, and Rice Grains (Oryza sativa) of Omor Rice Field, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiri-Nyarko, F.; Duah, A.A.; Karikari, A.Y.; Agyekum, W.A.; Manu, E.; Tagoe, R. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils at the Kpone Landfill Site, Ghana: Implication for Ecological and Health Risk Assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lei, M. Source-Specific Ecological and Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils in Southern Yunnan Province and Associated Uncertainty Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakanson, L. An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control.a Sedimentological Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Tavakol, T.; Lahijanzadeh, A.R.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Kermani, M. Ecological and Human Health Hazards of Heavy Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Road Dust of Isfahan Metropolis, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Gu, C.; Ying, H.; Feng, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, M.; Tan, W.; Wang, X. Fraction Distribution of Heavy Metals and Its Relationship with Iron in Polluted Farmland Soils around Distinct Mining Areas. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 130, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.B.V.; do Nascimento, C.W.A.; Araújo, P.R.M.; da Silva, F.L.; Lima, L.H.V. Soil Contamination by Metals with High Ecological Risk in Urban and Rural Areas. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diami, S.M.; Kusin, F.M.; Madzin, Z. Potential Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Surface Soils Associated with Iron Ore Mining in Pahang, Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 21086–21097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Baseline Human Health Risk Assessment Vasquez Boulevard and I-70 Superfund Site Demver, Co; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Exposure Factors Handbook (1997); EPA/600/P-95/002F; National Center for Environmental Assessment, US EPA Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- US EPA. Human Health Evaluation Manual. In Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund; EPA/540/1-89/002; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Superfund Public Health Evaluation Manual; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; pp. 1–86.
- Beijing Quality and Technology Supervision Bureau. Environmental Site Assessment Guideline; DB11/T 656-2009; Beijing Quality and Technology Supervision Bureau: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, D.G.; Dourson, M.; Dourson, M.; Preuss, P.; Barnes, D.G.; Bellin, J.; Derosa, C.; Engler, R.; Erdreich, L.; Farber, T.; et al. Reference Dose (RfD): Description and Use in Health Risk Assessments. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1988, 8, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; De Miguel, E. Geochemistry and Risk Assessment of Street Dust in Luanda, Angola: A Tropical Urban Environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Ding, Z. Bioaccessibility and Health Risk of Arsenic, Mercury and Other Metals in Urban Street Dusts from a Mega-City, Nanjing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E. Investigating the Sources and Potential Health Risks of Environmental Contaminants in the Soils and Drinking Waters from the Rural Clusters in Thiva Area (Greece). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Geochemical Evolution of the Continental Crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. 3.01—Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 1–64. ISBN 978-0-08-043751-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The Composition of the Continental Crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, M.J.; Keshavarzi, B.; Zaremoaiedi, F.; Rajabzadeh, M.A.; Moore, F. Ecological-Health Risk Assessment and Bioavailability of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) in Soil and Plant around a Copper Smelter. