Comparison of Immune Indicators Related to Phagocytosis of Five Species of Sea Urchins under Artificial Infection with the Pathogenic Bacterium of Black Mouth Disease
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Experimental Design
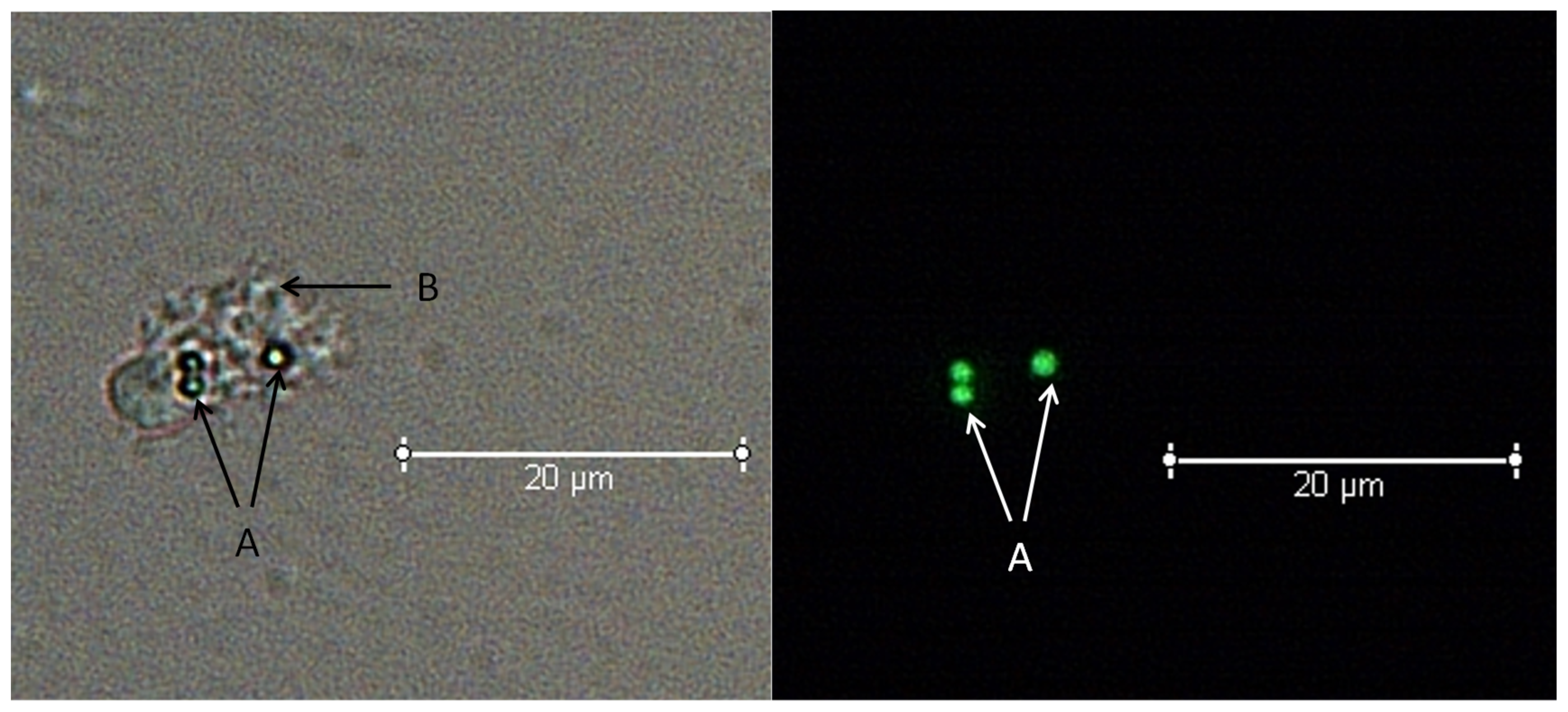
2.2.2. Categorical Counts of Coelomocytes
2.2.3. Determination of Phagocytosis-Related Immune Parameters
2.2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Species, Time and Species–Time Interaction on Immune Parameters
3.2. Comparison of Coelomocytes Density Changes
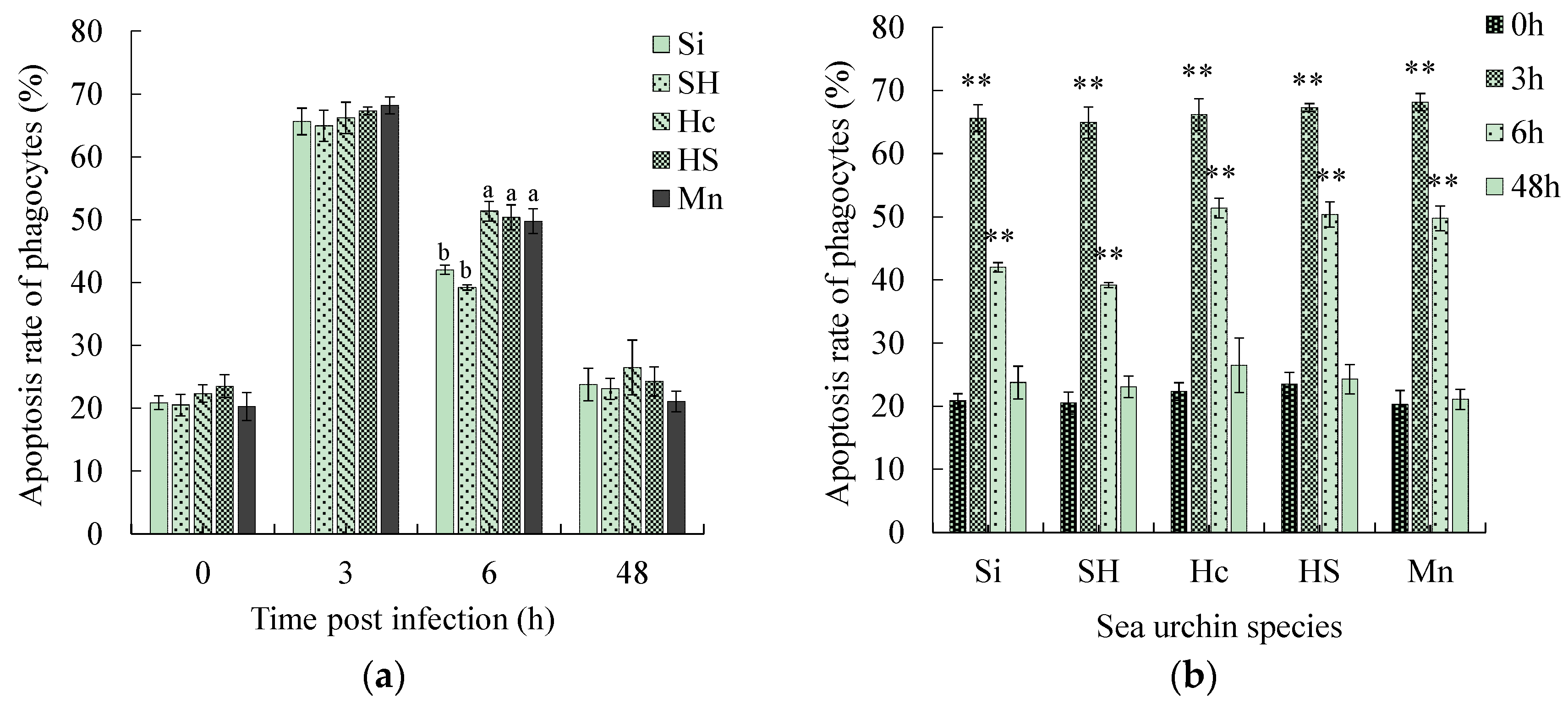
3.3. Comparison of Apoptosis Rate and Necrosis Rate of Phagocytes
3.4. Comparison of the Phagocytic Rate and Phagocytic Index
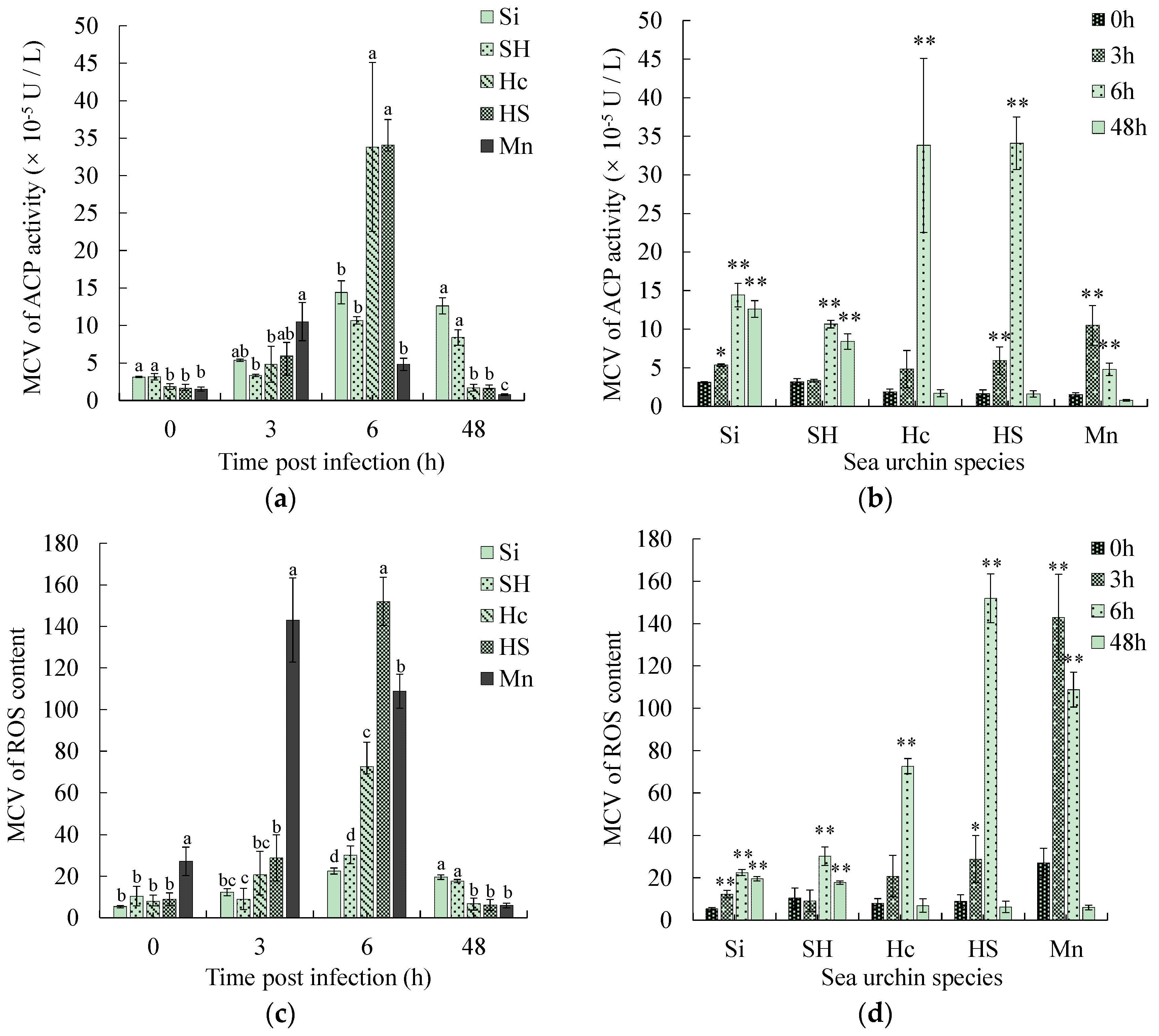
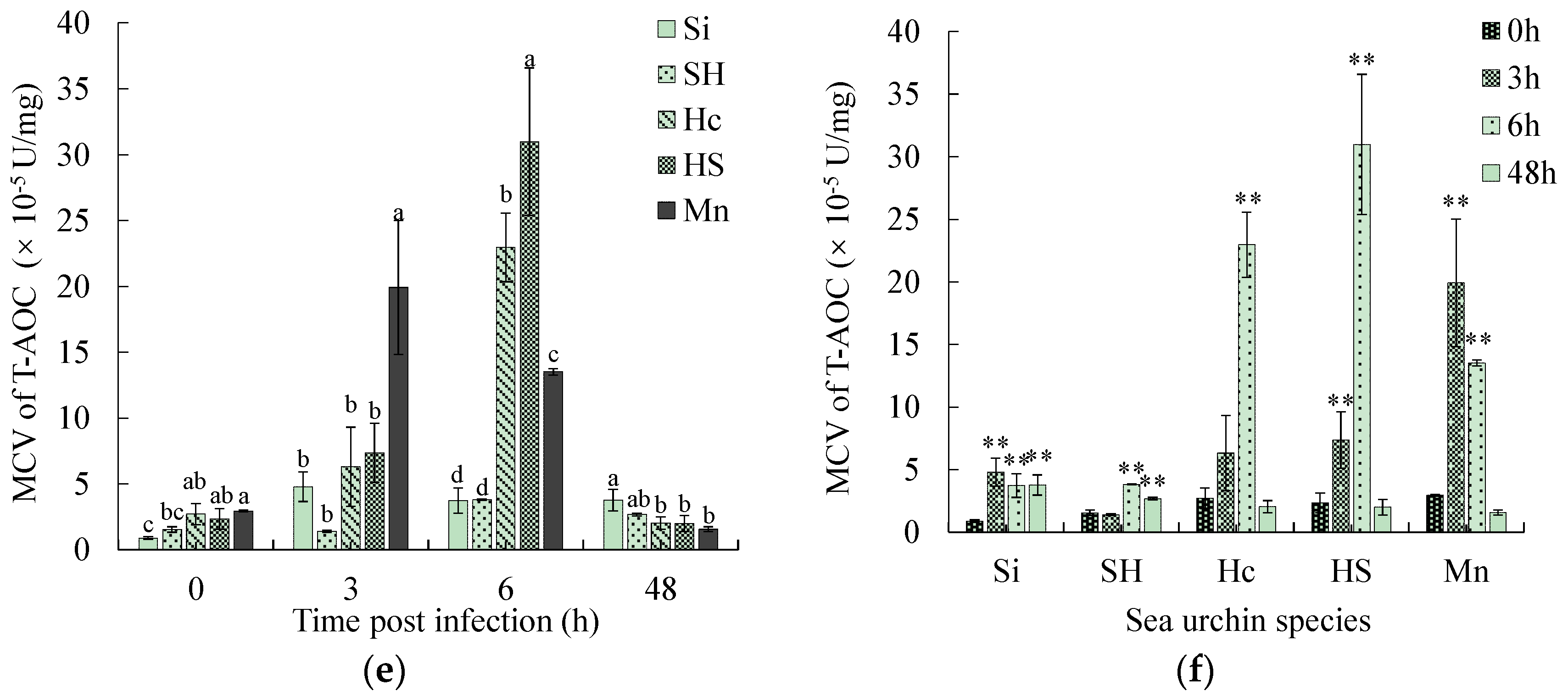
3.5. Comparison of Physiological Parameters Related to Phagocytosis
4. Discussion
4.1. Cellular Homeostasis and Phagocytic Index of Phagocytes Are Key Factors Determining Whether Sea Urchins Are Resistant to Black Mouth Disease
4.2. The Physiological Parameters Related to Phagocytosis of Disease-Resistant Sea Urchins Increase More Significantly for Rapid Sterilization and Can Timely Return Homeostasis
4.3. Similarities and Differences between Hybrid Sea Urchins and Their Parents
4.4. Screening of Sea Urchin Disease-Resistance Indicators
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, Y.; Ding, J.; Song, J.; Yang, W. Biology and Aquaculture of Sea Cucumbers and Sea Urchins; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brundu, G.; Monleón, L.V.; Vallainc, D.; Carboni, S. Effects of larval diet and metamorphosis cue on survival and growth of sea urchin post-larvae (Paracentrotus lividus; Lamarck, 1816). Aquaculture 2016, 465, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; He, M.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J. The effects of 3 different microalgae species on the growth, metamorphosis and MYP gene expression of two sea urchins, Strongylocentrotus intermedius and S. nudus. Aquaculture 2018, 492, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Gavilán, M.; Reznicov, M.; Turpin, V.; Decottignies, P.; Cognie, B. Sea urchin recruitment: Effect of diatom based biofilms on Paracentrotus lividus competent larvae. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Murata, Y.; Agatsuma, Y. Feeding the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida kelp shortens the culture duration for the production of high-quality gonads of Mesocentrotus nudus sea urchins from a barren. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Hirano, T.; Nakano, K.; Ezura, Y. Taxonomical study on the causative bacterium of spotting disease of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish. Sci. 1997, 63, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tajima, K.; Hirano, T.; Shimizu, M.; Ezura, Y. Isolation and pathogenicity of the causative bacterium of spotting disease of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish. Sci. 1997, 63, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Takeuchi, K.; Iqbal, M.M.; Nakano, K.; Shimizu, M.; Ezura, Y. Studies on a bacterial disease of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius occurring at low water temperatures. Fish. Sci. 1998, 64, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Tajima, K.; Iqbal, M.M.; Sawabe, T.; Ezura, Y. Taxonomical and serological studies on the causative bacteria of the disease of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius occurring at low water temperatures. Fish. Sci. 1999, 65, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Qu, J.; Zhao, X. Pathogenic mechanism of the causative vibrio found in “red spotting” diseased sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2005, 20, 11–15, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Kong, Y. Biological characteristic and pathogenicity of the pathogenic vibrio on the “red spot disease” of Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Fish. China 2006, 30, 371–376, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Lawrence, J.M. Disease in sea urchins. In Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology; Lawrence, J.M., Ed.; Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Elsevier: London, UK, 2013; pp. 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, N.; Li, Q.; Ding, J.; Zhan, Y.; Chang, Y. Isolation and characterization of bacteria associated with a syndrome disease of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius in North China. Aquacult. Rep. 2013, 44, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Leng, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, L.; Chang, Y. Transcriptome sequencing reveals phagocytosis as the main immune response in the pathogen-challenged sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Dang, H.; Huang, Y.; Quan, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, W.; Ding, J. Vibrio coralliilyticus as an agent of red spotting disease