eIF4B mRNA Translation Contributes to Cleavage Dynamics in Early Sea Urchin Embryos
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Sequenced Used
2.3. mRNA Production
2.4. In Vitro Translation Assays
2.5. In Vitro Biotinylated eIF4B Co-Purification with eIF4E
2.6. Handling of Gametes and Embryos
2.7. Determination of Cleavage Rates
2.8. In Vivo Translation Assays
2.9. Polysome Gradient Profile and Analysis of the Translational Status of eIF4B mRNA
2.10. Statistical Analysis
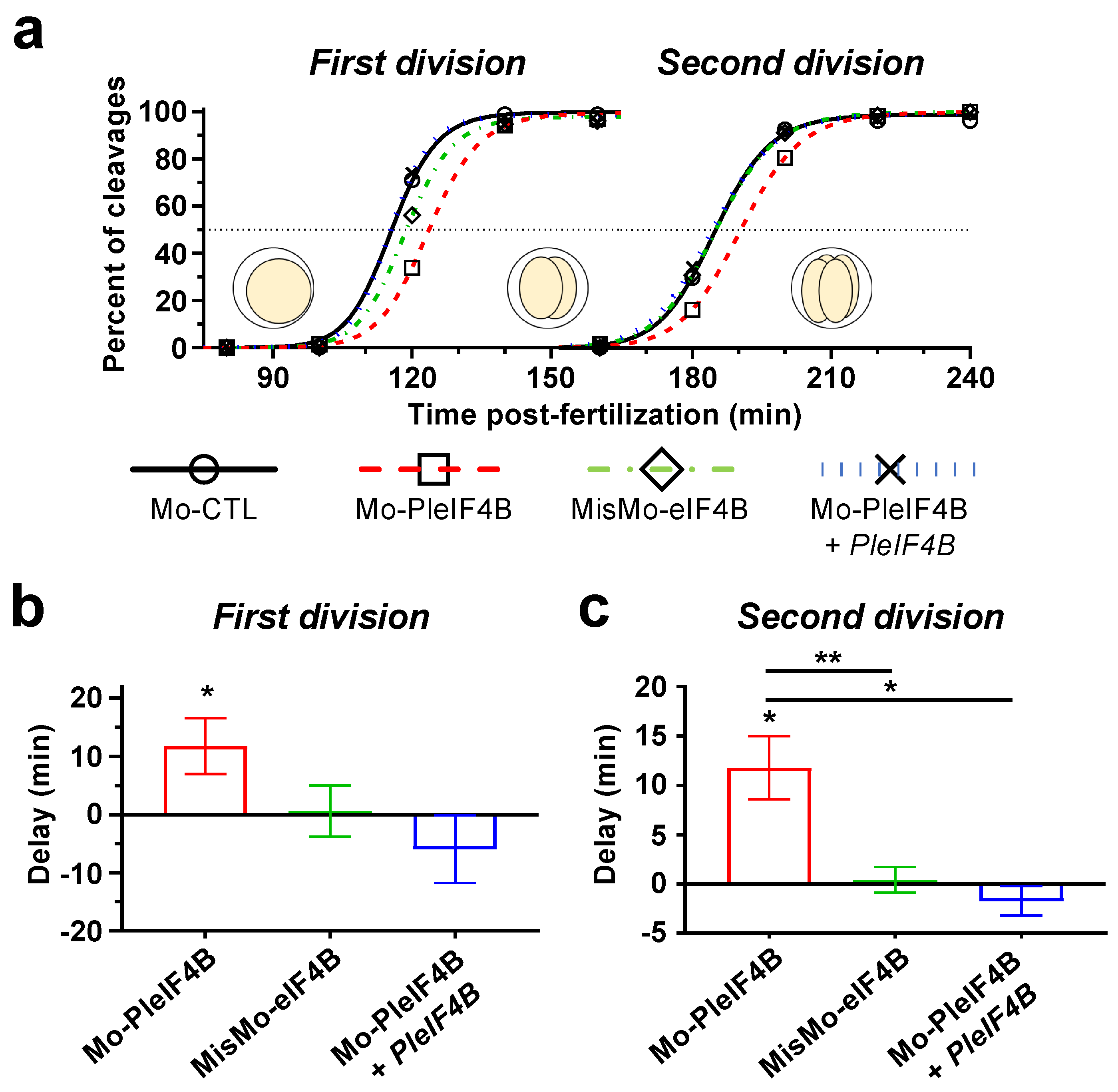
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morales, J.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Cosson, B.; Morin, E.; Bellé, R.; Bradham, C.A.; Beane, W.S.; Cormier, P. Translational Control Genes in the Sea Urchin Genome. Dev. Biol. 2006, 300, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormier, P.; Chassé, H.; Cosson, B.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Morales, J. Translational Control in Echinoderms: The Calm before the Storm. In Evolution of the Protein Synthesis Machinery and Its Regulation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, P.R.; Cousineau, G.H. Effects of Actinomycin D on Macromolecule Synthesis and Early Development in Sea Urchin Eggs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1963, 10, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassé, H.; Aubert, J.; Boulben, S.; Le Corguille, G.; Corre, E.; Cormier, P.; Morales, J. Translatome Analysis at the Egg-to-Embryo Transition in Sea Urchin. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 4607–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, P.; Pyronnet, S.; Morales, J.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Sonenberg, N.; Bellé, R. eIF4E Association with 4E-BP Decreases Rapidly Following Fertilization in Sea Urchin. Dev. Biol. 2001, 232, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaun, P.; Pyronnet, S.; Morales, J.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Bellé, R.; Sonenberg, N.; Cormier, P. eIF4E/4E-BP Dissociation and 4E-BP Degradation in the First Mitotic Division of the Sea Urchin Embryo. Dev. Biol. 2003, 255, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulhen, N.; Salaün, P.; Cosson, B.; Cormier, P.; Morales, J. After Fertilization of Sea Urchin Eggs, eIF4G Is Post-Translationally Modified and Associated with the Cap-Binding Protein eIF4E. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120 Pt 3, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiper, B.D.; Gan, W.; Rhoads, R.E. Protein Synthesis Initiation Factor 4G. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.; Sonenberg, N. The Organizing Principles of Eukaryotic Ribosome Recruitment. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 307–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M. Cyclin-Dependent Kinases. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehner, C.F.; O’Farrell, P.H. The Roles of Drosophila Cyclins A and B in Mitotic Control. Cell 1990, 61, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, H.W.; Knoblich, J.A.; Lehner, C.F. Drosophila Cyclin B3 Is Required for Female Fertility and Is Dispensable for Mitosis like Cyclin B. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, T.; Rosenthal, E.T.; Youngblom, J.; Distel, D.; Hunt, T. Cyclin: A Protein Specified by Maternal mRNA in Sea Urchin Eggs That Is Destroyed at Each Cleavage Division. Cell 1983, 33, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassé, H.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Boulben, S.; Glippa, V.; Morales, J.; Cormier, P. Cyclin B Translation Depends on mTOR Activity after Fertilization in Sea Urchin Embryos. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, J.-L.; Marques, F.; Barakat, A.; Schatt, P.; Lozano, J.-C.; Peaucellier, G.; Picard, A.; Genevière, A.