Phylogeny and Morphology of Novel Species and New Collections Related to Sarcoscyphaceae (Pezizales, Ascomycota) from Southwestern China and Thailand
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Morphological Examination, and Deposition
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
| Species Name | Country | Voucher/Strain Number | ITS | LSU | SSU | rpb2 | tef-1α | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chorioactis geaster ♦ | USA | ZZ2 FH | AY307935 | AY307943 | – | DQ017608 | – | [47] |
| Cookeina colensoi | Mexico | CUP 62500 | AF394040 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina colensoi | Australia | DAR 63642 | AF394038 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina colensoi | India | FH 00432432 | AF394532 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina colensoi | New Zealand | PDD 55306 | AF394037 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina cremeirosea | American Samoa | UTC000275474 | KU306964 | – | – | – | – | [49] |
| Cookeina cremeirosea | American Samoa | UTC000275475 | KU306963 | – | – | – | – | [49] |
| Cookeina garethjonesii ♦ | China | HKAS90509 | KY094617 | MG871315 | – | MG980711 | MG980686 | [50] |
| Cookeina garethjonesii ♦ | China | HKAS90513 | KY094622 | MG871316 | – | MG980712 | MG980687 | [50] |
| Cookeina indica | China | C.ind119 | AF394029 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina indica ♦ | China | MFLU 16-0610 | KY094621 | MG871343 | – | MG980727 | – | [3,50] |
| Cookeina indica | Thailand | MFLU 20-0548 | MT941004 | – | – | – | – | [51] |
| Cookeina indica ♦ | China | HKAS 121171 | OK170053 | OK398387 | OK398409 | – | OK557973 | This study |
| Cookeina indica | China | HKAS 121172 | OK170054 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina indica | China | HKAS 121173 | OK170055 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina indica ♦ | China | HKAS 121174 | OK170058 | OK398386 | OK398408 | – | OK557972 | This study |
| Cookeina insititia | China | FH Wang sp 2 | AF394033 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina insititia | China | HMAS 70078 | AF394030 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina insititia | China | HMAS 71942 | AF394031 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina korfii | Philippines | CUP-SA-1797 | KT893782 | – | – | – | – | [52] |
| Cookeina korfii | Philippines | CUP-SA-2454 | KT893781 | – | – | – | – | [52] |
| Cookeina sinensis | China | HKAS 14679 | AF394028 | – | – | – | – | [52] |
| Cookeina sinensis | China | HMAS 70088 | AF394027 | – | – | – | – | [52] |
| Cookeina sinensis ♦ | China | HKAS 121175 | OK170056 | OK398385 | OK398407 | – | OK557971 | This study |
| Cookeina sinensis | China | HKAS 121176 | OK170057 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina sinensis ♦ | China | HKAS 121177 | OK170059 | OK398384 | OK398406 | – | OK557970 | This study |
| Cookeina sinensis | China | HKAS 121178 | OK170060 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina sinensis | China | HKAS 121179 | OK170067 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina sinensis ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0155 | OK413269 | OK398383 | OK398405 | – | OK557969 | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | Malaysia | C TL 6035 | AF394018 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 1C-D4 | AF394011 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 1D-D6 | AF394016 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 1E-D5 | AF394003 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 2610 | AF394005 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 2D-D4 | AF394017 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 4A-D4 | AF394014 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 7A-D4 | AF394006 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Colombia | FH Muneton 296 | AF394013 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Thailand | FH Pfister 7131 | AF394009 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa | Thailand | FH Pfister 7143 | AF394010 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina speciosa ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0156 | OK413270 | OK398390 | OK398412 | OK585150 | OK557976 | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0157 | OK413271 | OK398391 | OK398413 | OK585151 | OK557977 | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0158 | OK413272 | OK398392 | OK398414 | OK585152 | OK557978 | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0159 | OK413273 | OK398393 | OK398415 | OK585153 | OK557979 | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | Thailand | MFLU 21-0160 | OK413274 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | Thailand | MFLU 21-0161 | OK413275 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | Thailand | MFLU 21-0162 | OK413276 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121180 | OK170044 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121181 | OK170045 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121182 | OK170047 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121183 | OK170048 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121184 | OK170049 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121185 | OK170050 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121186 | OK170064 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121187 | OK170065 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 121188 | OK170066 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina speciosa | China | HKAS 124640 | OP364889 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina sulcipes | Thailand | MFLU 15-2358 | KY094620 | – | – | – | – | [50] |
| Cookeina tricholoma | Thailand | FH Pfister 7170 | AF394020 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina tricholoma ♦ | China | HKAS87041 | KY094619 | MG871317 | – | – | MG980688 | [3,50] |
| Cookeina tricholoma ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 15-2359 | KY094618 | MG871318 | MG859240 | – | MG980689 | [3,50] |
| Cookeina tricholoma ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0165 | OK413279 | OK398394 | OK398416 | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0166 | OK413280 | OK398395 | OK398417 | – | OK557980 | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0167 | OK413281 | OK398396 | OK398418 | – | OK557981 | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma | Thailand | MFLU 21-0168 | OK413282 | OK398397 | OK398419 | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma | Thailand | MFLU 21-0169 | OK413283 | OK398398 | OK398420 | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma | Thailand | MFLU 21-0163 | OK413277 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma | Thailand | MFLU 21-0164 | OK413278 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma | China | HKAS 121189 | OK170043 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma | China | HKAS 121190 | OK170046 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina tricholoma | China | HKAS 121191 | OK170061 | – | – | – | – | This study |
| Cookeina venezuelae | Puerto Rico | FH00432502 | AF394041 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina venezuelae | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 6065 | AF394044 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina venezuelae | Venezuela | FH Iturriaga 6066 | AF394043 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Cookeina venezuelae | Guadeloupe | FH00432503 | AF394042 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Geodina guanacastensis ♦ | Bahamas | FH | MN096939 | MN096940 | MN096941 | MN103424 | MN090946 | [23] |
| Geodina guanacastensis | Costa Rica | CUP CA84 | MN096938 | – | – | – | – | [23] |
| Geodina guanacastensis | Dominican Republic | JBSD 127408 | MG597289 | – | – | – | – | [22,23] |
| Geodina guanacastensis | Dominican Republic | JBSD 127409 | MG597290 | – | – | – | – | [22,23] |
