Serological Variety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Reptiles
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Place
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Salmonella
2.3. Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Molecular Testing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Salmonella Prevalence in Reptiles
3.2. Serological Variety of the Salmonella Isolates
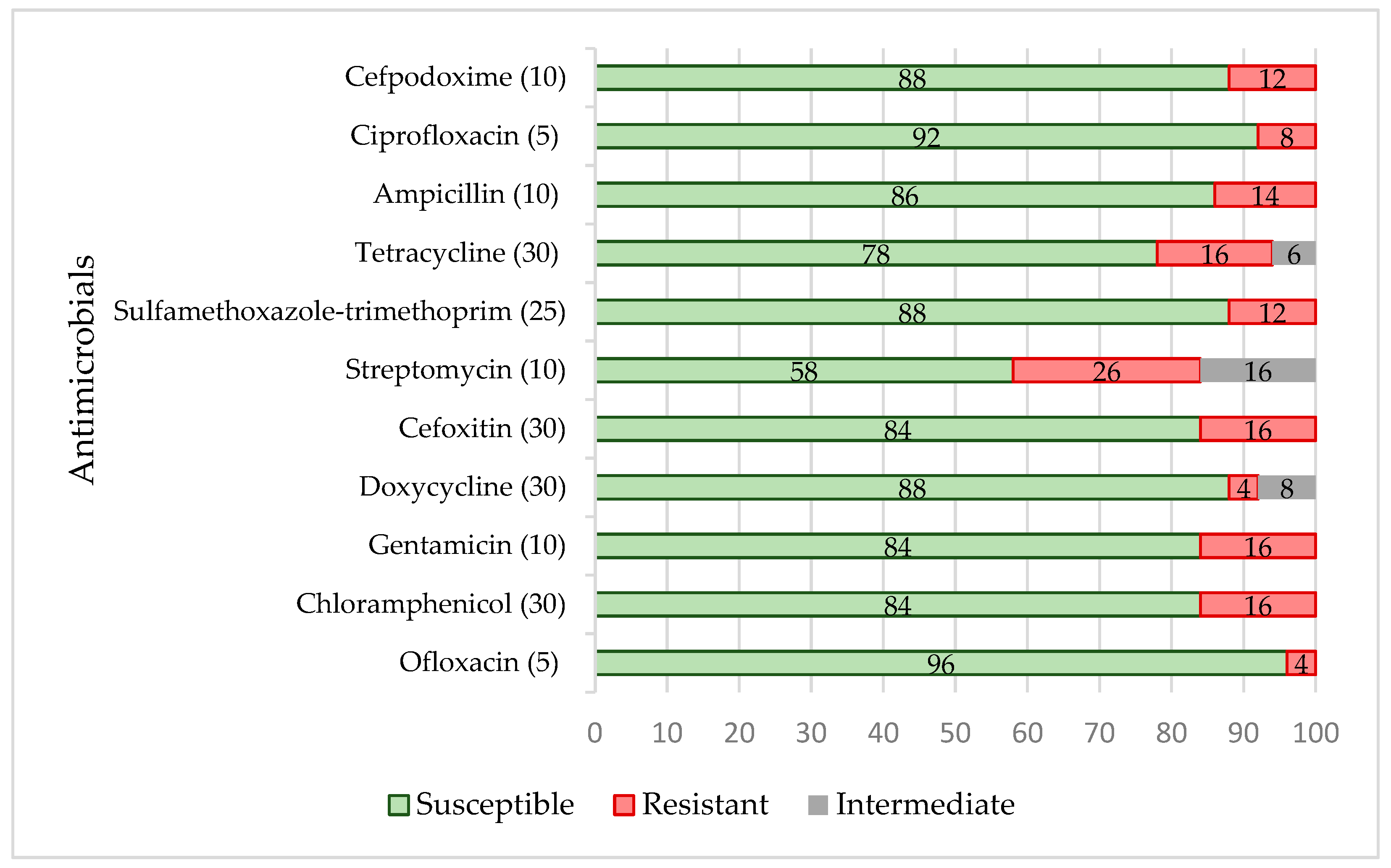
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bjelland, A.M.; Sandvik, L.M.; Skarstein, M.M.; Svendal, L.; Debenham, J.J. Prevalence of Salmonella serovars isolated from reptiles in Norwegian zoos. Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheelings, T.F.; Lightfoot, D.; Holz, P. Prevelence of Salmonella in Australian reptiles. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keusch, G.T. Salmonellosis. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine; Isselbacher, K.J., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mermin, J.; Hutwagner, L.; Vugia, D.; Shallow, S.; Daily, P.; Bender, J.; Koehler, J.; Marcus, R.; Angulo, R.J. Reptiles, amphibians, and human Salmonella infection: A population-based, case-control study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geue, L.; Loschner, U. Salmonella enterica in reptiles of German and Austrian origin. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 84, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrente, M.; Madio, A.; Friedrich, K.G.; Greco, G.; Desario, C.; Tagliabue, S.; D’Incau, M.; Campolo, M.; Buonavoglia, C. Isolation of Salmonella strains from reptile faeces and comparison of different culture media. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebani, V.V.; Cerri, D.; Fratini, F.; Meille, N.; Valentini, P.; Andreani, E. Salmonella enterica isolates from faeces of domestic reptiles and a study of their antimicrobial in vitro sensitivity. Res. Vet. Sci. 2005, 78, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Chin, S.C.; Lai, Y.H.; Tung, K.C.; Chiou, C.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Chang, C.C. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of salmonellae isolates from reptiles in Taiwan. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hydeskov, H.B.; Guardabassi, L.; Aalbaek, B.; Olsen, K.E.; Nielsen, S.S.; Bertelsen, M.F. Salmonella prevalence among reptiles in a zoo education setting. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; International Collaboration on Enteric Disease “Burden of Illness” Studies. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiley, H.; Gardner, M.G.; Ross, K. A review of Salmonella and Squamates (Lizards, Snakes and Amphisbians): Implications for public health. Pathogens 2017, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevelation. CFSPH Technical Fact Sheets. Salmonella (Non-Typhoidal). CDC Website. Salmonellosis at Reptiles and Amphibians. Available online: http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/DiseaseInfo/ (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Bertrand, S.; Rimhanen-Finne, R.; Weill, F.X.; Rabsch, W.; Thornton, L.; Perevoscikovs, J.; van Pelt, W.; Heck, M. Salmonella infections associated with reptiles: The current situation in Europe. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2008, 13, 18902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- CEN ISO/TR 6579-3:2014; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 3: Guidelines for Serotyping of Salmonella spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters Version 12.0. 2022. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- CLSI (2019); Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 29th ed. CLSI Supplement M100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019.
