Plasma miRNA Profile of Crohn’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients, Ethical Approval and Plasma Collection
2.2. RNA Isolation and miRNA Library Construction
2.3. miRNA Sequencing and Statistical Analyses
2.4. miRNA Gene Target Prediction, Pathways and Gene Ontology
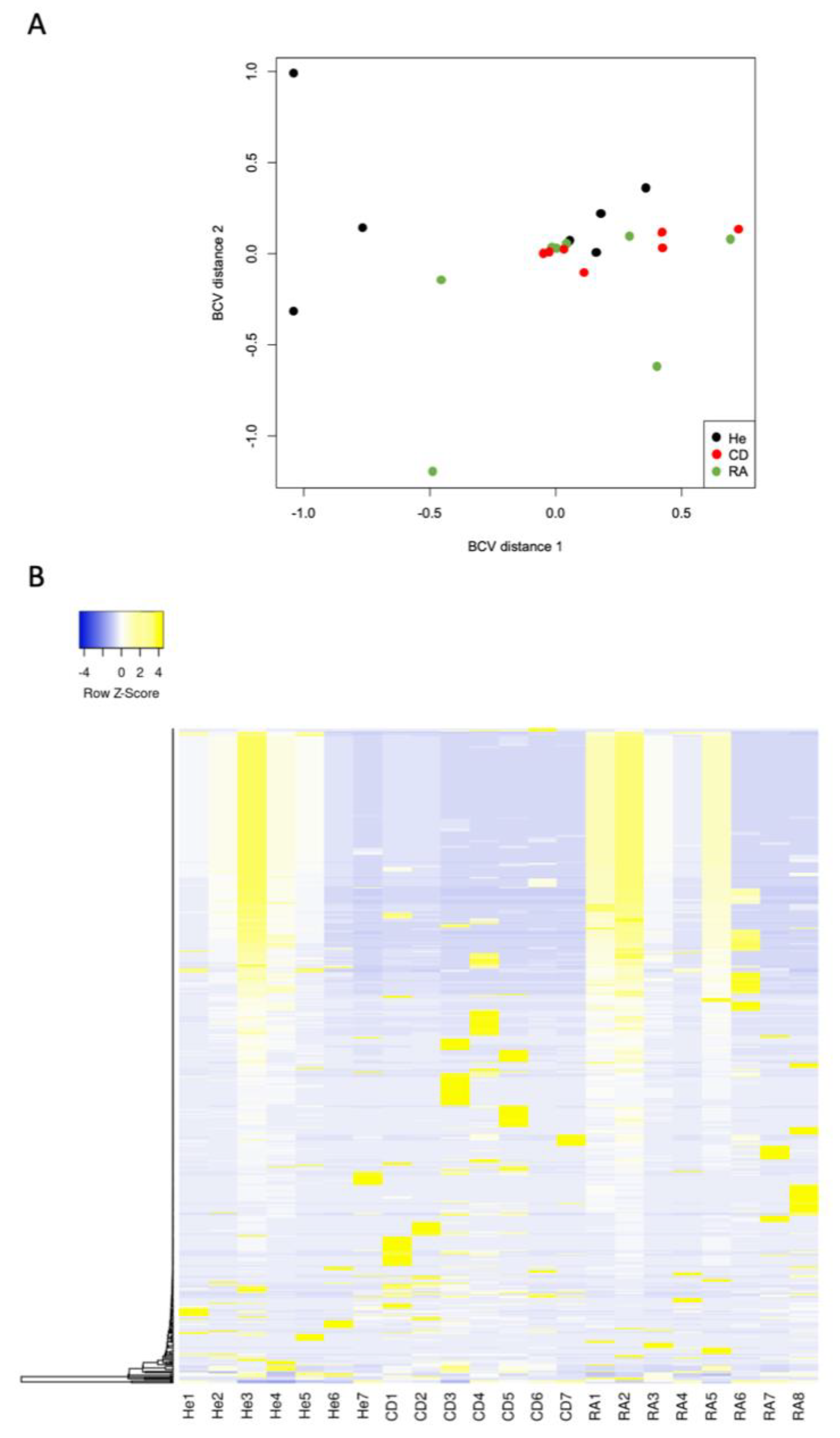
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shurin, M.R.; Smolkin, Y.S. Immune-mediated diseases: Where do we stand? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 601, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cardenas-Roldan, J.; Rojas-Villarraga, A.; Anaya, J.M. How do autoimmune diseases cluster in families? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Sandborn, W.J. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2012, 380, 1590–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.R.; Rodriguez, J.R. Clinical presentation of Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis, and indeterminate colitis: Symptoms, extraintestinal manifestations, and disease phenotypes. Semin. Pediatric Surg. 2017, 26, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, H.; Xin, L.; Wan, L.; Sun, Y.; Huang, D.; Sun, Y.; Long, Y.; et al. RNA-seq Reveals the Circular RNA and miRNA Expression Profile of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20193160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaeepoor, M.; Pourjafar, M.; Tahamoli-Roudsari, A.; Basiri, Z.; Hajilooi, M.; Solgi, G. Altered expression of microRNAs may predict therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Dassopoulos, T.; Harris, M.L.; Bayless, T.M.; Meltzer, S.J.; Brant, S.R.; Kwon, J.H. Identification of microRNAs associated with ileal and colonic Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, Z.; Li, L.; Cui, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Role of miR-150-targeting c-Myb in colonic epithelial disruption during dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis and human ulcerative colitis. J. Pathol. 2011, 225, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Mehta, S.; Hanna, L.N.; Rogalski, L.A.; Jeffery, R.; Nijhuis, A.; Kumagai, T.; Biancheri, P.; Bundy, J.G.; Bishop, C.L.; et al. Low Serum Levels of MicroRNA-19 Are Associated with a Stricturing Crohn’s Disease Phenotype. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beres, N.J.; Szabo, D.; Kocsis, D.; Szucs, D.; Kiss, Z.; Muller, K.E.; Lendvai, G.; Kiss, A.; Arato, A.; Sziksz, E.; et al. Role of Altered Expression of miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-122 in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Chang, C.; Lu, Q. Clinical significance of miRNAs in autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 109, 102438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stagakis, E.; Bertsias, G.; Verginis, P.; Nakou, M.; Hatziapostolou, M.; Kritikos, H.; Iliopoulos, D.; Boumpas, D.T. Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to human lupus disease activity and pathogenesis: miR-21 regulates aberrant T cell responses through regulation of PDCD4 expression. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Haupt, S.; Kreuzer, J.T.; Hammitzsch, A.; Proft, F.; Neumann, C.; Leipe, J.; Witt, M.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Skapenko, A. Decreased expression of miR-146a and miR-155 contributes to an abnormal Treg phenotype in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.-Q.; Ma, H.-D.; Lian, Z.