Variations in Rainbow Trout Immune Responses against A. salmonicida: Evidence of an Internal Seasonal Clock in Oncorhynchus mykiss
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. A. salmonicida for Stimulation Experiments
2.3. Fish
2.4. Sampling and Leukocyte Preparation
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. ELISA
3. Results
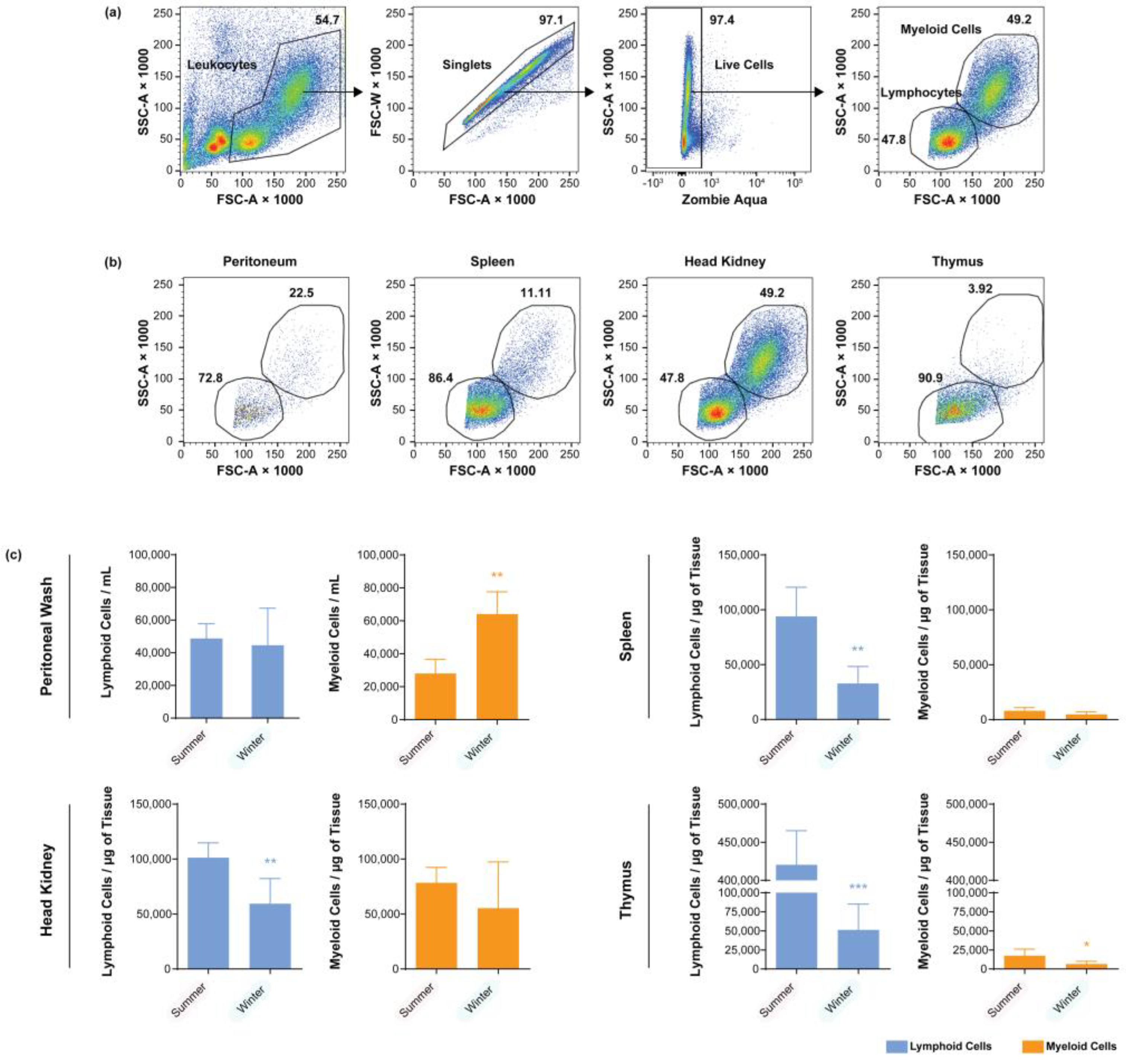
3.1. Seasonal Cell Composition of Unstimulated Fish
3.2. Seasonal Cell Composition of the Peritoneal Cavities of A. salmonicida-Stimulated Fish
3.3. Seasonal Cell Composition in the Spleens and Head Kidneys of A. salmonicida-Stimulated Fish
3.4. Response of Leukocyte Subpopulations in the Peritoneal Cavities of Stimulated Fish
3.5. Response of Leukocyte Subpopulations in the Spleens of Stimulated Fish
3.6. Response of Leukocyte Subpopulations in the Head Kidneys of Stimulated Fish
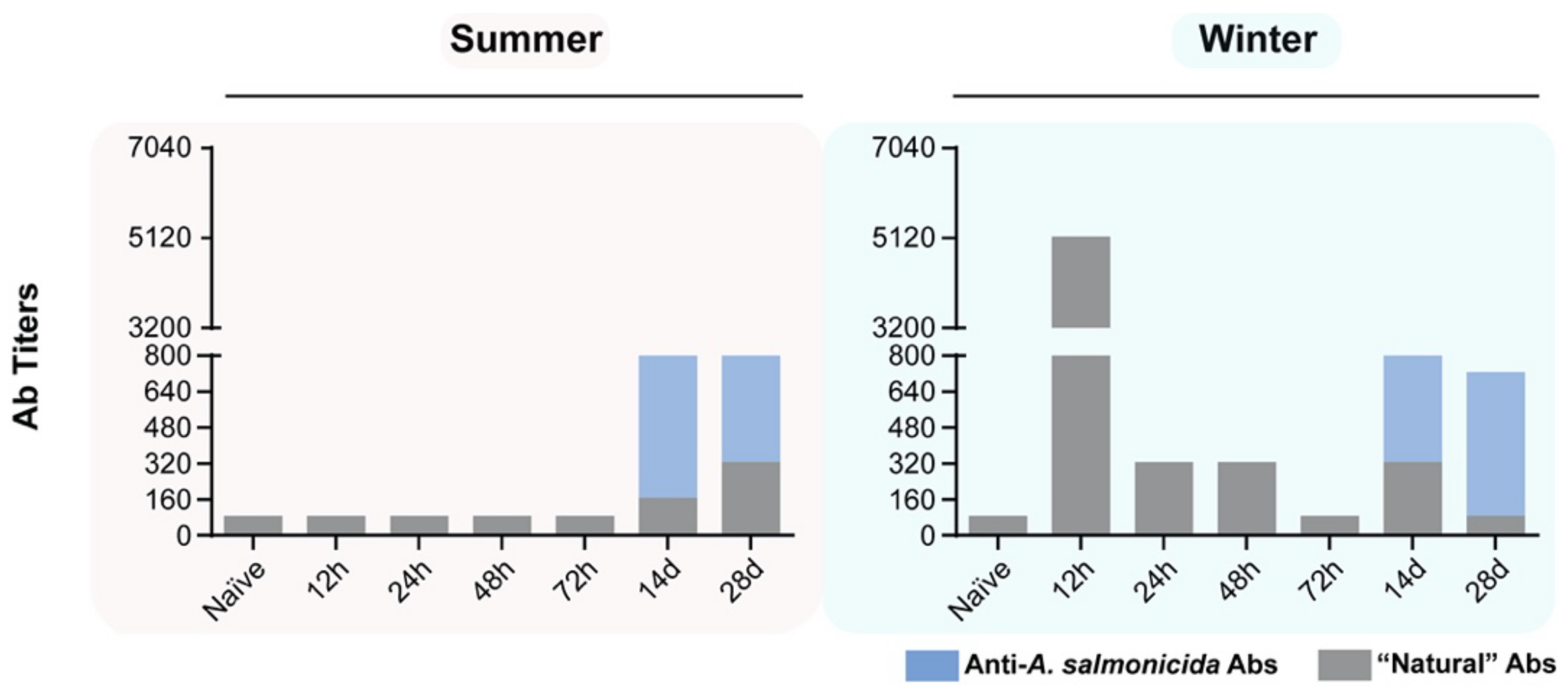
3.7. Specific and Non-Specific Antibody Titers in Fish Stimulated with A. salmonicida
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Immune Status: Immune Parameters Influenced by the Season
4.2. Peritoneal Cavity: Biphasic Response in Summer, Joint Response in Winter
4.3. Immune Response Skewed toward Innate Immune Responses in Winter in Trout
4.4. Seasonal and Circannual Rhythms Modulate the Immune Response of Trout
4.5. Temperature and Photoperiod: Key Parameters Influencing Immune Seasonal Variations in Trout
4.6. Indirect Evidence of a Potential Internal Circannual Clock in Trout
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Partonen, T.; Pollak, D.D. Editorial: Intrinsic Clocks. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tessmar-Raible, K.; Raible, F.; Arboleda, E. Another place, another timer: Marine species and the rhythms of life. Bioessays 2011, 33, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.S. Molecular components of the circadian clock in mammals. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 1), 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.S. Transcriptional architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orozco-Solis, R.; Aguilar-Arnal, L. Circadian Regulation of Immunity through Epigenetic Mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rebl, A.; Korytář, T.; Köbis, J.M.; Verleih, M.; Krasnov, A.; Jaros, J.; Kühn, C.; Köllner, B.; Goldammer, T. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Insight into Distinct Immune Responses to Aeromonas salmonicida in Gill of Two Rainbow Trout Strains. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, R.; Strzelczyk, J.E.; Tze Ho Chan, J.; Verleih, M.; Rebl, A.; Goldammer, T.; Köllner, B.; Korytář, T. Dawn to Dusk: Diurnal Rhythm of the Immune Response in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss). Biology 2019, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, L.B.; Weil, Z.M.; Nelson, R.J. Seasonal changes in vertebrate immune activity: Mediation by physiological trade-offs. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, B.J.; Nelson, R.J.; Zucker, I. 19—Mammalian Seasonal Rhythms: Behavior and Neuroendocrine Substrates. In Hormones, Brain and Behavior; Pfaff, D.W., Arnold, A.P., Fahrbach, S.E., Etgen, A.M., Rubin, R.T., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 93–156. [Google Scholar]