-M. Cdk2 Activity Is Dispensable for the Onset of DNA Replication during the First Mitotic Cycles of the Sea Urchin Early Embryo. Dev. Biol. 1998, 200, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voronina, E.; Marzluff, W.F.; Wessel, G.M. Cyclin B Synthesis Is Required for Sea Urchin Oocyte Maturation. Dev. Biol. 2003, 256, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassé, H.; Boulben, S.; Cormier, P.; Morales, J. Translational Control of Canonical and Non-Canonical Translation Initiation Factors at the Sea Urchin Egg to Embryo Transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, A.M.; Wong, K.C.; Malmström, S.A.; Browning, K.S. Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4B from Wheat and Arabidopsis Thaliana Is a Member of a Multigene Family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 266, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, G.; Vázquez-Pianzola, P.; Zurbriggen, A.; Altmann, M.; Sierra, J.M.; Rivera-Pomar, R. Two Functionally Redundant Isoforms of Drosophila Melanogaster Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4B Are Involved in Cap-Dependent Translation, Cell Survival, and Proliferation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 2923–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, D.; Parsyan, A.; Petroulakis, E.; Topisirovic, I.; Martineau, Y.; Gibbs, B.F.; Svitkin, Y.; Sonenberg, N. Control of Cell Survival and Proliferation by Mammalian Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4B. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreou, A.Z.; Harms, U.; Klostermeier, D. E-eIF4B Stimulates eIF4A ATPase and Unwinding Activities by Direct Interaction through Its 7-Repeats Region. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozovsky, N.; Butterworth, A.C.; Moore, M.J. Interactions between eIF4AI and Its Accessory Factors eIF4B and eIF4H. RNA 2008, 14, 2136–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroh, A.; Smith, A.B. The Phylogeny and Classification of Post-Palaeozoic Echinoids. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 2010, 8, 147–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Láruson, Á.J. Rates and Relations of Mitochondrial Genome Evolution across the Echinoidea, with Special Focus on the Superfamily Odontophora. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4543–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legagneux, V.; Omilli, F.; Osborne, H.B. Substrate-Specific Regulation of RNA Deadenylation in Xenopus Embryo and Activated Egg Extracts. RNA 1995, 1, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costache, V.; Bilotto, S.; Laguerre, L.; Bellé, R.; Cosson, B.; Cormier, P.; Morales, J. Dephosphorylation of eIF2α Is Essential for Protein Synthesis Increase and Cell Cycle Progression after Sea Urchin Fertilization. Dev. Biol. 2012, 365, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassé, H.; Boulben, S.; Glippa, V.; Pontheaux, F.; Cormier, P.; Morales, J. In Vivo Analysis of Protein Translation Activity in Sea Urchin Eggs and Embryos. Methods Cell Biol. 2019, 151, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nadai, C.; Huitorel, P.; Chiri, S.; Ciapa, B. Effect of Wortmannin, an Inhibitor of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, on the First Mitotic Divisions of the Fertilized Sea Urchin Egg. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 2507–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepicheva, N.A.; Song, J.L. High Throughput Microinjections of Sea Urchin Zygotes. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e50841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chassé, H.; Boulben, S.; Costache, V.; Cormier, P.; Morales, J. Analysis of Translation Using Polysome Profiling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Martindale, J.L.; Gorospe, M. Polysome Fractionation to Analyze mRNA Distribution Profiles. Bio-Protoc. 