MACC1 as a Potential Target for the Treatment and Prevention of Breast Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MACC1
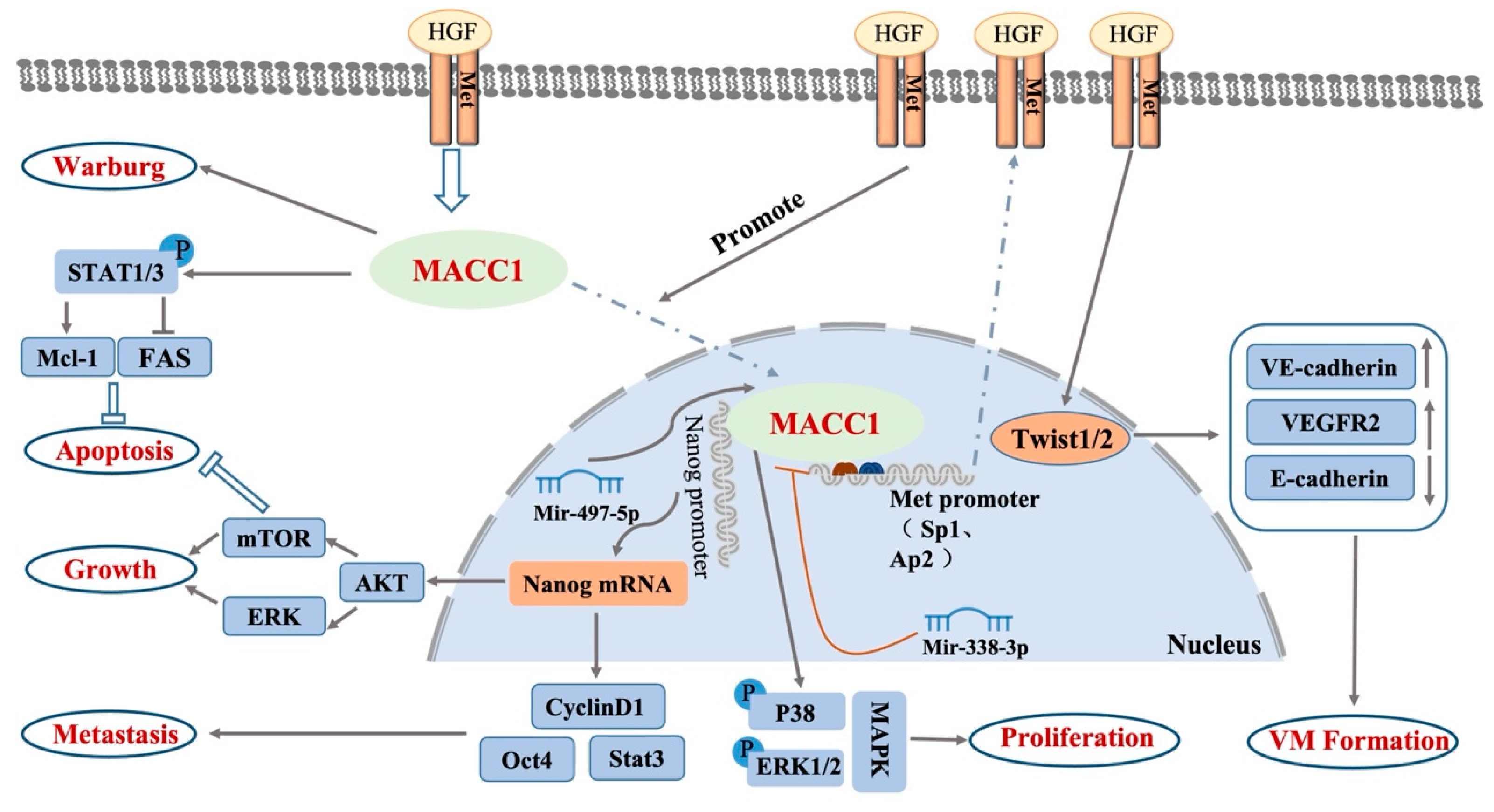
2.1. MACC1 Biology
2.2. Signaling Pathways in Which MACC1 Participates
3. Effect of MACC1 Overexpression on BC
4. Value of Serum MACC1 for BC
5. MACC1 Enhances Immune Escape in BC
6. MACC1 Enhances the Radiation Resistance of BC
7. Epigenetic Regulation of MACC1 in BC
8. MACC1-AS1 Participates in BC’s ceRNA Regulatory Network
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, W.; Chen, H.D.; Yu, Y.W.; Li, N.; Chen, W.Q. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.A.; Andrews, K.; Brooks, D.; DeSantis, C.E.; Fedewa, S.A.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Manassaram-Baptiste, D.; Brawley, O.W.; Wender, R.C. Cancer screening in the United States, 2016: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prat, A.; Pineda, E.; Adamo, B.; Galvan, P.; Fernandez, A.; Gaba, L.; Diez, M.; Viladot, M.; Arance, A.; Munoz, M. Clinical implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24 (Suppl. 2), S26–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barzaman, K.; Karami, J.; Zarei, Z.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Kazemi, M.H.; Moradi-Kalbolandi, S.; Safari, E.; Farahmand, L. Breast cancer: Biology, biomarkers, and treatments. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, C.; Haymond, A.; Davis, J.B.; Williams, A.; Espina, V. Protein biomarkers for subtyping breast cancer and implications for future research. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscitiello, C.; Vingiani, A.; Maisonneuve, P.; Viale, G.; Viale, G.; Curigliano, G. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in ER+/HER2- breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 183, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, V.; Das, A.B.; Saxena, U. Grade-specific diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer. Genomics 2020, 112, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoletov, K.; Beatty, P.H.; Lewis, J.D. Novel therapeutic targets for cancer metastasis. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2020, 20, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radhakrishnan, H.; Walther, W.; Zincke, F.; Kobelt, D.; Imbastari, F.; Erdem, M.; Kortüm, B.; Dahlmann, M.; Stein, U. MACC1—The first decade of a key metastasis molecule from gene discovery to clinical translation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 37, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, U.; Dahlmann, M.; Walther, W. MACC1—More than metastasis? Facts and predictions about a novel gene. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Gao, J.; Tong, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M. A potential role for metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 (MACC1) as a pan-cancer prognostic and immunological biomarker. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 8331–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, U.; Walther, W.; Arlt, F.; Schwabe, H.; Smith, J.; Fichtner, I.; Birchmeier, W.; Schlag, P.M. MACC1, a newly identified key regulator of HGF-MET signaling, predicts colon cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Zhou, L.; Long, Y.; Xiang, J.; Chen, L. MACC1 Is Associated With Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Can Predict Poor Prognosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 644120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treese, C.; Werchan, J.; von Winterfeld, M.; Berg, E.; Hummel, M.; Timm, L.; Rau, B.; Daberkow, O.; Walther, W.; Daum, S.; et al. Inhibition of MACC1-Induced Metastasis in Esophageal and Gastric Adenocarcinomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Zhu, C.; Pan, L.; Li, M. MACC1 regulates the AKT/STAT3 signaling pathway to induce migration, invasion, cancer stemness, and suppress apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, S. MACC1 promotes angiogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma by upregulating VEGFA. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Du, B.; Zhong, J. Association of MACC1 expression with lymphatic metastasis in colorectal cancer: A nested case-control study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Huang, H.; Liao, W.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, N.; Liao, Y.; Liao, W. MACC1 supports human gastric cancer growth under metabolic stress by enhancing the Warburg effect. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2700–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Chen, L.S.; Zhou, R.; Bin, J.P.; Liao, Y.L.; Liao, W.J. Metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 in gastric cancer: Beyond metastasis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6629–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Wang, M.; Yan, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.; Xu, M.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J. MACC1 Promotes the Progression and Is a Novel Biomarker for Predicting Immunotherapy Response in Colorectal Cancer. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 8326940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Huang, Q.; He, W.; Zhang, S.; Dong, S.; Wen, Z.; Rao, J.; Liao, W.; et al. The lncRNA MACC1-AS1 promotes gastric cancer cell metabolic plasticity via AMPK/Lin28 mediated mRNA stability of MACC1. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Steen, N.; Giovannetti, E.; Pauwels, P.; Peters, G.J.; Hong, D.S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Hirsch, F.R.; Rolfo, C. cMET Exon 14 Skipping: From the Structure to the Clinic. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Wei, Z.; Jin, H.; Wu, H.; Yu, C.; Wen, W.; Chan, L.N.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, M. Autoinhibition of UNC5b revealed by the cytoplasmic domain structure of the receptor. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichorner, A.; Sack, U.; Kobelt, D.; Kelch, I.; Arlt, F.; Smith, J.; Walther, W.; Schlag, P.M.; Stein, U. In vivo imaging of colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by targeting MACC1 with shRNA in xenografted mice. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, N.; Ohno, N.; Saitoh, S.; Seki, G.; Komada, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yamakawa, H.; Soleimani, M.; Ohno, S. Interaction of membrane skeletal protein, protein 4.1B and p55, and sodium bicarbonate cotransporter1 in mouse renal S1–S2 proximal tubules. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchmeier, C.; Birchmeier, W.; Gherardi, E.; Vande Woude, G.F. Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 4, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, S.P.J.; Spaargaren, M.; Clevers, H.; Pals, S.T. Hepatocyte growth factor/MET and CD44 in colorectal cancer: Partners in tumorigenesis and therapy resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1874, 188437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Godwin, A.K. Regulation of HGF and c-MET Interaction in Normal Ovary and Ovarian Cancer. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 24, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mhawech-Fauceglia, P.; Afkhami, M.; Pejovic, T. MET/HGF Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Carcinoma: Clinical Implications and Future Direction. Patholog. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 960327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, L. Endostar regulates EMT, migration and invasion of lung cancer cells through the HGF-Met pathway. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2019, 45, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gan, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, T.; Xie, W. The HGF-MET axis coordinates liver cancer metabolism and autophagy for chemotherapeutic resistance. Autophagy 2019, 15, 1258–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Xi, W.; Ji, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, C.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; et al. The prognostic value of HGF-c-MET signaling pathway in Gastric Cancer: A study based on TCGA and GEO databases. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1946–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayaparan, T.; Spicer, J.F.; Maher, J. The role of the HGF/Met axis in mesothelioma. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, C. The Flavonoid Quercetin Induces AP-1 Activation in FRTL-5 Thyroid Cells. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Hu, N. HGF/c-Met Promote Renal Carcinoma Cancer Stem Cells Enrichment Through Upregulation of Cir-CCDC66. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033819901114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, K.M.; Garraway, L.A. AKT signaling in physiology and disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 347, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.; Cheng, B.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Nong, Q.; He, L.