Polymorphism Analysis of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes and Their Association with Wool Traits in Subo Merino Sheep
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phenotype Measurement and Sample Collection
- (1)
- Blood samples were collected from the jugular vein of these 944 Subo Merino sheep using heparin anticoagulant tubes. After heparin is mixed with blood, the blood samples were immediately placed in an icebox, further transported to the laboratory, and finally stored at −20 °C refrigerator for DNA extraction;
- (2)
- While taking blood samples, the greasy fleece weight (GFW), live weight before shearing (LWBS), and live weight after shearing (LWAS) of these sheep were measured and recorded. Additionally, the staple length (SL), fineness count (FC), crimp, hair length (HL), and crimp number (CN) of these sheep were also measured and recorded [21];
- (3)
- Wool samples were collected from a site 10 cm posterior to the left scapular edge (midline region). Wool samples were further washed using the conventional washing process and allowed to dry naturally. Measurements of the mean fibre diameter (MFD), coefficient of variation of fibre diameter (CVFD), and fibre diameter standard deviation (FDSD) were taken in a laboratory maintained at a constant temperature (20 ± 2 °C) and humidity (65 ± 4%) using a fibre diameter optical analyser (OFDA2000, Ningbo Jiangnan Instrument Factory, Ningbo, China) [22]. The parameters measured included. Excel 2019 was used to compile the data on wool traits. SPSS 27.0 software [23] was employed to perform descriptive statistical analyses on the relevant wool trait data;
- (4)
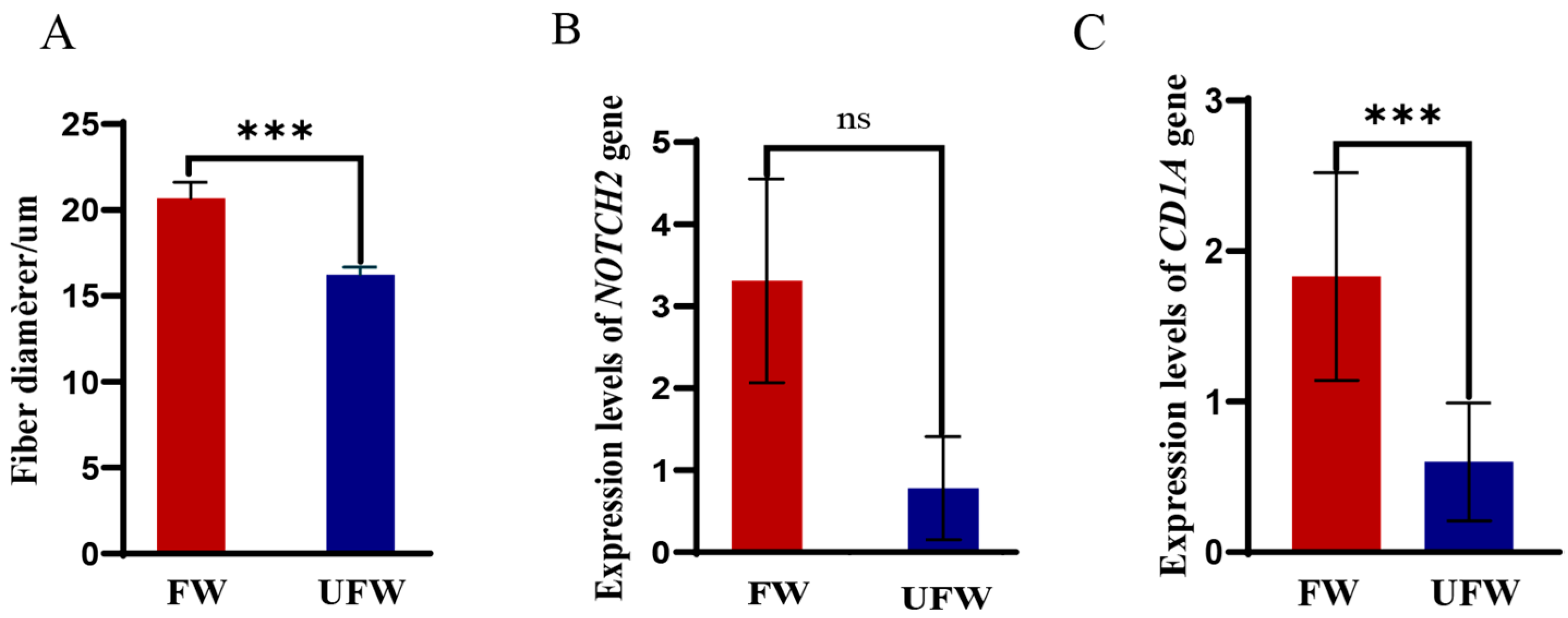
- Based on the results of MFD measurements, 10 sheep with the smallest MFD were designated as the ultra-fine wool fibre group (UFW, 16.21 ± 0.46 μm), and 10 with the largest MFD as the fine wool fibre group (FW, 20.68 ± 0.93 μm). For these two groups, additional wool samples were collected from the left forelimb and 5 cm posterior to the scapula and were further used to measure the MFD. 20 skin tissue samples (approximately 2 cm × 2 cm) from these two groups were collected using a skin sampler, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and were further stored at −80 °C refrigerator for RNA extraction.
