Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect and Cytoplasmic Irradiation Studies with Microbeams
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Non-Target Effects
2.1. Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect
2.2. Cytoplasmic Irradiation
3. Current Development of Microbeams
4. Studies of Non-Target Effects with Microbeams
4.1. Bystander Effect Observed with Microbeam Experiments
4.2. Cytoplasmic Irradiation with Microbeams
4.3. Mechanistic Studies of Non-Target Effect with Microbeams
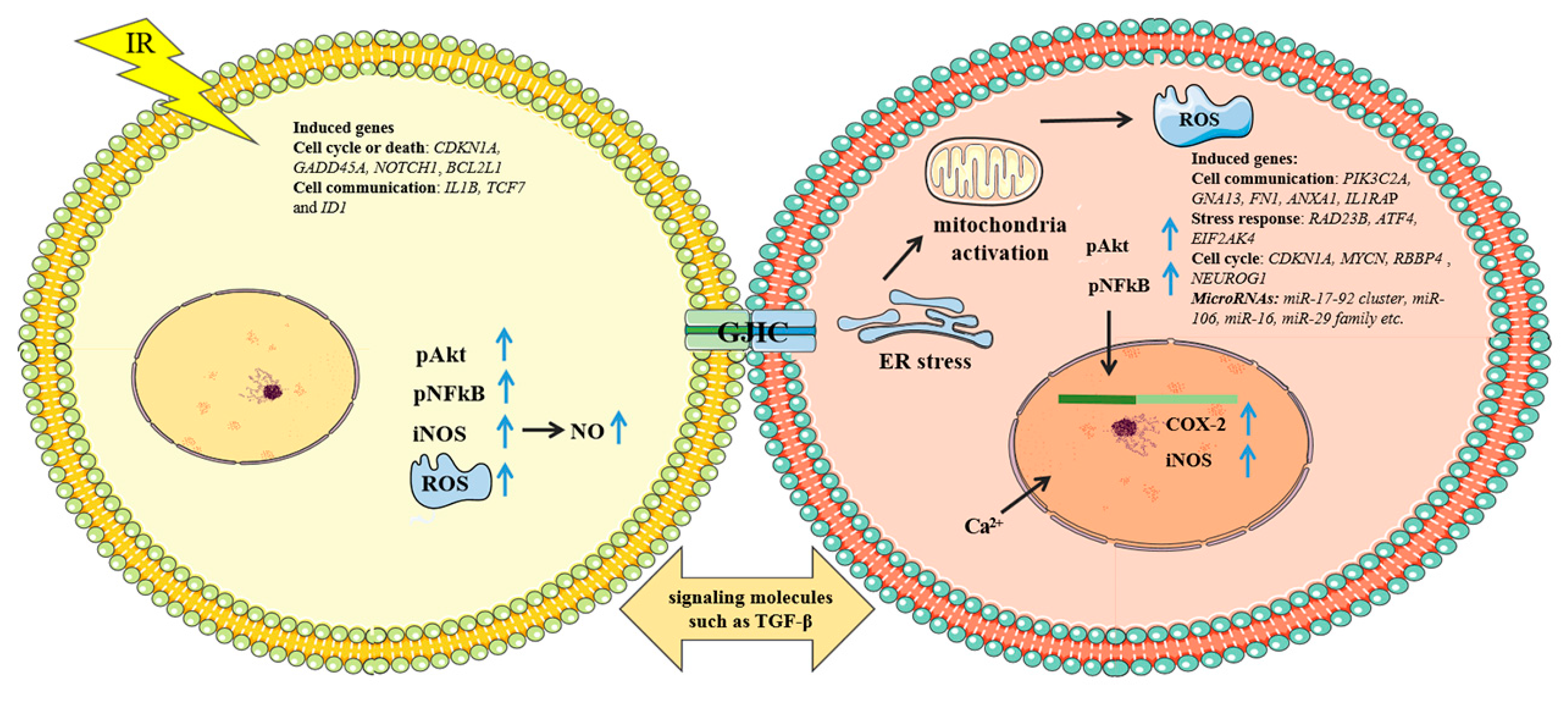
4.3.1. Mechanisms of Bystander Effect Induced by Microbeam Irradiation
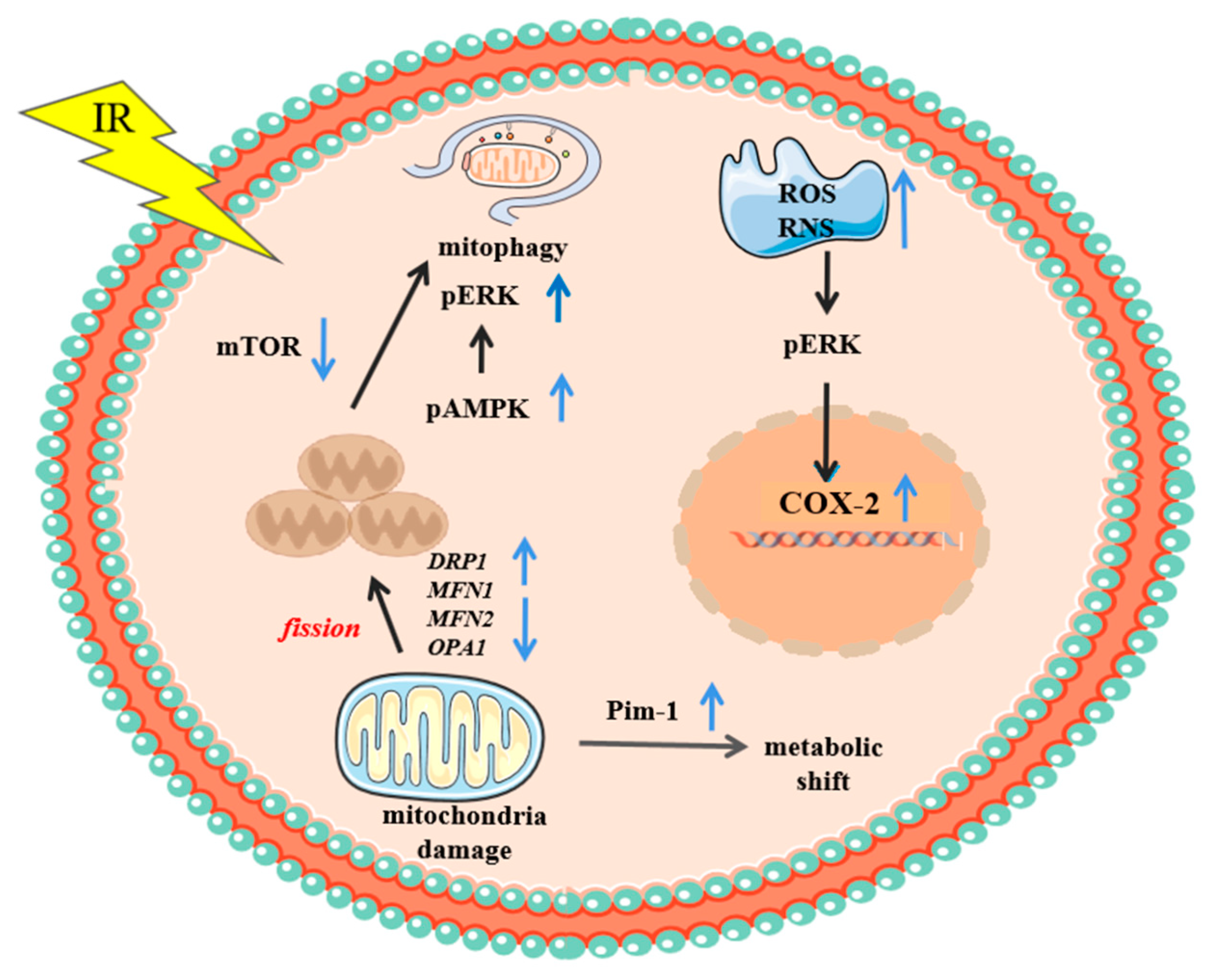
4.3.2. Mechanisms of Effects Derived from Cytoplasmic Irradiation
5. Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daguenet, E.; Louati, S.; Wozny, A.S.; Vial, N.; Gras, M.; Guy, J.B.; Vallard, A.; Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C.; Magné, N. Radiation-induced bystander and abscopal effects: Important lessons from preclinical models. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, T.K.; Zhou, H.; Ivanov, V.N.; Hong, M.; Lieberman, H.B.; Brenner, D.J.; Amudson, S.A.; Geard, C.R. Mechanism of radiation-induced bystander effects: A unifying model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Hong, M.; Chai, Y.; Hei, T.K. Consequences of cytoplasmic irradiation: Studies from microbeam. J. Radiat. Res. 2009, 50, A59–A65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagasawa, H.; Little, J.B. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges by extremely low doses of alpha-particles. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 6394–6396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pouget, J.P.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Ravanat, J.L. Targeted and off-target (bystander and abscopal) effects of radiation therapy: Redox mechanisms and risk/benefit analysis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1447–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Grabham, P.; Nie, J.; Balajee, A.S.; Zhou, H.; Hei, T.K.; Geard, C.R. Intrachromosomal changes and genomic instability in site-specific microbeam-irradiated and bystander human-hamster hybrid cells. Radiat. Res. 2012, 177, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, C.; Furusawa, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Funayama, T.; Wada, S. Bystander effect induced by counted high-LET particles in conflfluent human fifibroblasts: A mechanistic study. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, I.; Schwartz, J.L.; Stewart, R.D.; Emery, R.; Joiner, M.C.; Tucker, J.D. Neutron exposures in human cells: Bystander effect and relative biological effectiveness. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Millán, J.; Katz, I.S.S.; de Araujo Farias, V.; Linares-Fernánde, J.L.; López-Peñalver, J.; Ortiz-Ferrón, G.; Ruiz-Ruiz, C.; Oliver, F.J.; de Almodóvar, J.M.R. The importance of bystander effects in radiation therapy in melanoma skin-cancer cells and umbilical-cord stromal stem cells. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 102, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Nagase, K.; Aoki, S.; Udo, K.; Tobu, S.; Rikitake-Yamamoto, M.; Kubota, M.; Narita, T.; Noguchi, M. Bystander effects induced by the interaction between urothelial cancer cells and irradiated adipose tissue-derived stromal cells in urothelial carcinoma. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Kaminaga, K.; Kanari, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Yokoya, A. Three-dimensional culture of HeLa-FUCCI cells for study of bystander cell-cycle effect of high LET particles. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, i120–i121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widel, M.; Przybyszewski, W.M.; Cieslar-Pobuda, A.; Saenko, Y.V.; Rzeszowska Wolny, J. Bystander normal human fifibroblasts reduce damage response in radiation targeted cancer cells through intercellular ROS level modulation. Mutat. Res. 2012, 731, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.A.; Stevens, D.L.; Kadhim, M.; Blake-James, M.; Mill, A.J.; Goodhead, D.T. Experimental techniques for studying bystander effects in vitro by high and low-LET ionising radiation. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2006, 122, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.J.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Xu, A.; Waldren, C.A.; Geard, C.R.; Yu, Z.; Hei, T.K. Targeted cytoplasmic irradiation with alpha particles induces mutations in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4959–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Davidson, M.M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Walker, W.F.; Hei, T.K. Cytoplasmic irradiation results in mitochondrial dysfunction and DRP1-dependent mitochondrial fission. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6700–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Wuu, Y.R.; Davidson, M.M.; Hei, T.K. Targeted cytoplasmic irradiation and autophagy. Mutat. Res. 2017, 806, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hei, T.K. Focus small to find big-the microbeam story. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, S.A. 50 Years of the radiological research accelerator facility (RARAF). Radiat. Res. 2017, 187, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://www.crr.columbia.edu/raraf (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Merchant, M.; Jeynes, J.; Grime, G.; Palistin, V.; Tullis, I.; Barber, P.R.; Vojnovic, B.; Webb, R.P.; Kirkby, K.J. A focused scanning vertical beam for charged particle irradiation of living cells with single counted particles. Radiat. Res. 2012, 178, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funayama, T.; Wada, S.; Yokota, Y.; Fukamoto, K.; Sakashita, T.; Taguchi, M.; Kakizaki, T.; Hamada, N.; Suzuki, M.; Furusawa, Y.; et al. Heavy-ion microbeam system at JAEA-Takasaki for microbeam biology. J. Radiat. Res. 2008, 49, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barberet, P.; Heiss, M.; Du, G.; Fisher, B.E.; Taucher-Scholz, G. The GSI heavy ion microbeam: A tool for the investigation of cellular response to high LET radiations. Acta Phys. Pol. Ser. A 2006, 10950, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, G.A.; Siebenwirth, C.; Drexler, S.E.; Girst, S.; Greubel, C.; Dollinger, G.; Friedl, A.A. Live cell imaging at the Munich ion microbeam SNAKE—A status report. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, L.; Du, G.; Guo, J.; Wu, R.; Song, M.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, G. Focusing gigaelectronvolt heavy ions to micrometers at the Institute of Modern Physics. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 055113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barberet, P.; Seznec, H. Advances in microbeam technologies and applications to radiation biology. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 166, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prise, K.M.; Belyakov, O.V.; Folkard, M.; Michael, B.D. Studies of bystander effects in human fibroblasts using a charged particle microbeam. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1998, 74, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Waldren, C.A.; Vannais, D.; Hall, E.J.; Hei, T.K. Induction of a bystander mutagenic effect of alpha particles in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2099–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swant, S.G.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Geard, C.R.; Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. The bystander effect in radiation oncogenesis; Trans-formation in C3HT1/2 cells in vitro can be initiated in the un-irradiated neighbors of irradiated cells. Radiat. Res. 2001, 156, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminaga, K.; Noguchi, M.; Narita, A.; Hattori, Y.; Usami, N.; Yokoya, A. Cell cycle tracking for irradiated and unirradiated bystander cells in a single colony with exposure to a soft X-ray microbeam. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyng, F.M.; Maguire, P.; Kilmurray, N.; Mothersill, C.; Shao, C.; Folkard, M.; Prise, K.M. Apoptosis is initiated in human keratinocytes exposed to signalling factors from microbeam irradiated cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2006, 82, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Konishi, T.; Oikawa, M.; Pandey, B.N. Damaging and protective bystander cross-talk between human lung cancer and normal cells after proton microbeam irradiation. Mutat. Res. 2014, 763–764, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyakov, O.C.; Mithcll, S.A.; Parikh, D.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Marino, S.A.; Amundson, S.A.; Geard, C.R.; Brenner, D.J. Biological effects in unirradiated human tissue induced by radiation damage up to 1 mm away. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14203–14208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sedelnikova, O.A.; Nakamura, A.; Kovalchuk, O.; Koturbash, I.; Michell, S.A.; Marino, S.A.; Brenner, D.J.J.; Bonner, W.M. DNA double-strand breaks form in bystander cells after microbeam irradiation of three-dimensional human tissue models. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, T.; Dazai, K.; Sakashita, T.; Funayama, T.; Wada, S.; Hamada, N.; Kakizaki, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Higashitani, A. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans germline cells following heavy-ion microbeam irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2006, 82, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, A.; Pockck, R.D.J.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Brenner, D.J. Microbeam irradiation of the C. elegans nematode. J. Radiat. Res. 2009, 50, A49–A54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Sun, J.; Bian, P.; Chen, L.; Zhan, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, A.; Wang, Y.; Hei, T.K.; Wu, L. Radiation-induced bystander signaling from somatic cells to germ cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. Radiat. Res. 2013, 180, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, M.