The Self-Organization of Marine Microbial Networks under Evolutionary and Ecological Processes: Observations and Modeling
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
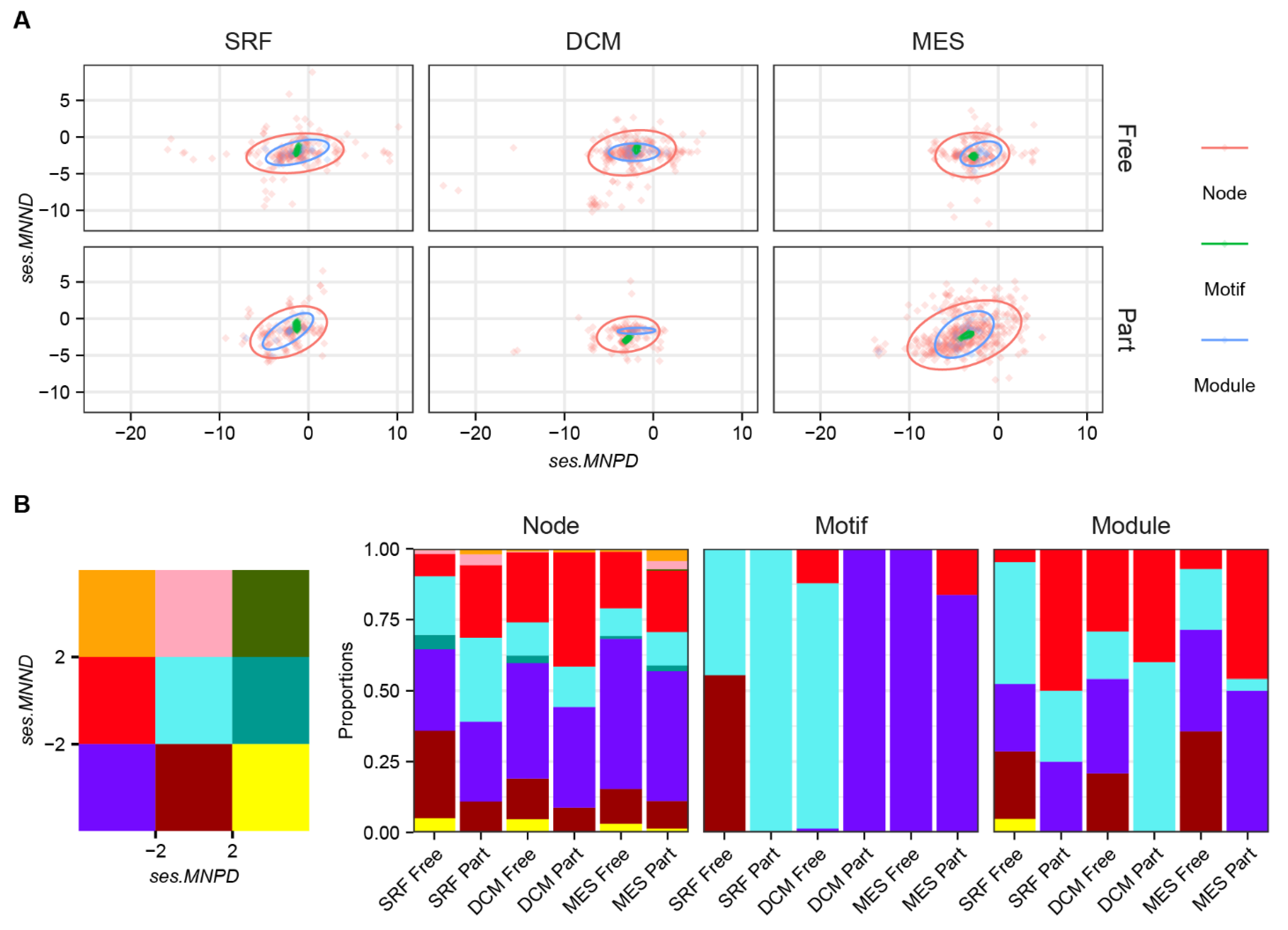
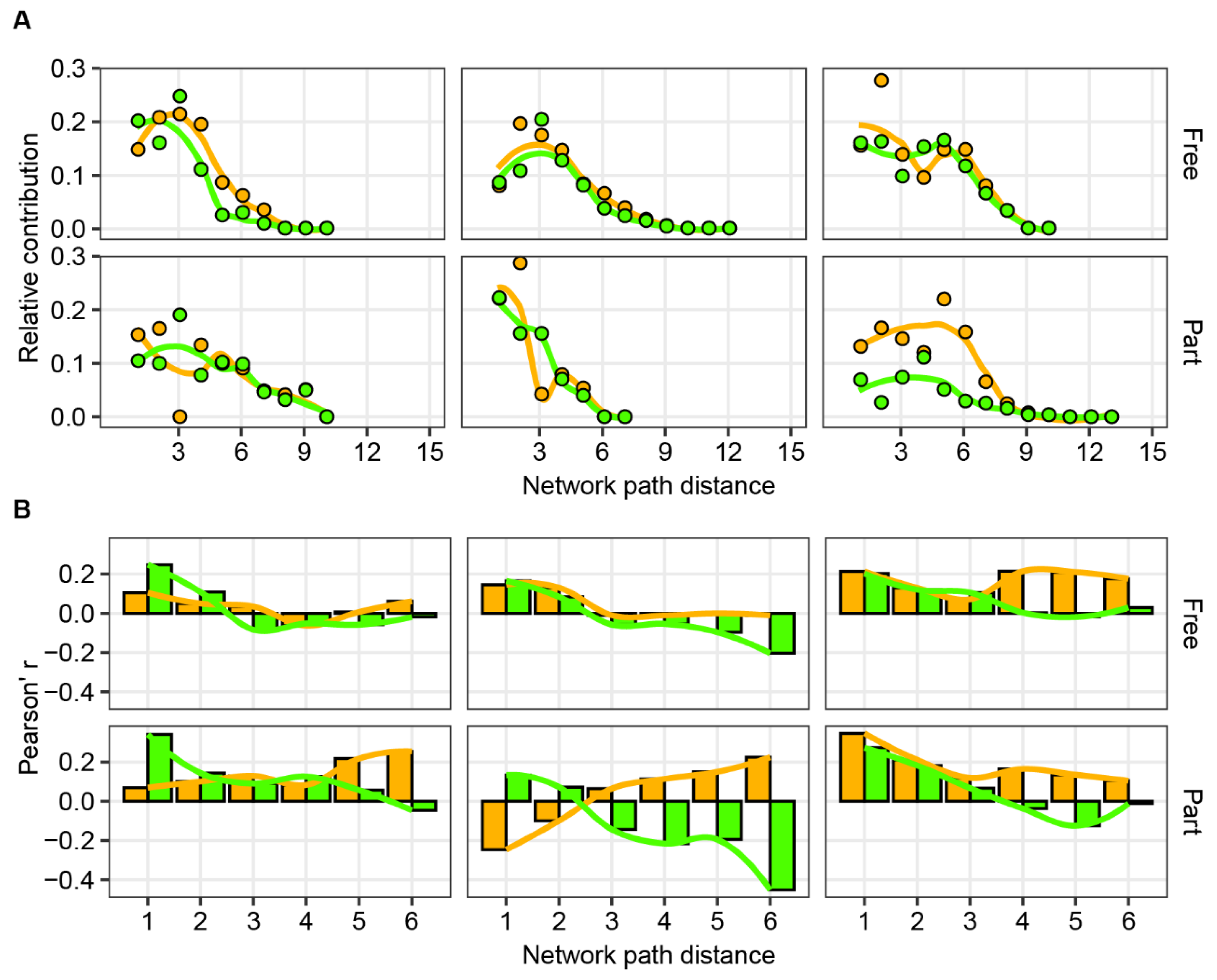
2.2. Network Construction, Motif and Latent Space Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analyses
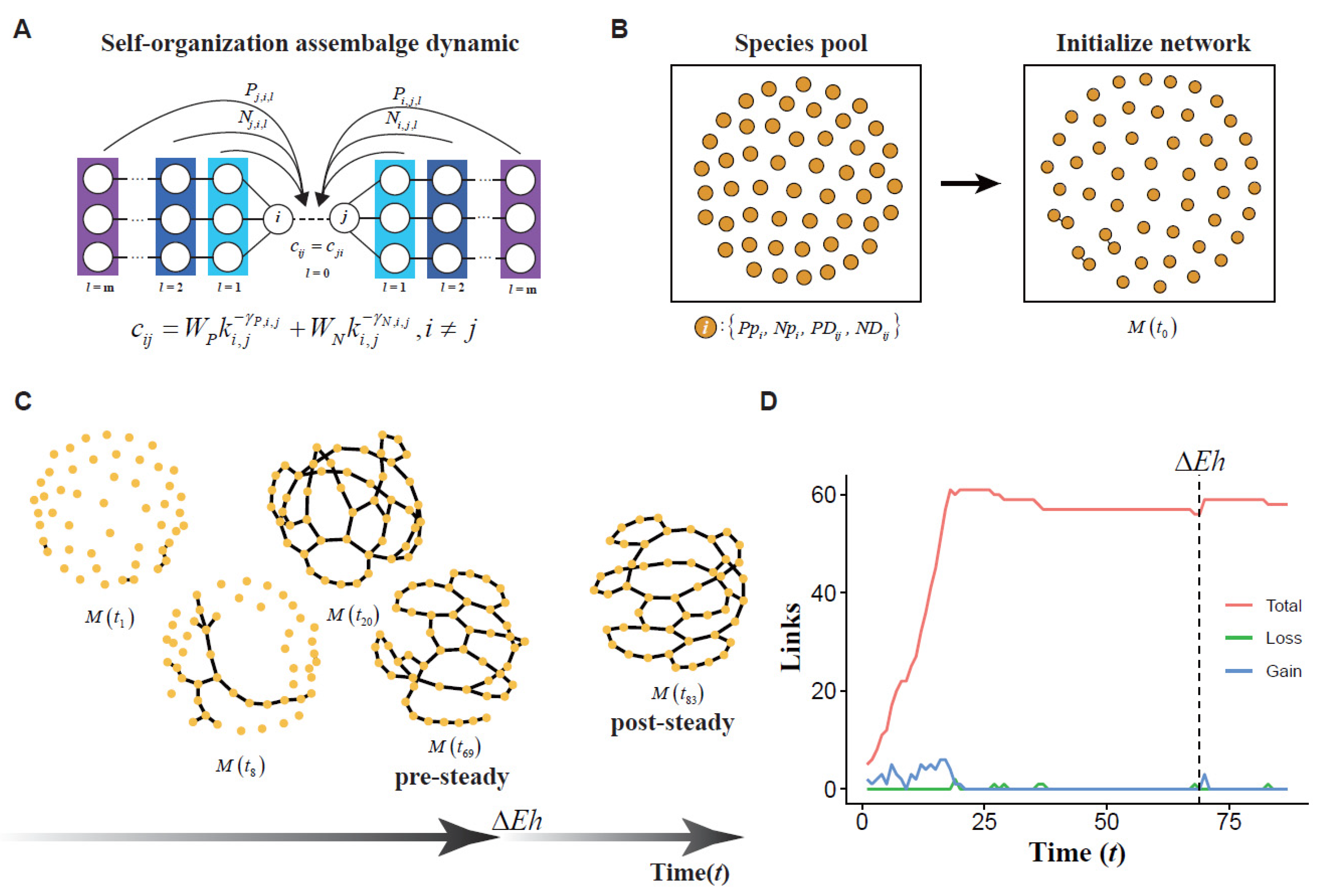
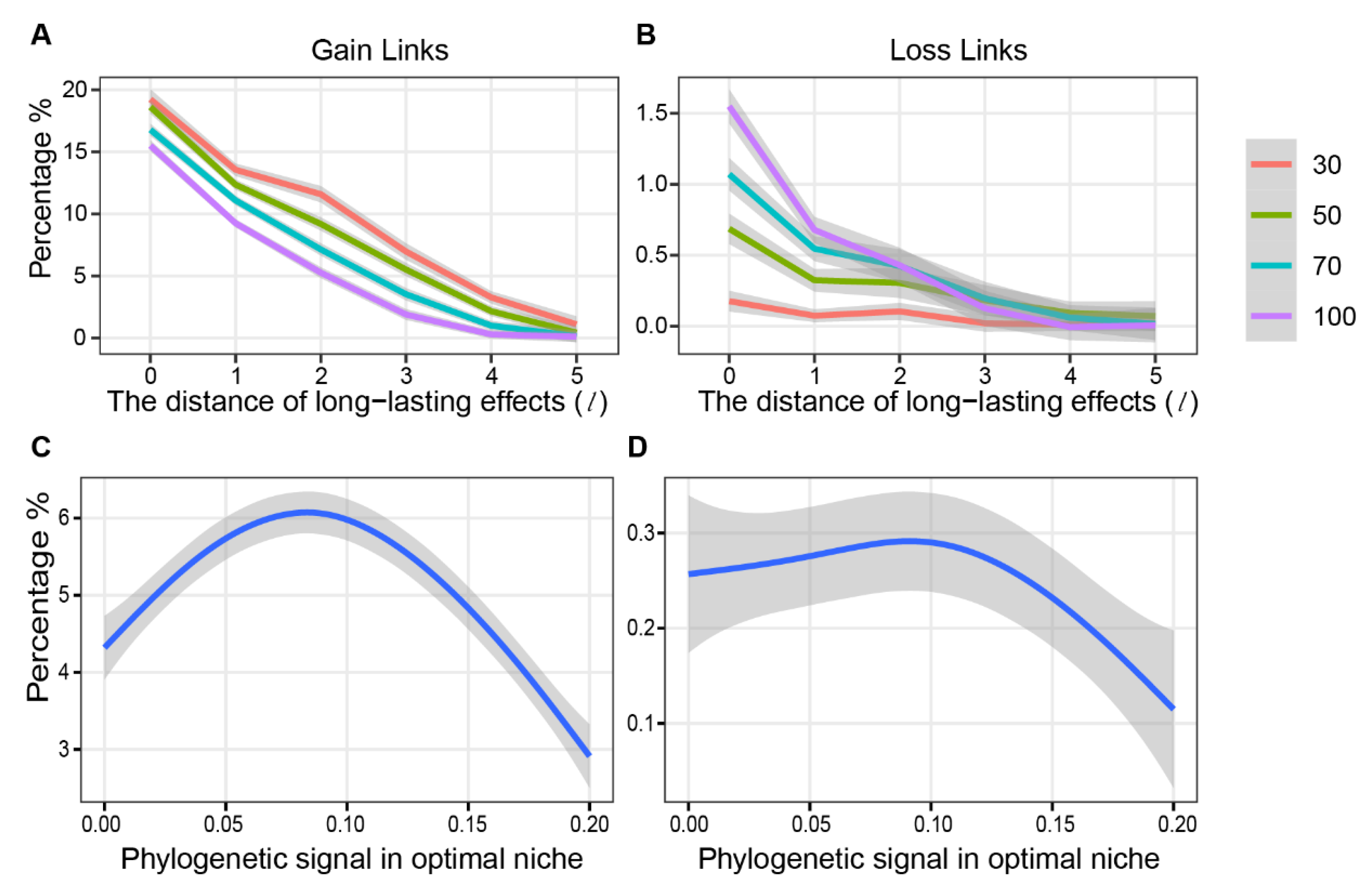
2.4. Mathematical Mechanism Model
2.4.1. The dynamic of a Scale-Free Network in Ecology Community
2.4.2. The Specie Pool Construction
2.4.3. Modeling of Network Assembly
2.4.4. Sensitive Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanders, D.; Sutter, L.; van Veen, F.J.F. The loss of indirect interactions leads to cascading extinctions of carnivores. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, I.; Petchey, O.L.; Kéfi, S.; Génin, A.; Jackson, A.L.; Yang, Q.; O’Connor, N.E. Loss of predator species, not intermediate consumers, triggers rapid and dramatic extinction cascades. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2962–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwin, C. The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection; Reprinted by The Modern Library; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1859. [Google Scholar]
- Godoy, O.; Kraft, N.J.; Levine, J.M. Phylogenetic relatedness and the determinants of competitive outcomes. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, N.J. The Evolution of Species Interactions. Science 1999, 284, 2116–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellissier, L.; Albouy, C.; Bascompte, J.; Farwig, N.; Graham, C.; Loreau, M.; Maglianesi, M.A.; Melian, C.J.; Pitteloud, C.; Roslin, T.; et al. Comparing species interaction networks along environmental gradients. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queller, D.; Strassmann, J. Kin preference in a social microbe. Nature 2006, 442, 881882. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, J.M.; Verdu, M.; Perfectti, F. Ecological interactions are evolutionarily conserved across the entire tree of life. Nature 2010, 465, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, R.J.; Caulk, N.C.; Stachowicz, J.J. Trait vs. phylogenetic diversity as predictors of competition and community composition in herbivorous marine amphipods. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuismer, S.L.; Harmon, L.J. Predicting rates of interspecific interaction from phylogenetic trees. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousseau, P.-M.; Gravel, D.; Handa, I.T.; Ferrari, M. Trait matching and phylogeny as predictors of predator-prey interactions involving ground beetles. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berlow, E.L.; Dunne, J.A.; Martinez, N.D.; Stark, P.B.; Williams, R.J.; Ulrich, B. Simple prediction of interaction strengths in complex food webs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cahill, J.F.; Kembel, S.W.; Lamb, E.G.; Keddy, P.A. Does phylogenetic relatedness influence the strength of competition among vascular plants? Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 10, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.K.; Borrett, S.R.; Baiser, B.; Gotelli, N.J.; Ellison, A.M. Ecological network metrics: Opportunities for synthesis. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milo, R.; Shen-Orr, S.; Itzkovitz, S.; Kashtan, N.; Chklovskii, D.; Alon, U. Network motifs: Simple building blocks of complex networks. Science 2002, 298, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasserman, S. Advances in Social Network Analysis: Research in the Social and Behavioral Sciences; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Niu, J.; Ren, Y.; Cong, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, F.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, J.; Xie, M.; et al. An integrated insight into the response of sedimentary microbial communities to heavy metal contamination. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.E.; Shi, Z.J.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Firestone, M.K. The interconnected rhizosphere: High network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Yang, Y. Phylogenetic molecular ecological network of soil microbial communities in response to elevated CO2. MBio 2011, 2, e00122-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giling, D.P.; Ebeling, A.; Eisenhauer, N.; Meyer, S.T.; Roscher, C.; Rzanny, M.; Voigt, W.; Weisser, W.W.; Hines, J. Plant diversity alters the representation of motifs in food webs. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bramon Mora, B.; Gravel, D.; Gilarranz, L.J.; Poisot, T.; Stouffer, D.B. Identifying a common backbone of interactions underlying food webs from different ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clauset, A.; Newman, M.E.; Moore, C. Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 066111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pons, P.; Latapy, M. Computing communities in large networks using random walks. J. Graph. Algorithms Appl. 2006, 10, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schleuning, M.; Ingmann, L.; Strauss, R.; Fritz, S.A.; Dalsgaard, B.; Matthias Dehling, D.; Plein, M.; Saavedra, F.; Sandel, B.; Svenning, J.C.; et al. Ecological, historical and evolutionary determinants of modularity in weighted seed-dispersal networks. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Kirkby, C.A.; Schmutter, D.; Bissett, A.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Richardson, A.E. Network analysis reveals functional redundancy and keystone taxa amongst bacterial and fungal communities during organic matter decomposition in an arable soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.; Steinberg, P.; Rusch, D.; Kjelleberg, S.; Thomas, T. Bacterial community assembly based on functional genes rather than species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14288–14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, F.; Xia, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T. Taxonomic relatedness shapes bacterial assembly in activated sludge of globally distributed wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, C.; Guimarães, P.R.; Kéfi, S.; Loeuille, N.; Memmott, J.; van der Putten, W.H.; van Veen, F.J.F.; Thébault, E. The ecological and evolutionary implications of merging different types of networks. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proulx, S.R.; Promislow, D.E.; Phillips, P.C. Network thinking in ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordi, B.; Stouffer, D.B. The assembly and disassembly of ecological networks. Philos. Trans. Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Pesant, S.; Not, F.; Picheral, M.; Kandels-Lewis, S.; Le Bescot, N.; Gorsky, G.; Iudicone, D.; Karsenti, E.; Speich, S.; Troublé, R. Open science resources for the discovery and analysis of Tara Oceans data. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective Dynamics of Small World Networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabási, A.-L. Scale-free networks: A decade and beyond. Science 2009, 325, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunagawa, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Chaffron, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Labadie, K.; Salazar, G.; Djahanschiri, B.; Zeller, G.; Mende, D.R.; Alberti, A. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 2015, 348, 1261359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, Z.D.; Muller, C.L.; Miraldi, E.R.; Littman, D.R.; Blaser, M.J.; Bonneau, R.A. Sparse and compositionally robust inference of microbial ecological networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, S.; Van Treuren, W.; Lozupone, C.; Faust, K.; Friedman, J.; Deng, Y.; Xia, L.C.; Xu, Z.Z.; Ursell, L.; Alm, E.J.; et al. Correl. Detect. Strateg. Microb. Data Sets Vary Widely Sensit. Precision. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, B.I.; Sweering, M.J.M.; Schillinger, M.; Dicks, L.V.; Sutherland, W.J.; Di Clemente, R.; Matthiopoulos, J. bmotif: A package for motif analyses of bipartite networks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salter-Townshend, M.; Murphy, T.B. Variational Bayesian inference for the Latent Position Cluster Model for network data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2013, 57, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJ. Complex Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichstein, J.W. Multiple regression on distance matrices: A multivariate spatial analysis tool. Plant Ecol. 2006, 188, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Package ‘vegan’. Community Ecol. Package Vers. 2013, 2, 1–295. [Google Scholar]
- Goslee, S.C.; Urban, D.L. The ecodist package for dissimilarity-based analysis of ecological data. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunne, J.A.; Williams, R.J.; Martinez, N.D. Food-web structure and network theory: The role of connectance and size. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12917–12922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montoya, J.M.; Sol, R.V. Small world patterns in food webs. J. Theor. Biol. 2002, 214, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Dsouza, M.; Lou, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.; Gilbert, J.A. Geographic patterns of co-occurrence network topological features for soil microbiota at continental scale in eastern China. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The smallest of all worlds: Pollination networks. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 240, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riverahutinel, A.; Bustamante, R.O.; Marín, V.H.; Medel, R. Effects of sampling completeness on the structure of plant-pollinator networks. Ecology 2012, 93, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strogatz, S.H. Exploring complex networks. Nature 2001, 410, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W. A random network based, node attraction facilitated network evolution method. Selforganizology 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, W.; Chung, F.; Lu, L. A Random Graph Model for Power Law Graphs. Exp. Math. 2001, 10, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, B.R. Analysis of Phylogenetics and Evolution with R. Biometrics 2007, 63, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kembel, S.W. Disentangling niche and neutral influences on community assembly: Assessing the performance of community phylogenetic structure tests. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Stefanescu, C.; Traveset, A. Strong, Long-Term Temporal Dynamics of an Ecological Network. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, G.G.; Schemske, D.W. Ecological and evolutionary perspectives on community assembly. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violle, C.; Nemergut, D.R.; Pu, Z.; Jiang, L. Phylogenetic limiting similarity and competitive exclusion. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, S.Y. Indirect effects in community ecology: Their definition, study and importance. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1991, 6, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.D.V. Stable Coexistence in Insect Communities Due to Density- and Trait-Mediated Indirect Effects. Ecology 2005, 86, 3182–3189. [Google Scholar]
- Cazelles, K.; Araújo, M.B.; Mouquet, N.; Gravel, D. A theory for species co-occurrence in interaction networks. Theor. Ecol. 2015, 9, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubski, A.J.; Westlund, E.E.; Vandermeer, J.; Pascual, M. Ecological Networks over the Edge: Hypergraph Trait-Mediated Indirect Interaction (TMII) Structure. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stouffer, D.B.; Sales-Pardo, M.; Sirer, M.I.; Bascompte, J. Evolutionary conservation of species’ roles in food webs. Science 2012, 335, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coux, C.; Rader, R.; Bartomeus, I.; Tylianakis, J.M. Linking species functional roles to their network roles. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezende, E.L.; Lavabre, J.E.; Guimarães, P.R.; Jordano, P.; Bascompte, J. Non-random coextinctions in phylogenetically structured mutualistic networks. Nature 2007, 448, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.; Fontaine, C.; van Veen, F.J. Evolutionary history and ecological processes shape a local multilevel antagonistic network. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, C.A.; Thaler, J.S. Insect predators affect plant resistance via density- and trait-mediated indirect interactions. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, S.; Qu, Y.; Ma, Q.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Long-term successional dynamics of microbial association networks in anaerobic digestion processes. Water Res. 2016, 104, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunstler, G.; Lavergne, S.; Courbaud, B.; Thuiller, W.; Vieilledent, G.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Kattge, J.; Coomes, D.A. Competitive interactions between forest trees are driven by species’ trait hierarchy, not phylogenetic or functional similarity: Implications for forest community assembly. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freilich, S.; Zarecki, R.; Eilam, O.; Segal, E.S.; Henry, C.S.; Kupiec, M.; Gophna, U.; Sharan, R.; Ruppin, E. Competitive and cooperative metabolic interactions in bacterial communities. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehdiabadi, N.J.; Jack, C.N.; Tiffany Talley, F.; Platt, T.G.; Kalla, S.E.; Gad, S.; Queller, D.C.; Strassmann, J.E. Social evolution: Kin preference in a social microbe. Nature 2006, 442, 881–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naughton, H.R.; Alexandrou, M.A.; Oakley, T.H.; Cardinale, B.J. Phylogenetic distance does not predict competition in green algal communities. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morueta-Holme, N.; Blonder, B.; Sandel, B.; McGill, B.J.; Peet, R.K.; Ott, J.E.; Violle, C.; Enquist, B.J.; Jørgensen, P.M.; Svenning, J.-C. A network approach for inferring species associations from co-occurrence data. Ecography 2016, 39, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thébault, E.; Fontaine, C. Stability of ecological communities and the architecture of mutualistic and trophic networks. Science 2010, 329, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Veen, F.F.; Memmott, J.; Godfray, H.C.J. Indirect Effects, Apparent Competition and Biological Control. In Trophic and Guild in Biological Interactions Control; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 145–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazoul, J. Floral diversity and the facilitation of pollination. J. Ecol. 2006, 94, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastolla, U.; Fortuna, M.A.; Pascual-García, A.; Ferrera, A.; Luque, B.; Bascompte, J. The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity. Nature 2009, 458, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, F.; Garant, D.; Hendry, A.P. Eco-evolutionary dynamics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, T.; Farnsworth, K.D.; Reid, D.G.; Rossberg, A.G. Impact of biodiversity loss on production in complex marine food webs mitigated by prey-release. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunne, J.A.; Williams, R.J.; Martinez, N.D. Network topology and biodiversity loss in food webs: Robustness increases with connectance. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garay-Narváez, L.; Flores, J.D.; Arim, M.; Ramos-Jiliberto, R. Food web modularity and biodiversity promote species persistence in polluted environments. Oikos 2014, 123, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonze, D.; Lahti, L.; Raes, J.; Faust, K. Multi-stability and the origin of microbial community types. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faust, K.; Sathirapongsasuti, J.F.; Izard, J.; Segata, N.; Gevers, D.; Raes, J.; Huttenhower, C. Microbial co-occurrence relationships in the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reshef, D.N.