| Kompsoscypha chudei ♦ | China | HKAS 107663 | MT907443 | MT907444 | – | – | – | [51] |
| Kompsoscypha phyllogena ♦ | Puerto Rico | DHP 10-690 | – | JQ260810 | JQ260820 | MN103430 | – | [15] |
| Microstoma floccosum | Mexico | FH K. Griffith (Micro45) | AF394046 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Microstoma floccosum | Mexico | FH K. Griffith (Micro46) | AF394045 | – | – | – | – | [48] |
| Nanoscypha striatispora | China | HMAS 61133 | U66016 | – | – | – | – | [21] |
| Nanoscypha tetraspora ♦ | Puerto Rico | FH 00464570 | AF117352 | DQ220374 | AF006314 | – | – | [21,53,54] |
| Nanoscypha aequispora ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0170 | OK413284 | OK398399 | OK398421 | OK585154 | – | This study |
| Nanoscypha aequispora ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 21-0171 | OK413285 | OK398400 | OK398422 | OK585155 | OK557982 | This study |
| Neournula pouchetii | USA | MO 205345 | KT968605 | – | – | – | – | [55] |
| Phillipsia carnicolor ♦ | Thailand | DHP-7126 (FH) | AF117353 | JQ260811 | JQ260821 | MN103426 | MN090948 | [53] |
| Phillipsia carnicolor | Thailand | MFLU 18-0713 | MH602282 | – | – | – | – | [56] |
| Phillipsia chinensis | China | HMAS 76094 | AY254710 | – | – | – | – | [57] |
| Phillipsia crispata | Ecuador | T. Læssøe AAU-44801 | AF117354 | – | – | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia crispata ♦ | Ecuador | T. Læssøe AAU-44895a | AF117355 | AY945845 | – | DQ017599 | – | [47] |
| Phillipsia domingensis | USA | CO-1864 (NO) | AF117363 | – | – | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia domingensis | Costa Rica | CO-2032 (NO) | AF117361 | – | – | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia domingensis ♦ | Thailand | DHP 7169 (FH) | AF117373 | JQ260817 | JQ260827 | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia domingensis | Dominican Republic | DR-321 (CFMR) | AF117370 | – | – | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia domingensis | Costa Rica | Franco-M 1270 (NY) | AF117358 | – | – | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia domingensis | Puerto Rico | PR-1583 (FH) | AF117365 | – | – | – | – | [47] |
| Phillipsia domingensis ♦ | China | HKAS 121192 | OK170062 | OK398388 | OK398410 | OK585148 | OK557974 | This study |
| Phillipsia domingensis ♦ | China | HKAS 121193 | OK170063 | OK398389 | OK398411 | OK585149 | OK557975 | This study |
| Phillipsia gelatinosa ♦ | Thailand | MFLU 15-2360 | KY498595 | KY498589 | – | MG980728 | – | [58] |
| Phillipsia gelatinosa | Thailand | MFLU 16-2956 | KY498593 | – | – | – | – | [58] |
| Phillipsia hydei | Thailand | MFLU 18-0714 | MH602283 | – | – | – | – | [56] |
| Phillipsia hydei | Thailand | MFLU 18-1329 | MH602284 | – | – | – | – | [56] |
| Phillipsia lutea ♦ | French Guiana | NY-4113 (NY) | AF117374 | JQ260816 | JQ260826 | [53] | ||
| Phillipsia olivacea | Costa Rica | Franco-M 1360 (NY) | AF117375 | – | – | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia olivacea ♦ | Venezuela | Halling-5456 (NY) | AF117376 | JQ260814 | JQ260824 | – | – | [53] |
| Phillipsia olivacea | Ecuador | T. Læssøe AAU-43162 (C) | AF117378 | – | – | – | – | [47] |
| Phillipsia subpurpurea | China | MFLU 16-0612 | KY498596 | – | – | – | – | [58] |
| Pithya cupressina ♦ | USA | mh 208 | U66009 | JQ260818 | AF006316 | – | – | [23,59] |
| Pithya sp. | China | DWS8m3 | KJ188703 | [60] | ||||
| Pithya sp. | USA | T5N32c | AY465469 | – | – | – | – | [61] |
| Pithya vulgaris | – | RK 90.01 | U66008 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Pithya villosa ♦ | China | HKAS 104653 | OK170069 | OK398401 | OK398423 | OK585156 | – | This study |
| Pithya villosa ♦ | China | HKAS 121194 | OK170068 | OK398402 | OK398424 | – | – | This study |
| Plectania nannfeldtii ♦ | USA | FH 00822732 | – | AY945853 | – | DQ017592 | KC109214 | [47,62] |
| Pseudopithyella minuscula ♦ | USA | FH 00465568 | – | AY945849 | AF006317 | DQ017600 | FJ238387 | [47] |
