A Cybertaxonomic Revision of the “Crocidura pergrisea” Species Complex with a Special Focus on Endemic Rocky Shrews: Crocidura armenica and Crocidura arispa (Soricidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Key Provisions of the Integrative Approach
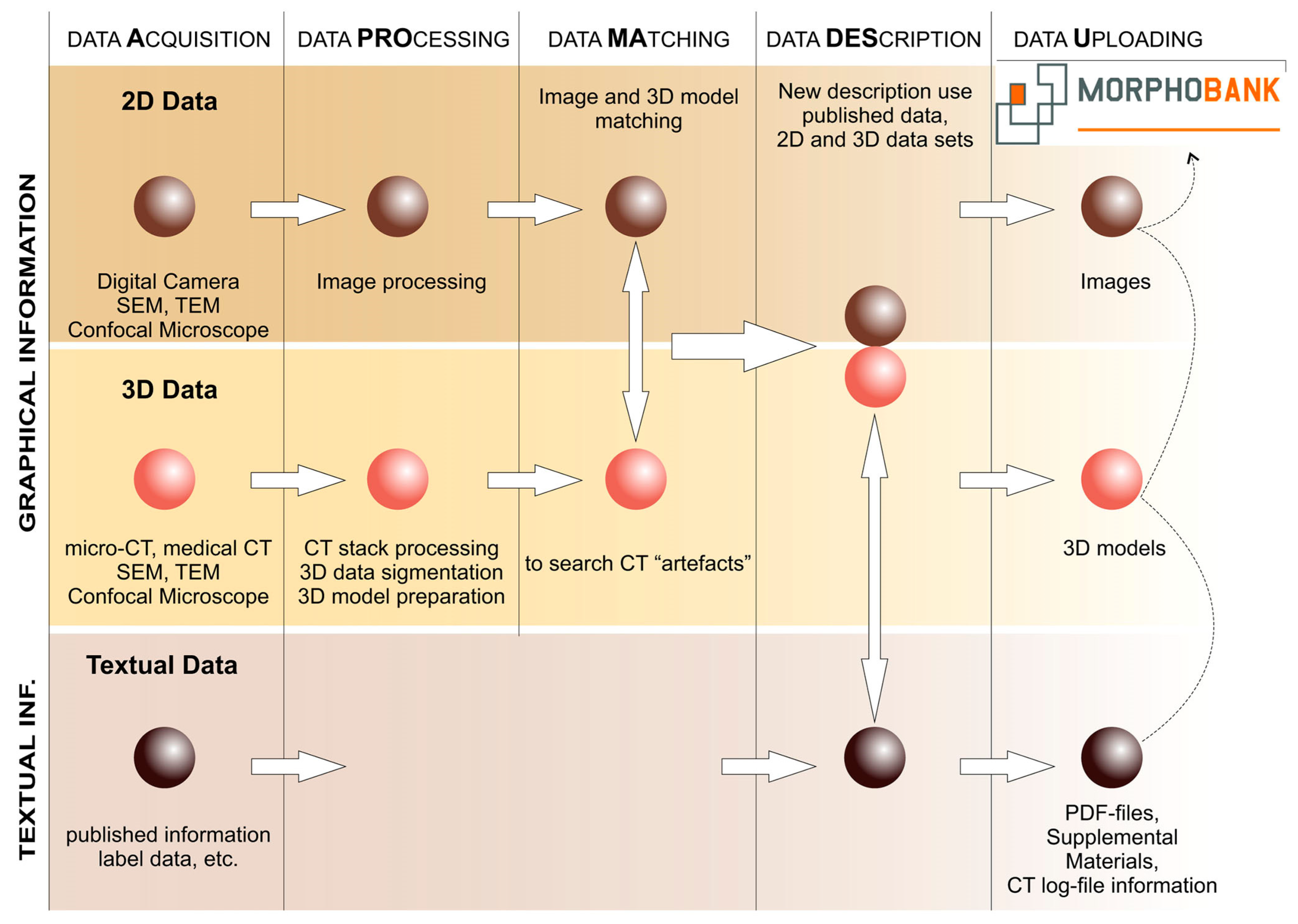
1.2. Cybertaxonomy of Mammals
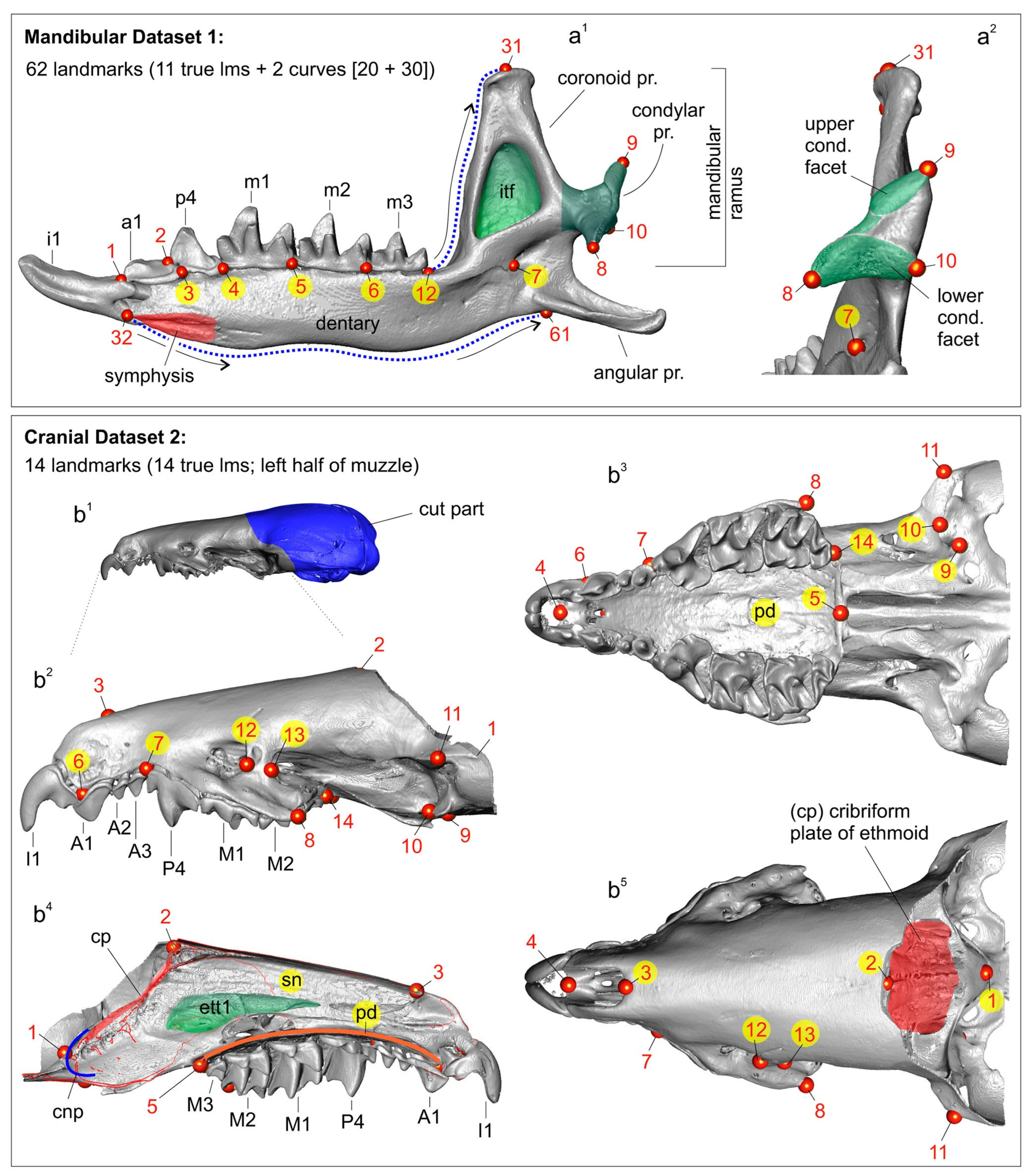
2. Materials and Methods
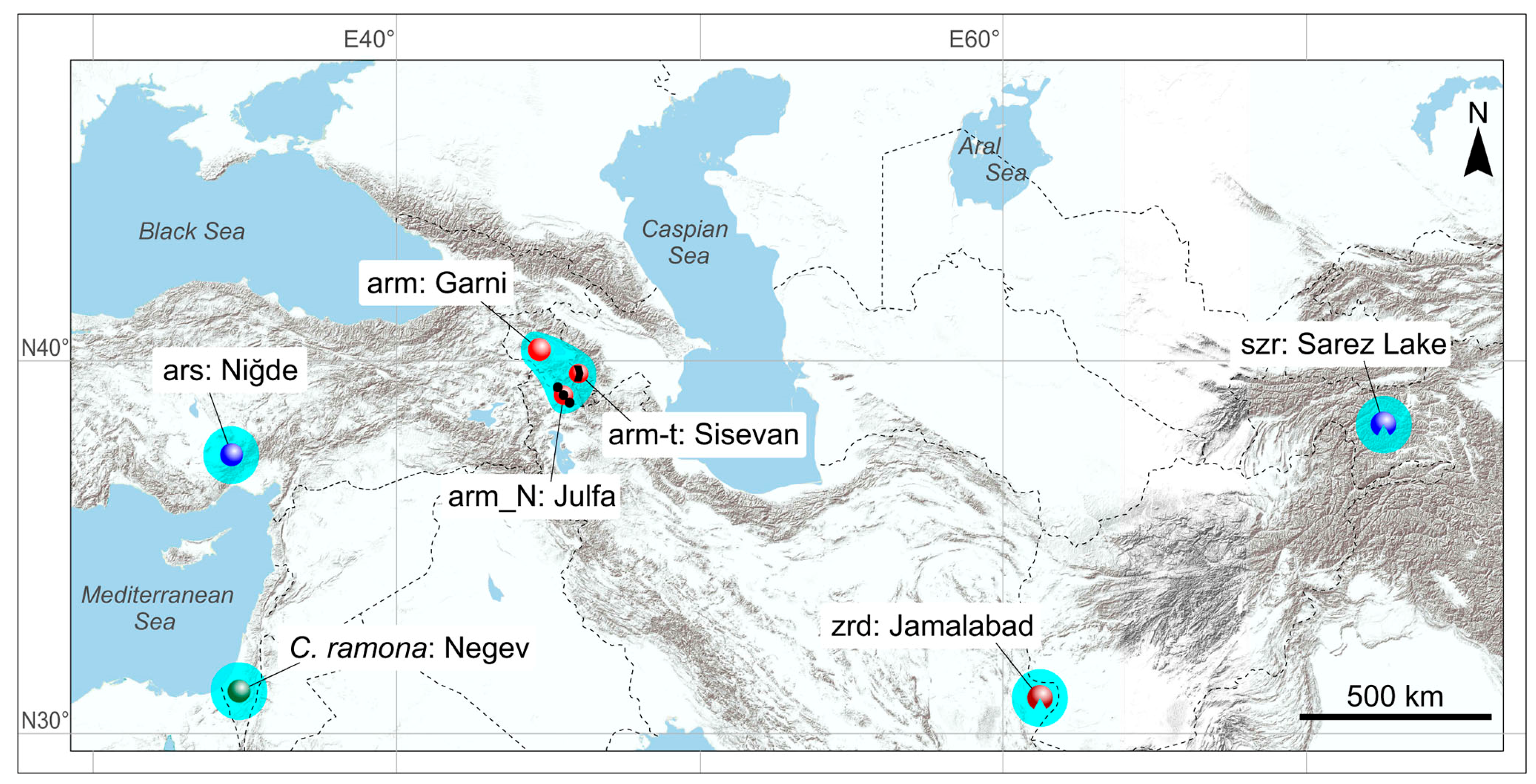
2.1. Sampling
2.2. The Choice of Species
2.3. Species Determination in 3D Models
2.4. Acquisition of Two-Dimensional Images and Measurement Techniques
2.5. Computed X-ray Micro-Tomography and Segmentation
2.6. Morphometric Analysis and Visualization of Results
2.7. Statistics
2.8. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.9. Terminology
2.10. Institutional Abbreviations
3. Results
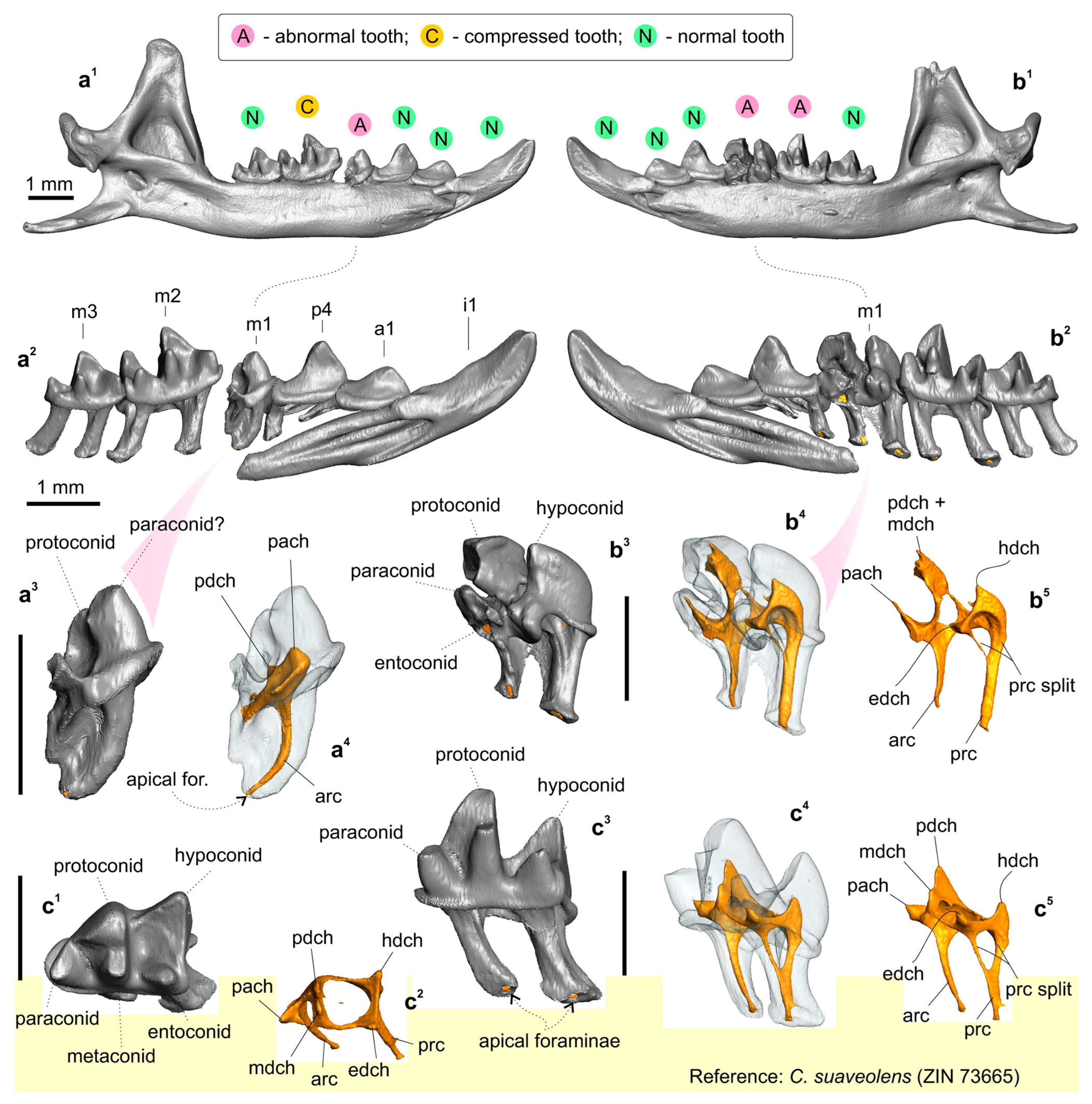
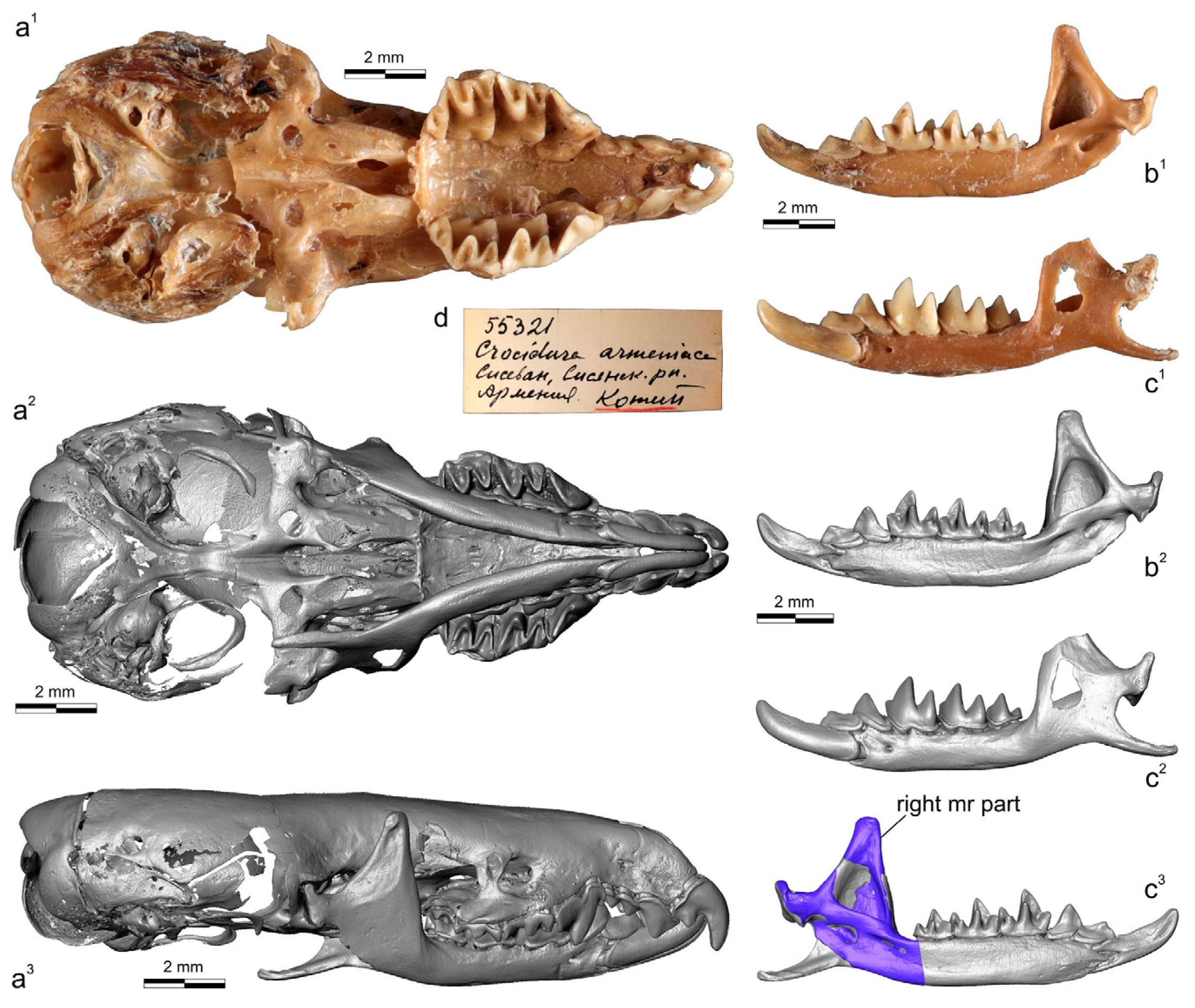
3.1. Description of Cybertypes
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Species Comparisons
3.4. Geometric Morphometric Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. General Remarks
4.2. Taxonomic Remarks
4.3. Cybertaxonomy of Shrews: Pipeline Development
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgin, C.J.; Colella, J.P.; Kahn, P.L.; Upham, N.S. How many species of mammals are there? J. Mammal. 2018, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, N.S.; Esselstyn, J.A.; Jetz, W. Inferring the mammal tree: Species-level sets of phylogenies for questions in ecology, evolution, and conservation. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutterer, R. Order Soricomorpha. In Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomical Reference, 3rd ed.; Wilson, D.E., Reeder, D.A., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 220–311. [Google Scholar]
- Burgin, C.J.; He, K. Family Soricidae. In Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Insectivores, Sloths and Colugos; Wilson, D.E., Russell, A.M., Eds.; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; Volume 8, pp. 332–551. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, P.D.; Abramov, A.V.; Rozhnov, V.V.; Makarova, O.V. Description of two new species of white-toothed shrews belonging to the genus Crocidura (Soricomorpha: Soricidae) from Ngoc Linh Mountain, Vietnam. Zootaxa 2007, 1589, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.D.; Lunde, D.P.; Moncrieff, C.B. Descriptions of new species of Crocidura (Soricomorpha: Soricidae) from Mainland Southeast Asia, with synopses of previously described species and remarks on biogeography. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2009, 331, 356–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.D.; Abramov, A.V.; Rozhnov, V.V.; Ollson, A. A new species of Crocidura (Soricomorpha: Soricidae) from southern Vietnam and north-eastern Cambodia. Zootaxa 2010, 2345, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.D.; Abramov, A.V.; Bannikova, A.A.; Rozhnov, V.V. Bones and genes: Resolution problems in three Vietnamese species of Crocidura (Mammalia, Soricomorpha, Soricidae) and the discription of an additional new species. Zookeys 2013, 313, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramov, A.V.; Jenkins, P.D.; Rozhnov, V.V.; Kalinin, A.A. Description of a new species of Crocidura (Soricimorpha: Soricidae) from the island of Phu Quoc, Vietnam. Mammalia 2008, 72, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrenchenko, L.A.; Voyta, L.L.; Hutterer, R. Diversity of shrews in Ethiopia, with the description of two new species of Crocidura (Mammalia: Lipotyphla: Soricidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4196, 38–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demos, T.C.; Achmadi, A.S.; Handika, H.; Maharadatunkamsi; Rowe, K.C.; Esselstyn, J.A. A new species of shrew (Soricomorpha: Crocidura) from Java, Indonesia: Possible character displacement despite interspecific gene flow. J. Mammal. 2017, 98, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, G.Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Yao, J.F.; You, S.; Wang, C.C.; Cheng, F.; Chen, J.P.; Tang, M.X.; Li, C.L.; et al. A new species of the genus Crocidura from China based on molecular and morphological data (Eulipotyphla: Soricidae). Zool. Syst. 2019, 44, 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, B. A new species of the genus Crocidura (Mammalia: Eulipotyphla: Soricidae) from Mount Huang, China. Zool. Syst. 2020, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Konečný, A.; Hutterer, R.; Meheretu, Y.; Bryja, J. Two new species of Crocidura (Mammalia: Soricidae) from Ethiopia and updates on the Ethiopian shrew fauna. J. Vertebr. Biol. 2020, 69, 20064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalakannan, M.; Sivaperuman, C.; Kundu, S.; Gokulakrishnan, G.; Vinkatraman, C.; Chandra, K. Discovery of a new mammal species (Soricidae: Eulipotyphla) from Narcondam volcanic island, India. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannikova, A.A.; Lisenkova, A.A.; Solovyeva, E.N.; Abramov, A.V.; Sheftel, B.I.; Kryštufek, B.; Lebedev, V.S. The first phylogenetic data on the elusive shrews of the Crocidura pergrisea species complex. Hystrix 2023, 34, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsev, M.V. Species composition and questions of systematics of white-toothed shrews (Mammalia, Insectivora) of the fauna of USSR. Zool. Inst. USSR Acad. Sci. 1991, 243, 3–46, (In Russian, with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Kryštufek, B.; Vohralĺk, V. Mammals of Turkey and Cyprus: Introduction, Checklist, Insectivora; Knjižnica Annales Majora: Koper, Slovenia, 2001; ISBN 961-6033-36-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsev, M.V.; Voyta, L.L.; Sheftel, B.I. The Mammals of Russia and Adjacent Territories. Lipotyphlans; Izdatelstvo Nauka: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 2014; ISBN 978-5-02-038380-7. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Voyta, L.L.; Abramov, A.V.; Lavrenchenko, L.A.; Nicolas, V.; Petrova, E.A.; Kryuchkova, L.Y. Dental polymorphisms in Crocidura (Soricomorpha: Soricidae) and evolutionary diversification of crocidurine shrew dentition. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2022, 196, 1069–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voet, I.; Denys, C.; Colyn, M.; Lalis, A.; Konečny, A.; Dlapré, A.; Nicolas, V.; Cornette, R. Incongruences between morphology and molecular phylogeny provide an insight into the diversifcation of the Crocidura poensis species complex. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, e10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meegaskumbura, S.; Schneider, C.J. A taxonomic evaluation of the shrew Suncus montanus (Soricidae: Crocidurinae) of Sri Lanka and India. Ceylon J. Sci. (Biol. Sci.) 2008, 37, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannikova, A.A.; Jenkins, P.D.; Solovyeva, E.N.; Pavlova, S.V.; Demidova, T.B.; Simanovsky, S.A.; Sheftel, B.I.; Lebedev, V.S.; Fang, Y.; Dalen, L.; et al. Who are you, Griselda? A replacement name for a new genus of the Asiatic short-tailed shrews (Mammalia, Eulipotyphla, Soricidae): Molecular and morphological analyses with the discussion of tribal affinities. ZooKeys 2019, 888, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulwetter, S.; Vasileiadou, A.; Kouratoras, M.; Dailianis, T.; Arvanitidis, C. Micro-computed tomography: Introducing new dimensions to taxonomy. ZooKeys 2013, 263, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulwetter, S.; Dailianis, T.; Vasileiadou, K.; Kouratoras, M.; Arvanitidis, C. Can micro-CT become an essential tool for the 21st century taxonomist? An evaluation using marine polychaetes. Microsc. Anal. 2014, 28, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Winterton, S.L. Revision of the stiletto fly genus Neodialineura Mann (Diptera: Therevidae): An empirical example of cybertaxonomy. Zootaxa 2009, 2157, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohana, K.; Bijoy, C. Cybertaxonomy: A novel tool in Biodiversity Science. In Biodiversity: Utilization, Threats and Cultural Linkages; Kumar, A.B., Nayar, M.P., Varma, R.V., Peethambaran, C.K., Eds.; Narendra Publishing House: Delhi, India, 2012; pp. 