-X. Epigenetics and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: A Comprehensive Review and Implications for Autoimmunity. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Zhang, W.; Jia, J.; Lu, Q.; Eric Gershwin, M. Exosomal microRNA in autoimmunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.Y. Secreted microRNAs: A new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids--the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedlander, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iborra, M.; Bernuzzi, F.; Correale, C.; Vetrano, S.; Fiorino, G.; Beltran, B.; Marabita, F.; Locati, M.; Spinelli, A.; Nos, P.; et al. Identification of serum and tissue micro-RNA expression profiles in different stages of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, A.M.; Thayu, M.; Hand, N.J.; Horner, A.; Leonard, M.B.; Friedman, J.R. Circulating microRNA is a biomarker of pediatric Crohn disease. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohnhaas, C.T.; Schmid, R.; Rolser, M.; Kaaru, E.; Langgartner, D.; Rieber, K.; Strobel, B.; Eisele, C.; Wiech, F.; Jakob, I.; et al. Fecal MicroRNAs Show Promise as Noninvasive Crohn’s Disease Biomarkers. Crohn’s Colitis 360 2020, 2, otaa003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Duan, T.; Xu, Q.; Wang, R.; Lu, L.; Jiao, Z. Plasma microRNA expression profiles in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42557–42568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.C.; Wu, L.Y.; Tsai, W.C.; Ou, T.T.; Wu, C.C.; Sung, W.Y.; Kuo, P.L.; Yen, J.H. Differential Expression Profiles of the Transcriptome and miRNA Interactome in Synovial Fibroblasts of Rheumatoid Arthritis Revealed by Next Generation Sequencing. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, H.; Oka, S.; Shimada, K.; Sugii, S.; Ohashi, J.; Matsui, T.; Ikenaka, T.; Nakayama, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Takaoka, H.; et al. Association of human leukocyte antigen with interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: A protective role for shared epitope. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oka, S.; Furukawa, H.; Shimada, K.; Hashimoto, A.; Komiya, A.; Fukui, N.; Tsuchiya, N.; Tohma, S. Plasma miRNA expression profiles in rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Liu, C.M.; Wei, L.L.; Shi, L.Y.; Pan, Z.F.; Mao, L.G.; Wan, X.C.; Ping, Z.P.; Jiang, T.T.; Chen, Z.L.; et al. A Group of Novel Serum Diagnostic Biomarkers for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis by iTRAQ-2D LC-MS/MS and Solexa Sequencing. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, S.; Guan, J.; Tan, W.; Cheng, S.; Wei, G.; Wu, W.; Wu, F.; Zhou, Y. Up-regulation of microRNA-126 may contribute to pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis via regulating NF-kappaB inhibitor IκBα. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-221-5p Inhibits Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Targeting Genomic Viral RNA and Activating the NF-κB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujioka, S.; Nakamichi, I.; Esaki, M.; Asano, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Kitazono, T. Serum microRNA levels in patients with Crohn’s disease during induction therapy by infliximab. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Grosshans, H.; Shingara, J.; Byrom, M.; Jarvis, R.; Cheng, A.; Labourier, E.; Reinert, K.L.; Brown, D.; Slack, F.J. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 2005, 120, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhao, X.; Luo, X.; Pan, W.; Huang, X.; Shen, N. Let-7/miR-98 regulate Fas and Fas-mediated apoptosis. Genes Immun. 2011, 12, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina, K.; Itoh, J.; Fukushima, K.; Kusugami, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kyokane, K.; Imada, A.; Binion, D.G.; Musso, A.; West, G.A.; et al. Resistance of Crohn’s disease T cells to multiple apoptotic signals is associated with a Bcl-2/Bax mucosal imbalance. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Moossavi, S.; Rezaei, N. Toll-like receptor signalling and their therapeutic targeting in colorectal cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 16, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Lu, J. The small molecule NSM00191 specifically represses the TNF-α/NF-кB axis in foot and ankle rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1732–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Tavallaee, G.; Tokar, T.; Nakamura, A.; Sundararajan, K.; Weston, A.; Sharma, A.; Mahomed, N.N.; Gandhi, R.; Jurisica, I.; et al. Identification of synovial fluid microRNA signature in knee osteoarthritis: Differentiating early- and late-stage knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, T.H.; Shang, Q.; Mak, W.Y.; Li, M.; Kwok, K.Y.; Yim, I.C.W.; Li, E.K.M.; Wong, P.C.H.; Lao, V.W.N.; Pang, H.T.; et al. SAT0073 MIR-186-5P targeting IL-33 gene as biomarker to predict subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aviña-Zubieta, J.A.; Choi, H.K.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Etminan, M.; Esdaile, J.M.; Lacaille, D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Diao, C.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Han, J.; Li, S. MiR-543 Promotes Migration, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Esophageal Cancer Cells by Targeting Phospholipase A2 Group IVA. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 48, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.H.; Guo, J.; Weng, X.D. MiR-543 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by targeting Dickkopf 1 through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3660–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Dai, B.; Feng, L. miR-543 promoted the cell proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting the JAM-A. Hum. Cell 2019, 32, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Song, G.; Zou, X.; Shan, X.; Liu, Q.; Xia, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, W. Circulating plasma microRNA signature for the diagnosis of cervical cancer. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2019, 26, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; Cao, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. miR-543 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting KLF4. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59246–59256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Xin, Y.; Liu, C. Long non-coding RNA ARAP1-AS1 accelerates cell proliferation and migration in breast cancer through miR-2110/HDAC2/PLIN1 axis. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20191764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Im, J.P.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.S.; Han, D.S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cohort Studies in Korea: Present and Future. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldblatt, F.; O’Neill, S.G. Clinical aspects of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Lancet 2013, 382, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettre, G.; Rioux, J.D. Autoimmune diseases: Insights from genome-wide association studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, R116–R121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baranzini, S.E. The genetics of autoimmune diseases: A networked perspective. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, C.W.; Barrett, J.C.; Parkes, M.; Satsangi, J. New IBD genetics: Common pathways with other diseases. Gut 2011, 60, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.R.; Choi, N.K.; Kim, M.S.; Chun, J.; Joo, S.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. Prevalence of extraintestinal manifestations in Korean inflammatory bowel disease patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Liu, L.; Barcellos, L.F.; Allison, J.E.; Herrinton, L.J. Clustering of inflammatory bowel disease with immune mediated diseases among members of a northern california-managed care organization. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappelman, M.D.; Galanko, J.A.; Porter, C.Q.; Sandler, R.S. Association of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease with other immune-mediated diseases. Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 96, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, M.L.; Kjeldsen, J.; Knudsen, T.; Nielsen, J.; Hansen, L.K. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease have increased risk of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6137–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.W.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, E.R.; Hong, S.N.; Chang, D.K.; Yang, M.; Kim, S.; Shin, M.H.; Kim, Y.H. Comorbid immune-mediated diseases in inflammatory bowel disease: A nation-wide population-based study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronzer, V.L.; Crowson, C.S.; Sparks, J.A.; Myasoedova, E.; Davis, J.M., 3rd. Comorbidities As Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Their Accrual After Diagnosis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 2488–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.R.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.D.; Bradfield, J.P.; Mentch, F.D.; Maggadottir, S.M.; Hou, C.; Abrams, D.J.; Chang, D.; Gao, F.; et al. Meta-analysis of shared genetic architecture across ten pediatric autoimmune diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruinsma, I.B.; van Dijk, M.; Bridel, C.; van de Lisdonk, T.; Haverkort, S.Q.; Runia, T.F.; Steinman, L.; Hintzen, R.Q.; Killestein, J.; Verbeek, M.M. Regulator of oligodendrocyte maturation, miR-219, a potential biomarker for MS. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rius, B.; Titos, E.; Morán-Salvador, E.; López-Vicario, C.; García-Alonso, V.; González-Périz, A.; Arroyo, V.; Clària, J. Resolvin D1 primes the resolution process initiated by calorie restriction in obesity-induced steatohepatitis. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2014, 28, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recchiuti, A.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Fredman, G.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. MicroRNAs in resolution of acute inflammation: Identification of novel resolvin D1-miRNA circuits. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2011, 25, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, N.; Lin, J.; Ruan, J.; Su, N.; Qing, R.; Liu, F.; He, B.; Lv, C.; Zheng, D.; Luo, R. MiR-219-5p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting glypican-3. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.X.; Hu, C.Y.; Jing, L.; Wang, M.C.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Nan, K.-J.; Wang, S.H. micro RNA-219-5p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, X.; He, S.; Liu, B.; Han, H.; Sun, X.J.G. MicroRNA-219-5p inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by targeting the Twist/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Gene 2017, 637, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Dai, S.; Qiu, C.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, C.; Yao, J.; Xu, Y. MicroRNA-219a-5p suppresses intestinal inflammation through inhibiting Th1/Th17-mediated immune responses in inflammatory bowel disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CD/Healthy | RA/Healthy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Mature miRNA | 2 CPM | 3 FC | 3 FDR | 3 FC | 3 FDR |
| Up-regulated | |||||
| hsa-let-7b-5p | 99,637 | 21.4 | 0.0025 | 9.2 | 0.0300 |
| hsa-let-7d-5p | 4113 | 440.7 | 0.000 | 59.4 | 0.001 |
| hsa-let-7e-5p | 1010 | 153.7 | 0.0006 | 45.8 | 0.0066 |
| hsa-miR-10b-5p | 706 | 136.0 | 0.0022 | 332.5 | 0.0008 |
| hsa-miR-125b-5p | 263 | 25.4 | 0.0216 | 421.2 | 0.0003 |
| hsa-miR-1260b | 1452 | 333.4 | 0.0002 | 147.6 | 0.0008 |
| hsa-miR-128-1-5p | 347 | 358.6 | 0.0002 | 83.1 | 0.0029 |
| hsa-miR-128-2-5p | 347 | 358.6 | 0.0002 | 83.1 | 0.0029 |
| hsa-miR-130b-5p | 373 | 92.4 | 0.0039 | 276.8 | 0.0010 |
| hsa-miR-143-5p | 538 | 66.8 | 0.0058 | 254.0 | 0.0009 |
| hsa-miR-181a-5p | 915 | 24.7 | 0.0228 | 373.8 | 0.0004 |
| hsa-miR-2110 | 446 | 62.4 | 0.0055 | 371.8 | 0.0005 |
| hsa-miR-223-3p | 1140 | 279.0 | 0.0001 | 41.8 | 0.0049 |
| hsa-miR-24-1-5p | 616 | 350.4 | 0.0003 | 89.5 | 0.0029 |
| hsa-miR-24-2-5p | 616 | 350.4 | 0.0003 | 89.5 | 0.0029 |
| hsa-miR-24-3p | 691 | 351.9 | 0.0002 | 77.8 | 0.0027 |
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | 274 | 122.0 | 0.0010 | 57.2 | 0.0046 |
| hsa-miR-30a-5p | 245 | 60.9 | 0.0039 | 98.8 | 0.0020 |
| hsa-miR-320d | 123 | 32.0 | 0.0022 | 15.0 | 0.0163 |
| hsa-miR-328-5p | 961 | 264.9 | 0.0004 | 265.5 | 0.0005 |
| hsa-miR-342-5p | 815 | 122.3 | 0.0014 | 268.0 | 0.0005 |
| hsa-miR-363-5p | 291 | 135.0 | 0.0019 | 318.2 | 0.0007 |
| hsa-miR-375-5p | 164 | 121.9 | 0.0013 | 118.0 | 0.0017 |
| hsa-miR-4433b-5p | 2843 | 509.1 | 0.0001 | 102.2 | 0.0003 |
| hsa-miR-4732-5p | 289 | 150.5 | 0.0008 | 62.4 | 0.0046 |
| hsa-miR-483-5p | 1939 | 410.0 | 0.0001 | 263.0 | 0.0003 |
| hsa-miR-532-5p | 78 | 103.3 | 0.0004 | 13.8 | 0.0353 |
| hsa-miR-574-5p | 133 | 288.5 | 0.0003 | 33.0 | 0.0148 |
| hsa-miR-584-5p | 468 | 208.4 | 0.0004 | 53.7 | 0.0049 |
| hsa-miR-652-5p | 1136 | 292.0 | 0.0001 | 181.4 | 0.0004 |
| hsa-miR-654-5p | 145 | 212.6 | 0.0004 | 16.8 | 0.0436 |
| hsa-miR-874-5p | 260 | 173.9 | 0.0006 | 69.1 | 0.0034 |
| hsa-miR-92b-5p | 597 | 281.9 | 0.0001 | 49.2 | 0.0031 |
| hsa-miR-9-5p | 481 | 42.9 | 0.0129 | 539.1 | 0.0004 |
| hsa-miR-99a-5p | 123 | 31.9 | 0.0124 | 180.6 | 0.0007 |
| hsa-miR-99b-5p | 528 | 150.1 | 0.0005 | 166.3 | 0.0005 |
| hsa-miR-197-5p | 298 | 256.7 | 0.0001 | - | - |
| hsa-miR-221-5p | 1154 | 457.6 | 0.0001 | - | - |
| hsa-miR-320e | 160 | 67.7 | 0.0004 | - | - |
| hsa-miR-382-5p | 521 | 250.4 | 0.0001 | - | - |