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Smilenov, L.B.; Kleiman, N.J.; Young, E.; Ponnayia, B.; Brenner, D.J. A mouse ear model for bystander studies induced by microbeam irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2015, 184, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, T.; Kamahori, M.; Nagata, K.; Watanabe-Asaka, T.; Suzuki, M.; Funayma, T.; Mitani, H.; Oda, S. Abscopal activation of microglia in embryonic fish brain following targeted irradiation with heavy-ion microbeam. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Palom, C.; Schültke, E.; Bräuer-Krisch, E.; Laissue, J.A.; Blattmann, H.; Seymour, C.; Mothersil, C. Investigation of abscopal and bystander effects in immunocompromised mice after exposure to pencilbeam and microbeam. Health Phys. 2016, 111, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dendy, P.P.; Smith, C.L. Effects of DNA synthesis of localized irradiation of cells in tissue culture by (i) a U.V. microbeam and (ii) an α-particle microbeam. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1964, 160, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T.; Kobayashi, A.; Ahmad, T.A.F.T.; Wang, J. Enhanced DNA double strand break repair triggered by microbeam irradiation induced cytoplasmic damage. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 9, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminaga, K.; Hamada, R.; Usami, N.; Suzuki, K.; Yokoya, A. Targeted nuclear irradiation with an X-ray microbeam enhances total JC-1 fluorescence from mitochondria. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wuu, Y.-R.; Zou, S.; Hei, T.K. Cytoplasmic irradiation induces metabolic shift in human small airway epithelial cells via activation of Pim-1 kinase. Radiat. Res. 2017, 187, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, C.; Folkard, M.; Michael, B.D.; Prise, K.M. Targeted cytoplasmic irradiation induces bystander responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13495–13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tartier, L.; Gilchrist, S.; Burdak-Rothkamm, S.; Folkard, M.; Prise, K.M. Cytoplasmic irradiation induces mitochondrial-dependent 53BP1 protein relocalization in irradiated and bystander cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5872–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hei, T.K.; Zhou, H.; Chai, Y.; Ponnaiya, B.; Ivanov, V.N. Radiation induced non-targeted response: Mechanism and potential clinical implications. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 4, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autsavapromporn, N.; Suzuki, M.; Funayam, T.; Usami, N.; Plante, I.; Yokota, Y.; Mutou, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Gap junction communication and the propagation of bystander effects induced by microbeam irradiation in human fibroblast cultures: The impact of radiation quality. Radiat. Res. 2013, 180, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Autsavapromporn, N.; Kobayashi, A.; Liu, C.; Jaikang, C.; Tengku Ahmad, T.A.; Oikawa, M.; Konishi, T. Hypoxia and proton microbeam: Role of gap junction intercellular communication in inducing bystander responses on human lung cancer cells and normal Cells. Radiat. Res. 2022, 197, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autsavapromporn, N.; Liu, C.; Kobayashi, A.; Tengku