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.S. Cybertaxonomy. In The Future of Scholarly Communication; Shorley, D., Jubb, M., Eds.; Facet Publishing: London, UK, 2013; pp. 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Voyta, L.L.; Omelko, V.E.; Tiunov, M.P.; Vinokurova, M.A. When beremendiin shrews disappeared in East Asia, or how we can estimate fossil redeposition. Hist. Biol. 2021, 33, 2656–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyta, L.L.; Omelko, V.E.; Tiunov, M.P.; Petrova, E.A.; Kryuchkova, L.Y. Temporal variation in soricid dentition: Which are first—Qualitative or quantitative features? Hist. Biol. 2022, 34, 901–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyta, L.L.; Omelko, V.E.; Izvarin, E.P.; Kropacheva, Y.E.; Eidinova, E.O.; Shemyakina, Y.A.; Nikiforova, V.S.; Strukova, T.V.; Smirnov, N.G. Late Quaternary communities of shrews, Soricidae, from Ural and Far East Regions of Russia: A protocol for the multifactorial morphospace building. Proc. Zool. Inst. RAS 2023, 327, 555–590, (In Russian, with English Summary). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyta, L.L.; Izvarin, E.P.; Shemyakina, Y.A.; Nikiforova, V.S.; Strukova, T.V.; Smirnov, N.G.; Melnikov, D.A.; Bobretsov, A.V. Morphospace dynamics and intraspecies variety of Sorex araneus and S. tundrensis according to recent and fossil data. Palaeontol. Electron. 2023, 26, a51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polly, P.D. Extinction and morphospace occupation: A critical review. Camb. Prism. Extinction 2023, 1, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.C. A generalized K statistic for estimating phylogenetic signal from shape and other high-dimensional multivariate data. Syst. Biol. 2014, 63, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terray, L.; Denys, C.; Goodman, S.M.; Soarimalala, V.; Lalis, A.; Cornette, R. Skull morphological evolution in Malagasy endemic Nesomyinae rodents. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e026304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, M.; Briggs, D.E.G.; Fortey, R.A. Disparity as an evolutionary index: A comparison of Cambrian and Recent arthropods. Paleobiology 1994, 20, 93–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannikova, A.A.; Yuzefovich, A.P.; Stefen, C.; Lebedev, V.S.; Abramov, A.V. Genetic variability in the Crocidura kegoensis–C. zaitsevi group (Mammalia, Eulipotyphla) and re-evaluation of C. zaitsevi fromVietnam. Mamm. Biol. 2023, 103, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics soft-ware package for and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. TpsDig2, Version 2.31; Sbmorphometrics. 2007. Available online: https://www.sbmorphometrics.org/soft-dataacq.html(accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Bookstein, F.L. Morphometric Tools for Landmark Data: Geometry and Biology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; ISBN 10:0521383854. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.M.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an Image Computing Platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polly, P.D. Paleophylogeography of Sorex araneus (Insectivora, Soricidae): Molar shape as a morphological marker for fossil shrews. Mammalia 2003, 68, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, S.; Pieper, S.; Porto, A.; Diamond, K.; Winchester, J.; Shan, S.; Kirveslahti, H.; Boyer, D.; Summers, A.; Maga, A.M. SlicerMorph: An open and extensible platform to retrieve, visualize and analyse 3D morphology. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2021, 12, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlager, S. Morpho and Rvcg—Shape Analysis in R: R-packages for geometric morphometrics, shape analysis and surface manipulations. In Statistical Shape and Deformation Analysis, 1st ed.; Zheng, G., Li, S., Szekely, G., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 217–256. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, D.; Murdoch, D. Package ‘rgl’, Version 1.2.8; CRAN. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rgl/rgl.pdf(accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Claude, J. Morphometrics with R; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0387777894. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.A. Stopping rules in principal components analysis: A comparison of heuristical and statistical approaches. Ecology 1993, 74, 2204–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyta, L.L.; Petrova, T.V.; Panitsina, V.A.; Bodrov, S.Y.; Abramson, N.I. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Asian endemic white-toothed shrews: Crocidura armenica and C. serezkyensis (Eulipotyphla: Soricidae). R.J.T. 2024; 23, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, S.; Zaitsev, M.; Cosson, J.-F.; Abdukadier, A.; Vogel, P. Pliocene and Pleistocene diversification and multiple refugia in a Eurasian shrew (Crocidura suaveolens group). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 38, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohdachi, S.D.; Iwasa, M.A.; Nesterenko, V.A.; Abe, H.; Masuda, R.; Haberl, W. Molecular phylogenetics of Crocidura shrews (Insectivora) in east and central Asia. J. Mammal. 2004, 85, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Cosson, J.-F.; Vohralĺk, V.; Kryštufek, B.; Deker, E.; Vogel, P. Molecular evidence of Pleistocene bidirectional faunal exchange between Europe and the Near East: The case of the bicoloured shrew (Crocidura leucodon, Soricidae). J. Evol. Biol. 2007, 20, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannikova, A.A.; Abramov, A.V.; Borisenko, A.V.; Lebedev, V.S.; Rozhnov, V.V. Mitochondrial diversity of the white-toothed shrews (Mammalia, Eulipotyphla, Crocidura) in Vietnam. Zootaxa 2011, 2812, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannikova, A.A.; Lebedev, V.S.; Kramerov, D.A.; Zaitsev, M.V. Phylogeny and systematics of Crocidura suaveolens species group: Corroboration and controversy between nuclear and mitochondrial DNA markers. Mammalia 2006, 70, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Nová, P.; Vogel, P.; Vohralĺk, V. Cytogenetic and molecular relationships between zarudny’s rock shrew, Crocidura zarudnyi (Mammalia: Soricomorpha) and Eurasian taxa. J. Mammal. 2007, 88, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohdachi, S.D.; Hasegawa, M.; Iwasa, M.A.; Vogel, P.; Oshida, T.; Lin, L.-K.; Abe, H. Molecular phylogenetics of soricid shrews (Mammalia) based on mitochondrial cytochrome b gene sequences: With special reference to the Soricinae. J. Zool. 2006, 270, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; XIe, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reumer, J.W.F. Ruscinian and Early Pleistocene Soricidae (Insectivora, Mammalia) from Tegelen (The Netherlands) and Hungary. Scr. Geol. 1984, 73, 1–173. [Google Scholar]
- Dannelid, E. Dental adaptations in shrew. In Evolution of Shrews; Wójcik, J.M., Wolsan, M., Eds.; Mammal Research Institute, Polish Academy of Sciences: Białowieża, Poland, 1998; pp. 157–174. [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin, A.V. Early Paleogene insectivore mammals of Asia and establishment of the major group of Insectivora. Paleontol. J. 2006, 40, 205–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wible, J.R. On the cranial osteology of the hispaniolan solenodon, Solenodon paradoxus Brandt, 1833 (Mammalia, Lipotyphla, Solenodontidae). Ann. Carnegie Mus. 2008, 77, 321–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, W.; Tröscher, A.; Ruf, I. The orbitotemporal region and the mandibular joint in the skull of shrews (Soricidae, Mammalia). Vertebr. Zool. 2022, 72, 1099–11244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyta, L.L.; Zazhigin, V.S.; Petrova, E.A.; Krjutchkova, L.Y. Shrew