Urinary Tract Infections Impair Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
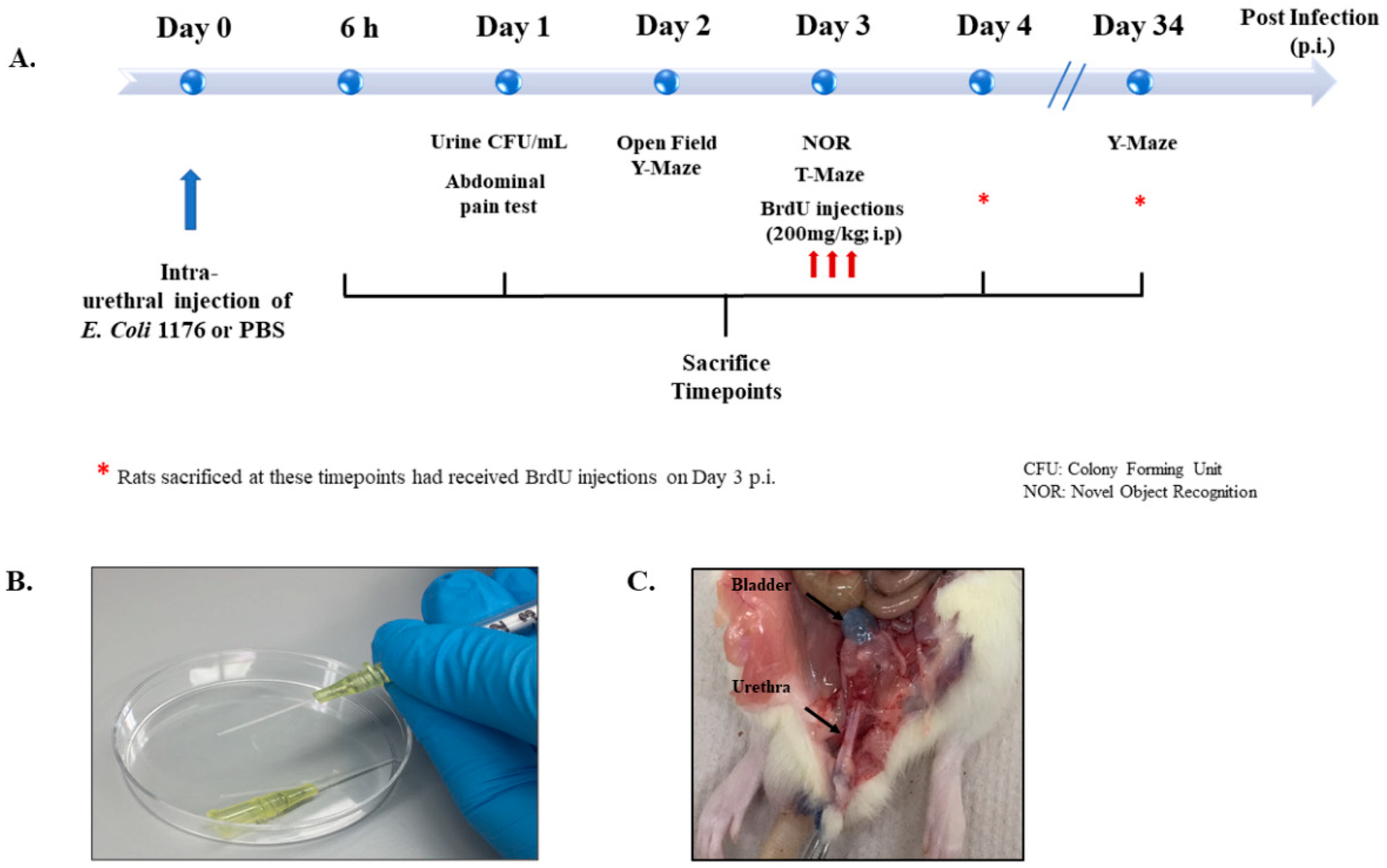
2.2. Experimental Groups and Design
2.3. Urinary Tract Infection
2.4. Treatment Regimens with the Antibiotics (Fosfomycin) and the NSAIDs (Piroxicam)
2.5. Behavioral Tests
2.5.1. Thermal Sensitivity Test
2.5.2. Open Field
2.5.3. Novel-Object-Recognition (NOR)
2.5.4. Y-Maze Test
2.5.5. T-Maze Test
2.6. BrdU Injections
2.7. Sacrifice and Tissue Collection
2.8. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.9. Cell Counting and Confocal Microscopy
2.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Assay
2.11. Conventional PCR
2.12. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Urine Infection and Increased Levels of Cytokines Following UTI
3.2. UTI Decreased Proliferation of Neural Stem Cells in the DG at Four Days Post Infection
3.3. UTI Decreased Neurogenesis in the DG at 34 Days Post Infection
3.4. Treatment with the Antibiotic Drug Fosfomycin Decreased Basal Levels of the Proliferation of NSCs
3.5. Treatment with the Anti-Inflammatory Drug Piroxicam Did Not Alter the Number of NSCs in the Sham Group and Rats with a UTI
3.6. UTI Elevated the mRNA Expression of Il-1β and Decreased That of Bdnf, Ngf, and Fgf2
3.7. UTI Did Not Induce Significant Changes in Microglial and Astrocytic Cells
3.8. Increased Heat Sensitivity in Urinary Tract Infected Rats
3.9. Rats with a UTI Displayed Normal Spontaneous Locomotor Activity and Exploratory Behavior
3.10. Rats with a UTI Had a Similar Tendency to Explore a Novel Object to Sham Rats
3.11. Rats with a UTI Spent Less Time Exploring the Novel Arm in the Y-Maze Test
3.12. Rats with a UTI Had Less Tendency to Spontaneously Alternate in the T-Maze Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuhn, H.G.; Toda, T.; Gage, F.H. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: A Coming-of-Age Story. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10401–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, T.; Parylak, S.L.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, T.; Gage, F.H. Review: Adult neurogenesis contributes to hippocampal plasticity. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, B.; Chamaa, F.; Al-Chaer, E.D.; Saadé, N.E.; Abou-Kheir, W. Intranigral Injection of Endotoxin Suppresses Proliferation of Hippocampal Progenitor Cells. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chamaa, F.; Bitar, L.; Darwish, B.; Saade, N.E.; Abou-Kheir, W. Intracerebroventricular injections of endotoxin (ET) reduces hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 315, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, G.; Moriya, T.; Inui, F.; Katura, T.; Nakahata, N. Involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-induced impairment of the newborn cell survival in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 2008, 155, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Zhao, C. Peripheral and Central Nervous System Immune Response Crosstalk in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, J.R.; Carranza, A.F.; Tully, L.M.; Knodt, A.R.; Jiang, J.; Irwin, M.R.; Hostinar, C.E. Associations between peripheral inflammation and resting state functional connectivity in adolescents. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 95, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, T.D.; Ware, L.B.; Bernard, G.R.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Thompson, J.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Jackson, J.C.; Dittus, R.S.; Ely, E.W. Associations of markers of inflammation and coagulation with delirium during critical illness. Intensiv. Care Med. 2012, 38, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonis, S.; Pechnick, R.N.; Ljubimov, V.A.; Mahgerefteh, M.; Wawrowsky, K.; Michelsen, K.S.; Chesnokova, V. Chronic intestinal inflammation alters hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safavynia, S.A.; Goldstein, P.A. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction: Moving from Hypothesis to Treatment. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnokova, V.; Pechnick, R.N.; Wawrowsky, K. Chronic peripheral inflammation, hippocampal neurogenesis, and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 58, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valero, J.; Mastrella, G.; Eneiva, I.; Sã¡nchez, S.; Malva, J.O. Long-term effects of an acute and systemic administration of LPS on adult neurogenesis and spatial memory. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Hou, Y.; Leverenz, J.B.; Kallianpur, A.; Mehra, R.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Pieper, A.A.; Jehi, L.; et al. Network medicine links SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 infection to brain microvascular injury and neuroinflammation in dementia-like cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnefeesi, Y.; Siegel, A.; Lui, L.M.W.; Teopiz, K.M.; Ho, R.C.M.; Lee, Y.; Nasri, F.; Gill, H.; Lin, K.; Cao, B.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 621773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Lu, S.; Chen, J.; Wei, N.; Wang, D.; Lyu, H.; Shi, C.; Hu, S. The landscape of cognitive function in recovered COVID-19 patients. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 129, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, S.; Bowden, A.; Sundvall, P.-D.; Gunnarsson, R. The scientific evidence for a potential link between confusion and urinary tract infection in the elderly is still confusing—A systematic literature review. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkelund, K.B.; Larsson, S.; Gustafson, L.; Andersson, E. The Organic Brain Syndrome (OBS) scale: A systematic review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juthani-Mehta, M.; Quagliarello, V.; Perrelli, E.; Towle, V.; Van Ness, P.H.; Tinetti, M. Clinical Features to Identify Urinary Tract Infection in Nursing Home Residents: A Cohort Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balogun, S.A.; Philbrick, J.T. Delirium, a Symptom of UTI in the Elderly: Fact or Fable? A Systematic Review. Can. Geriatr. J. 2014, 17, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juthani-Mehta, M.; Drickamer, M.A.; Towle, V.; Zhang, Y.; Tinetti, M.E.; Quagliarello, V.J. Nursing Home Practitioner Survey of Diagnostic Criteria for Urinary Tract Infections. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1986–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerejeira, J.; Lagarto, L.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B. The Immunology of Delirium. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.H.J.; Miller, B.J. Beyond Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) and Delirium. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2015, 21, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.; Castillo-Pino, E. An introduction to the epidemiology and burden of urinary tract infections. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2019, 11, 1756287219832172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poeppl, W.; Lingscheid, T.; Bernitzky, D.; Donath, O.; Reznicek, G.; Zeitlinger, M.; Burgmann, H. Assessing Pharmacokinetics of Different Doses of Fosfomycin in Laboratory Rats Enables Adequate Exposure for Pharmacodynamic Models. Pharmacology 2014, 93, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogue, J.M.; Lee, J.; Marchaim, D.; Yee, V.; Zhao, J.J.; Chopra, T.; Lephart, P.; Kaye, K.S. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Colistin-Associated Nephrotoxicity in a Large Academic Health System. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ordooei Javan, A.; Shokouhi, S.; Sahraei, Z. A review on colistin nephrotoxicity. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaa, F.; Bahmad, H.F.; Makkawi, A.-K.; Chalhoub, R.M.; Al-Chaer, E.D.; Bikhazi, G.B.; Nahas, Z.; Abou-Kheir, W. Nitrous Oxide Induces Prominent Cell Proliferation in Adult Rat Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, C.J.; Blocka, K.L.N.; Ross, S.G.; Verbeeck, R.K. Effects of age and sex on piroxicam disposition. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1985, 37, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Wooten, M.C. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 96, e52434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sestakova, N.; Puzserova, A.; Kluknavsky, M.; Bernatova, I. Determination of motor activity and anxiety-related behaviour in rodents: Methodological aspects and role of nitric oxide. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2013, 6, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chamaa, F.; Darwish, B.; Nahas, Z.; Al-Chaer, E.D.; Saadé, N.E.; Abou-Kheir, W. Long-term stimulation of the anteromedial thalamus increases hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial reference memory in adult rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 402, 113114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, R.M.J.; Rawlins, J.N.P. T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamaa, F.; Sweidan, W.; Nahas, Z.; Saade, N.; Abou-Kheir, W. Thalamic Stimulation in Awake Rats Induces Neurogenesis in the Hippocampal Formation. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, H.J.G.; Jensen, E.B.V.; Kieu, K.; Nielsen, J. The efficiency of systematic sampling in stereology-reconsidered. J. Microsc. 1999, 193, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chamaa, F.; Chebaro, M.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Saadeh, R.; Jabbur, S.J.; Saadé, N.E. Transcriptional expression of inflammatory mediators in various somatosensory relay centers in the brain of rat models of peripheral mononeuropathy and local inflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 297, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadé, N.E.; Massaad, C.A.; Ochoa-Chaar, C.I.; Jabbur, S.J.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Atweh, S.F. Upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and nerve growth factor by intraplantar injection of capsaicin in rats. J. Physiol. 2002, 545, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Salas, M.S.; Pérez-Domínguez, M.; Zepeda, A. Systemic Inflammation Impairs Proliferation of Hippocampal Type 2 Intermediate Precursor Cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eu, W.Z.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, W.-T.; Wu, K.-Y.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Cheng, S.-J.; Carter, R.N.; Huang, G.-J. The effect of nerve growth factor on supporting spatial memory depends upon hippocampal cholinergic innervation. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, M.E.; Ikezu, T. Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Signaling in Neurogenesis and Neurodegeneration. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stevens, H.E.; Jiang, G.Y.; Schwartz, M.L.; Vaccarino, F.M. Learning and Memory Depend on Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2 Functioning in Hippocampus. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, H.; Pitossi, F.; Balschun, D.; Wagner, A.; del Rey, A.; Besedovsky, H.O. A neuromodulatory role of interleukin-1β in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7778–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.-Y.; Kang, M.-J.; Han, J.-S. Interleukin-1 beta promotes neuronal differentiation through the Wnt5a/RhoA/JNK pathway in cortical neural precursor cells. Mol. Brain 2018, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewett, S.J.; Jackman, N.A.; Claycomb, R.J. Interleukin-1β in Central Nervous System Injury and Repair. Eur. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 1, 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Takemiya, T.; Fumizawa, K.; Yamagata, K.; Iwakura, Y.; Kawakami, M. Brain Interleukin-1 Facilitates Learning of a Water Maze Spatial Memory Task in Young Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labrousse, V.F.; Costes, L.; Aubert, A.; Darnaudery, M.; Ferreira, G.; Amédée, T.; Layé, S. Impaired Interleukin-1β and c-Fos Expression in the Hippocampus Is Associated with a Spatial Memory Deficit in P2X7 Receptor-Deficient Mice. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hein, A.M.; Stasko, M.R.; Matousek, S.B.; Scott-McKean, J.; Maier, S.F.; Olschowka, J.A.; Costa, A.; O’Banion, M.K. Sustained hippocampal IL-1β overexpression impairs contextual and spatial memory in transgenic mice. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, A.; Wu, M.; Shaftel, S.; Graham, K.; O’Banion, M.K. Sustained expression of interleukin-1β in mouse hippocampus impairs spatial memory. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibertini, M.; Newton, C.; Friedman, H.; Klein, T. Spatial Learning Impairment in Mice Infected with Legionella pneumophila or Administered Exogenous Interleukin-1-β. Brain, Behav. Immun. 1995, 9, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, C.; El-Okl, M.; Williams, A.L.; Cunningham, C.; Wilcockson, D.; Perry, V.H. Systemic infection, interleukin 1β, and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 788–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCusker, R.H.; Kelley, K.W. Immune–neural connections: How the immune system’s response to infectious agents influences behavior. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haddad, J.J.; Saadé, N.E.; Safieh-Garabedian, B. Cytokines and neuro–immune–endocrine interactions: A role for the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal revolving axis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 133, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, H.A.; Glover, L.R. Adult Neurogenesis: Beyond Learning and Memory. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 53–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Mutso, A.A.; Centeno, M.V.; Kan, L.; Wu, M.; Levinstein, M.; Banisadr, G.; Gobeske, K.T.; Miller, R.J.; Radulovic, J.; et al. Role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in persistent pain. Pain 2016, 157, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkis, R.; Saadé, N.; Atweh, S.; Jabbur, S.; Al-Amin, H. Chronic dizocilpine or apomorphine and development of neuropathy in two rat models I: Behavioral effects and role of nucleus accumbens. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 228, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M. Chronic pain and adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Translational implications from preclinical studies. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudick, C.N.; Billips, B.K.; Pavlov, V.I.; Yaggie, R.E.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Klumpp, D.J. Host-Pathogen Interactions Mediating Pain of Urinary Tract Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosen, J.; Klumpp, D.J. Mechanisms of pain from urinary tract infection. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, T.; Yifa, R.; Amer, M.; Krot, M.; Boshnak, N.; Ben-Shaanan, T.L.; Azulay-Debby, H.; Zalayat, I.; Avishai, E.; Hajjo, H.; et al. Insular cortex neurons encode and retrieve specific immune responses. Cell 2021, 184, 5902–5915.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F. Implications of immune-to-brain communication for sickness and pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7710–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, E.J.; Arms, L.; Vizzard, M.A. The Role(s) of Cytokines/Chemokines in Urinary Bladder Inflammation and Dysfunction. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 120525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.; Lorenzetti, B.; Poole, S.; Ferreira, S. Interleukin-8 as a mediator of sympathetic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 104, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, G.; Galdi, P.; Cabez, M.B.; Borbye-Lorenzen, N.; Stoye, D.Q.; Lamb, G.J.; Evans, M.J.; Quigley, A.J.; Thrippleton, M.J.; Skogstrand, K.; et al. Interleukin-8 dysregulation is implicated in brain dysmaturation following preterm birth. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2020, 90, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denninger, J.K.; Smith, B.M.; Kirby, E.D. Novel Object Recognition and Object Location Behavioral Testing in Mice on a Budget. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 141, e58593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, C.H.; Lee, A.Y.; Shin, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.G.; Cho, E.J. Comparison of the effect of three licorice varieties on cognitive improvementviaan amelioration of neuroinflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2018, 12, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, G.; Frenkel, C.; Entzian, W. Pharmacokinetic aspects of cerebrospinal fluid penetration of fosfomycin. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 1985, 5, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Tsegka, K.G.; Voulgaris, G.L.; Kyriakidou, M.; Falagas, M.E. Intravenous fosfomycin for the treatment of patients with central nervous system infections: Evaluation of the published evidence. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, M.R.; Vaughn, V.M.; Mann, J.; Townsend, W.; Chopra, V.; Patel, P.K. Is Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Therapy Non-Inferior to Antibiotic Therapy in Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections: A Systematic Review. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.-G.; Zhou, H.-J.; Huang, W.-X.; Jia, B. Efficacy of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs for Treatment of Uncomplicated Lower Urinary Tract Infections in Women: A Meta-analysis. Infect. Microbes Dis. 2020, 2, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, C.A.; McColl, A.; Cavanagh, J.; Graham, G.J. Peripheral inflammation is associated with remote global gene expression changes in the brain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]










| Time Point of Sacrifice | Groups/Treatments |
|---|---|
| 6 and 24 h post infection | UTI and sham (n = 5 each) |
| Day 4 post infection | UTI and sham (n = 9 each) Treatment with Piroxicam; UTI and sham (n = 5 each) Treatment with Fosfomycin; UTI and sham (n = 5 each) |
| Day 34 post infection | UTI (n = 6) and sham (n = 5) |
| Target Gene | Conventional PCR Primer Sequence (5′ 3′) |
|---|---|
| blaNDM-5 | F: 5′-GGCCAGCAAATGGAAACTGG-3′ R: 5′-CAAACCGTTGGAAGCGACTG-3′ |
| Rattus Norvegicus Primers | Sequence (5′->3′) | Product Length |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | F: TCACCATCTTCCAGGAGCGA R: GGCGGAGATGATGACCCTTT | 149 |
| IL-1β | F: AGGCTGACAGACCCCAAAAG R: GGTCGTCATCATCCCACGAG | 264 |
| IL-6 | F: ACAAGTCCGGAGAGGAGACT R: ACAGTGCATCATCGCTGTTC | 167 |
| Bdnf | F: CTCCGCCATGCAATTTCCAC R: CAGCCTTCATGCAACCGAAG | 279 |
| Ngf | F: CATCGCTCTCCTTCACAGAGTT R: TCTGTGTACGGTTCTGCCTG | 222 |
| Fgf2 | F: AGGATCCCAAGCGGCTCTAC R: TACCGGTTCGCACACACTC | 166 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darwish, B.; Chamaa, F.; Awada, B.; Lawand, N.; Saadé, N.E.; Abou Fayad, A.G.; Abou-Kheir, W. Urinary Tract Infections Impair Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Biology 2022, 11, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060891
Darwish B, Chamaa F, Awada B, Lawand N, Saadé NE, Abou Fayad AG, Abou-Kheir W. Urinary Tract Infections Impair Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Biology. 2022; 11(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarwish, Batoul, Farah Chamaa, Bassel Awada, Nada Lawand, Nayef E. Saadé, Antoine G. Abou Fayad, and Wassim Abou-Kheir. 2022. "Urinary Tract Infections Impair Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis" Biology 11, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060891
APA StyleDarwish, B., Chamaa, F., Awada, B., Lawand, N., Saadé, N. E., Abou Fayad, A. G., & Abou-Kheir, W. (2022). Urinary Tract Infections Impair Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Biology, 11(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060891