in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquacult. Rep. 2020, 16, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Leng, X.; Gao, H.; Jiang, H.; Chang, Y. Effects of artificial challenge of black mouth disease pathogen on phagocytosis related immune parameters in sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2021, 36, 241–247, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.C.; Rast, J.P.; Brockton, V.; Terwilliger, D.P. The sea urchin immune system. Invert. Surviv. J. 2006, 3, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Park, S.-I. Phagocytosis and agglutination of coelomocytes in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus with relation to water temperature. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2009, 24, 189–194, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yuan, C.; Wan, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, J. Effect of COS on phagocytic activity of coelomic cell of tropical sea cucumber (Holothuria scabra). Gen. Appl. Biol. 2017, 36, 237–240, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yui, M.A.; Bayne, C.J. Echinoderm immunology: Bacterial clearance by the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Biol. Bull. 1983, 165, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Matsutani, T.; Mori, K.; Nomura, T. Phagocytosis and hydrogen peroxide production by phagocytes of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus nudus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1992, 16, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, H.; Beck, G. Phylogeny of natural cytotoxicity: Cytotoxic activity of coelomocytes of the purple sea urchin, Arbacia punctulata. J. Exp. Zool. 2001, 290, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, P.S.; Al-Sharif, W.Z.; Clow, L.A.; Smith, L.C. Echinoderm immunity and the evolution of the complement system. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1999, 23, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clow, L.A.; Raftos, D.A.; Gross, P.S.; Smith, L.C. The sea urchin complement homologue, SpC3, functions as an opsonin. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Chang, Y.; Song, J.; Ye, S. Study of opsonin-like molecule from coelomic fluid of Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Fish. China 2014, 38, 684–690, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lv, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Chang, Y. Transcriptome profiling reveals key roles of phagosome and