Ahmad, T.A.F.; Oikawa, M.; Dukaew, N.; Wang, J.; Wongnoppavichb, A.; Konishi, T. Emerging role of secondary bystander effects induced by fractionated proton microbeam radiation. Radiat. Res. 2019, 191, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Lyng, F.M.; Folkard, M.; Prise, K.M. Calcium fluxes modulate the radiation-induced bystander responses in targeted glioma and fibroblast cells. Radiat. Res. 2006, 166, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ivanov, V.N.; Lien, Y.C.; Davidson, M.; Hei, T.K. Mitochondrial function and nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated signaling in radiation-induced bystander effects. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomita, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Funayama, T.; Yokota, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Maeda, M.; Kobayashi, Y. Nitric oxide-mediated bystander signal transduction induced by heavy-ion microbeam irradiation. Life Sci. Space Res. 2015, 6, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Tu, W.; He, M.; Fu, J.; Kobayashi, A.; Konishi, T.; Shao, C. Role of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrion in proton microbeam radiation-induced bystander effect. Radiat. Res. 2020, 193, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnaiya, B.; Jenkins-Baker, G.; Randers-Pherson, G.; Geard, C.R. Quantifying a bystander response following microbeam irradiation using single-cell RT-PCR analyses. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakawa, M.; Hamada, N.; Imadome, K.; Funayama, T.; Sakashita, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Imai, T. Expression profiles are different in carbon ion-irradiated normal human fibroblasts and their bystander cells. Mutat. Res. 2008, 642, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalchuk, O.; Zemp, F.J.; Filkowski, J.N.; Altamirano, A.M.; Dickey, J.S.; Jenkins-Baker, G.; Marino, S.A.; Brenner, D.J.; Bonner, W.M.; Sedelnikova, O.A. MicroRNAome changes in bystander three-dimensional human tissue models suggest priming of apoptotic pathways. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, M.; Xu, A.; Zhou, H.; Wu, L.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Santella, R.M.; Yu, Z.; Hei, T.K. Mechanism of genotoxicity induced by targeted cytoplasmic irradiation. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Folkard, M.; Prise, K.M. Role of TGF-β1 and nitric oxide in the bystander response of irradiated glioma cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Hong, M. Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect and Cytoplasmic Irradiation Studies with Microbeams. Biology 2022, 11, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070945
Zhang Z, Li K, Hong M. Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect and Cytoplasmic Irradiation Studies with Microbeams. Biology. 2022; 11(7):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070945
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ziqi, Kui Li, and Mei Hong. 2022. "Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect and Cytoplasmic Irradiation Studies with Microbeams" Biology 11, no. 7: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070945
APA StyleZhang, Z., Li, K., & Hong, M. (2022). Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect and Cytoplasmic Irradiation Studies with Microbeams. Biology, 11(7), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070945