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, S.-C.; Mohd Tahir, N. The Common Pitfall of Using Enrichment Factor in Assessing Soil Heavy Metal Pollution. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2017, 21, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, S.M.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Aris, A.Z. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Exposure in Urban Soil from Seri Kembangan (Malaysia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 9753–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Teng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Research on the Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in the Soil around a Pb–Zn Mine in the Huize County, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Characteristic and Environmental Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soil of Based on Speciation Analysis. In Informatics and Management Science I; Du, W., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2013; Volume 204, pp. 213–220. ISBN 978-1-4471-4801-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, G.H.; Wong, L.S.; Tan, A.L.; Yap, C.K. Effects of Metal-Contaminated Soils on the Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Gotu Kola (Centella asiatica) and the Potential Health Risks: A Study in Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 188, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarcinas, B.A.; Ishak, C.F.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Cozens, G. Heavy Metals in Soils and Crops in Southeast Asia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, J.; Bearer, C.F.; Etzel, R.A. Various Life Stages. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 996–1006. [Google Scholar]
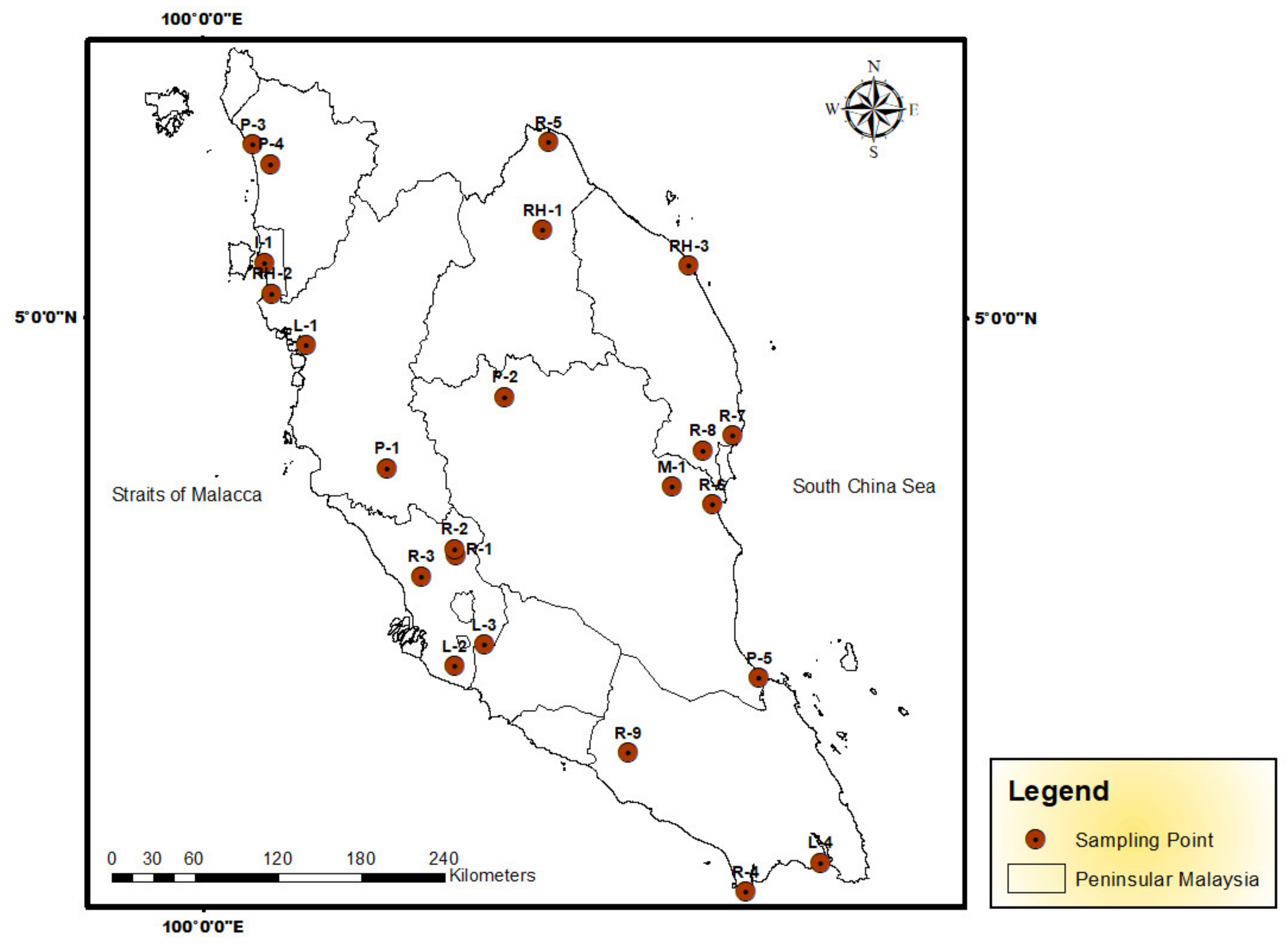


| Land Uses | Sampling Site | N | E | Date | Weather Condition | Time | Distance from the Road (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial | I-1 | Juru | 5°20′56.00″ | 100°24′45.10″ | 2 August 2011 | Sunny | 5.00 p.m. | 6.00 |
| Landfill | L-1 | Matang | 4°49′16″ | 100°40′44″ | 27 June 2011 | Cloudy | 2.00 p.m. | 5.00 |
| L-2 | Sepang | 2°44′57″ | 101°37′59″ | 2 July 2011 | Sunny | 11.25 a.m. | NA | |
| L-3 | Sg. Kembung | 2°53′8.30″ | 101°49′20.80″ | 2 July 2011 | Sunny | 3.00 p.m. | NA | |
| L-4 | Tanjung Langsat Landfill, Johor | 1°28′12.80″ | 103°59′33.10″ | 10 July 2011 | Sunny | 9.00 a.m. | 0.50 | |
| Mining (abandoned) | M-1 | Sg. Lembing | 3°54′29.40″ | 103°1′50.00″ | 22 July 2011 | Sunny | 1.30 p.m. | 13.0 |
| Plantation | P-1 | Kg. Ayer Hitam | 4°1′33.70″ | 101°12′9.20″ | 26 June 2011 | Sunny | 2.30 p.m. | 11.0 |
| P-2 | Perah, Kuala Lipis | 4°29′10.30″ | 101°57′24.60″ | 15 July 2011 | Cloudy | 1.45 p.m. | 13.0 | |
| P-3 | Alor Setar (Paddy) | 6°6′33.40″ | 100°20′10.00″ | 3 August 2011 | Sunny | 9.30 a.m. | 25.0 | |
| P-4 | Pendang (Paddy) | 5°59′4.80″ | 100°27′10.80″ | 3 August 2011 | Drizzle | 12.10 p.m. | 30.0 | |
| P-5 | Tg. Gemok | 2°40′4.90″ | 103°35′41.50″ | 17 November 2011 | Sunny | 10.30 a.m. | 5.20 | |
| Residential | R-1 | Kg. Bkt. Chandang | 3°27′55.60″ | 101°38′24.40″ | 8 June 2011 | Sunny | 11.00 a.m. | 6.00 |
| R-2 | Kg. Bkt. Rasa | 3°30′16.80″ | 101°38′0.80″ | 21 June 2011 | Sunny | 11.00 a.m. | 3.50 | |
| R-3 | Ijok | 3°19′38.00″ | 101°25′8.00″ | 21 June 2011 | Sunny | 3.30 p.m. | 5.00 | |
| R-4 | Tanjung Piai | 1°16′55.40″ | 103°30′34.70″ | 9 July 2011 | Sunny | 4.00 p.m. | 3.20 | |
| R-5 | Kota Bharu | 6°7′57.00″ | 102°14′8.20″ | 16 July 2011 | Cloudy | 8.30 a.m. | 80.0 | |
| R-6 | Kuantan | 3°47′31″ | 103°17′53″ | 22 July 2011 | Sunny | 4.00 p.m. | 4.00 | |
| R-7 | Chukai/Kemaman | 4°14′19.00″ | 103°25′19.30″ | 23 July 2011 | Cloudy | 9.15 a.m. | 15.0 | |
| R-8 | Cheneh | 4°8′29.70″ | 103°14′2.20″ | 23 July 2011 | Cloudy | 12.00 p.m. | 50.0 | |
| R-9 | Pagoh | 2°10′59.00″ | 102°44′46.00″ | 17 January 2012 | Cloudy | 11.00 a.m. | 7.00 | |