| Rickiella edulis ♦ | Argentina | BAFC 51697 | JQ260808 | JQ260809 | JQ260819 | MN103425 | MN090947 | [15] |
| Sarcoscypha austriaca | Norway | CUP 62771 | U66010 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha austriaca | USA | CUP 63162 | U66011 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha coccinea ♦ | – | AFTOL-ID 50 | DQ491486 | AY544647 | – | DQ497612 | – | [63] |
| Sarcoscypha coccinea ♦ | France | AFTOL-ID 930 | – | FJ176859 | FJ176805 | FJ713615 | – | [63] |
| Sarcoscypha coccinea | USA | CUP 62113 | U66013 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha coccinea | USA | CUP 63160 | U66015 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha dudleyi | USA | CUP 62775 | U66018 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha dudleyi | China | HMJAU36044 | KU234218 | – | – | – | – | [64] |
| Sarcoscypha dudleyi | – | mh 192 | U66019 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha emarginata | Luxembourg | CUP 62723 | U66020 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha emarginata | – | HB2861 | U66021 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha hosoyae | – | TRL 456 | U66031 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha humberiana | China | TNM F28630 | KT716833 | – | – | – | – | [65] |
| Sarcoscypha humberiana | China | CUP 63489 | U66028 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha javensis | China | HMAS 61198 | U66026 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha knixoniana | – | TRL 1006 | U66030 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha korfiana | – | mh 705 | AF026308 | – | – | – | – | [21] |
| Sarcoscypha longitudinalis ♦ | China | HKAS 121195 | OK170051 | OK398403 | OK398425 | OK585157 | – | This study |
| Sarcoscypha longitudinalis ♦ | China | HKAS 121196 | OK170052 | OK398404 | OK398426 | – | – | This study |
| Sarcoscypha macaronesica | Canary Islands | CUP-MM 2628 | U66022 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha macaronesica | – | TFC-MIC 6460 | U66023 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcpscypha mesocyatha | China | TNM F3688 | KT936558 | – | – | – | – | [65] |
| Sarcpscypha mesocyatha | China | TNM F5134 | KT936559 | – | – | – | – | [65] |
| Sarcoscypha mesocyatha | USA | CUP 62699 | U66029 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha minuta | China | TNM F28831 | KT716834 | – | – | – | – | [65] |
| Sarcoscypha occidentalis | USA | CUP 62777 | U66024 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha occidentalis | USA | CUP 63484 | U66025 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha sp. | China | HMAS 61202 | U66027 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Sarcoscypha tatakensis | China | TNM F0754 | KT716835 | – | – | – | – | [65] |
| Sarcoscypha tatakensis | China | TNM F0993 | KT716836 | – | – | – | – | [65] |
| Sarcoscypha vassiljevae ♦ | Chian | HKAS 89817 | MG871302 | MG871337 | – | MG980724 | MG980700 | [3] |
| Sarcoscypha vassiljevae | China | HMAS 61210 | U66017 | – | – | – | – | [59] |
| Urnula craterium ♦ | USA | DHP 04-511 | – | AY945851 | – | DQ017595 | KC109216 | [47,62] |
| Wynnea americana ♦ | USA | FH 00445979 | MK599141 | AY945848 | MK592785 | MN103435 | MN103417 | [23,66] |
| Wynnea americana | USA | HKAS 75484 | MG871308 | – | – | – | – | [3] |
| Wynnea gigantea | China | HKAS 101385 | MG871307 | – | – | – | – | [3] |
| Wynnea macrospora ♦ | China | FH 00445975 | MK335784 | MK335803 | MK335793 | MN103432 | MN103419 | [23,66] |
| Wynnea macrospora ♦ | – | CUP 2684 | – | MK335804 | MK335795 | – | MN103420 | [23,66] |
| Wynnea sparassoides ♦ | USA | FH 00445986 | – | EU360917 | MK335796 | MN103431 | MN103418 | [23,47] |
3. Results
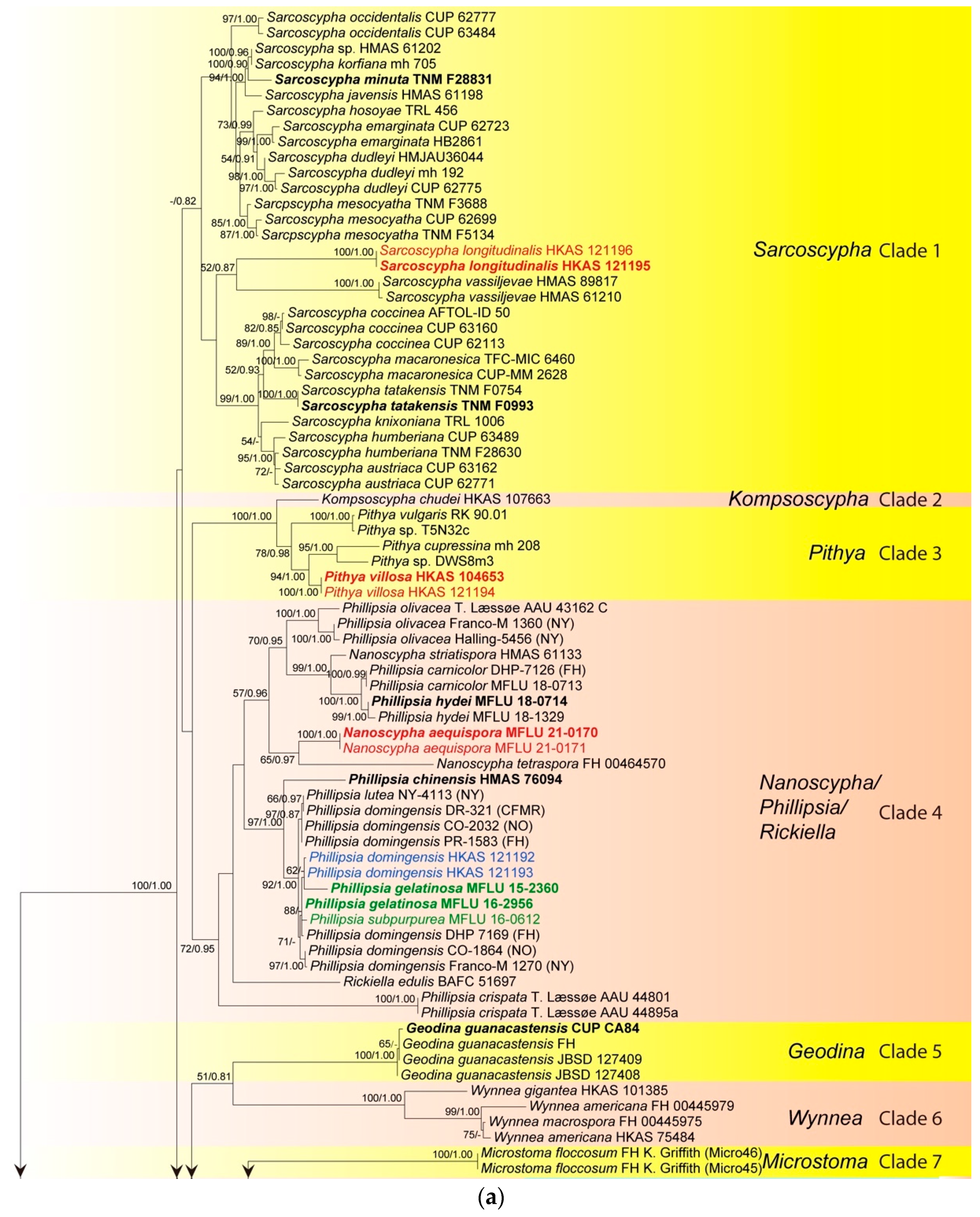
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2. Taxonomy


- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- Phillipsia domingensis (Berk.) Berk. ex Denison, Mycologia 61(2): 293 (1969); Figure 14
- 7.