2017, 7, e2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazian, D.; Roux, P.P.; Mieulet, V.; Cohen, M.S.; Raught, B.; Taunton, J.; Hershey, J.W.B.; Blenis, J.; Pende, M.; Sonenberg, N. The mTOR/PI3K and MAPK Pathways Converge on eIF4B to Control Its Phosphorylation and Activity. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gorp, A.G.M.; van der Vos, K.E.; Brenkman, A.B.; Bremer, A.; van den Broek, N.; Zwartkruis, F.; Hershey, J.W.; Burgering, B.M.T.; Calkhoven, C.F.; Coffer, P.J. AGC Kinases Regulate Phosphorylation and Activation of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4B. Oncogene 2009, 28, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.T.; Taylor, W.R.; Thornton, J.M. The Rapid Generation of Mutation Data Matrices from Protein Sequences. Bioinformatics 1992, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent Updates, New Developments and Status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellé, R.; Prigent, S.; Siegel, A.; Cormier, P. Model of Cap-Dependent Translation Initiation in Sea Urchin: A Step towards the Eukaryotic Translation Regulation Network. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2010, 77, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S.; Richard, A.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Morales, J.; Flament, D.; Glippa, V.; Bourdon, J.; Gosselin, P.; Siegel, A.; Cormier, P.; et al. Modelization of the Regulation of Protein Synthesis Following Fertilization in Sea Urchin Shows Requirement of Two Processes: A Destabilization of eIF4E:4E-BP Complex and a Great Stimulation of the 4E-BP-Degradation Mechanism, Both Rapamycin-Sensitive. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, V.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Bourdon, J.; Morales, J.; Cormier, P.; Siegel, A.; Bellé, R. Model of the Delayed Translation of Cyclin B Maternal mRNA after Sea Urchin Fertilization. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2016, 83, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moundoyi, H.; Demouy, J.; Le Panse, S.; Morales, J.; Sarels, B.; Cormier, P. Toward Multiscale Modeling of Molecular and Biochemical Events Occurring at Fertilization Time in Sea Urchins. In Marine Organisms as Model Systems in Biology and Medicine; Kloc, M., Kubiak, J.Z., Eds.; Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 65, pp. 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppolecchia, R.; Buser, P.; Stotz, A.; Linder, P. A New Yeast Translation Initiation Factor Suppresses a Mutation in the eIF-4A RNA Helicase. EMBO J 1993, 12, 4005–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, M.; Müller, P.P.; Wittmer, B.; Ruchti, F.; Lanker, S.; Trachsel, H. A Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Homologue of Mammalian Translation Initiation Factor 4B Contributes to RNA Helicase Activity. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, E.B. The Timing of Synthesis of Proteins Required for Mitosis in the Cell Cycle of the Sea Urchin Embryo. Exp. Cell Res. 1983, 144, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreen, C.C.; Chantranupong, L.; Keys, H.R.; Wang, T.; Gray, N.S.; Sabatini, D.M. A Unifying Model for mTORC1-Mediated Regulation of mRNA Translation. Nature 2012, 485, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, L.; van den Elzen, A.M.G.; Watson, M.J.; Thoreen, C.C. Global Analysis of LARP1 Translation Targets Reveals Tunable and Dynamic Features of 5′ TOP Motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5319–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holz, M.K.; Ballif, B.A.; Gygi, S.P.; Blenis, J. mTOR and S6K1 Mediate Assembly of the Translation Preinitiation Complex through Dynamic Protein Interchange and Ordered Phosphorylation Events. Cell 2005, 123, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milburn, S.C.; Hershey, J.W.; Davies, M.V.; Kelleher, K.; Kaufman, R.J. Cloning and Expression of Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4B cDNA: Sequence Determination Identifies a Common RNA Recognition Motif. EMBO J 1990, 9, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranda, T.; Strong, W.B.; Menaya, J.; Fabbri, B.J.; Hershey, J.W. Two Structural Domains of Initiation Factor eIF-4B Are Involved in Binding to RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14465–14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronja, I.; Orr-Weaver, T.L. Translational Regulation of the Cell Cycle: When, Where, How and Why? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2011, 366, 3638–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daga, R.R.; Jimenez, J. Translational Control of the Cdc25 Cell Cycle Phosphatase: A Molecular Mechanism Coupling Mitosis to Cell Growth. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, I.; Jung, M.-Y.; Sarkissian, M.; Cao, Q.; Richter, J.D. Translational Control of the Embryonic Cell Cycle. Cell 2002, 109, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilt, F.H. The Dynamics of Maternal Poly(A)-Containing mRNA in Fertilized Sea Urchin Eggs. Cell 1977, 11, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieth, J.; Whiteley, A.H. Effect of 3′-Deoxyadenosine (Cordycepin) on the Early Development of the Sand Dollar, Dendraster Excentricus. Dev. Biol. 1980, 79, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, N.K.; Hrabálková, L.; Scanlon, J.P.; Smith, R.W.P. Poly(A)-Binding Proteins and mRNA Localization: Who Rules the Roost? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, E.A. Mitotic Kinases as Regulators of Cell Division and Its Checkpoints. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Q.; Pomerening, J.R. Punctuated Cyclin Synthesis Drives Early Embryonic Cell Cycle Oscillations. MBoC 2012, 23, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benne, R.; Hershey, J.W. The Mechanism of Action of Protein Synthesis Initiation Factors from Rabbit Reticulocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 3078–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter-Cook, N.J.; Dever, T.E.; Hensold, J.O.; Merrick, W.C. Purification and Characterization of a New Eukaryotic Protein Translation Factor. Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4H. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7579–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.W.; Richter, N.J.; Lima, W.F.; Merrick, W.C. Modulation of the Helicase Activity of eIF4A by eIF4B, eIF4H, and eIF4F. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30914–30922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsyan, A.; Svitkin, Y.; Shahbazian, D.; Gkogkas, C.; Lasko, P.; Merrick, W.C.; Sonenberg, N. mRNA Helicases: The Tacticians of Translational Control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pontheaux, F.; Boulben, S.; Chassé, H.; Boutet, A.; Roch, F.; Morales, J.; Cormier, P. eIF4B mRNA Translation Contributes to Cleavage Dynamics in Early Sea Urchin Embryos. Biology 2022, 11, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101408
Pontheaux F, Boulben S, Chassé H, Boutet A, Roch F, Morales J, Cormier P. eIF4B mRNA Translation Contributes to Cleavage Dynamics in Early Sea Urchin Embryos. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101408
Chicago/Turabian StylePontheaux, Florian, Sandrine Boulben, Héloïse Chassé, Agnès Boutet, Fernando Roch, Julia Morales, and Patrick Cormier. 2022. "eIF4B mRNA Translation Contributes to Cleavage Dynamics in Early Sea Urchin Embryos" Biology 11, no. 10: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101408
APA StylePontheaux, F., Boulben, S., Chassé, H., Boutet, A., Roch, F., Morales, J., & Cormier, P. (2022). eIF4B mRNA Translation Contributes to Cleavage Dynamics in Early Sea Urchin Embryos. Biology, 11(10), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101408