| Rubbish heap | RH-1 | Kuala Krai | 5°33′45.40″ | 102°12′2.90″ | 15 July 2011 | Cloudy | 1.45 p.m. | 1.00 |
| RH-2 | Nibong Tebal | 5°9′2.80″ | 100°27′45.90″ | 2 August 2011 | Sunny | 3.00 p.m. | NA | |
| RH-3 | Kuala Terengganu | 5°20′7.70″ | 103°8′12.20″ | 16 November 2011 | Drizzle | 9.00 a.m. | NA | |
| CRM | Cd | Cu | Fe | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSC DC73319 Soil China | 111% | 85.0% | NA | NA | 99.8% | 99.7% |
| MESS-3 NRC | NA | 93.1% | NA | 102% | 116% | 82.8% |
| TH-1 Sediment Canada | 102% | 92.9% | 95.6% | 112% | 100% | 110% |
| SRM 1547 | NA | NA | 106% | NA | NA | 115% |
| IAEA Soil-5 | 156% | 91.3% | NA | 103% | 116% | 94.8% |
| Factor | Definition | Unit | Values | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adults | ||||
| IngR | Ingestion rate of soil | mg/day | 200 | 100 | [70] |
| InhR | Inhalation rate of soil | m3/day | 7.63 | 12.8 | [22] |
| BW | Bodyweight of the exposed individual | kg | 15 | 55.9 | [74] |
| EF | Exposure frequency | days/year | 350 | 350 | [74] |
| ED | Exposure duration | years | 6 | 24 | [70] |
| AT | Average time | days | 365 × ED | 365 × ED | [72] |
| PEF | Particle emission factor | m3/kg | 1.36 × 109 | 1.36 × 109 | [70] |
| SA | Exposed skin surface area | cm2 | 1600 | 4350 | [74] |
| AF | Skin adherence factor | mg/cm day | 0.2 | 0.7 | [75] |
| ABF | Dermal absorption factor | unitless | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−3 | [20] |
| Cd RfD | Reference dose for ingestion | mg/kg day | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−3 | [21] |
| Cd RfD | Reference dose for inhalation | mg/kg day | 1.00 × 10−3 | 1.00 × 10−3 | [21] |
| Cd RfD | Reference dose for dermal contact | mg/kg day | 1.00 × 10−5 | 1.00 × 10−5 | [21] |
| Ni RfD | Reference dose for ingestion | mg/kg day | 2.00 × 10−2 | 2.00 × 10−2 | [21] |
| Ni RfD | Reference dose for inhalation | mg/kg day | 2.06 × 10−2 | 2.06 × 10−2 | [21] |
| Ni RfD | Reference dose for dermal contact | mg/kg day | 5.40 × 10−3 | 5.40 × 10−3 | [21] |
| Cu RfD | Reference dose for ingestion | mg/kg day | 4.00 × 10−2 | 4.00 × 10−2 | [21] |
| Cu RfD | Reference dose for inhalation | mg/kg day | 4.02 × 10−2 | 4.02 × 10−2 | [21] |
| Cu RfD | Reference dose for dermal contact | mg/kg day | 1.20 × 10−2 | 1.20 × 10−2 | [21] |
| Pb RfD | Reference dose for ingestion | mg/kg day | 3.50 × 10−3 | 3.50 × 10−3 | [21] |
| Pb RfD | Reference dose for inhalation | mg/kg day | 3.52 × 10−3 | 3.52 × 10−3 | [21] |
| Pb RfD | Reference dose for dermal contact | mg/kg day | 5.25 × 10−4 | 5.25 × 10−4 | [21] |
| Zn RfD | Reference dose for ingestion | mg/kg day | 3.00 × 10−1 | 3.00 × 10−1 | [21] |
| Zn RfD | Reference dose for inhalation | mg/kg day | 3.00 × 10−1 | 3.00 × 10−1 | [21] |
| Zn RfD | Reference dose for dermal contact | mg/kg day | 6.00 × 10−2 | 6.00 × 10−2 | [21] |
| Land Uses | Sites | Cd | Cu | Fe | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial | I-1 | 3.98 a | 88.3 a | 39,315 bcd | 24.8 a | 262 b | 2369 b |
| Landfill | L-1 | 1.11 a | 8.42 a | 22,316 abc | 8.00 a | 90.3 a | 39.9 a |
| L-2 | 0.32 a | 7.76 a | 8941 ab | 3.36 a | 23.1 a | 11.1 a | |
| L-3 | 12.4 b | 1754 ab | 31,599 bcd | 75.7 b | 495 b | 3820 c | |
| L-4 | 1.78 a | 33.1 a | 33,886 cd | 12.4 a | 63.5 a | 294 a | |
| Mining | M-1 | 2.54 a | 517 a | 64,606 e | 19.3 a | 64.6 a | 225 a |
| Plantation | P-1 | 0.81 a | 7.33 a | 8548 ab | 9.41 a | 36.2 a | 29.3 a |
| P-2 | 1.74 a | 27.5 a | 79,058 f | 16.5 a | 48.7 a | 84.9 a | |
| P-3 | 1.12 a | 24.3 a | 37,595 cd | 19.5 a | 47.5 a | 99.4 a | |
| P-4 | 1.10 a | 20.96 a | 39,188 cd | 13.25 | 45.17 a | 55.17 a | |
| P-5 | 0.69 a | 11.84 a | 30,064 bcd | 10.66 a | 42.40 a | 100.81 a | |
| Residential | R-1 | 1.47 a | 156 a | 116,344 g | 11.2 a | 44.6 a | 262 a |
| R-2 | 0.24 a | 6.62 a | 17,421 abc | 3.44 a | 17.1 a | 11.0 a | |
| R-3 | 0.78 a | 4.66 a | 10,273 ab | 9.19 a | 32.5 a | 19.2 a | |
| R-4 | 1.06 a | 10.7 a | 27,434 bcd | 10.3 a | 34.3 a | 41.7 a | |