- Ružauskas, M.; Šiugždinienė, R.; Klimienė, I.; Virgailis, M.; Mockeliūnas, R.; Vaškevičiūtė, L.; Zienius, D. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus in companion animals: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2014, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van, T.T.; Chin, J.; Chapman, T.; Tran, L.T.; Coloe, P.J. Safety of raw meat and shellfish in Vietnam: An analysis of Escherichia coli isolations for antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojdana, D.; Sacha, P.B.; Wieczorek, P.; Czaban, B.; Michalska, A.; Jaworowska, J.; Jurczak, A.; Poniatowski, B.; Tryniszewska, E. The occurrence of blaCTX-M, blaSHV, and blaTEM genes in extended-spectrum 𝛽-lactamase-positive strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis in Poland. Int. J. Antibiot. 2014, 2014, 935842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bert, F.; Branger, C.; Lambert-Zechovsky, N. Identification of PSE and OXA β-lactamase genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using PCR–restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, L.; Dell’Amico, E.; Migliavacca, R.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Giacobone, E.; Amicosante, G.E.R.; Rossolini, G.M. Multiple CTX-M-type extended-spectrum β-lactamases in nosocomial isolates of Enterobacteriaceae from a hospital in northern Italy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4264–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasman, H.; Mevius, D.; Veldman, K.; Olesen, I.; Aarestrup, F.M. β-Lactamases among extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-resistant Salmonella from poultry, poultry products and human patients in The Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celenza, G.; Pellegrini, C.; Caccamo, M.; Segatore, B.; Amicosante, G.; Perilli, M. Spread of blaCTX-M-type and blaPER-2 β-lactamase genes in clinical isolates from Bolivian hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maynard, C.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Bekal, S.; Sanschagrin, F.; Levesque, R.C.; Brousseau, R.; Masson, L.; Larivière, S.; Harel, J. Antimicrobial resistance genes in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O149:K91 isolates obtained over a 23-year period from pigs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3214–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadollahi, P.; Akbari, M.; Soroush, S.; Taherikalani, M.; Asadollahi, K.; Sayehmiri, K. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and their encoding genes among Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from burned patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 38, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Wu, J.J.; Ko, W.C.; Tsai, S.H.; Chuang, C.L.; Wu, H.M.; Lu, Y.J.; Li, J.D. Plasmid-mediated 16S rRNA methylases conferring high-level aminoglycoside resistance in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from two Taiwanese hospitals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimand, M.; Courvalin, P.; Lambert, T. Plasmid-mediated high-level resistance to aminoglycosides in Enterobacteriaceae due to 16S rRNA methylation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frana, T.S.; Carlson, S.A.; Griffith, R.W. Relative distribution and conserovation of genes encoding aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in Salmonnella enterica serotype Typhimurium phage type DT104. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Odumosu, B.T.; Akintimehin, A.R. Occurrence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae isolates in communal water sources in Ogun State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. 2015, 16, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandvang, D.; Aarestrupp, F.M. Characterization of aminoglycoside resistance genes and class 1 integrons in porcine and bovine gentamicin-resistant Escherichia coli. Microb. Drug Resist. 2009, 6, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, R.; Kuhnert, P.; Boerlin, P. Antimicrobial resistance and resistance genes determinants in clinical Escherichia coli from different animal species in Switzerland. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 91, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassort-Bruneau, C.; Lesage-Descauses, M.; Martel, J.L.; Lafont, J.P.; Chaslus-Dancla, E. CAT III chloramphenicol resistance in Pasteurella haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolated from calves. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1996, 38, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keyes, K.; Hudson, C.; Maurer, J.J.; Thayer, S.; White, D.G.; Lee, M.D. Detection of florfenicol resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolated from sick chickens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christabel, M.; Budambula, N.; Kiiru, J.; Kariuki, S. Characterization of antibiotic resistance in environmental enteric pathogens from Kibera slum in Nairobi-Kenya. J. Bacteriol. Res. 2012, 4, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perreten, V.; Boerlin, P.A. New sulfonamide resistance gene (sul3) in Escherichia coli is widespread in the pig population of Switzerland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 44, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibreel, A.; Sköld, O. High-level resistance to trimethoprim in clinical isolates of Campylobacter jejuni by acquisition of foreign genes (dfr1 and dfr9) expressing drug-insensitive dihydrofolate reductases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 3059–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Šeputienė, V.; Povilonis, J.; Ružauskas, M.; Pavilonis, A.; Sužiedėlienė, E. Prevalence of trimethoprim resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolates of human and animal origin in Lithuania. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navia, M.M.; Ruiz, J.; Cespedes, S.J.; Vila, J. Detection of dihydrofolate reductase genes by PCR and RFLP. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 46, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robicsek, A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Sahm, D.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C. qnr prevalence in ceftazidime-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates from the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2872–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.H.; Deng, Y.T.; Zeng, Z.L.; Gao, J.H.; Chen, L.; Arakawa, Y.; Chen, Z.L. Coprevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants QepA, Qnr, and AAC(6′)-Ib-cr among 16S rRNA methylase RmtB-producing Escherichia coli isolates from pigs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2992–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.H.; Huang, C.C. Risk factor analysis for extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacter cloacae bloodstream infections in central Taiwan. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, C.; Lee, M.D.; Sanchez, S.; Hudson, C.; Phillips, B.; Register, B.; Grady, M.; Liebert, C.; Summers, A.O.; White, D.G.; et al. Incidence of class 1 and 2 integrases in clinical and commensal bacteria from livestock, companion animals, and exotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piasecki, T.; Chrząstek, K.; Wieliczko, A. Salmonella serovar spectrum associated with reptiles in Poland. Acta Vet. Brno 2014, 83, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losos, J.B.; Grrene, H.W. Ecological and evolutionary implications of diet in monitor lizards. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 35, 379–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzauskas, M.; Virgailis, M.; Špakauskas, V. Serological diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from different sources in Lithuania. Vet. Arh. 2005, 75, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zając, M.; Skarżyńska, M.; Lalak, A.; Kwit, R.; Śmiałowska-Węglińska, A.; Pasim, P.; Szulowski, K.; Wasyl, D. Salmonella in captive reptiles and their environment—Can We Tame the Dragon? Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, N.; Le Hello, S.; Weill, F.; de Thoisy, B.; Berger, F. Salmonella serotypes in reptiles and humans, French Guiana. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marin, C.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; Laso, O.; Villora-Gonzalez, J.; Vega, S. Pet Reptiles: A potential source of transmission of multidrug-resistant Salmonella. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 613718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkevičienė, L.; Klimienė, I.; Šiugždinienė, R.; Virgailis, M.; Mockeliūnas, R.; Ružauskas, M. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of multiresistant Escherichia coli in wild birds. Acta Vet. Brno 2018, 87, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Domesticated and Wild Reptile Species | |
|---|---|
| Snakes | Number |
| Grass snake (Natrix natrix) | 13 |
| California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) | 9 |
| King ratsnake (Elaphe carinata carinata) | 7 |
| Taiwan beauty ratsnake (Elaphe taeniura friesei) | 6 |
| Mexican vine snake (Oxybelis aeneus) | 6 |
| Corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus) | 5 |
| Milk snake (Lampropeltis triangulum) | 5 |
| Desert kingsnake (Lampropeltis splendida) | 5 |
| Smooth snake (Coronella austriaca) | 4 |
| Boa constrictor (Boa constrictor) | 3 |
| Brown house snake (Boaedon capensis) | 2 |
| Ball python (Python regius) | 2 |
| Western hognose snake (Heterodon nasicus) | 1 |
| Banded water snake (Nerodia fasciata) | 1 |
| Total: | 69 |
| Lizards | Number |
| Slow worm (Anguis fragilis) | 5 |
| Central bearded dragon (Pogona vitticeps) | 5 |
| Crested gecko (Correlophus ciliatus) | 4 |
| Great plated lizard (Gerrhosaurus major) | 3 |
| Frill-necked lizard (Chlamydosaurus kingii) | 2 |
| Plumed basilisk (Basiliscus plumifrons) | 2 |
| Chinese water dragon (Physignathus cocincinus) | 2 |
| Common chameleon (Chamaeleo chamaeleon) | 1 |
| Green iguana (Iguana iguana) | 1 |
| Common leopard gecko (Eublepharis macularius) | 1 |
| Total: | 26 |
| Turtles | Number |
| Central Asian tortoise (Testudo horsfieldii) | 2 |
| Total: | 2 |
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Size, bp and t (°C) | Target Gene | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaTEM-F | GAGTATTCAACATTTTCGT | 857 (50) | tem | [19] |
| blaTEM-R | ACCAATGCTTAATCAGTGA | |||
| blaSHV-F | TCGCCTGTGTATTATCTCCC | 768 (60) | shv | [20] |
| blaSHV-R | CGCAGATAAATCACCACAATG | |||
| oxa1-F | TCAACAAATCGCCAGAGAAG | 276 (55) | OXA group I | [21] |
