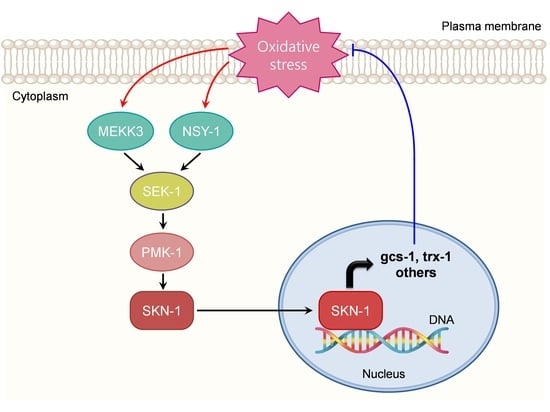
MEKK-3 Acts Cooperatively with NSY-1 in SKN-1-Dependent Manner against Oxidative Stress and Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Maintenance
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. RNAi
2.4. GFP Fusion Protein Scoring System
2.5. Oxidative Stress Resistance Assay
2.6. Lifespan Assay
2.7. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Concomitant Inhibition of mekk-3 and nsy-1 Significantly Suppresses the Oxidative Stress Resistance of SKN-1 Transgenic Worms
3.2. MEKK-3 Overexpression Displays Increased Resistance against Oxidative Stress
3.3. MEKK-3 Is Required for the Nuclear Localization of SKN-1
3.4. MEKK-3 Is Required for Optimal Activation of SKN-1 Target Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tosato, M.; Zamboni, V.; Ferrini, A.; Cesari, M. The aging process and potential interventions to extend life expectancy. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Barja, G. Updating the mitochondrial free radical theory of aging: An integrated view, key aspects, and confounding concepts. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1420–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Sowers, J.R.; Zhang, Y. Metabolic Stress, Autophagy, and Cardiovascular Aging: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutics. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossiello, F.; Jurk, D.; Passos, J.F.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Telomere dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, D. Aging: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziada, A.S.; Smith, M.R.; Cote, H.C.F. Updating the Free Radical Theory of Aging. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 575645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gems, D.; Doonan, R. Antioxidant defense and aging in C. elegans: Is the oxidative damage theory of aging wrong? Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herndon, L.A.; Schmeissner, P.J.; Dudaronek, J.M.; Brown, P.A.; Listner, K.M.; Sakano, Y.; Paupard, M.C.; Hall, D.H.; Driscoll, M. Stochastic and genetic factors influence tissue-specific decline in ageing C. elegans. Nature 2002, 419, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynes, R.; Juarez, C.; Pomatto, L.C.; Sieburth, D.; Davies, K.J. Aging and SKN-1-dependent Loss of 20S Proteasome Adaptation to Oxidative Stress in C. elegans. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grushko, D.; Boocholez, H.; Levine, A.; Cohen, E. Temporal requirements of SKN-1/NRF as a regulator of lifespan and proteostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0243522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dai, Y.; Tang, H.; Pang, S. SKN-1 Is a Negative Regulator of DAF-16 and Somatic Stress Resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeven, R.; McCallum, K.C.; Cruz, M.R.; Garsin, D.A. Ce-Duox1/BLI-3 generated reactive oxygen species trigger protective SKN-1 activity via p38 MAPK signaling during infection in C. elegans. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Su, L.; Su, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Ba, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, B.; et al. Arginine methylation of SKN-1 promotes oxidative stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbaugh, M.J.; Narasimhan, S.D.; Robida-Stubbs, S.; Moronetti Mazzeo, L.E.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Hourihan, J.M.; Raghavan, P.; Operana, T.N.; Esmaillie, R.; Blackwell, T.K. Lipid-mediated regulation of SKN-1/Nrf in response to germ cell absence. eLife 2015, 4, e07836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, J.D.; Turner, C.D.; Anderson, S.M.; Yen, C.A.; Dalton, H.M.; Cheesman, H.K.; Ruter, D.L.; Uma Naresh, N.; Haynes, C.M.; Soukas, A.A.; et al. Redirection of SKN-1 abates the negative metabolic outcomes of a perceived pathogen infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22322–22330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Su, L.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Lu, J.; et al. O-GlcNAcylation of SKN-1 modulates the lifespan and oxidative stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Feinbaum, R.; Alloing, G.; Emerson, F.E.; Garsin, D.A.; Inoue, H.; Tanaka-Hino, M.; Hisamoto, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Tan, M.W.; et al. A conserved p38 MAP kinase pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans innate immunity. Science 2002, 297, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka-Hino, M.; Sagasti, A.; Hisamoto, N.; Kawasaki, M.; Nakano, S.