| R-5 | 1.30 a | 28.8 a | 27,741 bcd | 16.9 a | 49.7 a | 357 a | |
| R-6 | 1.41 a | 50.4 a | 37,283 cd | 14.2 a | 84.2 a | 505 a | |
| R-7 | 0.24 a | 5.49 a | 2576 a | 2.39 a | 7.22 | 45.2 a | |
| R-8 | 0.48 a | 9.19 a | 15,236 abc | 2.38 a | 20.2 a | 15.1 a | |
| R-9 | 0.50 a | 9.55 a | 22,674 abc | 7.25 a | 47.25 a | 50.31 a | |
| Rubbish heap | RH-1 | 0.87 a | 9.81 | 17,429 abc | 6.20 a | 38.8 a | 75.5 a |
| RH-2 | 1.22 | 90.06 | 23,590 | 15 | 87.4 | 285 | |
| RH-3 | 7.49 a | 2363.37 b | 37,099 | 57.71 ab | 969.22c | 2981.23 bc | |
| Reference values | Cd | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Fe | |
| UCC [48] | 0.100 | 25.0 | 56.0 | 15.0 | 65.0 | 43,000 | |
| Pre-industrial reference level [65] | 1.00 | 50.0 | NA | 70.0 | 175 | NA | |
| UCC [79] | 0.098 | 25.0 | 44.0 | 17.0 | 71.0 | NA | |
| UCC [80] | 0.090 | 28.0 | 47.0 | 17.0 | 67.0 | NA | |
| UCC [81] | 0.102 | 14.3 | 19.0 | 17.0 | 52.0 | 30,900 | |
| Land Uses | Sites | Cd Igeo | Cu Igeo | Ni Igeo | Pb Igeo | Zn Igeo | Cd CF | Cu CF | Ni CF | Pb CF | Zn CF | PLI | Cd ER | Cu ER | Ni ER | Pb ER | Zn ER | PERI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial | I-1 | 4.73 | 1.24 | −1.76 | 3.54 | 4.60 | 39.8 | 3.53 | 0.44 | 17.5 | 36.4 | 8.31 | 1194 | 17.7 | 2.21 | 87.3 | 36.4 | 1338 |
| Landfill | L-1 | 2.89 | −2.15 | −3.39 | 2.00 | −1.29 | 11.1 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 6.02 | 0.61 | 1.15 | 333 | 1.68 | 0.71 | 30.1 | 0.61 | 366 |
| L-2 | 1.09 | −2.27 | −4.64 | 0.04 | −3.13 | 3.20 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 1.54 | 0.17 | 0.44 | 96 | 1.55 | 0.30 | 7.70 | 0.17 | 106 | |
| L-3 | 6.37 | 5.55 | −0.15 | 4.46 | 5.29 | 124 | 70.16 | 1.35 | 33.0 | 58.8 | 29.6 | 3720 | 351 | 6.76 | 165 | 58.8 | 4301 | |
| L-4 | 3.57 | −0.18 | −2.76 | 1.50 | 1.59 | 17.8 | 1.32 | 0.22 | 4.23 | 4.52 | 2.51 | 534 | 6.62 | 1.11 | 21.2 | 4.52 | 567 | |
| Mean | 3.48 | 0.23 | −2.74 | 2.00 | 0.62 | 39.0 | 18.0 | 0.44 | 11.2 | 16.0 | 8.43 | 1171 | 90.2 | 2.22 | 56.0 | 16.0 | 1335 | |
| Mining | M-1 | 4.08 | 3.79 | −2.12 | 1.52 | 1.21 | 25.4 | 20.7 | 0.34 | 4.31 | 3.46 | 4.86 | 762 | 103 | 1.72 | 21.5 | 3.46 | 892 |
| Plantation | P-1 | 2.43 | −2.36 | −3.16 | 0.69 | −1.73 | 8.10 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 2.41 | 0.45 | 0.85 | 243 | 1.47 | 0.84 | 12.1 | 0.45 | 258 |
| P-2 | 3.54 | −0.45 | −2.35 | 1.11 | −0.20 | 17.4 | 1.10 | 0.29 | 3.25 | 1.31 | 1.89 | 522 | 5.50 | 1.47 | 16.2 | 1.31 | 547 | |
| P-3 | 2.90 | −0.63 | −2.11 | 1.08 | 0.03 | 11.2 | 0.97 | 0.35 | 3.17 | 1.53 | 1.79 | 336 | 4.86 | 1.74 | 15.8 | 1.53 | 360 | |
| P-4 | 2.87 | −0.84 | −2.66 | 1.01 | −0.82 | 11.0 | 0.84 | 0.24 | 3.01 | 0.85 | 1.41 | 330 | 4.19 | 1.18 | 15.1 | 0.85 | 351 | |
| P-5 | 2.20 | −1.66 | −2.98 | 0.91 | 0.05 | 6.90 | 0.47 | 0.19 | 2.83 | 1.55 | 1.22 | 207 | 2.37 | 0.95 | 14.1 | 1.55 | 226 | |
| Mean | 2.79 | −1.19 | −2.65 | 0.96 | −0.54 | 10.9 | 0.74 | 0.25 | 2.93 | 1.14 | 1.43 | 328 | 3.68 | 1.24 | 14.7 | 1.14 | 348 | |
| Residential | R-1 | 3.29 | 2.06 | −2.91 | 0.99 | 1.43 | 14.7 | 6.24 | 0.20 | 2.97 | 4.03 | 2.94 | 441 | 31.20 | 1.00 | 14.9 | 4.03 | 492 |
| R-2 | 0.68 | −2.50 | −4.61 | −0.40 | −3.15 | 2.40 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 1.14 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 72 | 1.32 | 0.31 | 5.70 | 0.17 | 80 | |
| R-3 | 2.38 | −3.01 | −3.19 | 0.53 | −2.34 | 7.80 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 2.17 | 0.30 | 0.69 | 234 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 10.8 | 0.30 | 247 | |
| R-4 | 2.82 | −1.81 | −3.03 | 0.61 | −1.23 | 10.6 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 2.29 | 0.64 | 1.04 | 318 | 2.14 | 0.92 | 11.4 | 0.64 | 333 | |
| R-5 | 3.12 | −0.38 | −2.31 | 1.14 | 1.87 | 13.0 | 1.15 | 0.30 | 3.31 | 5.49 | 2.42 | 390 | 5.76 | 1.51 | 16.6 | 5.49 | 419 | |
| R-6 | 3.23 | 0.43 | −2.56 | 1.90 | 2.37 | 14.1 | 2.02 | 0.25 | 5.61 | 7.77 | 3.16 | 423 | 10.1 | 1.27 | 28.1 | 7.77 | 470 | |
