Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota in Wild, Domesticated, and Cultured Gymnocypris potanini firmispinatus
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Analysis
2.4. Diversity Indices and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Prediction of Molecular Functions Using PICRUSt2
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Depth
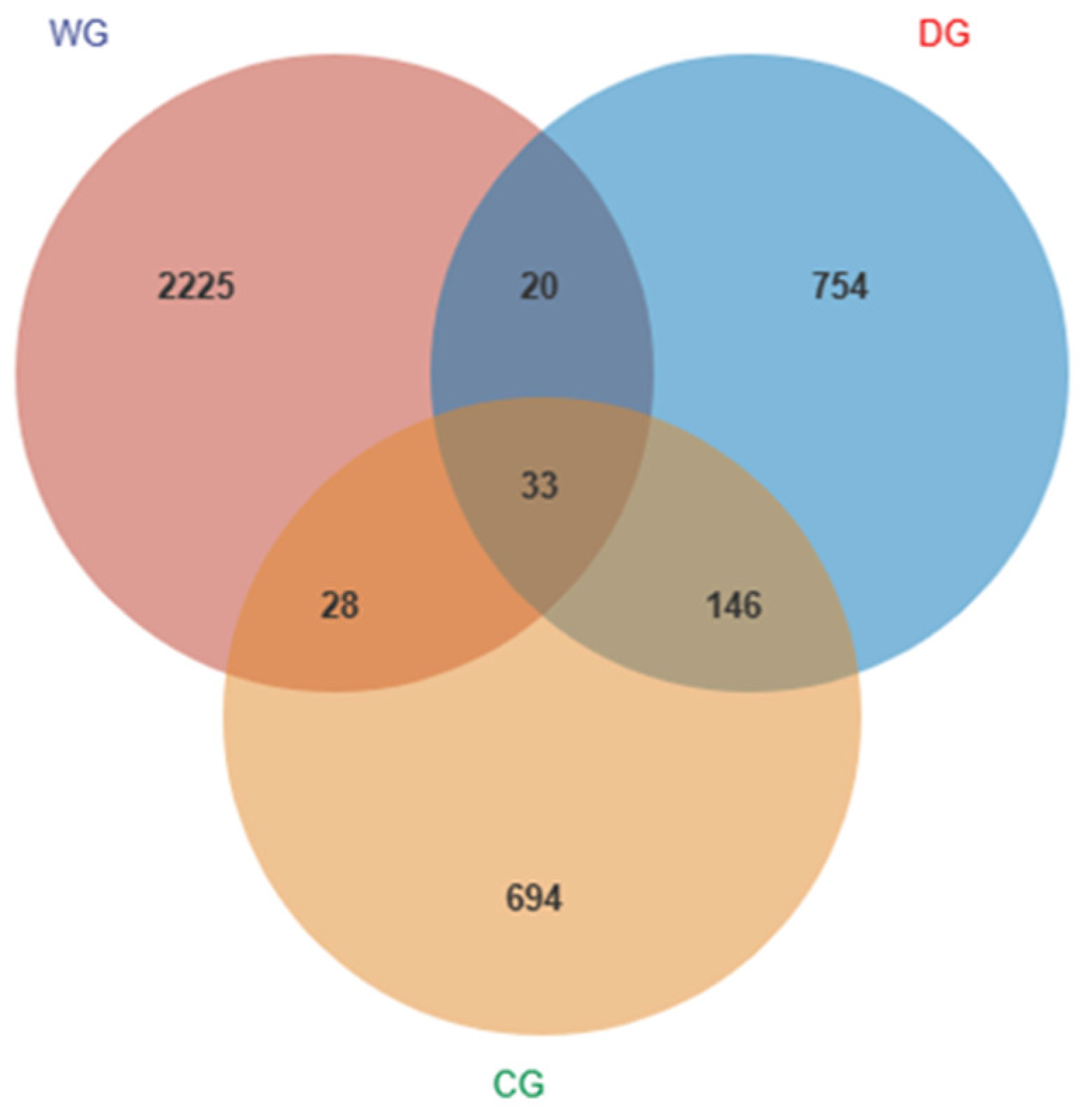
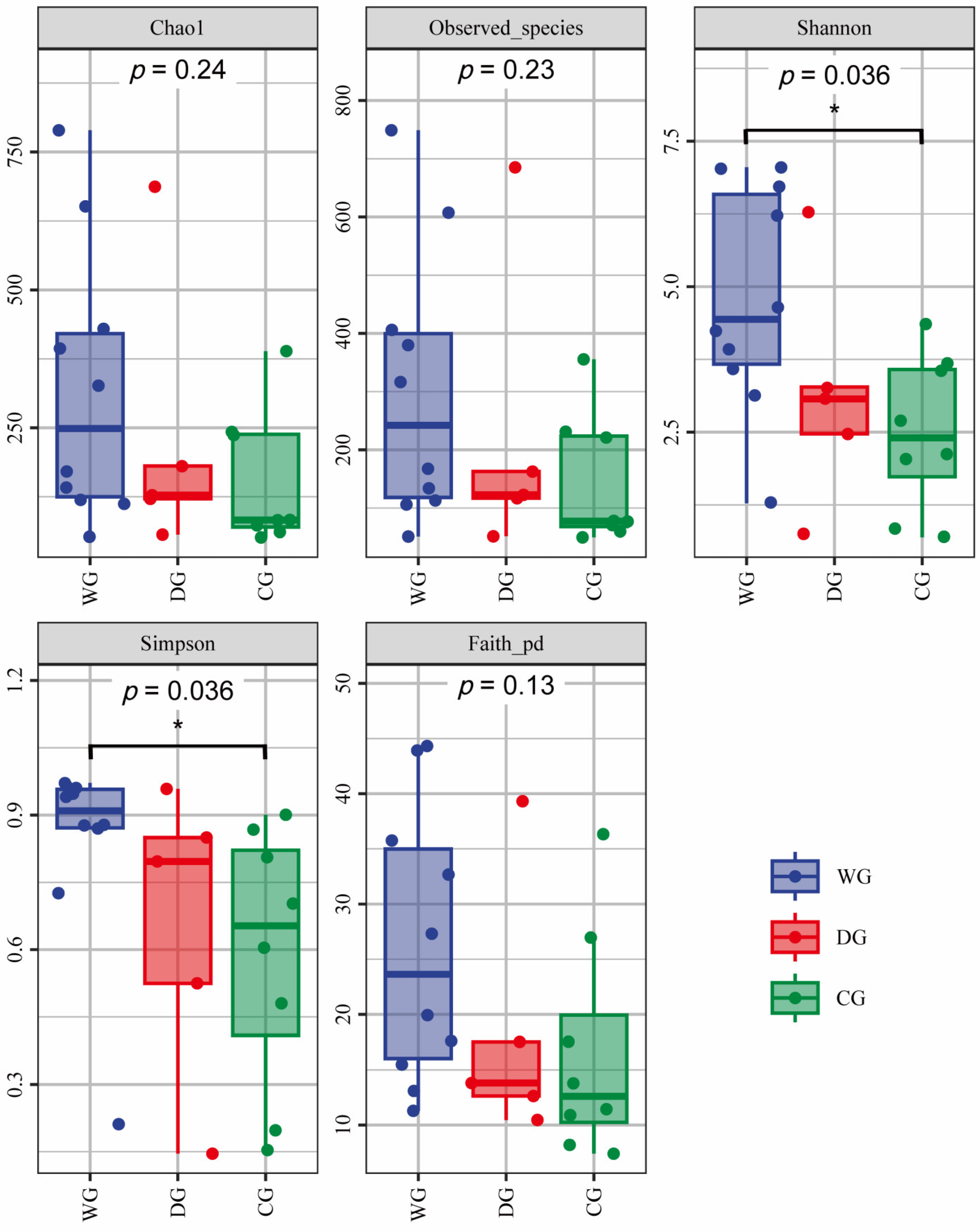
3.2. Diversity of Intestinal Microbial Communities
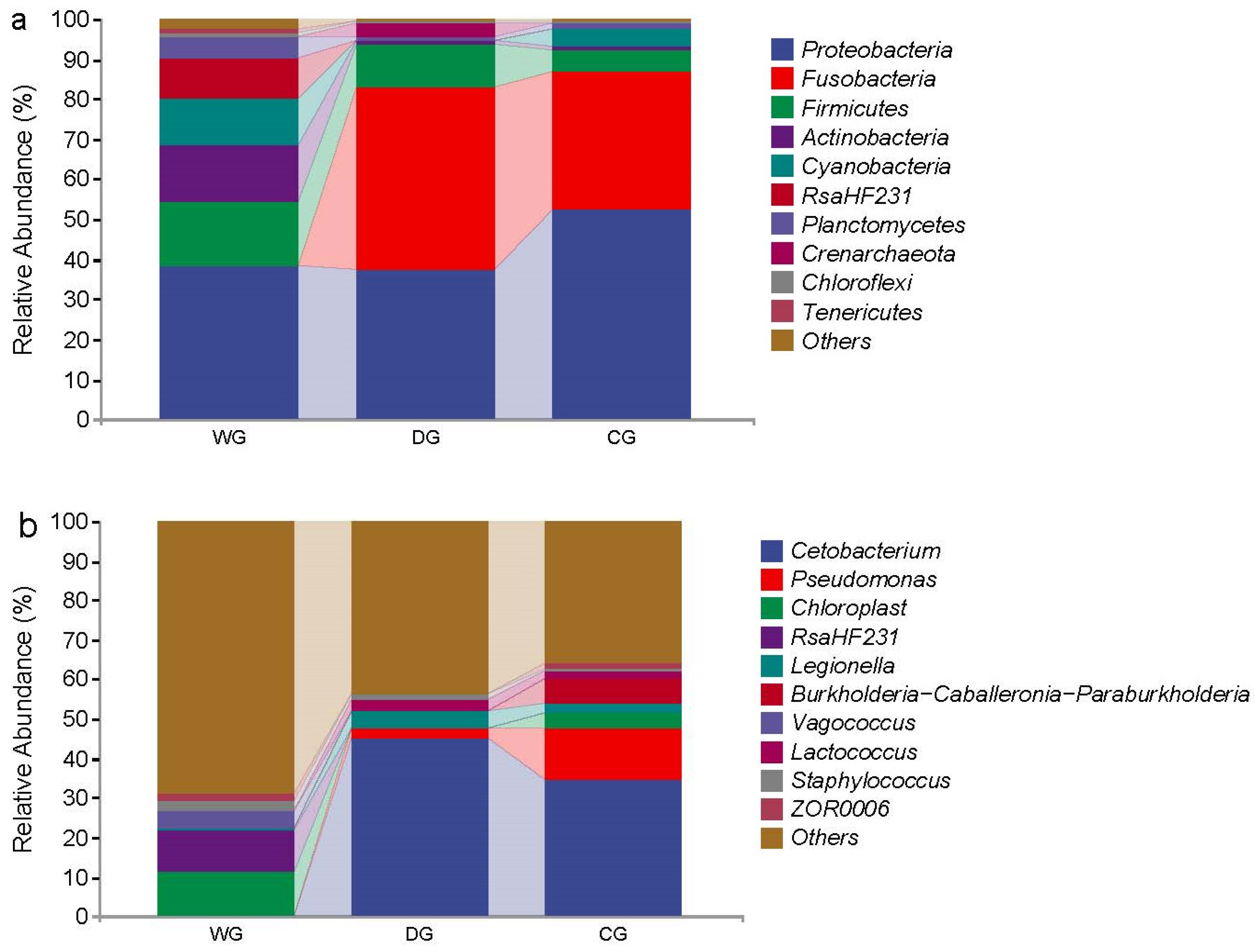
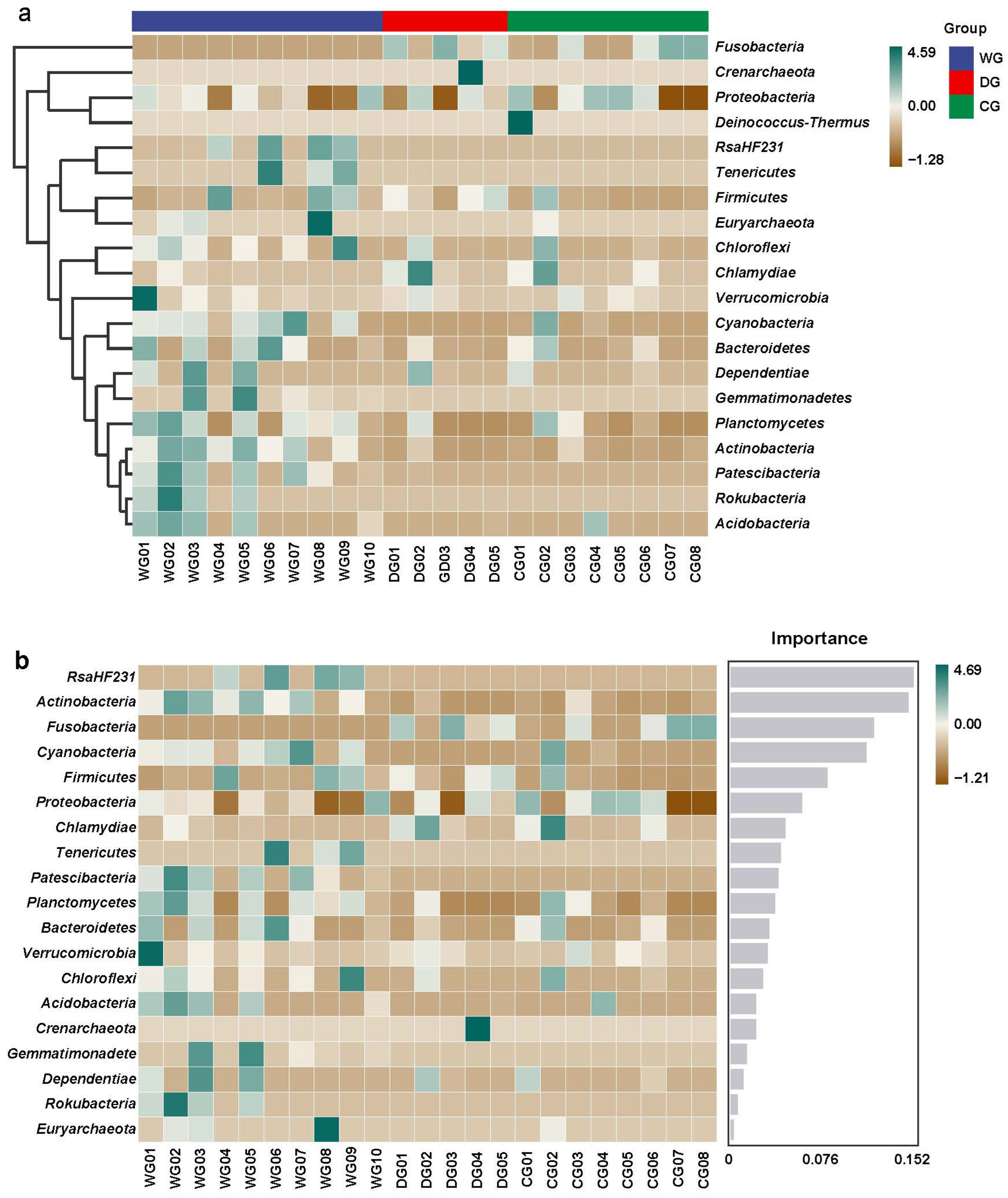
3.3. Differences in the Microbiota Composition Among the Three Groups
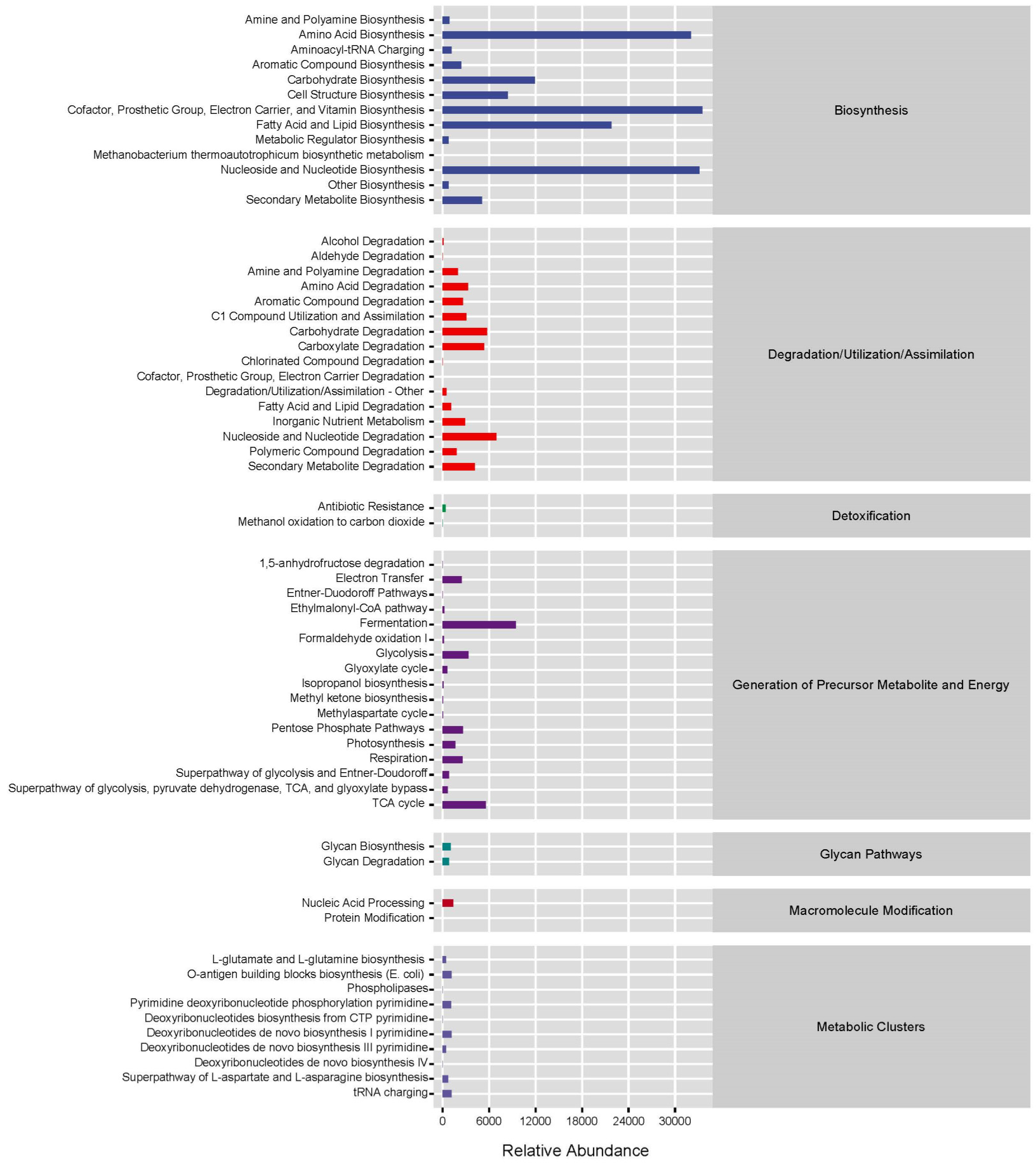
3.4. Functional Pathways with Significant Differences Among the Three Groups
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity of the Intestinal Microbiota
4.2. Species Composition of the Intestinal Microbiota
4.3. Metabolic Function Analysis of the Intestinal Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, Y.; Qin, N.; Yang, R. Human microbiota: A neglected “organ” in precision medicine. Infect. Dis. Transl. Med. 2015, 1, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, J.; Díaz, O.; Miranda, C.D.; Rojas, R. Red cusk-eel (Genypterus chilensis) gut microbiota description of wild and aquaculture specimens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semova, I.; Carten, J.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Mackey, L.C.; Knight, R.; Farber, S.A.; Rawls, J.F. Microbiota regulate intestinal absorption and metabolism of fatty acids in the zebrafish. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, S.; Cai, Z.; Song, D.; Yang, L.; Nie, G. The probiotic properties of different preparations using Lactococcus lactis Z-2 on intestinal tract, blood and hepatopancreas in Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ji, D.; Yao, J.; Zou, Y.; Yan, M. Comparative analysis of intestinal characteristics of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and intestinal flora with different growth rates. Fishes 2022, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Han, C.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lin, H. Rabbitfish (Siganus oramin) gut microbiota description of farmed and wild specimens. Aquacult. Rep. 2024, 35, 101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Villegas, J.; García-Moreno, D.; De Oliveira, S.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. Regulation of immunity and disease resistance by commensal microbes and chromatin modifications during zebrafish development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2605–E2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O. Nutritional immunity of fish intestines: Important insights for sustainable aquaculture. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 13, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, A.D.; Harke, S.N.; Panche, A. Impact of climate change on the gut microbiome of fish and shellfish. In Microbiome of Finfish and Shellfish; Diwan, A.D., Harke, S.N., Panche, A., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquacult. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piewngam, P.; De Mets, F.; Otto, M. Intestinal microbiota: The hidden gems in the gut? Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karl, J.P.; Margolis, L.M.; Madslien, E.H.; Murphy, N.E.; Castellani, J.W.; Gundersen, Y.; Hoke, A.V.; Levangie, M.W.; Kumar, R.; Chakraborty, N. Changes in intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G559–G571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Leiva, J.; Opazo, R.; Remond, C.; Uribe, E.; Velez, A.; Romero, J. Characterization of the intestinal microbiota of wild-caught and farmed fine flounder (Paralichthys adspersus). Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 45, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Hu, C. Analysis of the intestinal flora in Male versus female swamp eels (Monopterus albus). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, C.; Romero, J. Fine flounder (Paralichthys adspersus) microbiome showed important differences between wild and reared specimens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, C.; Romero, J. The microbiome of Seriola lalandi of wild and aquaculture origin reveals differences in composition and potential function. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ponzoni, R.W. Some aspects of design and analysis of selection programmes in aquaculture species. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2015, 132, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xu, B.; Wei, K.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, J. Feeding habits of the cyprinid Gymnocypris firmispinatus in the Anning River, China. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Yu, Y.L.; Lu, K.; Chu, Z.P.; Jin, J.L.; Li, D.P.; Ma, B.S. Analysis and evaluation of muscle nutritional composition among wild, domesticated and cultured Gymnocypris potanini firmispinatus. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Wei, K.