dentition (Lipotyphla: Soricidae)—Endodontic morphology and its phylogenetic resolving power. Mammal Res. 2020, 65, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, G.G. Types in modern taxonomy. Am. J. Sci. 1940, 238, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, G.I.; Gureev, A.A.; Strelkov, P.P. Type Specimens Catalogue of Collections of the Zoological Institute of USSR Academy of Sciences. Mammals (Mammalia). Insectivores (Insectivora), Bats (Chiroptera), Lagomorphs (Lagomorpha); Izdatelstvo Nauka: Leningrad, USSR, 1981; Available online: https://zin.ru/labs/theriology/eng/collections/catalog/catalog_zin_mammalia_is1_1981.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024). (In Russian)
- Rich, T.R.; Flannery, T.F.; Trusler, P.; Kool, L.; van Klaveren, N.A.; Vickers-Rich, P. A second tribosphenic mammal from the Mesozoic of Australia. Rec. Queen Vic. Mus. Launceston 2001, 110, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zazhigin, V.S.; Voyta, L.L. New Neogene anourosoricin shrews from northern Asia. Palaeontol. Electron. 2022, 25, a29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haring, E.; Voyta, L.L.; Däubl, B.; Tiunov, M.P. Comparison of genetic and morphological characters in fossil teeth of grey voles from the Russian Far East (Rodentia: Cricetidae: Alexandromys). Mamm. Biol. 2015, 80, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, N.I.; Petrova, T.V. Genetic analysis of type material of the Amur lemming resolves nomenclature issues and creates challenges for the taxonomy of true lemmings (Lemmus, Rodentia: Cricetidae) in the eastern Palearctic. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 182, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, N.I.; Bodrov, S.Y.; Bondareva, O.V.; Genelt-Yanovskiy, E.A.; Petrova, T.V. A mitochondrial genome phylogeny of voles and lemmings (Rodentia: Arvicolinae): Evolutionary and taxonomic implications. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafodatsky, A.S.; Radzhabli, S.I.; Sharshov, A.V.; Zaitsev, M.V. Karyotypes of five Crocidura species of the USSR fauna. Citology 1988, 30, 1247–1250. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gureev, A.A. Insectivora—Insectivores. In Mammals Fauns of USSR. Part 1; Sokolov, I.I., Ed.; Izdatelstvo Akademii Nauk SSSR: Moskva–Leningrad, USSR, 1963; pp. 54–122. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Spitzenberger, F. Eine neue, tiergeographish bemerkenswerte Crocidura (Insectivora, Mammalia) aus der Türkei. Ann. Des Naturhistorischen Mus. Wien 1971, 75, 539–552. [Google Scholar]
- Ognev, S.I. 1928. Zveri Vostochnoi Evropy i Severnoi Azii. Tom I. Nasekomoyadnye i Letuchie Myshi. (The Mammals of the Eastern Europe and the Northern Asia. Vol. I. Insectivora and Chiroptera); Glavnauka: Moscow, Russia, 1928; ISBN 978-5-4458-4583-6. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, T.S. The Structure of Scientific Revolutions; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1970; ISBN 13:978-0226458083. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, T.S. Second thoughts on paradigms. In The Structure of Scientific Theories; Suppe, F., Ed.; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1977; pp. 459–482. [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik, L.; Ramalhinho, G.; Polly, P.D. Response to environmental factors and competition: Skull, mandible and tooth shapes in Polish water shrews (Neomys, Soricidae, Mammalia). J. Zoolog. Syst. 2006, 44, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheverud, J.M. The relationship between development and evolution through heritable variation. In Tinkering: The Microevolution of Development: Novartis Foundation Symposium 285; Bock, G., Goode, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007; Volume 285, pp. 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, T.J. Tinkering: A metaphor uniting evolutionary and developmental biology. Bioessays 2006, 28, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallgrimsson, B.; Lieberman, D.E.; Young, N.M.; Parsons, T.; Wat, S. Evolution of covariance in the mammalian skull. In Tinkering: The Microevolution of Development: Novartis Foundation Symposium 285; Bock, G., Goode, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2007; Volume 285, pp. 164–190. [Google Scholar]