- Pithya villosa M. Zeng, Q. Zhao & K.D. Hyde, sp. nov.; Figure 18
- 8.
- Sarcoscypha longitudinalis M. Zeng, Q. Zhao & K.D. Hyde, sp. nov.; Figure 19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baral, H.O. Taxonomische und ökologische Studien über Sarcoscypha coccinea agg., Zinnoberrote Kelchbecherlinge. Z. Mykol. 1984, 50, 117–145. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, D.H. Chapter 2. Pezizomycotina: Pezizomycetes, Orbiliomycetes. In Systematics and Evolution. The Mycota (a Comprehensive Treatise on Fungi as Experimental Systems for Basic and Applied Research; McLaughlin, D., Spatafora, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 7B, pp. 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ekanayaka, A.H.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; Zhao, Q. Taxonomy and phylogeny of operculate discomycetes: Pezizomycetes. Fungal Divers. 2018, 90, 161–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, M. Les Discomycètes suboperculés. Bull. Trimest. Soc. Mycol. Fr. 1946, 62, 218–240. [Google Scholar]
- Eckblad, F.E. The genera of the operculate discomycetes. A re-evaluation of their taxonomy, phylogeny and nomenclature. Nytt Mag. Bot. 1968, 15, 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W.Y. Hyaloscyphaceae, Sarcoscyphaceae et Sarcosomataceae. In Flora Fungorum Sinicorum; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004; Volume 21, pp. 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Gentekaki, E.; Hyde, K.D.; Zhao, Q. Donadinia echinacea and Plectania sichuanensis, two novel species of Sarcosomataceae from southwestern China. Phytotaxa 2021, 508, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korf, R.P. Nomenclatural notes. VII. Family and tribe names in the Sarcoscyphineae (Discomycetes) and a new taxonomic disposition of the genera. Taxon 1970, 19, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadefaud, M. Les asques para-operculés et la position systématique de la Pézize Sarcoscypha coccinea Fries ex Jacquin. C R Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. 1946, 222, 753–755. [Google Scholar]
- Eckblad, F.E. The suboperculate ascus, a review. Persoonia 1972, 6, 439–443. [Google Scholar]
- van Brummelen, J. Light and electron microscopic studies of the ascus top in Sarcoscypha coccinea. Persoonia 1975, 8, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- van Brummelen, J. The operculate ascus and allied forms. Persoonia 1978, 10, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson, D.A. The apical apparatus of the suboperculate ascus. Can. J. Bot. 1975, 53, 2660–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, D.A.; Benny, L.; Kimbrough, J.W. Asci of the Pezizales. VII. The apical apparatus of Galiella rufa and Sarcosoma globosum: Reevaluation of the suboperculate ascus. Can. J. Bot. 1980, 58, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.I.; Robledo, G.; LoBuglio, K.F.; Pfister, D.H. Rickiella edulis and its phylogenetic relationships within Sarcoscyphaceae. Kurtziana 2012, 37, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Al-Ani, L.K.T.; Tedersoo, L.; Haelewaters, D.; Rajeshkumar, K.C.; Zhao, R.L.; Aptroot, A.; Leontyev, D.V.; Saxena, R.K.; et al. Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 1060–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, L.; Perez-Moreno, J. Los hongos comestibles silvestres de Mexico, un enfoque integral. Micol. Neotrop. Apl. 1989, 2, 77–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, J.E.; Martin, A.M.; Sánchez, A.D. Evaluation of Cookeina sulcipes as an edible mushroom: Determination of its biomass composition. In Developments in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 37, pp. 1165–1172. [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk, H.; Onguene, N.A.; Kuyper, T.W. Knowledge and utilization of edible mushrooms by local populations of the rain forest of south Cameroon. Ambio. 2003, 32, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, D. Mushrooms Demystified: A Comprehensive Guide to the Fleshy Fungi; Ten Speed Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1986; pp. 1–836. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, F.A.; Pfister, D.H.; Potter, D.; Donoghue, M.J. Phylogenetic studies within the Pezizales. I. 18S rRNA sequence data and classification. Mycologia 1999, 91, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, C.; Medardi, G.; Alvarado, P. Contribution to the study of neotropical discomycetes: A new species of the genus Geodina (Geodina salmonicolor sp. nov.) from the Dominican Republic. Mycosphere 2018, 9, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.H.; Quijada, L.; LoBuglio, K.F. Geodina (Pezizomycetes: Wynneaceae) has a single widespread species in tropical America. Fungal Syst. Evol. 2020, 5, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAL Color Chart. Available online: https://www.ralcolor.com/ (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Kušan, I.; Matočec, N.; Antonić, O.; Hairaud, M. Biogeographical variability and re-description of an imperfectly known species Hamatocanthoscypha rotundispora (Helotiales, Hyaloscyphaceae). Phytotaxa 2014, 170, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayasiri, S.C.; Hyde, K.D.