NOD-like receptor pathway in spotting diseased Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yin, W.; Ou, F.; Tian, W.; Liu, L.; Chang, Y. Isolation and identification of pathogenic bacteria associated with black-mouth disease in sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2022, 37, 793–801, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.C.; Ghosh, J.; Buckley, K.M.; Clow, L.A.; Dheilly, N.M.; Haug, T.; Henson, J.H.; Li, C.; Lun, C.; Majeske, A.J.; et al. Echinoderm immunity. In Invertebrate Immunity; Söderhäll, K., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 260–301. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Chang, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhang, W. Immune effect of four immune opotentiators on two sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus intermedius) with different tube foot colours. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2011, 29, 9–16, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Monari, M.; Matozzo, V.; Foschi, J.; Cattani, O.; Serrazanetti, G.P.; Marin, M.G. Effects of high temperatures on functional responses of haemocytes in the clam Chamelea gallina. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Song, J.H.; Choi, M.C.; Park, S.W. Effects of water temperature change on immune function in surf clams, Mactra veneriformis (Bivalvia: Mactridae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 102, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matranga, V.; Pinsino, A.; Celi, M.; Natoli, A.; Bonaventura, R.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Monitoring chemical and physical stress using sea urchin immune cells. In Echinodermata; Matranga, V., Ed.; Progress in Molecular and Subcellular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 39, pp. 85–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zapata-Vívenes, E.; Bastidas, M.; Marcano, L.D.V.; Sonnenholzner-Varas, J. Colorless spherule cells and lysozyme contribute to innate immunological responses in the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus, exposed to bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arizza, V.; Giaramita, F.T.; Parrinello, D.; Cammarata, M.; Parrinello, N. Cell cooperation in coelomocyte cytotoxic activity of Paracentrotus lividus coelomocytes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, V.; Custódio, M.R. Characterisation of the spherulocyte subpopulations in Eucidaris tribuloides (Cidaroida: Echinoidea). Ital. J. Zool. 2015, 82, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhan, W.; Xing, J. Effect of water temperature on phagocytic activitiy of the haemocytes of scallop (Chlamys farreri) after stimulated by Lipopolysaccharide. J. Ocean Univ. China 2015, 45, 31–38, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Lin, T.; Zhan, W. Variations of enzyme activities in the haemocytes of scallop Chlamys farreri after infection with the acute virus necrobiotic virus (AVNV). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, G. Activity change of seven enzymes in haemolymph in scallop Chlamys farreri after challenge with Escherichia coli. Mar. Sci. 1999, 5, 40–44, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, J.; Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, Z. Response of Immune-related Enzyme Activities in the Coelomocytes of Juvenile Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Challenged with Different Pathogenic Bacteria. Fish. Sci. 2018, 37, 295–300, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Chang, Y. Thermal resistance of juvenile sea urchin hybrids Strongylocentrotus intermedius and Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2019, 34, 47–52, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Li, S.; Ma, J. Diseases resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), Blue tilapia (Oreochromis aureus) and their hybrid (female Nile tilapia×male blue tilapia) to Aeromonas sobria. Aquaculture 2004, 229, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Yang, A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L. Preliminary cytological identification and immunological traits of hybrid scallop from Chlamys farreri (♀) × Patinopecten yessoensis (♂). J. Fish. Sci. China 2006, 13, 597–602, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]




| Immune Parameters | Statistical Parameters | Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Species | Time × Species | ||
| Density of phagocytic amoebocyte | F (df) | F (3) = 30.069 | F (4) = 25.070 | F (12) = 6.406 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| Density of colorless spherule cell | F (df) | F (3) = 4.230 | F (4) = 15.611 | F (12) = 5.878 |
| p value | p = 0.011 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| Density of vibratile cell | F (df) | F (3) = 4.780 | F (4) = 3.879 | F (12) = 4.148 |
| p value | p = 0.006 | p = 0.009 | p < 0.0001 | |
| Density of red spherule cell | F (df) | F (3) = 6.835 | F (4) =18.544 | F (12) = 4.283 |
