Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes Secreted from Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Isolation and Culture
2.2. Viral Transduction
2.3. Exosome Extraction
2.4. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.5. Sample Preparation for Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Liquid Chromatography, Mass Spectrometry Data Acquisition Parameters
2.7. Data Analysis
2.8. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
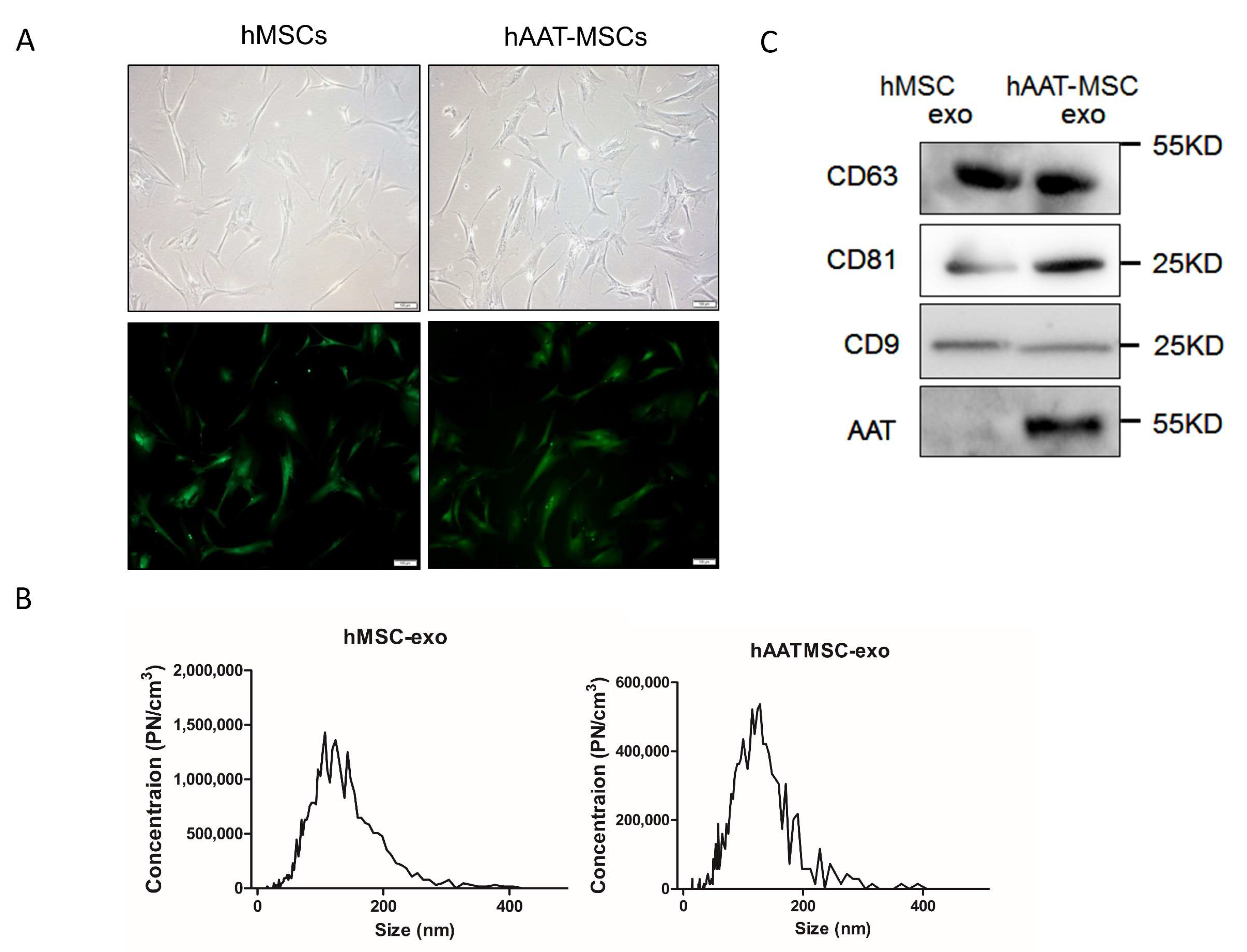
3.1. Generation and Characterization of hMSCs, hAAT-MSCs and Their Exosomes
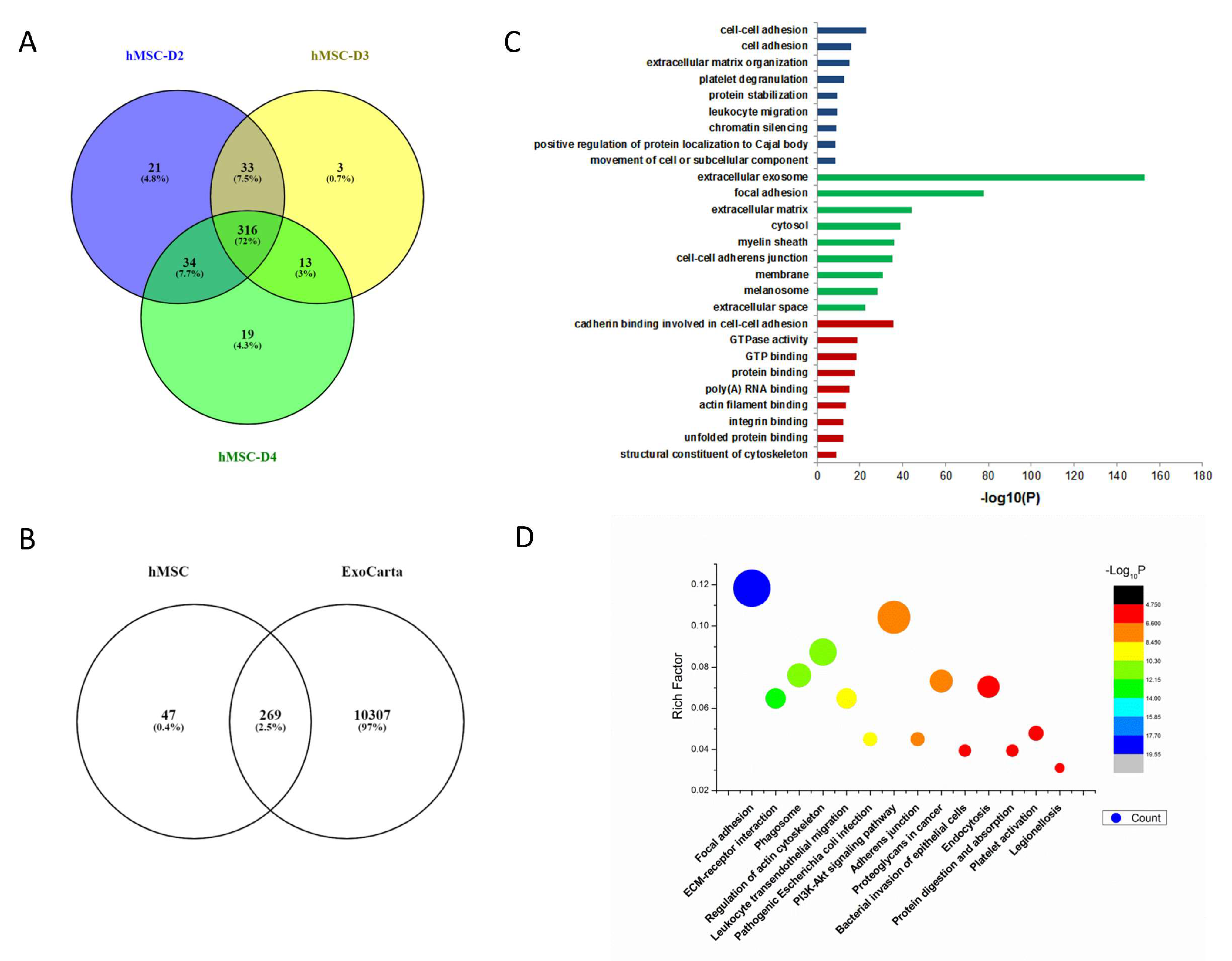
3.2. Bioinformatic Analysis of Proteins in MSC-Exosomes from Individual Donors
3.3. Bioinformatic Analysis of Proteins in hAAT-MSC-Exosomes from Individual Donors
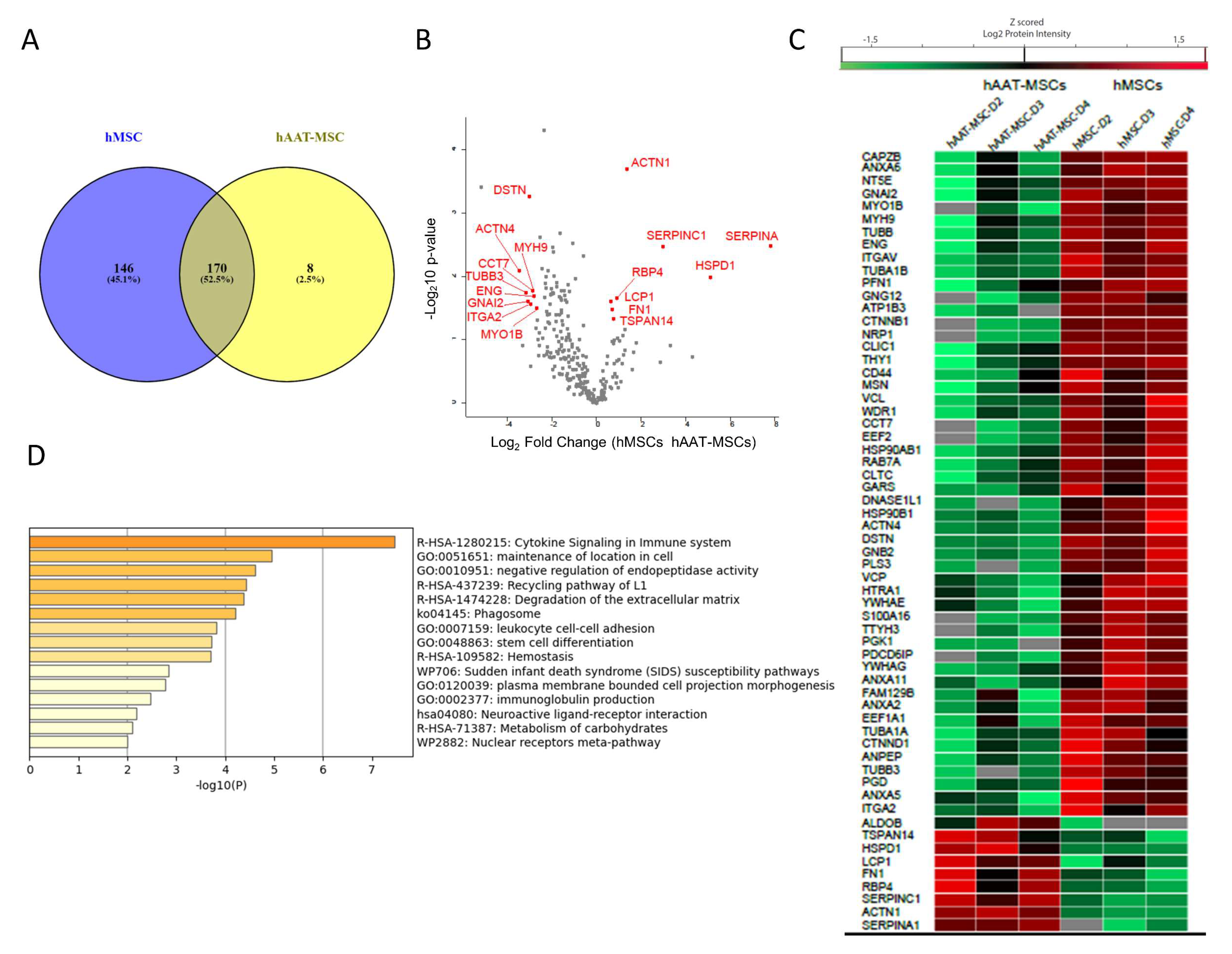
3.4. Comparation of Proteins from hMSCs- and hAAT-MSC-Exosomes by Horizontal Bioinformatic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galipeau, J.; Sensebe, L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Discher, D.E.; Peault, B.M.; Phinney, D.G.; Hare, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen. Med. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tse, H.F.; Lian, Q. Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: Current status and perspectives. Cell Transpl. 2014, 23, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, O.; Kuai, R.; Siren, E.M.J.; Bhere, D.; Milton, Y.; Nissar, N.; De Biasio, M.; Heinelt, M.; Reeve, B.; Abdi, R.; et al. Shattering barriers toward clinically meaningful MSC therapies. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Q.; Zhu, J.; Ankrum, J.A. Manufacturing of primed mesenchymal stromal cells for therapy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Drescher, K.M.; Chen, X.M. Exosomal miRNAs: Biological Properties and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heldring, N.; Mager, I.; Wood, M.J.; Le Blanc, K.; Andaloussi, S.E. Therapeutic Potential of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles. Hum. Gene Ther. 2015, 26, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.J.; Picou, A.A.; Kish, S.L.; Giraldo, A.M.; Godke, R.A.; Bondioli, K.R. Isolation