| R-7 | 0.68 | −2.77 | −5.14 | −1.64 | −1.11 | 2.40 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.70 | 0.38 | 72 | 1.10 | 0.21 | 2.41 | 0.70 | 76 | |
| R-8 | 1.68 | −2.03 | −5.14 | −0.16 | −2.69 | 4.80 | 0.37 | 0.04 | 1.35 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 144 | 1.84 | 0.21 | 6.73 | 0.23 | 153 | |
| R-9 | 1.74 | −1.97 | −3.53 | 1.07 | −0.95 | 5.00 | 0.38 | 0.13 | 3.15 | 0.77 | 0.90 | 150 | 1.91 | 0.65 | 15.8 | 0.77 | 169 | |
| Mean | 2.18 | −1.33 | −3.60 | 0.45 | −0.64 | 8.31 | 1.25 | 0.15 | 2.50 | 2.23 | 1.37 | 249 | 6.25 | 0.77 | 12.48 | 2.23 | 271 | |
| Rubbish heap | RH-1 | 2.54 | −1.93 | −3.76 | 0.79 | −0.37 | 8.70 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 2.59 | 1.16 | 1.03 | 261 | 1.96 | 0.55 | 12.9 | 1.16 | 278 |
| RH-2 | 3.02 | 1.26 | −2.49 | 1.96 | 1.55 | 12.2 | 3.60 | 0.27 | 5.83 | 4.38 | 3.13 | 366 | 18.0 | 1.34 | 29.1 | 4.38 | 419 | |
| RH-3 | 5.64 | 5.98 | −0.54 | 5.43 | 4.93 | 74.9 | 94.5 | 1.03 | 64.6 | 45.9 | 29.3 | 2247 | 473 | 5.15 | 323 | 45.9 | 3094 | |
| Mean | 3.73 | 1.77 | −2.26 | 2.72 | 2.04 | 31.9 | 32.8 | 0.47 | 24.3 | 17.1 | 11.2 | 958 | 164 | 2.35 | 122 | 17.1 | 1263 |
| No. | Location (Land Use; Sampling Year; Mesh Size) | Metal | Concentrations | Igeo | CF | PLI | ER | PERI (Mean) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Peninsular Malaysia (agricultural crops; unspecified; 2 mm) | Cd | 0.01–2.02 (1.12) | −3.91–3.75 (2.90) | 0.10–20.2 (11.2) | 0.03–4.33 (1.13) | 3.00–606 (336) | 350 | [88] |
| Cu | 0.37–114 (16.40) | −6.66–1.60 (−1.19) | 0.01–4.56 (0.66) | 0.07–22.80 (3.28) | |||||
| Ni | 0.40–73.5 (13.70) | −7.71–−0.19 (−1.45) | 0.01–1.31 (0.24) | 0.04–6.56 (1.22) | |||||
| Pb | 0.84–90 (26.4) | −2.96–2.61 (−0.51) | 0.06–6.00 (1.76) | 0.28–30.00 (8.8) | |||||
| Zn | 2.90–137 (38.0) | −5.07–0.49 (0.02) | 0.04–2.11 (0.58) | 0.04–2.11 (0.58) | |||||
| 2 | Bestari Jaya, Malaysia (reclaimed ex-tin mining area; 2010; 2 mm) | Cu | 11.0–47.0 (29.0) | −1.77–0.33 (−0.37) | 0.44–1.88 (1.16) | 0.47–2.30 (1.39) | 2.20–9.40 (6) | 24.0 | [17] |
| Pb | 13.0–89 (51.00) | −0.32–1.66 (0.44) | 0.87–5.93 (3.40) | 4.33–29.7 (17) | |||||
| Zn | 18.0–71 (44.50) | −2.44–−0.46 (0.25) | 0.28–1.09 (0.68) | 0.28–1.09 (1) | |||||
| 3 | Bestari Jaya, Malaysia (mine dumps; 2010; 2 mm) | Cu | 761–2781 (1771) | 4.34–6.21 (5.56) | 30.4–111 (70.8) | 22.1–115 (68.8) | 152–556 (354) | 1075 | [17] |
| Pb | 541–3589 (2065) | 4.83–7.36 (5.78) | 36.1–239 (138) | 180–1196 (688) | |||||
| Zn | 638–3698 (2168) | 2.71–5.25 (5.85) | 9.82–56.9 (33.4) | 9.82–56.9 (33) | |||||
| 4 | Xinxiang City, China (farmland; unspecified; unspecified) | Cd | 6.74–29.4 (18.1) | 5.49–7.61 (6.91) | 67.4–294 (181) | 7.00–35.6 (21.8) | 2022–8820 (5430) | 5566 | [86] |
| Cu | 29.6–133 (81.3) | −0.34–1.83 (1.12) | 1.18–5.32 (3.25) | 5.92–26.6 (16.3) | |||||
| Ni | 157–2090 (1124) | 0.90–4.64 (4.90) | 2.80–37.3 (20.1) | 14.0–187 (100) | |||||
| Zn | 696–1793 (1245) | 2.84–4.20 (5.05) | 10.7–27.6 (19.2) | 10.71–27.6 (19.2) | |||||
| 5 | Huize County, China (mining, 2011; 6mm) | Cd | 0.10–9.50 (4.80) | −0.58–5.98 (5.00) | 1.00–95.0 (48.0) | 0.84–23.4 (13.2) | 30.0–2850 (1440) | 14,778 | [85] |
| Cu | 14.0–52.0 (33.0) | −1.42–0.47 (−0.18) | 0.56–2.08 (1.32) | 2.80–10.4 (6.60) | |||||
| Pb | 4.80–2186 (1095) | 3.02–4.92 (4.87) | 0.32–146 (73.0) | 1.60–729 (365) | |||||
| Zn | 183–679 (431) | 0.91–2.80 (3.52) | 2.82–10.5 (6.63) | 2.82–10.5 (6.63) | |||||
| 6 | Seri Kembangan, Malaysia (Industry and residential; 2013; 2 mm) | Cd | 11.3–67.5 (47.5) | 6.24–8.81 (8.31) | 113–675 (475) | 24.16–500 (291) | 3390–20250 (14250) | 15,140 | [84] |
| Pb | 77.5–5547 (2669) | −4.22–−2.60 (6.15) | 5.17–370 (178) | 25.8–1849 (890) | |||||
| 7 | Anshan city, China (steel industry; 2014; 0.149 mm) | Cd | 0.27–1.87 (0.86) | 0.85–3.64 (2.52) | 2.70–18.7 (8.60) | 0.69−11.2 (2.54) | 81.0–561 (258) | 290 | [21] |
| Cu | 11.0–514 (52.3) | −1.77–3.78 (0.48) | 0.44–20.56 (2.09) | 2.20–103 (10.5) | |||||