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Wang, S. MACC1 regulates PDL1 expression and tumor immunity through the c-Met/AKT/mTOR pathway in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 7044–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, C.; Guo, L.; Wu, M.; Guo, J.; Peng, S.; Wu, Q.; Zuo, Q. A new mechanism of trastuzumab resistance in gastric cancer: MACC1 promotes the Warburg effect via activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, T.; Chen, W.; Yuan, X.; Shen, J.; Qin, C.; Wang, L. miR-944 inhibits metastasis of gastric cancer by preventing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via MACC1/Met/AKT signaling. FEBS Open Bio. 2017, 7, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Dou, C.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Q. MACC1 suppresses cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the HGF/c-MET/AKT pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, C.J.; Wang, J.X.; Dai, T.; Ye, Y.P.; Cui, Y.M.; Liao, W.T.; Wu, X.L.; Ou, J.P. Metastasis-Associated in Colon Cancer-1 Associates With Poor Prognosis and Promotes Cell Invasion and Angiogenesis in Human Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2015, 25, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Tian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Xue, N.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Guo, X. MACC1 is involved in the regulation of proliferation, colony formation, invasion ability, cell cycle distribution, apoptosis and tumorigenicity by altering Akt signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma. Tumour. Biol. 2014, 35, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Sun, L.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Su, Y.; Wang, C. Cisplatin resistance in lung cancer is mediated by MACC1 expression through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway activation. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Kang, M.X.; Lu, W.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.L. MACC1: A potential molecule associated with pancreatic cancer metastasis and chemoresistance. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, F.; Li, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Kang, L.; Zhen, T.; Dai, S.; Dong, Y.; et al. MACC1 down-regulation inhibits proliferation and tumourigenicity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through Akt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, H.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Ma, W.; Hu, Y.; Feng, S.; Miao, G. MACC1 facilitates chemoresistance and cancer stem celllike properties of colon cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8747–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Shi, Q.Y.; Qiu, X.; Wu, X.B.; Zheng, B.L.; Jiang, H.X.; Qin, S.Y. IFN-gamma affects pancreatic cancer properties by MACC1-AS1/MACC1 axis via AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Combination of Endothelial-Monocyte-Activating Polypeptide-II with Temozolomide Suppress Malignant Biological Behaviors of Human Glioblastoma Stem Cells via miR-590-3p/MACC1 Inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signal Pathway. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.; Huang, N.; Shi, M.; Bin, J.; Liao, Y.; et al. MACC-1 Promotes Endothelium-Dependent Angiogenesis in Gastric Cancer by Activating TWIST1/VEGF-A Signal Pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, F.F.; Liu, S.S.; Zhu, L.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Liang, X.; Ma, N.; Shi, H.R. MiRNA-338-3p regulates cervical cancer cells proliferation by targeting MACC1 through MAPK signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 5342–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, C.; Hardt, M.S.; Juneja, M.; Voss, C.; Forster, S.; Jerchow, B.; Haider, W.; Blaker, H.; Stein, U. MACC1 Induces Tumor Progression in Transgenic Mice and Colorectal Cancer Patients via Increased Pluripotency Markers Nanog and Oct4. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2812–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shenoy, A.R.; Kirschnek, S.; Hacker, G. IL-15 regulates Bcl-2 family members Bim and Mcl-1 through JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT pathways in T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 2500–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, F.; Praditsuktavorn, P.; Fernando, T.M.; Kwiatkowski, N.; Marullo, R.; Calvo-Vidal, M.N.; Phillip, J.; Pera, B.; Yang, S.N.; Takpradit, K.; et al. Corrigendum: THZ1 targeting CDK7 suppresses STAT transcriptional activity and sensitizes T-cell lymphomas to BCL2 inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radhakrishnan, H.; Ilm, K.; Walther, W.; Shirasawa, S.; Sasazuki, T.; Daniel, P.T.; Gillissen, B.; Stein, U. MACC1 regulates Fas mediated apoptosis through STAT1/3—Mcl-1 signaling in solid cancers. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cai, J.; Fang, L.; Wu, J.; Ye, C.; Zhu, X.; Li, M. Overexpression of MACC1 and Its significance in human Breast Cancer Progression. Cell Biosci. 2013, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srabovic, N.; Mujagic, Z.; Mujanovic-Mustedanagic, J.; Softic, A.; Muminovic, Z.; Rifatbegovic, A.; Begic, L. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 expression in breast cancer and its correlation to vascular endothelial growth factor A. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2013, 2013, 746749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toi, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Bando, H. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Its prognostic, predictive, and therapeutic implications. Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyleyici, N.A.; Aslan, F.; Avcykurt, A.S.; Akgun, G.A. Importance of MACC1 expression in breast cancer and its relationship with pathological prognostic markers. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2020, 63, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prguda-Mujic, J.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Mueller, V.; Suljagic, M.; Coric, J.; Ler, D. The Predictive Significance of Metastasis-Associated in Colon Cancer-1 (MACC1) in Primary Breast Cancer. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 48, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, Y.W.; Hur, H.; Lee, D. Increased MACC1 expression indicates a poor prognosis independent of MET expression in gastric adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loo, P.; Nilsen, G.; Nordgard, S.H.; Vollan, H.K.; Borresen-Dale, A.L.; Kristensen, V.N.; Lingjaerde, O.C. Analyzing cancer samples with SNP arrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 802, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Gao, S.; Yang, Z.; Xie, H.; Zhang, C.; Lin, B.; Wu, L.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, L. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 gene predict the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after transplantation. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, A.H.; Geller-Rhomberg, S.; Winder, T.; Stark, N.; Gasser, K.; Hartmann, B.; Kohler, B.; Grizelj, I.; Drexel, H.; Muendlein, A. A common variant of the MACC1 gene is significantly associated with overall survival in colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, R.H.; Chuang, C.Y.; Lin, C.W.; Su, S.C.; Chang, L.C.; Wu, S.W.; Liu, Y.F.; Yang, S.F. Effect of MACC1 Genetic Polymorphisms and Environmental Risk Factors in the Occurrence of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Liu, X.H.; Kang, H.F.; Wang, X.J.; Jin, T.B.; Zhang, S.Q.; Feng, T.; Ma, X.B.; Wang, M.; Feng, Y.J.; et al. Genetic Variation in Metastasis-Associated in Colon Cancer-1 and the Risk of Breast Cancer Among the Chinese Han Population: A STROBE-Compliant Observational Study. Medicine 2016, 95, e2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muendlein, A.; Hubalek, M.; Geller-Rhomberg, S.; Gasser, K.; Winder, T.; Drexel, H.; Decker, T.; Mueller-Holzner, E.; Chamson, M.; Marth, C.; et al. Significant survival impact of MACC1 polymorphisms in HER2 positive breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuse, N.; Kuboki, Y.; Kuwata, T.; Nishina, T.; Kadowaki, S.; Shinozaki, E.; Machida, N.; Yuki, S.; Ooki, A.; Kajiura, S.; et al. Prognostic impact of HER2, EGFR, and c-MET status on overall survival of advanced gastric cancer patients. Gastric. Cancer 2016, 19, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fan, L.; Xu, H.; Jiang, H. Prognostic significance of the expression of metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 in gynecologic cancers and breast cancer: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e24255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Xie, X.; Li, L.; Tang, H.; Ye, X.; Chen, L.; Tang, W.; Gao, J.