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Bargmann, C.I.; Matsumoto, K. SEK-1 MAPKK mediates Ca2+ signaling to determine neuronal asymmetric development in Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagasti, A.; Hisamoto, N.; Hyodo, J.; Tanaka-Hino, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Bargmann, C.I. The CaMKII UNC-43 activates the MAPKKK NSY-1 to execute a lateral signaling decision required for asymmetric olfactory neuron fates. Cell 2001, 105, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naji, A.; Houston Iv, J.; Skalley Rog, C.; Al Hatem, A.; Rizvi, S.; van der Hoeven, R. The activation of the oxidative stress response transcription factor SKN-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans by mitis group streptococci. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, R.S.; Martinez-Campos, M.; Zipperlen, P.; Fraser, A.G.; Ahringer, J. Effectiveness of specific RNA-mediated interference through ingested double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, RESEARCH0002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canovas, B.; Nebreda, A.R. Diversity and versatility of p38 kinase signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganner, A.; Gerber, J.; Ziegler, A.K.; Li, Y.; Kandzia, J.; Matulenski, T.; Kreis, S.; Breves, G.; Klein, M.; Walz, G.; et al. CBP-1/p300 acetyltransferase regulates SKN-1/Nrf cellular levels, nuclear localization, and activity in C. elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 126, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, N.; Reddy, E.P. Signaling by dual specificity kinases. Oncogene 1998, 17, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subbannayya, Y.; Pinto, S.M.; Bosl, K.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Kandasamy, R.K. Dynamics of Dual Specificity Phosphatases and Their Interplay with Protein Kinases in Immune Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. MEK1/2 dual-specificity protein kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, Y.D.; Seger, R. The MEK/ERK cascade: From signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamoli, M.; Singh, A.; Malik, Y.; Mukhopadhyay, A. A novel kinase regulates dietary restriction-mediated longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillin, A.; Hsu, A.L.; Arantes-Oliveira, N.; Lehrer-Graiwer, J.; Hsin, H.; Fraser, A.G.; Kamath, R.S.; Ahringer, J.; Kenyon, C. Rates of behavior and aging specified by mitochondrial function during development. Science 2002, 298, 2398–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Gomez, M.; Kwak, M.K.; Dolan, P.M.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Talalay, P.; Kensler, T.W. Sensitivity to carcinogenesis is increased and chemoprotective efficacy of enzyme inducers is lost in nrf2 transcription factor-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3410–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, J.W.; Haristoy, X.; Dolan, P.M.; Kensler, T.W.; Scholtus, I.; Stephenson, K.K.; Talalay, P.; Lozniewski, A. Sulforaphane inhibits extracellular, intracellular, and antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori and prevents benzo[a]pyrene-induced stomach tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7610–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thimmulappa, R.K.; Mai, K.H.; Srisuma, S.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M.; Biswal, S. Identification of Nrf2-regulated genes induced by the chemopreventive agent sulforaphane by oligonucleotide microarray. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5196–5203. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz, L.; Ammit, A.J. Targeting p38 MAPK pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenda, A.; Rousseau, S. p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, M.; Shrestha, C.; Kang, S.; Kim, J. MEKK-3 Acts Cooperatively with NSY-1 in SKN-1-Dependent Manner against Oxidative Stress and Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biology 2022, 11, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101526
Hwang M, Shrestha C, Kang S, Kim J. MEKK-3 Acts Cooperatively with NSY-1 in SKN-1-Dependent Manner against Oxidative Stress and Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101526
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Min, Chandani Shrestha, Shinwon Kang, and Jiyoon Kim. 2022. "MEKK-3 Acts Cooperatively with NSY-1 in SKN-1-Dependent Manner against Oxidative Stress and Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans" Biology 11, no. 10: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101526
APA StyleHwang, M., Shrestha, C., Kang, S., & Kim, J. (2022). MEKK-3 Acts Cooperatively with NSY-1 in SKN-1-Dependent Manner against Oxidative Stress and Aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biology, 11(10), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101526