Classification Model for Diabetic Foot, Necrotizing Fasciitis, and Osteomyelitis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
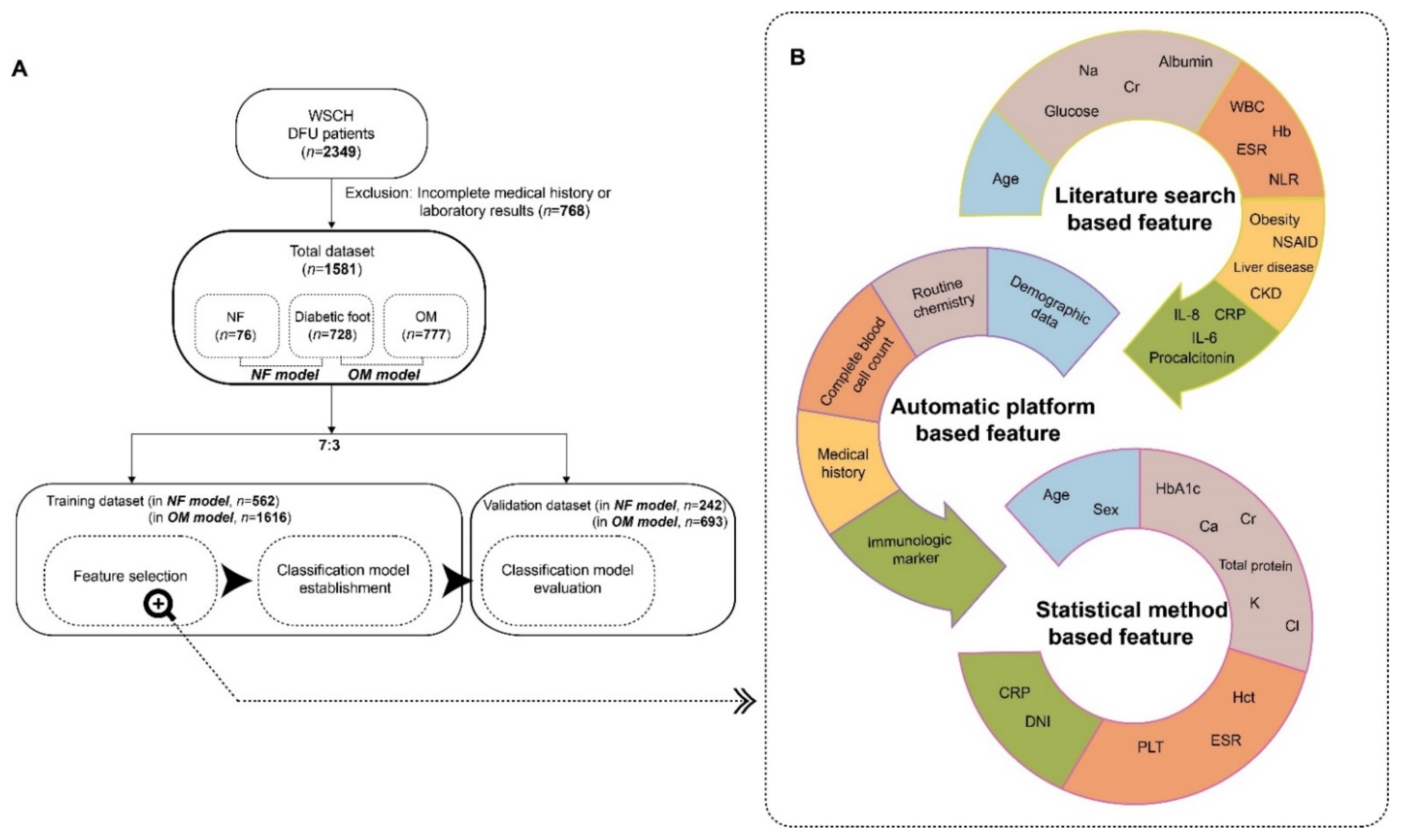
2.1. Participants
2.2. Selection of Predictors for Necrotizing Fasciitis and Osteomyelitis
2.3. Establishment of a Prediction Model
2.4. Statistics
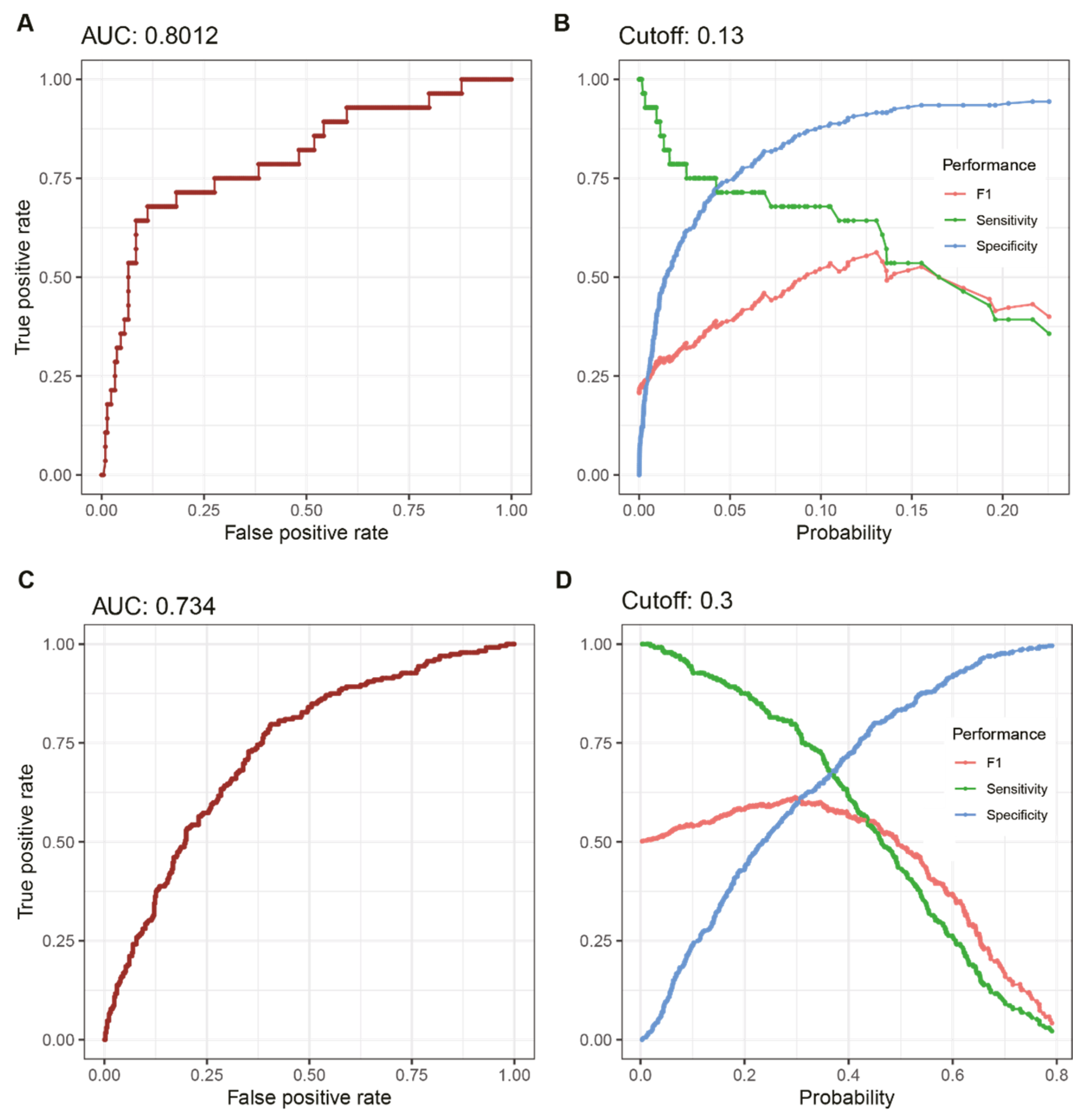
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barshes, N.R.; Sigireddi, M.; Wrobel, J.S.; Mahankali, A.; Robbins, J.M.; Kougias, P.; Armstrong, D.G. The system of care for the diabetic foot: Objectives, outcomes, and opportunities. Diabet. Foot Ankle 2013, 4, 21847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompers, L.; Huijberts, M.; Apelqvist, J.; Jude, E.; Piaggesi, A.; Bakker, K.; Edmonds, M.; Holstein, P.; Jirkovska, A.; Mauricio, D.; et al. High prevalence of ischaemia, infection and serious comorbidity in patients with diabetic foot disease in Europe. Baseline results from the Eurodiale study. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, E.; Kacıra, B.K. Predictors of Lower Extremity Amputation and Reamputation Associated With the Diabetic Foot. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017, 56, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Cornia, P.B.; Pile, J.C.; Peters, E.J.G.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deery, H.G.; Embil, J.M.; Joseph, W.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; et al. 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infectionsa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e132–e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, T.; Goh, L.G.; Ang, C.H.; Wong, C.H. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, e119–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiakos, E.P.; Bagias, G.; Patapis, P.; Sotiropoulos, D.; Kanavidis, P.; Machairas, A. Current Concepts in the Management of Necrotizing Fasciitis. Front. Surg. 2014, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopi, E.; Coppelli, A.; Goretti, C.; Piaggesi, A. Necrotizing Fasciitis and The Diabetic Foot. Int. J. Low. Extremity Wounds 2015, 14, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Diggle, M.; Embil, J.; Kono, S.; Lavery, L.; Senneville, É.; Urbančič-Rovan, V.; Van Asten, S.; Peters, E.J.G.; et al. IWGDF guidance on the diagnosis and management of foot infections in persons with diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurato, L.; Meloni, M.; Izzo, V.; Uccioli, L. Osteomyelitis in diabetic foot: A comprehensive overview. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A. Bone of Contention: Diagnosing Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, M.T.; Abad, C.L.; Safdar, N. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Physical Examination and Imaging Tests for Osteomyelitis Underlying Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Meta-Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonham, P. A critical review of the literature: Part I: Diagnosing osteomyelitis in patients with diabetes and foot ulcers. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 2001, 28, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubitschung, K.; Sherwood, A.; Crisologo, A.P.; Bhavan, K.; Haley, R.W.; Wukich, D.K.; Castellino, L.; Hwang, H.; La Fontaine, J.; Chhabra, A.; et al. Pathophysiology and Molecular Imaging of Diabetic Foot Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüsers, J.; Hafer, G.; Heggemann, J.; Wiemeyer, S.; John, S.M.; Hübner, U. Predicting the amputation risk for patients with diabetic foot ulceration—A Bayesian decision support tool. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, Z.; Mathisen, A.; Svendsen, K.; Engberg, S.; Thomsen, T.R.; Kirketerp-Møller, K. Toward Machine-Learning-Based Decision Support in Diabetes Care: A Risk Stratification Study on Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Amputation. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 601602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, M.; Reeves, N.D.; Rajbhandari, S.; Ahmad, N.; Wang, C.; Yap, M.H. Recognition of ischaemia and infection in diabetic foot ulcers: Dataset and techniques. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 117, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandakar, A.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Ali, S.H.M.; Hasan, M.A.; Kiranyaz, S.; Rahman, T.; Alfkey, R.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Malik, R.A. A machine learning model for early detection of diabetic foot using thermogram images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, S.L.; Nir, G.; Salcudean, S.E. A new era: Artificial intelligence and machine learning in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2019, 16, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Senneville, É.; Abbas, Z.G.; Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Diggle, M.; Embil, J.M.; Kono, S.; Lavery, L.A.; Malone, M.; van Asten, S.A.; et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of foot infection in persons with diabetes (IWGDF 2019 update). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anaya, D.A.; Dellinger, E.P. Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection: Diagnosis and Management. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.; Min, S. Development of a suicide index model in general adolescents using the South Korea 2012–2016 national representative survey data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.-J.; Ahn, S.-G.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-K. Development of the Hypertension Index Model in General Adult Using the Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey and the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Yoo, G.; Lee, T.; Uh, Y.; Kim, J. Identification of the robust predictor for sepsis based on clustering analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, E.K.; Suganthan, P.N.; Yao, X. Gene selection algorithms for microarray data based on least squares support vector machine. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.; Jang, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Oh, C.-M. Development and validation of a new diabetes index for the risk classification of present and new-onset diabetes: Multicohort study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Lee, H. Shared Blood Transcriptomic Signatures between Alzheimer’s Disease and Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Víquez-Molina, G.; López-Valverde, M.E.; Aragón-Hernández, J.; Rojas-Bonilla, J.M.; Murillo-Vargas, C. Clinical, microbiological and inflammatory markers of severe diabetic foot infections. Diabet. Med. 2021, 38, e14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Soares, M.