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Grossman, S.R.; McVean, G.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Lander, E.S.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting novel associations in large data sets. Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, Q.; Dutta, D.; Schwalbach, M.S.; Steele, J.A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Sun, F. Local similarity analysis reveals unique associations among marine bacterioplankton species and environmental factors. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2532–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackmann, J.; Rodrigues, J.F.M.; von Mering, C. Rapid inference of direct interactions in large-scale ecological networks from heterogeneous microbial sequencing data. Cell Syst. 2019, 9, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tara Oceans. Available online: http://ocean-microbiome.embl.de/companion.html (accessed on 18 July 2019).


| Size Fraction | Layer | ses.MNPD | ses.MNND |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free-living | SRF | 0.133 | −0.0236 |
| DCM | 0.2302 | 0.8291 * | |
| MES | −0.1677 | −0.2277 | |
| Particle-associated | SRF | 0.7122 *** | −0.0927 |
| DCM | 0.3903 ** | −0.0811 | |
| MES | 0.1315 | −0.7282 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Meng, D.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Gu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, C.; Yin, H. The Self-Organization of Marine Microbial Networks under Evolutionary and Ecological Processes: Observations and Modeling. Biology 2022, 11, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040592
Liu Z, Wang J, Meng D, Li L, Liu X, Gu Y, Yan Q, Jiang C, Yin H. The Self-Organization of Marine Microbial Networks under Evolutionary and Ecological Processes: Observations and Modeling. Biology. 2022; 11(4):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040592
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhenghua, Jianjun Wang, Delong Meng, Liangzhi Li, Xueduan Liu, Yabing Gu, Qingyun Yan, Chengying Jiang, and Huaqun Yin. 2022. "The Self-Organization of Marine Microbial Networks under Evolutionary and Ecological Processes: Observations and Modeling" Biology 11, no. 4: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040592
APA StyleLiu, Z., Wang, J., Meng, D., Li, L., Liu, X., Gu, Y., Yan, Q., Jiang, C., & Yin, H. (2022). The Self-Organization of Marine Microbial Networks under Evolutionary and Ecological Processes: Observations and Modeling. Biology, 11(4), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040592