and characterization of porcine adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs 2008, 188, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ding, Q.; Yaqoob, U.; de Assuncao, T.M.; Verma, V.K.; Hirsova, P.; Cao, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Huebert, R.C.; Shah, V.H. Exosome Adherence and Internalization by Hepatic Stellate Cells Triggers Sphingosine 1-Phosphate-dependent Migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30684–30696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, L.; Dong, J.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes reduce apoptosis and inflammatory response during spinal cord injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fevrier, B.; Raposo, G. Exosomes: Endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; Wang, S.; Zhao, R.C. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: A new therapeutic paradigm. Biomark. Res. 2019, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gowen, A.; Shahjin, F.; Chand, S.; Odegaard, K.E.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Challenges in Clinical Applications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.J. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: A review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Kwon, M.; Choi, J.C.; Shin, J.W.; Park, I.W.; Choi, B.W.; Kim, J.Y. Familial occurrence of pulmonary embolism after intravenous, adipose tissue-derived stem cell therapy. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Baixauli, F.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Mittelbrunn, M. Sorting it out: Regulation of exosome loading. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 28, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toh, W.S.; Lai, R.C.; Zhang, B.; Lim, S.K. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, G.; Zheng, G.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Shu, Q.; Xu, J. Functional proteins of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuda, T.; Kosaka, N.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K.; Yang, C.; Su, Y.; Luo, J.C.; Luo, M.H.; Huang, D.L.; Tu, G.W.; Luo, Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Acute Kidney Injury. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 684496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galieva, L.R.; James, V.; Mukhamedshina, Y.O.; Rizvanov, A.A. Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles for the Treatment of Nerve Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellin, G.; Gardin, C.; Ferroni, L.; Chachques, J.C.; Rogante, M.; Mitrecic, D.; Ferrari, R.; Zavan, B. Exosome in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Complex World Full of Hope. Cells 2019, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Contreras, M.; Brooks, R.W.; Boccuzzi, L.; Robbins, P.D.; Ricordi, C. Exosomes as biomarkers and therapeutic tools for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 2940–2956. [Google Scholar]
- Perlino, E.; Cortese, R.; Ciliberto, G. The human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene is transcribed from two different promoters in macrophages and hepatocytes. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2767–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, J.C.; Oton-Gonzalez, L.; Selvatici, R.; Rizzo, P.; Pavasini, R.; Campo, G.C.; Lanzillotti, C.; Mazziotta, C.; De Mattei, M.; Tognon, M.; et al. SERPINA1 Gene Promoter Is Differentially Methylated in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Pregnant Women. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 550543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Gou, W.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Lee, J.; Strange, C.; Wang, H. Overexpression of alpha-1 antitrypsin in mesenchymal stromal cells improves their intrinsic biological properties and therapeutic effects in nonobese diabetic mice. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2021, 10, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, S.; Ozay, E.I.; Geumann, U.; Hereth, M.K.; Magnusson, T.; Shanthalingam, S.; Hirsch, D.; Kalin, S.; Gunther, C.; Osborne, B.A.; et al. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin-Expressing Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Confer a Long-Term Survival Benefit in a Mouse Model of Lethal GvHD. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1436–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, A.A.; Kwok, L.W.; Hovav, A.H.; Ohle, S.J.; Little, F.F.; Fine, A.; Kotton, D.N. Sustained expression of alpha1-antitrypsin after transplantation of manipulated hematopoietic stem cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Sun, Z.; Kim, D.S.; Gou, W.; Strange, C.; Dong, H.; Cui, W.; Gilkeson, G.; Morgan, K.A.; Adams, D.B.; et al. Adipose stem cells from chronic pancreatitis patients improve mouse and human islet survival and function. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fattore, A.; Luciano, R.; Saracino, R.; Battafarano, G.; Rizzo, C.; Pascucci, L.; Alessandri, G.; Pessina, A.; Perrotta, A.; Fierabracci, A.; et al. Differential effects of extracellular vesicles secreted by mesenchymal stem cells from different sources on glioblastoma cells. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Shi, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; He, Q.; Huang, H. Exosome secreted from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates diabetic nephropathy by promoting autophagy flux and inhibiting apoptosis in podocyte. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.D.; Johansson, H.J.; Graham, C.S.; Vesterlund, M.; Pham, M.T.; Bramlett, C.S.; Montgomery, E.N.; Mellema, M.S.; Bardini, R.L.; Contreras, Z.; et al. Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Reveals Modulation of Angiogenesis via Nuclear Factor-KappaB Signaling. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, D.R.; Galluzzi, L.; Kroemer, G. Cell biology. Metabolic control of cell death. Science 2014, 345, 1250256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sbrana, F.V.; Cortini, M.; Avnet, S.; Perut, F.; Columbaro, M.; De Milito, A.; Baldini, N. The Role of Autophagy in the Maintenance of Stemness and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2016, 12, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katajisto, P.; Dohla, J.; Chaffer, C.L.; Pentinmikko, N.; Marjanovic, N.; Iqbal, S.; Zoncu, R.; Chen, W.; Weinberg, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. Stem