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M. A new diabetic foot risk assessment tool: DIAFORA. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.J.; Crisologo, P.A.; Sivaganesan, S.; Caldwell, C.C.; Henning, J. Evaluation of the Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) score for detecting necrotizing soft tissue infections in patients with diabetes and lower extremity infection. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 171, 108520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.-H.; Park, S.; Park, Y.U.; Kwack, K.-S.; Jeon, S.W.; Lee, H.Y. Multivariate analyses of MRI findings for predicting osteomyelitis of the foot in diabetic patients. Acta Radiol. 2020, 61, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.-H.; Khin, L.-W.; Heng, K.-S.; Tan, K.-C.; Low, C.-O. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: A tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribb, B.I.; Wang, M.T.M.; Kulasegaran, S.; Gamble, G.D.; MacCormick, A.D. The SIARI Score: A Novel Decision Support Tool Outperforms LRINEC Score in Necrotizing Fasciitis. World J. Surg. 2019, 43, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; McWilliams, B.; Khan, S.U. Reliability of the Laboratory Risk Indicator in Necrotising Fasciitis (LRINEC) score. Surgeon 2018, 17, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shammaree, S.A.W.; Abu, A.B.A.; Salman, I.N. Procalcitonin levels and other biochemical parameters in patients with or without diabetic foot complications. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Asten, S.A.; Jupiter, D.C.; Mithani, M.; La Fontaine, J.; Davis, K.E.; Lavery, L.A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein to monitor treatment outcomes in diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, D.; Papanas, N.; Dascalu, A.M.; Kempler, P.; Raz, I.; Rizvi, A.A.; Rizzo, M.; Tudor, C.; Tudosie, M.S.; Tanasescu, D.; et al. Significance of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Platelet Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) in Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Potential New Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Low. Extremity Wounds 2021, 15347346211057742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompers, L.; Schaper, N.; Apelqvist, J.; Edmonds, M.; Jude, E.; Mauricio, D.; Uccioli, L.; Urbancic, V.; Bakker, K.; Holstein, P.; et al. Prediction of outcome in individuals with diabetic foot ulcers: Focus on the differences between individuals with and without peripheral arterial disease. The EURODIALE Study. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhubail, A.; Sewify, M.; Messenger, G.; Masoetsa, R.; Hussain, I.; Nair, S.; Tiss, A. Microbiological profile of diabetic foot ulcers in Kuwait. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakil, S.; Khan, A.U. Infected foot ulcers in male and female diabetic patients: A clinico-bioinformative study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2010, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavery, L.A.; Armstrong, D.G.; Wunderlich, R.P.; Mohler, M.J.; Wendel, C.S.; Lipsky, B.A. Risk Factors for Foot Infections in Individuals With Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Parker, C.N.; Parker, T.J.; Kinnear, E.M.; Derhy, P.H.; Alvarado, A.M.; Huygens, F.; Lazzarini, P.A. Incidence and risk factors for developing infection in patients presenting with uninfected diabetic foot ulcers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-X.; Wang, Y.