| oxa1-R | TCCCACACCAGAAAAACCAG | |||
| oxa3-F | TTTTCTGTTGTTTGGGTTTT | 427 (52) | OXA group III | |
| oxa3-R | TTTCTTGGCTTTTATGCTTG | |||
| OXA 5 group-F | AGCCGCATATTTAGTTCTAG | 644 (56) | OXA group V | |
| OXA 5 group-R | ACCTCAGTTCCTTTCTCTAC | |||
| CTX-M-F | ATGTGCAGYACCAGTAARGT | 593 (50) | ctxM | [22] |
| CTX-M-R | TGGGTRAARTARGTSACCAGA | |||
| cmy2-F | GCACTTAGCCACCTATACGGCAG | 758 (58) | cmy | [23] |
| cmy2-R | GCTTTTCAAGAATGCGCCAGG | |||
| PER-1-F | ATGAATGTCATTATAAAAGCT | 927 (48) | per | [24] |
| PER-1-R | TTAATTTGGGCTTAGGG | |||
| PER-2-F | ATGAATGTCATCACAAAATG | 927 (49) | ||
| PER-2-R | TCAATCCGGACTCACT | |||
| tetA-F | GTGAAACCCAACATACCCC | 888 (55) | tetA | [25] |
| tetA-R | GAAGGCAAGCAGGATGTAG | |||
| tetB-F | CCTTATCATGCCAGTCTTGC | 774 (55) | tetB | |
| tetB-R | ACTGCCGTTTTTTCGCC | |||
| aadB-F | ATGGACACAACGCAGGTCGC | 534 (55) | aadB | [26] |
| aadB-R | TTAGGCCGCATATCGCGACC | |||
| aadA-F | GTGGATGGCGGCCTGAAGCC | 528 (68) | aadA | |
| aadA-R | AATGCCCAGTCGGCAGCG | |||
| rmtB-F | ATGAACATCAACGATGCCCT | 769 (55) | rmtB | [27] |
| rmtB-R | CCTTCTGATTGGCTTATCCA | |||
| armA-F | CAAATGGATAAGAATGATGTT | 774 (55) | armA | [28] |
| armA-R | TTATTTCTGAAATCCACT | |||
| aphA1-F | AAACGTCTTGCTCGAGGC | 500 (55) | aphA1 | [29] |
| aphA1-R | CAAACCGTTATTCATTCGTGA | |||
| aacA4-F | ATGACTGAGCATGACCTTGCG | 487 (55) | aacA4 | [30] |
| aacA4-R | TTAGGCATCACTGCGTGTTCG | |||
| aac(3)II-F | TGAAACGCTGACGGAGCCTC | 369 (65) | aac(3)II | [31] |
| aac(3)II-R | GTCGAACAG GTAGCACTGAG | |||
| strA-F | CCTGGTGATAACGGCAATTC | 546 (55) | strA | [32] |
| strA-R | CCAATCGCAGATAGAAGGC | |||
| strB-F | ATCGTCAAGGGATTGAAACC | 509 (55) | strB | |
| strB-R | GGATCGTAGAACATATTGGC | |||
| catII-F | ACACTTTGCCCTTTATCGTC | 495 (55) | catII | [33] |
| catII-R | TGAAAGCCATCACATACTGC | |||
| cmlA-F | TTGCAACAGTACGTGACAT | 293 (55) | cmlA | [34] |
| cmlA-R | ACACAACGTGTACAACCAG | |||
| sul1-F | TTCGGCATTCTGAATCTCAC | 822 (55) | sul1-F | [35] |
| sul1-R | ATGATCTAACCCTCGGTCTC | |||
| sul2-F | CGGCATCGTCAACATAACC | 722 (50) | sul2-F | [36] |
| sul2-R | GTGTGCGGATGAAGTCAG | |||
| sul3-F | GAGCAAGATTTTTGGAATCG | 792 (51) | sul3-F | |
| sul3-R | CATCTGCAGCTAACCTAGGGCTTTGA | |||
| Dfr1-F | ACGGATCCTGGCTGTTGGTTGGACGC | 254 (55) | dfr1 | [37] |
| Dfr1-R | CGGAATTCACCTTCCGGCTCGATGTC | |||
| Dfr5-F | GCBAAAGGDGARCAGCT | 394 (44) | dfr5 | [38] |
| Dfr5-R | TTTMCCAYATTTGATAGC | |||
| DfrA7-F | AAAATTTCATTGATTTCTGCA | 471 (44) | dfr7 | [39] |
| DfrA7-R | TTAGCCTTTTTTCCAAATCT | |||
| qnrA-F | ATTTCTCACGCCAGGATTTG | 516 (53) | qnrA | [40] |
| qnrA-R | GATCGGCAAAGGTTAGGTCA | |||
| qnrB-F | GATCGTGAAAGCCAGAAAGG | 469 (53) | qnrB | |
| qnrB-R | ACGATGCCTGGTAGTTGTCC | |||
| qnrS-F | ACGACATTCGTCAACTGCAA | 417(53) | qnrS | |
| qnrS-R | TAAATTGGCACCCTGTAGGC | |||
| qepA-F | CAGTGGACATAAGCCTGTTC | 218 (60) | qepA | [41] |
| qepA-R | CCCGAGGCATAGACTGTA | |||
| teg1-F | TTATTGCTGGGATTAGGC | 164 (55) | integrase I class | [42] |
| teg1-R | ACGGCTACCCTCTGTTATC | |||
| teg2-F | ACGACATTCGTCAACTGCAA | 233 (50) | integrase II class | [43] |
| teg2-R | TAAATTGGCACCCTGTAGGC |
| Domesticated Reptile Species | Number of Salmonella Carriers/Tested |
|---|---|
| California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) | 8 of 9 |
| Desert kingsnake (Lampropeltis splendida) | 5 of 5 |
| Mexican vine snake (Oxybelis aeneus) | 5 of 6 |
| Taiwan beauty rat snake (Elaphe taeniura friesei) | 5 of 6 |
| Corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus) | 4 of 5 |
| Milk snake (Lampropeltis triangulum) | 4 of 5 |
| King ratsnake (Elaphe carinata carinata) | 4 of 7 |
