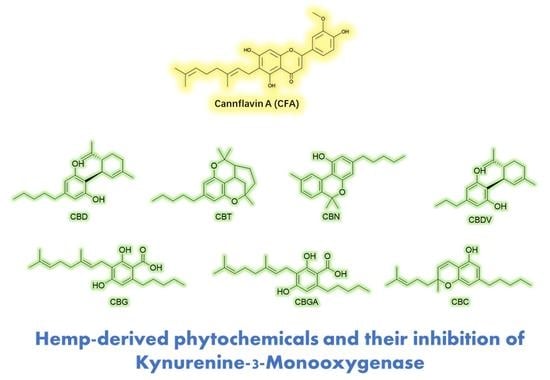
Gram-Scale Preparation of Cannflavin A from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Its Inhibitory Effect on Tryptophan Catabolism Enzyme Kynurenine-3-Monooxygenase
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
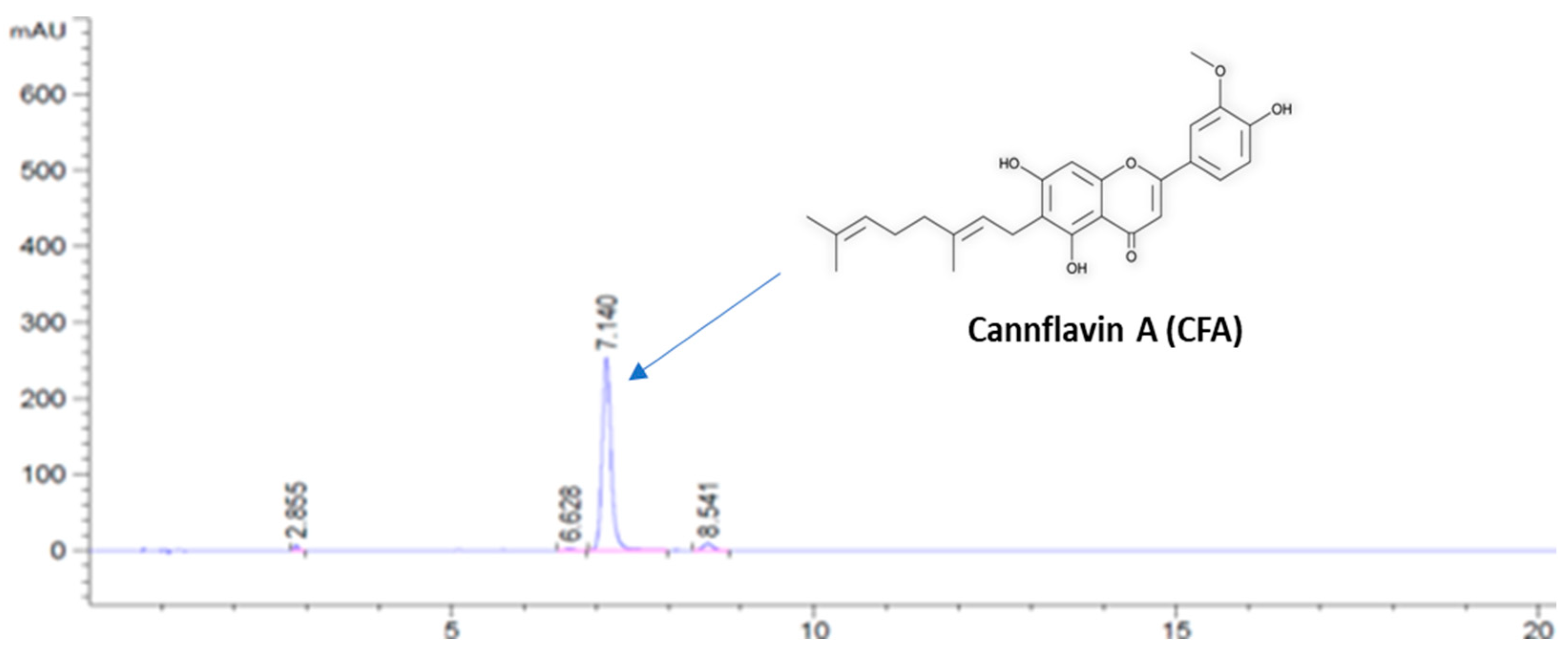
2.2. Preparation of Cannflavin A (CFA)
2.3. HPLC Analysis of CFA
2.4. Enzyme Activity Assay
2.5. Molecular Docking
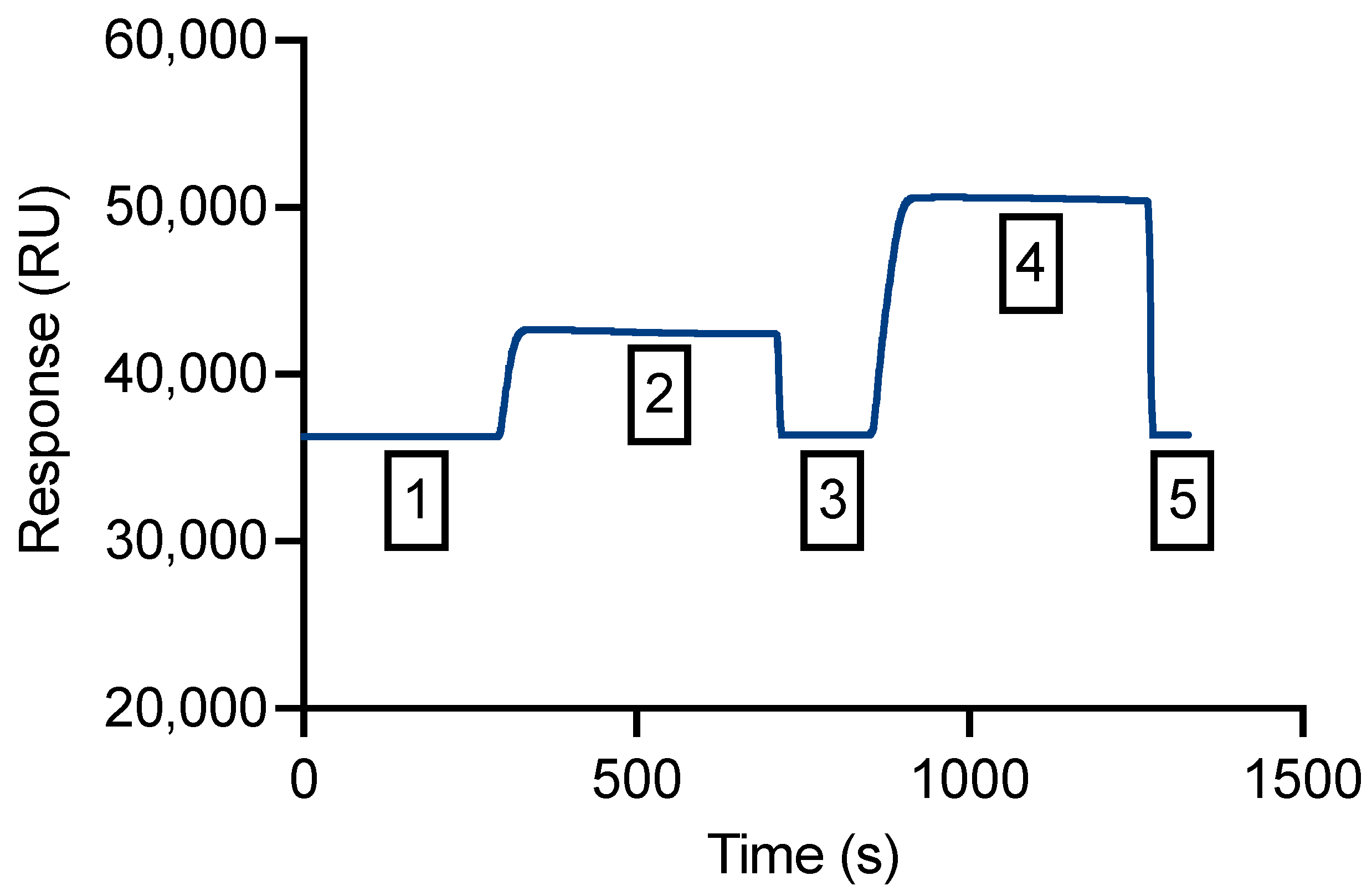
2.6. SPR Immobilization
2.7. SPR Assay
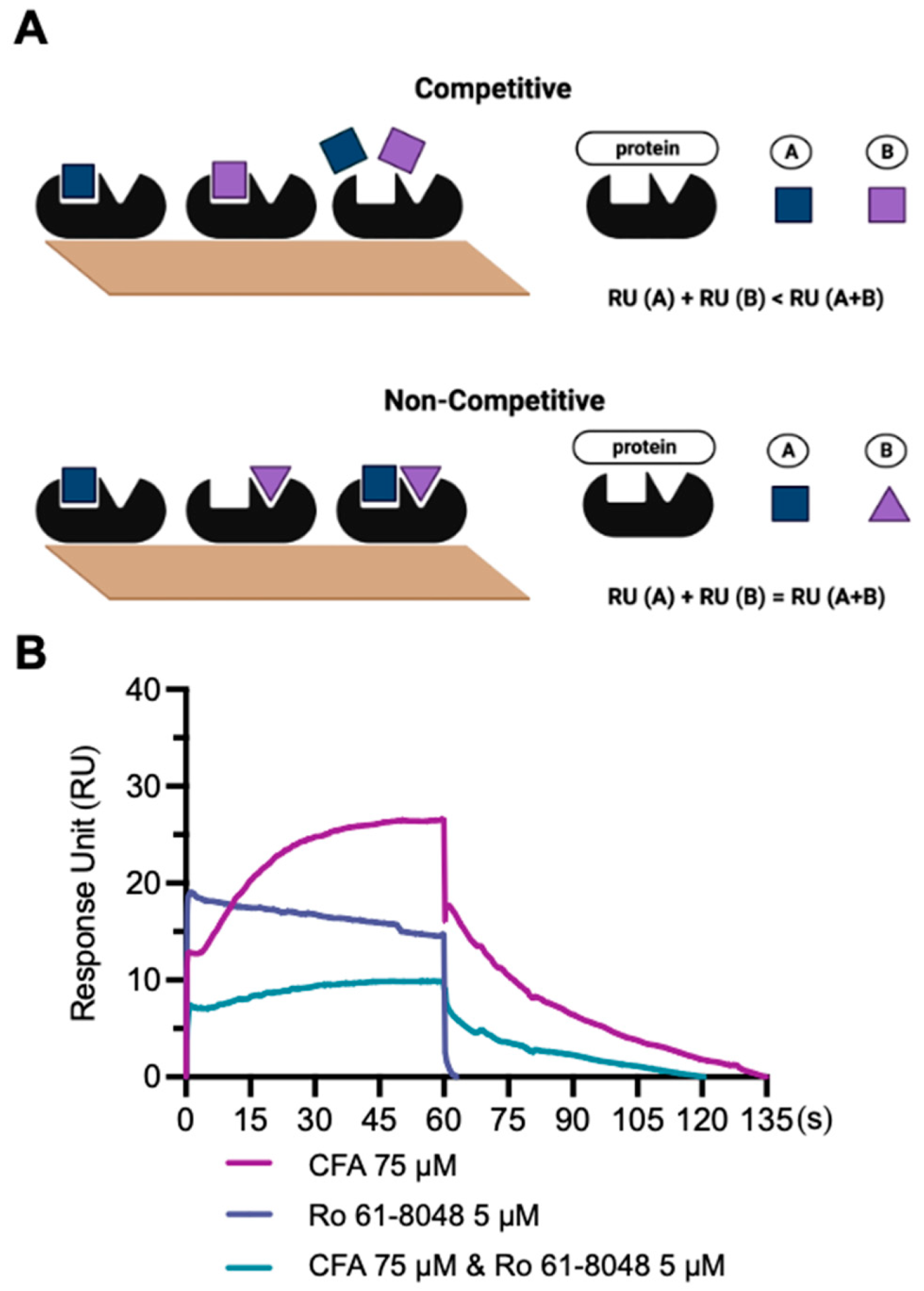
2.8. Competitive SPR Assay
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of CFA at a Gram-Scale
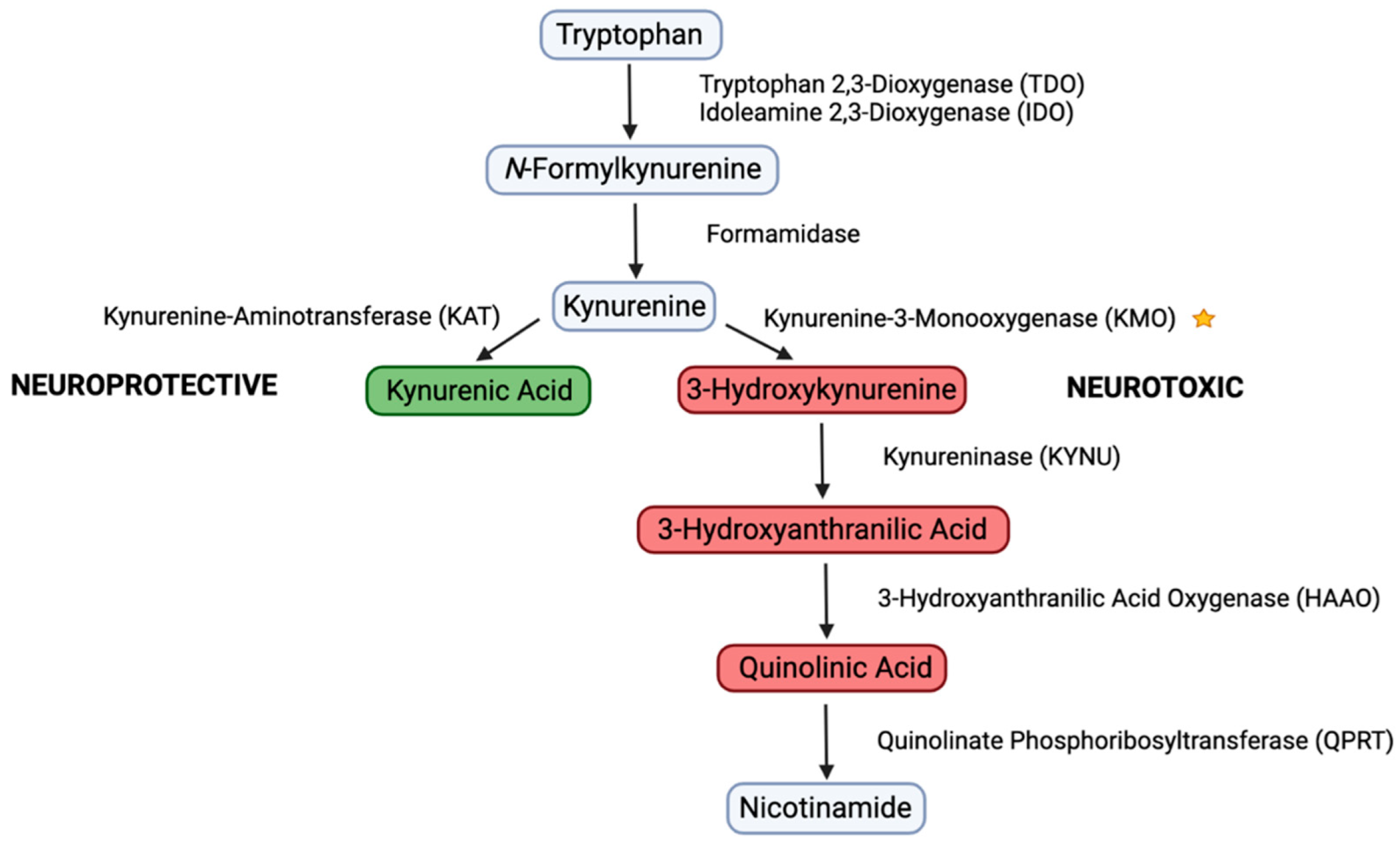
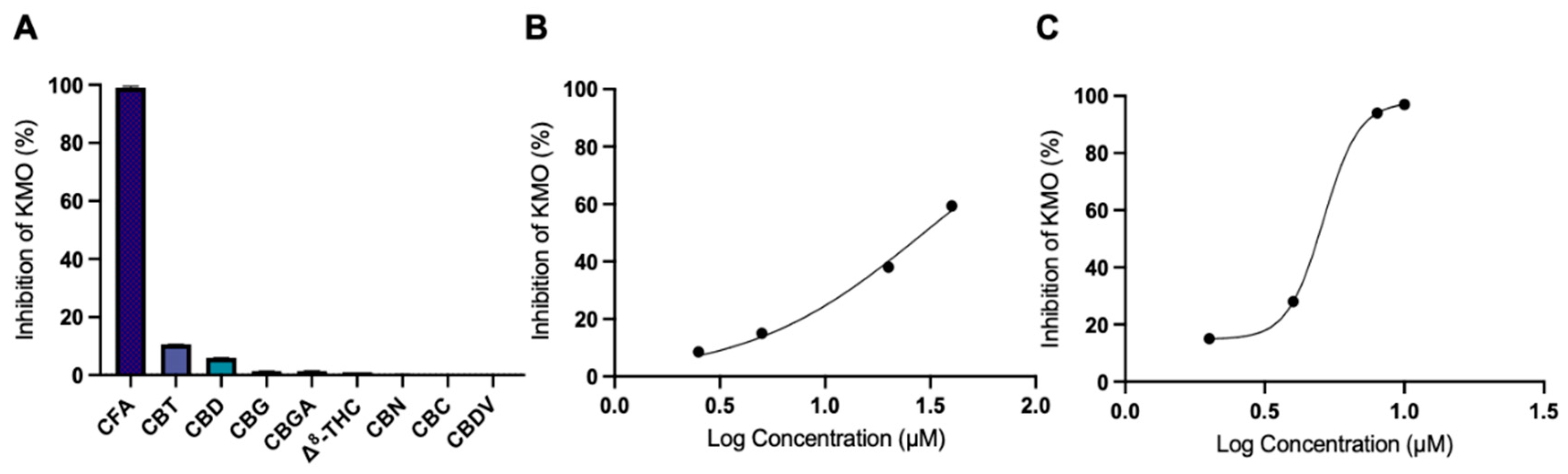
3.2. CFA Inhibits KMO Enzyme Activity
3.3. Molecular Docking Analysis
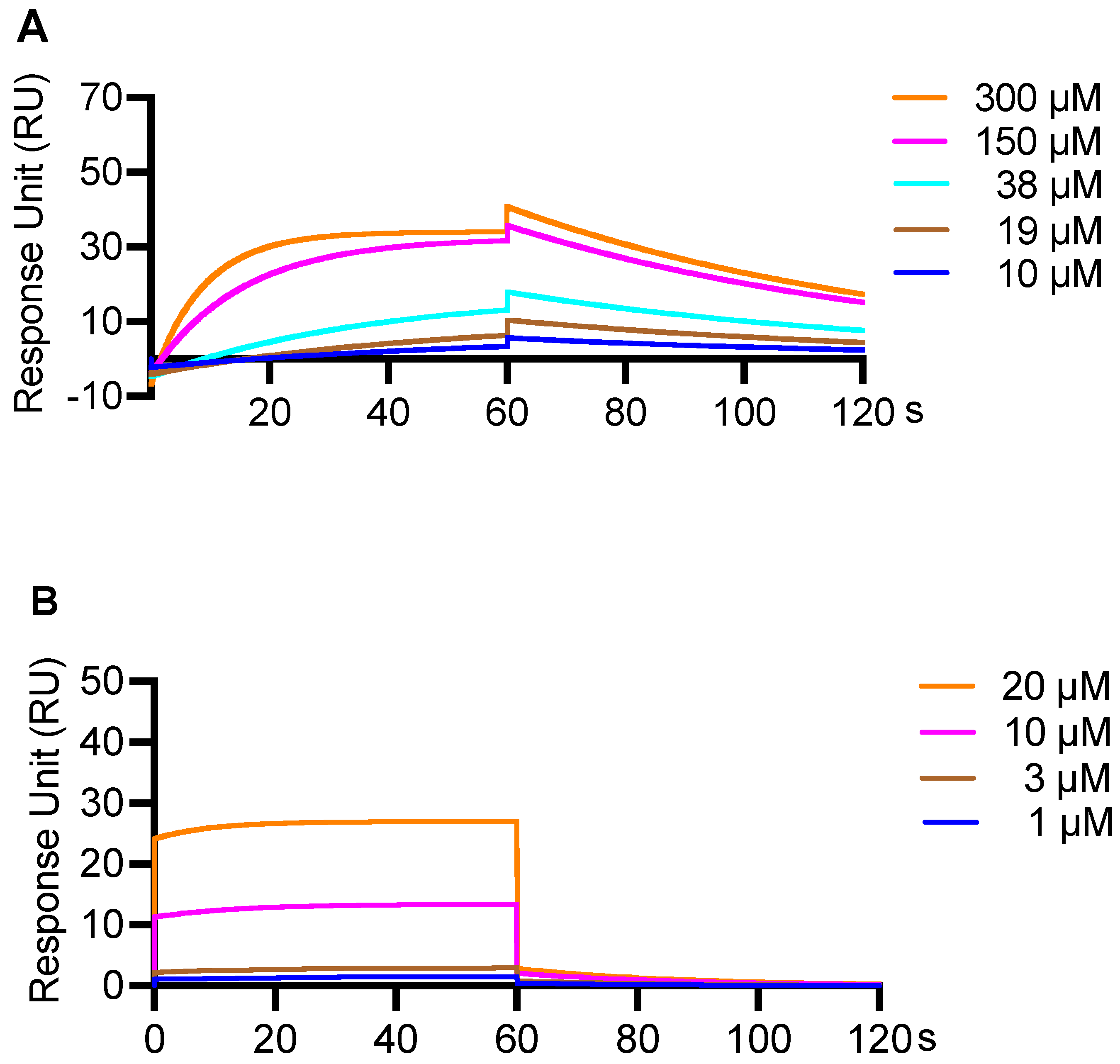
3.4. An SPR Method Was Validated for Measurement of Binding Affinity
3.5. Competitive SPR Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, T.D.; Güner, O.F.; Iradukunda, E.C.; Phillips, R.S.; Bowen, J.P. The Kynurenine Pathway and Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazarei, G.; Leavitt, B.R. Indoleamine 2,3 Dioxygenase as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Huntington’s Disease. J. Huntingt. Dis. 2015, 4, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dounay, A.B.; Tuttle, J.B.; Verhoest, P.R. Challenges and Opportunities in the Discovery of New Therapeutics Targeting the Kynurenine Pathway. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8762–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, D.C.; Giorgini, F. The kynurenine pathway and neurodegenerative disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostapiuk, A.; Urbanska, E.M. Kynurenic acid in neurodegenerative disorders—Unique neuroprotection or double-edged sword? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.H. Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway is dysregulated in inflammation and immune activation. Front. Biosci. 2015, 20, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, F.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. The Role of the Kynurenine Signaling Pathway in Different Chronic Pain Conditions and Potential Use of Therapeutic Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ala, M. The footprint of kynurenine pathway in every cancer: A new target for chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 896, 173921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, A. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Pathophysiologic and Therapeutic Considerations. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2020, 18, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Suda, H.; Kassai, M.; Endo, M.; Deai, Y.; Yahata, M.; Miyajima, M.; Isobe, Y. N-(6-phenylpyridazin-3-yl)benzenesulfonamides as highly potent, brain-permeable, and orally active kynurenine monooxygenase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 33, 127753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K.R.; Castellano-Gonzalez, G.; Guillemin, G.J.; Lovejoy, D.B. Major Developments in the Design of Inhibitors along the Kynurenine Pathway. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2471–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwilling, D.; Huang, S.Y.; Sathyasaikumar, K.V.; Notarangelo, F.M.; Guidetti, P.; Wu, H.Q.; Lee, J.; Truong, J.; Andrews-Zwilling, Y.; Hsieh, E.W.; et al. Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase Inhibition in Blood Ameliorates Neurodegeneration. Cell 2011, 145, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Bowden, B.F.; Kapoor, V. Screening marine natural products for selective inhibitors of key kynurenine pathway enzymes. Redox Rep. 2000, 5, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huang, J.; Lei, H.; Wu, F.; Chen, C.; Song, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; et al. Icariside I—A novel inhibitor of the kynurenine-AhR pathway with potential for cancer therapy by blocking tumor immune escape. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sordillo, P.P.; Sordillo, L.A.; Helson, L. The Kynurenine Pathway: A Primary Resistance Mechanism in Patients with Glioblastoma. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 2159–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Seeram, N.P. Evaluation of cannabidiol’s inhibitory effect on alpha-glucosidase and its stability in simulated gastric and intestinal fluids. J. Cannabis Res. 2021, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Slitt, A.L.; Seeram, N.P. Inhibitory Effect of Cannabidiol on the Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Is Associated with Its Modulation of the P2X7 Receptor in Human Monocytes. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2025–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puopolo, T.; Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P. Inhibitory Effects of Cannabinoids on Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Enzyme Activities. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2022, 5, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erridge, S.; Mangal, N.; Salazar, O.; Pacchetti, B.; Sodergren, M.H. Cannflavins—From plant to patient: A scoping review. Fitoterapia 2020, 146, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, J.L.; Yu, S.; Tian, L. Flavonoids in Cannabis sativa: Biosynthesis, Bioactivities, and Biotechnology. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5119–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotina, L.; Seo, S.H.; Kim, C.W.; Lim, S.M.; Pae, A.N. Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening of Novel Competitive Inhibitors of the Neurodegenerative Disease Target Kynurenine-3-Monooxygenase. Molecules 2021, 26, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cai, A.; Li, H.; Deng, N.; Cho, B.P.; Seeram, N.P.; Ma, H. Characterization of molecular interactions between cannabidiol and human plasma proteins (serum albumin and γ-globulin) by surface plasmon resonance, microcalorimetry, and molecular docking. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 214, 114750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perspicace, S.; Banner, D.; Benz, J.; Müller, F.; Schlatter, D.; Huber, W. Fragment-Based Screening Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Technology. SLAS Discov. 2009, 14, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Shao, M.; Wu, T. Kynurenine-3-monooxygenase: A new direction for the treatment in different diseases. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sakuma, M.; Deora, G.S.; Levy, C.W.; Klausing, A.; Breda, C.; Read, K.D.; Edlin, C.D.; Ross, B.P.; Muelas, M.W.; et al. A brain-permeable inhibitor of the neurodegenerative disease target kynurenine 3-monooxygenase prevents accumulation of neurotoxic metabolites. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujigaki, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Saito, K. L-Tryptophan-kynurenine pathway enzymes are therapeutic target for neuropsychiatric diseases: Focus on cell type differences. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantouris, G.; Mowat, C.G. Antitumour agents as inhibitors of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Okuno, A.; Suzuki, K.; Ohsawa, N.; Inoue, E.; Miyaguchi, Y.; Toyoda, A. Dietary intake of the citrus flavonoid hesperidin affects stress-resilience and brain kynurenine levels in a subchronic and mild social defeat stress model in mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1756–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, M.; Santer, E.; Pirich, E.; Schennach, H.; Fuchs, D. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol modulate mitogen-induced tryptophan degradation and neopterin formation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 207, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Giacomo, V.; Chiavaroli, A.; Orlando, G.; Cataldi, A.; Rapino, M.; di Valerio, V.; Leone, S.; Brunetti, L.; Menghini, L.; Recinella, L.; et al. Neuroprotective and Neuromodulatory Effects Induced by Cannabidiol and Cannabigerol in Rat Hypo-E22 cells and Isolated Hypothalamus. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomko, A.M.; Whynot, E.G.; Dupré, D.J. Anti-cancer properties of cannflavin A and potential synergistic effects with gemcitabine, cisplatin, and cannabinoids in bladder cancer. J. Cannabis Res. 2022, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasiłowicz, A.; Tomala, A.; Podolak, I.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Cannabis sativa L. as a Natural Drug Meeting the Criteria of a Multitarget Approach to Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, G.; Lim, C.K.; Brew, B.J.; Guillemin, G.J. Kynurenine pathway modulation reverses the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mouse disease progression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, A.; Carpenedo, R.; Moroni, F. Kynurenine Hydroxylase Inhibitors Reduce Ischemic Brain Damage: Studies with (m-Nitrobenzoyl)-Alanine (mNBA) and 3,4-Dimethoxy-[-N-4-(Nitrophenyl)Thiazol-2YL]-Benzenesulfonamide (Ro 61-8048) in Models of Focal or Global Brain Ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1999, 19, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouattara, B.; Belkhir, S.; Morissette, M.; Dridi, M.; Samadi, P.; Grégoire, L.; Meltzer, L.T.; Di Paolo, T. Implication of NMDA Receptors in the Antidyskinetic Activity of Cabergoline, CI-1041, and Ro 61-8048 in MPTP Monkeys with Levodopa-induced Dyskinesias. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2009, 38, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, A.M.; Parrott, J.M.; Tuñon, A.; Delgado, J.; Redus, L.; O’Connor, J.C. Kynurenine pathway metabolic balance influences microglia activity: Targeting kynurenine monooxygenase to dampen neuroinflammation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Raw Hemp Mass | Dry Hemp Mass | CFA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kg | Kg | g | Purity a | Yield |
| 300 | 262.32 | 38.73 | 96.45% | 0.013% |
| Inhibitor | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| CFA | 29.4 |
| Ro 61-8048 | 5.1 |
| Binding Parameters | CFA | Ro 61-8048 |
|---|---|---|
| Estimated Free Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | −7.95 | −9.75 |
| Estimated Inhibition Constant; Ki (μM) | 1.49 | 0.07 |
| Final Intermolecular Energy (kcal/mol) | −10.93 | −11.84 |
| Electrostatic Energy (kcal/mol) | −0.38 | −1.34 |
| Unbound System’s Energy (kcal/mol) | −1.82 | −0.63 |
| Total Internal Energy (kcal/mol) | −1.82 | −0.63 |
| Ligand | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CFA | 0.3 | 14.2 | 4.1 |
| Ro 61-8048 | 3.7 | 38.5 | 1.1 |
| Ligand | Experimental RU | Theoretically Calculated RU | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Competitive | Competitive | ||
