A Novel Automatic Quantification Protocol for Biomarkers of Tauopathies in the Hippocampus and Entorhinal Cortex of Post-Mortem Samples Using an Extended Semi-Siamese U-Net
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
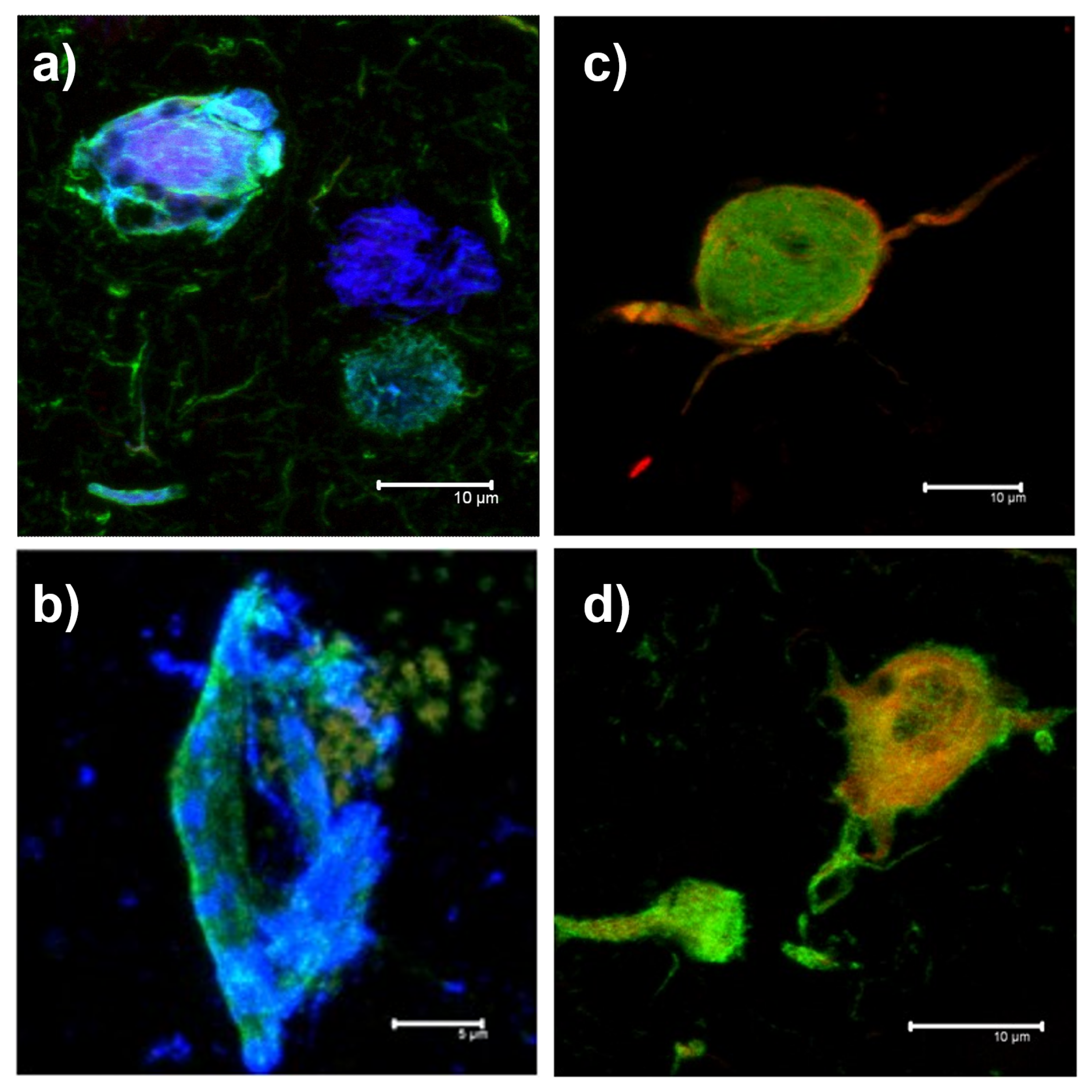
2.1. Data Acquisition
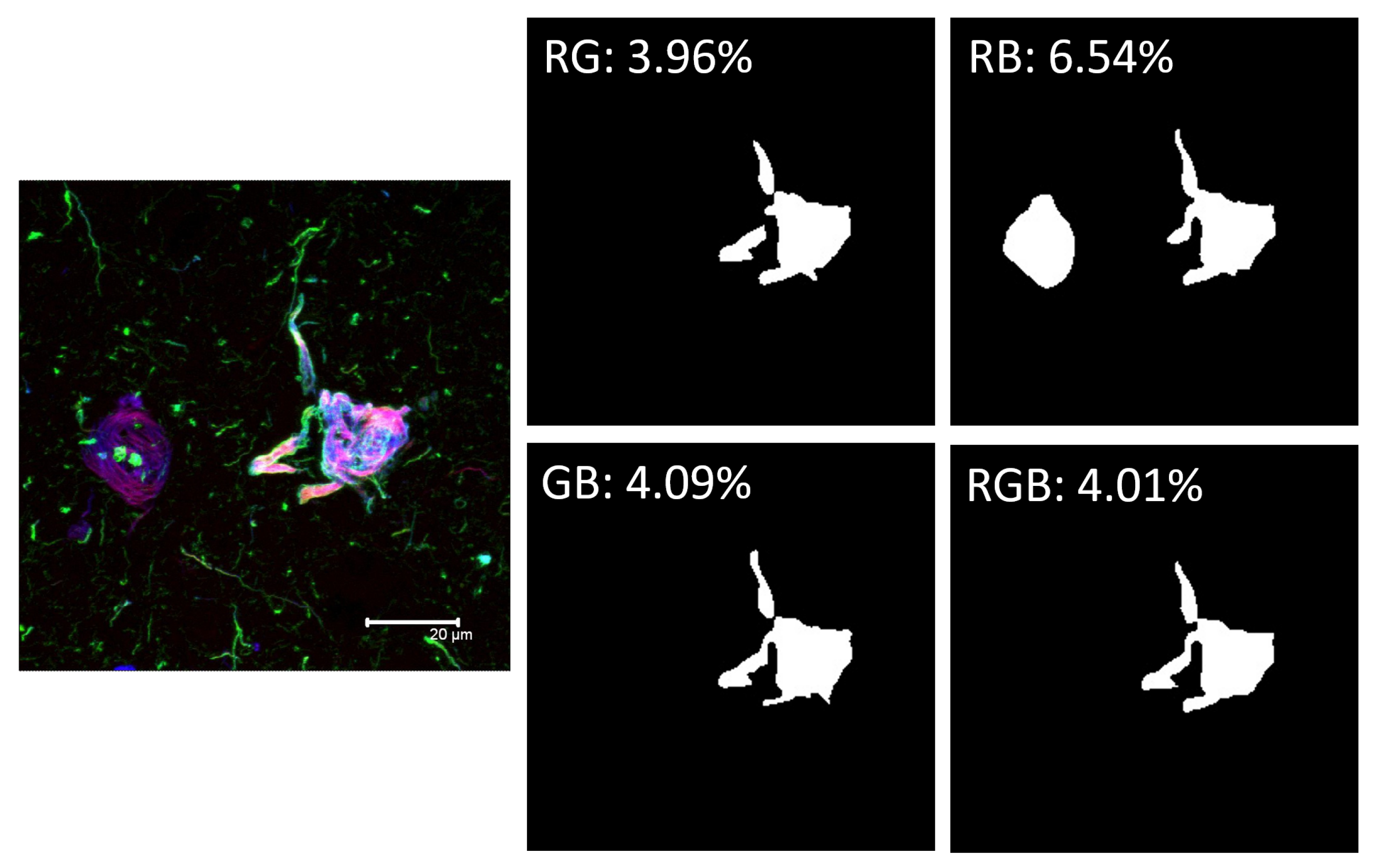
- Red Channel: Thiazine red and the antibodies TG3 (regional conformational change with phosphorylation at amino acid threonine 231), pT231 (phosphorylation at threonine 231), Alz50 (structural conformational change), pS396 (phosphorylation at serine 396), and AT100 (regional conformational change and phosphorylation at serine 202, threonine 205, threonine 212, and serine 214).