-T.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.-L. Sex Differences in Osteomyelitis of the Foot in Persons With Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Wound Manag. Prev. 2021, 67, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavery, L.A.; Peters, E.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Wendel, C.S.; Murdoch, D.P.; Lipsky, B.A. Risk factors for developing osteomyelitis in patients with diabetic foot wounds. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 83, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Korean Society for Chemotherapy; The Korean Society of Infectious Diseases; The Korean Orthopaedic Association. Clinical Guidelines for the Antimicrobial Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections in Korea. Infect. Chemother. 2014, 46, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morocho-Cayamcela, M.E.; Lee, H.; Lim, W. Machine Learning for 5G/B5G Mobile and Wireless Communications: Potential, Limitations, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 137184–137206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lee, H. Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease using blood gene expression data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Game, F.L.; Selby, N.M.; McIntyre, C.W. Chronic kidney disease and the foot in diabetes—Is inflammation the missing link? Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2013, 123, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, K.L.; Abusamaan, M.S.; Voss, B.F.; Thurber, E.G.; Al-Hajri, N.; Gopakumar, S.; Le, J.T.; Gill, S.; Blanck, J.; Prichett, L.; et al. Glycemic control and diabetic foot ulcer outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Diabetes its Complicat. 2020, 34, 107638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornik, I.; Gornik, O.; Gašparović, V. HbA1c is outcome predictor in diabetic patients with sepsis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S73–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniluk, A.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M.; Kamińska, J.; Kemona, H.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. Mean Platelet Volume (MPV): New Perspectives for an Old Marker in the Course and Prognosis of Inflammatory Conditions. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 9213074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.K.; Seo, G.H.; Han, E. The incidence and seasonal variation of necrotizing fasciitis in Korea: A nationwide cross-sectional study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1090.e1–1090.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.S. Diagnosis and management of necrotising fasciitis: A multiparametric approach. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 75, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, K.; Kato, M.; Morishita, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Nakatsukasa, S.; Kuwata, T. Hepatitis influences the diagnosis of Necrotising soft-tissue infection: A proposed modification to the Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotising Fasciitis (LRINEC) score from a retrospective study at a single institution. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2021, 74, 644–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitché, P.; Diata, A.B.; Faye, O.; Tounkara, T.M.; Niamba, P.; Mouhari-Toure, A.; Ly, F.; Soumah, M.M.; Some-Korsaga, N.; Akakpo, A.S.; et al. Risk factors associated with necrotizing fasciitis of the lower limbs: A multicenter case-control study. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 148, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, D.; Kanlic, E.; Bader, J.; Ortiz, M.; Abdelgawad, A. Hepatitis C viral infection as an associated risk factor for necrotizing fasciitis. Orthopedics 2012, 35, e510–e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Song, Z. Modified Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (m-LRINEC) Score System in Diagnosing Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Nested Case-Control Study. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishino, T.; Asai, N.; Ohashi, W.; Sakanashi, D.; Kato, H.; Shiota, A.; Hagihara, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamagishi, Y.; Suematsu, H.; et al. Usefulness of serum procalcitonin for necrotizing fasciitis as an early diagnostic tool. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisologo, P.A.; Davis, K.E.; Ahn, J.; Farrar, D.; Van Asten, S.; La Fontaine, J.; Lavery, L.A. The infected diabetic foot: Can serum biomarkers predict osteomyelitis after hospital discharge for diabetic foot infections? Wound Repair. Regen. 2020, 28, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.H.; Wu, K.H.; Hsiao, C.T.; Wu, S.R.; Chang, C.P. Utility of modified Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (MLRINEC) score in distinguishing necrotizing from non-necrotizing soft tissue infections. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2021, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Hsu, R.W.; Huang, K.C.; Huang, T.J. Laboratory indicators for early detection and surgical treatment of vibrio necrotizing fasciitis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harasawa, T.; Kawai-Kowase, K.; Tamura, J.; Nakamura, M. Accurate and quick predictor of necrotizing soft tissue infection: Usefulness of the LRINEC score and NSTI assessment score. J. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 26, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer Balin, S.; Sagmak Tartar, A.; Uğur, K.; Kilinç, F.; Telo, S.; Bal, A.; Balin, M.; Akbulut, A. Pentraxin-3: A new parameter in predicting the severity of diabetic foot infection? Int. Wound J. 2019, 16, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, A.E.; Didyk, A.A.; Woods, J.B.; Burns, S.E.; Wrobel, J.S.; Armstrong, D.G. Combined clinical and laboratory testing improves diagnostic accuracy for osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2009, 48, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diabetic Foot (Ref) | Necrotizing Fasciitis (p-Value, vs. Ref) | Osteomyelitis (p-Value, vs. Ref) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 728 | 76 | 777 |
| Age, years | 70.2 ± 0.47 | 69.8 ± 1.55 (0.788) | 66.9 ± 0.49 (<0.001) |
