Lipid Messenger Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate Is Increased by Both PPARα Activators and Inhibitors: Relevance for Intestinal Cell Differentiation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. In-Cell ELISA (ICE)
2.3. Multiplex Immunofluorescent Staining
2.4. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Fenofibrate, WY-14643 and GW6471 on Levels of Lipid Messenger PIP2 in Colorectal Carcinoma HT-29 and Caco2 Cell Lines
3.2. Effect of Fenofibrate, WY-14643 and GW6471 on Expression of PIP5K1C, PI3K (p85/p55) and PTEN in Colorectal Carcinoma HT-29 and Caco2 Cell Lines
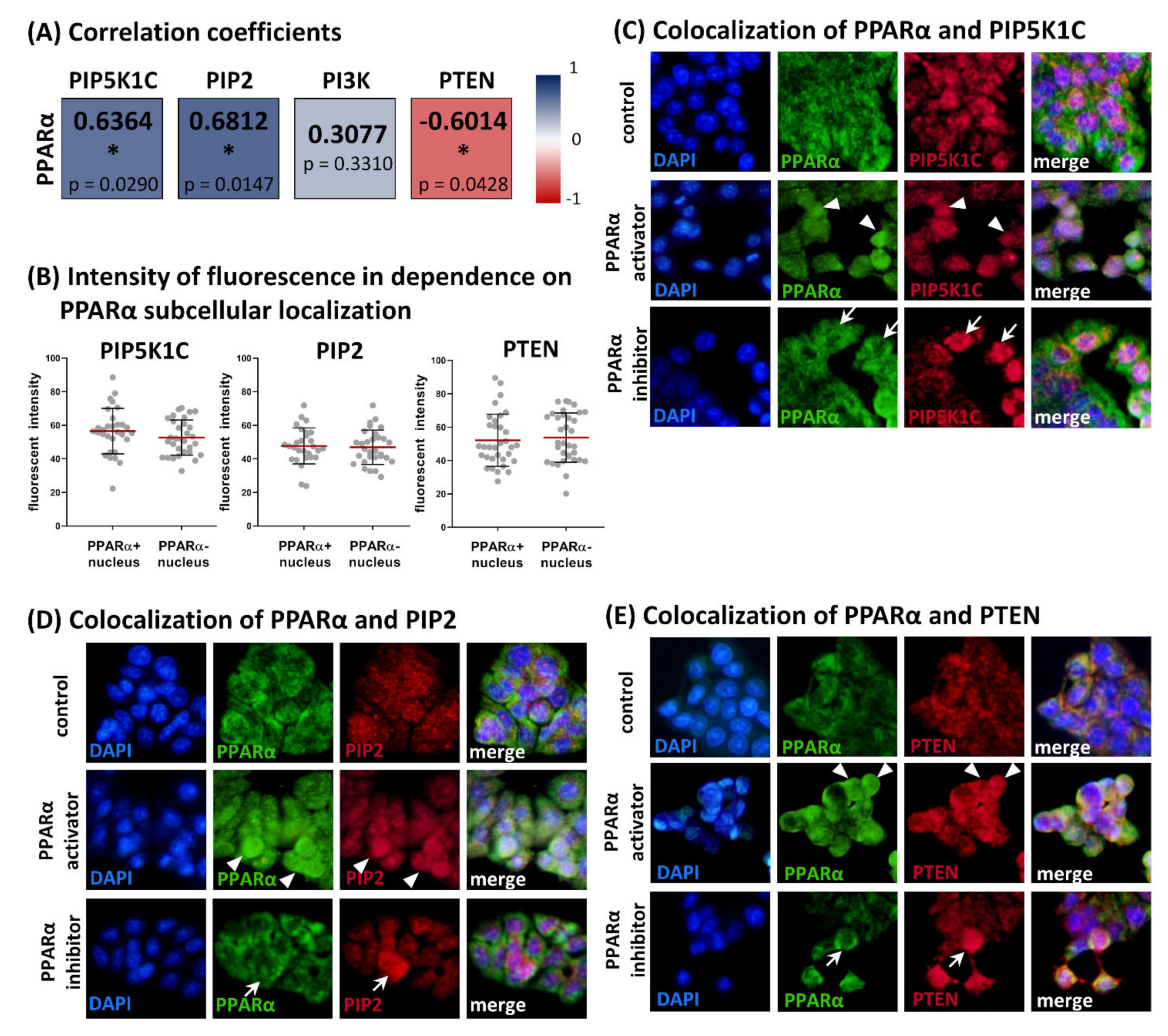
3.3. Relationships between Levels of PPARα and PIP5K1C, PIP2, PI3K (p85/p55) and PTEN in HT-29 Cell Line
3.4. Comparison of PIP5K1C, PIP2, PI3K (p85α), PTEN and PPARα in Grade 3 Colorectal Carcinomas and Adjacent Normal Tissue Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, B.D.; Wood, C.R.; Watkins, A.M.; Das, K.P.; Lau, C.S. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors Alpha, Beta, and Gamma mRNA and Protein Expression in Human Fetal Tissues. PPAR Res. 2010, 2010, 690907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pyper, S.R.; Viswakarma, N.; Yu, S.; Reddy, J.K. PPARalpha: Energy combustion, hypolipidemia, inflammation and cancer. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2010, 8, e002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, J.M.; Shah, Y.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in carcinogenesis and chemoprevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morinishi, T.; Tokuhara, Y.; Ohsaki, H.; Ibuki, E.; Kadota, K.; Hirakawa, E. Activation and Expression of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha Are Associated with Tumorigenesis in Colorectal Carcinoma. PPAR Res. 2019, 2019, 7486727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras, A.V.; Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. PPAR-α as a key nutritional and environmental sensor for metabolic adaptation. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umemoto, T.; Fujiki, Y. Ligand-dependent nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, PPARalpha and PPARgamma. Genes Cells Devoted Mol. Cell. Mech. 2012, 17, 576–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougarne, N.; Weyers, B.; Desmet, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Ray, D.W.; Staels, B.; De Bosscher, K. Molecular Actions of PPARα in Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 760–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokuno, A.; Hirano, T.; Hayashi, T.; Mori, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Nagashima, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Adachi, M. The effects of statin and fibrate on lowering small dense LDL- cholesterol in hyperlipidemic patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2007, 14, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keech, A.; Simes, R.J.; Barter, P.; Best, J.; Scott, R.; Taskinen, M.R.; Forder, P.; Pillai, A.; Davis, T.; Glasziou, P.; et al. Effects of long-term fenofibrate therapy on cardiovascular events in 9795 people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the FIELD study): Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.A.; Vanden Heuvel, J.P. Modulation of PPAR activity via phosphorylation. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2007, 1771, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Liang, X.G.; Lou, Y.J. Time-dependence of cardiomyocyte differentiation disturbed by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha inhibitor GW6471 in murine embryonic stem cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goto, T.; Lee, J.Y.; Teraminami, A.; Kim, Y.I.; Hirai, S.; Uemura, T.; Inoue, H.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha stimulates both differentiation and fatty acid oxidation in adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benameur, T.; Tual-Chalot, S.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Martínez, M.C. PPARalpha is essential for microparticle-induced differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells and angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifpanah, F.; Wartenberg, M.; Hannig, M.; Piper, H.M.; Sauer, H. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonists enhance cardiomyogenesis of mouse ES cells by utilization of a reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanism. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergori, L.; Lauret, E.; Gaceb, A.; Beauvillain, C.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Martinez, M.C. PPARα regulates endothelial progenitor cell maturation and myeloid lineage differentiation through a NADPH oxidase-dependent mechanism in mice. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Qu, B.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J.; Liao, D.; Zheng, W.; Pan, X. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α Facilitates Osteogenic Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells via the Sirtuin 1-Dependent Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kömüves, L.G.; Hanley, K.; Lefebvre, A.M.; Man, M.Q.; Ng, D.C.; Bikle, D.D.; Williams, M.L.; Elias, P.M.; Auwerx, J.; Feingold, K.R. Stimulation of PPARalpha promotes epidermal keratinocyte differentiation in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cizkova, K.; Foltynkova, T.; Hanyk, J.; Kamencak, Z.; Tauber, Z. When Activator and Inhibitor of PPARα Do the Same: Consequence for Differentiation of Human Intestinal Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Zhao, P.; Tomar, A.; Galea, C.A.; Khurana, S. Association of villin with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates the actin cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 3096–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurana, S.; George, S.P. Regulation of cell structure and function by actin-binding proteins: Villin’s perspective. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2128–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Chung, D.H.; Evers, B.M. Regulation of PTEN expression in intestinal epithelial cells by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation and nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7773–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florio, R.; De Lellis, L.; di Giacomo, V.; Di Marcantonio, M.C.; Cristiano, L.; Basile, M.; Verginelli, F.; Verzilli, D.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Prasad, S.C.; et al. Effects of PPARα inhibition in head and neck paraganglioma cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Dai, J.; Tang, M.; Wei, Y.; Kuang, H.; Xu, G.; et al. Fenofibrate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic reprogramming reversal: The anti-tumor effects in gastric carcinoma cells mediated by the PPAR pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 428–446. [Google Scholar]
- De Araújo, W.M.; Vidal, F.C.; de Souza, W.F.; de Freitas, J.C., Jr.; de Souza, W.; Morgado-Diaz, J.A. PI3K/Akt and GSK-3β prevents in a differential fashion the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, D.; Kawabe, N.; Nakamura, H.; Tachibana, K.; Ishimoto, K.; Tanaka, T.; Aburatani, H.; Sakai, J.; Hamakubo, T.; Kodama, T.; et al. Fenofibrate suppresses growth of the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell via PPARα-independent mechanisms. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, Y.; Upadhyay, R.; Alhousseiny, S.; Taha, T.; Musthak, A.; Shaheen, Y.; Jameel, M.; Triggle, C.R.; Ding, H. Potent and PPARα-independent anti-proliferative action of the hypolipidemic drug fenofibrate in VEGF-dependent angiosarcomas in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.; Cockcroft, S. Phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate: Diverse functions at the plasma membrane. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehama, T.; Dixon, J.E. The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13375–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, H.; Shao, J.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Evers, B.M. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediates proliferative signals in intestinal epithelial cells. Gut 2003, 52, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cizkova, K.; Birke, P.; Malohlava, J.; Tauber, Z.; Huskova, Z.; Ehrmann, J. HT-29 and Caco2 Cell Lines Are Suitable Models for Studying the Role of Arachidonic Acid-Metabolizing Enzymes in Intestinal Cell Differentiation. Cells Tissues Organs 2019, 208, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamata, S.; Oyama, T.; Saito, K.; Honda, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Suda, K.; Ishikawa, R.; Itoh, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Shibata, T.; et al. PPARα Ligand-Binding Domain Structures with Endogenous Fatty Acids and Fibrates. iScience 2020, 23, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, A.; Souza, P.C.T.; Muniz, J.R.C.; Ricci, C.G.; Ayers, S.D.; Parekh, N.M.; Godoy, A.S.; Trivella, D.B.B.; Reinach, P.; Webb, P.; et al. Molecular Mechanism of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α Activation by WY14643: A New Mode of Ligand Recognition and Receptor Stabilization. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 2878–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willson, T.M.; Brown, P.J.; Sternbach, D.D.; Henke, B.R. The PPARs: From Orphan Receptors to Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgine, J.; Billaut-Laden, I.; Happillon, M.; Lo-Guidice, J.M.; Maunoury, V.; Imbenotte, M.; Broly, F. Gene expression profiling of systems involved in the metabolism and the disposition of xenobiotics: Comparison between human intestinal biopsy samples and colon cell lines. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2012, 40, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Qiao, L.; Chan, K.W.; Zou, B.; Ma, J.; Lan, H.Y.; Gu, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wong, B.L.; et al. Loss of XIAP sensitizes rosiglitazone-induced growth inhibition of colon cancer in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2858–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Lin, M.S.; Bai, X. Induction of apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma activation up-regulating PTEN and inhibiting PI3K activity. Chin. Med. J. 2005, 118, 1477–1481. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, H.E.; Peraza, M.A.; Billin, A.N.; Willson, T.M.; Ward, J.M.; Kennett, M.J.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Peters, J.M. Ligand Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor β Inhibits Colon Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4394–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laprise, P.; Chailler, P.; Houde, M.; Beaulieu, J.F.; Boucher, M.J.; Rivard, N. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase controls human intestinal epithelial cell differentiation by promoting adherens junction assembly and p38 MAPK activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8226–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hernandez, A.; Kim, S.; Evers, B.M. Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway contributes to HT29 and Caco-2 intestinal cell differentiation. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Domon-Dell, C.; Wang, Q.; Chung, D.H.; Di Cristofano, A.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Freund, J.N.; Evers, B.M. PTEN and TNF-alpha regulation of the intestinal-specific Cdx-2 homeobox gene through a PI3K, PKB/Akt, and NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waniczek, D.; Śnietura, M.; Lorenc, Z.; Nowakowska-Zajdel, E.; Muc-Wierzgoń, M. Assessment of PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling pathway activity in colorectal cancer using quantum dot-conjugated antibodies. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Calegari, M.A.; Loupakis, F.; Fassan, M.; Di Stefano, B.; Bensi, M.; Bria, E.; Tortora, G. PTEN in Colorectal Cancer: Shedding Light on Its Role as Predictor and Target. Cancers 2019, 11, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.; Huang, W.; Ge, X.; Xue, L.; Zhao, W.; Xue, J. Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase promotes tumor growth by facilitating Warburg effect in colorectal cancer. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bader, A.G.; Kang, S.; Zhao, L.; Vogt, P.K. Oncogenic PI3K deregulates transcription and translation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, J.; Du, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Gao, W. Expression of factors and key components associated with the PI3K signaling pathway in colon cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5465–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rychahou, P.G.; Jackson, L.N.; Silva, S.R.; Rajaraman, S.; Evers, B.M. Targeted molecular therapy of the PI3K pathway: Therapeutic significance of PI3K subunit targeting in colorectal carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenoue, T.; Kanai, F.; Hikiba, Y.; Obata, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Imamura, J.; Ohta, M.; Jazag, A.; Guleng, B.; Tateishi, K.; et al. Functional analysis of PIK3CA gene mutations in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4562–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, K.S.; Song, Y.S.; Jang, S.H.; Min, K.W.; Na, W.; Jang, S.M.; Jun, Y.J.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, D.; Paik, S.S. Clinicopathological significance of nuclear PTEN expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Histopathology 2010, 56, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Winnay, J.; Kondo, T.; Bronson, R.T.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Alemán, J.O.; Luo, J.; Stephanopoulos, G.; Weissleder, R.; Cantley, L.C.; et al. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit p85alpha can exert tumor suppressor properties through negative regulation of growth factor signaling. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5305–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thorpe, L.M.; Spangle, J.M.; Ohlson, C.E.; Cheng, H.; Roberts, T.M.; Cantley, L.C.; Zhao, J.J. PI3K-p110α mediates the oncogenic activity induced by loss of the novel tumor suppressor PI3K-p85α. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7095–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chagpar, R.B.; Links, P.H.; Pastor, M.C.; Furber, L.A.; Hawrysh, A.D.; Chamberlain, M.D.; Anderson, D.H. Direct positive regulation of PTEN by the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5471–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| No. | Sex | Age | Diagnosis | Localization | TNM Staging | Grading | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | N | M | ||||||
| 1 | male | 66 | adenocarcinoma | c. sigmoideum | T3 | N0 | M0 | G3 |
| 2 | male | 63 | adenocarcinoma | c. descendens, rectum | T3 | N2b | M0 | G3 |
| 3 | male | 54 | adenocarcinoma | c. sigmoideum | T2 | N0 | M0 | G3 |
| 4 | female | 70 | adenocarcinoma | c. descendens, rectum | T3 | N2a | M0 | G3 |
| 5 | male | 69 | adenocarcinoma | c. sigmoideum | T3 | N0 | M0 | G3 |
| 6 | female | 39 | adenocarcinoma | c.sigmoideum | T3 | N1a | M0 | G3 |
| 7 | male | 77 | adenocarcinoma | c. sigmoideum | T3 | N0 | M0 | G3 |
| 8 | female | 50 | adenocarcinoma | c. sigmoideum | T3 | N2b | M1b | G3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cizkova, K.; Koubova, K.; Tauber, Z. Lipid Messenger Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate Is Increased by Both PPARα Activators and Inhibitors: Relevance for Intestinal Cell Differentiation. Biology 2022, 11, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070997
Cizkova K, Koubova K, Tauber Z. Lipid Messenger Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate Is Increased by Both PPARα Activators and Inhibitors: Relevance for Intestinal Cell Differentiation. Biology. 2022; 11(7):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070997
Chicago/Turabian StyleCizkova, Katerina, Katerina Koubova, and Zdenek Tauber. 2022. "Lipid Messenger Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate Is Increased by Both PPARα Activators and Inhibitors: Relevance for Intestinal Cell Differentiation" Biology 11, no. 7: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070997
APA StyleCizkova, K., Koubova, K., & Tauber, Z. (2022). Lipid Messenger Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate Is Increased by Both PPARα Activators and Inhibitors: Relevance for Intestinal Cell Differentiation. Biology, 11(7), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070997