| hsa-miR-432-5p | 2428 | 396.0 | 0.0001 | - | - |
| hsa-miR-186-5p | 249 | - | - | 468.5 | 0.00006 |
| Down-regulated | |||||
| hsa-miR-219a-5p | 243 | −970.1 | 0.0001 | −351.2 | 0.0002 |
| hsa-miR-186-5p | 249 | −30.1 | 0.0119 | - | - |
| hsa-miR-320e | 160 | - | - | −7.2 | 0.044 |
| hsa-miR-221-5p | 1154 | - | - | −18.2 | 0.008 |
| hsa-miR-197-5p | 298 | - | - | −19.2 | 0.005 |
| hsa-miR-382-5p | 521 | - | - | −19.9 | 0.005 |
| hsa-miR-432-5p | 2428 | - | - | −25.0 | 0.003 |
| CD × Healthy Patients | RA × Healthy Patients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonly KEGG Pathways of Up-Regulated miRNAs | 1p Value | 2 Genes | 3 miRNAs | 1p Value | 2 Genes | 3 miRNAs |
| Alzheimer disease–amyloid secretase pathway | <0.0001 | 67 | 13 | 0.0001 | 67 | 9 |
| Alzheimer disease–presenilin pathway | <0.0001 | 124 | 22 | <0.0001 | 124 | 22 |
| Androgen/estrogen/progesterone biosynthesis | 0.00132 | 12 | 4 | 0.012 | 12 | 3 |
| Angiogenesis | <0.0001 | 172 | 43 | <0.0001 | 172 | 34 |
| Angiotensin II-stimulated signaling through G proteins and beta-arrestin | 0.00275 | 39 | 6 | 0.043 | 39 | 4 |
| Apoptosis signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 115 | 27 | <0.0001 | 115 | 23 |
| B cell activation | <0.0001 | 70 | 20 | <0.0001 | 70 | 15 |
| Cadherin signaling pathway | 0.00341 | 160 | 13 | <0.0001 | 160 | 15 |
| CCKR signaling map | <0.0001 | 172 | 59 | <0.0001 | 172 | 40 |
| Cell cycle | <0.0001 | 22 | 7 | 0.0001 | 22 | 6 |
| Cytoskeletal regulation by Rho GTPase | 0.0024 | 83 | 9 | 0.039 | 83 | 6 |
| EGF receptor signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 136 | 30 | <0.0001 | 136 | 19 |
| Endothelin signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 82 | 13 | <0.0001 | 82 | 13 |
| FAS signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 35 | 10 | 0.034 | 35 | 4 |
| FGF signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 121 | 25 | <0.0001 | 121 | 16 |
| Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor pathway | <0.0001 | 232 | 51 | <0.0001 | 232 | 37 |
| Hedgehog signaling pathway | 0.0002 | 22 | 6 | 0.001 | 22 | 5 |
| Huntington disease | <0.0001 | 143 | 16 | 0.0018 | 143 | 11 |
| Hypoxia response via HIF activation (P00030) | 0.00019 | 32 | 7 | <0.0001 | 32 | 8 |
| Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 255 | 43 | <0.0001 | 255 | 24 |
| Insulin/IGF pathway-mitogen activated protein kinase kinase/MAP kinase cascade | <0.0001 | 31 | 13 | <0.0001 | 31 | 10 |
| Insulin/IGF pathway-protein kinase B signaling cascade | <0.0001 | 39 | 14 | <0.0001 | 39 | 12 |
| Integrin signalling pathway | <0.0001 | 191 | 28 | <0.0001 | 191 | 22 |
| Interferon-gamma signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 31 | 15 | <0.0001 | 31 | 7 |
| Interleukin signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 88 | 31 | <0.0001 | 88 | 21 |
| JAK/STAT signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 17 | 9 | 0.032 | 17 | 3 |
| Notch signaling pathway | 0.00027 | 45 | 8 | 0.0028 | 45 | 6 |
| Oxidative stress response | <0.0001 | 55 | 11 | 0.0072 | 55 | 6 |
| p38 MAPK pathway | <0.0001 | 40 | 10 | <0.0001 | 40 | 8 |
| p53 pathway | <0.0001 | 87 | 24 | <0.0001 | 87 | 20 |
| p53 pathway by glucose deprivation | <0.0001 | 22 | 7 | 0.0082 | 22 | 4 |
| p53 pathway feedback loops 2 | <0.0001 | 50 | 26 | <0.0001 | 50 | 20 |
| Parkinson disease | <0.0001 | 98 | 11 | 0.0018 | 98 | 9 |
| PDGF signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 145 | 37 | <0.0001 | 145 | 27 |