| Crested gecko (Correlophus ciliatus) | 2 of 4 |
| Boa constrictor (Boa constrictor) | 2 of 3 |
| Brown house snake (Boaedon capensis) | 2 of 2 |
| Western hognose snake (Heterodon nasicus) | 1 of 1 |
| Great plated lizard (Gerrhosaurus major) | 1 of 3 |
| Banded water snake (Nerodia fasciata) | 1 of 1 |
| Common leopard gecko (Eublepharis macularius) | 1 of 1 |
| Chinese water dragon (Physignathus cocincinus) | 1 of 2 |
| Total: | 46 of 60 |
| Wild reptile species | Number |
| Grass snake (Natrix natrix) | 3 of 13 |
| Smooth snake (Coronella austriaca) | 1 of 4 |
| Total: | 4 of 17 |
| Reptile Species | Identification by Biochemical Testing | Phenotypic Resistance | Genotypic Resistance | Serovar or Serogroup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boa constrictor (Boa constrictor) | Salmonella sub.2 | TE, CN, PX | tetA | IIIa, enterica arizonae; IIIb enterica diarizonae |
| Milk snake (Lampropeltis triangulum) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | TE, CN, C, PX | aadA, | IIIa, enterica arizonae; IIIb enterica diarizonae |
| Boa constrictor (Boa constrictor) | Salmonella sub.4 | TE, CN, C, STR, AMP, CIP | aadA, | O:8 |
| Brown house snake (Boaedon capensis) | Salmonella sub.3B | CN, STR | aadA, | Florida |
| Taiwan beauty rat snake (Elaphe taeniura friesei) | Salmonella sub.5 | CN | - | O:4 |
| Corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | CN | armA | O:65 |
| King ratsnake (Elaphe carinata carinata) | Salmonella sub.2 | FOX, CN, STR, PX | armA | O:4 |
| Crested gecko (Correlophus ciliatus) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | FOX, C | - | Sherbrooke |
| Crested gecko (Correlophus ciliatus) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | STR | - | Maiduguri |
| Desert kingsnake (Lampropeltis splendida) | Salmonella sub.I A S. enterica | FOX, TE, | tetA, tet B | O:41 |
| Mexican vine snake (Oxybelis aeneus) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | STR | - | Waycross |
| California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) | Salmonella sub.1 S. enterica | DO, TE, | tetA, tet B | Waycross |
| California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) | S. enterica subsp. S bongori V | STX, STR | dfr1 | O48, IIIa/IIIb |
| Corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus) | Salmonella group 2 S. enterica subsp. arizonae | CN, SXT, STR, AMP | armA, sul2, dfr1 | O:4 |
| Corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus) | Salmonella group2 S. enterica subsp. arizonae | STR | - | O44 IIIa/IV |
| Milk snake (Lampropeltis triangulum) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | STR | - | O:57 |
| Western hognose snake (Heterodon nasicus) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | STR | - | O:65 IIIb |
| Great plated lizard (Gerrhosaurus major) | Salmonella sub.2 | C | - | O:41 |
| California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) | Salmonella sub.2 | STR | - | O:8 |
| Banded water snake (Nerodia fasciata) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp.arizonae | STR | - | O:50 |
| Milk snake (Lampropeltis triangulum) | Salmonella sub.2 | AMP | - | O:30 |
| Common leopard gecko (Eublepharis macularius) | Salmonella sub.2 | STR | - | O:18 |
| Taiwan beauty rat snake (Elaphe taeniura friesei) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | STR | - | O:18 (K) |
| Brown house snake (Boaedon capensis) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | C | - | O:8 (C2–C3) |
| Desert kingsnake (Lampropeltis splendida) | Salmonella sub.2 | CIP | - | O:3,10 (E1) |
| King ratsnake (Elaphe carinata carinata) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | TE | tetA, tet B | O:3.10 (E1) |