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.; Zhu, X.; Nie, Y. Reproductive characteristics of Gymnocypris firmispinatus in the Anning River, China. Fish. Sci. 2018, 84, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Nie, Y.; Wei, K.; Xu, B.; Zhu, X.; Xu, J. Estimates on age, growth, and mortality of Gymnocypris firmispinatus (Cyprinidae: Schizothoracinae) in the Anning River, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xie, C.; Huo, B.; Yang, X.; Li, P. Age validation, and comparison of otolith, vertebra and opercular bone for estimating age of Schizothorax o’connori in the Yarlung Tsangpo River, Tibet. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2011, 90, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. QIIME 2: Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science. PeerJ 2018, 6, e27295v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Fulcher, C.A.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Latendresse, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, Q.; Ong, W.K.; et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D633–D639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugetti, D.; Pastorino, P.; Beltramo, C.; Audino, T.; Arillo, A.; Esposito, G.; Prearo, M.; Bertoli, M.; Pizzul, E.; Bozzetta, E. The gut microbiota of farmed and wild brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis): Evaluation of feed-related differences using 16S rRNA gene metabarcoding. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zeng, B.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, J. Structural analysis of intestinal microflora in wild and cultured Schizothorax o’connori. Fish. Sci. 2020, 39, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Restivo, V.E.; Kidd, K.A.; Surette, M.G.; Bucking, C.; Wilson, J.Y. The gut content microbiome of wild-caught rainbow darter is altered during laboratory acclimation. Comp. Biochem. Phys. Part D 2021, 