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Bhat, J.; Buyck, B.; Cai, L.; Dai, Y.C.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Ertz, D.; Hidayat, I.; et al. The Faces of Fungi database: Fungal names linked with morphology, phylogeny and human impacts. Fungal Divers. 2015, 74, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Index Fungorum. Available online: http://www.indexfungorum.org/names/names.asp (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Chaiwan, N.; Gomdola, D.; Wang, S.; Monkai, J.; Tibpromma, S.; Doilom, M.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Mortimer, P.E.; Lumyong, S.; Hyde, K.D. https://gmsmicrofungi.org: An online database providing updated information of microfungi in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Mycosphere 2021, 12, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.L. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protoc. Guide Methods Appl. 1990, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among Ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerase II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rehner, S.A.; Buckley, E. A Beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF1-α sequences: Evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs. Mycologia 2005, 97, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. TrimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, A. AliView: A fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nylander, J.A.; Ronquist, J.P.; Huelsenbeck, F.; Nieves-Aldrey, J.L. Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of combined data. Syst Biol. 2004, 53, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuin, P.A.S.; University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada. MTgui–A Simple Interface to ModelTest. Personal communication, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, D.; Buckley, T.R. Model selection and model averaging in phylogenetics: Advantages of akaike information criterion and bayesian approaches over likelihood ratio tests. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rannala, B.; Yang, Z. Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: A new method of phylogenetic inference. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 43, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Jeewon, R.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic evaluation and taxonomic revision of Schizothecium based on ribosomal DNA and protein coding genes. Fungal Divers. 2005, 19, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- FigTree. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Pfister, D.H.; Slater, C.; Hansen, K. Chorioactidaceae: A new family in the Pezizales (Ascomycota) with four genera. Mycol. Res. 2008, 112, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, R.N.; Pfister, D.H.; Iturriaga, T. A phylogenetic study of the genus Cookeina. Mycologia 2002, 94, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropp, B.R. Cookeina cremeirosea, a new species of cup fungus from the South Pacific. Mycoscience 2016, 58, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayaka, A.H.; Hyde, K.D.; Zhao, Q. The genus Cookeina. Mycosphere 2016, 7, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chethana, K.W.T.; Niranjan, M.; Dong, W.; Samarakoon, M.C.; Bao, D.; Calabon, M.S.; Chaiwan, N.; Chuankid, B.; Dayarathne, M.C.; de Silva, N.I.; et al. AJOM new records and collections of fungi: 101–150. Asian J. Mycol. 2021, 4, 113–260. [Google Scholar]
- Iturriaga, T.; Xu, F.; Pfister, D.H. Cookeina korfii, a new species hidden in Cookeina tricholoma. Ascomyceteorg. 2015, 7, 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.; Pfister, D.H.; Hibbett, D.S. Phylogenetic relationships among species of Phillipsia inferred from molecular and morphological data. Mycologia 1999, 91, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, B.A.; Hansen, K.; Pfister, D.H. A phylogenetic overview of the family Pyronemataceae (Ascomycota, Pezizales). Mycol Res. 2007, 11, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/KT968605 (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Zeng, M.; Ekanayaka, A.H.; Zhao, Q. Phylogeny and morphology of Phillipsia hydei sp. nov. (Sarcoscyphaceae) from Thailand. Phytotaxa 2019, 395, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.Y. Re-dispositions of Phillipsia (Pezizales) collections from China. Mycotaxon 2003, 86, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Ekanayaka, A.H.; Bhat, D.J.