| Sex (Male), n | 539 (74.0%) | 42 (55.3%, 0.001) | 442 (56.9%, <0.001) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 4.9 ± 0.26 | 12.9 ± 1.32 (<0.001) | 3.5 ± 0.41 (<0.001) |
| BUN, mg/dL | 26.6 ± 0.69 | 24.7 ± 1.91 (0.349) | 17.9 ± 0.6 (<0.001) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.12 (<0.001) | 1.2 ± 0.04 (<0.001) |
| Total protein, g/dL | 6.6 ± 0.03 | 5.9 ± 0.13 (<0.001) | 6.8 ± 0.04 (<0.001) |
| Ca, mg/dL | 8.8 ± 0.03 | 8.3 ± 0.11 (<0.001) | 9.1 ± 0.03 (<0.001) |
| Na, mmol/L | 137.3 ± 0.18 | 136.9 ± 0.74 (0.664) | 138.7 ± 0.23 (<0.001) |
| K, mmol/L | 4.5 ± 0.03 | 4.1 ± 0.08 (<0.001) | 4.3 ± 0.02 (<0.001) |
| Cl, mmol/L | 101 ± 0.21 | 101.5 ± 0.77 (0.603) | 102.8 ± 0.24 (<0.001) |
| HbA1c, % | 8.3 ± 0.08 | 7.8 ± 0.22 (0.031) | 7.9 ± 0.07 (<0.001) |
| ESR, mm/h | 50 ± 1.19 | 53.7 ± 3.6 (0.339) | 39.5 ± 1.13 (<0.001) |
| WBC, ×109/L | 10.1 ± 0.22 | 16 ± 1.29 (<0.001) | 9.1 ± 0.4 (<0.001) |
| RBC, ×1012/L | 3.8 ± 0.03 | 3.8 ± 0.09 (0.654) | 4.2 ± 0.03 (<0.001) |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.6 ± 0.08 | 11.6 ± 0.27 (0.859) | 12.6 ± 0.08 (<0.001) |
| Hematocrit, % | 34.8 ± 0.22 | 34.8 ± 0.81 (0.962) | 37.6 ± 0.25 (<0.001) |
| Platelet, ×109/L | 280.2 ± 4.42 | 242.1 ± 15.66 (0.021) | 288.7 ± 4.9 (0.158) |
| MPV, fL | 8 ± 0.04 | 8.4 ± 0.16 (0.005) | 7.7 ± 0.05 (<0.001) |
| MPC, g/dL | 26.5 ± 0.07 | 26.5 ± 0.17 (0.975) | 26.6 ± 0.05 (0.354) |
| DNI, % | 0.9 ± 0.11 | 9.1 ± 1.62 (<0.001) | 0.7 ± 0.51 (0.029) |
| MPXI | 0.1 ± 0.17 | 1.8 ± 0.53 (0.003) | 0.4 ± 0.17 (0.172) |
| NLR, % | 7.8 ± 0.46 | 24.6 ± 2.7 (<0.001) | 5 ± 0.84 (<0.001) |
| Univariate | Multivariate (Model 1) | Multivariate (Model 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Age | 1.003 (0.98–1.026) | NS | NS |
| Sex (Female) | 3.42 (1.875–6.24) | 5.161 (2.183–12.203) | 5.394 (2.3–12.65) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 1.103 (1.07–1.137) | 1.07 (1.017–1.125) | 1.07 (1.021–1.121) |
| BUN, mg/dL | 0.993 (0.975–1.011) | NS | NS |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.716 (0.551–0.932) | 0.486 (0.305–0.774) | 0.482 (0.305–0.763) |
| Total protein, g/dL | 0.399 (0.285–0.558) | 0.864 (0.46–1.623) | NS |
| Ca, mg/dL | 0.397 (0.276–0.57) | 0.566 (0.289–1.107) | 0.49 (0.299–0.803) |
| Na, mmol/L | 1 (0.939–1.064) | NS | NS |
| K, mmol/L | 0.36 (0.218–0.594) | 0.708 (0.354–1.416) | NS |
| Cl, mmol/L | 1.037 (0.983–1.094) | NS | NS |
| HbA1c, % | 0.791 (0.666–0.939) | 0.79 (0.641–0.973) | 0.767 (0.626–0.939) |
| ESR, mm/h | 1.006 (0.997–1.015) | NS | NS |
| WBC, ×109/L | 1.078 (1.037–1.121) | 0.952 (0.882–1.027) | NS |
| RBC, ×1012/L | 0.924 (0.607–1.407) | NS | NS |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 0.959 (0.834–1.103) | NS | NS |
| Hematocrit, % | 0.996 (0.949–1.046) | NS | NS |
| Platelet, ×109/L | 0.998 (0.996–1.001) | NS | NS |
| MPV, fL | 1.243 (0.956–1.616) | NS | NS |
| MPC, g/dL | 0.968 (0.833–1.125) | NS | NS |
| DNI, % | 1.258 (1.157–1.369) | 1.137 (1.063–1.216) | 1.14 (1.065–1.22) |
| MPXI | 1.097 (1.025–1.174) | 0.991 (0.907–1.083) | NS |
| NLR, % | 1.072 (1.05–1.093) | 1.072 (1.031–1.114) | 1.055 (1.025–1.085) |
| Univariate | Multivariate (Model 1) | Multivariate (Model 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Age | 0.984 (0.978–0.991) | 0.985 (0.977–0.993) | 0.984 (0.977–0.992) |