- Tamagnini, D.; Meloro, C.; Raia, P.; Maiorano, L. Testing the occurrence of convergence in the cranio-mandibular shape evolution of living carnivorans. Evolution 2021, 75, 1738–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliev, A.G.; Vasilieva, I.A.; Kourova, T.P.; Chibiryak, M.V. An isolated population of bicolored white-toothed shrew on the northern border of its distribution range in the Orenburg region. Fauna Ural Sib. 2022, 2, 87–108, (In Russian, with English summary). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foote, M. Morphologic patterns of diversification: Examples from trilobites. Palaeontology 1991, 34, 461–485. [Google Scholar]
- Churchfield, S. Foraging strategies of shrews, and the evidence from field studies. In Advances in the Biology of Shrews; Merritt, J.F., Kirkland, G.L., Jr., Rose, R.K., Eds.; Carnegie Museum of Natural History: Pittsburg, PA, USA, 1994; pp. 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hanski, I. Population biological consequences of body size in Sorex. In Advances in the Biology of Shrews; Merritt, J.F., Kirkland, G.L., Jr., Rose, R.K., Eds.; Carnegie Museum of Natural History: Pittsburg, PA, USA, 1994; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cornette, R.; Tresset, A.; Houssin, C.; Pascal, M.; Herrel, A. Does bite force provide a competitive advantage in shrews? The case of the greater white-toothed shrew. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 114, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernvall, J.; Keränen, S.V.E.; Thesleff, I. Evolutionary modification of development in mammalian teeth: Quantifying gene expression patterns and topography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14444–14448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Cho, S.-W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, M.-J.; Cha, Y.-G.; Jung, H.-S. Patterning the size and number of tooth and its cusps. Dev. Biol. 2007, 304, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, K.D.; Evans, A.R.; Jernvall, J. Predicting evolutionary patterns of mammalian teeth from development. Nature 2007, 449, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Ciudad, I. Tooth morphogenesis in vivo, in vitro, and in silico. Curr. Top Dev. Biol. 2008, 81, 341–371. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, A.G. Dispelling dog dogma: An investigation of heterochrony in dogs using 3D geometric morphometric analysis of skull shape. Evol. Dev. 2011, 13, 204–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prost, S.; Klietmann, J.; van Kolfschoten, T.; Guralnick, R.P.; Waltari, E.; Vrieling, K.; Stiller, M.; Nagel, D.; Rabeder, G.; Hofreiter, M.; et al. Effects of Late Quaternary climate change on Palearctic shrews. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Qing, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tang, M.; Murphy, R.W.; Pu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, K.; Guo, K.; et al. Multilocus phylogeny and cryptic diversity of white-toothed shrews (Mammalia, Eulipotyphla, Crocidura) in China. BMC Evol. Biol. 2020, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaudo, M.E.; Arnal, M.; Ekdale, E.G. The auditory region of a caviomorph rodent (Hystricognathi) from the early Miocene of Patagonia (South America) and evolutionary considerations. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 2020, 40, e1777557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandalos, P.; van den Hoek Ostende, L.W. Wear-dependent molar morphology in hypsodont rodents: The case of the spalacine Pliospalax. Palaeontol. Electron. 2023, 26, a47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