2.2. DNA Extraction and SNP Typing
2.3. Genetic Diversity Analysis
2.4. Correlation Analysis
2.5. Biological Function Prediction
2.6. RNA Extraction
2.7. Primer Design and qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Wool Traits
3.2. Analysis of Mutation Sites in the NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes
3.3. Analysis of Genotype Frequencies and Allele Frequencies of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes
3.4. Population Genetic Analysis of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes
3.5. Genetic Effects of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes on Wool Traits
3.5.1. Variance Analysis of Different Genotypes of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes on Wool Traits
3.5.2. Association Analysis of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes with Wool Traits
3.6. LD and Haplotype Analysis
3.7. Analysis of Protein Structure Changes
3.8. qPCR Results of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UFW | Ultra-fine wool fibre group |
| FW | Fine wool fibre group |
| MFD | Mean fibre diameter |
| CVFD | Fibre diameter variation coefficient |
| FDSD | Fibre diameter standard deviation |
| SL | Staple length |
| FC | Fineness count |
| HL | Hair length |
| CN | Crimp number |
| GFW | Greasy fleece weight |
| LWBS | Live weight before shearing |
| LWAS | Live weight after shearing |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| Ho | Homozygosity |
| He | Heterozygosity |
| Ne | Effective number of alleles |
| PIC | Polymorphism information content |
| qPCR | quantitative PCR |
References
- Li, Y. Production status and healthy development way of fine wool in China. Anim. Breed. Feed. 2018, 3, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, G.; Wan, P. Current Status of Xinjiang Fine-wool Sheep Breeding and Measures for Genetic Resource Conservation and Utilization. Xinjiang Farm Res. Sci. Technol. 2024, 47, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Di, J.; Xu, X. Exploring the Breeding Status and Development Trends of Fine-Wool Sheep. Jilin Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2020, 41, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhaba, A.; Tian, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yang, X.; Tian, K.; Huang, X. A New SNP Mutation of GPR143 Gene of Chinese Merino Sheep (Xinjiang Type) and Its Genetic Effect Analysis. Grass-Feed. Livest. 2019, 5, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Suo, L.; Yan, X.; Li, W.; Su, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Ji, D.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Fleece Traits in Northwest Xizang White Cashmere Goat. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1409084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, R.; Li, F.; Yue, X. Association of SNPs within PTPN3 Gene with Wool Production and Growth Traits in a Dual-Purpose Sheep Population. Anim. Biotechnol. 2023, 34, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.; Zhou, H.; Forrest, R.H.J.; Gong, H.; Hodge, S.; Hickford, J.G.H. Polymorphism of KRT83 and Its Association with Selected Wool Traits in Merino-Cross Lambs. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 155, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. Molecular Characterization of KRT24, KRT33B, KRT39 and KRT84 Genes and Association Analysis of Their Variations with Wool Traits in Gansu Alpine Fine—Wool Sheep. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B. Screen the Differentially Expressed Genes of Skin Tissue in Fine—Wool Sheep and Analysis of Genetic Effects. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, D.; Han, W.; Wu, Z.; Shang, F.; Hai, E.; Wei, Y.; Su, R.; et al. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Transcriptional and Alternative Splicing Regulation in the Early Embryonic Development of Hair Follicles in the Cashmere Goat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, B.C.; Passmore, E.A.; Nesci, A.; Dunn, S.M. The Notch Signalling Pathway in Hair Growth. Mech. Dev. 1998, 78, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Thomson, C.; Botto, S.A.; Cam, G.R.; Moore, G.P.M. Notch Pathway Gene Expression and Wool Follicle Cell Fates. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2008, 48, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wei, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Mao, J.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, W.; Tian, K.; Liu, G. MiR-23b and miR-133 Cotarget TGFβ2/NOTCH1 in Sheep Dermal Fibroblasts, Affecting Hair Follicle Development. Cells 2024, 13, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauclair, S.; Nicolas, M.; Barrandon, Y.; Radtke, F. Notch1 Is Essential for Postnatal Hair Follicle Development and Homeostasis. Dev. Biol. 2005, 284, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X. Selection of Regulatory Factors Related to Cashmere Fiber Diameter Trait from Transcriptome and Proteome Profiles in Tibetan Cashmere Goats. Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hardman, C.S.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wegrecki, M.; Ng, S.W.; Murren, R.; Mangat, D.; Silva, J.-P.; Munro, R.; Chan, W.Y.; O’Dowd, V.; et al. CD1a Promotes Systemic Manifestations of Skin Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Ogg, G. CD1a and Skin T Cells: A Pathway for Therapeutic Intervention. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Tian, K.; Shi, G.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Di, J.; Yang, Y. Effect of Different Generations on Wool Traits during Upgrading Cross Stages in Subo Merino Nuleus Herd. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 51, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Integrating Transcriptome and miRNA Data to Analyze the Molecular Mechanism of Hair Follicle Development in Subo Merino Sheep. Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Long, L.; Huang, X.; Tian, K.; Tian, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Genes Associated with Wool Fineness in Merinos. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Fu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; Di, J. Methods on measuring and assessing major wool traits in fine wool sheep. Wool Text. J. 2024, 52, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Xing, W.; Lu, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Fan, B.; Quan, K.; Liu, J. Study on the Detection Results of Fine Wool Fiber Diameter in Different Temperature and Humidity Environments. Grass Feed. Livest. 2024, 4, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, R.E.; Snider, D.; Thompson, C.; Mantravadi, S. IBM Watson Analytics: Automating Visualization, Descriptive, and Predictive Statistics. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2016, 2, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Genetic Effect Analysis and Breeding Application of Growth Trait Genes in Ujumqin Sheep. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Selection, Identification and SNP Analysis of Correlation Geneswith Cashmere Growth on Cashmere Goats. Ph.D. Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, J.C. Haploview: Visualization and Analysis of SNP Genotype Data. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009, 2009, pdb.ip71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jia, G.; Diao, X. geneHapR: An R Package for Gene Haplotypic Statistics and Visualization. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Analysis of Covariance by the SAS GLM Procedure. Comput. Biol. Med. 1987, 17, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. SOPMA: Significant Improvements in Protein Secondary Structure Prediction by Consensus Prediction from Multiple Alignments. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1995, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Z.; Usman, T.; Tian, K.C.; Di, J.; Huang, X.X.; Xu, X.M.; Tulafu, H.; Wu, W.W.; Fu, X.F.; Bai, Y.; et al. Comparative Study of 13 Candidate Genes Applying Multi-Reference Normalization to Detect the Expression of Different Fineness in Skin Tissues of Wool Sheep. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16, gmr16018905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; HanikeziI, T.; Liu, J.; Shi, G.; Fu, X.; Yu, L.; Lazhate, A.; Di, J. Genome-wide association of wool length and yield of Chinese Merino sheep (Xinjiang type). J. Northwest A F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, Q. Association of ALX4 gene with wool traits in Tan sheep and its expression in skin tissue. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2025, 60, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, W.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y. Genome-Wide Association Study of Birth Wool Length, Birth Weight, and Head Color in Chinese Tan Sheep Through Whole-Genome Re-Sequencing. Animals 2024, 14, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Hickford, J.G.H.; Luo, Y.; Gong, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Song, Y.; Ke, N.; et al. Identification of the Ovine Keratin-Associated Protein 2-1 Gene and Its Sequence Variation in Four Chinese Sheep Breeds. Genes 2020, 11, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hu, R.; Li, F.; Yue, X. Two Strongly Linked Blocks within the KIF16B Gene Significantly Influence Wool Length and Greasy Yield in Fine Wool Sheep (Ovis aries). Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 53, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Lu, Z.; Guo, T.; Liu, J.; Yuan, C.; Yang, B. Association of SLIT3 and ZNF280B Gene Polymorphisms with Wool Fiber Diameter. Animals 2023, 13, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Kao, C.-H.; Lin, K.M.-C.; Kaartinen, V.; Yang, L.-T. Notch Signaling Regulates Late-Stage Epidermal Differentiation and Maintains Postnatal Hair Cycle Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, X.; Shi, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; et al. Polymorphism of Notch2 Gene and Its Association Analysis with Cashmere and Growth Traits in Shaanbei White Cashmere Goats. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2023, 50, 3630–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilinare, A. Genetic Effect Study of KRT85, Notch2 and ADAM9 Genes on Wool Traits of Chinese Merino (Xinjiang Type) Sheep. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.; Kannourakis, G. Does CD1a Expression Influence T Cell Function in Patients with Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 773598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Pei, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xu, T.; Zuo, M.; Han, B.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Zhou, B.; et al. Genome-wide Selective Signal Identification and Association Analysis of Candidate Genes for Tibetan Sheep Wool Traits. Acta Vet. Et Zootech. Sin. 2024, 55, 5511–5526. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, R.; Lan, J.; Chen, L.; He, X. Advances in the application of AlphaFold2: A protein structure prediction model. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 1406–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Based on WGS to Analyze the Genetic Diversity and Selection Signals of 7 Meat Goat Breeds in Southwest China. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C. Screening of miRNAs and circRNAs in Yak Muscle Tissue and Correlation Analysis of ACACB Gene. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wen, M.; Zhou, B.; Chen, Z.; Yue, J. Polymorphism analysis of TLR2 gene in different breeds of sheep based on sequencing technology. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. 2018, 40, 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Lan, M.; Alatansuhe; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z. Effects of 5 SNP mutation sites on the body weight of Ujimqin sheep at different time points. Sci. Sin. (Vitae) 2024, 54, 951–961. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Bai, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Hickford, J.G.H. Ovine KRTAP36-2: A New Keratin-Associated Protein Gene Related to Variation in Wool Yield. Genes 2023, 14, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.; Ibrahim, M.; Siraj, M.; Bangash, S.A.K.; Khan, S.H.; Khan, M.; Tayyab, M.; Ahmad, S. Novel Mutations in Exon 2 of Follistatin (FST) Gene Associated with Wool Fiber Diameter in Sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2025, 243, 107426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | Product Size (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOTCH2 | F:GCTTCACTGGTTCCTTCTGC | 119 | 60 |
| R:ATAGCCCAATGGACAGATGC | |||
| CD1A | F:TGACGTCTTGCCTAATGCTG | 124 | 60 |
| R:GATGATGTCCTGGCCTCCTA | |||
| GAPDH | F:GGTGATGCTGGTGCTGAGTA | 118 | 59.86 |
| R:CAGCAGAAGGTGCAGAGATG |
| Traits | Number | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFD | 944 | 17.71 | 1.84 | 12.80 | 24.00 | 10.39 |
| FDSD | 944 | 4.14 | 0.57 | 2.80 | 6.40 | 13.77 |
| CVFD | 944 | 23.38 | 2.24 | 17.00 | 30.80 | 9.58 |
| SL | 944 | 88.26 | 11.77 | 50.00 | 130.00 | 13.34 |
| FC | 937 | 66.82 | 2.52 | 60.00 | 80.00 | 3.77 |
| crimp | 936 | 1.84 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 33.70 |
| HL | 937 | 9.89 | 0.95 | 6.00 | 14.00 | 9.61 |
| LWBS | 936 | 33.18 | 5.03 | 22.00 | 50.00 | 15.16 |
| LWAS | 668 | 34.13 | 4.96 | 22.00 | 50.00 | 14.53 |
| GFW | 765 | 3.33 | 0.54 | 2.00 | 5.60 | 16.22 |
| CN | 932 | 13.89 | 3.00 | 8.00 | 21.00 | 21.60 |
| Genes | SNPs | Area | Chromosome: Location | Nucleotide Variation | Amino Acid Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOTCH2 | SNP1 | Exon30 | 1: 96432471 | c. 5413A/C | p. Met1805Leu |
| SNP2 | Exon24 | 1: 96438799 | c. 3919G/A | p. Val1307Met | |
| CD1A | SNP3 | Exon2 | 1: 107486485 | c. 232G/A | p. Asp78Asn |
| SNP4 | Exon3 | 1: 107487136 | c. 368A/C | p. His123Pro | |
| SNP5 | Exon3 | 1: 107487147 | c. 379G/A | p. Ala127Thr | |
| SNP6 | Exon4 | 1: 107487782 | c. 809A/T | p. Glu270Val |
| Genes | SNPs | Genotype Frequency | Allele Frequency | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOTCH2 | SNP1 | TT (0.03), TG (0.26), GG (0.71) | T (0.16), G (0.84) | 0.702 | p > 0.05 |
| SNP2 | CC (0.76), CT (0.22), TT (0.02) | C (0.87), T (0.13) | 0.661 | p > 0.05 | |
| CD1A | SNP3 | GG (0.47), GA (0.44), AA (0.09) | G (0.70), A (0.30) | 0.258 | p > 0.05 |
| SNP4 | AA (0.47), AC (0.44), CC (0.09) | A (0.69), C (0.31) | 0.216 | p > 0.05 | |
| SNP5 | GG (0.46), GA (0.45), AA (0.09) | G (0.68), A (0.32) | 0.386 | p > 0.05 | |
| SNP6 | AA (0.21), AT (0.25), TT (0.54) | A (0.33), T (0.67) | 7.86 × 10−40 | p < 0.05 |
| Genes | SNPs | Ho | He | Ne | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOTCH2 | SNP1 | 0.739 | 0.261 | 1.360 | 0.230 |
| SNP2 | 0.783 | 0.217 | 1.285 | 0.197 | |
| CD1A | SNP3 | 0.559 | 0.441 | 1.737 | 0.334 |