| PI3 kinase pathway | <0.0001 | 52 | 15 | <0.0001 | 52 | 13 |
| Plasminogen activating cascade | 0.00045 | 18 | 4 | 0.035 | 18 | 3 |
| Ras Pathway | <0.0001 | 74 | 27 | <0.0001 | 74 | 19 |
| T cell activation | <0.0001 | 88 | 22 | <0.0001 | 88 | 16 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 98 | 21 | <0.0001 | 98 | 16 |
| Toll receptor signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 57 | 13 | <0.0001 | 57 | 11 |
| VEGF signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 68 | 17 | <0.0001 | 68 | 18 |
| Wnt signaling pathway | <0.0001 | 317 | 37 | <0.0001 | 317 | 33 |
| KEGG pathways of up-regulated miRNAS in CD patients only | ||||||
| Axon guidance mediated by Slit/Robo | 0.0005 | 27 | 6 | - | - | - |
| BMP/activin signaling pathway | 0.0093 | 3 | 2 | - | - | - |
| GBB signaling pathway | 0.0571 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - |
| MYO signaling pathway | 0.057 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - |
| KEGG pathways of up-regulated miRNAS in RA patients only | ||||||
| Dopamine receptor mediated signaling pathway | - | - | - | 0.035 | 57 | 5 |
| CD × Health Patients | RA × Health Patients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathways of Down-Regulated miRNAs | 1p Value | 2 Genes | 3 miRNAs | 1p Value | 2 Genes | 3 miRNAs |
| CCKR signaling map | <0.0001 | 112 | 2 | - | - | - |
| Interleukin signaling pathway | 0.0006 | 88 | 3 | - | - | - |
| Toll receptor signaling pathway | - | - | - | <0.0001 | 57 | 5 |
| p53 pathway feedback loops 2 | - | - | - | <0.0001 | 50 | 4 |
| Hypoxia response via HIF activation | - | - | - | 0.0007 | 32 | 2 |
| Insulin/IGF pathway-protein kinase B signaling cascade | - | - | - | 0.0011 | 39 | 2 |
| p38 MAPK pathway | - | - | - | 0.0011 | 40 | 2 |
| p53 pathway | - | - | - | <0.0001 | 87 | 4 |
| B cell activation | - | - | - | 0.0033 | 70 | 2 |
| EGF receptor signaling pathway | - | - | - | 0.0005 | 136 | 3 |
| PDGF signaling pathway | - | - | - | 0.0007 | 145 | 3 |
| Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | - | - | - | <0.0001 | 255 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saccon, T.D.; Dhahbi, J.M.; Schneider, A.; Nunez Lopez, Y.O.; Qasem, A.; Cavalcante, M.B.; Sing, L.K.; Naser, S.A.; Masternak, M.M. Plasma miRNA Profile of Crohn’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Biology 2022, 11, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040508
Saccon TD, Dhahbi JM, Schneider A, Nunez Lopez YO, Qasem A, Cavalcante MB, Sing LK, Naser SA, Masternak MM. Plasma miRNA Profile of Crohn’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Biology. 2022; 11(4):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040508
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaccon, Tatiana D., Joseph M. Dhahbi, Augusto Schneider, Yury O. Nunez Lopez, Ahmad Qasem, Marcelo B. Cavalcante, Lauren K. Sing, Saleh A. Naser, and Michal M. Masternak. 2022. "Plasma miRNA Profile of Crohn’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients" Biology 11, no. 4: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040508
APA StyleSaccon, T. D., Dhahbi, J. M., Schneider, A., Nunez Lopez, Y. O., Qasem, A., Cavalcante, M. B., Sing, L. K., Naser, S. A., & Masternak, M. M. (2022). Plasma miRNA Profile of Crohn’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Biology, 11(4), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040508