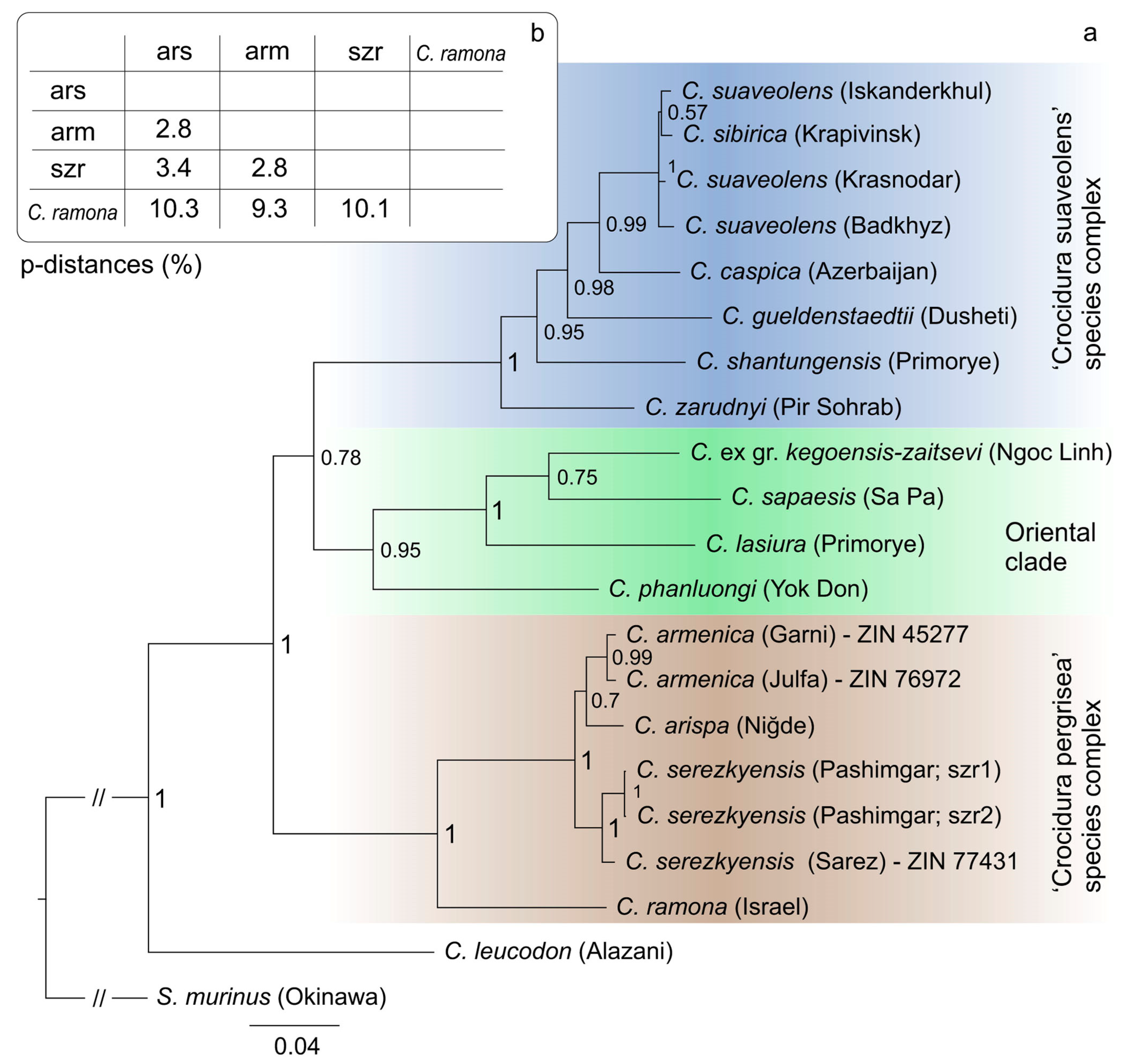
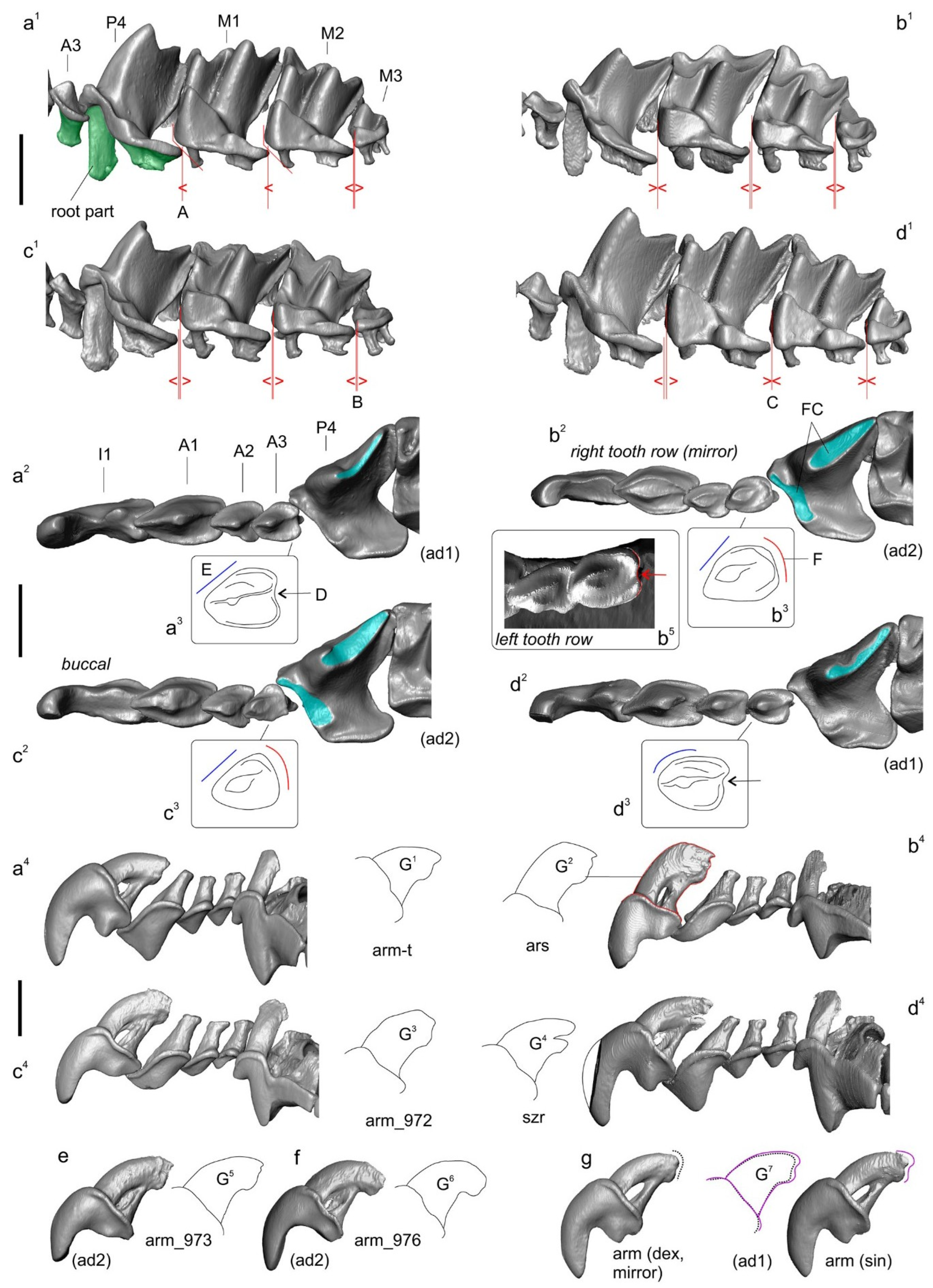

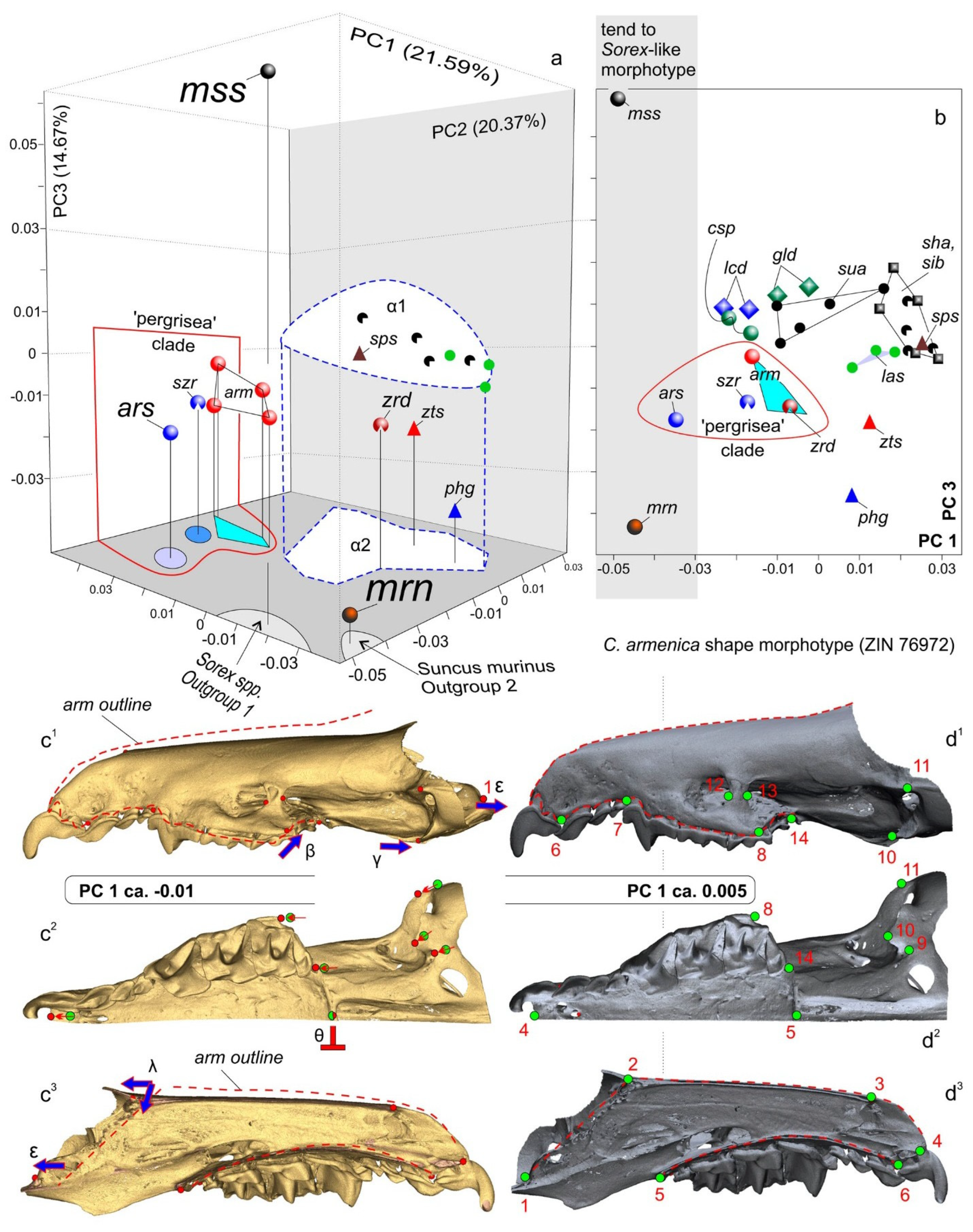
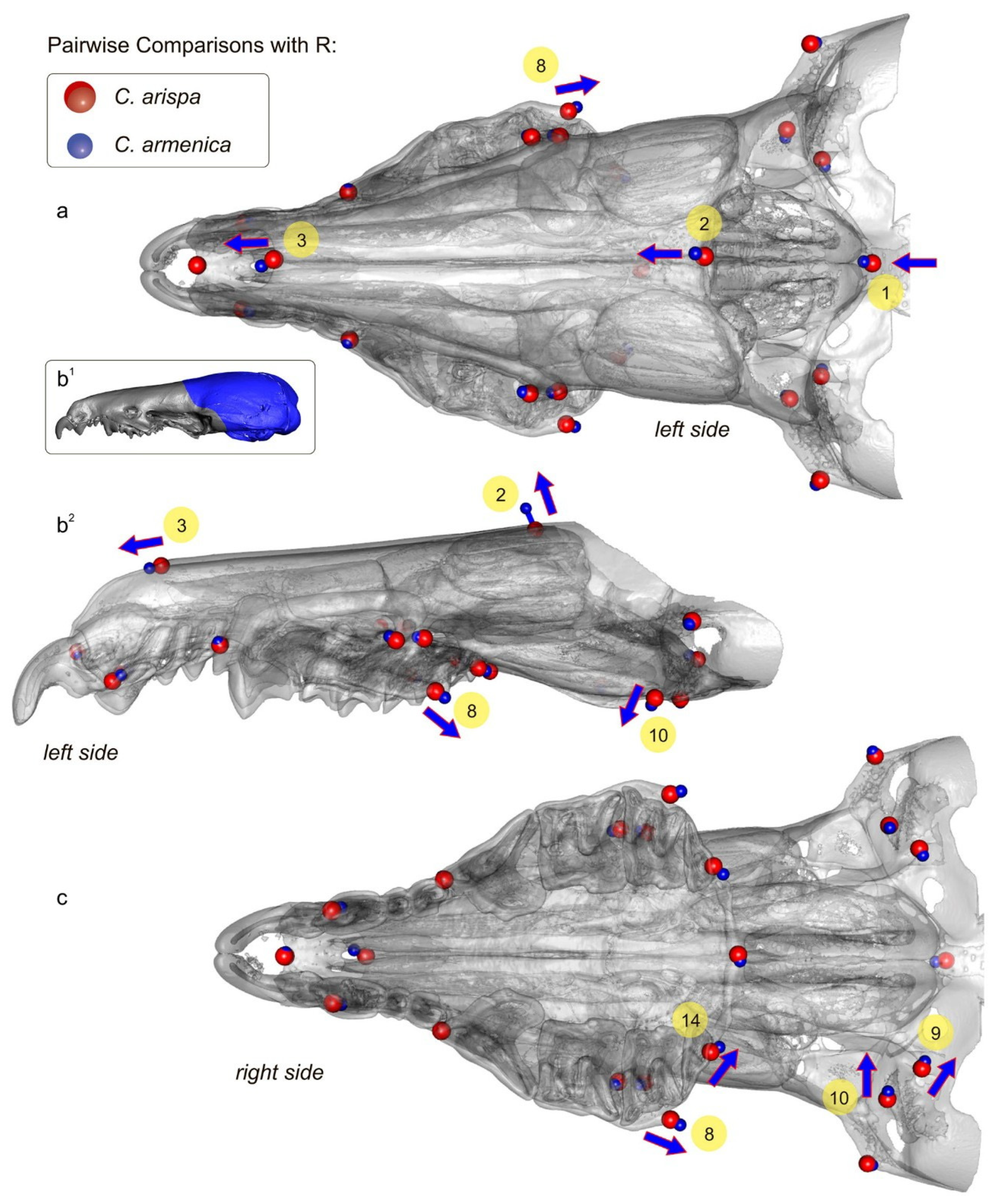

| Species/Collection Number of Voucher/spp. Abbr. | Locality | GenBank ID |
|---|---|---|
| C. armenica, holotype, ZIN 45277 (ZIN-TER-M-5876); arm | Garni S3, Armenia; | OR449074 |
| C. armenica, ZIN 77972 (ZIN-TER-M-5877); arm_972 | Julfa S3, Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of Azerbaijan; | OR449075 |
| C. arispa, holotype, NHMW 13284; ars | Niğde S3, Turkey; | OP599553 [17] |
| C. caspica, IZEA 7793; csp | Azerbaijan; | AY843487 [49] |
| C. gueldenstaedtii, IZEA 2687; gld | Dusheti, Georgia; | AY843497 [49] |
| C. ex gr. kogoensis-zaitsevi, ZIN 96320; zts | Ngoc Linh S3, Vietnam; | HM587003 [37] |
| C. lasiura, ?; las | Kraskino, Primorye, Russia; | AB077072 [50] |
| C. leucodon, IZEA 23629; lcd | Alazani, Georgia; | DQ994756 [51] |
| C. phanluongi, holotype, ZIN 97092; php | Yok Don S3, Vietnam; | HM587020 [52] |
| C. ramona, TAUM12771 | Israel; | LR536374 [?] |
| C. sapaensis, ZIN 97792; sps | Sa Pa S3, Vietnam; | MW075591 [?] |
| C. serezkyensis, ZIN 77431 (ZIN-TER-M-5875); szr | Sarez Lake S3, Tajikistan; | OR449076 |
| C. serezkyensis, ZMMU S-111841; szr1 | Tajikistan, Pamir, Peter I Range, Pashimgar; | OP599554 [17] |
| C. serezkyensis, ZMMU S-111842; szr2 | ibid.; | OP599555 [17] |
| C. shantungensis, ?; sha | Popov Island, Primorye, Russia; | AB077278 [49] |
| C. sibirica, ZMMU S- 177776; sib | Krapivinsk, Kemerovo Oblast’, Russia; | AY994389 [53] |
| C. suaveolens, ZIN 73479 | Krasnodar Krai, Russia; | AY843476 [49] |
| C. suaveolens, ZIN 73756; sua_756 | Badhyz S3, Turkmenistan; | AY843479 [49] |
| C. suaveolens, ZIN 77220; sua_220 | Iskanderkhul S3, Tajikistan; | AY843482 [49] |
| C. zarudnyi, I-89; zrd | Pir Sohrab, Iran; | AY925211 [54] |
| Suncus murinus, ?; mrn | Okinawa, Japan. | AB175074 [55] |
| Total: 15 spp.; n = 21 |
| Species, Specimens | MBH | MRH | LML | CIL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. arm | 1.11 | 4.26 | 3.48 | n.a. |
| 2. arm-t | 1.22 | 4.33 | 3.80 | n.a. |
| 3. arm_972 | 1.23 | 4.30 | 3.88 | 17.96 |
| 4. arm_973 | 1.23 | 4.33 | 3.81 | 19.06 |
| 5. arm_976 | 1.12 | 4.29 | 3.79 | 18.88 |
| 6. ars | 1.25 | 3.88 | 3.78 | 17.92 |
| 7. szr | 1.05 | 3.92 | 3.86 | 17.91 |
| 8. gld | 1.19 ± 0.02/0.11/ 0.97–1.39/30 | 4.4 ± 0.05/0.30/ 3.68–4.89/30 | 3.93 ± 0.03/0.21/ 3.34–4.25/30 | 17.95 ± 0.21/1.08/ 15.39–19.52/25 |
| 9. lcd | 1.34 ± 0.02/0.09/ 1.22–1.50/12 | 4.72 ± 0.05/0.17/ 4.42–4.97/12 | 4.06 ± 0.04/0.16/ 3.80–4.38/12 | 18.4 ± 0.18/0.65/ 17.42–19.24/12 |
| 10. sua | 1.13 ± 0.01/0.07/ 0.98–1.25/29 | 4.21 ± 0.03/0.18/ 3.73–4.58/29 | 3.78 ± 0.02/0.09/ 3.63–3.98/29 | 16.99 ± 0.08/0.40/ 16.22–17.78/28 |
| 11. zrd | 1.49 | 3.95 | 4.70 | 18.8 |
| PL | UML | ZYG | EGW | |
| 1. arm | 6.92 | 2.93 | 5.22 | n.a. |
| 2. arm-t | 6.95 | 3.04 | 5.41 | 6.21 |
| 3. arm_972 | 7.14 | 3.18 | 5.56 | 6.24 |
| 4. arm_973 | 7.61 | 3.41 | 6.14 | 6.54 |
| 5. arm_976 | 7.63 | 3.42 | 5.89 | 6.30 |
| 6. ars | 7.31 | 3.10 | 5.37 | 6.14 |
| 7. szr | 7.43 | 3.27 | 5.59 | 6.17 |
| 8. gld | 7.66 ± 010/0.52/ 6.27–8.39/27 | 3.27 ± 0.04/0.21/ 2.74–3.54/27 | 5.64 ± 0.06/0.36/ 4.79–6.30/27 | 5.95 ± 0.07/0.40/ 5.07–6.57/27 |
| 9. lcd | 7.88 ± 0.08/0.29/ 7.33–8.32/12 | 3.31 ± 0.03/0.13/ 3.08–3.49/12 | 6.17 ± 0.06/0.22/ 5.87–6.53/12 | 6.35 ± 0.05/0.20/ 6.07–6.74/12 |
| 10. sua | 7.18 ± 0.05/0.25/ 6.74–7.72/29 | 3.15 ± 0.02/0.09/ 2.98–3.28/29 | 5.46 ± 0.03/0.14/ 5.19–5.70/29 | 5.71 ± 0.03/0.18/ 5.43–6.02/29 |
| 11. zrd | 7.99 | 3.34 | 6.06 | 6.32 |
| P4s/d | HB | C | Pl. | |
| 1. arm | 0.91 | 60.0 2 | 45.0 | 12.0 |
| 2. arm-t | 0.97 | — | — | — |
| 3. arm_972 | 0.98 | 57.0 3 | 41.0 | 11.6 |
| 4. arm_973 | 1.13 | 65.0 3 | 50.5 | 11.4 |
| 5. arm_976 | 1.12 | -3 | - | - |
| 6. ars | 1.04 | 70.0 | 48.0 | 12.5 1 |
| 7. szr | 1.14 | 62.0 | 48.0 | 10.0 |
| 8. gld | 1.17 ± 0.02/0.11/ 0.86–1.42/27 | Lim. 57–80 4 | Lim. 41–53 | Lim. 11–14 |
| 9. lcd | 1.13 ± 0.01/0.06/ 1.04–1.22/12 | Lim. 59–82 4 | Lim. 31–39 | Lim. 12–15 |