- Dopico, X.C.; Evangelou, M.; Ferreira, R.C.; Guo, H.; Pekalski, M.L.; Smyth, D.J.; Cooper, N.; Burren, O.S.; Fulford, A.J.; Hennig, B.J.; et al. Widespread seasonal gene expression reveals annual differences in human immunity and physiology. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Hablützel, P.; Friberg, I.M.; Thomason, A.G.; Stewart, A.; Pachebat, J.A.; Jackson, J.A. Seasonal immunoregulation in a naturally-occurring vertebrate. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, A.; Hablützel, P.I.; Watson, H.V.; Brown, M.; Friberg, I.M.; Cable, J.; Jackson, J.A. Physical Cues Controlling Seasonal Immune Allocation in a Natural Piscine Model. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miresan, V.; Cocan, D.; Constantinescu, R.; Raducu, C.; Negrea, O. Variation in Blood Parameters of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under the Influence of Seasons and Growth Systems. Bull. UASVM Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 71, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, I.; Reshi, Q.M.; Fazio, F. The influence of the endogenous and exogenous factors on hematological parameters in different fish species: A review. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 869–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, N.; Houston, A.H. Temperature, oxygen, photoperiod, and the hemoglobin system of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Can. J. Zool. 1986, 64, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.L.; Thompson, K.D.; Auchinachie, N.A.; Migaud, H. The effect of seasonality on normal haematological and innate immune parameters of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss L. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, C.H.; Schreck, C.B. Season and physiological parameters modulate salmonid leucocyte androgen receptor affinity and abundance. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1998, 8, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.G.; Varas, A.; Torroba, M. Seasonal variations in the immune system of lower vertebrates. Immunol. Today 1992, 13, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippen, T.L.; Bootland, L.M.; Leong, J.-A.C.; Fitzpatrick, M.S.; Schreck, C.B.; Vella, A.T. Analysis of Salmonid Leukocytes Purified by Hypotonic Lysis of Erythrocytes. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2001, 13, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korytář, T.; Dang Thi, H.; Takizawa, F.; Köllner, B. A multicolour flow cytometry identifying defined leukocyte subsets of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 2017–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.; Andrews, M.T. Circannual transitions in gene expression: Lessons from seasonal adaptations. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2013, 105, 247–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bassity, E.; Clark, T.G. Functional identification of dendritic cells in the teleost model, rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, F.; Razquin, B.E.; Villena, A.J.; Zapata, A.G. Seasonal changes in the lymphoid organs of wild brown trout, Salmo trutta L: A morphometrical study. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 64, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, H.F.; El-Zoghby, I.; Hussein, M.; Bakry, H. Seasonal changes in the thymus gland of Tilapia Nilotica Fish. Minufiya Vet. J. 2010, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Honma, Y.; Tamura, E. Studies on the Endocrine Glands of a Salmonoid Fish, the Ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis Temminck et Schlegel-VIII. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1972, 38, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T. Seasonal changes in the humoral immune response and the lymphoid tissues of the marine teleost, Sebastiscus marmoratus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1986, 12, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korytář, T.; Jaros, J.; Verleih, M.; Rebl, A.; Kotterba, G.; Kühn, C.; Goldammer, T.; Köllner, B. Novel insights into the peritoneal inflammation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, D.; Gray, M.; Barr, T. Innate responses of B cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 3304–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Modulation of immune responses through direct activation of Toll-like receptors to T cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 160, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakariar, R.; Lawrence, T.; Bystrom, J.; Hilliard, M.; Colville-Nash, P.; Bellingan, G.; Fitzgerald, D.; Yaqoob, M.M.; Gilroy, D.W. Novel biphasic role for lymphocytes revealed during resolving inflammation. Blood 2008, 111, 4184–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X. Regulatory functions of innate-like B cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 10, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parra, D.; Rieger, A.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.A.; Randall, L.M.; Hunter, C.A.; Barreda, D.R.; Sunyer, J.O. Pivotal advance: Peritoneal cavity B-1 B cells have phagocytic and microbicidal capacities and present phagocytosed antigen to CD4+ T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.-Y.; Lin, A.-F.; Shao, T.; Nie, L.; Dong, W.-R.; Xiang, L.-X.; Shao, J.-Z. B Cells in Teleost Fish Act as Pivotal Initiating APCs in Priming Adaptive Immunity: An Evolutionary Perspective on the Origin of the B-1 Cell Subset and B7 Molecules. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2699–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abós, B.; Bird, S.; Granja, A.G.; Morel, E.; More Bayona, J.A.; Barreda, D.R.; Tafalla, C. Identification of the First Teleost CD5 Molecule: Additional Evidence on Phenotypical and Functional Similarities between Fish IgM+ B Cells and Mammalian B1 Cells. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothstein, T.L.; Griffin, D.O.; Holodick, N.E.; Quach, T.D.; Kaku, H. Human B-1 cells take the stage. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1285, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, L.V.; Kortet, R.; Sinclair, B.J. Eco-immunology in the cold: The role of immunity in shaping the overwintering survival of ectotherms. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb163873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norris, K.; Evans, M.R. Ecological immunology: Life history trade-offs and immune defense in birds. Behav. Ecol. 2000, 11, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDade, T.W.; Georgiev, A.V.; Kuzawa, C.W. Trade-offs between acquired and innate immune defenses in humans. Evol. Med. Public Health 2016, 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, R.; Guthmiller, J.J.; Sturtz, A.J.; Surette, F.A.; Rogers, K.J.; Sompallae, R.R.; Li, F.; Pope, R.L.; Chan, J.A.; de Labastida Rivera, F.; et al. Infection-induced plasmablasts are a nutrient sink that impairs humoral immunity to malaria. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Kaattari, I.M.; Ma, C.; Kaattari, S. The teleost humoral immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Qin, Z.; Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Ye, J.; Li, J. Recent Advances on Phagocytic B Cells in Teleost Fish. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, Q.H.; Dixon, B.; Katzenback, B.A. Impacts of Low Temperature on the Teleost Immune System. Biology 2017, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brock, M.A. Seasonal rhythmicity in lymphocyte blastogenic responses of mice persists in a constant environment. J. Immunol. 1983, 130, 2586–2588. [Google Scholar]
- Planelles, D.; Hernández-Godoy, J.; Montoro, A.; Montoro, J.; González-Molina, A. Seasonal variation in proliferative response and subpopulations of lymphocytes from mice housed in a constant environment. Cell Prolif. 1994, 27, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.; Garrido, E.; Leceta, J.; Gomariz, R.P. Relationships between neuroendocrine and immune systems in amphibians and reptiles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1983, 7, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMurray, J.P.; Barker, J.P.; Armstrong, J.D.; Bozzetti, L.P.; Kuhn, I.N. Circannual changes in immune function. Life Sci. 1983, 32, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tort, L. Stress and immune modulation in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Teles, M.; Mackenzie, S.; Tort, L. Stress-related hormones modulate cytokine expression in the head kidney of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A. Cortisol modulates the induction of inflammatory gene expression in a rainbow trout macrophage cell line. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.; Bird, D.J. Modulation of the fish immune system by hormones. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2000, 77, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwollo, P. Why spawning salmon return to their natal stream: The immunological imprinting hypothesis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raible, F.; Takekata, H.; Tessmar-Raible, K. An Overview of Monthly Rhythms and Clocks. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreatta, G.; Tessmar-Raible, K. The Still Dark Side of the Moon: Molecular Mechanisms of Lunar-Controlled Rhythms and Clocks. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 3525–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.; Loudon, A. The pars tuberalis: The site of the circannual clock in mammals? Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 258, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, G.A.; Hazlerigg, D.G. Mammalian circannual pacemakers. Soc. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 2010, 67, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, H.; Maronde, E.; Albrecht, U. The circadian clock as a molecular calendar. Chronobiol. Int. 2002, 19, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, G. A brief history of circannual time. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 31, e12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazlerigg, D.G.; Lincoln, G.A. Hypothesis: Cyclical histogenesis is the basis of circannual timing. J. Biol. Rhythms 2011, 26, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, M.A.; Rodríguez-Illamola, A.; Conde-Sieira, M.; Soengas, J.L.; Míguez, J.M. Daily rhythmic expression patterns of clock1a, bmal1, and per1 genes in retina and hypothalamus of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Chronobiol. Int. 2011, 28, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montero, R.; Chan, J.T.H.; Müller, C.; Just, P.N.; Ostermann, S.; Øverland, M.; Maisey, K.; Korytář, T.; Köllner, B. Variations in Rainbow Trout Immune Responses against A. salmonicida: Evidence of an Internal Seasonal Clock in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Biology 2022, 11, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020174
Montero R, Chan JTH, Müller C, Just PN, Ostermann S, Øverland M, Maisey K, Korytář T, Köllner B. Variations in Rainbow Trout Immune Responses against A. salmonicida: Evidence of an Internal Seasonal Clock in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Biology. 2022; 11(2):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020174
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontero, Ruth, Justin Tze Ho Chan, Claudia Müller, Philip Niclas Just, Sven Ostermann, Margareth Øverland, Kevin Maisey, Tomáš Korytář, and Bernd Köllner. 2022. "Variations in Rainbow Trout Immune Responses against A. salmonicida: Evidence of an Internal Seasonal Clock in Oncorhynchus mykiss" Biology 11, no. 2: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020174
APA StyleMontero, R., Chan, J. T. H., Müller, C., Just, P. N., Ostermann, S., Øverland, M., Maisey, K., Korytář, T., & Köllner, B. (2022). Variations in Rainbow Trout Immune Responses against A. salmonicida: Evidence of an Internal Seasonal Clock in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Biology, 11(2), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020174