| Sex (Female) | 2.2 (1.769–2.735) | 2.547 (1.961–3.308) | 2.597 (2.011–3.353) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.954 (0.937–0.971) | 1.011 (0.988–1.036) | NS |
| BUN, mg/dL | 0.953 (0.944–0.963) | 0.992 (0.978–1.005) | NS |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.679 (0.615–0.75) | 0.87 (0.779–0.97) | 0.839 (0.77–0.915) |
| Total protein, g/dL | 1.538 (1.355–1.746) | 1.232 (1.025–1.48) | 1.282 (1.102–1.491) |
| Ca, mg/dL | 1.791 (1.539–2.084) | 1.134 (0.907–1.418) | NS |
| Na, mmol/L | 1.089 (1.062–1.117) | 1.001 (0.959–1.046) | NS |
| K, mmol/L | 0.66 (0.554–0.785) | 0.618 (0.497–0.769) | 0.611 (0.496–0.752) |
| Cl, mmol/L | 1.073 (1.051–1.095) | 1.05 (1.012–1.09) | 1.047 (1.021–1.073) |
| HbA1c, % | 0.934 (0.886–0.984) | 0.881 (0.826–0.941) | 0.88 (0.825–0.938) |
| ESR, mm/h | 0.99 (0.986–0.993) | 0.995 (0.99–1) | 0.996 (0.991–1.001) |
| WBC, ×109/L | 0.961 (0.942–0.981) | 1.019 (0.983–1.056) | NS |
| RBC, ×1012/L | 1.925 (1.648–2.248) | 0.805 (0.496–1.307) | NS |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 1.232 (1.171–1.297) | 0.937 (0.7–1.255) | NS |
| Hematocrit, % | 1.076 (1.057–1.096) | 1.11 (0.995–1.238) | 1.067 (1.042–1.092) |
| Platelet, ×109/L | 1.001 (1–1.002) | 1.002 (1–1.003) | 1.002 (1.001–1.003) |
| MPV, fL | 0.704 (0.627–0.79) | 0.87 (0.756–1.001) | 0.87 (0.761–0.996) |
| MPC, g/dL | 1.029 (0.978–1.084) | NS | NS |
| DNI, % | 0.91 (0.86–0.964) | 0.981 (0.935–1.029) | NS |
| MPXI | 1.008 (0.984–1.031) | NS | NS |
| NLR, % | 0.944 (0.927–0.962) | 0.972 (0.948–0.996) | 0.977 (0.96–0.994) |
| Necrotizing Fasciitis | Osteomyelitis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Beta-Coefficient | Predictors | Beta-Coefficient |
| Constants | 2.733 | Constants | −5.218 |
| Sex (Female) | 1.685 | Sex (Female) | 0.954 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.068 | Age | −0.016 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | −0.73 | Creatinine, mg/dL | −0.175 |
| Ca, mg/dL | −0.713 | Total protein, g/dL | 0.248 |
| HbA1c, % | −0.266 | HbA1c, % | −0.128 |
| DNI, % | 0.131 | K, mmol/L | −0.493 |
| NLR, % | 0.053 | Cl, mmol/L | 0.046 |
| Hematocrit, % | 0.065 | ||
| MPV, fL | −0.139 | ||
| Platelet, ×109/L | 0.002 | ||
| ESR, mm/h | −0.004 | ||
| NLR, % | −0.023 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Yoo, G.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, D.M.; Kim, J. Classification Model for Diabetic Foot, Necrotizing Fasciitis, and Osteomyelitis. Biology 2022, 11, 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091310
Kim J, Yoo G, Lee T, Kim JH, Seo DM, Kim J. Classification Model for Diabetic Foot, Necrotizing Fasciitis, and Osteomyelitis. Biology. 2022; 11(9):1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091310
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jiye, Gilsung Yoo, Taesic Lee, Jeong Ho Kim, Dong Min Seo, and Juwon Kim. 2022. "Classification Model for Diabetic Foot, Necrotizing Fasciitis, and Osteomyelitis" Biology 11, no. 9: 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091310
APA StyleKim, J., Yoo, G., Lee, T., Kim, J. H., Seo, D. M., & Kim, J. (2022). Classification Model for Diabetic Foot, Necrotizing Fasciitis, and Osteomyelitis. Biology, 11(9), 1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091310