39, 100835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajardo, K.; Jaramillo-Torres, A.; Kortner, T.M.; Merrifield, D.L.; Tinsley, J.; Bakke, A.M.; Krogdahl, Å. Alternative protein sources in the diet modulate microbiota and functionality in the distal intestine of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Appl. Environ. Microb. 2017, 83, e02615–e02616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, V.; Amaral-Zettler, L.; Davidson, J.; Summerfelt, S.; Good, C. Influence of fishmeal-free diets on microbial communities in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) recirculation aquaculture systems. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2016, 82, 4470–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holben, W.E.; Williams, P.; Saarinen, M.; Särkilahti, L.K.; Apajalahti, J.H.A. Phylogenetic analysis of intestinal microflora indicates a novel Mycoplasma phylotype in farmed and wild salmon. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 44, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormas, K.A.; Meziti, A.; Mente, E.; Frentzos, A. Dietary differences are reflected on the gut prokaryotic community structure of wild and commercially reared sea bream (Sparus aurata). Microbiologyopen 2014, 3, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Population Genetic Structure and Gut Microbial Diversity of the Schizopygopsis malacanthus. Master’s Thesis, Qinghai University, Xining, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity of Microbiome of Silurus meridionalis. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanasiri, A.K.S.; Brunvold, L.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Korsnes, K.; Bergh, Ø.; Kiron, V. Changes in the intestinal microbiota of wild Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. upon captive rearing. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, G.; Li, Q. Intestinal microbiota analysis in gibel carp Carassius auratus gibelio based on 16S rRNA gene sequence. Fish. Sci. 2022, 41, 266–272. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Cai, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J. Host habitat as a dominant role in shaping the gut microbiota of wild crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Fishes 2023, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, F. The intestinal microbiota diversities of Procambarus clarkia at different sexes and growth stages. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z. Study on Intestinal Microbiota of Wild and Cultured Coreius guichenoti. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Xu, Q.; Qian, L.; Ai, T.; Xiang, W.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Comparative analysis on intestinal microflora of wild and cultured Tench Tinca tinca. Fish. Sci. 2023, 42, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, C.; Sakata, T.; Sugita, H. Novel ecological niche of Cetobacterium somerae, an anaerobic bacterium in the intestinal tracts of freshwater fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, N.; Zhong, M.; Wang, K. Intestinal microbial community of wild and cultured Onychostoma macrolepi based on 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2021, 30, 963–970. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.L.; Shan, C.J.; Du, Z.Y. Research advances on probiotics and fish gut health. J. Fish. China 2021, 45, 147–157. [Google Scholar]



| Ingredient | Feed 2.0 | Feed 4.0 | Mealworm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 12.43 ± 0.01 | 12.45 ± 0.07 | 61.80 ± 1.96 |