- Green channel: AT8 (phosphorylation at serine 202, threonine 205 and serine 208), CP13 (phosphorylation at serine 202), 499 (amino terminal end), Tau-7 (carboxyl terminal end), TauC3 (proteolysis at aspartic 421 carboxyl terminal end) antibodies, PHF1 (phosphorylation at serines 396 and 404), AD2 (phosphorylation at amino acids serine 396 and serine 404), and 423 (proteolysis at glutamic 391 of the carboxyl-terminal end).
- Blue Channel: Antibodies pS396, S-199 (phosphorylation at amino acid serine 199), pT231, and Alz50.
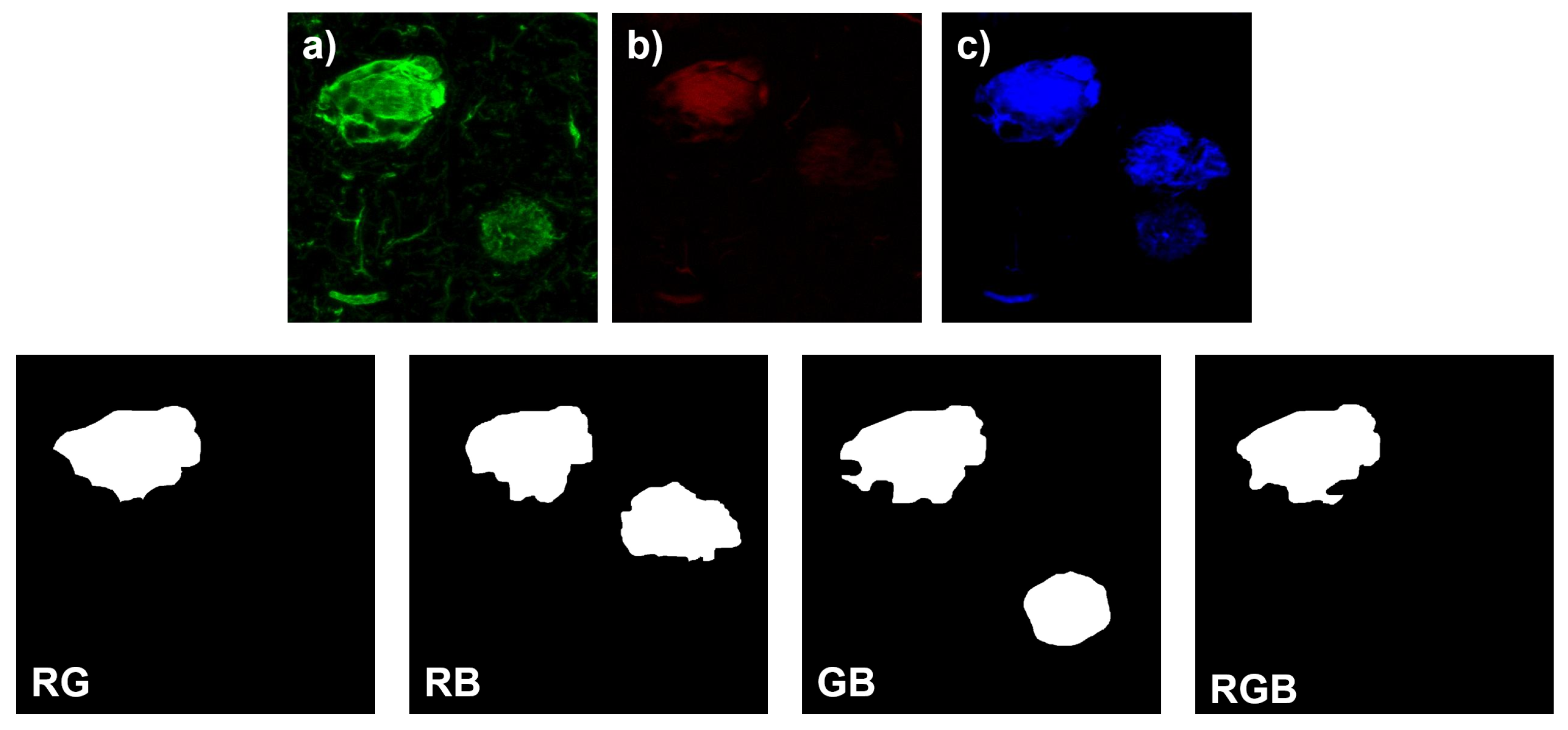
2.2. Manual Segmentation of Biomarker Signals
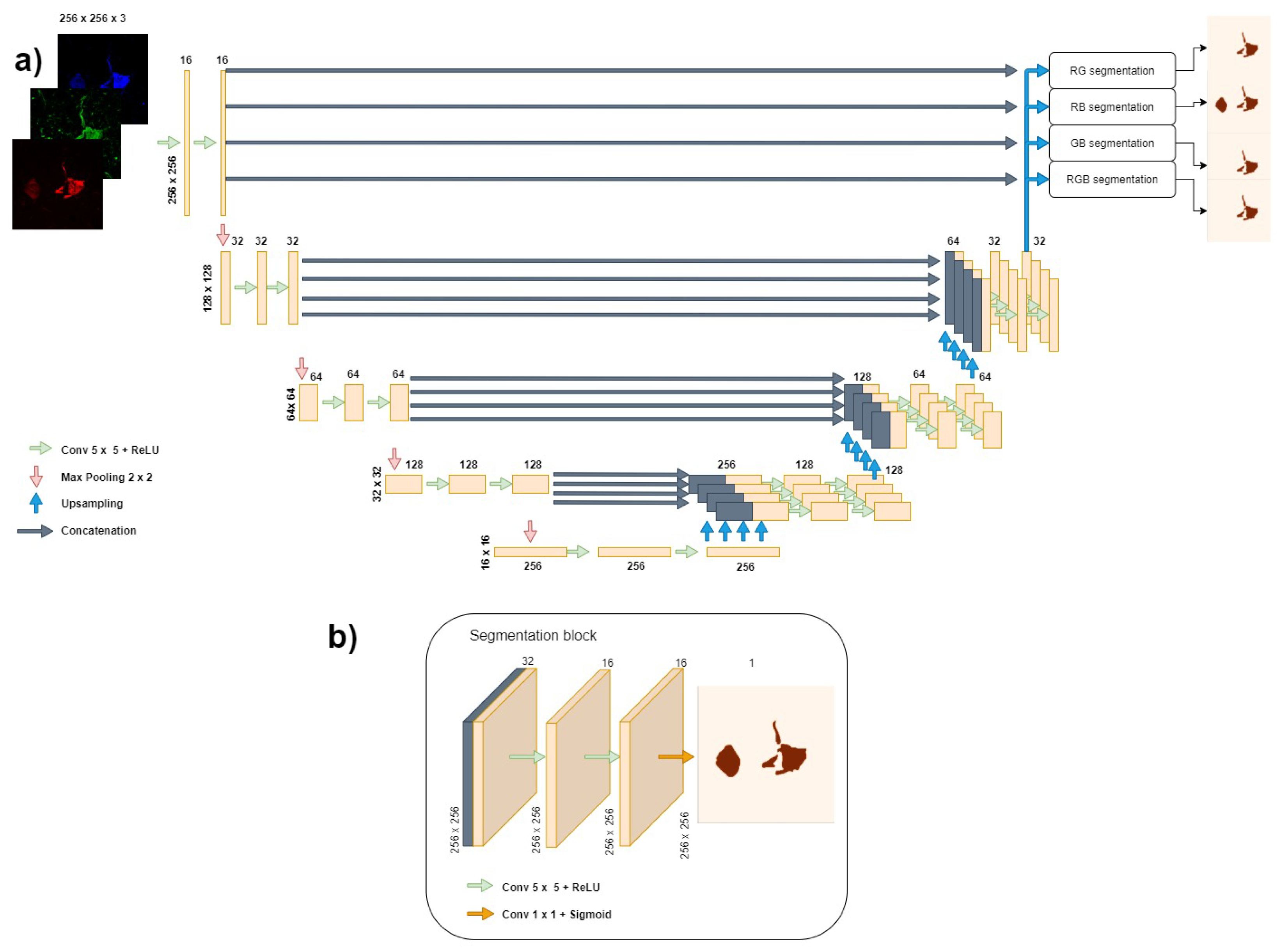
2.3. Network Architecture
2.4. Evaluation Criteria
2.5. Training Methods and Experimental Design
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NFTs | Neurofibrillary Tangles |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| FTD | Frontotemporal Dementia |
| PSP | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy |
| TO | Tangle Only |
| PTMs | Post-Translational Modifications |
| PHFs | Paired Helical Filaments |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| TP | True Positive |
| FP | False Positive |
| IOU | Intersection Over Union |
References
- Martínez-Maldonado, A.; Ontiveros-Torres, M.A.; Harrington, C.R.; Montiel-Sosa, J.F.; Prandiz, R.G.T.; Bocanegra-Lopez, P.; Sorsby-Vargas, A.M.; Bravo-Muñoz, M.; Florán-Garduño, B.; Villanueva-Fierro, I.; et al. Molecular Processing of Tau Protein in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Neuronal and Glial Degeneration. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 79, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Ono, T.; Takamatsu, J.; Yamamoto, H.; Ikegami, K.; Kondo, A.; Hasegawa, M.; Ihara, Y.; Miyamoto, E.; Miyakawa, T. Sequential changes of tau-site-specific phosphorylation during development of paired helical filaments. Dementia 1996, 7, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, L.; Mallajosyula, S.S. Phosphorylation-induced structural reorganization in tau-paired helical filaments. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, D.M.; Mancinelli, C.; Bracken, C.; Eliezer, D. Post-translational modifications within tau paired helical filament nucleating motifs perturb microtubule interactions and oligomer formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, E.; Eid, S.; Weber, C.; Kowalski, A.; Bichmann, M.; Behrendt, A.; Matthes, F.; Krauss, S.; Reinhardt, P.; Fulle, S.; et al. A validated antibody panel for the characterization of tau post-translational modifications. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reyes-Pablo, A.E.; Campa-Córdoba, B.B.; Luna-Viramontes, N.I.; Ontiveros-Torres, M.A.; Villanueva-Fierro, I.; Bravo-Muñoz, M.; Sáenz-Ibarra, B.; Barbosa, O.; Guadarrama-Ortíz, P.; Garcés-Ramírez, L.; et al. National Dementia BioBank: A Strategy for the Diagnosis and Study of Neurodegenerative Diseases in México. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 76, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, M.; Morbiducci, U.; Amadeo, F.; Santoro, R.; Angelini, F.; Chimenti, I.; Massai, D.; Messina, E.; Giacomello, A.; Pesce, M.; et al. Automated Segmentation of Fluorescence Microscopy Images for 3D Cell Detection in human-derived Cardiospheres. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawanabe, T.; Kamarudin, N.D.; Ooi, C.Y.; Kobayashi, F.; Mi, X.; Sekine, M.; Wakasugi, A.; Odaguchi, H.; Hanawa, T. Quantification of tongue colour using machine learning in Kampo medicine. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2016, 8, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Eycke, Y.R.; Balsat, C.; Verset, L.; Debeir, O.; Salmon, I.; Decaestecker, C. Segmentation of glandular epithelium in colorectal tumours to automatically compartmentalise IHC biomarker quantification: A deep learning approach. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 49, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier, A.; Syben, C.; Lasser, T.; Riess, C. A gentle introduction to deep learning in medical image processing. Z. Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodneland, E.; Kaliyugarasan, S.; Wagner-Larsen, K.S.; Lura, N.; Andersen, E.; Bartsch, H.; Smit, N.; Halle, M.K.; Krakstad, C.; Lundervold, A.S.; et al. Fully Automatic Whole-Volume Tumor Segmentation in Cervical Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y. Tumor Segmentation in Breast Ultrasound Image by Means of Res Path Combined with Dense Connection Neural Network. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.F.; Cheng, K.S. Semi-Siamese U-Net for separation of lung and heart bioimpedance images: A simulation study of thorax EIT. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Diamant, I.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. GAN-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased CNN performance in liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 321, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shi, Y.J.; Li, X.T.; Sun, Y.S. Automatic segmentation of rectal tumor on diffusion-weighted images by deep learning with U-Net. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Murao, K.; Satoh, S.; Nakayama, H. Learning More with Less: GAN-based Medical Image Augmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.00838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-Net and Its Variants for Medical Image Segmentation: A Review of Theory and Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82031–82057. [Google Scholar]
- O’Mara, A.R.; Collins, J.M.; King, A.E.; Vickers, J.C.; Kirkcaldie, M.T.K. Accurate and Unbiased Quantitation of Amyloid-β Fluorescence Images Using ImageSURF. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giong, H.K.; Subramanian, M.; Yu, K.; Lee, J.S. Non-rodent genetic animal models for studying tauopathy: Review of Drosophila, zebrafish, and C. elegans models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, H.G.; Collij, L.E.; Heeman, F.; Bollack, A.; Shekari, M.; Salvadó, G.; Alves, I.L.; Garcia, D.V.; Battle, M.; Buckley, C.; et al. Quantification of amyloid PET for future clinical use: A state-of-the-art review. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbater, O.; Efrati, M.; Gannot, I. Quantification of Two Fluorophores’ Concentration Ratio in a Mice Model in Preparation for a Proposed Method for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- den Haan, J.; Morrema, T.H.J.; Verbraak, F.D.; de Boer, J.F.; Scheltens, P.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Bergen, A.A.B.; Bouwman, F.H.; Hoozemans, J.J. Amyloid-beta and phosphorylated tau in post-mortem Alzheimer’s disease retinas. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association Between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. The Distribution of the Flora in the Alpine Zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, P.Y.; Steinkraus, D.; Platt, J.C. Best practices for convolutional neural networks applied to visual document analysis. In Proceedings of the Icdar, Edinburgh, UK, 6 August 2003; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, A.K.; Rivera, B.I.; Polanco, C.M.; Jara, C.; Tapia-Rojas, C. Phosphorylated tau as a toxic agent in synaptic mitochondria: Implications in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1645. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Guzmán-Martínez, L.; Maccioni, R.B. Plasma tau variants detected by a novel anti-tau monoclonal antibody: A potential biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 77, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Farías, G.A.; Fuentes, P.; Navarrete, L.P. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

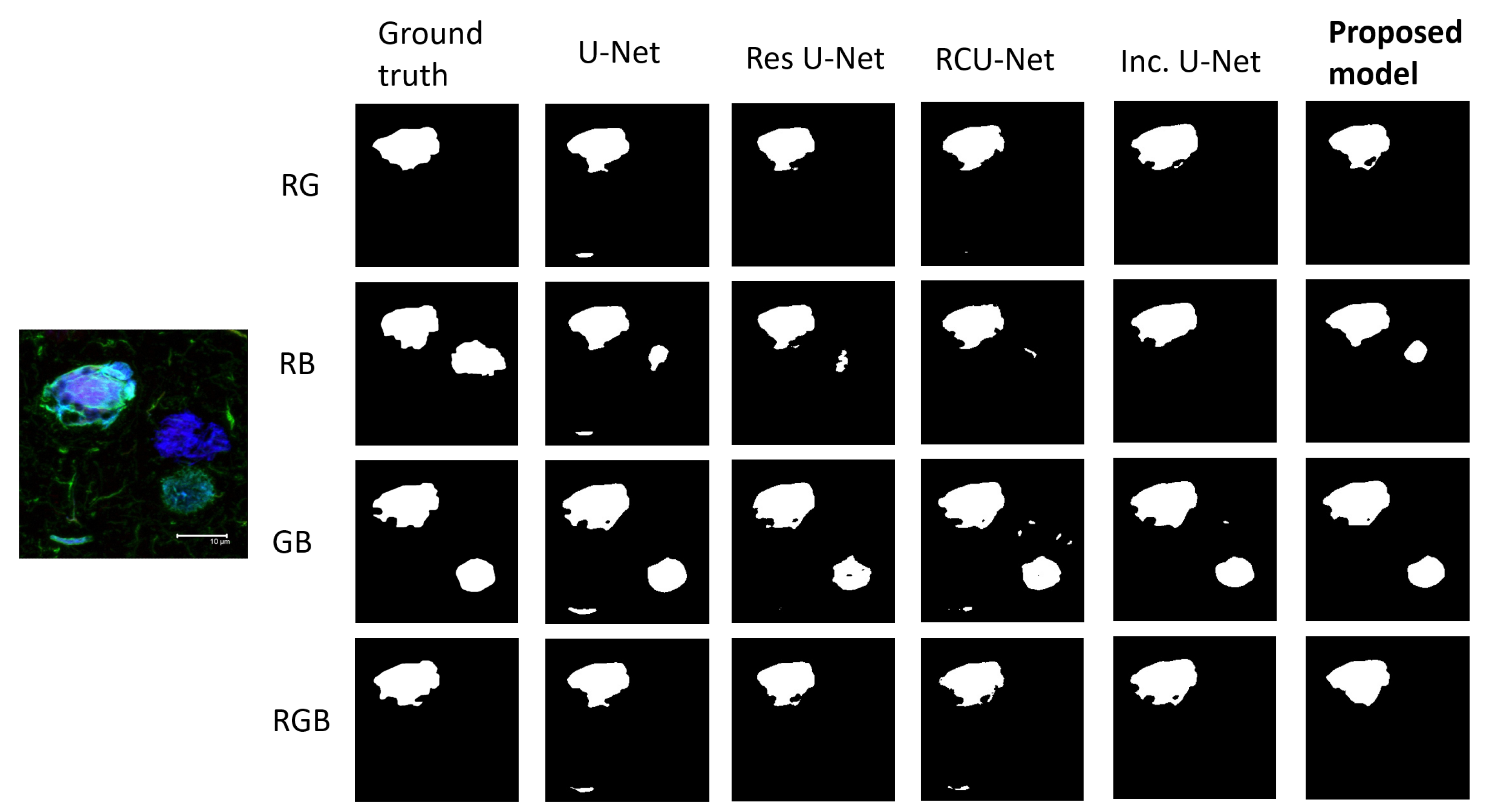
| Model | DC | FP | IOU | TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed model | 0.9064 ± 0.0223 | 0.0437 ± 0.0201 | 0.8268 ± 0.0402 | 0.8690 ± 0.0424 |
| Inception U-Net | 0.8938 ± 0.028 | 0.0638 ± 0.0252 | 0.8092 ± 0.0459 | 0.8593 ± 0.0408 |