| Ni | 13.1–49.6 (33.5) | −2.68–−0.76 (−0.16) | 0.23–0.89 (0.60) | 1.17–4.43 (2.99) | |||||
| Pb | 14.6–208 (45.1) | 0.76–6.72 (0.27) | 0.97–13.87 (3.01) | 4.87–69.33 (15.03) | |||||
| Zn | 38.1–2368 (213) | −1.36–4.60 (2.51) | 0.59–36.43 (3.28) | 0.59–36.43 (3.28) | |||||
| 8 | Peninsular Malaysia (Habitat topsoils of Centella asiatica; 2010; 63 µm) | Cd | 1.21–3.72 (1.92) | 3.01–4.63 (3.68) | 12.10–37.20 (19.2) | 0.87–4.70 (2.56) | 363–1116 (576) | 625 | [87] |
| Cu | 22.3–147 (65.9) | −0.75–1.97 (0.81) | 0.89–5.88 (2.64) | 4.46–29.4 (13.2) | |||||
| Ni | 4.01–13.5 (9.25) | −4.39–−2.64 (−2.02) | 0.07–0.24 (0.17) | 0.36–1.21 (0.83) | |||||
| Pb | 24.7–179 (98.0) | 0.21–3.40 (1.39) | 1.65–11.9 (6.53) | 8.23–59.7 (32.7) | |||||
| Zn | 26.1–237 (130) | −1.90–1.28 (1.79) | 0.40–3.65 (2.00) | 0.40–3.65 (2) | |||||
| Fe | 1.37–2.79 (2.21) | - | - | - | |||||
| 9 | Hyderabad, India (Industrial area; unspecified; 200-mesh size) | Cu | 7.90–184 (31.9) | −2.25–2.29 (−0.23) | 0.32–7.36 (1.28) | 0.43–13.0 (2.08) | 1.58–36.8 (6.38) | 69.2 | [61] |
| Ni | 10.2–130 (43.0) | −3.04–0.63 (0.20) | 0.18–2.32 (0.77) | 0.91–11.6 (3.84) | |||||
| Pb | 25.3–1830 (172) | 0.08–5.29 (2.20) | 1.69–122 (11.5) | 8.43–610 (57.3) | |||||
| Zn | 23.8–879 (108) | −2.03–3.17 (1.53) | 0.37–13.5 (1.66) | 0.37–13.5 (1.66) | |||||
| 10 | Kuala Lipis, Pahang, Malaysia (active iron ore-mining sites; 2015; 2 mm) | Cd | 0.063–0.42 (0.28) | −1.25–1.49 (0.90) | 0.63–4.20 (2.80) | 0.67–1.80 (1.31) | 18.9–126 (84) | 127 | [69] |
| Cu | 67.5–166 (110) | 0.85–2.15 (1.55) | 2.70–6.64 (4.40) | 13.5–33.2 (22) | |||||
| Ni | 1.45–4.36 (2.93) | −5.86–−4.27 (−3.68) | 0.03–0.08 (0.05) | 0.13–0.39 (0.26) | |||||
| Pb | 32–72.5 (56.0) | 2.05–2.37 (0.58) | 2.13–4.83 (3.73) | 10.7–24.2 (18.7) | |||||
| Zn | 93–116 (105) | −0.07–0.25 (1.49) | 1.43–1.78 (1.62) | 1.43–1.78 (1.62) | |||||
| Fe | 6.82–12.9 (10.8) | - | - | - | |||||
| 11 | Bukit Ibam, Pahang, Malaysia (An abandoned mine; 2015; 2 mm) | Cd | 0.03–0.06 (0.04) | −2.32–−1.32 (−1.91) | 0.30–0.60 (0.40) | 0.49–1.30 (0.91) | 9.00–18.0 (12) | 51.8 | [69] |
| Cu | 67.5–185 (145) | 0.85–2.30 (1.95) | 2.70–7.40 (5.80) | 13.5–37.0 (29) | |||||
| Ni | 1.34–7.96 (3.91) | −5.97–−3.40 (−3.26) | 0.02–0.14 (0.07) | 0.12–0.71 (0.35) | |||||
| Pb | 9.65–34.5 (23.8) | 2.75–2.91 (−0.66) | 0.64–2.30 (1.59) | 3.22–11.5 (7.93) | |||||
| Zn | 151–169 (161) | 0.63–0.79 (2.10) | 2.32–2.60 (2.48) | 2.32–2.60 (2.48) | |||||
| Fe | 7.59–21.1 (13.50) | - | - | - | |||||
| 12 | Recife, Brazil (metropolitan region; unspecified; 0.149 mm) | Cd | 0.00–4.3 (1.50) | 0.00–4.84 (3.32) | 0.00–43.0 (15.0) | 0.00–20.4 (0.99) | 0.00–1290 (450) | 460 | [68] |
| Cu | 0.10–1228 (12.80) | −8.55–5.03 (−1.55) | 0.00–49.1 (0.51) | 0.02–246 (2.56) | |||||
| Ni | 0.10–42.5 (6.30) | −9.71–−0.98 (−2.57) | 0.00–0.76 (0.11) | 0.01–3.79 (0.56) | |||||
| Pb | 0.10–333 (16.50) | −7.81–8.15 (−1.18) | 0.01–22.2 (1.10) | 0.03–111 (5.5) | |||||
| Zn | 0.10–6400 (65.20) | −9.93–6.04 (0.80) | 0.00–98.5 (1.00) | 0.00–98.5 (1) | |||||
| 13 | Kuala Terengganu (urban; unspecified; 0.6 mm) | Cd | 0.38–6.78 (1.28) | 1.34–5.50 (3.09) | 3.80–67.8 (12.8) | 0.14–5.25 (0.92) | 114–2034 (384) | 395 | [83] |
| Cu | 0.82–148 (10.9) | −5.52–1.98 (−1.78) | 0.03–5.92 (0.44) | 0.16–29.60 (2.18) | |||||
| Ni | 1.91–16.7 (7.02) | −5.46–−2.33 (−2.42) | 0.03–0.30 (0.13) | 0.17–1.49 (0.63) | |||||
| Pb | 2.54–160 (23.6) | −2.29–3.18 (−0.67) | 0.17–10.67 (1.57) | 0.85–53.33 (7.87) | |||||
| Zn | 4.61–204 (38.3) | −4.40–1.07 (0.03) | 0.07–3.14 (0.59) | 0.07–3.14 (0.59) | |||||
| Fe | 0.22–7.70 (1.57) | - | - | - | |||||
| 14 | Southwest Guizhou, China (thallium mine area; 2018; 200-mesh) | Cd | 0.14–5.17 (1.14) | −0.10–5.11 (2.93) | 1.40–51.7 (11.4) | 0.82–9.92 (3.74) | 42.0–1551 (342) | 375 | [50] |
| Cu | 33.6–150 (79.6) | −0.16–2.00 (1.09) | 1.34–6.00 (3.18) | 6.72–30.00 (15.9) | |||||
| Pb | 12.7–96.5 (44.4) | −0.28–3.81 (0.24) | 0.85–6.43 (2.96) | 4.23–32.2 (14.8) | |||||
| Zn | 18.5–316 (118) | −2.40–1.70 (1.65) | 0.28–4.86 (1.82) | 0.28–4.86 (1.82) | |||||