| CFA | 27 | ||
| Ro 61-8048 | 19 | ||
| CFA + Ro 61-8048 | 7 | 46 | 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puopolo, T.; Chang, T.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Ma, H.; Seeram, N.P. Gram-Scale Preparation of Cannflavin A from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Its Inhibitory Effect on Tryptophan Catabolism Enzyme Kynurenine-3-Monooxygenase. Biology 2022, 11, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101416
Puopolo T, Chang T, Liu C, Li H, Liu X, Wu X, Ma H, Seeram NP. Gram-Scale Preparation of Cannflavin A from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Its Inhibitory Effect on Tryptophan Catabolism Enzyme Kynurenine-3-Monooxygenase. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101416
Chicago/Turabian StylePuopolo, Tess, Tanran Chang, Chang Liu, Huifang Li, Xu Liu, Xian Wu, Hang Ma, and Navindra P. Seeram. 2022. "Gram-Scale Preparation of Cannflavin A from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Its Inhibitory Effect on Tryptophan Catabolism Enzyme Kynurenine-3-Monooxygenase" Biology 11, no. 10: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101416
APA StylePuopolo, T., Chang, T., Liu, C., Li, H., Liu, X., Wu, X., Ma, H., & Seeram, N. P. (2022). Gram-Scale Preparation of Cannflavin A from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Its Inhibitory Effect on Tryptophan Catabolism Enzyme Kynurenine-3-Monooxygenase. Biology, 11(10), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101416