| California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | FOX, TE, SXT, PX, AMP, OFX | tetA, tetB | O:1; 3.19 (E) |
| Taiwan beauty rat snake (Elaphe taeniura friesei) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | FOX, CIP, | - | O:40 (R) |
| Mexican vine snake (Oxybelis aeneus) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | TE | tetA, tetB | O:44 (V) |
| Chinese water dragon (Physignathus cocincinus) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | FOX, TE, SXT, C, STR, PX, AMP | sul2, dfr7 | O:30 |
| Reptile Species | Identification by Biochemical Testing | Phenotypic Resistance | Genotypic Resistance | Serovar or Serogroup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth snake (Coronella austriaca) | Salmonella group I | TE, STR | tetA, tetB | O:43 (U) |
| Grass snake (Natrix natrix) | Salmonella sub.3 A S. enterica subsp. arizonae | DO, FOX, TE, SXT, STR, PX, AMP | dfr1 | O:3,10 (E1), Macallen |
| Grass snake (Natrix natrix) | Salmonella sub.2 | FOX, TE, C, STR, AMP | tetA, tetB | O:18 |
| Grass snake (Natrix natrix) | Salmonella sub.2 | TE, SXT, AMP, CIP, OFX | sul2 | O:18 (K) |
| Domesticated Reptile Species | Number |
|---|---|
| California kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) | 4 |
| Corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus) | 3 |
| Milk snake (Lampropeltis triangulum) | 3 |
| Taiwan beauty rat snake (Elaphe taeniura friesei) | 3 |
| Desert kingsnake (Lampropeltis splendida) | 2 |
| Mexican vine snake (Oxybelis aeneus) | 2 |
| King ratsnake (Elaphe carinata carinata) | 2 |
| Crested gecko (Correlophus ciliatus) | 2 |
| Boa constrictor (Boa constrictor) | 2 |
| Brown house snake (Boaedon capensis) | 2 |
| Western hognose snake (Heterodon nasicus) | 1 |
| Great plated lizard (Gerrhosaurus major) | 1 |
| Banded water snake (Nerodia fasciata) | 1 |
| Common leopard gecko (Eublepharis macularius) | 1 |
| Chinese water dragon (Physignathus cocincinus) | 1 |
| Total: | 30 |
| Wild reptile species | Number |
| Grass snake (Natrix natrix) | 3 |
| Smooth snake (Coronella austriaca) | 1 |
| Total: | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merkevičienė, L.; Butrimaitė-Ambrozevičienė, Č.; Paškevičius, G.; Pikūnienė, A.; Virgailis, M.; Dailidavičienė, J.; Daukšienė, A.; Šiugždinienė, R.; Ruzauskas, M. Serological Variety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Reptiles. Biology 2022, 11, 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060836
Merkevičienė L, Butrimaitė-Ambrozevičienė Č, Paškevičius G, Pikūnienė A, Virgailis M, Dailidavičienė J, Daukšienė A, Šiugždinienė R, Ruzauskas M. Serological Variety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Reptiles. Biology. 2022; 11(6):836. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060836
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerkevičienė, Lina, Česlova Butrimaitė-Ambrozevičienė, Gerardas Paškevičius, Alma Pikūnienė, Marius Virgailis, Jurgita Dailidavičienė, Agila Daukšienė, Rita Šiugždinienė, and Modestas Ruzauskas. 2022. "Serological Variety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Reptiles" Biology 11, no. 6: 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060836
APA StyleMerkevičienė, L., Butrimaitė-Ambrozevičienė, Č., Paškevičius, G., Pikūnienė, A., Virgailis, M., Dailidavičienė, J., Daukšienė, A., Šiugždinienė, R., & Ruzauskas, M. (2022). Serological Variety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Reptiles. Biology, 11(6), 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060836