| 15 | Guangzhou-Foshan, South China (urban-agriculture; unspecified; 74 μm) | Cd | 0.001–1.37 (0.20) | −7.23–3.19 (0.42) | 0.01–13.70 (2.00) | 0.09–17.4 (0.89) | 0.30–411 (60.00) | 77.3 | [45] |
| Cu | 2.37–290 (19.3) | −3.98–2.95 (−0.96) | 0.09–11.60 (0.77) | 0.47–58.00 (3.86) | |||||
| Ni | 2.3–442 (12.2) | −5.19–2.40 (−1.62) | 0.04–7.89 (0.22) | 0.21–39.46 (1.09) | |||||
| Pb | 12.3–2447 (34.8) | −0.65–4.47 (−0.11) | 0.82–163 (2.32) | 4.10–816 (11.6) | |||||
| Zn | 14.3–500 (45.7) | −2.77–2.36 (0.29) | 0.22–7.69 (0.70) | 0.22–7.69 (0.7) | |||||
| 16 | Ogere, Nigeria (5 land uses; 2017; 0.15 mm and 0.50 mm) | Cd | 0.2–2.4 (0.70) | 0.42–4.00 (2.22) | 2.00–24.0 (7.00) | 1.02–3.50 (1.83) | 60.00–720 (210) | 223 | [28] |
| Cu | 17.9–57.6 (29.6) | −1.07–0.62 (−0.34) | 0.72–2.30 (1.18) | 3.58–11.52 (5.92) | |||||
| Pb | 14.4–23.4 (19.4) | 1.16–2.33 (−0.95) | 0.96–1.56 (1.29) | 4.80–7.80 (6.47) | |||||
| Zn | 50.4–113 (68.3) | −0.95–0.21 (0.86) | 0.78–1.74 (1.05) | 0.78–1.74 (1.05) | |||||
| 17 | Harran Plain, Turkey (agriculture; 2015; 0.50 mm) | Cu | 15.0–47.0 (27.0) | −1.32–0.33 (−0.47) | 0.60–1.88 (1.08) | 0.59–2.47 (1.06) | 3.00–9.40 (5.4) | 17.9 | [51] |
| Ni | 47.0–334 (89.0) | −0.84–1.99 (1.25) | 0.84–5.96 (1.59) | 4.20–29.8 (7.95) | |||||
| Pb | 5.80–16.5 (10.6) | −0.58–1.06 (−1.82) | 0.39–1.10 (0.71) | 1.93–5.50 (3.53) | |||||
| Zn | 40.0–197 (68.0) | −1.29–1.01 (0.86) | 0.62–3.03 (1.05) | 0.62–3.03 (1.05) | |||||
| Fe | 2.19–6.52 (3.71) | - | - | - | |||||
| 18 | Khatoon Abad, Iran (copper smelter; unspecified; 63 µm) | Cd | 0.2–30.4 (6.00) | 0.42–7.66 (5.32) | 2.00–304 (60.0) | 1.14–56.5 (15.6) | 60.0–9120 (1800) | 2598 | [82] |
| Cu | 38.9–10,000 (3618) | 0.05–8.06 (6.59) | 1.56–400 (145) | 7.78–2000 (724) | |||||
| Ni | 21.2–83.2 (58.0) | −1.99–−0.01 (0.63) | 0.38–1.49 (1.04) | 1.89–7.43 (5.18) | |||||
| Pb | 17.5–940 (180) | 2.01–7.20 (2.26) | 1.17–62.7 (12.0) | 5.83–313 (60) | |||||
| Zn | 90.9–3310 (548) | −0.10–5.09 (3.87) | 1.40–50.9 (8.43) | 1.40–50.9 (8.43) | |||||
| 19 | Dabaoshan, Linxiang, and Daye of China (Farmland in mining areas; unspecified; 100-mesh) | Cd | 0.82–4.12 (2.67) | 2.45–4.78 (4.15) | 8.20–41.2 (26.7) | 2.47–21.2 (10.4) | 246–1236 (800) | 913 | [67] |
| Cu | 26.6–524 (241) | −0.50–3.80 (2.68) | 1.06–21.0 (9.64) | 5.32–105 (48.2) | |||||
| Pb | 41.4–469 (183) | 2.15–4.43 (2.29) | 2.76–31.3 (12.2) | 13.8–156 (61) | |||||
| Zn | 100–486 (244) | 0.04–2.32 (2.70) | 1.54–7.48 (3.76) | 1.54–7.48 (3.76) | |||||
| 20 | Southern Yunnan Province, China (Agriculture; 2018; 0.149mm) | Cd | 0.03–4.70 (0.74) | −2.32–4.97 (2.30) | 0.30–47.0 (7.40) | 0.27–12.2 (2.53) | 9.00–1410 (222) | 260 | [64] |
| Cu | 6.13–144 (48.3) | −2.61–1.94 (0.37) | 0.25–5.76 (1.93) | 1.23–28.8 (9.66) | |||||
| Ni | 4.32–197 (50.9) | −4.28–1.23 (0.44) | 0.08–3.52 (0.91) | 0.39–17.6 (4.54) | |||||
| Pb | 17.0–558 (67.6) | −0.58–4.46 (0.85) | 1.13–37.2 (4.51) | 5.67–186 (22.5) | |||||
| Zn | 15.1–495 (114) | −2.69–2.34 (1.60) | 0.23–7.62 (1.75) | 0.23–7.62 (1.75) | |||||
| 21 | Panzhihua, China (industrial mining city; unspecified; 200-mesh) | Cd | 0.01–2.37 (1.10) | −3.91–3.98 (2.87) | 0.10–23.7 (11.0) | 0.17–11.1 (3.76) | 3.00–711 (330) | 326 | [55] |
| Cu | 4.84–121 (46.2) | −2.95–1.69 (0.30) | 0.19–4.84 (1.85) | 0.97–24.2 (9.24) | |||||
| Pb | 0.57–142 (39.3) | −11.14–−3.25 (0.07) | 0.04–9.47 (2.62) | 0.19–47.3 (13.1) | |||||
| Zn | 68.9–895 (244) | −0.50–3.20 (2.70) | 1.06–13.8 (3.75) | 1.06–13.8 (3.75) | |||||
| 22 | Overall Peninsular Malaysia (6 different land uses; 2011–2012; 63 µm) | Cd | 0.24–12.4 (1.94) | 0.68–6.37 (2.93) | 2.40–124 (19.4) | 0.38–29.6 (4.34) | 72.0–3720 (582) | 675 | This study |
| Cu | 4.66–2363 (228) | −3.01–5.98 (−0.29) | 0.19–94.5 (9.12) | 0.93–473 (45) | |||||
| Ni | 2.38–75.7 (16.0) | −5.14–−0.15 (−2.93) | 0.04–1.35 (0.29) | 0.21–6.76 (1.43) | |||||
| Pb | 7.22–969 (115) | −1.64–5.43 (1.31) | 0.48–64.6 (7.67) | 2.41–323 (38.3) | |||||