| SNP4 | 0.556 | 0.444 | 1.741 | 0.335 | |
| SNP5 | 0.554 | 0.446 | 1.764 | 0.339 | |
| SNP6 | 0.753 | 0.247 | 1.797 | 0.345 |
| Genes | SNPs | MFD /μm | FDSD /μm | CVFD /% | SL /cm | FC /Count | HL /cm | Crimp | LWAS /kg | LWBS /kg | GFW /kg | CN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOTCH2 | SNP1 | 4.40 * | 2.41 | 2.24 | 1.06 | 1.53 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.43 | 0.63 | 2.07 | 0.63 |
| SNP2 | 0.19 | 1.66 | 2.78 * | 0.63 | 0.30 | 1.69 | 0.99 | 1.59 | 1.26 | 2.42 | 1.28 | |
| CD1A | SNP3 | 2.07 | 2.19 | 1.18 | 0.02 | 1.26 | 1.83 | 2.10 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.38 | 1.42 |
| SNP4 | 0.94 | 2.43 | 2.39 | 2.74 * | 0.96 | 2.60 | 2.12 | 0.31 | 1.40 | 0.16 | 1.53 | |
| SNP5 | 2.06 | 2.41 | 1.56 | 0.31 | 1.54 | 0.54 | 1.17 | 0.62 | 0.25 | 1.04 | 1.93 | |
| SNP6 | 0.70 | 3.04 * | 2.63 * | 0.37 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 1.20 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.10 |
| Genes | SNPs | Genotype | MFD /μm | FDSD /μm | CVFD /% | SL /cm | FC /Count | HL /cm | Crimp | LWAS /kg | LWBS /kg | GFW /kg | CN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOTCH2 | SNP1 | GG | 17.688 ± 0.057 | 4.191 ± 0.023 | 23.437 ± 0.087 a | 88.447 ± 0.458 | 66.835 ± 0.096 | 10.114 ± 0.035 | 1.832 ± 0.025 | 32.826 ± 0.202 | 33.063 ± 0.160 | 3.320 ± 0.027 a | 13.931 ± 0.088 |
| TG | 17.881 ± 0.094 | 4.230 ± 0.037 | 23.500 ± 0.144 a | 88.151 ± 0.756 | 66.887 ± 0.159 | 10.164 ± 0.058 | 1.864 ± 0.040 | 33.201 ± 0.327 | 33.418 ± 0.264 | 3.200 ± 0.046 b | 13.852 ± 0.146 | ||
| TT | 17.710 ± 0.292 | 4.007 ± 0.117 | 22.291 ± 0.448 b | 84.186 ± 2.357 | 66.451 ± 0.494 | 9.919 ± 0.179 | 1.840 ± 0.126 | 32.446 ± 0.968 | 32.949 ± 0.820 | 3.228 ± 0.143 | 14.051 ± 0.453 | ||
| SNP2 | CC | 17.771 ± 0.055 | 4.201 ± 0.022 | 23.391 ± 0.083 | 88.457 ± 0.439 | 66.796 ± 0.092 | 10.142 ± 0.033 | 1.841 ± 0.023 | 33.001 ± 0.194 | 33.188 ± 0.153 | 3.263 ± 0.027 | 13.842 ± 0.085 | |
| TC | 17.699 ± 0.103 | 4.208 ± 0.041 | 23.596 ± 0.156 a | 87.676 ± 0.824 | 66.948 ± 0.173 | 10.056 ± 0.063 | 1.858 ± 0.044 | 32.667 ± 0.369 | 33.197 ± 0.287 | 3.356 ± 0.049 | 14.055 ± 0.160 | ||
| TT | 17.634 ± 0.356 | 4.002 ± 0.142 | 22.422 ± 0.542 b | 87.795 ± 2.858 | 66.504 ± 0.600 | 10.189 ± 0.217 | 1.588 ± 0.152 | 30.434 ± 1.579 | 31.979 ± 0.992 | 3.552 ± 0.201 | 14.756 ± 0.549 | ||
| CD1A | SNP3 | AA | 17.885 ± 0.146 | 4.154 ± 0.065 | 23.361 ± 0.252 | 87.994 ± 1.325 | 66.942 ± 0.277 | 10.125 ± 0.112 | 1.89 ± 0.070 | 33.269 ± 0.536 | 33.087 ± 0.460 | 3.241 ± 0.077 | 14.367 ± 0.254 a |
| GA | 17.810 ± 0.072 | 4.253 ± 0.029 a | 23.571 ± 0.110 | 88.278 ± 0.580 | 66.674 ± 0.122 | 10.198 ± 0.049 a | 1.78 ± 0.031 a | 32.778 ± 0.260 | 33.033 ± 0.202 | 3.283 ± 0.035 | 13.799 ± 0.112 b | ||
| GG | 17.683 ± 0.070 | 4.159 ± 0.028 b | 23.293 ± 0.107 | 88.292 ± 0.561 | 66.936 ± 0.118 | 10.050 ± 0.047 b | 1.89 ± 0.030 b | 32.971 ± 0.242 | 33.302 ± 0.196 | 3.298 ± 0.034 | 13.920 ± 0.108 | ||
| SNP4 | AA | 17.673 ± 0.07 | 4.158 ± 0.028 a | 23.300 ± 0.107 | 88.216 ± 0.571 | 66.935 ± 0.119 | 10.122 ± 0.429 | 1.885 ± 0.030 a | 32.968 ± 0.242 | 33.269 ± 0.197 | 3.298 ± 0.034 | 13.926 ± 0.109 | |
| AC | 17.809 ± 0.072 | 4.254 ± 0.029 b | 23.580 ± 0.110 | 88.244 ± 0.576 | 66.689 ± 0.121 | 10.145 ± 0.044 | 1.785 ± 0.031 b | 32.768 ± 0.260 | 33.035 ± 0.201 | 3.281 ± 0.035 | 13.797 ± 0.111 a | ||
| CC | 17.887 ± 0.165 | 4.154 ± 0.065 | 23.358 ± 0.251 | 88.013 ± 1.319 | 66.941 ± 0.277 | 9.968 ± 0.100 | 1.885 ± 0.070 | 33.272 ± 0.536 | 33.094 ± 0.460 | 3.242 ± 0.077 | 14.366 ± 0.254 b | ||
| SNP5 | AA | 17.901 ± 0.157 | 4.153 ± 0.062 | 23.355 ± 0.240 | 88.836 ± 1.264 | 66.921 ± 0.265 | 10.006 ± 0.096 | 1.850 ± 0.067 | 33.206 ± 0.515 | 33.142 ± 0.440 | 3.244 ± 0.073 | 14.360 ± 0.242 a | |