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum MACC1 in breast cancer patients. Res. Pap. 2016, 7, 84408–84415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, D.A.; El-Guindy, D.M.; Elrashidy, M.A.; Sabry, N.M.; Kabel, A.M.; Gaber, R.A.; Ibrahim, R.R.; Samy, S.M.; Shalaby, M.M.; Salama, S.A.; et al. The Prognostic Significance of MACC1 Expression in Breast Cancer and Its Relationship to Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment and Patient Survival. Medicina 2021, 57, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueta, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Hayashi, M.; Takeshita, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Omoto, Y.; Iwase, H. Differential role of MACC1 expression and its regulation of the HGF/cMet pathway between breast and colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: Biology and clinical significance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekari, N.; Baradaran, B.; Shanehbandi, D.; Kazemi, T. Circulating MicroRNAs: Valuable Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gion, M.; Trevisiol, C.; Fabricio, A.S.C. State of the art and trends of circulating cancer biomarkers. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2020, 35, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj Ahmed, M.A. Serum MACC-1: A new biomarker for breast cancer. Res. Pap. 2020, 11, 4521–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil Del Alcazar, C.R.; Alečković, M.; Polyak, K. Immune Escape during Breast Tumor Progression. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, R.N.; Amano, M.T.; Paes Leme, A.F.; Fox, J.W.; de Oliveira, A.K. Editorial: Tumor microenvironment (TME) and tumor immune microenvironment (TIME): New perspectives for prognosis and therapy. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 971275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Ding, S. The Crosstalk Between Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) and Tumor Cells and the Corresponding Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 590941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krneta, T.; Gillgrass, A.; Poznanski, S.; Chew, M.; Lee, A.J.; Kolb, M.; Ashkar, A.A. M2-polarized and tumor-associated macrophages alter NK cell phenotype and function in a contact-dependent manner. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, S.M.; Paasch, D.; Morgan, M.; Lachmann, N. CARs and beyond: Tailoring macrophage-based cell therapeutics to combat solid malignancies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Du, L.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Cui, L.; Li, X. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: Warriors fight against tumors powerfully. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeifard, S.; Talei, A.; Shariat, M.; Erfani, N. Tumor infiltrating NK cell (TINK) subsets and functional molecules in patients with breast cancer. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 136, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielson, A.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; Kallakury, B.; Gatalica, Z.; Reddy, S.; Kleiner, D.; Fishbein, T.; Johnson, L.; et al. Intratumoral CD3 and CD8 T-cell Densities Associated with Relapse-Free Survival in HCC. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Attwood, K.; Bshara, W.; Mohler, J.L.; Guru, K.; Xu, B.; Kalinski, P.; Chatta, G. High intratumoral CD8(+) T-cell infiltration is associated with improved survival in prostate cancer patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Prostate 2021, 81, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Li, S.H.; Fu, X.; Yan, X.P.; Chen, J.; Qiu, Y.D.; Guo, R.P. Relationship between PD-L1 expression, CD8+ T-cell infiltration and prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients. Cancer Cell. Int. 2021, 21, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, L. Less expression of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells might reflect the severity of infection and predict worse prognosis in patients with COVID-19: Evidence from a pooled analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 510, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Nam, J.M.; Harada, H. Tumor microenvironment and radioresistance. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.S.; Han, W.; Kim, I.A. Tumor mutation burden, immune checkpoint crosstalk and radiosensitivity in single-cell RNA sequencing data of breast cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 142, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Gu, W. LncRNA MACC1-AS1 sponges multiple miRNAs and RNA-binding protein PTBP1. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.; Yang, X.; Tian, W.; Guo, S.; Huang, W.; Zhao, W. Increased Expression of c-Met is Associated with Chemotherapy-Resistant Breast Cancer and Poor Clinical Outcome. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 8239–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Qin, X. miR-182 regulates trastuzumab resistance by targeting MET in breast cancer cells. Cancer Gene. Ther. 2019, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shattuck, D.L.; Miller, J.K.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd; Sweeney, C. Met receptor contributes to trastuzumab resistance of Her2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parr, C.; Ali, A.Y. Boswellia frereana suppresses HGF-mediated breast cancer cell invasion and migration through inhibition of c-Met signalling. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkatesh, J.; Wasson, M.D.; Brown, J.M.; Fernando, W.; Marcato, P. LncRNA-miRNA axes in breast cancer: Novel points of interaction for strategic attack. Cancer Lett. 2021, 509, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadaliha, M.; Gholamalamdari, O.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Petracovici, A.; Hao, Q.; Tariq, A.; Kim, T.G.; Holton, S.E.; Singh, D.K.; et al. A natural antisense lncRNA controls breast cancer progression by promoting tumor suppressor gene mRNA stability. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, M.D.; Brown, J.M.; Venkatesh, J.; Fernando, W.; Marcato, P. Datasets exploring putative lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axes in breast cancer cell lines. Data Brief 2021, 37, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Li, T. LncRNA MACC1-AS1 Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Proliferation by Downregulating PTEN. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Qiu, W.; Peng, C.; Shen, B.; Zhu, Z. MACC1-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and proliferation by regulating PAX8. Albany NY 2020, 12, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhong, J.; Wu, F.; Zhan, Z. Long noncoding RNA MACC1-AS1 promotes the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by antagonizing miR-145. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520920411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Geng, X. Long noncoding RNA MACC1-AS1 is a potential sponge of microRNA-34a in cervical squamous cell carcinoma and upregulates cyclin-dependent kinase 6. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, C.; Xiaofeng, C.; Dongen, L.; Liang, Y.; Liping, X.; Yue, H.; Jianshuai, J. Long non-coding RNA MACC1-AS1 promoted pancreatic carcinoma progression through activation of PAX8/NOTCH1 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.D.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Gu, W. Two lncRNAs, MACC1-AS1 and UCA1, co-mediate the expression of multiple mRNAs through interaction with individual miRNAs in breast cancer cells. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022, 7, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ref. | Histopathology | Staging | ER | HER2 | PR | Ki-67 | OS | DFS/RFS | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [55] | + | + | − | − | − | … | + | + | 397 |
| [58] | − | − | + | + | − | − | … | … | 91 |
| [59] | − | − | + | … | − | … | − | + | 105 |
| [68] | + | + | … | … | … | … | + | + | 1811 |
| [69] | + | + | − | − | … | + | … | … | 538 |
| [70] | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | 120 |
| [71] | − | − | − | … | … | … | … | + | 300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, M.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, B.; Ye, M.; Di, W.; Su, W.; Zhong, J. MACC1 as a Potential Target for the Treatment and Prevention of Breast Cancer. Biology 2023, 12, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030455
Lv M, Jiao Y, Yang B, Ye M, Di W, Su W, Zhong J. MACC1 as a Potential Target for the Treatment and Prevention of Breast Cancer. Biology. 2023; 12(3):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030455
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Mengmeng, Yunjuan Jiao, Bowen Yang, Mengchen Ye, Wenyu Di, Wei Su, and Jiateng Zhong. 2023. "MACC1 as a Potential Target for the Treatment and Prevention of Breast Cancer" Biology 12, no. 3: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030455
APA StyleLv, M., Jiao, Y., Yang, B., Ye, M., Di, W., Su, W., & Zhong, J. (2023). MACC1 as a Potential Target for the Treatment and Prevention of Breast Cancer. Biology, 12(3), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030455