| p value | p = 0.001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| Apoptosis rate | F (df) | F (3) = 1661.179 | F (4) = 12.292 | F (12) = 5.279 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| Necrosis rate | F (df) | F (3) = 230.247 | F (4) = 18.252 | F (12) = 57.740 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| phagocytic rate | F (df) | F (2) = 69.699 | F (4) = 4.762 | F (8) = 1.126 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.004 | p = 0.375 | |
| phagocytic index | F (df) | F (2) = 24.512 | F (4) = 7.990 | F (8) = 2.887 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.016 | |
| ACP | F (df) | F (3) = 212.771 | F (4) = 29.462 | F (12) = 35.625 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| ROS | F (df) | F (3) = 125.294 | F (4) = 25.846 | F (12) = 20.015 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
| T-AOC | F (df) | F (3) = 132.514 | F (4) = 41.273 | F (12) = 33.100 |
| p value | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, W.; Wang, Z.; Leng, X.; Liu, P.; Guo, H.; Jiang, X.; Ou, F.; Jia, T.; Ding, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Comparison of Immune Indicators Related to Phagocytosis of Five Species of Sea Urchins under Artificial Infection with the Pathogenic Bacterium of Black Mouth Disease. Biology 2024, 13, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070495
Tian W, Wang Z, Leng X, Liu P, Guo H, Jiang X, Ou F, Jia T, Ding J, Zhang W, et al. Comparison of Immune Indicators Related to Phagocytosis of Five Species of Sea Urchins under Artificial Infection with the Pathogenic Bacterium of Black Mouth Disease. Biology. 2024; 13(7):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070495
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Wenzhuo, Zhong Wang, Xiaofei Leng, Peng Liu, Hao Guo, Xuechun Jiang, Fanjiang Ou, Tongshan Jia, Jun Ding, Weijie Zhang, and et al. 2024. "Comparison of Immune Indicators Related to Phagocytosis of Five Species of Sea Urchins under Artificial Infection with the Pathogenic Bacterium of Black Mouth Disease" Biology 13, no. 7: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070495
APA StyleTian, W., Wang, Z., Leng, X., Liu, P., Guo, H., Jiang, X., Ou, F., Jia, T., Ding, J., Zhang, W., & Chang, Y. (2024). Comparison of Immune Indicators Related to Phagocytosis of Five Species of Sea Urchins under Artificial Infection with the Pathogenic Bacterium of Black Mouth Disease. Biology, 13(7), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13070495