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; Zhao, Q. The genus Phillipsia from China and Thailand. Phytotaxa 2017, 316, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, F.A.; Potter, D. Phylogenetic relationships within Sarcoscypha based upon nucleotide sequences of the internal transcribed spacer of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Mycologia 1997, 89, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Walsh, E.; Naik, A.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, K.; Cai, L.; Zhang, N. Temperate pine barrens and tropical rain forests are both rich in undescribed fungi. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganley, R.J.; Newcombe, G. Fungal endophytes in seeds and needles of Pinus monticola. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.; Perry, B.A.; Dranginis, A.W.; Pfister, D.H. A phylogeny of the highly diverse cup-fungus family Pyronemataceae (Pezizomycetes, Ascomycota) clarifies relationships and evolution of selected life history traits. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 67, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celio, G.J.; Padamsee, M.; Dentinger, B.T.M.; Bauer, R.; McLaughlin, D.J. Assembling the Fungal Tree of Life: Constructing the Structural and Biochemical Database. Mycologia 2006, 98, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.H.; Bau, T.; Li, Y. Newly recorded genus and species of Pezizales in China. Mycosystem 2016, 35, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Huang, C.L.; Wei, J.L. Two new species of Sarcoscypha (Sarcosyphaceae, Pezizales) from Taiwan. Phytotaxa 2016, 245, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; LoBuglio, K.F.; Pfister, D.H. On the co-occurrence of species of Wynnea (Ascomycota, Pezizales, Sarcoscyphaceae) and Armillaria (Basidiomycota, Agaricales, Physalacriaceae). Fungal Syst. Evol. 2019, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturriaga, T.; Pfister, D.H. A monograph of the genus Cookeina (Ascomycota, Pezizales, Sarcoscyphaceae). Mycotaxon 2006, 95, 137–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, D.H.; Kaushal, R. Cookeina indica, a new species from India with a key to the species of Cookeina. Mycotaxon 1984, 20, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.L. Several noteworthy higher fungi from southern Yunnan, China. Mycotaxon 1990, 38, 407–416. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Taxonomy of Cookeina in China. Mycotaxon 1997, 62, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, A.; Patil, M.S.; Dangat, B.T. Cookeina Sinensis from India. Mycosphere 2012, 3, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, R.W.G. Plumier’s Discomycetes. Mycotaxon 1994, 51, 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Denison, W.C. Central American Pezizales. IV. The genera Sarcoscypha, Pithya, and Nanoscypha. Mycologia 1972, 64, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, F.A. Relationships among Sarcoscypha species: Evidence from molecular and morphological characters. Mycologia 1998, 90, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, D.C.; Prasad, V. Indian Sarcoscyphaceous Fungi. In Technology & Engineering; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2008; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Berkeley, M.J. On a collection of fungi from Cuba. Part II. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1869, 10, 341–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick, J.E. Pilze aus Rio Grande do Sul (Brazilien). Brotéria 1906, 5, 5–53. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, D.H. Notes on Caribbean Discomycetes. V. A preliminary annotated checklist of the Caribbean Pezizales. J. Agric. Univ. P R 1974, 58, 358–378. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W.Y. Some new species and new records of discomycetes in China. IV. Mycotaxon 1991, 40, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Denison, W.C. Central American Pezizales. III. The genus Phillipsia. Mycologia 1969, 61, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turland, N.J.; Wiersema, J.H.; Barrie, F.R.; Greuter, W.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Herendeen, P.S.; Knapp, S.; Kusber, W.H.; Li, D.Z.; Marhold, K.; et al. International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Shenzhen Code) Adopted by the Nineteenth International Botanical Congress Shenzhen, China, July 2017; Regnum Vegetabile 159; Koeltz Botanical Books: Glashütten, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seaver, F.J. The North American Cup-Fungi (Operculates); Lancaster Press: New York, NY, USA, 1928; p. 533. [Google Scholar]
- Spooner, B. The larger cup fungi in Britain, part 4, Sarcoscyphaceae and Sarcosomataceae. Field Mycol. 2002, 3, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, P.M.; Cannon, P.F.; Minter, D.W.; Stalpers, J.A. Ainsworth & Bisby’s Dictionary of the Fungi, 10th ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Rajeshkumar, K.C.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Madrid, H.; Kirk, P.M.; Braun, U.; Singh, R.V.; Crous, P.W.; Kukwa, M.; et al. Notes for genera: Ascomycota. Fungal Divers. 2017, 86, 1–594. [Google Scholar]
