Role of Gut Microbiota through Gut–Brain Axis in Epileptogenesis: A Systematic Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
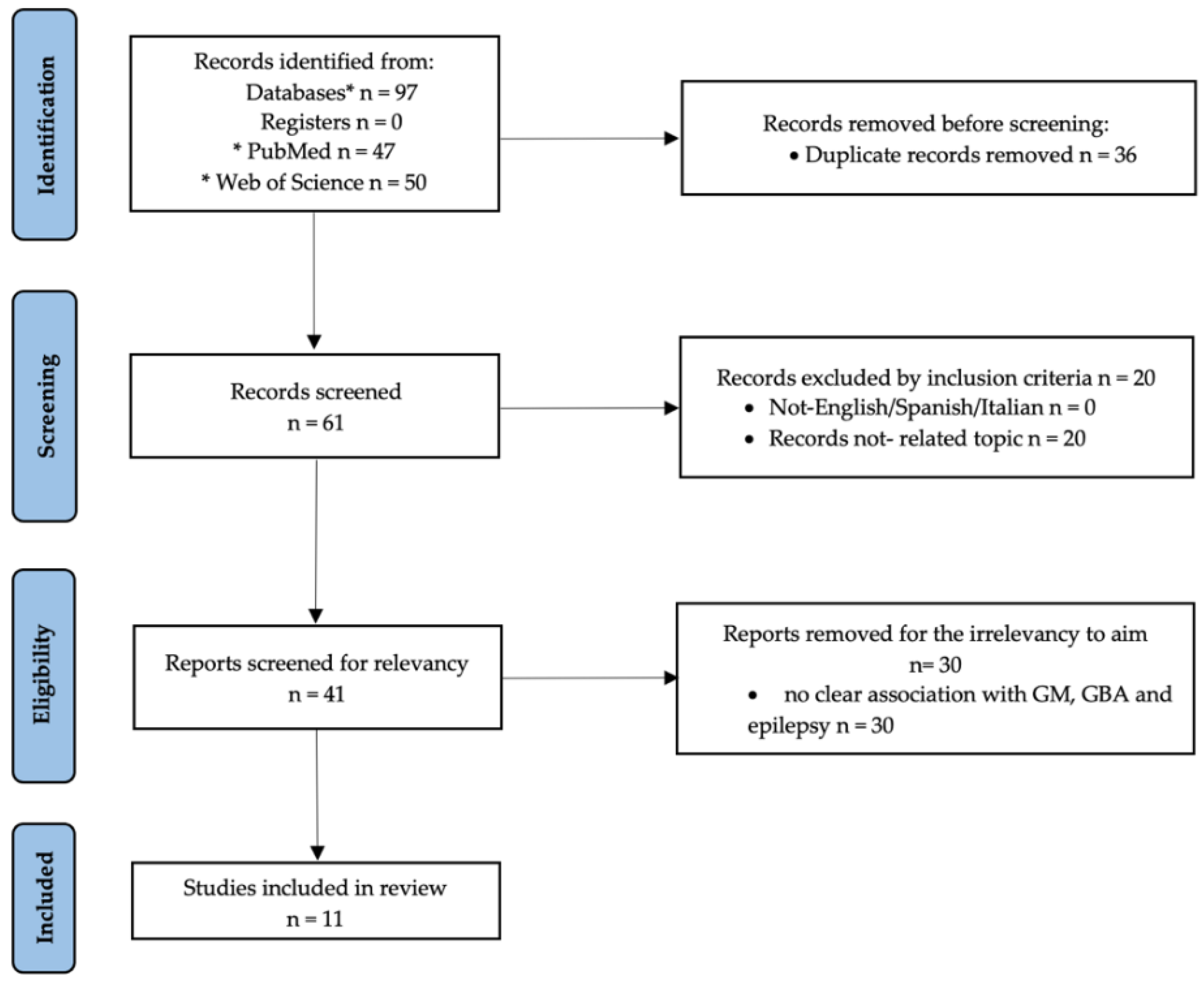
1. Introduction
2. Gut–Brain Axis
3. Gut–Brain Axis Gut Microbiota and Epilepsy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heijtz, R.D.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonnaya, E.S.; Clarke, G.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Leary, O.F. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis Is Regulated by the Microbiome. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, e7–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.A.; Hsiao, E.Y. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, A.E.; Stilling, R.M.; Ryan, F.J.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Claesson, M.J.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. Regulation of prefrontal cortex myelination by the microbiota. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Grenham, S.; Scully, P.; Fitzgerald, P.; Moloney, R.D.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Ling, Y.; Wang, F.; Gong, T.; Yang, C.; Ye, S.; Ye, K.; Wei, D.; Song, Z.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviated Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, L.F.; Preda, A.; Blottière, H.M.; Clarke, G.; Albani, D.; Belcastro, V.; Carotenuto, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Citraro, R.; Ferraris, C.; et al. Microbiota-gut brain axis involvement in neuropsychiatric disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.J.; Yang, X.Z.; Tong, Q.; Shen, P.; Ma, S.J.; Wu, S.N.; Zheng, Z.L.; Wang, H.G. Fecal microbiota transplantation therapy for Parkinson’s disease: A preliminary study. Medicine 2020, 99, e22035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, K.B.; Leone, V.; Chang, E.B. Microbial metabolites in health and disease: Navigating the unknown in search of function. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8553–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Gershon, M.D. The bowel and beyond: The enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, M.; Prast-Nielsen, S. The gut microbiome and epilepsy. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluehmann, G.; Doherr, M.G.; Jaggy, A. Canine neurological diseases in a referral hospital population between 1989 and 2000 in Switzerland. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2006, 47, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Epilepsy: Key Facts; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/factsheets/detail/epilepsy (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; et al. ILAE Official Report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafstrom, C.E.; Carmant, L. Seizures and epilepsy: An overview for neuroscientists. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a022426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Galic, M.A.; Kuzmiski, J.B.; Ho, W.; Sharkey, K.A.; Pittman, Q.J. Microglial activation and TNFα production mediate altered CNS excitability following peripheral inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17151–17156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Balosso, S.; Ravizza, T. The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Galic, M.A.; Pittman, Q.J. Contributions of peripheral inflammation to seizure susceptibility: Cytokines and brain excitability. Epilepsy Res. 2010, 89, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Galic, M.A.; Kentner, A.C.; Reid, A.Y.; Sharkey, K.; Pittman, Q.J. Microglia-Dependent Alteration of Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity in the Hippocampus during Peripheral Inflammation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4942–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Rao, Y.; Miao, J.; Lu, X. Intestinal Microbiota as an Alternative Therapeutic Target for Epilepsy. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 9032809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blander, J.M.; Longman, R.S.; Iliev, I.D.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Artis, D. Regulation of inflammation by microbiota interactions with the host. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Haq, R.; Schlachetzki, J.C.; Glass, C.K.; Mazmanian, S.K. Microbiome–microglia connections via the gut–brain axis. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 216, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, Y.M.; Borcherding, D.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kim, H.J.; Willette, A.A.; Jergens, A.; Allenspach, K.; Mochel, J.P. The Gut-Brain Axis in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Relevance of the Canine Model: A Review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Role of the Canine Gut Microbiome and Metabolome in Health and Gastrointestinal Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-X.; Wang, Y.-P. Gut Microbiota-brain Axis. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A. The neurobiology of stress and gastrointestinal disease. Gut 2000, 47, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, S.; Dillon, J.F. Microbial biofilms in the human gastrointestinal tract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, J.; Bijlsma, P.; Van Kalkeren, A.; Kiliaan, A.; Saunders, P.; Perdue, M. Stress-induced decrease of the intestinal barrier function: The role of muscarinic receptor activation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 915, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, C.; Yang, P.C.; Darmoul, D.; Amadesi, S.; Saito, T.; Cottrell, G.S.; Coelho, A.M.; Singh, P.; Grady, E.F.; Perdue, M.; et al. Mast cell tryptase controls paracellular permeability of the intestine: Role of protease-activated receptor 2 and β-arrestins. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31936–31948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiliaan, A.J.; Saunders, P.R.; Bijlsma, P.B.; Berin, M.C.; Taminiau, J.A.; Groot, J.A.; Perdue, M.H. Stress stimulates transepithelial macromolecular uptake in rat jejunum. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1998, 275, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderholm, J.D.; Yates, D.A.; Gareau, M.G.; Yang, P.-C.; MacQueen, G.; Perdue, M.H. Neonatal maternal separation predisposes adult rats to colonic barrier dysfunction in response to mild stress. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, D.A.; Santos, J.; Söderholm, J.D.; Perdue, M.H. Adaptation of stress-induced mucosal pathophysiology in rat colon involves opioid pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.R.; Ho, W.; Linden, D.R.; Mawe, G.M.; Sharkey, K.A. Enteroendocrine cells and 5-HT availability are altered in mucosa of guinea pigs with TNBS ileitis. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonhoff, S.E.; Giel-Moloney, M.; Leiter, A.B. Minireview: Development and Differentiation of Gut Endocrine Cells. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2639–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.H.; Pothoulakis, C.; Mayer, E.A. Principles and clinical implications of the brain–gut–enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Xing, C.; Long, W.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.-F. Impact of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological diseases: The gut-brain axis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tilocca, B.; Pieroni, L.; Soggiu, A.; Britti, D.; Bonizzi, L.; Roncada, P.; Greco, V. Gut–Brain Axis and Neurodegeneration: State-of-the-Art of Meta-Omics Sciences for Microbiota Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Recent developments in understanding the role of the gut microbiota in brain health and disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1420, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.L.; Andrew, A.M.; Wichems, C.H.; Li, Q.; Tohda, M.; Greenberg, B. Brain Serotonin Neurotransmission: An Overview and Update with an Emphasis on Serotonin Subsystem Heterogeneity, Multiple Receptors, Interactions with Other Neurotransmitter Systems, and Consequent Implications for Understanding the Actions of Serotonergi. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Tillisch, K.; Gupta, A. Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Author, Year | Type of Article | Study Population |
|---|---|---|
| Riazi K. et al., 2008 [20] | Original article | Rats |
| Vezzani A. et al., 2008 [21] | Review | Humans, rats, and mice |
| Riazi K. et al., 2010 [22] | Review | In vitro |
| Riazi K. et al., 2015 [23] | Original article | Rats |
| Wu J. et al., 2016 [24] | Review | Humans and mice |
| Blander J. et al., 2017 [25] | Review | Humans and mice |
| Haq R.A. et al., 2018 [26] | Review | Humans and mice |
| Ambrosini Y. et al., 2019 [27] | Review | Humans, dogs, and mice |
| Dahlin M. et al., 2019 [14] | Review | Rats and mice |
| Iannone L.F. et al., 2019 [9] | Review | Humans |
| Pilla R. et al., 2020 [28] | Review | Dogs |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gernone, F.; Uva, A.; Silvestrino, M.; Cavalera, M.A.; Zatelli, A. Role of Gut Microbiota through Gut–Brain Axis in Epileptogenesis: A Systematic Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine. Biology 2022, 11, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091290
Gernone F, Uva A, Silvestrino M, Cavalera MA, Zatelli A. Role of Gut Microbiota through Gut–Brain Axis in Epileptogenesis: A Systematic Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine. Biology. 2022; 11(9):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091290
Chicago/Turabian StyleGernone, Floriana, Annamaria Uva, Marco Silvestrino, Maria Alfonsa Cavalera, and Andrea Zatelli. 2022. "Role of Gut Microbiota through Gut–Brain Axis in Epileptogenesis: A Systematic Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine" Biology 11, no. 9: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091290
APA StyleGernone, F., Uva, A., Silvestrino, M., Cavalera, M. A., & Zatelli, A. (2022). Role of Gut Microbiota through Gut–Brain Axis in Epileptogenesis: A Systematic Review of Human and Veterinary Medicine. Biology, 11(9), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091290