| 10. sua | 1.17 ± 0.02/0.08/ 0.99–1.31/28 | Lim. 47–74 4 | Lim. 25–40 4 | Lim. 9–13 4 |
| 11. zrd | 1.32 | 60.8 5 | 47.5 5 | 13.0 5 |
| Species | MBH * | MRH | LML | CIL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. gueldenstaedtii | 0.97/0.76/30 | 0.88/0.004/30 | 0.48/<0.001/30 | 0.86/0.003/25 |
| C. lasiura | 0.84/0.01/14 | 0.85/0.01/17 | 0.84/0.008/17 | 0.83/0.006/17 |
| C. leucodon | 0.92/0.33/12 | 0.93/0.47/12 | 0.98/0.98/12 | 0.87/0.08/12 |
| C. sapaensis | 0.58/<0.001/11 | 0.94/0.60/11 | 0.97/0.89/11 | 0.93/0.48/11 |
| C. shantungensis | 0.93/0.16/23 | 0.97/0.85/22 | 0.96/0.49/23 | 0.96/0.61/23 |
| C. sibirica | 0.97/0.67/30 | 0.94/0.16/30 | 0.92/0.04/29 | 0.93/01./27 |
| C. suaveolens | 0.98/0.88/29 | 0.97/0.65/29 | 0.96/0.54/27 | 0.97/0.64/28 |
| C. zaitsevi | 0.96/0.85/7 | 0.89/0.30/7 | 0.89/0.30/7 | 0.98/0.98/7 |
| Species | PL | UML | ZYG | EGW |
| C. gueldenstaedtii | 0.89/0.009/27 | 0.89/0.01/27 | 0.94/0.17/27 | 0.91/0.02/27 |
| C. lasiura | 0.89/0.04/17 | 0.96/0.79/17 | 0.83/0.008/16 | 0.85/0.01/17 |
| C. leucodon | 0.94/0.49/12 | 0.91/0.26/12 | 0.93/0.40/12 | 0.96/0.82/12 |
| C. sapaensis | 0.94/0.55/11 | 0.93/0.51/11 | 0.83/0.02/11 | 0.89/0.16/11 |
| C. shantungensis | 0.96/0.54/23 | 0.97/0.90/23 | 0.95/0.44/23 | 0.93/0.14/23 |
| C. sibirica | 0.95/0.19/29 | 0.95/0.19/29 | 0.96/0.54/29 | 0.96/0.52/29 |
| C. suaveolens | 0.96/0.53/29 | 0.93/0.07/29 | 0.96/0.33/29 | 0.94/0.10/29 |
| C. zaitsevi | 0.94/0.67/7 | 0.81/0.05/7 | 0.85/0.13/7 | 0.92/0.49/7 |
| Specimens | HCD | LLF |
|---|---|---|
| 1. C. armenica, ZIN 45277 | 1.29 | 1.19 |
| 2. C. armenica, ZIN 55321 | 1.20 * | 1.19 |
| 3. C. armenica, ZIN 77972 | 1.34 | 1.19 |
| 4. C. armenica, ZIN 77973 | 1.31 | 1.18 |
| 5. C. armenica, ZIN 77976 | 1.38 | 1.13 * |
| 6. C. arispa, NHMW 13284 | 1.19 * | 1.13 * |
| 7. C. serezkyensis, ZIN 77431 | 1.07 | 1.00 |
| 8. C. gueldenstaedtii, ZIN 72843 | 1.64 | 1.27 |
| 9. C. gueldenstaedtii, ZIN 72872 | 1.42 | 1.18 |
| 10. C. leucodon, ZIN 72918 | 1.60 | 1.48 |
| 11. C. leucodon, ZIN 72921 | 1.58 | 1.46 |
| 12. C. suaveolens, ZIN 73665 B | 1.33 | 1.24 |
| 13. C. suaveolens, ZIN 73756 B | 1.29 | 1.17 |
| 14. C. suaveolens, ZIN 77220 I | 1.26 | 1.13 |
| 15. C. suaveolens, ZIN 98863 I | 1.31 | 1.14 |
| 16. C. suaveolens, ZIN 98864 I | 1.27 | 1.17 |
| mean: C. suaveolens, n = 5 | 1.29 ± 0.01/0.02 1.26–1.33 | 1.17 ± 0.01/0.04/ 1.13–1.24 |
| 17. C. zarudnyi, ZIN 6506 | 1.54 | 1.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voyta, L.L.; Petrova, T.V.; Panitsina, V.A.; Bodrov, S.Y.; Winkler, V.; Kryuchkova, L.Y.; Abramson, N.I. A Cybertaxonomic Revision of the “Crocidura pergrisea” Species Complex with a Special Focus on Endemic Rocky Shrews: Crocidura armenica and Crocidura arispa (Soricidae). Biology 2024, 13, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060448
Voyta LL, Petrova TV, Panitsina VA, Bodrov SY, Winkler V, Kryuchkova LY, Abramson NI. A Cybertaxonomic Revision of the “Crocidura pergrisea” Species Complex with a Special Focus on Endemic Rocky Shrews: Crocidura armenica and Crocidura arispa (Soricidae). Biology. 2024; 13(6):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060448
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoyta, Leonid L., Tatyana V. Petrova, Valentina A. Panitsina, Semyon Yu. Bodrov, Viola Winkler, Lyudmila Yu. Kryuchkova, and Natalia I. Abramson. 2024. "A Cybertaxonomic Revision of the “Crocidura pergrisea” Species Complex with a Special Focus on Endemic Rocky Shrews: Crocidura armenica and Crocidura arispa (Soricidae)" Biology 13, no. 6: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060448
APA StyleVoyta, L. L., Petrova, T. V., Panitsina, V. A., Bodrov, S. Y., Winkler, V., Kryuchkova, L. Y., & Abramson, N. I. (2024). A Cybertaxonomic Revision of the “Crocidura pergrisea” Species Complex with a Special Focus on Endemic Rocky Shrews: Crocidura armenica and Crocidura arispa (Soricidae). Biology, 13(6), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060448