| Zn | 11.0–3820 (512) | −3.15–5.29 (0.26) | 0.17–58.8 (7.88) | 0.17–58.8 (7.88) | |||||
| Fe | 0.26–11.6 (3.26) | - | - | - | |||||
| 23 | Peninsular Malaysia (industry; 2011–2012; 63 µm) | Cd | (3.98) | (4.73) | (39.8) | (8.31) | (1194) | 1338 | This study |
| Cu | (88.3) | (1.24) | (3.53) | (17.7) | |||||
| Ni | (24.8) | (−0.60) | (0.44) | (2.21) | |||||
| Pb | (262) | (2.80) | (17.5) | (87.3) | |||||
| Zn | (2369) | (5.98) | (36.5) | 36.5 | |||||
| Fe | (39,315) | - | - | - | |||||
| 24 | Peninsular Malaysia (landfill; 2011–2012; 63 µm) | Cd | (3.90) | (4.70) | (39.0) | (8.43) | (1170) | 1335 | This study |
| Cu | (451 | (3.59) | (18.0) | (90.2) | |||||
| Ni | (24.9) | (−0.59) | (0.44) | (2.22) | |||||
| Pb | (168) | (2.16) | (11.2) | (56.0) | |||||
| Zn | (1041) | (4.79) | (16.0) | (16.0) | |||||
| Fe | (24,186) | - | - | - | |||||
| 25 | Peninsular Malaysia (mining; 2011–2012; 63 µm) | Cd | (2.54) | (4.08) | (25.4) | (4.86) | (762) | 892 | This study |
| Cu | (517) | (3.79) | (20.7) | (103) | |||||
| Ni | (19.3) | (−0.96) | (0.34) | (1.72) | |||||
| Pb | (64.6) | (0.78) | (4.31) | (21.5) | |||||
| Zn | (225) | (2.58) | (3.46) | (3.46) | |||||
| Fe | (64,606) | ||||||||
| 26 | Peninsular Malaysia (plantation; 2011–2012; 63 µm) | Cd | (1.09) | (2.86) | (10.9) | (1.43) | (327) | 348 | This study |
| Cu | (18.4) | (−1.03) | (0.74) | (3.68) | |||||
| Ni | (13.9) | (−1.43) | (0.25) | (1.24) | |||||
| Pb | (44.0) | (0.23) | (2.93) | (14.7) | |||||
| Zn | (73.9) | (0.98) | (1.14) | (1.14) | |||||
| Fe | (38,891) | - | - | - | |||||
| 27 | Peninsular Malaysia (residential; 2011–2012; 63 µm) | Cd | (0.83) | (2.47) | (8.30) | (1.37) | (249) | 271 | This study |
| Cu | (31.3) | (−0.26) | (1.25) | (6.26) | |||||
| Ni | (8.58) | (−2.13) | (0.15) | (0.77) | |||||
| Pb | (37.5) | (0.00) | (2.50) | (12.5) | |||||
| Zn | (145) | (1.95) | (2.23) | (2.23) | |||||
| Fe | (30,738) | - | - | - | |||||
| 28 | Peninsular Malaysia (rubbish heap; 2011–2012; 63 µm) | Cd | (3.19) | (4.41) | (31.9) | (11.2) | (957) | 1263 | This study |
| Cu | (821) | (4.45) | (32.8) | (164) | |||||
| Ni | (26.3) | (−0.51) | (0.47) | (2.35) | |||||
| Pb | (365) | (3.28) | (24.3) | (122) | |||||
| Zn | (1114) | (4.89) | (17.1) | (17.1) | |||||
| Fe | (26,039) | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yap, C.K.; Chew, W.; Al-Mutairi, K.A.; Nulit, R.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Wong, K.W.; Bakhtiari, A.R.; Sharifinia, M.; Ismail, M.S.; Leong, W.J.; et al. Assessments of the Ecological and Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Topsoils of Different Land Uses: A Case Study in Peninsular Malaysia. Biology 2022, 11, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010002
Yap CK, Chew W, Al-Mutairi KA, Nulit R, Ibrahim MH, Wong KW, Bakhtiari AR, Sharifinia M, Ismail MS, Leong WJ, et al. Assessments of the Ecological and Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Topsoils of Different Land Uses: A Case Study in Peninsular Malaysia. Biology. 2022; 11(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleYap, Chee Kong, Weiyun Chew, Khalid Awadh Al-Mutairi, Rosimah Nulit, Mohd. Hafiz Ibrahim, Koe Wei Wong, Alireza Riyahi Bakhtiari, Moslem Sharifinia, Mohamad Saupi Ismail, Wah June Leong, and et al. 2022. "Assessments of the Ecological and Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Topsoils of Different Land Uses: A Case Study in Peninsular Malaysia" Biology 11, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010002
APA StyleYap, C. K., Chew, W., Al-Mutairi, K. A., Nulit, R., Ibrahim, M. H., Wong, K. W., Bakhtiari, A. R., Sharifinia, M., Ismail, M. S., Leong, W. J., Tan, W. S., Cheng, W. H., Okamura, H., You, C. F., & Al-Shami, S. A. (2022). Assessments of the Ecological and Health Risks of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Topsoils of Different Land Uses: A Case Study in Peninsular Malaysia. Biology, 11(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010002