| Crude protein | 42.00 ± 0.57 | 40.00 ± 0.77 | 18.94 ± 0.01 |
| Crude fat | 5.74 ± 0.04 | 5.31 ± 0.52 | 6.70 ± 0.10 |
| Ash | 11.74 ± 0.03 | 9.29 ± 0.05 | 5.59 ± 0.01 |
| Sample Source | Bray–Curtis | Weighted UniFrac | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PERMANOVA | ANOSIM | PERMANOVA | ANOSIM | |
| WG vs. DG | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| WG vs. CG | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| DG vs. CG | 0.529 | 0.923 | 0.729 | 0.768 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Chu, Z.; Liu, J.; Jin, J.; Zhong, L. Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota in Wild, Domesticated, and Cultured Gymnocypris potanini firmispinatus. Biology 2024, 13, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13120983
Ma B, Zhang J, Li D, Chu Z, Liu J, Jin J, Zhong L. Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota in Wild, Domesticated, and Cultured Gymnocypris potanini firmispinatus. Biology. 2024; 13(12):983. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13120983
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Baoshan, Jiaqi Zhang, Dapeng Li, Zhipeng Chu, Jieya Liu, Jiali Jin, and Liqiao Zhong. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota in Wild, Domesticated, and Cultured Gymnocypris potanini firmispinatus" Biology 13, no. 12: 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13120983
APA StyleMa, B., Zhang, J., Li, D., Chu, Z., Liu, J., Jin, J., & Zhong, L. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota in Wild, Domesticated, and Cultured Gymnocypris potanini firmispinatus. Biology, 13(12), 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13120983







