Differential Contributions of Fibroblast Subpopulations to Intercellular Communication in Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. scRNA-Seq Data Analysis
2.3. Identification of Fibroblast Subpopulations
2.4. DEGs and GSEA/Hallmark Database
2.5. Cell–Cell Interaction
2.6. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.7. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
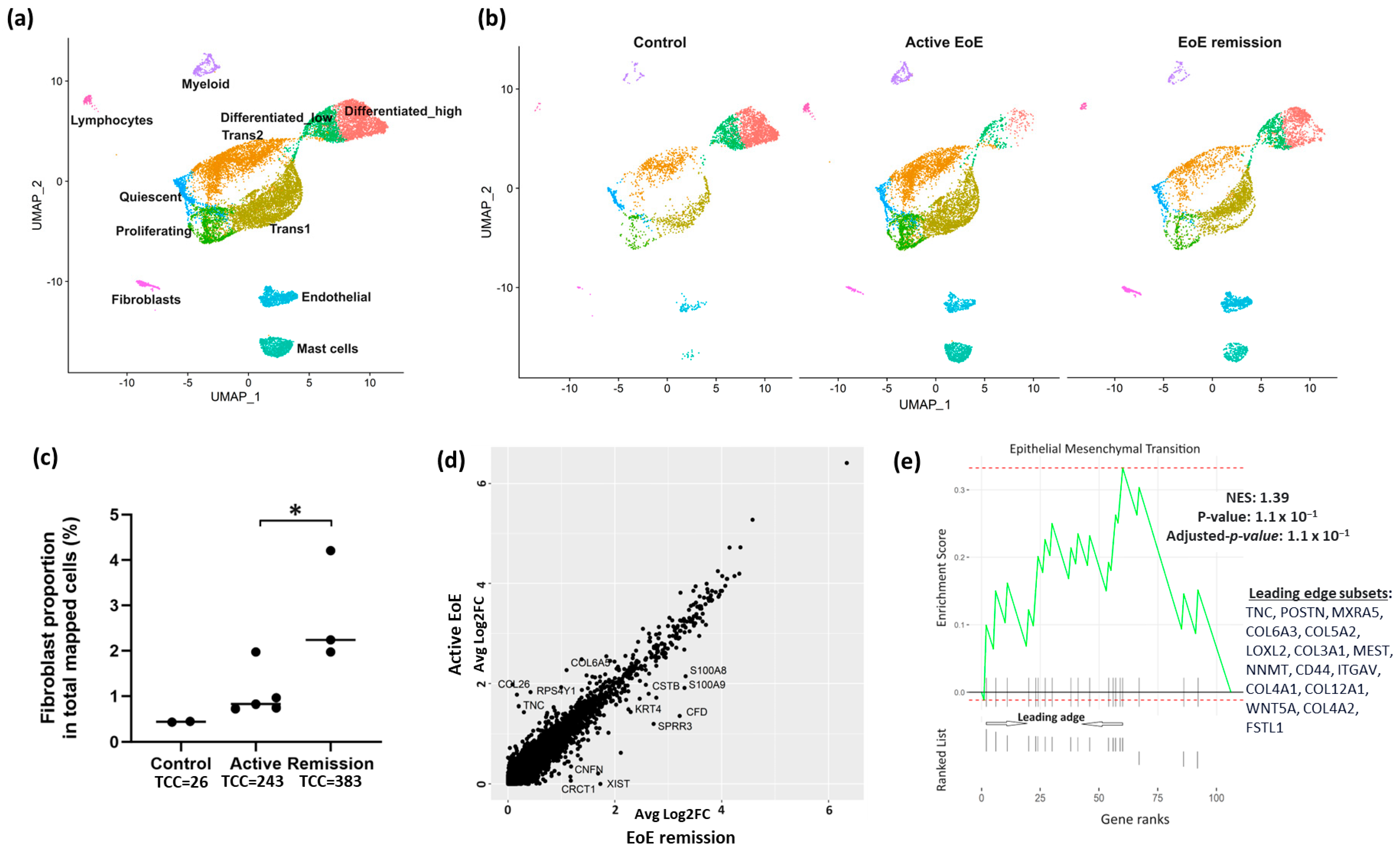
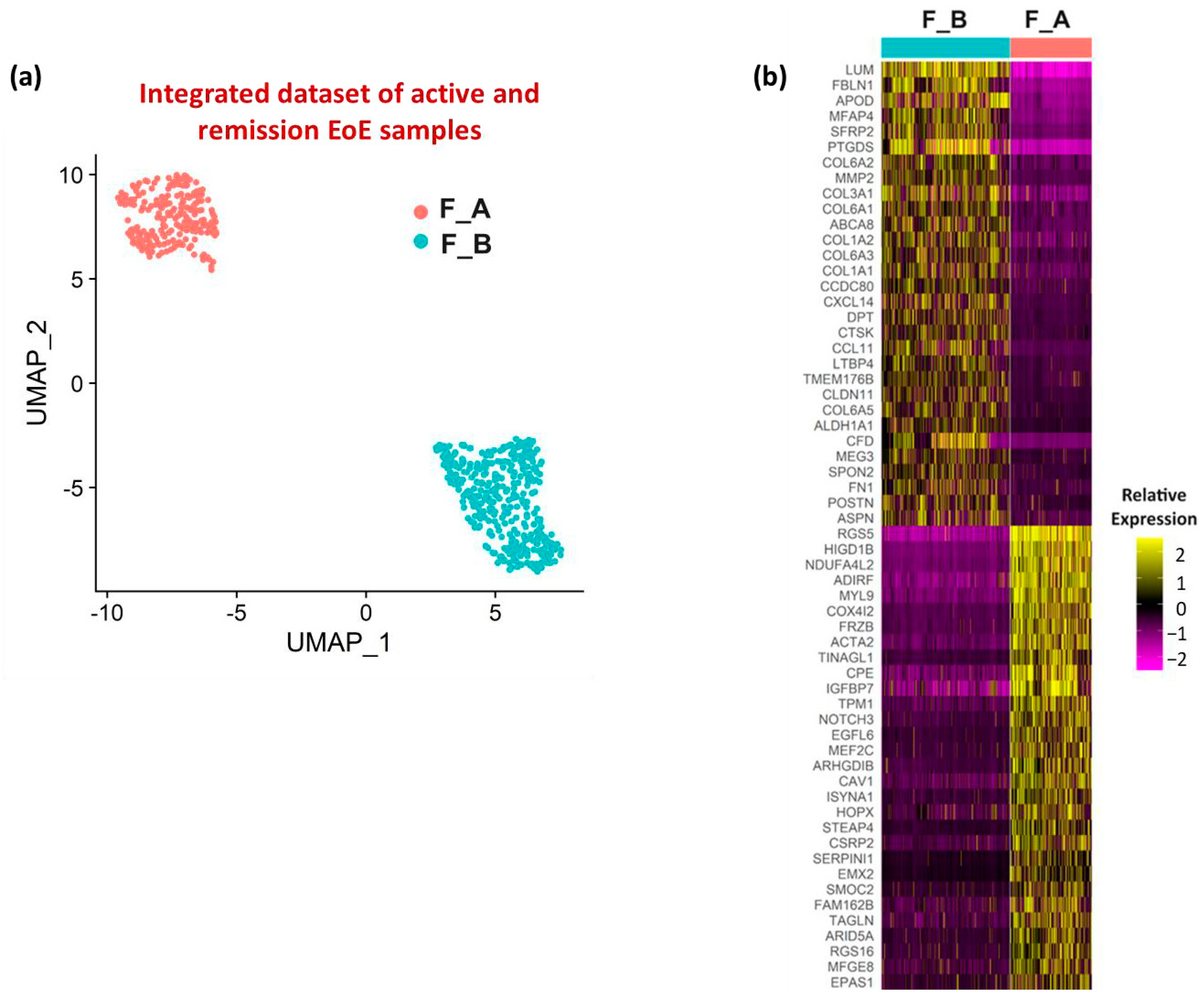
3.1. Fibroblast Sub-Clusters in Total Dataset
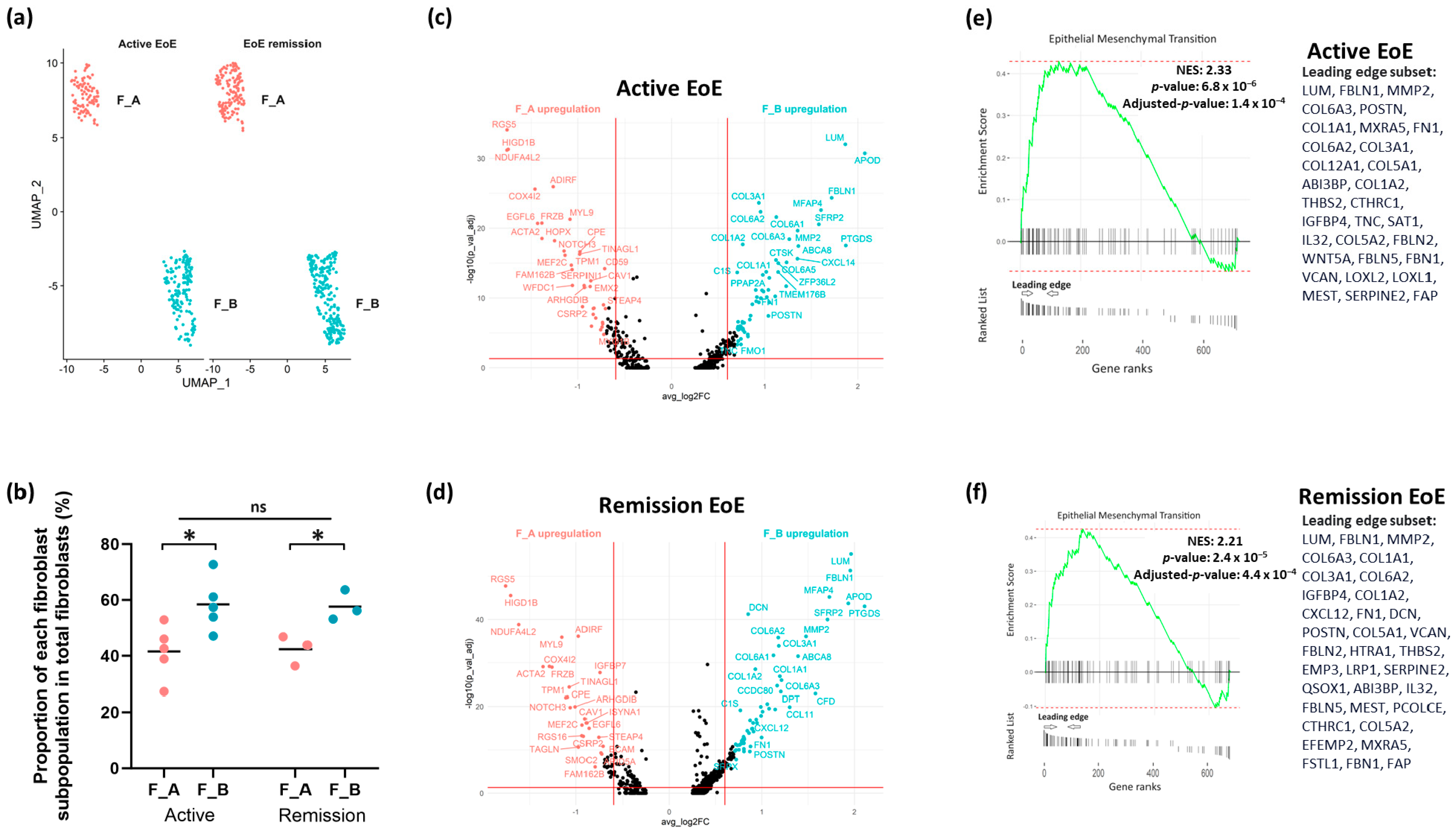
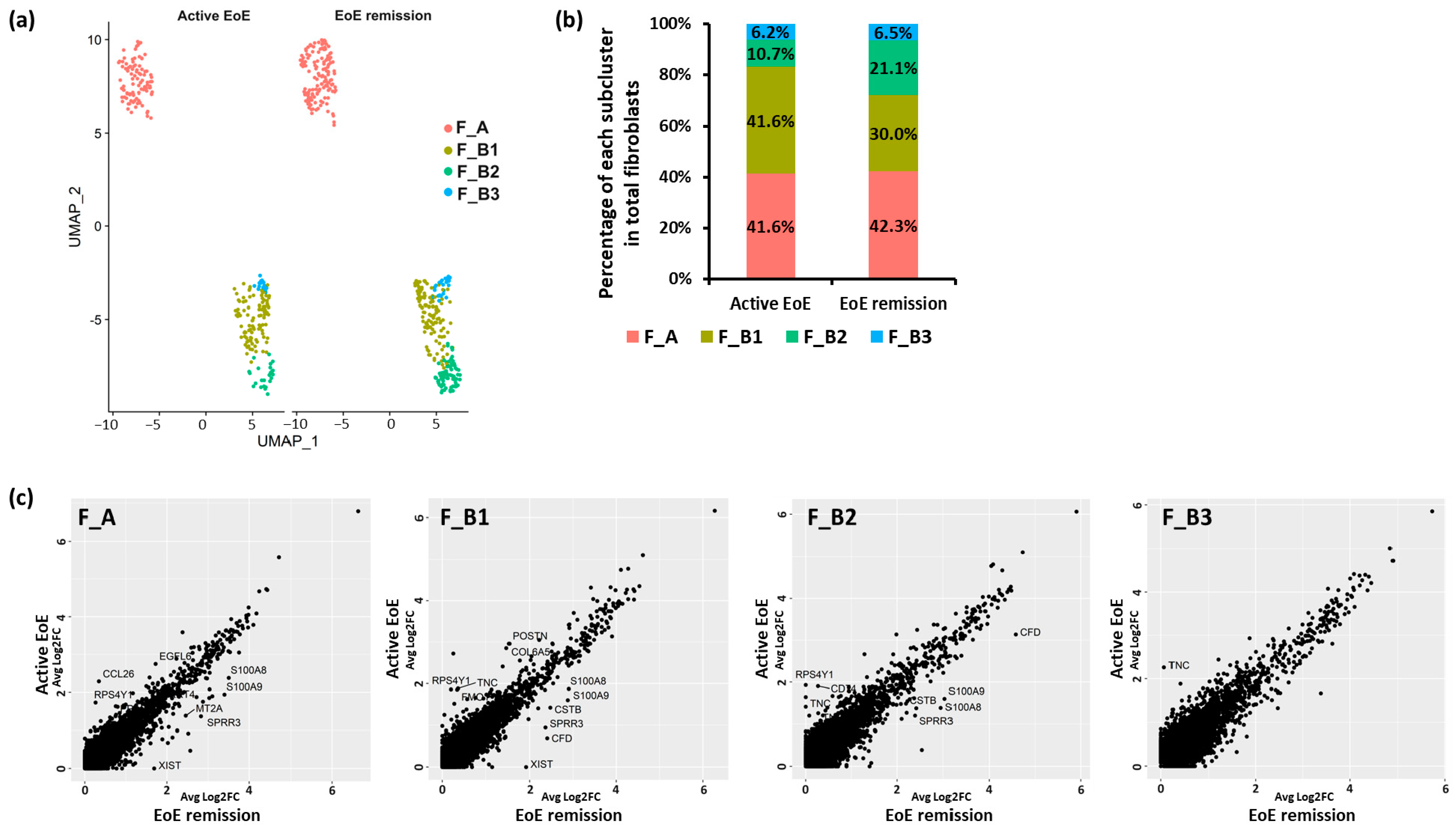
3.2. Fibroblast Subclusters in Active EoE and in Remission EoE
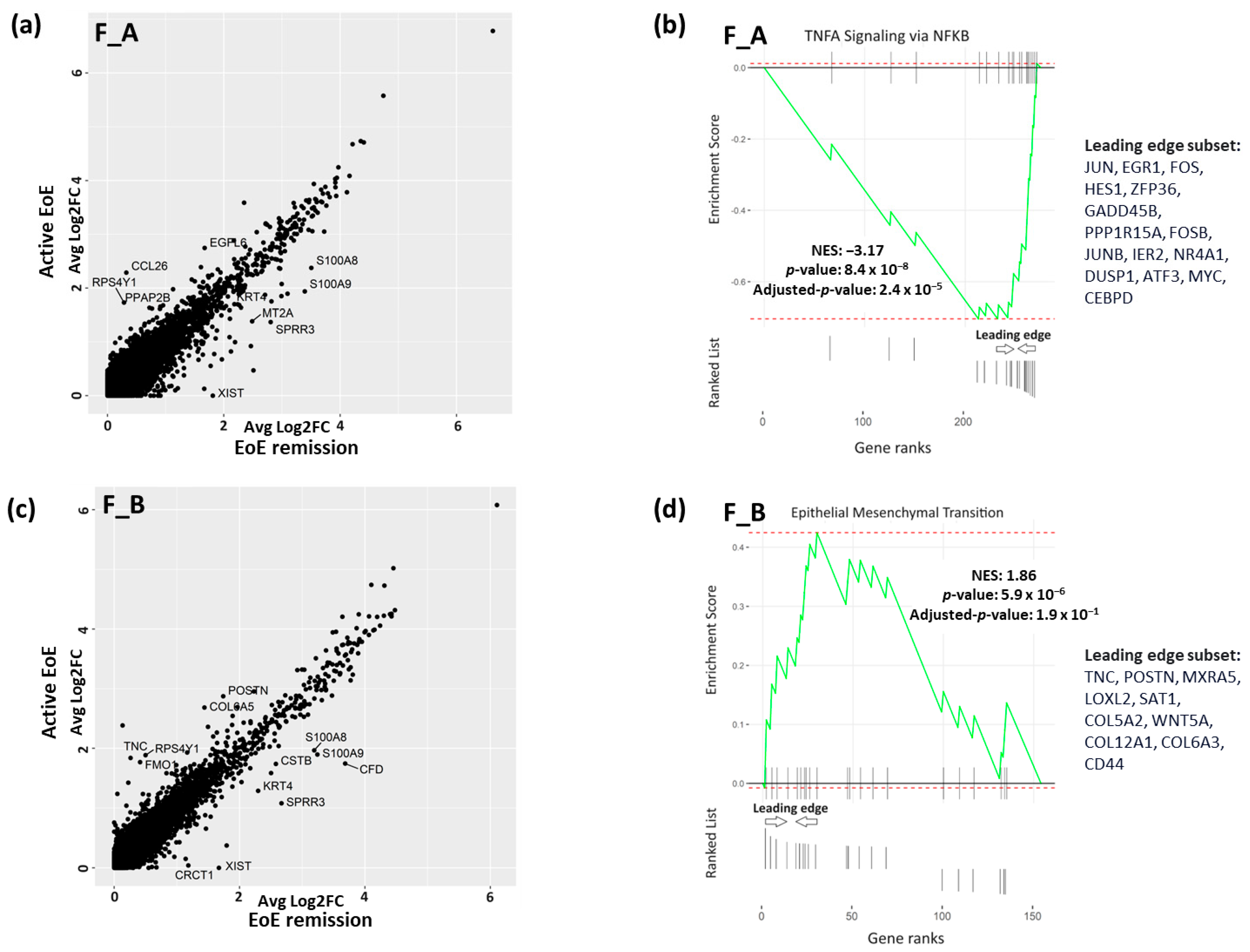
3.3. DEGs and Pathways in Fibroblast Sub-Clusters in Active versus Remission EoE
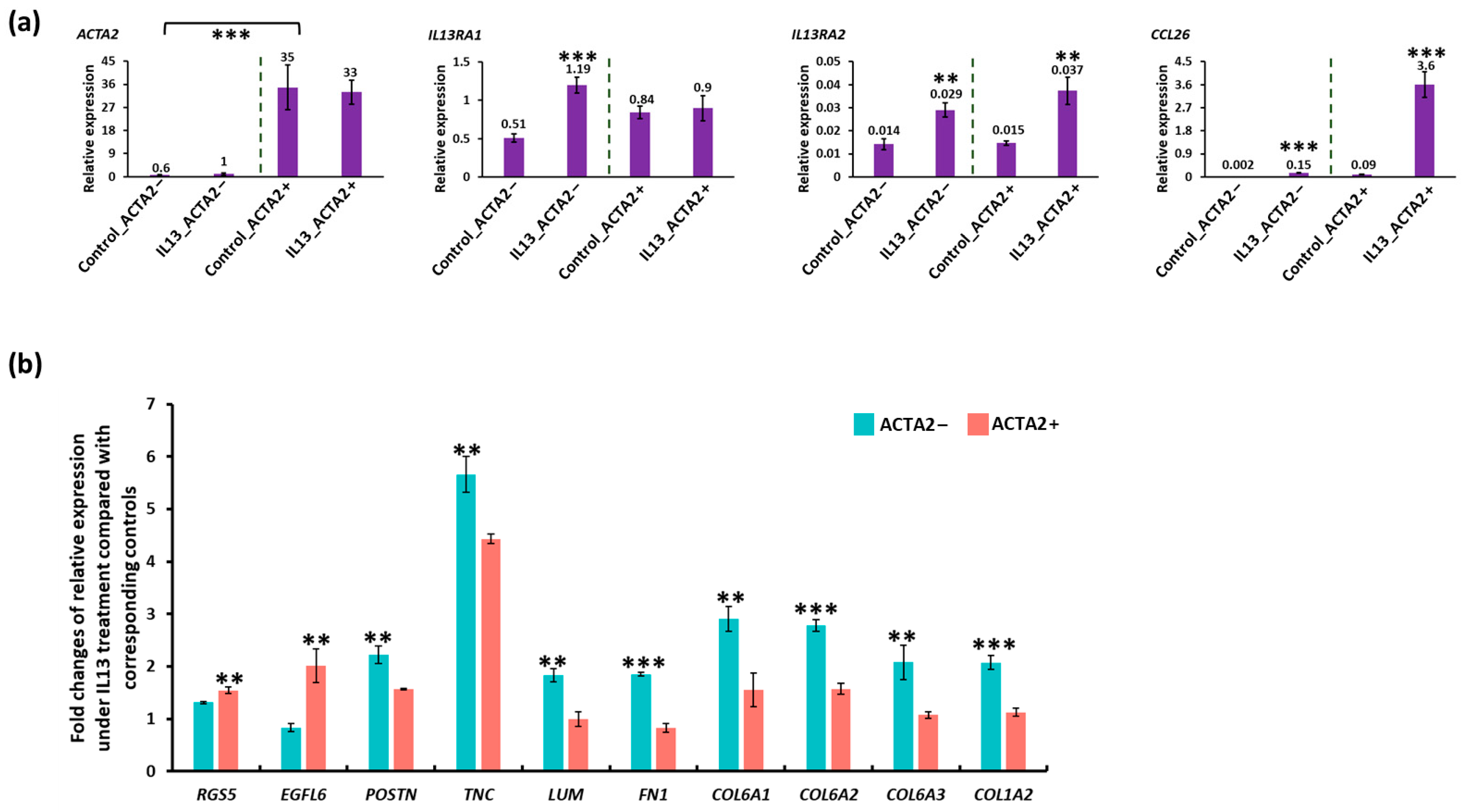
3.4. In Vitro Modeling of Active EoE in ACTA2+ and ACTA2− Fibroblast Cultures
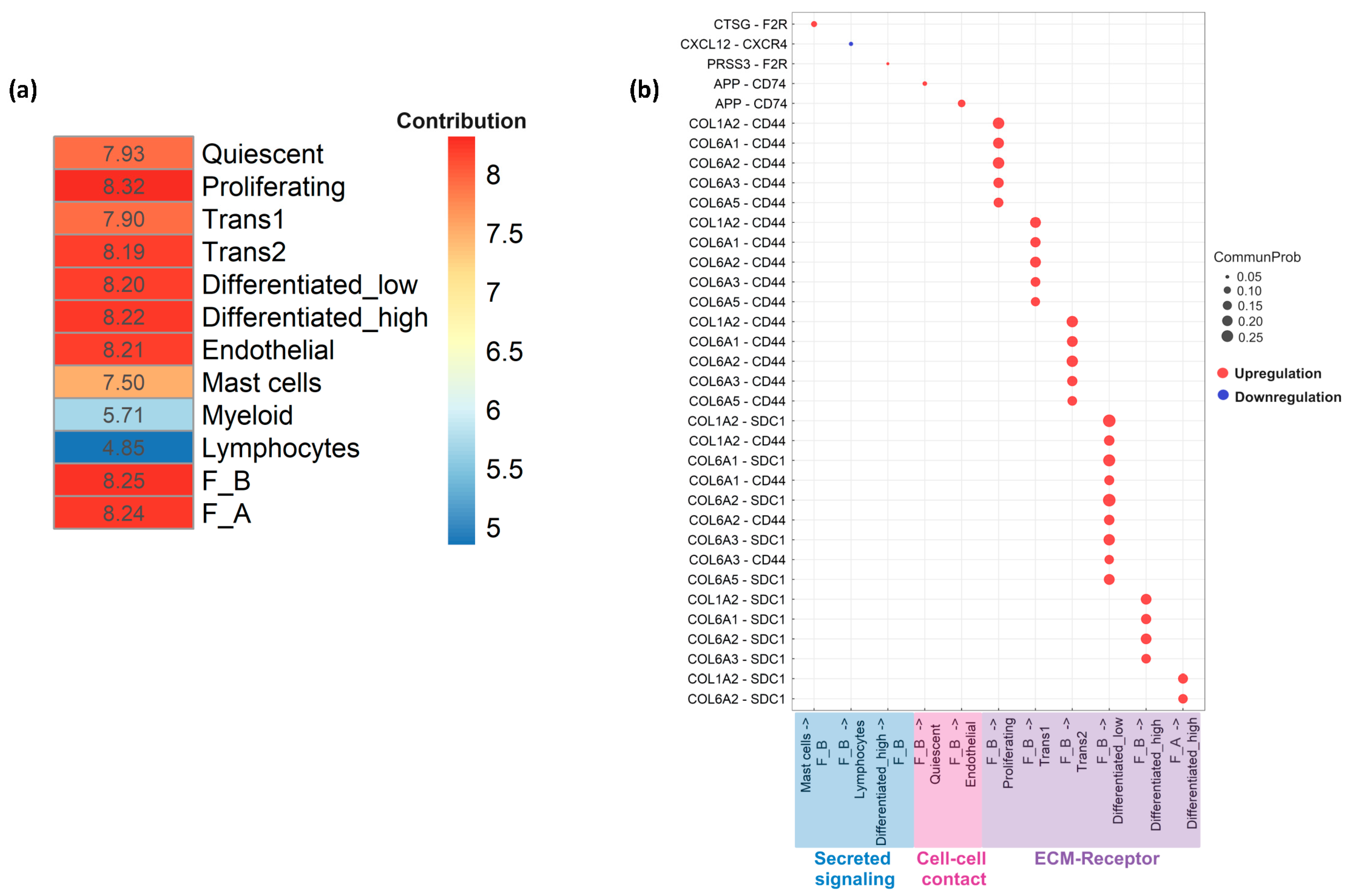
3.5. Cell–Cell Communication Analysis
3.6. Additional Subsets in the F_B Fibroblast Sub-Cluster
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Straumann, A.; Spichtin, H.P.; Grize, L.; Bucher, K.A.; Beglinger, C.; Simon, H.U. Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: A follow-up of 30 adult patients for up to 11.5 years. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoepfer, A.M.; Safroneeva, E.; Bussmann, C.; Kuchen, T.; Portmann, S.; Simon, H.U.; Straumann, A. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1230–1236.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Kim, H.P.; Sperry, S.L.; Rybnicek, D.A.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J. A phenotypic analysis shows that eosinophilic esophagitis is a progressive fibrostenotic disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, 577–585.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipka, S.; Kumar, A.; Richter, J.E. Impact of Diagnostic Delay and Other Risk Factors on Eosinophilic Esophagitis Phenotype and Esophageal Diameter. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warners, M.J.; Oude Nijhuis, R.A.B.; de Wijkerslooth, L.R.H.; Smout, A.; Bredenoord, A.J. The natural course of eosinophilic esophagitis and long-term consequences of undiagnosed disease in a large cohort. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, A. Esophageal remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2024, 40, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, R.T.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Fibroblasts in fibrosis: Novel roles and mediators. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, J.H.W.; Gyorfi, A.H.; Ramanujam, M.; Whitfield, M.L.; Konigshoff, M.; Lafyatis, R. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Souza, R.F.; Spechler, S.J. Tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1175–G1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.B.; Dods, K.; Henry, S.J.; Benitez, A.J.; Lee, D.; Whelan, K.A.; DeMarshall, M.; Hammer, D.A.; Falk, G.; Wells, R.G.; et al. Eosinophilic Esophagitis-Associated Chemical and Mechanical Microenvironment Shapes Esophageal Fibroblast Behavior. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, T.; Wen, T.; Caldwell, J.M.; Ben-Baruch Morgenstern, N.; Osswald, G.A.; Rochman, M.; Mack, L.E.; Felton, J.M.; Abonia, J.P.; Arva, N.C.; et al. Loss of Endothelial TSPAN12 Promotes Fibrostenotic Eosinophilic Esophagitis via Endothelial Cell-Fibroblast Crosstalk. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasagi, Y.; Dods, K.; Wang, J.X.; Chandramouleeswaran, P.M.; Benitez, A.J.; Gambanga, F.; Kluger, J.; Ashorobi, T.; Gross, J.; Tobias, J.W.; et al. Fibrostenotic eosinophilic esophagitis might reflect epithelial lysyl oxidase induction by fibroblast-derived TNF-alpha. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, A.B.; Dods, K.; Noah, Y.; Toltzis, S.; Chandramouleeswaran, P.M.; Lee, A.; Benitez, A.; Bedenbaugh, A.; Falk, G.W.; Wells, R.G.; et al. Esophageal epithelial cells acquire functional characteristics of activated myofibroblasts after undergoing an epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 330, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinchen, J.; Chen, H.H.; Parikh, K.; Antanaviciute, A.; Jagielowicz, M.; Fawkner-Corbett, D.; Ashley, N.; Cubitt, L.; Mellado-Gomez, E.; Attar, M.; et al. Structural Remodeling of the Human Colonic Mesenchyme in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell 2018, 175, 372–386.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicki-Osuch, K.; Zhuang, L.; Cheung, T.S.; Black, E.L.; Masque-Soler, N.; Devonshire, G.; Redmond, A.M.; Freeman, A.; di Pietro, M.; Pilonis, N.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Unifies Developmental Programs of Esophageal and Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1346–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manresa, M.C.; Chiang, A.W.T.; Kurten, R.C.; Dohil, R.; Brickner, H.; Dohil, L.; Herro, R.; Akuthota, P.; Lewis, N.E.; Croft, M.; et al. Increased Production of LIGHT by T Cells in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Promotes Differentiation of Esophageal Fibroblasts Toward an Inflammatory Phenotype. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1778–1792.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manresa, M.C.; Wu, A.; Nhu, Q.M.; Chiang, A.W.T.; Okamoto, K.; Miki, H.; Kurten, R.; Pham, E.; Duong, L.D.; Lewis, N.E.; et al. LIGHT controls distinct homeostatic and inflammatory gene expression profiles in esophageal fibroblasts via differential HVEM and LTbetaR-mediated mechanisms. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, M.; Wen, T.; Kotliar, M.; Dexheimer, P.J.; Ben-Baruch Morgenstern, N.; Caldwell, J.M.; Lim, H.W.; Rothenberg, M.E. Single-cell RNA-Seq of human esophageal epithelium in homeostasis and allergic inflammation. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e159093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargus, M.; Niu, C.; Vallone, J.G.; Binkley, J.; Rubin, D.C.; Shaker, A. Human esophageal myofibroblasts secrete proinflammatory cytokines in response to acid and Toll-like receptor 4 ligands. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G904–G923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargus, M.; Niu, C.; Shaker, A. Isolation of myofibroblasts from mouse and human esophagus. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 18, e52215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Kiran, K.C.; Blanchard, C.; Stucke, E.M.; Kemme, K.A.; Collins, M.H.; Abonia, J.P.; Putnam, P.E.; Mukkada, V.A.; Kaul, A.; et al. Analysis and expansion of the eosinophilic esophagitis transcriptome by RNA sequencing. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.D.; Munro, S.A.; Knutson, T.P.; LaRue, R.S.; Heltemes-Harris, L.M.; Farrar, M.A. Single-cell analysis identifies dynamic gene expression networks that govern B cell development and transformation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Dedhia, P.H.; Jin, S.; Ruiz-Vega, R.; Ma, D.; Liu, Y.; Yamaga, K.; Shestova, O.; Gay, D.L.; Yang, Z.; et al. Single-cell analysis reveals fibroblast heterogeneity and myeloid-derived adipocyte progenitors in murine skin wounds. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, K.; Ni, C.; Wan, J.; Duan, X.; Lou, X.; Yao, X.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Gu, Z.; et al. Transgelin promotes lung cancer progression via activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts with enhanced IL-6 release. Oncogenesis 2023, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmelzer, C.E.H.; Duca, L. Elastic fibers: Formation, function, and fate during aging and disease. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 3704–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, M.R.; Derian, C.K.; Santulli, R.J.; Andrade-Gordon, P. Differential expression of protease-activated receptors-1 and -2 in stromal fibroblasts of normal, benign, and malignant human tissues. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, M.G.; Pereira-Simon, S.; Zigmond, Z.M.; Varona Santos, J.; Perla, M.; Santos Falcon, N.; Stoyell-Conti, F.F.; Salama, A.; Yang, X.; Long, X.; et al. Single-Cell Analyses Offer Insights into the Different Remodeling Programs of Arteries and Veins. Cells 2024, 13, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z. Bioinformatics analysis identifies coagulation factor II receptor as a potential biomarker in stomach adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, B.; Troutman, T.D.; Schwartz, J.T. Breaking down the complex pathophysiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marella, S.; Sharma, A.; Ganesan, V.; Ferrer-Torres, D.; Krempski, J.W.; Idelman, G.; Clark, S.; Nasiri, Z.; Vanoni, S.; Zeng, C.; et al. IL-13-induced STAT3-dependent signaling networks regulate esophageal epithelial proliferation in eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 1550–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Salomon, M.; Shao, L.; Khalatbari, A.; Castle, J.D.; Shaker, A. Differential Contributions of Fibroblast Subpopulations to Intercellular Communication in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Biology 2024, 13, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070461
Li T, Salomon M, Shao L, Khalatbari A, Castle JD, Shaker A. Differential Contributions of Fibroblast Subpopulations to Intercellular Communication in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Biology. 2024; 13(7):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070461
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tao, Matthew Salomon, Ling Shao, Atousa Khalatbari, Joshua D. Castle, and Anisa Shaker. 2024. "Differential Contributions of Fibroblast Subpopulations to Intercellular Communication in Eosinophilic Esophagitis" Biology 13, no. 7: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070461
APA StyleLi, T., Salomon, M., Shao, L., Khalatbari, A., Castle, J. D., & Shaker, A. (2024). Differential Contributions of Fibroblast Subpopulations to Intercellular Communication in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Biology, 13(7), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070461