| RCU-Net | 0.8984 ± 0.0233 | 0.0519 ± 0.0202 | 0.8164 ± 0.0385 | 0.8536 ± 0.0424 |
| Res U-Net | 0.893 ± 0.0335 | 0.0699 ± 0.0561 | 0.8083 ± 0.0535 | 0.8589 ± 0.0439 |
| U-Net | 0.8894 ± 0.0333 | 0.0749 ± 0.0443 | 0.8025 ± 0.0539 | 0.8618 ± 0.0396 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campero-Garcia, L.A.; Cantoral-Ceballos, J.A.; Martinez-Maldonado, A.; Luna-Muñoz, J.; Ontiveros-Torres, M.A.; Gutierrez-Rodriguez, A.E. A Novel Automatic Quantification Protocol for Biomarkers of Tauopathies in the Hippocampus and Entorhinal Cortex of Post-Mortem Samples Using an Extended Semi-Siamese U-Net. Biology 2022, 11, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081131
Campero-Garcia LA, Cantoral-Ceballos JA, Martinez-Maldonado A, Luna-Muñoz J, Ontiveros-Torres MA, Gutierrez-Rodriguez AE. A Novel Automatic Quantification Protocol for Biomarkers of Tauopathies in the Hippocampus and Entorhinal Cortex of Post-Mortem Samples Using an Extended Semi-Siamese U-Net. Biology. 2022; 11(8):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081131
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampero-Garcia, Luis A., Jose A. Cantoral-Ceballos, Alejandra Martinez-Maldonado, Jose Luna-Muñoz, Miguel A. Ontiveros-Torres, and Andres E. Gutierrez-Rodriguez. 2022. "A Novel Automatic Quantification Protocol for Biomarkers of Tauopathies in the Hippocampus and Entorhinal Cortex of Post-Mortem Samples Using an Extended Semi-Siamese U-Net" Biology 11, no. 8: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081131
APA StyleCampero-Garcia, L. A., Cantoral-Ceballos, J. A., Martinez-Maldonado, A., Luna-Muñoz, J., Ontiveros-Torres, M. A., & Gutierrez-Rodriguez, A. E. (2022). A Novel Automatic Quantification Protocol for Biomarkers of Tauopathies in the Hippocampus and Entorhinal Cortex of Post-Mortem Samples Using an Extended Semi-Siamese U-Net. Biology, 11(8), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081131