cells. Asymmetric apportioning of aged mitochondria between daughter cells is required for stemness. Science 2015, 348, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherr, C.J.; DePinho, R.A. Cellular senescence: Mitotic clock or culture shock? Cell 2000, 102, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pattappa, G.; Heywood, H.K.; de Bruijn, J.D.; Lee, D.A. The metabolism of human mesenchymal stem cells during proliferation and differentiation. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Cai, S. Aldolase B Overexpression is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Promotes Tumor Progression by Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, P.; Chen, K.Y.; Xiang, K.; Johnson, C.; Crown, S.B.; Rakhilin, N.; Ai, Y.; Wang, L.; Xi, R.; Astapova, I.; et al. Aldolase B-Mediated Fructose Metabolism Drives Metabolic Reprogramming of Colon Cancer Liver Metastasis. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1249–1262.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Green, E.; Ball, L.; Fan, H.; Lee, J.; Strange, C.; Wang, H. Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes Secreted from Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Biology 2022, 11, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010009
Wei H, Green E, Ball L, Fan H, Lee J, Strange C, Wang H. Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes Secreted from Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Biology. 2022; 11(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Hua, Erica Green, Lauren Ball, Hongkuan Fan, Jennifer Lee, Charlie Strange, and Hongjun Wang. 2022. "Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes Secreted from Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stromal Cells" Biology 11, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010009
APA StyleWei, H., Green, E., Ball, L., Fan, H., Lee, J., Strange, C., & Wang, H. (2022). Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes Secreted from Human Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Biology, 11(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010009