- Fuckel, L. Symbolae mycologicae. Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Rheinischen Pilze. Jahrb. Nassau. Ver. Naturkd. 1870, 23–24, 1–459. [Google Scholar]
- Krieglsteiner, G.J. On some new, rare and critical Macromycetes in the Federal Republic of Germany. Z. Mykol. 1985, 51, 85–130. [Google Scholar]
- Meléndez-Howell, L.M.; Coute, A.; Mascarell, G.; Bellemère, A. Ultrastructure des asques et des ascospores de Desmazierella acicola (Sarcoscyphaceae, Pezizales, Ascomycetes). Intérêt Systematique et Biologique. Mycotaxon 1998, 68, 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Castellano, M.A.; Smith, J.E.; O’Dell, T.; Cázares, E.; Nugent, S. Handbook to Strategy 1 Fungal Taxa from the Northwest Forest Plan; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1999; pp. 1–195. [Google Scholar]
- Benkert, D. Pithya cupressina und P. vulgaris (Pezizales)–identisch oder nicht? Mycol. Bavarica. 2008, 10, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sammut, C. Pithya cupressina (Ascomycota: Pezizomycetes Sarcoscyphaceae): A new addition to the Maltese mycobiota. Cent. Mediterr. Nat. 2012, 5, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kunca, V. Pithya vulgaris znovuobjavená na Slovensku. Catathelasma 2015, 16, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-López, I.; Valenzuela, R.; Gay-González, A.D.; Lara-Chávez, M.B.N.; López-Villegasy, E.O.; Raymundo, T. La Familia Sarcoscyphaceae (Pezizales, Ascomycota) en México. Acta Bot. Mex. 2019, 126, e1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Index of Fungi 2: 444. Available online: http://sftp.kew.org/pub/data-repositories/LibriFungorum/IXF2/IXF2-444.jpg (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Saccardo, P.A. Discomyceteae et Phymatosphaeriaceae. Syll. Fung. 1889, 8, 1–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Petrak’s Lists 7: 982. Available online: http://sftp.kew.org/pub/data-repositories/LibriFungorum/Petrak7/Petrak7-982.jpg (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Döbbeler, P. Octosporella erythrostigma (Pezizales) and Pithyella frullaniae (Helotiales), two remarkable ascomycetes on Frullania dilatate. Feddes Repert. 2004, 115, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Species | Apothecia | Hymenium | Excipulum | Asci | Paraphyses | Ascospores | References |
| Nanoscypha aequispora |
|
|
|
|
|
| This study |
| Nanoscypha bella |
| – | – | – | – |
| [76,78] |
| Nanoscypha denisonii |
|
|
|
|
|
| [75] |
| Nanoscypha euspora |
| – | – |
|
|
| [77] |
| Nanoscypha macrospora |
|
|
|
|
|
| [73] |
| Nanoscypha pulchra |
|
|
|
|
|
| [6,73] |
| Nanoscypha striatispora |
|
|
|
|
|
| [74,79] |
| Nanoscypha tetraspora |
|
|
|
|
|
| [73] |
| Species | Asci | Ascospores | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phillipsia gelatinosa | 340–570 × 20–27 μm | 27–36 × 14–17 μm | [58] |
| Phillipsia gelatinosa MFLU15-2360 | 327–392 × 11–15 µm | 23.2–26.5 × 12.1–13.7 µm (Q = 1.77–2.25, Q = 1.93 ± 0.11) | In this study |
| Phillipsia gelatinosa MFLU 16-2956 | 350–380 × 12–15 µm | 21.4–24.1 × 11.0–12.1 µm (Q = 1.76–2.14, Q = 1.97± 0.10) | In this study |
| Phillipsia gelatinosa MFLU 16-2992 | 359–390 × 11–15 µm | 21.8–24.8 × 11.4–12.6 µm (Q = 1.71–2.15, Q = 1.95 ± 0.11) | In this study |
| Phillipsia subpurpurea MFLU16-0612 | 470–530 × 25–30 μm | 30–40 × 15–20 μm | [58] |
| Phillipsia subpurpurea MFLU 16-0612 | 339–414 × 13–16 µm | 22.1–24.7 × 12.1–14.3 µm (Q = 1.57–2.00, Q = 1.78 ± 0.12) | In this study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, M.; Gentekaki, E.; Hyde, K.D.; Zhao, Q.; Matočec, N.; Kušan, I. Phylogeny and Morphology of Novel Species and New Collections Related to Sarcoscyphaceae (Pezizales, Ascomycota) from Southwestern China and Thailand. Biology 2023, 12, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010130
Zeng M, Gentekaki E, Hyde KD, Zhao Q, Matočec N, Kušan I. Phylogeny and Morphology of Novel Species and New Collections Related to Sarcoscyphaceae (Pezizales, Ascomycota) from Southwestern China and Thailand. Biology. 2023; 12(1):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010130
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Ming, Eleni Gentekaki, Kevin D. Hyde, Qi Zhao, Neven Matočec, and Ivana Kušan. 2023. "Phylogeny and Morphology of Novel Species and New Collections Related to Sarcoscyphaceae (Pezizales, Ascomycota) from Southwestern China and Thailand" Biology 12, no. 1: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010130
APA StyleZeng, M., Gentekaki, E., Hyde, K. D., Zhao, Q., Matočec, N., & Kušan, I. (2023). Phylogeny and Morphology of Novel Species and New Collections Related to Sarcoscyphaceae (Pezizales, Ascomycota) from Southwestern China and Thailand. Biology, 12(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010130