| GA | 17.812 ± 0.072 | 4.251 ± 0.029 a | 23.563 ± 0.109 | 88.155 ± 0.576 | 66.693 ± 0.121 | 10.137 ± 0.044 | 1.798 ± 0.031 | 32.839 ± 0.260 | 33.055 ± 0.201 | 3.288 ± 0.035 | 13.784 ± 0.111 b | ||
| GG | 17.655 ± 0.071 | 4.156 ± 0.028 b | 23.289 ± 0.108 | 88.209 ± 0.570 | 66.914 ± 0.120 | 10.132 ± 0.044 | 1.877 ± 0.030 | 32.945 ± 0.244 | 33.274 ± 0.199 | 3.296 ± 0.035 | 13.937 ± 0.110 | ||
| SNP6 | AA | 17.682 ± 0.123 | 4.201 ± 0.049 | 23.462 ± 0.187 | 87.582 ± 0.985 | 66.863 ± 0.207 | 10.130 ± 0.075 | 1.867 ± 0.053 | 32.817 ± 0.494 | 33.231 ± 0.344 | 3.345 ± 0.652 | 13.828 ± 0.190 | |
| AT | 17.864 ± 0.103 | 4.309 ± 0.041 A | 23.768 ± 0.157 a | 88.159 ± 0.826 | 66.747 ± 0.174 | 10.119 ± 0.063 | 1.774 ± 0.044 | 33.254 ± 0.380 | 33.005 ± 0.289 | 3.299 ± 0.051 | 13.858 ± 0.160 | ||
| TT | 17.722 ± 0.077 | 4.152 ± 0.030 B | 23.284 ± 0.117 b | 88.658 ± 0.617 | 66.813 ± 0.130 | 10.129 ± 0.047 | 1.854 ± 0.033 | 32.756 ± 0.275 | 33.158 ± 0.216 | 3.258 ± 0.037 | 13.953 ± 0.119 |
| SNPs | SNP1 | SNP2 | SNP3 | SNP4 | SNP5 | SNP6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP1 | - | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| SNP2 | 0.027 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| SNP3 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.972 |
| SNP4 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.998 | - | 1.000 | 0.972 |
| SNP5 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.954 | 0.956 | - | 0.973 |
| SNP6 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.211 | 0.212 | 0.224 | - |
| Genes | SNPs | Genotype | α-Helix (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random Coil (%) | Extension Strand (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOTCH2 | SNP1 | Wild type | 14.29 | 0.00 | 71.43 | 14.29 |
| Mutant type | 10.71 | 0.00 | 71.43 | 17.86 | ||
| SNP2 | Wild type | 0.00 | 0.00 | 73.68 | 26.32 | |
| Mutant type | 0.00 | 0.00 | 71.05 | 28.95 | ||
| CD1A | SNP3 | Wild type | 49.44 | 0.00 | 33.71 | 16.85 |
| Mutant type | 49.44 | 0.00 | 33.71 | 16.85 | ||
| SNP4 | Wild type | 37.63 | 0.00 | 41.94 | 20.43 | |
| Mutant type | 38.71 | 0.00 | 40.86 | 20.43 | ||
| SNP5 | Wild type | 37.63 | 0.00 | 41.94 | 20.43 | |
| Mutant type | 37.63 | 0.00 | 41.94 | 20.43 | ||
| SNP6 | Wild type | 0.00 | 0.00 | 60.22 | 39.78 | |
| Mutant type | 0.00 | 0.00 | 62.37 | 37.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, S.; Liu, W.; Anwar, A.; Tang, S.; Wang, Y.; Aimaier, G.; Wu, C.; Fu, X. Polymorphism Analysis of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes and Their Association with Wool Traits in Subo Merino Sheep. Biology 2025, 14, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101336
Ma S, Liu W, Anwar A, Tang S, Wang Y, Aimaier G, Wu C, Fu X. Polymorphism Analysis of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes and Their Association with Wool Traits in Subo Merino Sheep. Biology. 2025; 14(10):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101336
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Shengchao, Wenna Liu, Asma Anwar, Sen Tang, Yaqian Wang, Gulinigaer Aimaier, Cuiling Wu, and Xuefeng Fu. 2025. "Polymorphism Analysis of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes and Their Association with Wool Traits in Subo Merino Sheep" Biology 14, no. 10: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101336
APA StyleMa, S., Liu, W., Anwar, A., Tang, S., Wang, Y., Aimaier, G., Wu, C., & Fu, X. (2025). Polymorphism Analysis of NOTCH2 and CD1A Genes and Their Association with Wool Traits in Subo Merino Sheep. Biology, 14(10), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14101336





